The Effect of Cucumaria frondosa Tentacles Hydrolysates on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis: Integrated Metagenomics and Metabolomics Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of CFTHs
2.3. Structural and Physicochemical Characterization
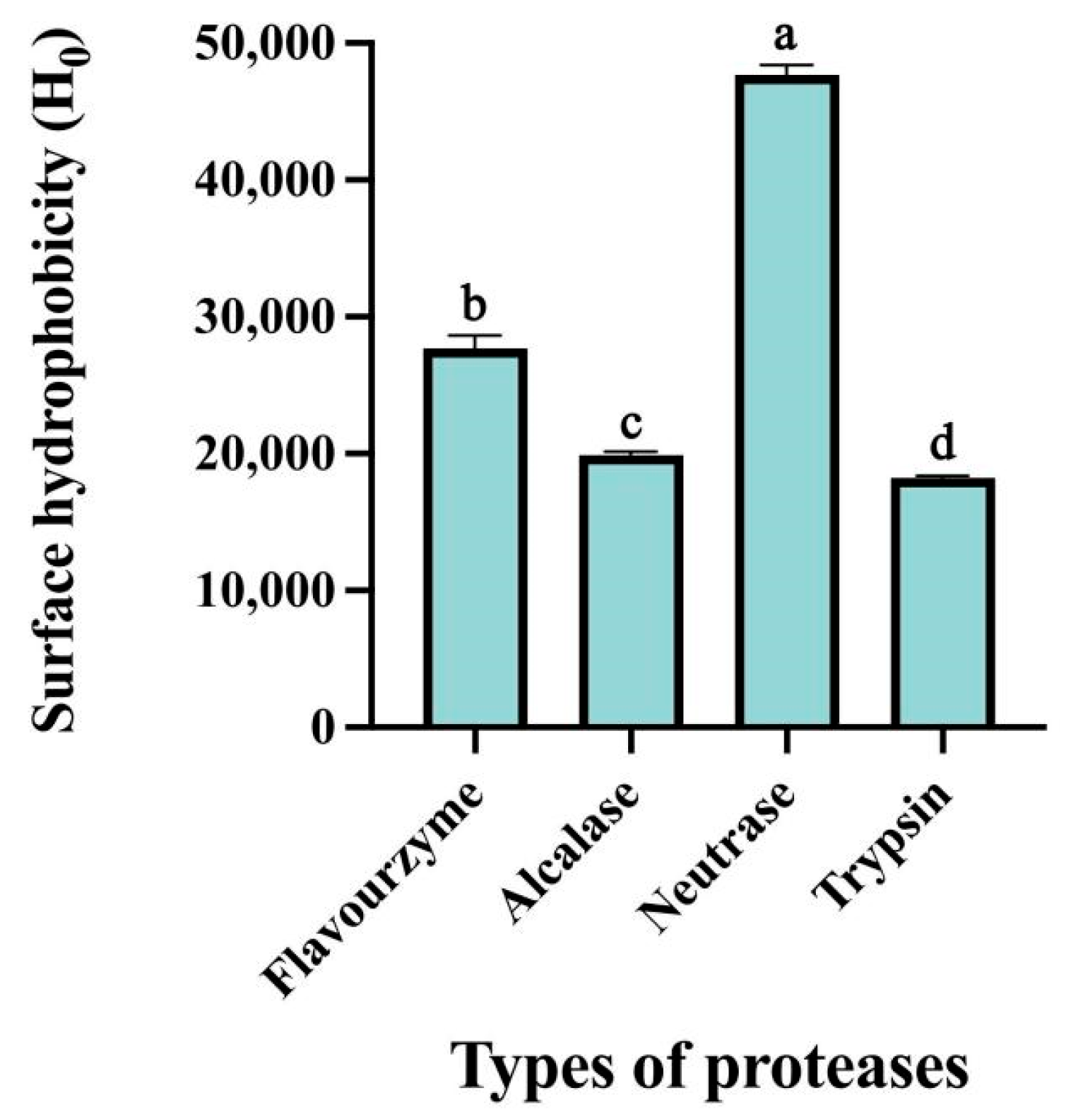
2.3.1. Surface Hydrophobicity
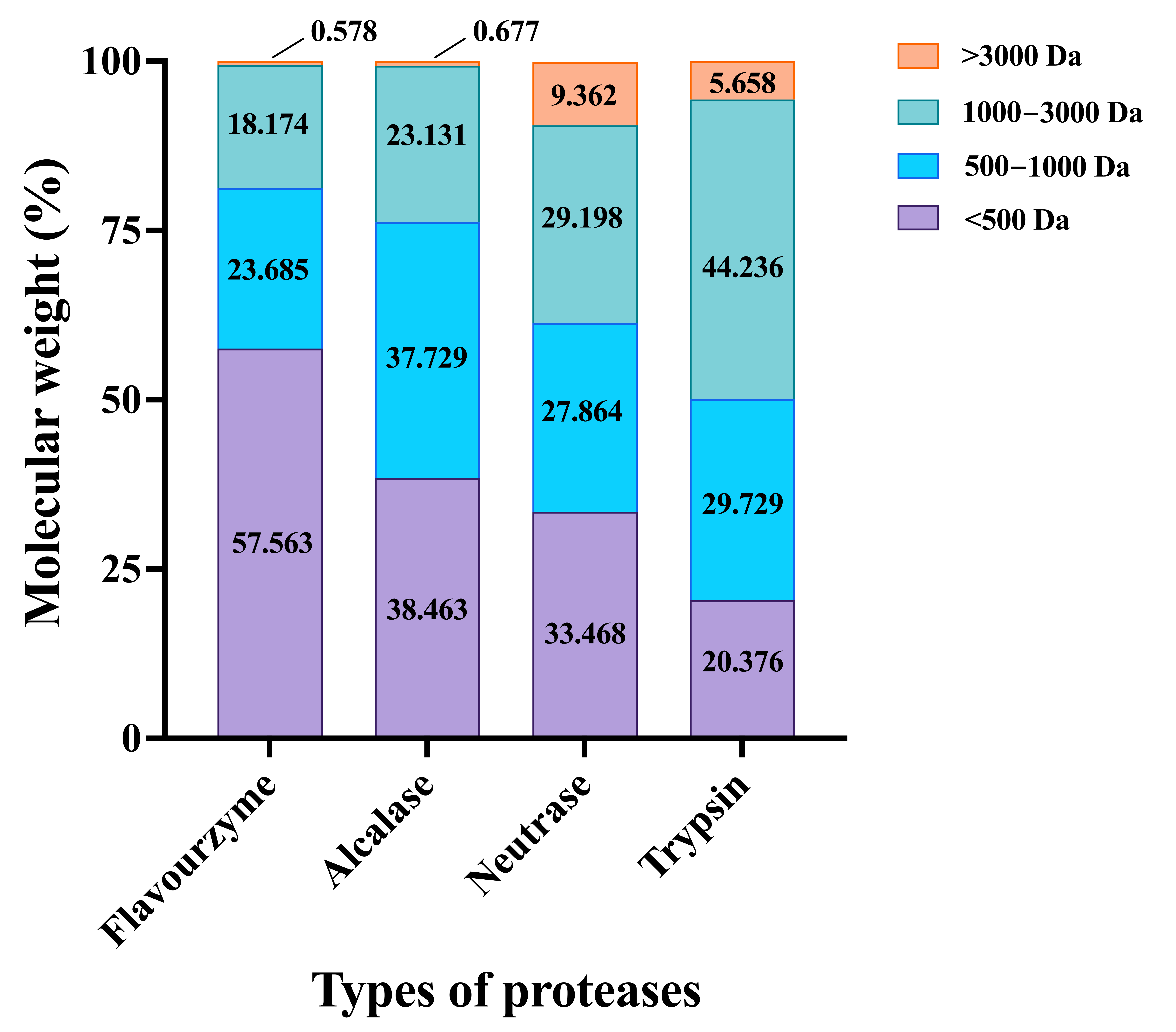
2.3.2. Molecular Weight Distribution
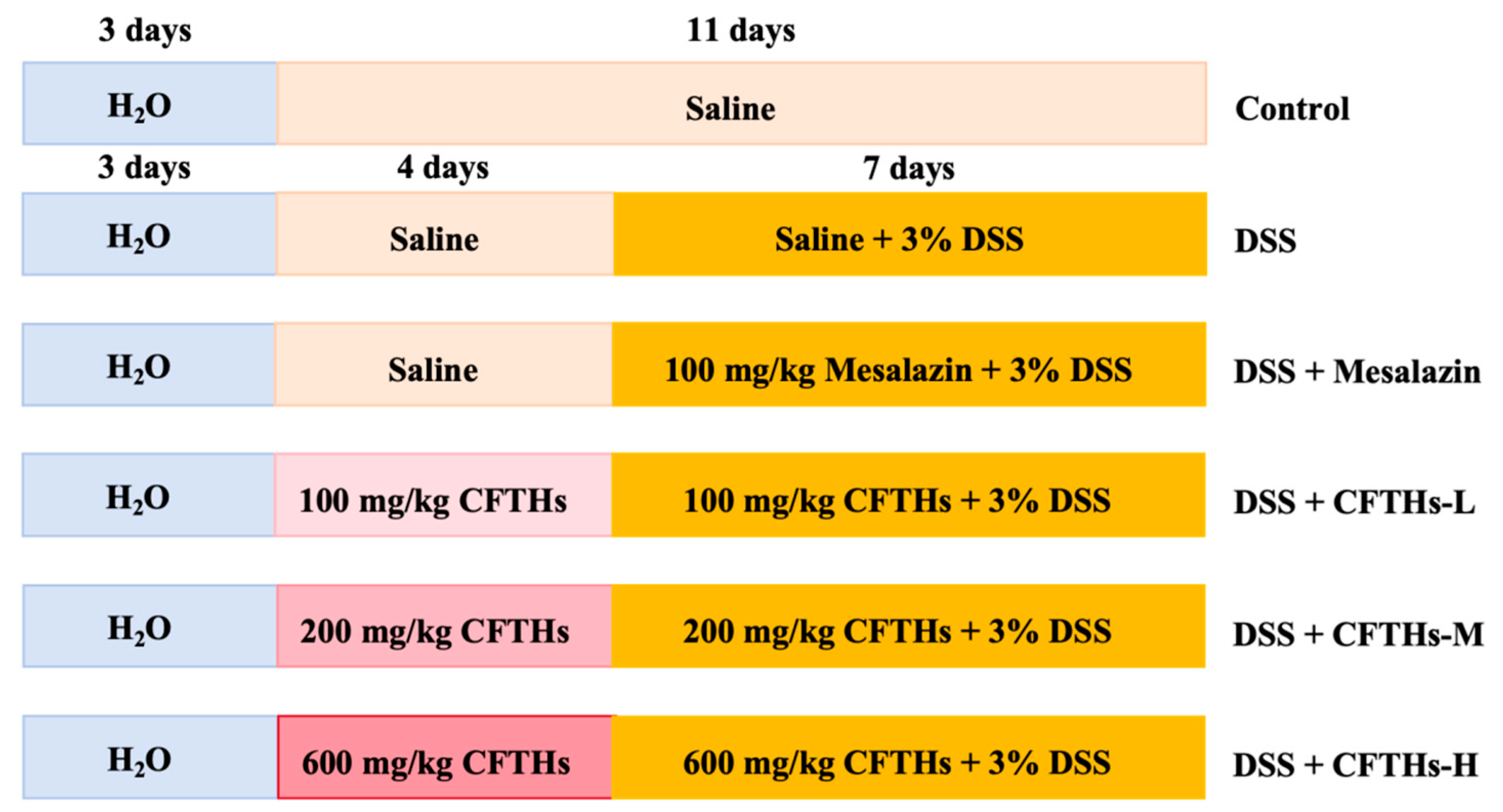
2.4. Animals and Experimental Design
2.5. Disease Activity Index (DAI)
2.6. ELISA
2.7. Hematoxylin–Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.8. Microbiome Profiling via High-Throughput Sequencing
2.9. Non-Targeted Metabolomics
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characteristics and Physicochemical Properties of CFTHs
3.1.1. Surface Hydrophobicity of CFTHs
3.1.2. Molecular Weight Distribution of CFTHs
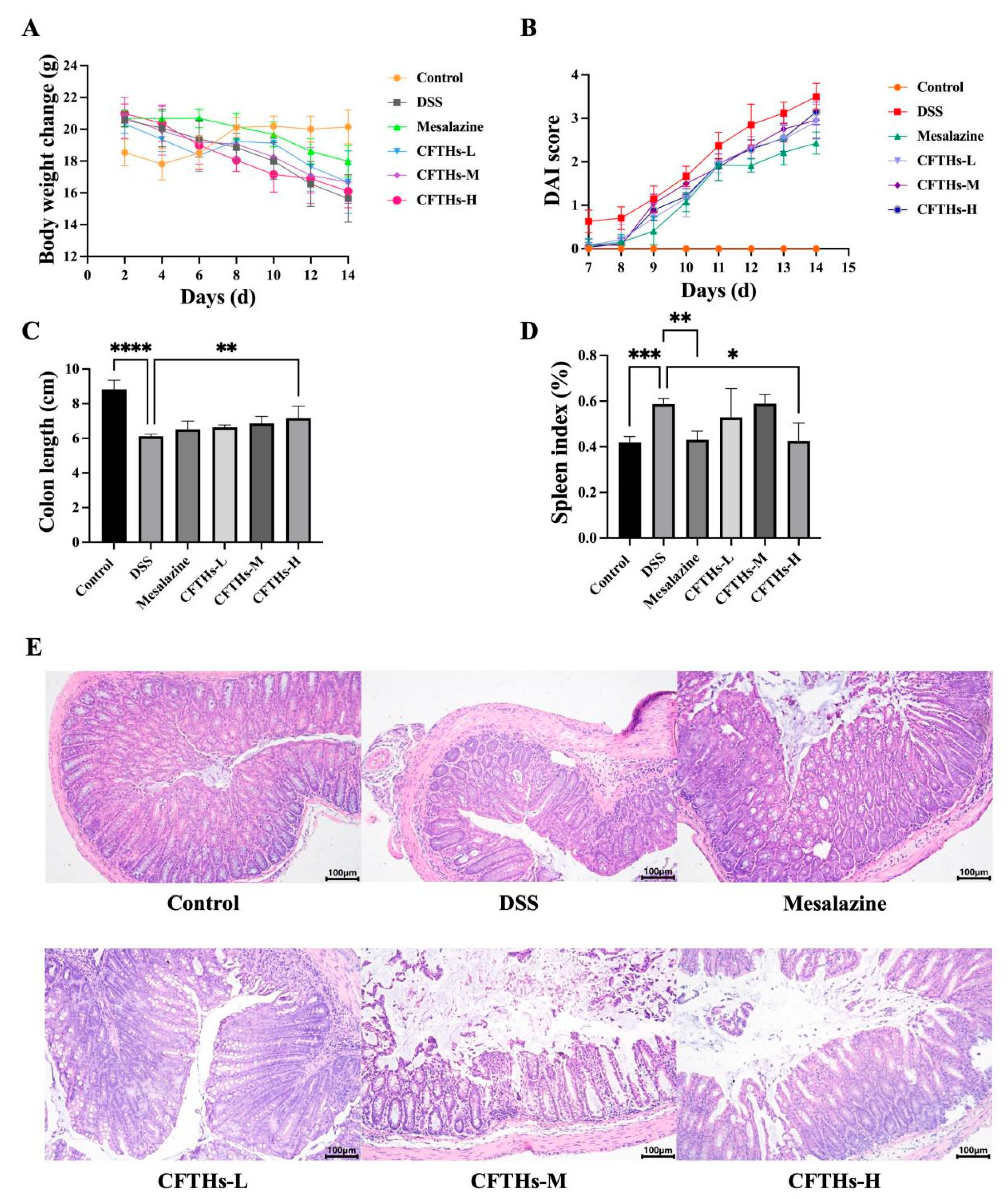
3.2. CFTHs Alleviated the Symptoms of DSS-Induced Colitis
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of CFTHs
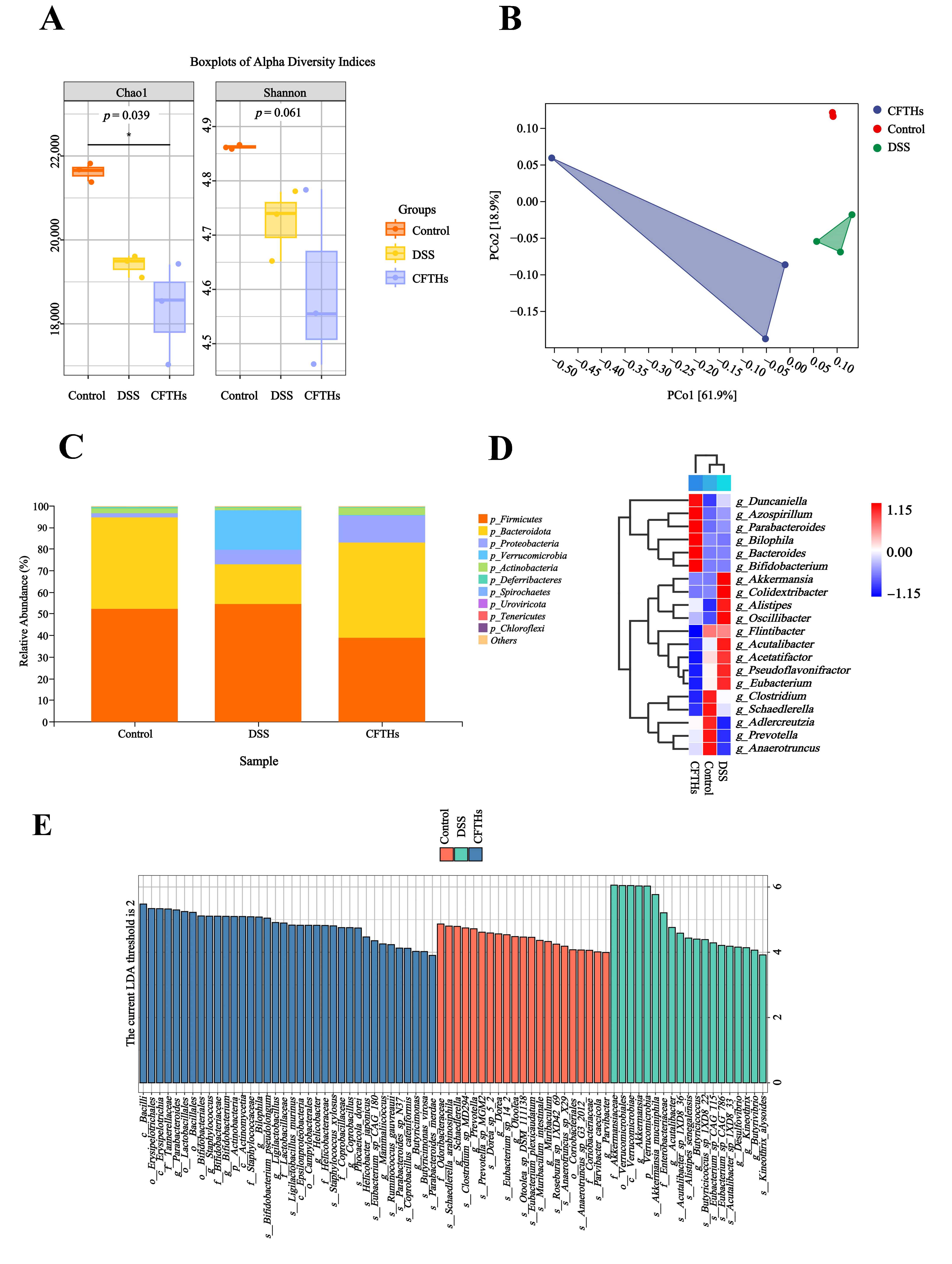
3.4. CFTHs Modulated the Gut Microbiota
3.5. CFTHs Altered the Functional Profile of the Gut Microbial Metagenome
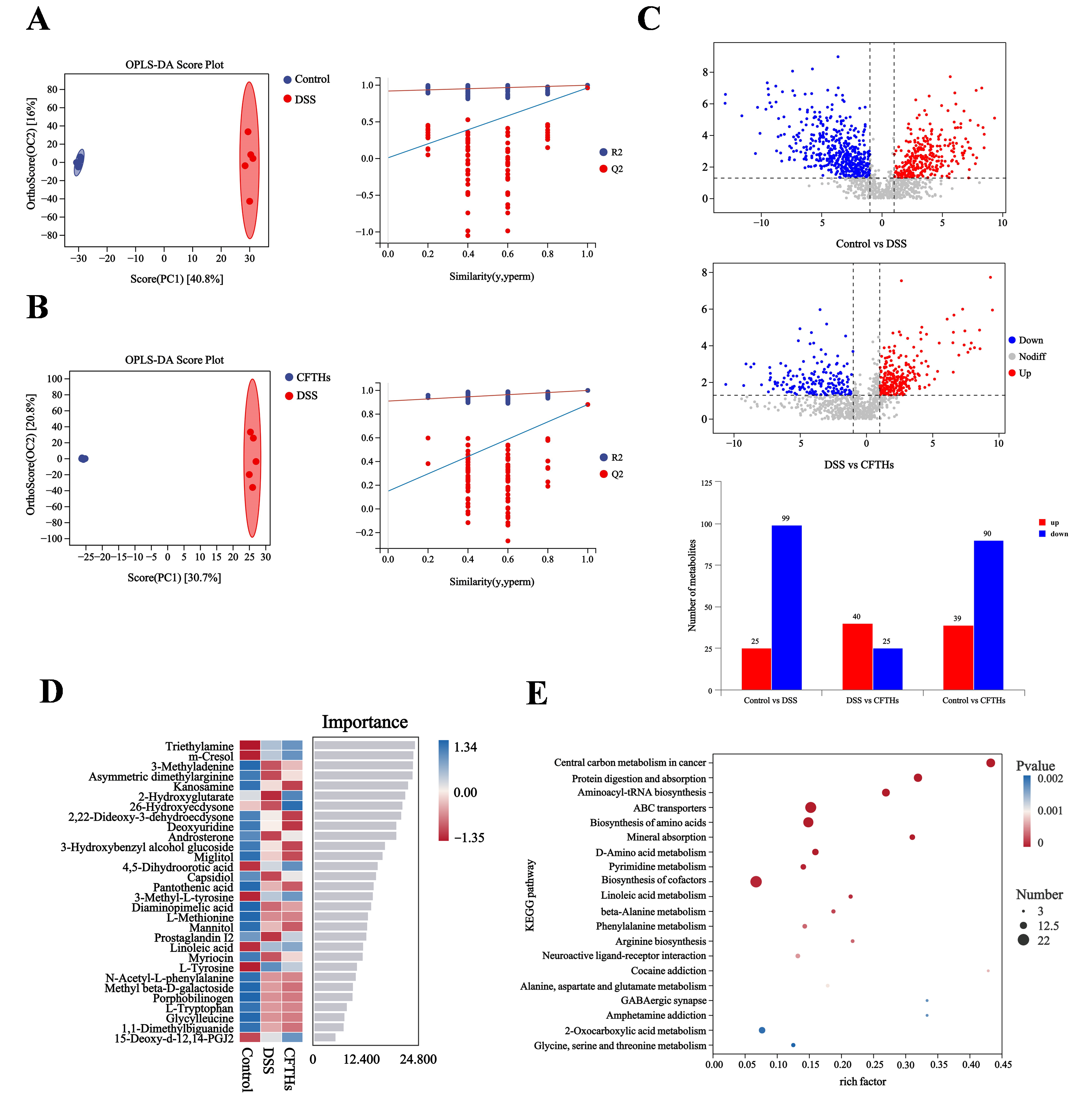
3.6. Modulation of the Metabolome in Colitis by CFTHs
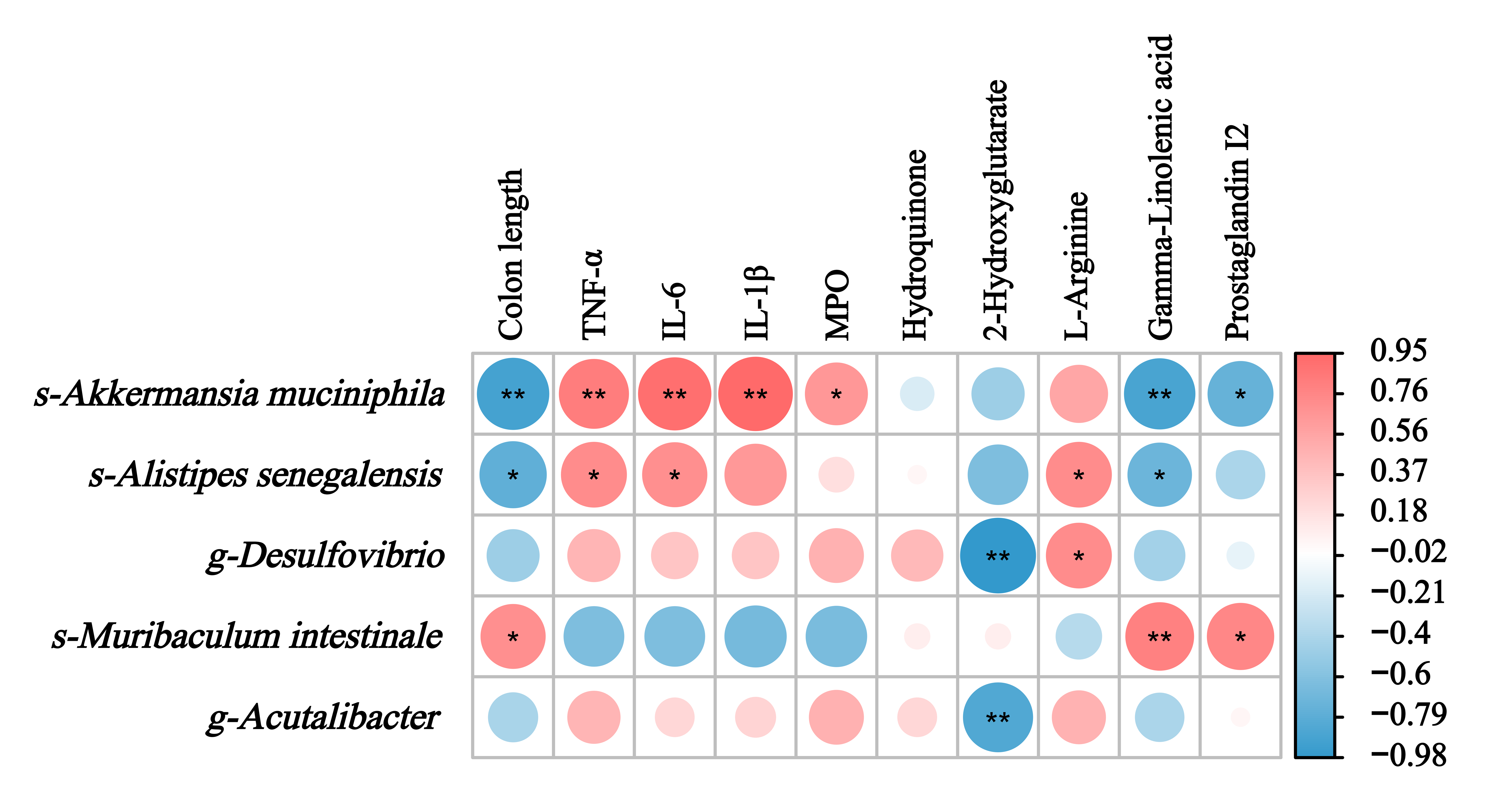
3.7. Integrating Multi-Omics: Correlations Among Gut Flora, Metabolites, and Host Physiology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFTHs | Cucumaria frondosa tentacles hydrolysates |
| DSS | Dextran sulfate sodium |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| UC | Ucerative colitis |
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| ANS | 1-anilino-8-naphthalenesulfonate |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| CFTHs-L | Cucumaria frondosa tentacles hydrolysates low-dose group |
| CFTHs-M | Cucumaria frondosa tentacles hydrolysates medium-dose group |
| CFTHs-H | Cucumaria frondosa tentacles hydrolysates high-dose group |
| DAI | Disease activity index |
| H&E | Hematoxylin-eosin |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
| PCoA | Principal Coordinates Analysis |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| KO | Orthology |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis |
| MMA | Methylmalonic acid |
| QC | Quality control |
| UPLC | Ultra-performance liquid chromatograph |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| Ah | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| FC | Fold change |
References
- Hossain, A.; Dave, D.; Shahidi, F. Northern Sea Cucumber (Cucumaria frondosa): A Potential Candidate for Functional Food, Nutraceutical, and Pharmaceutical Sector. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.T.; Falch, E.; Elvevoll, E.O.; Jensen, I.J. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Orange-Footed Sea Cucumber (Cucumaria frondosa)-Effect of Different Enzymes on Protein Yield and Bioactivity. Foods 2023, 12, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbohun, O.F.; Rollins, A.; Mattern, L.; Cipollini, K.; Rupasinghe, H.V. Frondoside A of Cucumaria frondosa (Gennerus, 1767): Chemistry, biosynthesis, medicinal applications, and mechanism of actions. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2024, 77, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Song, W.; Sun, L. Characteristics, Antioxidant Activity Stability, and Anti-Fatigue Activity of Hydrolysates from Cucumaria frondosa Tentacles. Molecules 2025, 30, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.X.; Luo, S.W.; Song, J.F.; Dai, Z.Q.; Li, D.J.; Wu, C.E. Effect of sodium alginate-based hydrogel loaded with lutein on gut microbiota and inflammatory response in DSS-induced colitis mice. Food Sci. Hum. Well. 2023, 12, 2428–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albtoush, N.; Queisser, K.A.; Zawerton, A.; Lauer, M.E.; Beswick, E.J.; Petrey, A.C. TSG6 hyaluronan matrix remodeling dampens the inflammatory response during colitis. Matrix Biol. 2023, 121, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.Q.; Chen, S.M.; Song, Y.T.; Liu, S.H.; Duan, Y.Q.; Cai, M.H.; Kong, T.Y.; Zhang, H.H. A novel Sagittaria sagittifolia L. polysaccharides mitigate DSS-induced colitis via modulation of gut microbiota and MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.H.; Liu, G.; Fang, J. Progress on the mechanisms of Lactobacillus plantarum to improve intestinal barrier function in ulcerative colitis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2024, 124, 109505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.J.; Li, A.; Wang, Y.Y.F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.M.; Wang, S. D-Psicose intake exacerbates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice through alteration in the gut microbiota and dysfunction of mucosal barrier. Food Sci. Hum. Well. 2024, 13, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senadheera, T.R.L.; Hossain, A.; Dave, D.; Shahidi, F. In Silico Analysis of Bioactive Peptides Produced from Underutilized Sea Cucumber By-Products-A Bioinformatics Approach. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, K.; Shanthi, C. Purified fish skin collagen hydrolysate attenuates TNF-α induced barrier dysfunction in-vitro and DSS induced colitis in-vivo model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambigaipalan, P.; Shahidi, F. Bioactive peptides from shrimp shell processing discards: Antioxidant and biological activities. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 34, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Tuo, Y.; You, H.X.; Li, J.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Liu, X.B.; Ding, L. Quinoa protein and its hydrolysate ameliorated DSS-induced colitis in mice by modulating intestinal microbiota and inhibiting inflammatory response. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Zhao, Y.J.; Wang, L.C.; Wu, T.; Jin, Y.; Meng, J.; Zhang, M. Sea Cucumber Peptide Alleviates Ulcerative Colitis Induced by Dextran Sulfate Sodium by Alleviating Gut Microbiota Imbalance and Regulating miR-155/SOCS1 Axis in Mice. Foods 2023, 12, 3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanya, S.B.; Chandran, S.; Almarzooqi, S.; Raj, V.; Al Zahmi, A.S.; Al Katheeri, R.A.; Al Zadjali, S.A.; Collin, P.D.; Adrian, T.E. Frondanol, a Nutraceutical Extract from Cucumaria frondosa, Attenuates Colonic Inflammation in a DSS-Induced Colitis Model in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.T.; Tu, Z.C.; Xiao, H.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.Q.; Liu, G.X.; Liu, C.M.; Shi, Y.; Fan, L.L.; Lin, D.R. Influence of ultrasonic treatment on the structure and emulsifying properties of peanut protein isolate. Food Bioprod. Process. 2014, 92, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chen, Y.A.; Qi, Z.G.; Chen, Q.; Cao, Y.J.; Kong, Q.S. Preparation and identification of a novel peptide with high antioxidant activity from corn gluten meal. Food Chem. 2023, 424, 136389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.W.; Zhou, X.L.; Wang, R.; Shu, C.H.; Zhou, Y.F.; Ying, X.G.; Zheng, B. Protective Effect of Tuna Bioactive Peptide on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Deng, T.; Ali, M.; Farooqui, N.A.; Alsholi, D.M.; Siddiqui, N.Z.; Rehman, A.U.; Ali, S.; Ilyas, M.; Wang, L.; et al. Sea Conch Peptides Hydrolysate Alleviates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice through Immune Modulation and Gut Microbiota Restoration. Molecules 2023, 28, 6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.H.; Li, L.X.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X.; Xia, Y.A.; Li, B.; Liu, C.; Zuo, X.L. Tilapia skin peptides, a by-product of fish processing, ameliorate DSS-induced colitis by regulating inflammation and inhibiting apoptosis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 988758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.H.; Zhang, L.N.; Tang, X.; Hu, W.; Zhou, P. Major yolk protein from sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus) attenuates acute colitis via regulation of microbial dysbiosis and inflammatory responses. Food Res. Int. 2022, 151, 110841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.Z.; Wang, X.X.; Ren, H.L.; Chang, J.; Guo, J.; He, Z.Q.; Shi, R.R.; Hu, X.Y.; Jin, Y.Y.; Lu, S.Y.; et al. Lactobacillus paracasei Jlus66 relieves DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in a murine model by maintaining intestinal barrier integrity, inhibiting inflammation, and improving intestinal microbiota structure. Eur. J. Nutr. 2024, 63, 2185–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadimu, G.J.; Gill, H.; Farahnaky, A.; Truong, T. Improving the enzymolysis efficiency of lupin protein by ultrasound pretreatment: Effect on antihypertensive, antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of the hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Fang, Y.; Wang, L.L.; Xie, M.H.; Hu, B.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Zhao, E.M.; Pei, F.; Shen, F.; Li, P.; et al. Effect of enzyme types on the stability of oil-in-water emulsions formed with rice protein hydrolysates. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2019, 99, 6731–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.M.; Ning, C.; Ren, Y.F.; Hu, F.Q.; Wang, M.X.; Li, W.X. Characterisation and comparison of enzymatically prepared donkey milk whey protein hydrolysates. Food Chem.-X. 2024, 22, 101360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhedi, O.; Mora, L.; Jridi, M.; Toldrá, F.; Nasri, M. Proteolysis Coupled with Membrane Separation for the Isolation of Bioactive Peptides from Defatted Smooth Hound Byproduct Proteins. Waste Biomass Valori. 2024, 15, 1959–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffernan, S.; Giblin, L.; O’Brien, N. Assessment of the biological activity of fish muscle protein hydrolysates using in vitro model systems. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.X.; Gao, Y.; Kan, R.T.; Ren, P.F.; Xue, C.H.; Kong, B.; Tang, Q.J. Alginate Oligosaccharides Prevent Dextran-Sulfate-Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis via Enhancing Intestinal Barrier Function and Modulating Gut Microbiota. Foods 2023, 12, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, G.R.D.; Machado, F.D.F.; Perico, L.L.; de Faria, F.M.; Luiz-Ferreira, A.; Brito, A.; Pellizzon, C.H.; Hiruma-Lima, C.A.; Tavares, J.F.; Barbosa, J.M.; et al. Anti-inflammatory intestinal activity of Combretum duarteanum Cambess. in trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis model. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.R.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, T.T.; Zhou, G.; Chen, Y.X. Ethyl acetate extract of Terminalia chebula alleviates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in C57BL/6 mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1229772. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.Y.; Liu, J.C.; Hang, R.Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, D. Neutrophils: From Inflammatory Bowel Disease to Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 18, 925–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lan, L.L.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.J.; He, W.X.; Xiang, D.; Liu, D.; Ren, X.H.; Zhang, C.L. IL-6 downregulates hepatic carboxylesterases via NF-κB activation in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 1567–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.M.; Li, M.B.; Gao, J.R.; Huang, S.J.; Song, W.K.; Sun, L.L. Cucumaria frondosa intestines and ovum hydrolysates intervention ameliorates the symptoms of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by modulating gut microbiota and its metabolites. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e70106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakase, H.; Sato, N.; Mizuno, N.; Ikawa, Y. The influence of cytokines on the complex pathology of ulcerative colitis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipour, M.; Zaidi, D.; Valcheva, R.; Jovel, J.; Martínez, I.; Sergi, C.; Walter, J.; Mason, A.L.; Wong, G.K.S.; Dieleman, L.A.; et al. Mucosal Barrier Depletion and Loss of Bacterial Diversity are Primary Abnormalities in Paediatric Ulcerative Colitis. J. Crohns Colitis 2016, 10, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolsega, S.; Basic, M.; Smoczek, A.; Buettner, M.; Eberl, C.; Ahrens, D.; Odum, K.A.; Stecher, B.; Bleich, A. Composition of the Intestinal Microbiota Determines the Outcome of Virus-Triggered Colitis in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.N.; Li, P.Z.; An, Y.Y.; Ren, J.; Yan, D.; Cui, J.Z.; Li, D.; Li, M.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhong, G.S. Phloretin ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice by regulating the gut microbiota. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 150, 104489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Tian, Y.W.; Xia, J.J.; Deng, X.Y.; Chen, J.; Jian, T.Y.; Ma, J. Li-Hong Tang alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis by regulating NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway and gut microbiota. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1413666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Lv, Y.J.; Quan, M.; Ma, M.F.; Shang, Q.S.; Yu, G.L. Bacteroides salyersiae Is a Candidate Probiotic Species with Potential Anti-Colitis Properties in the Human Colon: First Evidence from an In Vivo Mouse Model. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, F.; Docherty, N.G.; Murphy, M.; Murphy, B.; Coffey, J.C.; O’Connell, P.R. Desulfovibrio Bacterial Species Are Increased in Ulcerative Colitis. Dis. Colon Rectum 2010, 53, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.X.; Zheng, Y.L.; Zhang, N.; Huang, G.H.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, Q.N.; Ren, X.C. Desulfovibrio vulgaris caused gut inflammation and aggravated DSS-induced colitis in C57BL/6 mice model. Gut Pathog. 2024, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziarski, R.; Park, S.Y.; Kashyap, D.R.; Dowd, S.E.; Gupta, D. Pglyrp-Regulated Gut Microflora Prevotella falsenii, Parabacteroides distasonis and Bacteroides eggerthii Enhance and Alistipes finegoldii Attenuates Colitis in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Zou, Y.Y.; Peng, J.; Lu, F.G.; Yin, Y.N.; Li, F.J.; Yang, J.W. Lactobacillus acidophilus Suppresses Colitis-Associated Activation of the IL-23/Th17 Axis. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 909514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.F.; Lu, Y.M.; Zhang, T.; Xie, J.J.; Han, S.Y.; Zhang, S.B.; Fei, Y.Q.; Ling, Z.X.; Wu, J.J.; Hu, Y.; et al. Improved functionality of Ligilactobacillus salivarius Li01 in alleviating colonic inflammation by layer-by-layer microencapsulation. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.J.; Zhang, W.Q.; Zhang, T.; He, Q.W.; Kwok, L.Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, H.P. Heat-Killed Bifidobacterium bifidum B1628 May Alleviate Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice, and the Anti-Inflammatory Effect Is Associated with Gut Microbiota Modulation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Nie, Q.X.; Sun, Y.G.; Zuo, S.; Chen, C.H.; Li, S.; Yang, J.R.; Hu, J.L.; Zhou, X.T.; Yu, Y.K.; et al. Bacteroides uniformis degrades β-glucan to promote Lactobacillus johnsonii improving indole-3-lactic acid levels in alleviating colitis. Microbiome 2024, 12, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venegas, D.P.; De la Fuente, M.K.; Landskron, G.; González, M.J.; Quera, R.; Dijkstra, G.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Faber, K.N.; Hermoso, M.A. Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, H.; Jain, D.; Tang, D.W.T.; Wong, S.H.; Lal, D. Gut microbiota in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and therapeutics of inflammatory bowel disease. Intest. Res. 2024, 22, 15–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbulut, S. An assessment of serum vitamin B12 and folate in patients with Crohn’s disease. Medicine 2022, 101, e31892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.G.; Kariyawasam, V.C.; Mogan, S.B.; Patel, K.V.; Pantelidou, M.; Sobczynska-Malefora, A.; Porté, F.; Griffin, N.; Anderson, S.H.C.; Sanderson, J.D.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Functional Vitamin B12 Deficiency in Patients with Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2839–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mahdy, R.N.; Nader, M.A.; Helal, M.G.; Abu-Risha, S.E.; Abdelmageed, M.E. Eicosapentaenoic acid mitigates ulcerative colitis-induced by acetic acid through modulation of NF-κB and TGF-β/EGFR signaling pathways. Life Sci. 2023, 327, 121820. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Role of EPA in Inflammation: Mechanisms, Effects, and Clinical Relevance. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.Y.; Feng, Y.M.; Kong, W.S.; Li, S.N.; Sun, X.J.; Zhou, G.; Xie, R.F.; Zhou, X. Gallic acid ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1095721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.J.; Zheng, J.Y.; Sun, L.; Yang, H.C.; Cao, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.H.; Zheng, L.T.; Zhen, X.C. The oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate inhibits microglial activation via the AMPK/mTOR/NF-κB pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Proteases | Temperature (°C) | pH | Solid–Liquid Ratio (w/v) | Proteases Addition (U/g Protein) | Time (h) | Degree of Hydrolysis (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trypsase | 55 | 8.0 | 1:4 | 9500 | 4 | 14.88 ± 0.54 |
| Flavourzyme | 40 | 5.8 | 1:6 | 10,000 | 7 | 40.47 ± 0.86 |
| Alcalase | 55 | 9.5 | 1:8 | 8500 | 7 | 25.87 ± 0.91 |
| Neutrase | 45 | 7.2 | 1:10 | 7500 | 5 | 13.90 ± 0.86 |
| Score | Diarrhea | Stool Bleeding | Body Weight Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | normal | normal | 0–1 |
| 1 | slightly loose stools | little reddish | 1–5 |
| 2 | loose stools | brown reddish color | 5–10 |
| 3 | diarrhea | visible blood | 10–20 |
| 4 | watery diarrhea | rectal bleeding | >20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Gong, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Sun, L. The Effect of Cucumaria frondosa Tentacles Hydrolysates on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis: Integrated Metagenomics and Metabolomics Analysis. Foods 2025, 14, 3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203483
Zhang S, Wang Q, Gong S, Li M, Zhang Y, Sun L, Sun L. The Effect of Cucumaria frondosa Tentacles Hydrolysates on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis: Integrated Metagenomics and Metabolomics Analysis. Foods. 2025; 14(20):3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203483
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Senyu, Qiuting Wang, Shunmin Gong, Mingbo Li, Yu Zhang, Leilei Sun, and Liqin Sun. 2025. "The Effect of Cucumaria frondosa Tentacles Hydrolysates on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis: Integrated Metagenomics and Metabolomics Analysis" Foods 14, no. 20: 3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203483
APA StyleZhang, S., Wang, Q., Gong, S., Li, M., Zhang, Y., Sun, L., & Sun, L. (2025). The Effect of Cucumaria frondosa Tentacles Hydrolysates on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis: Integrated Metagenomics and Metabolomics Analysis. Foods, 14(20), 3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203483






