Synergistic Effects of Anthocyanin-Enriched Morus alba L. Extract and Vitamin C: Promising Nutraceutical Ingredients in Functional Food Development for Neuroprotection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Extraction of Anthocyanin-Enriched Morus alba L. Extract
2.3. Determination of Optimal Ratio and Synergistic Effects of Morus alba L. Extract Combined with Vitamin C
- •
- CI < 1: synergism
- •
- CI = 1: additive effect
- •
- CI > 1: antagonism
2.4. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Protein Measurement
2.7. Evaluation of Lipid Peroxidation
2.8. Evaluation of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species
2.9. Assessment of Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
2.10. Western Blotting Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
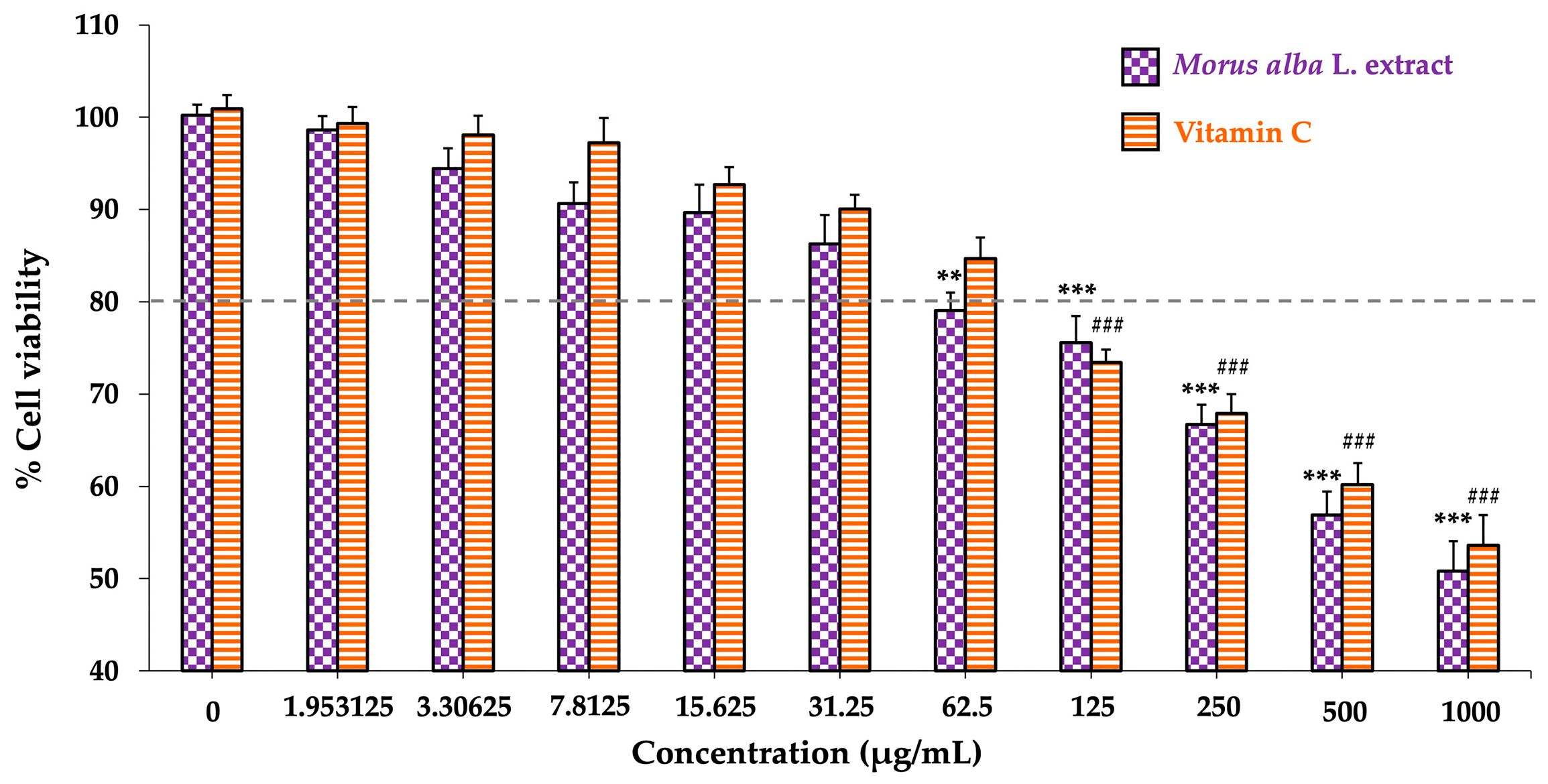
3.1. Determination of Non-Toxic Doses of Morus alba L. Extract and Vitamin C
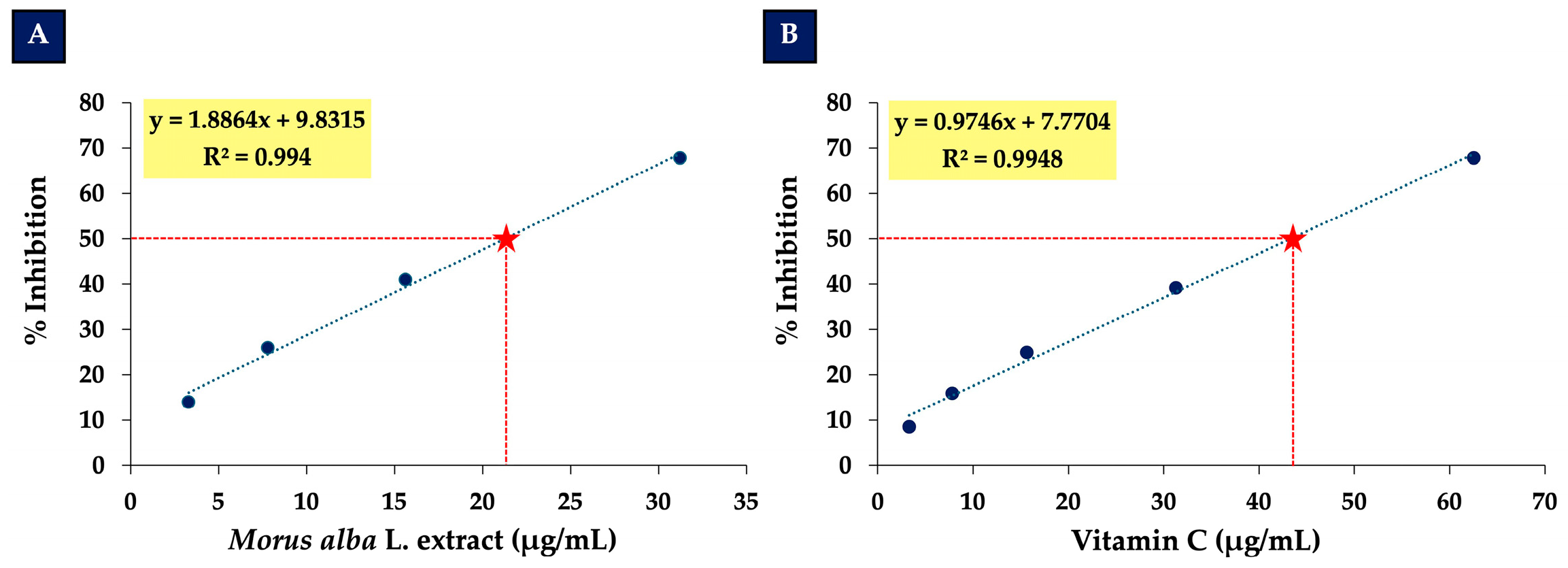
3.2. Determination of EC50 Values for Morus alba L. Extract and Vitamin C
3.3. Evaluation of Synergistic Effects of Morus alba L. Extract and Vitamin C
3.4. Identification of Synergistic Dose Combinations of Morus alba L. Extract and Vitamin C
3.5. Determination of Neuroprotective Effects of MAC
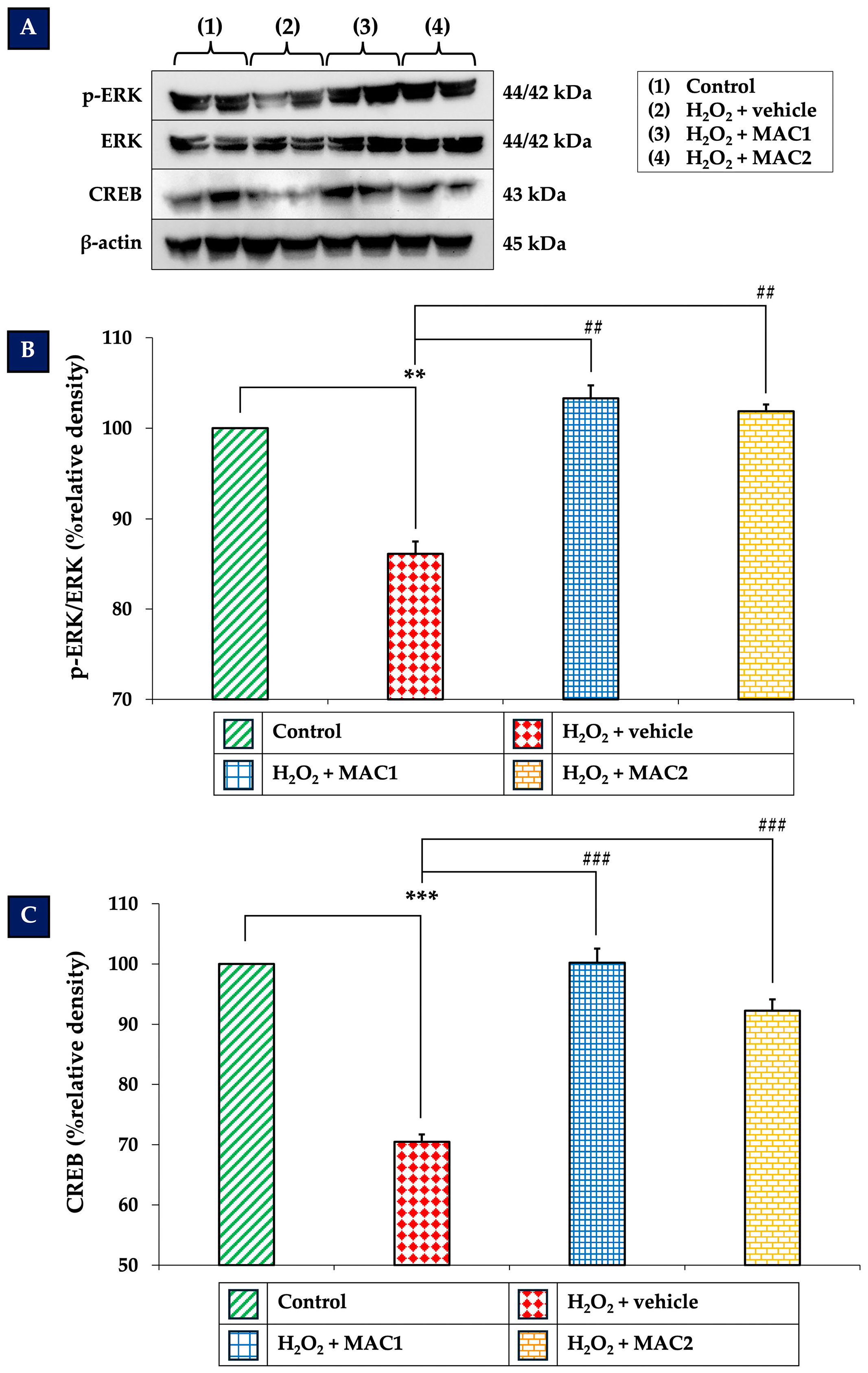
3.6. Effects of MAC on ERK/CREB Signaling Pathway
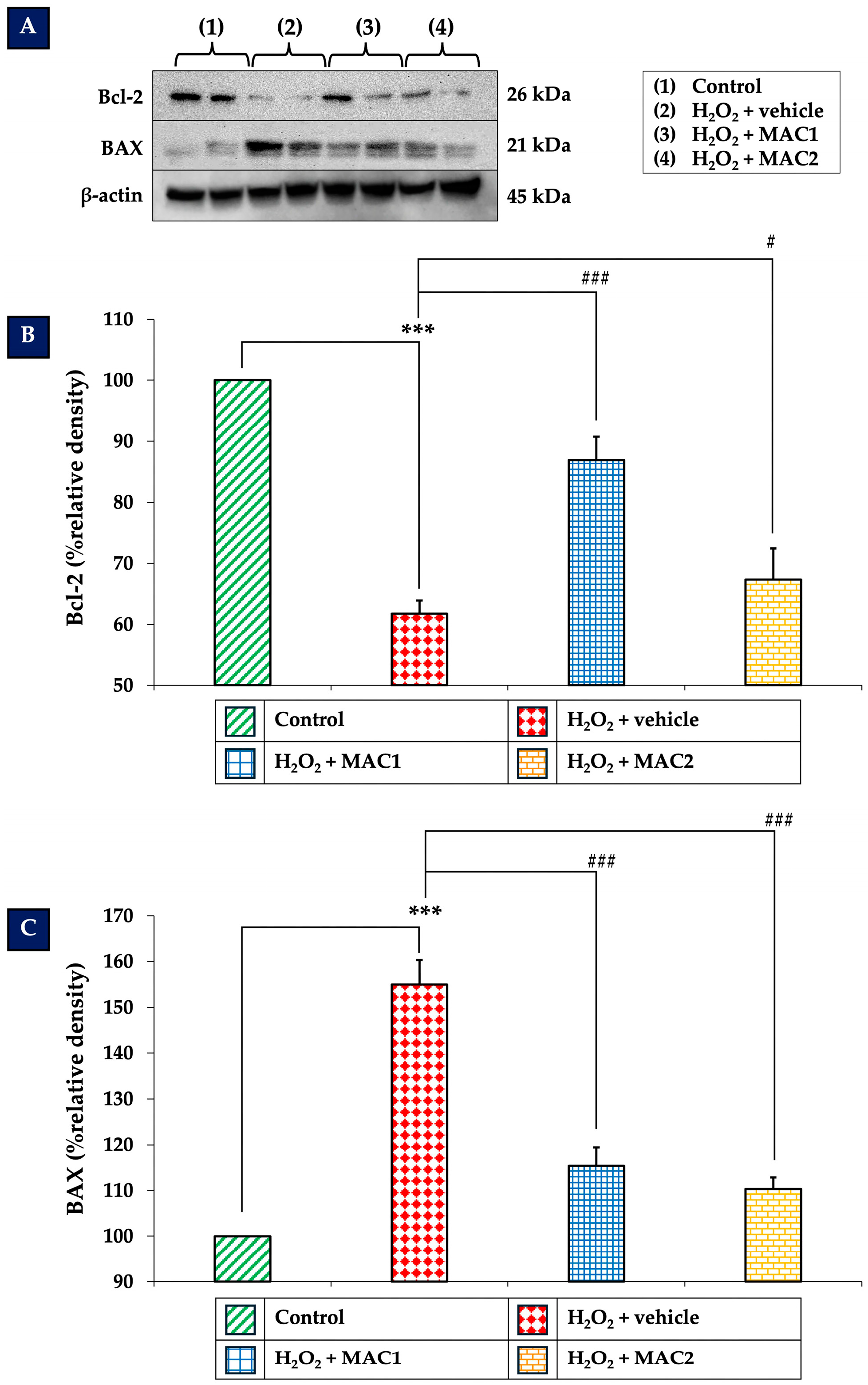
3.7. Effect of MAC on Bcl-2 and BAX Expression
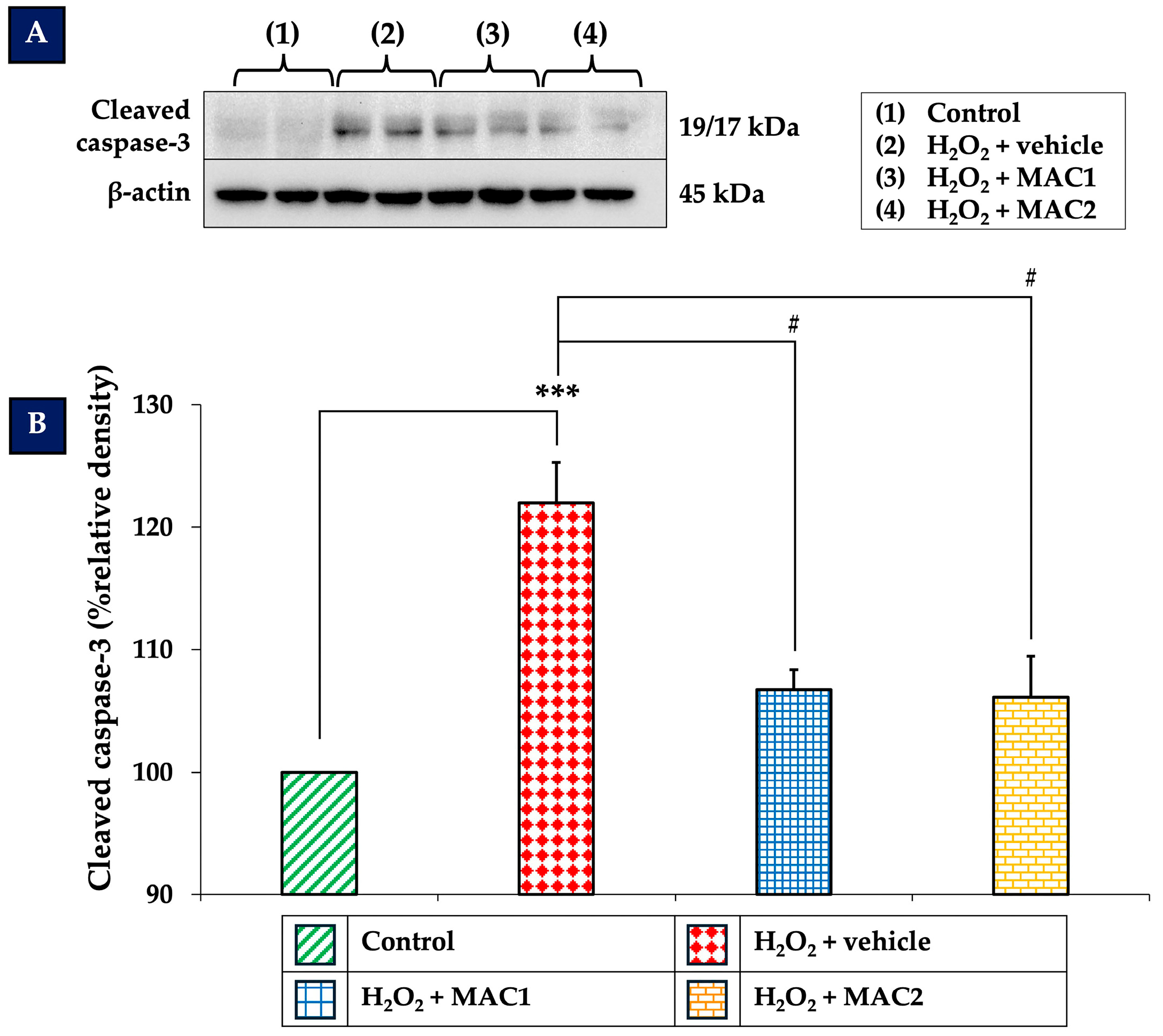
3.8. Effect of MAC on Cleaved Caspase-3 Expression
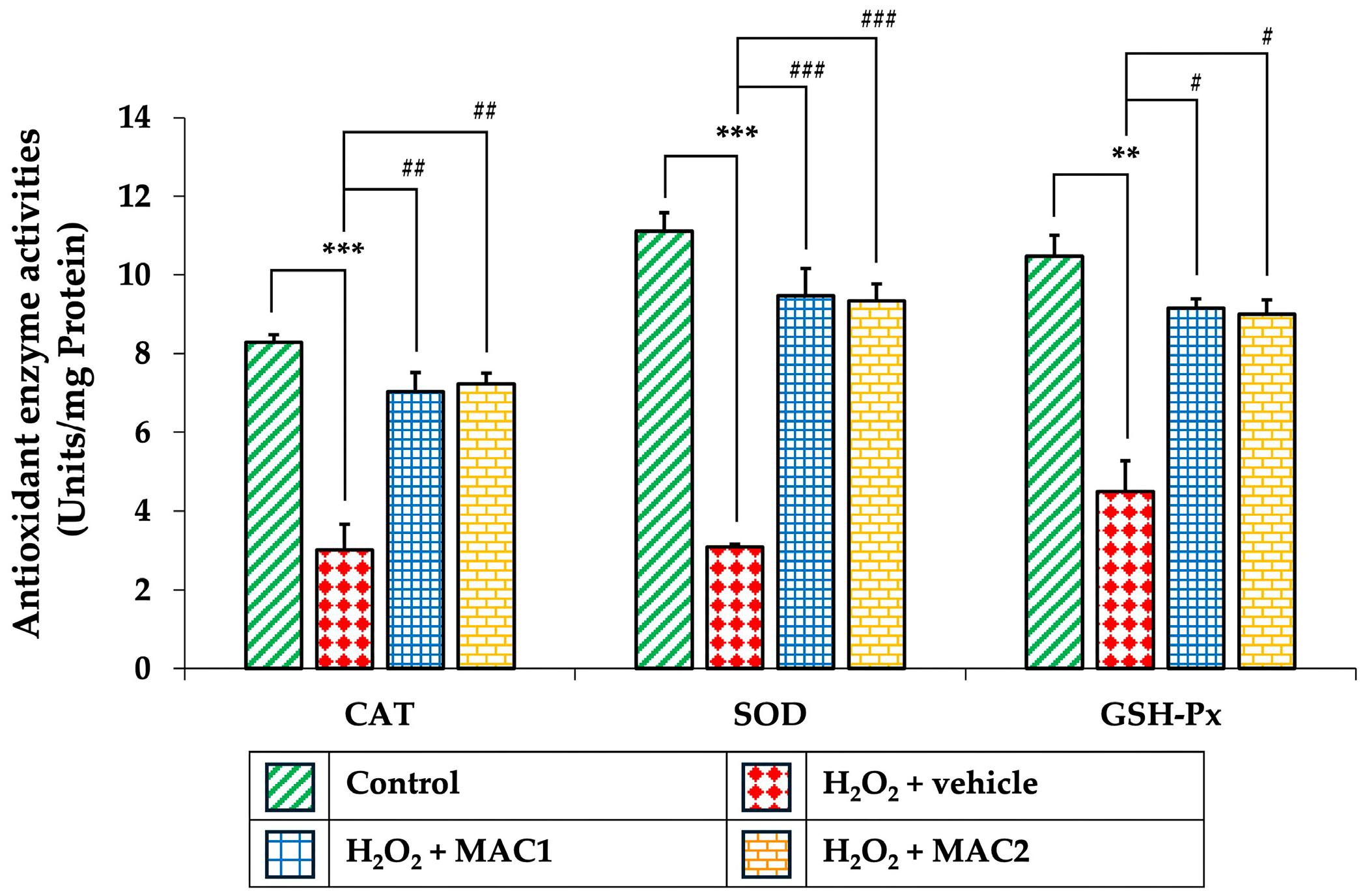
3.9. Effect of MAC on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
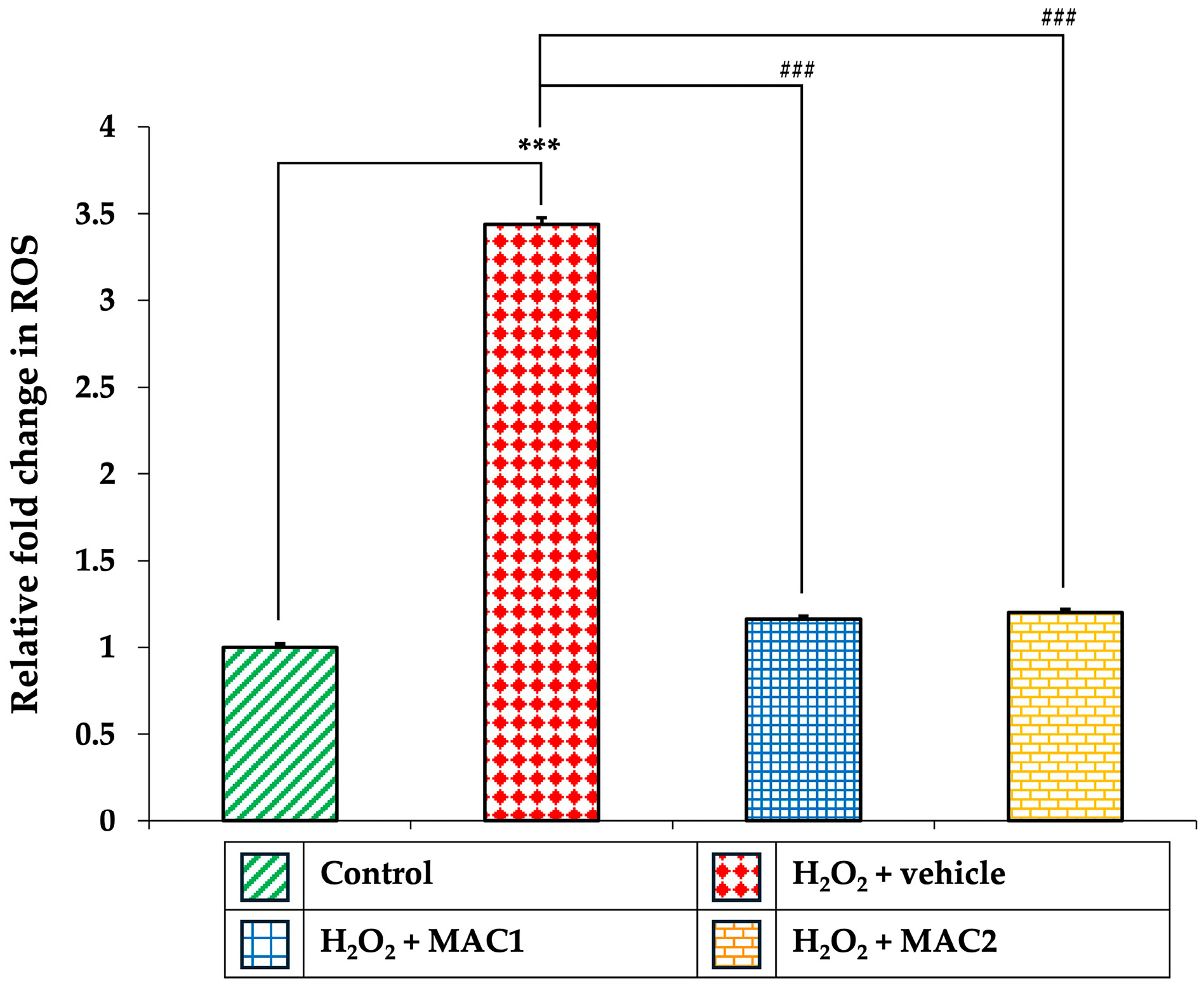
3.10. Effect of MAC on Intracellular ROS Production
3.11. Effect of MAC on Lipid Peroxidation (MDA Levels)
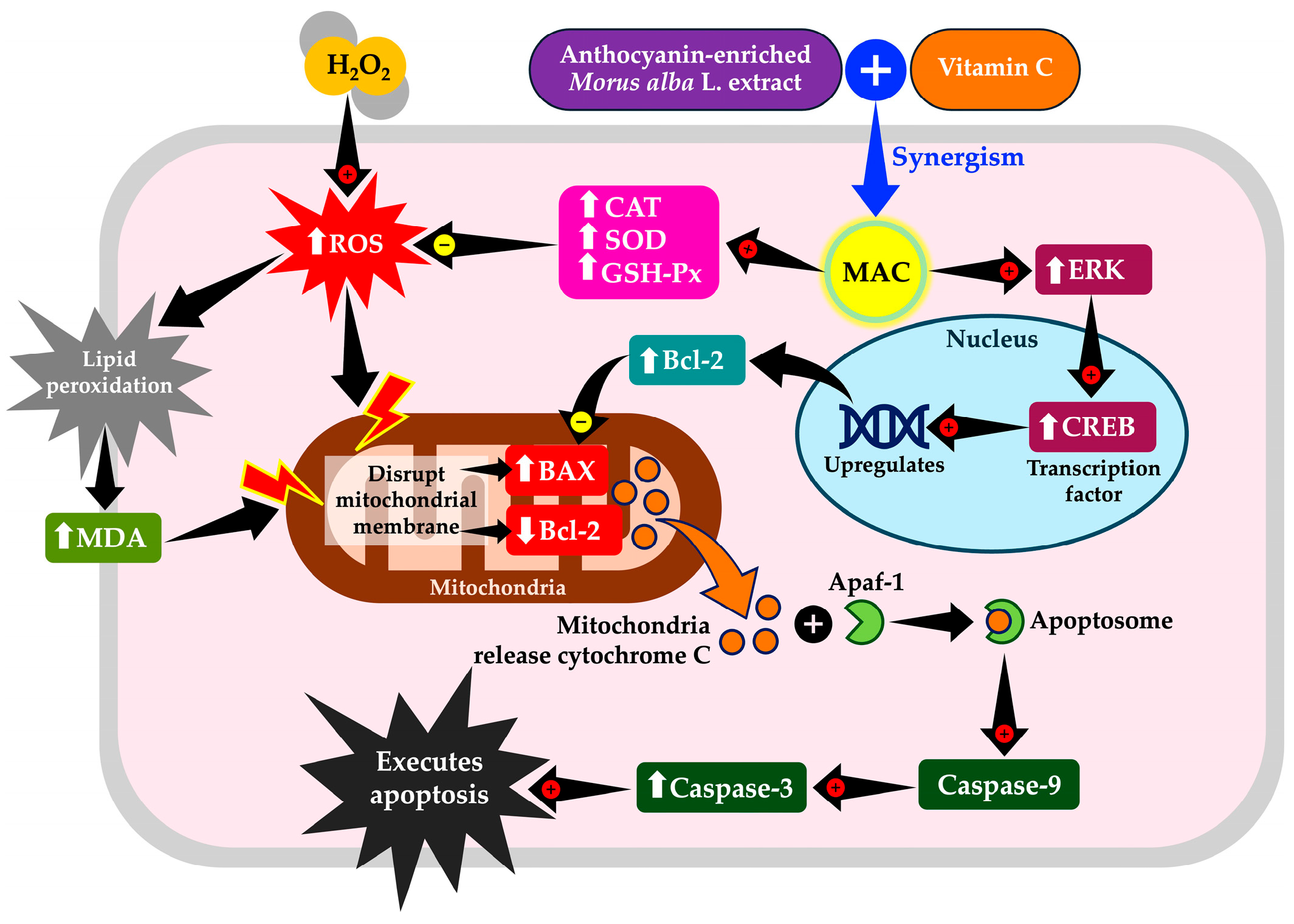
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on the Public Health Response to Dementia; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240033245 (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- Dorsey, E.R.; Bloem, B.R. The Parkinson Pandemic—A Call to Action. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, A.; Meng, F.; Zhang, J. The Expanding Burden of Neurodegenerative Diseases: An Unmet Medical and Social Need. Aging Dis. 2024, 16, 2937–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, S.; Guillemin, G.J.; Abiramasundari, R.S.; Essa, M.M.; Akbar, M.; Akbar, M.D. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Huntington’s Disease: A Mini Review. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 8590578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.Z.; Souayah, N. Oxidative Stress: Pathological Driver in Chronic Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; O, W.; Li, W.; Jiang, Z.-G.; Ghanbari, H.A. Oxidative Stress and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 24438–24475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, M.; Marcuzzi, A.; Gonelli, A.; Celeghini, C.; Maximova, N.; Rimondi, E. Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidants, an Innovative Class of Antioxidant Compounds for Neurodegenerative Diseases: Perspectives and Limitations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D. Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Damage and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Xun, Y.; Liu, H.; Wei, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Yuan, S.; Liu, N.; Xiang, S. Polydatin Protects Neuronal Cells from Hydrogen Peroxide Damage by Activating CREB/Ngb Signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 25, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, M.; Tian, Z.; Cui, Y.; Deng, D.; Rong, T.; Liu, Z.; Song, M.; Li, Z.; Ma, X.; et al. Exogenous Glutathione Protects IPEC-J2 Cells against Oxidative Stress through a Mitochondrial Mechanism. Molecules 2022, 27, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mairuae, N.; Palachai, N.; Noisa, P. The Neuroprotective Effects of the Combined Extract of Mulberry Fruit and Mulberry Leaf against Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; López, J.M. Understanding MAPK Signaling Pathways in Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.I.; Fang, K.M.; Kuo, C.Y.; Huang, C.F.; Liu, S.H.; Liu, J.M.; Lai, W.C.; Chang, K.C.; Su, C.C.; Chen, Y.W. Roles of Oxidative Stress/JNK/ERK Signals in Paraquat-Triggered Hepatic Apoptosis. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 6, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollville, E.; Romero, S.E.; Deshmukh, M. Apoptotic Cell Death Regulation in Neurons. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 3276–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Nie, Q.; Gao, M.; Yang, L.; Xiang, J.W.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, F.Y.; Gong, X.D.; Fu, J.L.; Wang, Y.; et al. The Transcription Factor CREB Acts as an Important Regulator Mediating Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis by Suppressing αB-Crystallin Expression. Aging 2020, 12, 13594–13617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Khan, M.; Shah, S.A.; Saeed, K.; Kim, M.O. Natural Antioxidant Anthocyanins—A Hidden Therapeutic Candidate in Metabolic Disorders with Major Focus in Neurodegeneration. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Wong, C.Y.; Koh, R.Y.; Lim, C.L.; Kok, Y.Y.; Chye, S.M. Natural Bioactive Compounds from Macroalgae and Microalgae for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2024, 97, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaa, C.A.; Marcelo, Á.J.; An, Z.; Medina-Franco, J.L.; Velasco-Velázquez, M.A. Anthocyanins: Molecular Aspects on Their Neuroprotective Activity. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rębas, E. Role of Flavonoids in Protecting against Neurodegenerative Diseases—Possible Mechanisms of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabuj, M.S.S.; Islam, M.S.; Akanda, M.R.; Lee, J.; Kim, R.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Oh, J.M.; Ro, H.G.; Kim, I.S.; et al. Macluraparishin C Enhances Neuroprotection against Oxidative Stress-Induced Neurodegeneration by Activating the Antioxidant/MAPK Signaling Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 13736–13747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Cha, M.; Lee, B.H. Neuroprotective Effect of Antioxidants in the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covarrubias-Pinto, A.; Acuña, A.I.; Beltrán, F.A.; Torres-Díaz, L.; Castro, M.A. Old Things New View: Ascorbic Acid Protects the Brain in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 28194–28217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, F.E.; May, J.M. Vitamin C Function in the Brain: Vital Role of the Ascorbate Transporter SVCT2. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palachai, N.; Wattanathorn, J.; Muchimapura, S.; Thukham-Mee, W. Antimetabolic Syndrome Effect of Phytosome Containing the Combined Extracts of Mulberry and Ginger in an Animal Model of Metabolic Syndrome. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5972575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanathorn, J.; Kawvised, S.; Thukham-Mee, W. Encapsulated Mulberry Fruit Extract Alleviates Changes in an Animal Model of Menopause with Metabolic Syndrome. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5360560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Shuang, F.-F.; Fu, Q.-Y.; Ju, Y.-X.; Zong, C.-M.; Zhao, W.-G.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Yao, X.-H.; Cao, F.-L. Evaluation of the Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Mulberry (Morus alba L.) Fruits from Different Varieties in China. Molecules 2022, 27, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khongrum, J.; Mairuae, N.; Thanchomnang, T.; Zhang, M.; Bai, G.; Palachai, N. Synergistic Neuroprotection through Epigenetic Modulation by Combined Curcumin-Enriched Turmeric Extract and L-Ascorbic Acid in Oxidative Stress-Induced SH-SY5Y Cell Damage. Foods 2025, 14, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairuae, N.; Noisa, P.; Palachai, N. Phytosome-Encapsulated 6-Gingerol- and 6-Shogaol-Enriched Extracts from Zingiber officinale Roscoe Protect against Oxidative Stress-Induced Neurotoxicity. Molecules 2024, 29, 6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanathorn, J.; Palachai, N.; Thukham-Mee, W.; Muchimapura, S. Memory-Enhancing Effect of a Phytosome Containing the Combined Extract of Mulberry Fruit and Ginger in an Animal Model of Ischemic Stroke with Metabolic Syndrome. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 3096826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairuae, N.; Palachai, N.; Noisa, P. An Anthocyanin-Rich Extract from Zea mays L. var. ceratina Alleviates Neuronal Cell Death Caused by Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairuae, N.; Palachai, N. Synergistic Antioxidant Effects of C3G-Enriched Oryza sativa L. cv. RD83 Extract and α-Tocopherol against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in SH-SY5Y Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palachai, N.; Supawat, A.; Kongsui, R.; Klimaschewski, L.; Jittiwat, J. Galangin’s Neuroprotective Role: Targeting Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Ischemic Stroke in a Rat Model of Permanent Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X. Mitochondrial Defects and Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer Disease and Parkinson Disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- urcău, M.C.; Andronie-Cioara, F.L.; Jurcău, A.; Marcu, F.; Ţiț, D.M.; Pașcalău, N.; Nistor-Cseppentö, D.C. The Link between Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neuroinflammation in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s Disease: Therapeutic Implications and Future Perspectives. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, Y.A.; Zakharova, I.O.; Avrova, N.F. The Effects of Alpha-Tocopherol and H2O2 on the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and Bax/Bcl-xL Ratio in PC12 Cells. Neurochem. J. 2016, 10, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-K.; Cheng, C.-H.; Chen, S.-D.; Liou, C.-W.; Huang, C.-R.; Chuang, Y.-C. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress Promote Apoptotic Cell Death in the Striatum via Cytochrome c/Caspase-3 Signaling Cascade Following Chronic Rotenone Intoxication in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8722–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Li, L.Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Gong, H.Y.; Cui, Y. Protective Effect of Rosamultin against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in H9c2 Cardiomyocytes. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 8415610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaad, C.A.; Klann, E. Reactive Oxygen Species in the Regulation of Synaptic Plasticity and Memory. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 2013–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezri, M.R.; Yousefi, K.; Esmaeili, A.; Ghasemnejad-Berenji, M. The Role of ERK1/2 Pathway in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s Disease: An Overview and Update on New Developments. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 43, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Kwon, Y.J.; Seo, E.B.; Lee, H.S.; Sohn, J.O.; Shin, H.M.; Kim, S.J.; Ye, S.K. Neuroprotective Effects of STAT3 Inhibitor on Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Neuronal Cell Death via the ERK/CREB Signaling Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2024, 50, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Feng, Y.; Shao, B.; Zhang, Y. Activation of the ERK/CREB/Bcl-2 Pathway Protects Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells against Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 3649–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.M.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.H.; He, L.C.; Feng, Y.; Liu, H.S. Low-Dose Aspirin Inhibits Trophoblast Cell Apoptosis by Activating the CREB/Bcl-2 Pathway in Pre-Eclampsia. Cell Cycle 2022, 21, 2223–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olufunmilayo, E.O.; Gerke-Duncan, M.B.; Holsinger, R.M.D. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shichiri, M. The Role of Lipid Peroxidation in Neurological Disorders. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2014, 54, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allowitz, K.; Taylor, J.; Harames, K.; Yoo, J.; Baloch, O.; Ramana, K.V. Oxidative Stress-Mediated Lipid Peroxidation-Derived Lipid Aldehydes in the Pathophysiology of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2025, 23, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, F.; Yu, D.F.; Wu, P.F.; Chen, J.G. The Cytotoxic Mechanism of Malondialdehyde and Protective Effect of Carnosine via Protein Cross-Linking/Mitochondrial Dysfunction/Reactive Oxygen Species/MAPK Pathway in Neurons. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 650, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xing, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, F. Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress Impairs Redox Status and Damages Aerobic Metabolism of Breast Muscle in Broilers. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Abdul Manap, A.S.; Attiq, A.; Albokhadaim, I.; Kandeel, M.; Alhojaily, S.M. From Imbalance to Impairment: The Central Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Oxidative Stress-Induced Disorders and Therapeutic Exploration. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1269581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fuente, A.; Vázquez, F.; Viéitez, J.M.; Alonso, F.J.G.; Martín, J.I.; Ferrer, J. CISNE: An Accurate Description of Dose-Effect and Synergism in Combination Therapies. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caesar, L.K.; Cech, N.B. Synergy and Antagonism in Natural Product Extracts: When 1 + 1 Does Not Equal 2. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 869–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enaru, B.; Drețcanu, G.; Pop, T.D.; Stǎnilǎ, A.; Diaconeasa, Z. Anthocyanins: Factors Affecting Their Stability and Degradation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska-Bartosz, I.; Bartosz, G. Antioxidant Activity of Anthocyanins and Anthocyanidins: A Critical Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, F. Review: Enhancing the Bioavailability and Stability of Anthocyanins for the Prevention and Treatment of Central Nervous System-Related Diseases. Foods 2025, 14, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, S.Y.; Burritt, D.J.; Hocquel, A.; Penberthy, A.; Oey, I. The Relationship between the Anthocyanin and Vitamin C Contents of Red-Fleshed Sweet Cherries and the Ability of Fruit Digests to Reduce Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress in Caco-2 Cells. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Xie, K.; Liao, X.; Tan, J. Factors Affecting the Stability of Anthocyanins and Strategies for Improving Their Stability: A Review. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Ratios (Dose Level) | % Inhibition | Combination Index Value | Interaction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morus alba L. Extract | Vitamin C | |||
| 0.125X | 0.125X | 50.03 ± 0.61 | 1.58 ± 0.05 | Antagonism |
| 0.25 | 0.125X | 41.11 ± 1.79 | 1.43 ± 0.06 | Moderate antagonism |
| 0.5X | 0.125X | 22.36 ± 0.71 | 0.90 ± 0.03 | Nearly additive effect |
| 1X | 0.125X | 20.29 ± 0.69 | 1.16 ± 0.04 | Slight antagonism |
| 2X | 0.125X | 17.35 ± 0.82 | 1.01 ± 0.05 | Nearly additive effect |
| 0.125X | 0.25 | 45.31 ± 0.62 | 1.41 ± 0.03 | Moderate antagonism |
| 0.25 | 0.25 | 38.31 ± 1.08 | 1.36 ± 0.06 | Moderate antagonism |
| 0.5X | 0.25 | 20.91 ± 1.18 | 0.89 ± 0.06 | Slight synergism |
| 1X | 0.25 | 18.49 ± 1.07 | 1.04 ± 0.05 | Nearly additive effect |
| 2X | 0.25 | 20.89 ± 1.06 | 1.23 ± 0.07 | Moderate antagonism |
| 0.125X | 0.5X | 43.15 ± 0.47 | 1.34 ± 0.02 | Moderate antagonism |
| 0.25 | 0.5X | 35.94 ± 0.50 | 1.25 ± 0.02 | Moderate antagonism |
| 0.5X | 0.5X | 11.20 ± 0.58 | 0.46 ± 0.02 | Synergism |
| 1X | 0.5X | 9.85 ± 1.12 | 0.61 ± 0.08 | Synergism |
| 2X | 0.5X | 20.31 ± 1.48 | 1.23 ± 0.11 | Moderate antagonism |
| 0.125X | 1X | 41.23 ± 1.32 | 1.28 ± 0.04 | Moderate antagonism |
| 0.25 | 1X | 30.04 ± 0.57 | 1.05 ± 0.02 | Nearly additive effect |
| 0.5X | 1X | 17.45 ± 0.87 | 0.74 ± 0.04 | Moderate synergism |
| 1X | 1X | 8.66 ± 0.98 | 0.52 ± 0.06 | Synergism |
| 2X | 1X | 18.73 ± 0.73 | 1.09 ± 0.05 | Nearly additive effect |
| 0.125X | 2X | 44.23 ± 0.82 | 1.37 ± 0.03 | Moderate antagonism |
| 0.25 | 2X | 31.60 ± 2.02 | 1.11 ± 0.07 | Slight antagonism |
| 0.5X | 2X | 23.46 ± 1.91 | 1.02 ± 0.09 | Nearly additive effect |
| 1X | 2X | 19.64 ± 1.37 | 1.12 ± 0.08 | Slight antagonism |
| 2X | 2X | 20.63 ± 1.29 | 1.17 ± 0.07 | Slight antagonism |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mairuae, N.; Jittiwat, J.; Apaijit, K.; Noisa, P.; Bai, G.; Hou, Y.; Palachai, N. Synergistic Effects of Anthocyanin-Enriched Morus alba L. Extract and Vitamin C: Promising Nutraceutical Ingredients in Functional Food Development for Neuroprotection. Foods 2025, 14, 3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213630
Mairuae N, Jittiwat J, Apaijit K, Noisa P, Bai G, Hou Y, Palachai N. Synergistic Effects of Anthocyanin-Enriched Morus alba L. Extract and Vitamin C: Promising Nutraceutical Ingredients in Functional Food Development for Neuroprotection. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213630
Chicago/Turabian StyleMairuae, Nootchanat, Jinatta Jittiwat, Kwanjit Apaijit, Parinya Noisa, Gang Bai, Yuanyuan Hou, and Nut Palachai. 2025. "Synergistic Effects of Anthocyanin-Enriched Morus alba L. Extract and Vitamin C: Promising Nutraceutical Ingredients in Functional Food Development for Neuroprotection" Foods 14, no. 21: 3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213630
APA StyleMairuae, N., Jittiwat, J., Apaijit, K., Noisa, P., Bai, G., Hou, Y., & Palachai, N. (2025). Synergistic Effects of Anthocyanin-Enriched Morus alba L. Extract and Vitamin C: Promising Nutraceutical Ingredients in Functional Food Development for Neuroprotection. Foods, 14(21), 3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213630






