4. Discussion
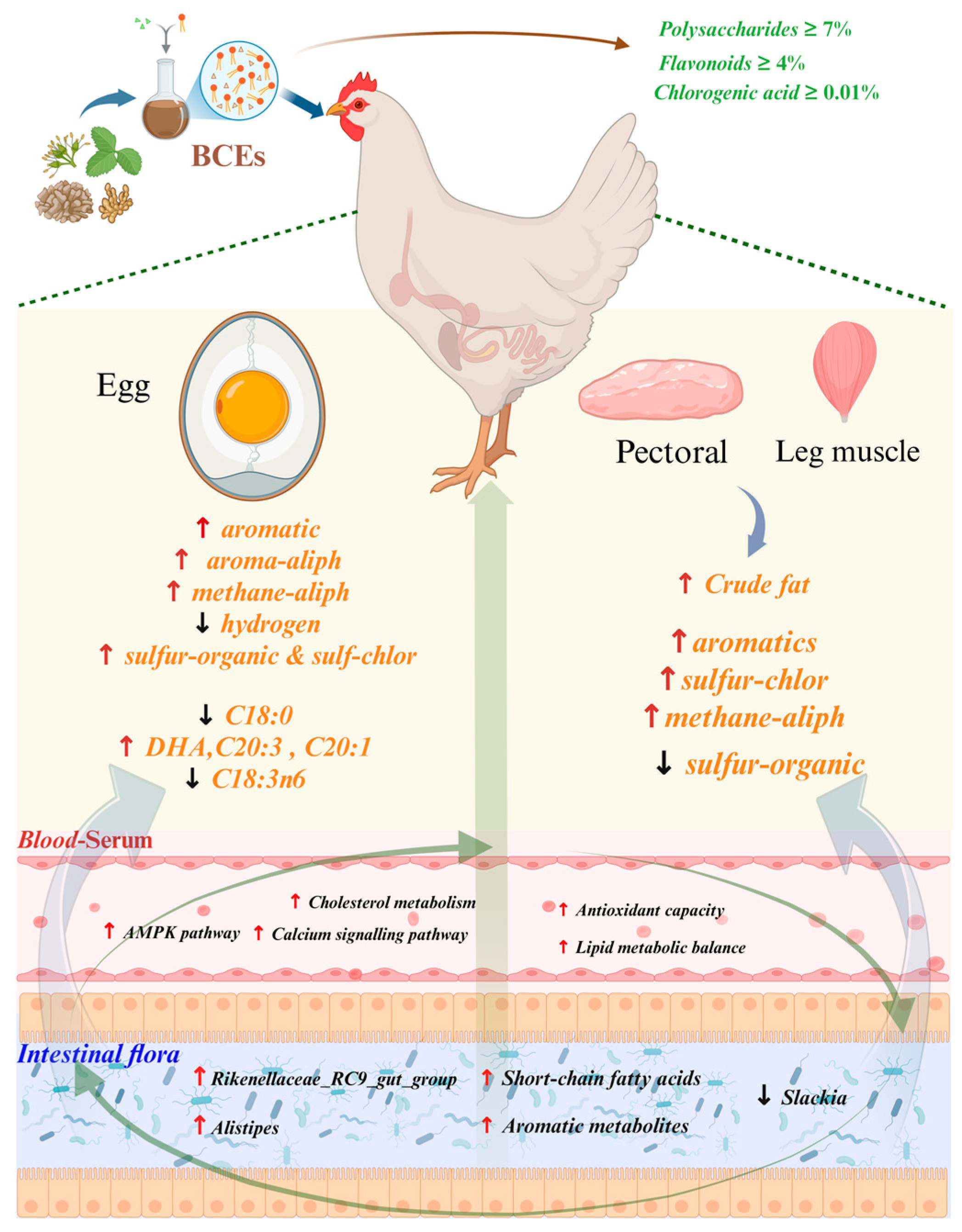
The decline in product quality during the late laying period represents a significant challenge to the sustainability of the poultry industry. This study demonstrates that dietary supplementation with BCEs systemically enhances the quality of eggs and meat from aged laying hens. BCEs are a botanical compound composed of crude extracts of various Chinese herbal medicines, including honeysuckle, mulberry leaves,
Codonopsis pilosula, and magnolia bark. They are rich in polysaccharides, flavonoids, and chlorogenic acid. Different botanical ingredients exhibit synergy and complementarity in their chemical structures and targets and can coordinately regulate metabolic homeostasis through multi-target and multi-pathway mechanisms, demonstrating systemic advantages that are distinct from single botanical additives [
13,
14]. Existing studies have also confirmed that Chinese herbal compounds have great application potential in improving the health status and product quality of aged laying hens [
15,
16]. More importantly, our integrated analysis reveals that these improvements are mediated through a coordinated “gut microbiota-host metabolism” axis, underscoring the potential of BCEs as a novel functional feed strategy.
In terms of flavor quality, electronic nose testing showed that BCE treatment significantly enhanced the release of aromatic (arom-aliph) and fat-soluble (methane-aliph) volatiles in eggs, while reducing hydrogen signals related to off-flavors, indicating that it helps optimize the composition of flavor substances and reduce the accumulation of off-flavor substances [
17]. Similar plant polyphenols, such as resveratrol, have been shown to interfere with the aroma metabolic pathway and optimize the volatile components of eggs [
18]. In addition, chlorogenic acid in BCEs may indirectly affect the generation and transformation of volatile precursors by regulating liver lipid metabolism and antioxidant pathways [
19]. This study found that the flavor improvement effect was particularly significant in cooked eggs, which may be related to the formula promoting the release of aroma precursors under thermal processing conditions or inhibiting oxidative degradation, which is consistent with the report of Zhang et al. that antioxidants improve the stability of egg aroma [
20].
Fatty acid analysis revealed that BCEs significantly promoted the enrichment of high-nutritional-value n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (such as C22:6, DHA) in egg yolk without markedly increasing the level of saturated fatty acids (such as C18:0), while also simultaneously improving the n-6/n-3 ratio. This beneficial modulation may be achieved by promoting fatty acid elongation reactions (such as increasing C20:1 and decreasing C18:3n6), thereby improving lipid metabolism efficiency [
21]. Related studies have shown that polyphenols in plant residues can enhance DHA deposition and improve antioxidant capacity [
22]. The synergistic effect of plant polyphenols and oils also has a positive impact on the enrichment and stability of n-3 PUFA [
23]. The combined effects of polysaccharides and polyphenols in the BCEs formula likely work synergistically in lipid synthesis [
24], transport, and deposition [
25], thereby achieving comprehensive regulation of fatty acid composition [
26]. Amino acid analysis results showed that BCE treatment led to a significant decrease in the content of glycine, methionine, and histidine in the egg white and yolk mixture, and the total amount of 16 amino acids showed a downward trend. Although amino acids are important indicators of the nutritional value of eggs, their excessive accumulation may lead to an increase in bitterness or an increase in ammonia nitrogen load [
27]. Traditional Chinese medicine formulas can regulate protein synthesis and amino acid homeostasis by regulating the expression of amino acid synthases, mTOR signaling pathways, and transmembrane transporters [
28]. This nutritional reconfiguration establishes a functionally complementary relationship between DHA enrichment and moderated amino acid levels. The substantial elevation of DHA—a fatty acid with well-documented significance in human nutrition—enhances the functional lipid profile of eggs [
29]. Simultaneously, the selective reduction in specific amino acids potentially improves sensory characteristics by minimizing bitterness precursors [
30] while optimizing nitrogen metabolism [
31]. Consequently, BCEs mediate a fundamental shift in nutritional architecture, prioritizing high-value lipid deposition while maintaining protein quality. This strategic reallocation of metabolic resources transforms eggs from basic nourishment to functionally optimized food, enhancing health-promoting properties without compromising essential nutritional value.
In terms of slaughter performance, BCE treatment significantly improved the slaughter rate on the 60th day of the experiment. Although there was no statistical difference in body weight, eviscerated weight, and abdominal fat weight, the overall indicators showed an upward trend, suggesting that it may promote the development of the body cavity and fat storage in the early stage of late egg production. The temporal specificity of these effects—evident at 60 days but attenuated by 100 days—corresponds to the established concept of a critical window in nutritional physiology, wherein the organism’s responsiveness to dietary interventions is temporally restricted to specific developmental or metabolic transition phases [
32]. This stage-dependent efficacy indicates that BCEs primarily modulate physiological processes during periods of heightened metabolic plasticity, with diminished effects following the establishment of a new homeostatic equilibrium [
33]. Further longitudinal investigations are required to precisely define the temporal boundaries of this responsive period and to clarify the underlying regulatory mechanisms governing this time-limited physiological response [
34].
Plant active ingredients such as chlorogenic acid and quercetin are believed to regulate fatty acid synthase (FAS) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) pathways [
35], and promote tissue lipid accumulation [
36]. Muscle nutritional analysis showed that long-term feeding of BCEs significantly reduced the crude protein content of breast muscle and increased the crude fat level. The leg muscle also showed a similar trend, suggesting that it may induce protein-fat metabolic redistribution in muscle. This change may be related to the regulation of protein synthesis and lipid deposition by flavonoids in BCEs through the AMPK/mTOR pathway [
37]; similar mechanisms have also been reported in mammalian studies [
38]. This nutrient repartitioning phenomenon represents a beneficial improvement in meat quality rather than a nutritional deficiency. The reduction in crude protein, accompanied by increased intramuscular fat, reflects a strategic shift in energy substrate allocation that enhances the sensory characteristics of meat. For spent laying hens, which typically exhibit tough texture and poor palatability, this metabolic reprogramming significantly improves tenderness and flavor intensity [
39]. Intramuscular fat deposition serves as a natural tenderizer by separating muscle fibers and contributing to juiciness, while also serving as a reservoir for flavor precursors [
40]. This mechanism aligns with the established positive correlation between moderate intramuscular fat content and meat quality attributes in poultry. Therefore, the BCE-induced metabolic shift optimizes the eating quality of spent hen meat through targeted nutrient repartitioning, representing a valuable approach to enhancing the utilization of this protein resource.
Although the protein content is slightly reduced, the moderate increase in fat content helps to improve the flavor, tenderness, and juiciness of the meat [
41], which has a positive significance for improving the edible quality of eliminated chicken. Analysis of flavor compounds showed that BCE treatment could regulate the composition of volatile compounds such as aromatics, alcohols/aldehydes, and sulfur-containing compounds in chicken. At 60 days of age, the response to alcohol/aldehyde and methane-aliph compounds increased, indicating that BCEs may improve muscle flavor by regulating lipid oxidation and the production of sulfur-containing volatiles [
42]. At 100 days of age, some odor signals showed a reversal of response, suggesting that their regulation is metabolically adaptive and accumulation-dependent [
43].
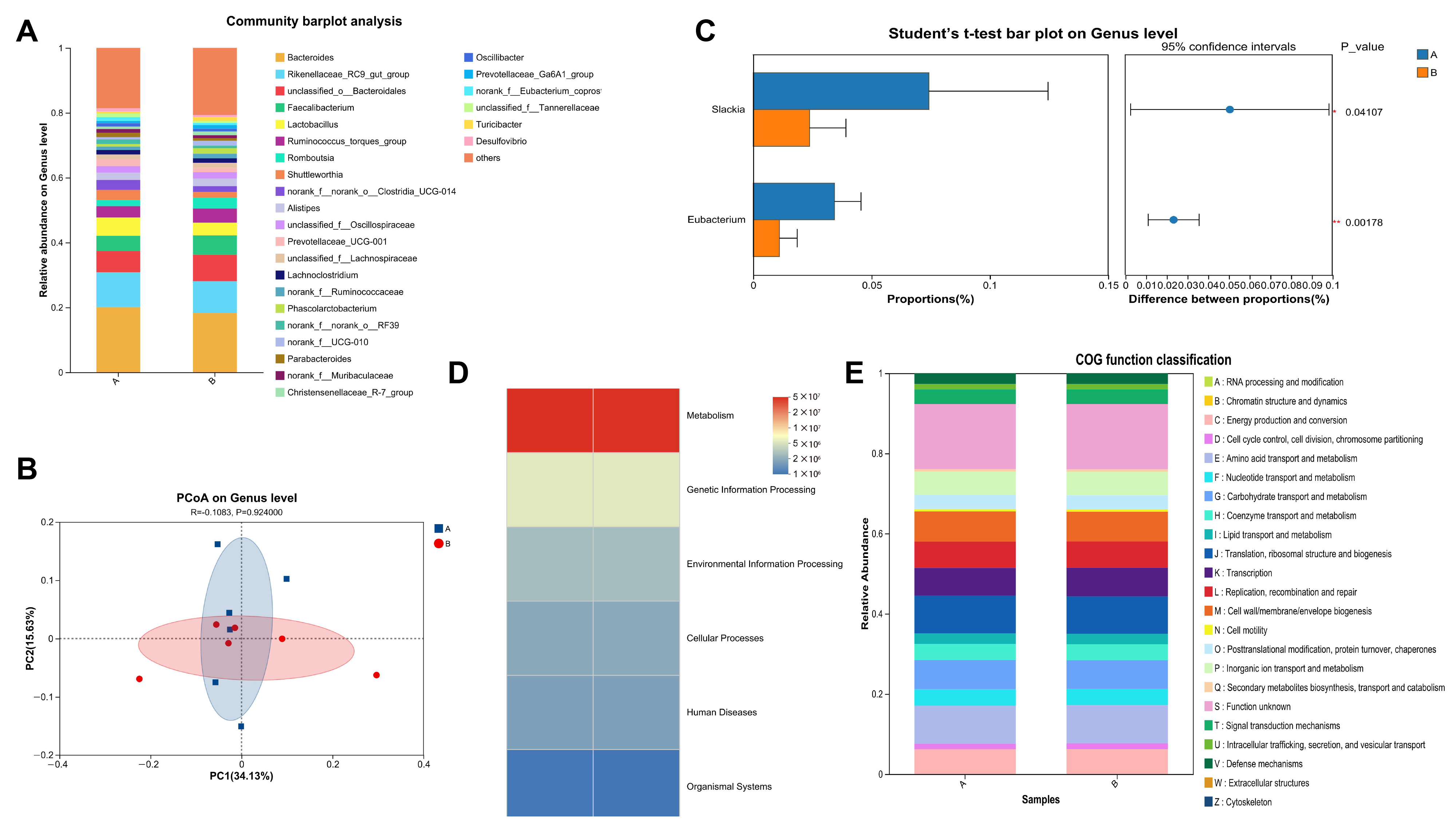
In terms of intestinal microecology, although the difference in the alpha diversity index did not reach a significant level, the species richness of the BCEs group showed an upward trend, suggesting that it may have a positive effect on microbial stability and ecological redundancy. The Venn diagram and species composition bar chart showed that BCE treatment significantly reshaped the structure of the cecal microbial community, and the abundance of some dominant OTUs changed. Plant active ingredients such as polysaccharides and polyphenols can serve as microbial substrates or regulatory factors, promoting the enrichment of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting potentially harmful bacteria [
44]. In this study, BCEs significantly reduced the relative abundance of Slackia and Eubacterium genera, which are closely related to protein fermentation and endotoxin production [
45], their reduction helps maintain the intestinal mucosal barrier and the stability of the inflammatory state [
46]. It is particularly noteworthy that alpha diversity primarily reflects community richness and evenness, whereas functional differences often stem from the regulation of specific core bacterial genera. Our results demonstrate that although overall diversity showed no significant changes, key functional bacteria (such as
Slackia and
Eubacterium) were significantly affected, indicating that BCEs possess a selective microecological intervention capability. This finding aligns with the current perspective in microbial ecology: the specific regulation of functional bacterial groups is more decisive for host health than overall diversity changes [
47,
48].
Beta diversity analysis revealed significant separation between the BCEs group and the control group at the genus level, suggesting that BCEs primarily achieve microecological intervention by regulating low- and medium-abundance microbiota. PICRUSt2 functional prediction revealed that BCEs significantly enhanced functional pathways related to secondary metabolites (short-chain fatty acids, phenols, etc.), suggesting that they can enhance microbial metabolic activity and contribute to the maintenance of host energy metabolism and immune homeostasis.
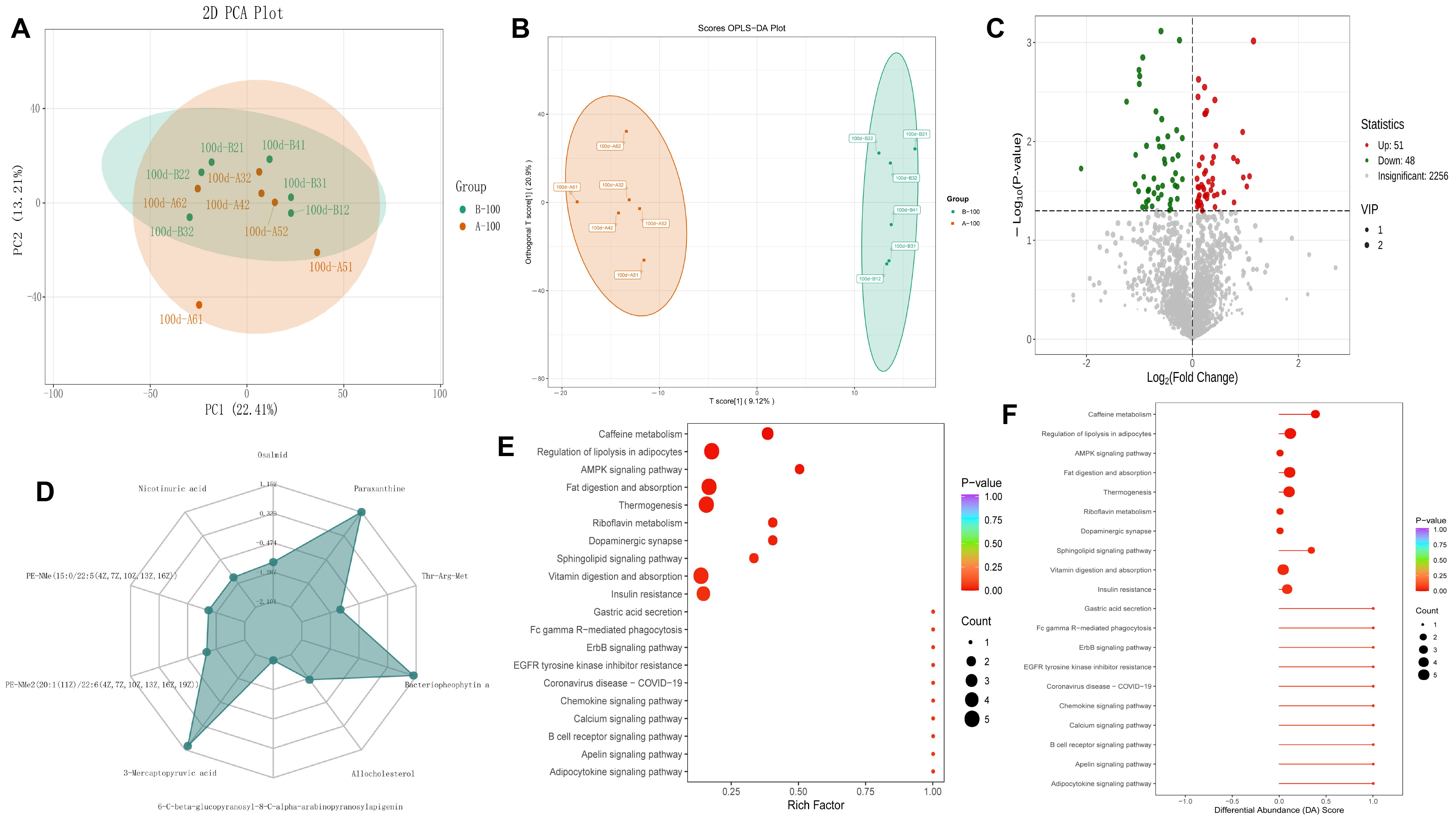
Metabolomics results further support these conclusions. PCA and OPLS-DA analyses revealed that BCEs significantly altered the serum metabolic profile of laying hens in the late laying period. Among the differentially expressed metabolites, substances with antioxidant and lipid-regulating functions, such as niacin, apigenin, and paraxanthine, were significantly upregulated. KEGG analysis revealed that the differentially expressed metabolites were enriched in multiple metabolic and signaling pathways, including AMPK, calcium signaling, and caffeine metabolism, suggesting that BCEs may improve lipid metabolism and inflammation by activating the AMPK pathway, a hub of energy metabolism. Furthermore, adipose cytokine signaling, insulin resistance, and cholesterol metabolism pathways were also affected, further demonstrating that BCEs have the potential to regulate metabolic networks at multiple pathways and levels.
In the correlation between serum metabolites and phenotypic characteristics, paraxanthine showed a significant positive correlation with the “hydrogen” signal in the leg muscle electronic nose and a negative correlation with the amino acid glycine, suggesting that it may be involved in the regulation of muscle mitochondrial energy metabolism and amino acid synthesis/transport balance. Literature shows that paraxanthine has the potential to promote muscle fat oxidation and energy allocation [
49]. In addition, nicotinuric acid showed a moderate negative correlation with methionine, indicating that it may indirectly participate in the regulation of nitrogen metabolism by intervening in the purine-sulfur amino acid pathway. Some serum metabolites may also affect the formation of flavor precursors. Bacteriopheophytin a was highly positively correlated with the “sulfur.organic” signal in eggs, which may be related to the accumulation or release of sulfur-containing flavor precursors. Sulfur-containing compounds are key components of egg aroma, and their release is regulated by multiple factors such as lipid oxidation, protein degradation, and the Maillard reaction [
50]. This suggests that BCEs change the basis of flavor substances by regulating the metabolite spectrum.
In the interaction between microbiota, metabolites, and flavor nutrition, the intestinal microbiota plays a bridging role. Phylum-level analysis showed that Bacteroidota was significantly positively correlated with hydrogen flavor characteristics, while
Firmicutes was negatively correlated, suggesting that the two may have a metabolic division of labor in the fermentation end products, hydrogen production, and utilization pathways, thereby affecting the smell of meat. In addition, Desulfobacterota was positively correlated with the “aromatic” signal, indicating that it may play a role in the degradation or transformation of aromatic compounds, affecting the flavor formation pathway [
19]. At the genus level, Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group showed a significant positive correlation with the DHA content in egg yolk. This genus is believed to be related to the synthesis or accumulation of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids [
51], and its functions may involve bile acid transport, lipid absorption regulation, and other links. In contrast, Alistipes showed a strong negative correlation with aromatic-aliphatic odor signals (arom.aliph). The activity of this bacterial community in amino acid degradation and short-chain fatty acid metabolism may lead to the degradation of flavor-active precursors [
52], thereby reducing aroma complexity.
The microbial community is also directly related to flavor and nutritional indicators. At the phylum level, Spirochaetota was positively correlated with leg muscle methane signals, suggesting that it may be involved in methane metabolism or the production of lipid fermentation end products [
53], and Proteobacteria was negatively correlated with glycine, possibly reflecting its participation in amino acid degradation [
54]. At the genus level, Faecalibacterium was positively correlated with egg “arom.aliph” signals, while the positive correlation between Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group and DHA was again verified, emphasizing its central role in lipid nutrition improvement [
55].
Overall, BCEs not only influence the composition of the gut microbiome but also achieve multi-dimensional regulation of flavor and nutrition through metabolite pathways. Their active ingredients, such as polysaccharides, flavonoids, and chlorogenic acid, complement each other in regulating fatty acid synthesis, amino acid homeostasis, and antioxidant pathways, establishing a systematic regulatory network centered on the “microbiome-metabolism-phenotype” network. This study acknowledges several limitations, including the absence of commercial additive comparisons, the 100-day duration potentially limiting long-term effect assessment, and incomplete safety evaluation data. Future research should prioritize comparative efficacy studies, extended trial periods, and systematic safety assessments to facilitate BCEs’ translation into practical applications.