Preparation and Characterization of Camellia Oil Microcapsules Using Spray Drying Coupled with Sodium Caseinate/Xanthan Gum-Stabilized Emulsion Template
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Camellia Oil Emulsion
2.3. Rheological Analysis of Camellia Oil Emulsion
2.4. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy of Camellia Oil Emulsion
2.5. Preparation of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
2.6. Color Variation in Camellia Oil Microcapsules
2.7. Powder Yield of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
2.8. Moisture Content of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
2.9. Bulk Density of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
2.10. Solubility of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
2.11. Microscopic and Particle Size Analysis of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
2.12. Oil Content Analysis of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
2.13. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectra of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
2.14. Thermal Stability Measurement of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
2.15. Encapsulation Efficiency of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
2.16. Antioxidant Activity Assay of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
2.17. In Vitro Digestion Analysis of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
2.18. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheological Properties of Camellia Oil Emulsion
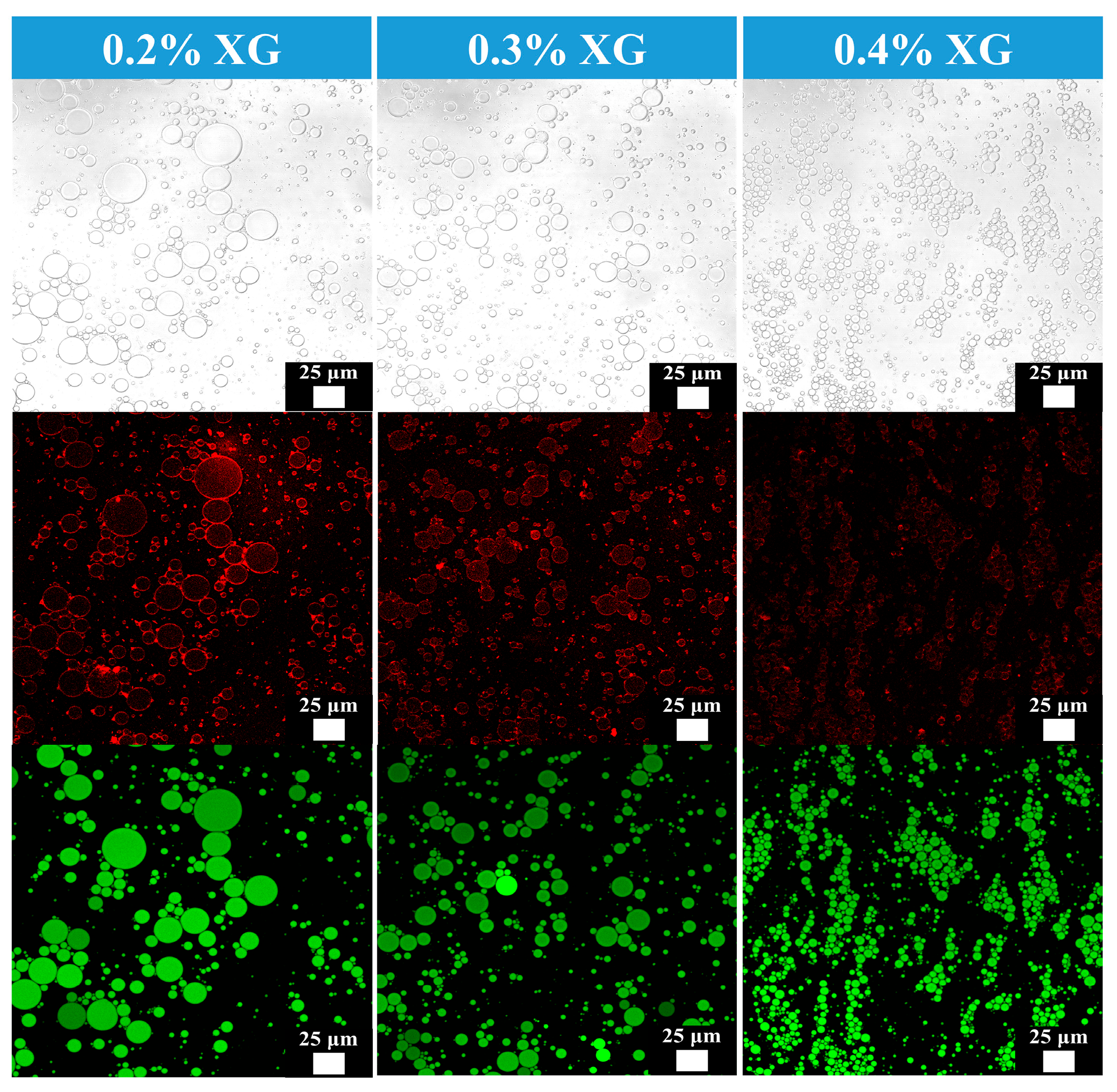
3.2. Confocal Laser Microscopy of Camellia Oil Emulsion
3.3. Appearance and Color Parameters of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
3.4. Powder Yield, Moisture Content, and Bulk Density of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
3.5. SEM and Particle Size Distributions of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
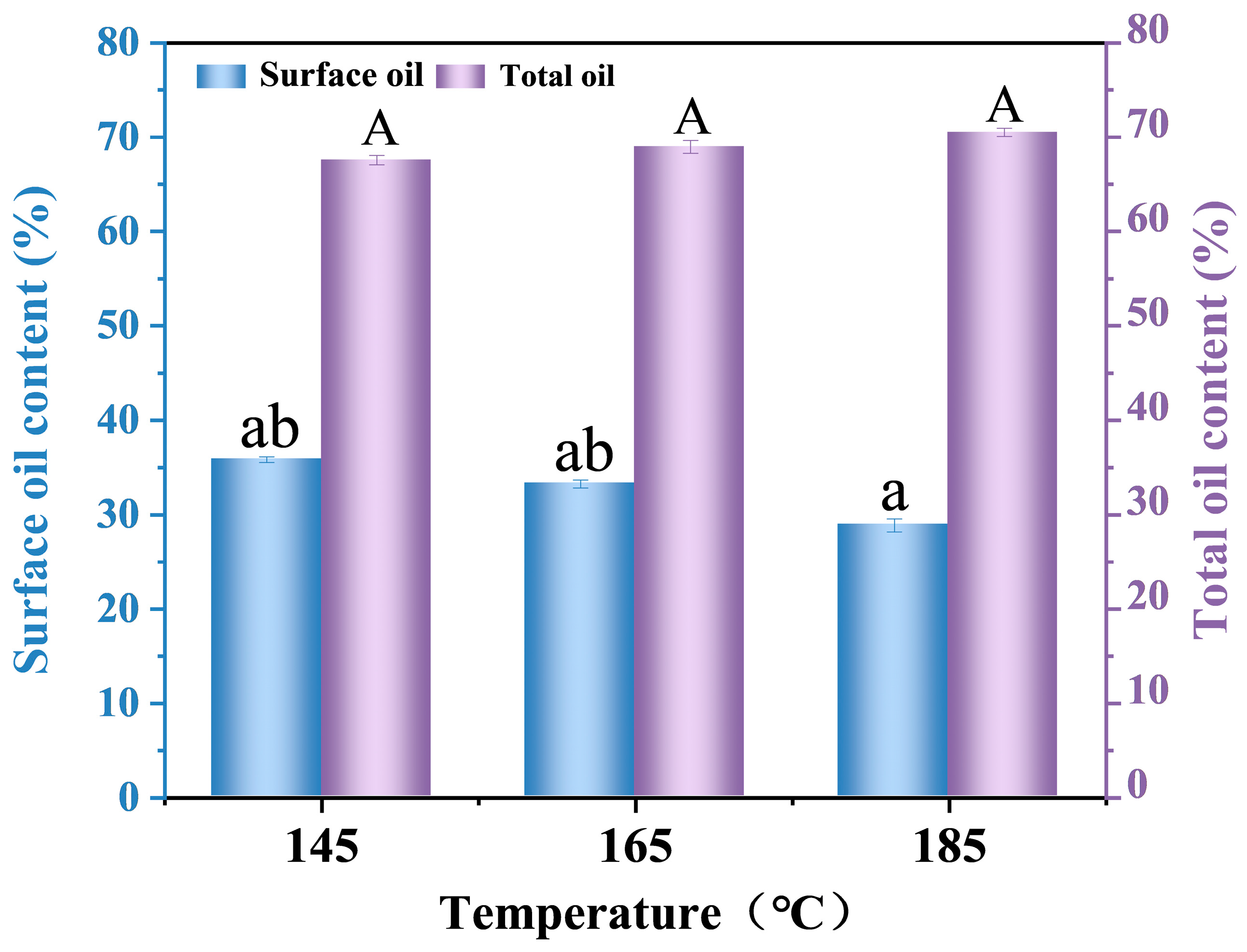
3.6. Oil Content of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
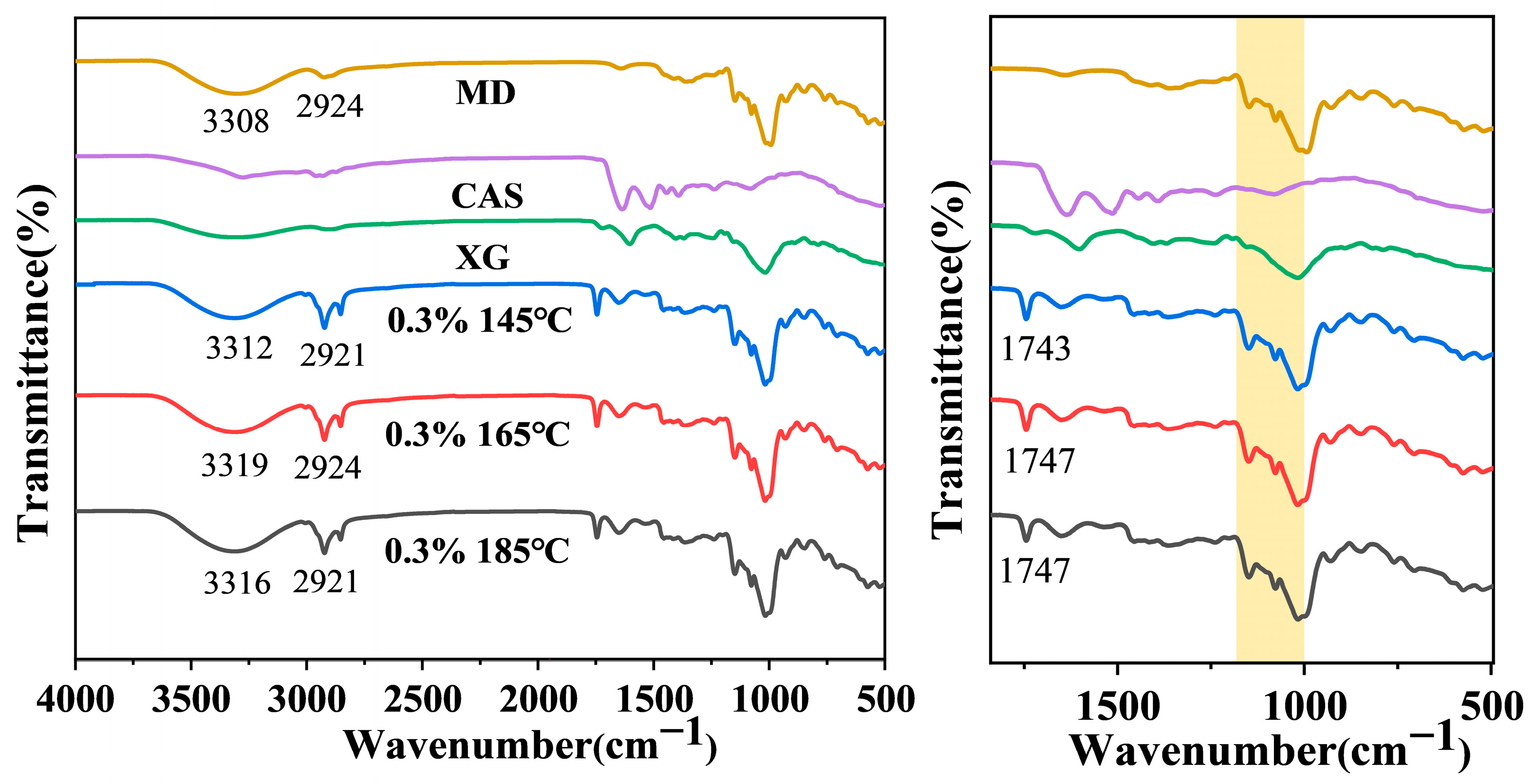
3.7. FTIR Analysis of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
3.8. Thermal Stability of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
3.9. Encapsulation Efficiency and Antioxidant Activity of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
3.10. In Vitro Digestion of Camellia Oil Microcapsules
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Hu, Z.; Lv, Q.; Liu, G. Preparation of Camellia Oil Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Glycated Whey Protein Isolate and Chitooligosaccharide: Effect on Interfacial Behavior and Emulsion Stability. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 153, 112515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Hu, X.; Pan, L.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, L.; Pang, M.; Hou, Z.; Jiang, S. Preparation of Camellia Oil-Based W/O Emulsions Stabilized by Tea Polyphenol Palmitate: Structuring Camellia Oil as a Potential Solid Fat Replacer. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yan, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Fang, X.; Huang, C.; He, X.; Li, L.; Li, Q. Preparation of Soybean Protein Isolate-Quercetin Particles and Its Application in Curcumin-Camellia Oil Pickering Emulsion. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 18, 2086–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, A.; Du, Q.; Zhu, W.; Liu, H.; Naeem, A.; Guan, Y.; Chen, L.; Ming, L. Bioactive Substances and Therapeutic Potential of Camellia Oil: An Overview. Food Biosci. 2022, 49, 101855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, D.; Yu, H. In Vitro Fermentation and Camellia Oil Emulsification Characteristics of Konjac Glucomannan Octenyl Succinate. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 3912–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ao, F.; Ge, X.; Shen, W. Food-Grade Pickering Emulsions: Preparation, Stabilization and Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Liu, H.; Huang, Q. Fabrication and Characterization of Resistant Starch Stabilized Pickering Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Luo, X.; Pei, Y.; Liu, S. Edible Oil Powders Based on Spray-Dried Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Soy Protein/Cellulose Nanofibrils. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wei, R.; Jia, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Xu, B.; Xu, B. Preparation of Piper Nigrum Microcapsules by Spray Drying and Optimization with Response Surface Methodology. J. Oleo Sci. 2022, 71, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, N.; Wani, S.M.; Padder, S.A.; Habib, S.; Ayaz, Q.; Mustafa, S.; Amin, T.; Malik, A.R.; Hussain, S.Z. Optimizing Prodigiosin Nanoencapsulation in Different Wall Materials by Freeze Drying: Characterization and Release Kinetics. Food Chem. 2025, 477, 143587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Tian, Y.; Bai, X.; Cao, Y.; Fu, Z. Influence of the Emulsifier Sodium Caseinate-Xanthan Gum Complex on Emulsions: Stability and Digestive Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, R.; Chang, C.; Li, J.; Xiong, W.; Yang, Y.; Gu, L. Emulsion-Templated Liquid Oil Structuring with Egg White Protein Microgel- Xanthan Gum. Foods 2023, 12, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, C.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, W.; Luo, D.; Shah, B.R. Stability, Microstructural and Rheological Properties of Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Xanthan Gum/Lysozyme Nanoparticles Coupled with Xanthan Gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2387–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özbek, Z.A.; Ergönül, P.G. Optimisation of Wall Material Composition of Freeze–Dried Pumpkin Seed Oil Microcapsules: Interaction Effects of Whey Protein, Maltodextrin, and Gum Arabic by D–Optimal Mixture Design Approach. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 107, 105909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Luo, D.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Kang, M.; Shah, B.R.; Wei, X.; Xu, W. Construction of Pickering Double Emulsions Based on Xanthan Gum/Lysozyme Nanoparticles: Structure, Stability, and Co-Encapsulation of Epigallocatechin Gallate and β-Carotene. Foods 2025, 14, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerster, M.; Liu, C.; Gengenbach, T.; Woo, M.W.; Selomulya, C. Reduction of Surface Fat Formation on Spray-Dried Milk Powders through Emulsion Stabilization with λ-Carrageenan. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Hu, H.; Zhu, G.; Duan, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lin, L.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Z. Microencapsulation of Pickering Nanoemulsions Containing Walnut Oil Stabilized Using Soy Protein–Curcumin Composite Nanoparticles: Fabrication and Evaluation of a Novel Plant-Based Milk Substitute. Food Chem. 2025, 470, 142654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yin, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Luo, D.; Kang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. Fabrication and Characterization of Epigallocatechin Gallate and β-Carotene Co-Encapsulated Pickering Double Emulsions Stabilized by Xanthan Gum/Lysozyme Nanoparticles and Konjac Glucomannan. Food Res. Int. 2025, 218, 116923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouziane, H.; Seddari, S.; Boudjema, F.; Moulai-Mostefa, N. Preparation and Characterization of Sodium Caseinate/Xanthan Gum Complexes in Acidic Conditions and Their Use for the Stabilization of Oil-in-Water Emulsions. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2024, 101, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ning, Y.; Chai, L.; Yin, Y.; Luo, D.; Xu, W. Physicochemical Properties and in Vitro Digestive Behavior of Astaxanthin Loaded Pickering Emulsion Gel Regulated by Konjac Glucomannan and κ-Carrageenan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.I.; Rodrigues, M.Z.; Pinto, M.R.M.R.; Vanzela, E.S.L.; Stringheta, P.C.; Perrone, Í.T.; Ramos, A.M. Morphological Characterization of Pequi Extract Microencapsulated through Spray Drying. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, G.-Q.; Li, X.-D.; Xiao, J.-X. Preparation of Powdered Oil by Spray Drying the Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Ovalbumin—Gum Arabic Polyelectrolyte Complex. Food Chem. 2022, 391, 133223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goula, A.M.; Adamopoulos, K.G. A Method for Pomegranate Seed Application in Food Industries: Seed Oil Encapsulation. Food Bioprod. Process. 2012, 90, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Yang, Y. Fabricating Multilayer Emulsions by Using OSA Starch and Chitosan Suitable for Spray Drying: Application in the Encapsulation of β-Carotene. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Tian, G.; Zhao, S.; Yang, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Lian, Y.; Wang, F.; Du, H.; et al. Effects of Spray-Drying Temperature on the Physicochemical Properties and Polymethoxyflavone Loading Efficiency of Citrus Oil Microcapsules. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 133, 109954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Sun, H.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Zheng, S.; Luo, D.; Ning, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shah, B.R. Preparation and Characterization of Tea Oil Powder with High Water Solubility Using Pickering Emulsion Template and Vacuum Freeze-Drying. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 160, 113330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Luo, Z. Effect of Wall Materials on Physicochemical Properties and Bitterness Masking of Freeze-Dried Navel Orange Peel Powder. Food Biosci. 2025, 66, 106226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Mu, H.; Peng, L.; Tan, C.; Chen, Y.; Sheng, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, C. Effect and Application of Spray Drying and Freeze Drying on Characterization of Walnut Oil Microcapsules. J. Food Eng. 2024, 376, 112083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X.; Gao, J.; Lu, J.; Ma, C.; Lv, J.; Adhikari, B.; Wang, B. Preparation and Drying of Water-in-Oil-in-Water (W/O/W) Double Emulsion to Encapsulate Soy Peptides. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z. Preparation, Characterization and in Vitro Digestion of Jujube Polysaccharide Microcapsules. Food Bioprod. Process. 2024, 145, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.K.S.; Lim, H.-P.; Tey, B.-T.; Chan, E.-S. Spray-Dried Alginate-Coated Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Chitosan for Improved Oxidative Stability and in Vitro Release Profile. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

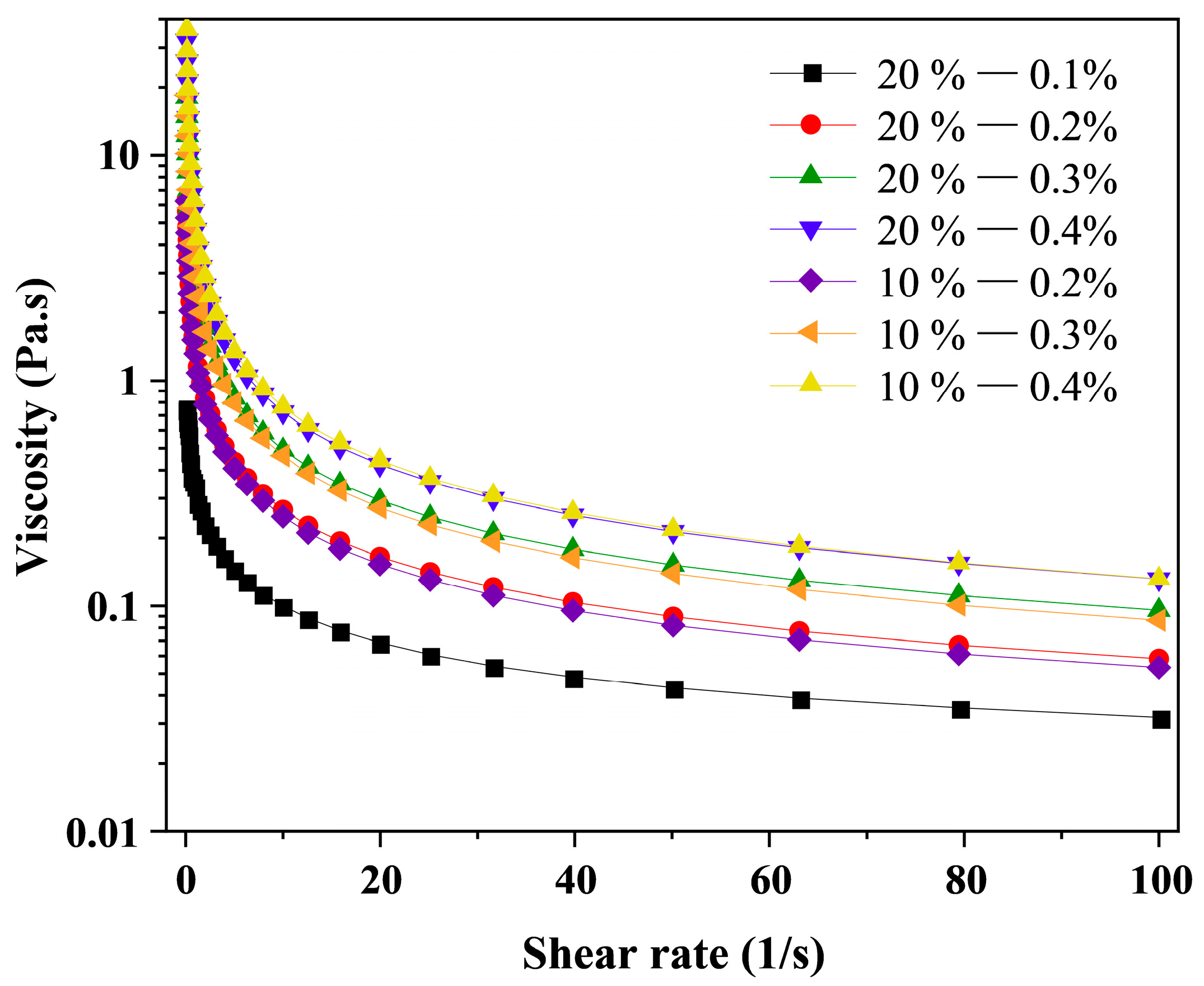




| Samples | Oil Phase (%) | k (Pa·sn) | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1%XG | 20 | 0.314 | 0.577 | 0.986 |
| 0.2%XG | 20 | 1.395 | 0.329 | 0.999 |
| 0.3%XG | 20 | 2.860 | 0.205 | 0.999 |
| 0.4%XG | 20 | 4.593 | 0.158 | 0.999 |
| 0.2%XG | 10 | 1.288 | 0.314 | 0.999 |
| 0.3%XG | 10 | 2.770 | 0.184 | 0.999 |
| 0.4%XG | 10 | 5.083 | 0.154 | 0.999 |
| Samples | Inlet Air Temperature (°C) | L | a* | b* | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2%XG | 145 °C | 93.15 ± 0.10 cA | −0.61 ± 0.02 bA | 5.14 ± 0.05 aB | 5.82 ± 0.09 bA |
| 165 °C | 89.88 ± 0.15 aA | −0.85 ± 0.02 aA | 6.74 ± 0.12 bC | 5.31 ± 0.15 aA | |
| 185 °C | 91.24 ± 0.06 bA | −0.83 ± 0.01 aA | 9.42 ± 0.15 cC | 8.26 ± 0.13 cB | |
| 0.3%XG | 145 °C | 94.32 ± 0.14 cB | −0.62 ± 0.02 cA | 5.73 ± 0.05 aC | 7.31 ± 0.25 bB |
| 165 °C | 93.62 ± 0.28 bB | −0.72 ± 0.02 bB | 5.08 ± 0.13 aB | 6.58 ± 0.21 aB | |
| 185 °C | 93.23 ± 0.02 aB | −0.77 ± 0.01 aB | 7.50 ± 0.30 bB | 7.52 ± 0.21 bA | |
| 0.4%XG | 145 °C | 95.75 ± 0.05 bC | −0.55 ± 0.03 bB | 4.48 ± 0.04 aA | 7.76 ± 0.05 bC |
| 165 °C | 95.66 ± 0.05 bC | −0.56 ± 0.01 bC | 4.40 ± 0.07 aA | 7.65 ± 0.06 bC | |
| 185 °C | 94.83 ± 0.11 aC | −0.63 ± 0.01 aC | 5.57 ± 0.12 bA | 7.42 ± 0.11 aA |
| Samples | Inlet Air Temperature (°C) | Powder Yield (%) | Moisture Content (%) | Bulk Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2%XG | 185 °C | 49.16 ± 0.40 cB | 2.68 ± 0.03 cC | 0.32 ± 0.007 aB |
| 165 °C | 46.52 ± 0.28 bB | 2.39 ± 0.02 bB | 0.46 ± 0.018 bC | |
| 145 °C | 43.59 ± 0.39 aB | 1.77 ± 0.02 aA | 0.46 ± 0.010 bC | |
| 0.3%XG | 185 °C | 49.51 ± 0.43 bB | 2.29 ± 0.04 bB | 0.31 ± 0.004 aA |
| 165 °C | 53.68 ± 0.38 cC | 1.89 ± 0.03 aA | 0.36 ± 0.003 bB | |
| 145 °C | 34.96 ± 0.82 aB | 1.92 ± 0.04 aB | 0.40 ± 0.007 cB | |
| 0.4%XG | 185 °C | 28.07 ± 0.43 aA | 2.08 ± 0.07 aA | 0.31 ± 0.002 aA |
| 165 °C | 36.97 ± 0.25 bA | 2.49 ± 0.04 bC | 0.33 ± 0.007 bA | |
| 145 °C | 27.60 ± 0.51 aA | 2.84 ± 0.04 cC | 0.35 ± 0.009 cA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Xin, Y.; Xue, J.; Li, Z.; Shah, B.R.; Xu, W. Preparation and Characterization of Camellia Oil Microcapsules Using Spray Drying Coupled with Sodium Caseinate/Xanthan Gum-Stabilized Emulsion Template. Foods 2025, 14, 3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213610
Zhang L, Li L, Xin Y, Xue J, Li Z, Shah BR, Xu W. Preparation and Characterization of Camellia Oil Microcapsules Using Spray Drying Coupled with Sodium Caseinate/Xanthan Gum-Stabilized Emulsion Template. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213610
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lihua, Lala Li, Yingying Xin, Jiawei Xue, Zhenwei Li, Bakht Ramin Shah, and Wei Xu. 2025. "Preparation and Characterization of Camellia Oil Microcapsules Using Spray Drying Coupled with Sodium Caseinate/Xanthan Gum-Stabilized Emulsion Template" Foods 14, no. 21: 3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213610
APA StyleZhang, L., Li, L., Xin, Y., Xue, J., Li, Z., Shah, B. R., & Xu, W. (2025). Preparation and Characterization of Camellia Oil Microcapsules Using Spray Drying Coupled with Sodium Caseinate/Xanthan Gum-Stabilized Emulsion Template. Foods, 14(21), 3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213610





