Creation of TGMS Lines of Waxy Rice with Elite Physicochemical Properties of Starch via Waxy Gene Editing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Phenotype and Genotype Assays
2.3. Grain Morphology and Endosperm Starch Staining
2.4. Pollen Viability Assay
2.5. Total Protein and Amylose Content Determination
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.7. Gel Consistency
2.8. Pasting Properties by Rapid Visco Analyzer
2.9. Thermal Properties by Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.10. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.11. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.12. Amylopectin Chain-Length Distribution
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
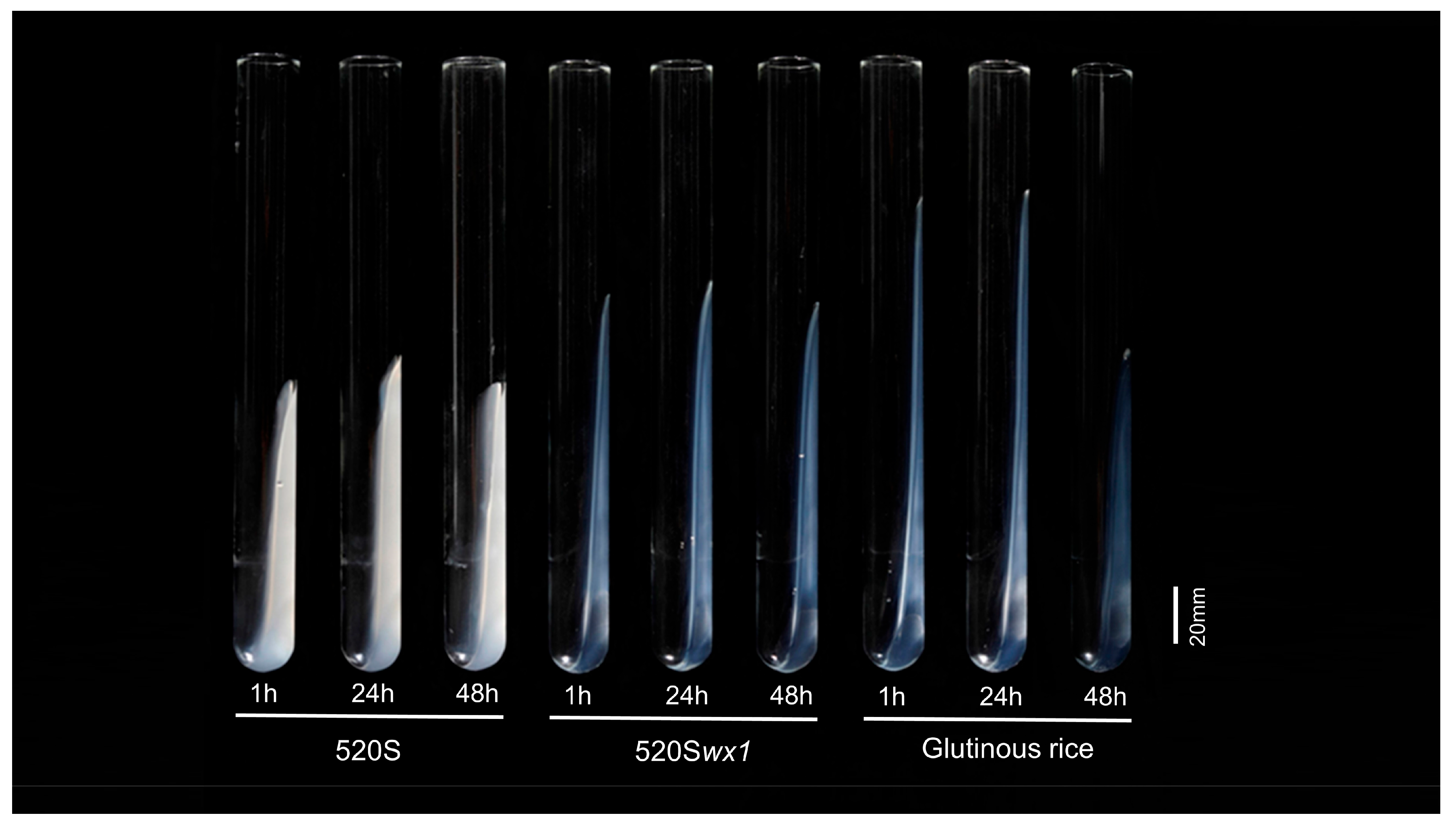
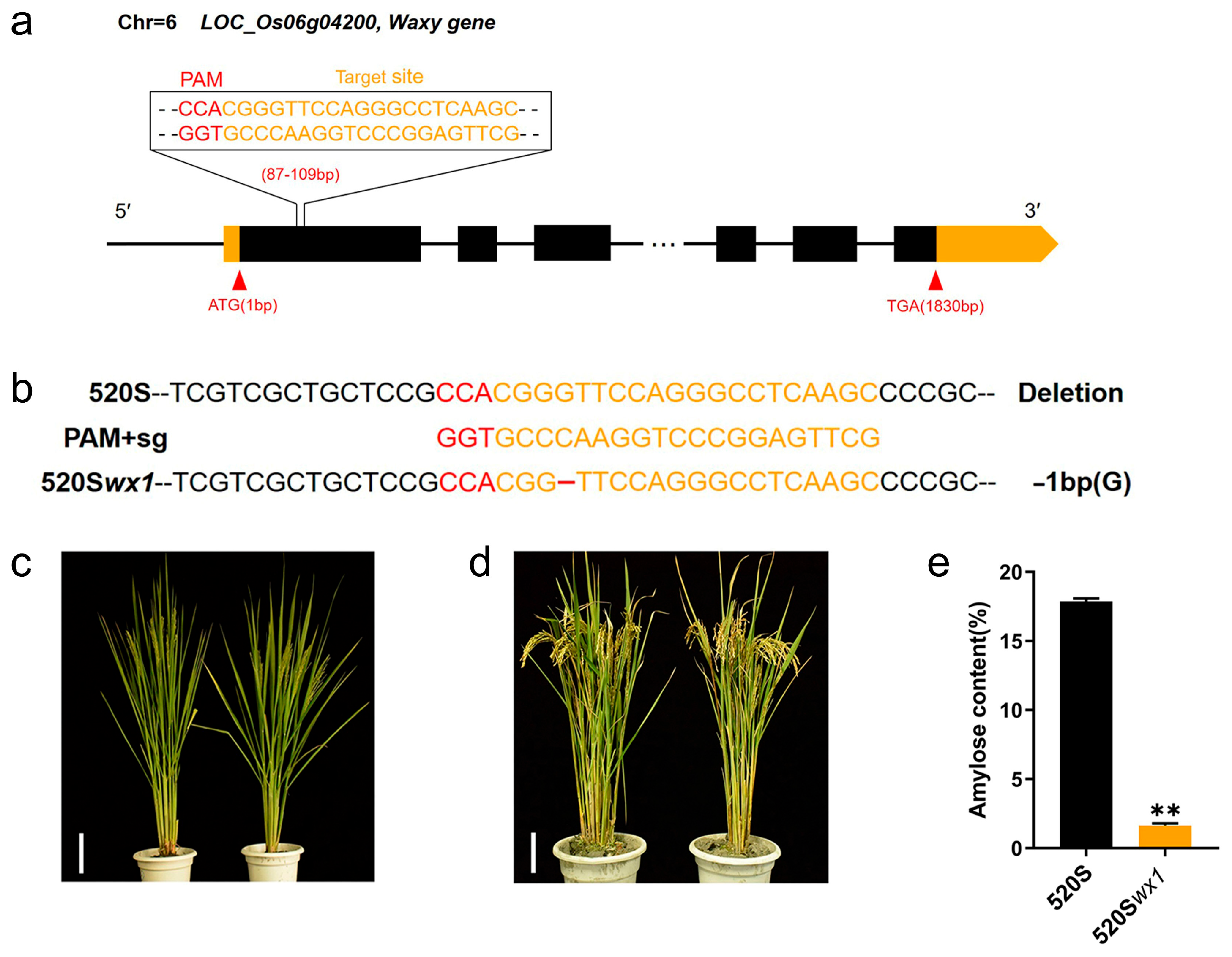
3.1. Generation of a New Wx TGMS Line
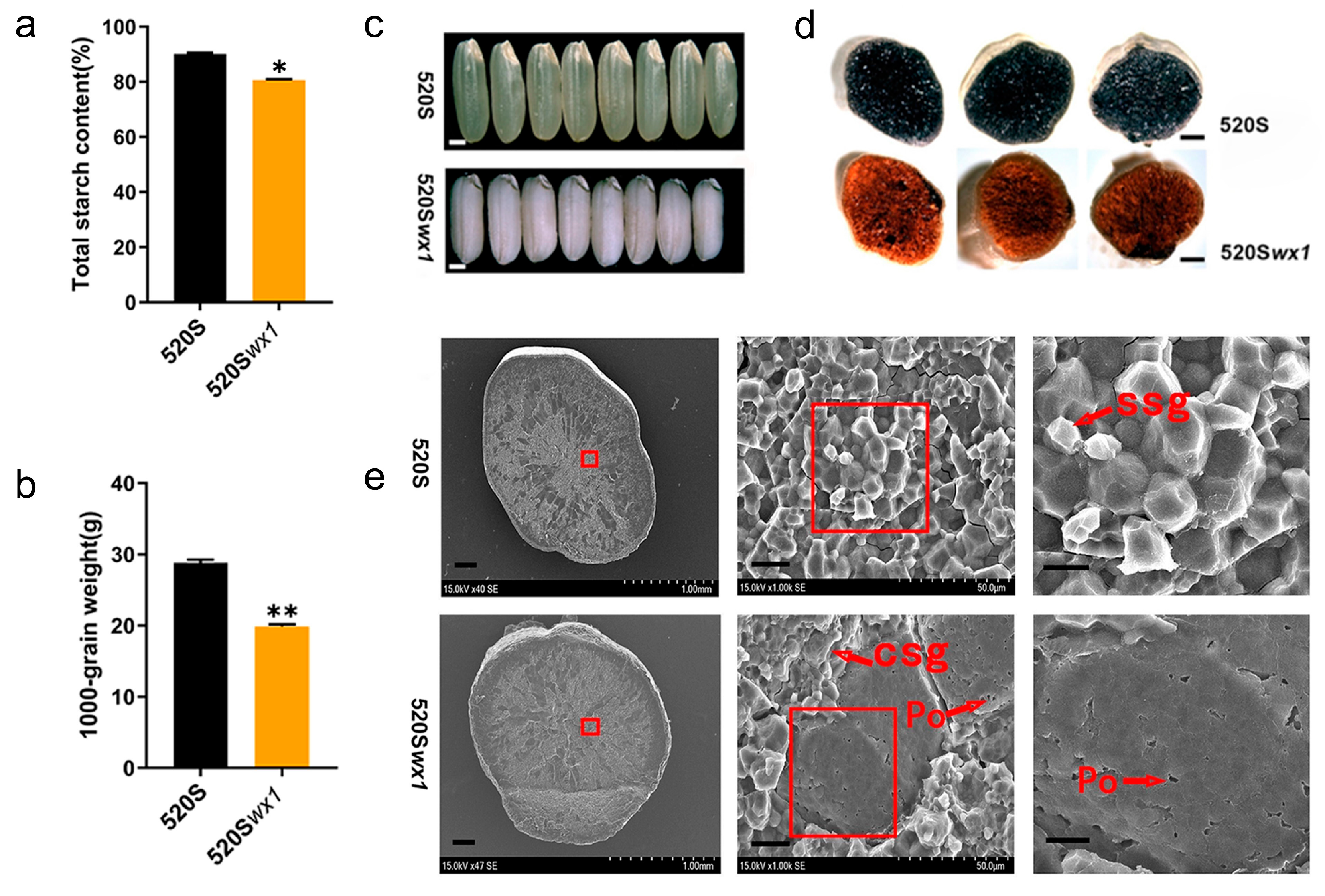
3.2. Grain Quality
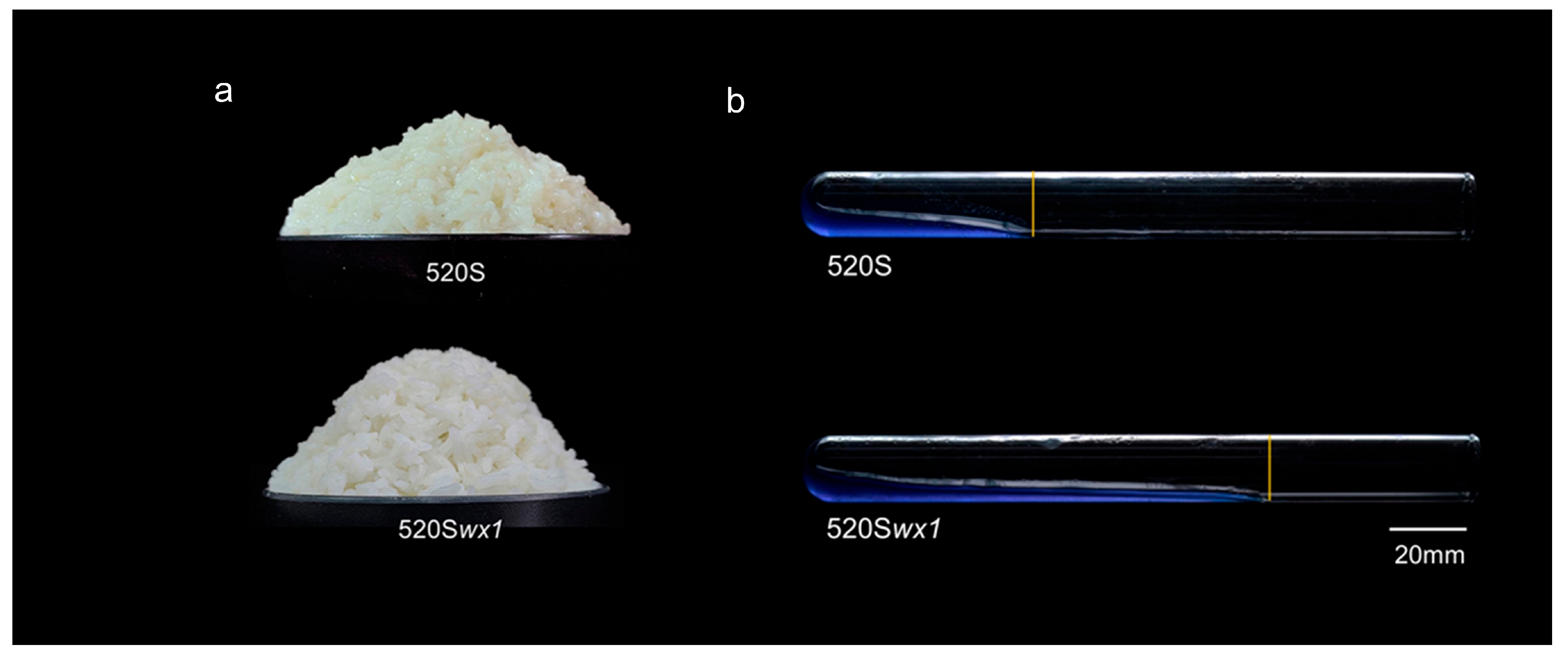
3.3. Cooking Quality
3.4. Gel Properties
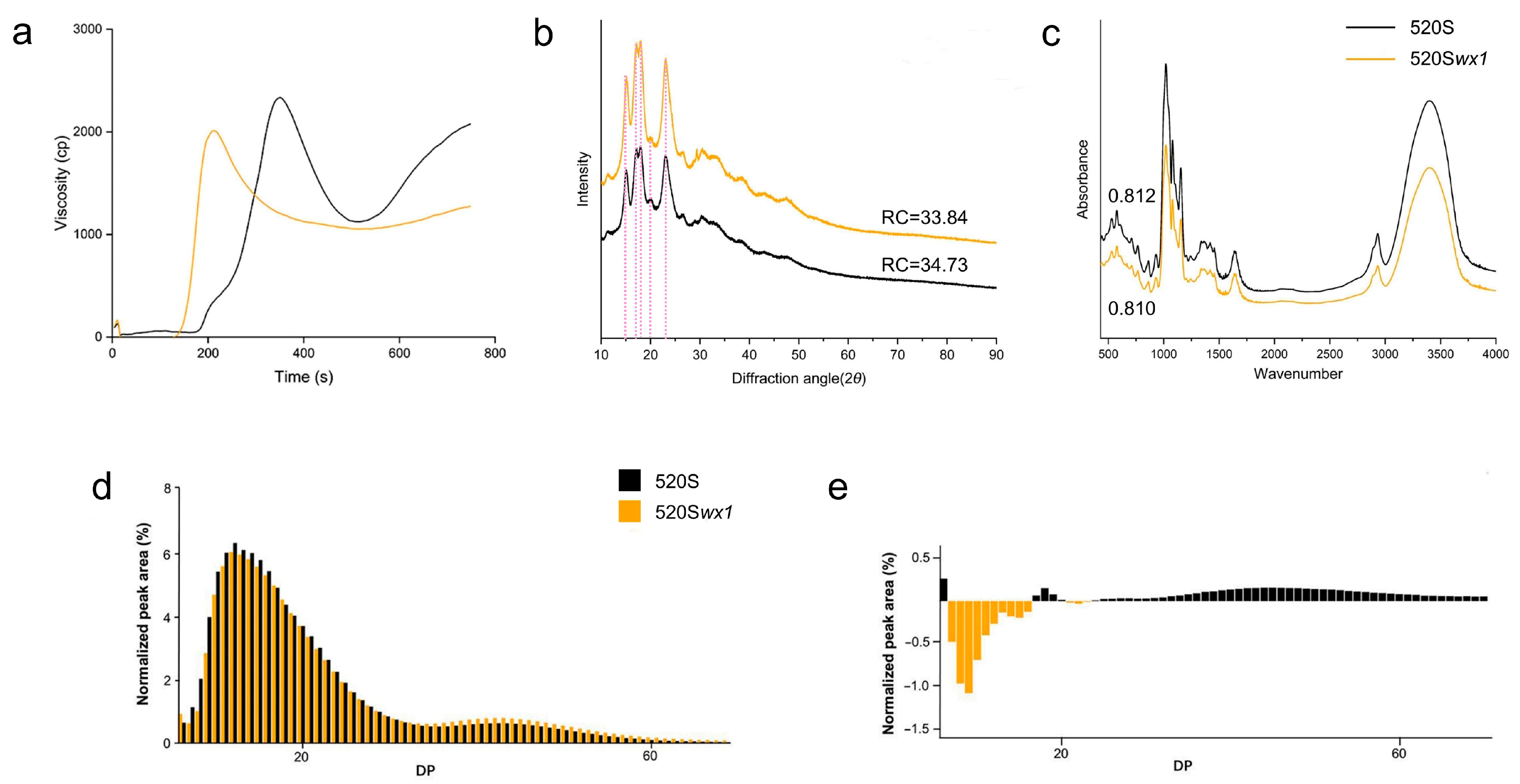
3.5. Pasting and Thermal Properties of Starches
3.6. Crystalline Structure and FTIR Spectroscopy
3.7. Fine Structure of Amylopectin
3.8. Potential Application
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahromrit, A.; Ledward, D.A. Kinetics of High Pressure Facilitated Starch Gelatinisation in Thai Glutinous Rice. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Kohyama, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Noel, T.R.; Ring, S. Physicochemical Characteristics of Waxy Rice Starch Influencing the in Vitro Digestibility of a Starch Gel. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.M.; Shin, M. Physicochemical Properties and Molecular Structures of Korean Waxy Rice Starches. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, B.O. Varietal Impact on Rice Quality. Cereal Foods World 1998, 43, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Yu, S.J. Effects of Waxy Rice Starch and Short Chain Amylose (Sca) on the Formation of 2-Amino-1-Methyl-6-Phenylimidazo[4,5-B]Pyridine (Phip) in a Model System. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongsutjarittam, N.; Charoenrein, S. Influence of Waxy Rice Flour Substitution for Wheat Flour on Characteristics of Batter and Freeze-Thawed Cake. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apriyanto, A.; Compart, J.; Fettke, J. A Review of Starch, a Unique Biopolymer-Structure, Metabolism and in Planta Modifications. Plant Sci. 2022, 318, 111223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.H.; Singh, H.; Ciao, J.Y.; Kao, W.T.; Huang, W.H.; Chang, Y.H. Genotype Diversity in Structure of Amylopectin of Waxy Rice and Its Influence on Gelatinization Properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1858–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Gu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yu, J.; Chu, R.; Tan, H.; Zhao, D.; Fan, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; et al. Improving Rice Eating and Cooking Quality by Coordinated Expression of the Major Starch Synthesis-Related Genes, Ssii and Wx, in Endosperm. Plant Mol. Biol. 2021, 106, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, L.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q.; Fan, X.; Tang, S.; et al. A Rare Waxy Allele Coordinately Improves Rice Eating and Cooking Quality and Grain Transparency. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Hua, Y.; Luo, T.; Liu, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Tao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Generating Waxy Rice Starch with Target Type of Amylopectin Fine Structure and Gelatinization Temperature by Waxy Gene Editing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 306, 120595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaochanpong, N.; Puttanlek, C.; Rungsardthong, V.; Puncha-arnon, S.; Uttapap, D. Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Debranched Waxy Rice, Waxy Corn and Waxy Potato Starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Deng, X.W. Development of the “Third-Generation” Hybrid Rice in China. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.S. The Discovery and Study of the Photosensitive Recessive Male-Sterile Rice (Oryza Sativa L. Subsp. Japonica). Sci. Agric. Sin. 1985, 2, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Barman, H.N.; Sheng, Z.; Fiaz, S.; Zhong, M.; Wu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Wang, W.; Jiao, G.; Tang, S.; Wei, X.; et al. Generation of a New Thermo-Sensitive Genic Male Sterile Rice Line by Targeted Mutagenesis of Tms5 Gene through Crispr/Cas9 System. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, L.; Wu, P.; Lu, S.; Li, F.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. Photoperiod- and Thermo-Sensitive Genic Male Sterility in Rice Are Caused by a Point Mutation in a Novel Noncoding Rna That Produces a Small Rna. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yang, S.; Gong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Q.; Gong, H.; Li, W.; Zhan, Q.; Cheng, B.; Xia, J.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Hybrid Rice Varieties Reveals Numerous Superior Alleles That Contribute to Heterosis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yun, P.; Xia, J.; Zhou, K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B.; Yin, D.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Crispr/Cas9-Mediated Editing of Wx and Badh2 Genes Created Glutinous and Aromatic Two-Line Hybrid Rice. Mol. Breed. 2023, 43, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Su, F.; Huang, S.; Mei, F.; Niu, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, J.K.; Zhang, J. Novel Wx Alleles Generated by Base Editing for Improvement of Rice Grain Quality. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Luo, T.; Hua, Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, R.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Assessment of the Characteristics of Waxy Rice Mutants Generated by Crispr/Cas9. Front. Plant. Sci. 2022, 13, 881964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Wei, P.; Yang, J. Use of Crispr/Cas Genome Editing Technology for Targeted Mutagenesis in Rice. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1498, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiei, Y.; Ishida, Y.; Komari, T. Progress of Cereal Transformation Technology Mediated by Agrobacterium Tumefaciens. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milligan, B.G. Purification of Chloroplast DNA Using Hexadecyltrimethylammonium Bromide. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 1989, 7, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Ma, C.; Wu, M.; Fan, Q.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Bian, X.; Zhang, N. Effects of Extrusion Technology on Physicochemical Properties and Microstructure of Rice Starch Added with Soy Protein Isolate and Whey Protein Isolate. Foods 2024, 13, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.; Liang, C.; Zhang, O.; Xu, H.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, X. Variation of Resistant Starch Content in Different Processing Types and Their Starch Granules Properties in Rice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 276, 118742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Liu, F.; Qin, B.; Li, R. Development of Soft Rice Lines by Regulating Amylose Content Via Editing the 5’utr of the Wx Gene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Chang, R.; Lu, H.; Ma, R.; Qiu, L.; Tian, Y. Effect of Amino Acids Composing Rice Protein on Rice Starch Digestibility. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 146, 111417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Botella, J.R.; Zhu, J.K. Generation of New Glutinous Rice by Crispr/Cas9-Targeted Mutagenesis of the Waxy Gene in Elite Rice Varieties. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Shen, S.-q.; Sun, M.; Corke, H. Analysis of Genotypic Diversity in the Starch Physicochemical Properties of Nonwaxy Rice: Apparent Amylose Content, Pasting Viscosity and Gel Texture. Starch-Stärke 2006, 58, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, M.M.; Esser, C.; Nishita, K.D. Some Physicochemical and Food Aplplication Characteristics of California Waxy Rice Varieties. Cereal Chem. 1984, 61, 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Z.; Liu, L.; Yu, T.; Ge, G.; Chen, B.; Wang, T. Creating of Novel Wx Allelic Variations Significantly Altering Wx Expression and Rice Eating and Cooking Quality. J. Plant Physiol. 2024, 303, 154384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Yu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, S.; Shi, W.; Pan, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Genetic Improvement of Eating and Cooking Quality of Rice Cultivars in Southern China. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2025, 23, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, B.; Zhang, T.; Liu, P.; Yang, W.; Zheng, L.; Dai, Y.; Wang, H.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, X.; et al. The Lcg1-Osbp5/Osebp89-Wx Module Regulates the Grain Chalkiness and Taste Quality in Rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2025, 23, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-A.; Lim, S.-T. Effect of Γ-Irradiation on Pasting and Emulsification Properties of Octenyl Succinylated Rice Starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1480–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yu, J.; Shen, H.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Z.; Fan, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Huang, L.; et al. Creating a Superior Wx Allele with Temperature-Responsive Amylose Regulation and a Novel Transcriptional Pattern in Rice Via Crispr/Cas9-Mediated Promoter Editing. Foods 2025, 14, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Han, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, D.; Jiang, C.; Li, Q.; Hu, Y.; Xiang, X. The High Molecular Weight and Large Particle Size and High Crystallinity of Starch Increase Gelatinization Temperature and Retrogradation in Glutinous Rice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 348, 122756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, T.; Deng, F.; Yang, F.; Zhong, X.; Li, Q.; Ren, W. Changes in Chemical Composition and Starch Structure in Rice Noodle Cultivar Influence Rapid Visco Analysis and Texture Analysis Profiles under Shading. Food Chem. X 2022, 14, 100360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Ruan, B.; Yang, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, H.; Fang, G.; Ding, S.; et al. Genetic Analysis for Cooking and Eating Quality of Super Rice and Fine Mapping of a Novel Locus Qgc10 for Gel Consistency. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Precha-Atsawanan, S.; Puncha-arnon, S.; Wandee, Y.; Uttapap, D.; Puttanlek, C.; Rungsardthong, V. Physicochemical Properties of Partially Debranched Waxy Rice Starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.R.; Obanni, M.; BeMiller, J.N. Retrogradation of Starches from Different Botanical Sources. Cereal Chem. 1997, 74, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biduski, B.; Silva, W.M.F.d.; Colussi, R.; Halal, S.L.d.M.E.; Lim, L.-T.; Dias, Á.R.G.; Zavareze, E.d.R. Starch Hydrogels: The Influence of the Amylose Content and Gelatinization Method. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Zhu, P.; Sui, Z.; Bao, J. Physicochemical Properties of Starches from Diverse Rice Cultivars Varying in Apparent Amylose Content and Gelatinisation Temperature Combinations. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xu, J.; Guo, D.; Long, C.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, H.; Wen, P.; He, H.; He, X. Research on the Relationship between the Amylopectin Structure and the Physicochemical Properties of Starch Extracted from Glutinous Rice. Foods 2023, 12, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Effect of Annealing on the Physico-Chemical Properties of Rice Starch and the Quality of Rice Noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 84, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, I.; Zhuo, G.-Y.; Chakraborty, I.; Melanthota, S.K.; Mal, S.S.; Sarmah, B.; Baruah, V.J.; Mahato, K.K.; Mazumder, N. Investigation of Structural and Physico-Chemical Properties of Rice Starch with Varied Amylose Content: A Combined Microscopy, Spectroscopy, and Thermal Study. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Lv, D.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Y.; Hao, W.; Huang, L.; Fan, X.; Zhao, D.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; et al. Combined Effects of Ssii-2rnai and Different Wx Alleles on Rice Grain Transparency and Physicochemical Properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 308, 120651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Li, Z.; Qu, J.; Bertoft, E.; Li, M.; Zhu, F.; Blennow, A.; Liu, X. Relationship between Molecular Structure and Lamellar and Crystalline Structure of Rice Starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 258, 117616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chu, R.; Gu, Z.; Tan, H.; Zhao, D.; Fan, X.; Liu, Q. Creating Novel Wx Alleles with Fine-Tuned Amylose Levels and Improved Grain Quality in Rice by Promoter Editing Using Crispr/Cas9 System. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2164–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Qu, J.; Li, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, F.; Blennow, A.; Liu, X. Rice Starch Multi-Level Structure and Functional Relationships. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 275, 118777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika Reddy, K.; Zakiuddin Ali, S.; Bhattacharya, K.R. The Fine Structure of Rice-Starch Amylopectin and Its Relation to the Texture of Cooked Rice. Carbohydr. Polym. 1993, 22, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Li, C.; Yu, W.; Gilbert, R.G.; Li, E. How Amylose Molecular Fine Structure of Rice Starch Affects Functional Properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 204, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syahariza, Z.A.; Sar, S.; Hasjim, J.; Tizzotti, M.J.; Gilbert, R.G. The Importance of Amylose and Amylopectin Fine Structures for Starch Digestibility in Cooked Rice Grains. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Lou, G.; He, Y. Creation of Two-Line Fragrant Glutinous Hybrid Rice by Editing the Wx and Osbadh2 Genes Via the Crispr/Cas9 System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.T.; Virmani, S.S. Development of Tgms Lines for Developing Two-Line Rice Hybrids for the Tropics. Euphytica 2000, 114, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Miao, Z.; Kong, D.; Zhang, A.; Wang, F.; Liu, G.; Yu, X.; Luo, L.; Liu, Y. Application of Crispr/Cas9 Technology in Rice Germplasm Innovation and Genetic Improvement. Genes 2024, 15, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Cultivar | AC(%) | GC of Flour (mm) | GC of Starch (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h | 24 h | 48 h | |||
| 520S | 17.89 ± 0.12 a | 59.34 ± 0.42 a | 83.24 ± 0.16 a | 86.12 ± 0.37 a | 83.09 ± 0.12 a |
| 520Swx1 | 1.63 ± 0.34 b | 102.56 ± 0.31 b | 104.35 ± 0.25 b | 106.31 ± 0.19 b | 103.52 ± 0.34 b |
| Cultivar | To (℃) | Tp (℃) | Tc (℃) | ΔH (J/g) | Tc-To (℃) | DP6-12 (%) | DP13-24 (%) | DP25-70 (%) | ACR | AFST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 520S | 76.29 ± 0.06 a | 79.42 ± 0.28 a | 83.28 ± 0.14 a | 13.87 ± 0.43 a | 6.99 ± 0.05 a | 25.48 ± 0.15 a | 54.44 ± 0.34 a | 22.83 ± 0.18 a | 0.17 ± 0.01 a | H |
| 520Swx1 | 74.70 ± 0.05 b | 79.32 ± 0.16 a | 88.27 ± 0.22 b | 15.17 ± 0.31 b | 13.57 ± 0.24 b | 21.68 ± 0.26 b | 51.04 ± 0.29 b | 27.39 ± 0.15 b | 0.14 ± 0.01 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, R.; Li, W.; Gan, T.; Wan, J.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, M.; Xu, H.; et al. Creation of TGMS Lines of Waxy Rice with Elite Physicochemical Properties of Starch via Waxy Gene Editing. Foods 2025, 14, 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203530
Zhu J, Wang Z, Zhao R, Li W, Gan T, Wan J, Sun H, Liu Y, Wei M, Xu H, et al. Creation of TGMS Lines of Waxy Rice with Elite Physicochemical Properties of Starch via Waxy Gene Editing. Foods. 2025; 14(20):3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203530
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jun, Zhenchao Wang, Ruipeng Zhao, Weiyi Li, Tanghuang Gan, Jiaxin Wan, Haoliang Sun, Ying Liu, Min Wei, Hongyan Xu, and et al. 2025. "Creation of TGMS Lines of Waxy Rice with Elite Physicochemical Properties of Starch via Waxy Gene Editing" Foods 14, no. 20: 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203530
APA StyleZhu, J., Wang, Z., Zhao, R., Li, W., Gan, T., Wan, J., Sun, H., Liu, Y., Wei, M., Xu, H., Luo, T., Hua, Y., Li, S., Fu, Y., & Li, P. (2025). Creation of TGMS Lines of Waxy Rice with Elite Physicochemical Properties of Starch via Waxy Gene Editing. Foods, 14(20), 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203530






