Abstract
An imbalance of pro-oxidants and antioxidants causes oxidative stress, contributing to various chronic diseases. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) have recognised antioxidant activities that can help reduce oxidative stress. This study isolated fifty LAB strains from various fermented foods and raw vegetable products and evaluated their radical scavenging activity using DPPH and ABTS assays. Among them, four strains Lacticaseibacillus paracasei D2, Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus JL, Latilactobacillus sakei F1, and Weissella cibaria JLK were selected and assessed for their tolerance to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Antioxidant mechanisms were investigated at the molecular level. Genome analysis revealed that the catalase gene (katE) was present in L. sakei F1, while it was absent in other strains. After exposure to H2O2, expression of genes associated with various antioxidant systems in the bacterial strains were measured at different growth phases. The results revealed that NADH oxidase-peroxidase, thioredoxin, and glutathione peroxidase systems play a role in antioxidant activity in L. paracasei D2 and L. rhamnosus JL strains, while genes associated with these systems in L. sakei F1 and Weissella cibaria JLK strains showed no upregulation. A different antioxidant mechanism was observed in L. sakei F1. The findings suggest that the four LAB strains are promising probiotic candidates with significant enzymatic or non-enzymatic antioxidant properties, which may aid in developing antioxidant-rich functional foods.
1. Introduction
Oxidative stress in health occurs when intracellular oxygen radical levels increase, leading to damage in lipids, proteins, and DNA [1,2,3,4]. An excessive accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as superoxide anion (O2−), hydroxyl radicals (HO·), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), can lead to cellular damage, which may contribute to the development of chronic conditions such as arthritis, diabetes, neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer [5,6,7,8]. To cope, most living organisms have developed protective mechanisms, including enzymatic as well as non-enzymatic antioxidant mechanisms [9,10,11,12]. However, these defence systems are often insufficient alone to fully prevent oxidative damage. To counteract this, antioxidants in the diet (either natural or exogenous food additives) are able to protect the human body from oxidative damage. For example, vitamins C and E may be added to foods, while synthetic antioxidants such as butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) are widely used to delay lipid oxidation. However, some safety concerns have emerged regarding the latter due to potential liver toxicity and carcinogenic effects [13,14].
Humans are routinely exposed to lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and their metabolic byproducts in the diet, and they provide a wide range of health benefits, including supporting intestinal homeostasis, detoxifying harmful compounds, and strengthening immune responses [15,16,17]. In addition, certain LAB strains possess significant antioxidant properties, and these can be utilised as effective, natural antioxidants [9]. LAB are a broad group of Gram-positive bacteria commonly found in nature, and they exhibit inherent antioxidant activity for managing oxidative stress through both enzymatic and non-enzymatic mechanisms. The enzymatic mechanisms contain different systems, such as NADH oxidase-peroxidase [18], glutathione peroxidase [19], thioredoxin (Trx) [20,21], as well as catalase [22] and superoxide dismutase [23]. In addition, LAB can produce various non-enzymatic antioxidant metabolites such as glutathione (GSH), butyrate, and folate, and metal-binding proteins (MBPs), which efficiently lower ROS to non-toxic levels and thus shield cells from oxidative stress [24,25,26]. Moreover, there has been a growing interest in heat-killed (HK) LAB, as they can be stored longer and transported more easily than live LAB [27]. Although HK LAB do not secrete soluble metabolites, they may exert their effects through alternative mechanisms. However, there remains a lack of conclusive evidence regarding the impact of non-viable LAB on the biological activities of the host [28,29].
The oxygen sensitivity of LAB strains varies considerably, despite all being classified as aerotolerant anaerobes. These bacteria generally lack a functional electron transport chain, although they may contain some components that compromise their ability to survive in aerobic environments. High oxygen levels promote the formation of ROS. When these ROS accumulate, they induce oxidative stress, which ultimately causes cell death [6,30]. However, the antioxidant mechanisms of LAB are intricate, with different strains utilising distinct approaches. It has been proposed that LAB may exert antioxidant effects by scavenging ROS, chelating metals, increasing antioxidant enzyme levels, and modulating the gut microbiota [6]. A variety of methods have been developed to evaluate the antioxidant properties of LAB, including assays targeting free radical scavenging, metal ion chelation, enzyme activity, and antioxidant end-products. Due to the absence of a standardised testing protocol, it is difficult to directly compare the antioxidant capacities of different strains. Therefore, a combination of analytical approaches is necessary to effectively identify and characterise novel probiotic LAB strains for use in food production as functional food additives [31].
Earlier studies have primarily concentrated on single bacterial strains, exploring their molecular mechanisms without offering comparisons across different strains. Although Weisella cibaria is gaining recognition for its potential probiotic applications in humans, research on its antioxidant activity remains limited. In addition, there has been little investigation into the molecular mechanisms of W. cibaria and its gene expression in response to oxidative stress. Understanding the role of environmental LAB in antioxidant processes may provide new insights into how microorganisms influence both food production and human health. Employing specific bacterial strains could potentially reduce the use of synthetic antioxidants in foods by leveraging the strain’s natural antioxidant properties. This study reports on the isolation of 50 LAB strains from raw and fermented food products, evaluates their in vitro antioxidant properties, and investigates the antioxidant mechanisms of four selected strains at the genetic level to investigate their potential as natural beneficial strains for food applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of LAB Strains
LAB strains were isolated from seven types of raw vegetables and fermented food products. The dilution-plate method was used to isolate LAB on de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) agar and MRS broth (BD Biosciences, Sparks, MD, USA). A 10 g food sample was mixed with 40 mL of sterilised MRS broth to create a 20% suspension. Decimal dilutions ranging from 10−1 to 10−10 were prepared to reduce microbial concentration, and 100 μL of each dilution was plated onto MRS agar plates. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24–48 h in anaerobic conditions generated by AnaeroGen™ sachets (Oxoid, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Basingstoke, UK). Following incubation, colonies exhibiting different morphological characteristics were selected and sub-cultured twice to ensure purity for further analysis [32,33]. For long-term preservation, the stock bacterial cultures in MRS broth containing 30% (v/v) sterile glycerol (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) were stored at −80 °C [33].
2.2. Preparation and Identification of Isolates for Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS)
Frozen stock cultures were revived for 24 h at 37 °C in freshly prepared MRS broth. Each culture was streaked onto MRS agar plates to obtain single colonies and incubated at 37 °C for 12–18 h [34]. Colonies were applied onto the MALDI-TOF MS spots, after which 1 μL of formic acid (70%, v/v) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was added and the samples were allowed to dry at room temperature. Dried spots were covered with 1 μL of α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (HCCA) matrix (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany) prepared from Bruker’s instant soluble formulation. Then the samples were left to dry at room temperature [35]. Bacterial isolates were identified using a Bruker MALDI Biotyper system (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany). Data were analysed using the Bruker MALDI Biotyper 4.1.80 software package.
2.3. Preparing Live and HK LAB for the Antioxidant Assays
The strains were cultured in MRS broth at 37 °C for 16 h. HK LAB samples were prepared by heating the cells at 80 °C for 30 min. After the heat treatment, bacterial suspensions were serially diluted in MRS broth up to 10−5 and spread onto MRS agar plates. The plates were then incubated at 37 °C for 48 h to observe colony growth and confirm the complete loss of bacterial viability. Both live and heat-killed (HK) cells were subsequently centrifuged using the Shandon Cytospin® 4 cytocentrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) at 14,000× g for 5 min and washed twice with 0.85% (w/v) saline solution. The bacterial cells were subsequently resuspended in saline water and diluted to a final concentration of 107 CFU/mL [27,36].
2.4. Ability to Scavenge DPPH Free Radical and ABTS Radicals
In vitro antioxidant activities of isolates were assessed based on their scavenging ability against 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH·) and 2,2’-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS·) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). The ABTS radical scavenging activity was assessed following the method described by Shi et al. [37] with slight modifications. Briefly, the ABTS radical cation was generated by mixing 7 mM ABTS with 2.45 mM potassium persulfate (1:1 v/v) and allowing the mixture to incubate in the dark at room temperature for 16–18 h. The resulting ABTS solution was then diluted with methanol until an initial absorbance of 0.700 ± 0.020 at 734 nm. For the assay, 50 µL of live or HK sample was mixed with 100 µL of ABTS solution and incubated at room temperature for 10 min. The absorbance of the reaction mixture was then measured at 734 nm. Each assay was conducted in triplicate, and the scavenging rate was determined using the formula:
where: A test = absorbance of the test sample; A control = absorbance of the saline water control sample.
ABTS scavenging activity (%) = (1 − A test/A control) × 100%
DPPH radical scavenging activity was assessed according to the method described by Lin and Yen [38] with some modifications. DPPH solution was prepared freshly by dissolving DPPH in absolute ethanol to a final concentration of 0.2 mM. For the assay, 80 µL of live or HK cells were combined with 100 µL of DPPH solution and incubated in the dark for 30 min. For the control, the bacterial suspension was replaced with saline water. Meanwhile, the blank group was set up by substituting the DPPH radicals with an equal volume of ethanol. The absorbance was recorded at 517 nm. The scavenging activity was calculated using the formula:
DPPH scavenging activity (%) = [1 − (A sample − A blank)/A control] × 100
2.5. Growth of the Strains in the Presence of H2O2
H2O2 tolerance was examined as described in previous studies [39,40] with some changes. The eight top-performing strains common across both antioxidant assays were further evaluated for their tolerance to oxidative stress by culturing them in MRS broth supplemented with increasing concentrations of H2O2 up to 0–6 mM for 24 h at 37 °C. Tolerance was assessed by visually observing the turbidity of cells and checking the mass of bacterial pellets after centrifugation. Based on the results of DPPH, ABTS antioxidant assays and H2O2 tolerance, four bacterial strains were selected for further study.
2.6. Whole Genome Sequencing and Detection of Genes Involved in Antioxidant Activity
Pure cultures of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei D2, Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus JL, Latilactobacillus sakei F1 and Weissella cibaria JLK were grown in MRS broth up to 108 CFU/mL, and DNA was extracted using the DNeasy® PowerSoil® Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Total DNA quality and concentrations were measured using NanoDrop and QubitTM Fluorometric Quantitation (ThermoFisher, Waltham, MA, USA), respectively. Whole genome sequencing was carried out using Illumina Nextera XT DNA Library Preparation Kit and sequenced on an Illumina MiSeq platform with 2 × 300 bp reads. The genomes were assembled using A5-miseq [41], and the assembled genomes were annotated with the Rapid Annotation using Subsystem Technology pipeline (RAST) [42]. Genes associated with antioxidants were identified in the RAST output and also confirmed with Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST+ 2.17.0) search [43].
2.7. Bio-Screen Assay and Expression Levels of Genes Involved in Antioxidant Activity
The bio screen assay was conducted with the four most promising LAB strains based on DPPH, ABTS antioxidant results and the tolerance of H2O2 to assess biomass proliferation. Pure cultures of L. sakei F1, L. paracasei D2, L. rhamnosus JL, and W. cibaria JLK were standardised to 107 CFU/mL and inoculated into MRS broth containing varying concentrations of H2O2 from 0.5–8 mM. The control medium for all strains contained no added H2O2. Then, the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) was recorded every 3 h for 40 h after brief shaking of the plate for strains JL, JLK, and D2 [44]. For strain F1, OD600 measurements were taken at specific time points: 0, 4, 8, 10, 13, 23, 26, and 29 h with high concentrations of H2O2 (0–8 mM) due to the shown higher tolerance to H2O2. For all strains, cells were collected at mid-logarithmic phase and the start of the stationary phase for RNA extraction, except strain F1, where cells were harvested at the start of the stationary phase only [44]. The libraries were prepared using the Illumina TruSeq Stranded Total RNA with Ribo-Zero Plus workflow (rRNA depletion) (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA), and sequencing was carried out with the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA), and 150-bp paired-end reads were generated at the Australian Genome Research Facility (AGRF). RNA-seq data, including quality check, mapping reads, and quantification of gene expression levels, were analysed using the Galaxy Australia platform (https://usegalaxy.org.au, accessed on 23 May 2025).
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using Minitab® 18 and GraphPad Prism 10.4.2 statistical software. Results are expressed as mean ± standard error (SEM), with all experiments performed in triplicate. The mean values and standard errors were calculated, and a probability level of p < 0.05 was utilised to test the statistical significance of the experimental data. During the screening phase, fifty bacterial strains were evaluated using a Two-way Analysis of Variance (two-way ANOVA) in Minitab® 18. To assess the significance of differences between group means in multiple comparisons, Tukey’s post-hoc test was applied, enabling the identification of the top strains with the highest antioxidant activities. For the selected top eight strains, a two-way ANOVA followed by Šídák’s multiple comparisons test was conducted using GraphPad Prism 10.4.2 statistical software to uncover treatment-specific differences among the strains.
3. Results
3.1. Identification of LAB Using MALDI-TOF Analysis
For species-level identification, LAB strains were subjected to MALDI-TOF analysis (Table 1). A total of 50 isolates were identified, with the majority belonging to the Latilactobacillus genus, including L. sakei (12 isolates) and L. curvatus (8). Other genera included Leuconostoc: L. mesenteroides (5), L. citreum (3); Lacticaseibacillus: L. paracasei (5), and L. rhamnosus (1); Weisella: W. cibaria (3) and W. koreensis (1); Levilactobacillus brevis (3); Pediococcus: P. pentosaceus (2) and P. acidilactici (1); Lactococcus lactis (2); Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (2); Furfurilactobacillus rossiae (1); Lactobacillus delbrueckii (1).

Table 1.
Isolated microorganisms from different food products.
3.2. DPPH and ABTS Free Radical Scavenging Activities
The antioxidant activity of live and HK LAB strains, isolated from both raw and fermented food products, was assessed by measuring their ability to scavenge free radicals using the ABTS and DPPH assays, as presented in Table 2. The findings indicate that both live and HK LAB strains have varying abilities to scavenge different free radicals. After conducting a screening process, we identified the top eight strains, including F1, D2, L4, L7, L8, JL, JLK, and FR2, based on their consistently high antioxidant activity across two assays, as illustrated in Figure 1 and Figure 2. In Figure 1, the F1 strain demonstrated the highest DPPH radical scavenging activity in live cells, recorded at 29.84 ± 0.39%, while the JL strain exhibited the highest activity in its HK form, measuring 23.75 ± 0.24%. Overall, live cells demonstrated a significantly (p < 0.05) strong DPPH radical scavenging ability across all strains, except for L4, L7, and L8, which did not exhibit significant differences between the live and HK groups (p < 0.05). Results from the ABTS radical scavenging activity tests indicated that the JL strain exhibited the highest radical scavenging activity in both live and HK forms, showing values of 39.90 ± 1.34% and 35.87 ± 0.29%, respectively. Generally, live bacterial cultures demonstrated significantly higher radical scavenging activity (p < 0.05), except for the L8 strain. Furthermore, there were no significant differences between the two groups for the D2 and L4 strains. The findings indicate that live cultures typically demonstrate superior antioxidant activity; however, HK forms of certain strains also reveal noteworthy antioxidant properties, which necessitated further investigation.

Table 2.
Antioxidant properties of LAB strains.
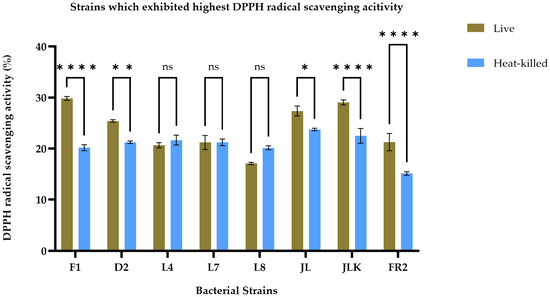
Figure 1.
DPPH radical scavenging activity of live (brown bars) and heat-killed (blue bars) bacterial strains. Statistical analysis by two-way ANOVA followed by Šídák’s multiple comparisons test revealed strain-dependent differences. Strains F1, D2, JL, JKL and FR2 exhibited significantly higher scavenging activity in live cells compared to their heat-killed counterparts (p < 0.01 to p < 0.0001). No significant differences were observed for strains L4, L7, and L8 (p > 0.05). Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). ns = not significant; * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, **** p ≤ 0.0001.
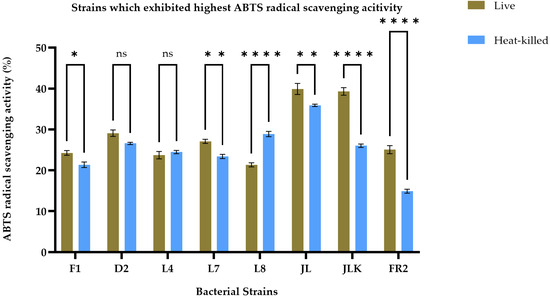
Figure 2.
ABTS radical scavenging activity of live (olive brown bars) and heat-killed (blue bars) bacterial strains. Statistical analysis by two-way ANOVA followed by Šídák’s multiple comparisons test revealed treatment-specific differences across strains. L8 showed a modest but significant increase in heat-killed cells compared with live forms. No significant differences were observed for D2 and L4. Strains F1, L7, JL, JLK, and FR2 exhibited significantly higher activity in live cells than in their heat-killed counterparts (p < 0.01 to p < 0.0001). Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). ns = not significant; * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, **** p ≤ 0.0001.
3.3. Genome Sequences of L. paracasei D2, L. rhamnosus JL, W. cibaria JLK, L. sakei F1
After the assessment of antioxidant activity, the oxidative stress tolerance of selected strains was evaluated in the presence of H2O2. Based on the ability of strains to grow under different H2O2 conditions, four strains, including F1, JLK, JLFS, and D2, were selected for further characterisation with the bio-screen assay and assessed for the expression levels of genes involved in antioxidant activity.
The genome size and GC content of the four bacterial strains are shown in Table 3. The genome size ranges from 1.98 to 3.36 Mbp. Among them, strain F1 exhibited the smallest genome size, while D2 had the largest genome. The GC content also showed considerable variation across the strains ranging from 41 to 46.6%.

Table 3.
Basic genomic features of L. paracasei D2, L. rhamnosus JL, W. cibaria JLK, L. sakei F1.
Based on the annotation results and a literature search on common antioxidant-related genes in LAB [44,45,46], a total of eight antioxidant-related genes were identified in the strains, as shown in Table 4. L. sakei F1 is the only strain that contains the katE gene, and L. rhamnosus JL is the only strain with the nox gene.

Table 4.
Antioxidant-related gene comparison of strains D2, JL, JLK, and F1.
3.4. Analysis of the Transcript Levels of the Genes Involved in Antioxidant Activity in LAB Strains Exposed to H2O2
The growth of JLK, JL and D2 showed tolerance against H2O2 at 1, 2, and 3 mM as illustrated in Figure 3a–c. F1 exhibited bacterial growth under 4 mM, as shown in Figure 3d. The presence of H2O2 reduced the bacterial growth, and the lag phases were considerably prolonged with the increasing H2O2 concentrations, indicating that H2O2 caused oxidative damage to the bacteria.
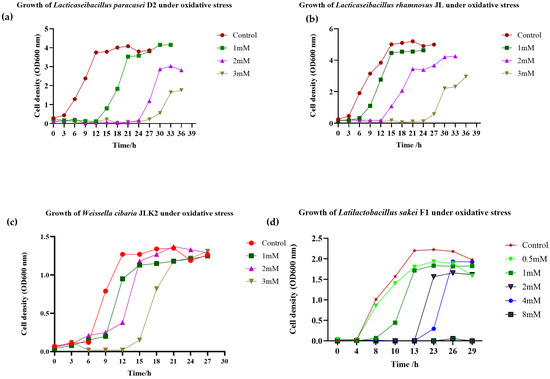
Figure 3.
Growth of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei D2 (a), Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus JL (b), and Weissella cibaria JLK (c) under oxidative stress. The strains were cultured in MRS broth supplemented with H2O2 at concentrations of 1, 2, and 3 mM. In contrast, Latilactobacillus sakei F1 (d) was grown under a broader range of H2O2 concentrations (0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8 mM).
To unravel the potential mechanism of antioxidant activity in selected strains, gene expression via RNA was measured. We focused on the upregulation of antioxidant-related genes at two growth phases: the mid-log and the start of the stationary phases. This was conducted across two concentrations per strain: control and 2 mM for strain D2, control and 2 mM for strain JL, and control and 3 mM for strain JLK. For strain F1, the relative expression levels were assessed at the start of the stationary phase using three different concentrations: control, 2 mM and 4 mM.
As shown in Table 5, genes associated with the NADH oxidase-peroxidase system, including nox and npx, showed considerable upregulation in D2 and JL strains. Specifically, the npx gene exhibited a notable upregulation at the mid-log phase, with increases of 1.42-fold in D2 and 1.44-fold in JL, suggesting their direct involvement in antioxidant activity. The nox gene, which is absent in the D2 strain but present in the JL strain, also demonstrated upregulation at the mid-log phase. Furthermore, genes associated with the Trx systems, such as tpx and trxB, showed mild upregulation in both strains. The glutathione peroxidase system, including gpx and gshR genes, displayed slight upregulation in the early stationary phase in the D2 strain. In contrast, these genes showed a slight upregulation at the mid-log phase in the JL strain. All isolates contain the sodA gene, but none of the strains exhibited any upregulation for this gene, indicating that sodA might not directly contribute to antioxidant activity in these strains. For the L. sakei F1 and W. cibaria JLK strains, only katE and npx showed upregulation at 4 mM and 3 mM H2O2, with fold changes of 1.26 and 1.10, respectively. Interestingly, for the F1 strain only, significant upregulation of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase was observed (5.45—fold change). This enzyme does not directly neutralise ROS but indirectly contributes to antioxidant activity [47].

Table 5.
Upregulation of genes involved in antioxidant activity of strain L. paracasei D2 and L. rhamnosus JL at 2 mM H2O2 vs. Control.
4. Discussion
Living organisms continuously produce ROS during their physiological activities. Malfunctioning oxidative systems and an increase in free radicals leads to oxidative stress, which can irreversibly damage cells and their components [48]. LAB have been extensively studied for their antioxidant activity using various approaches. Their antioxidant effects have been demonstrated, including free radical-scavenging capacities, lipid peroxidation-inhibition capacities, and metal-chelating abilities, along with a variety of antioxidant enzyme activities [28,36,49]. Thermal treatment or heat-killing (HK) is the most common method for microbial inactivation of live probiotic strains to produce ‘paraprobiotics’ [28]. Research has shown that LAB subjected to thermal treatment exhibit a wide range of biological activities, including some with beneficial physiological effects [28,50,51,52]. In this study, fifty live and HK LAB strains, isolated from fermented and raw food products, were tested for their in vitro antioxidant properties based on biochemical assays of DPPH- and ABTS-scavenging activities. Notably, the results from the ABTS radical cation scavenging assay were comparable to those from the DPPH radical scavenging tests, showing similar trends in the mean values across most bacterial strains with varied treatments. Both antioxidant assays can be monitored with a spectrophotometer. Specifically, the ABTS assay is based on the formation of blue/green ABTS·+, which can be reduced by antioxidants, while the DPPH assay relies on the reduction of purple DPPH· to its non-radical hydrazine form, leading to a loss of colour [53]. In addition to these assays, there are other methods for assessing the antioxidant activity of LAB, such as the ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay, the hydroxyl radical scavenging test, the ferrous ion-chelating assay, and the determination of superoxide anion radical scavenging capacity [54]. In the present study, we considered that a bio-screen growth assay under H2O2 stress and transcriptomic analysis of antioxidant-related genes, in addition to the two chemical assays, produced more complete information. This approach offered a multifaceted evaluation of the antioxidant activity of the strains by providing both physiological and molecular evidence of antioxidant capacity.
Overall, most of the live LAB strains exhibited higher antioxidant potential in both the DPPH and ABTS assays compared to HK cells. These results are in line with the previous work done by Li, et al. [55]. They investigated the radical scavenging activity of live/HK L. sakei MS103 and found that live cells exhibited higher antioxidant activity. This could be attributed to certain cell surface-active compounds, such as proteins, polysaccharides, exopolysaccharides (EPS), and lipoteichoic acid, which have been observed in L. plantarum C88, Bifidobacterium spp., and L. brevis KU15147, as documented by Li [56], Yi, et al. [57], Kim, et al. [58]. It is interesting to note that HK L8 demonstrated higher antioxidant activity compared to its live cells in the ABTS assay. However, in the DPPH assay, both L8 live cells and HK cells exhibited no significant differences. We observed similar results in a study conducted by Xu, et al. [59] with Loigolactobacillus coryniformis NA-3, where the heat-killed strain also exhibited activities similar to those of live bacteria. Additionally, in our study, the HK forms of certain strains, including SK1, D6, SK 5-1, RSK 1, SK®3 4, Broc 03, Kim 1-1, Kim 1-2, and Kim 2-1, demonstrated significantly higher radical scavenging activity (p < 0.05) compared to their live forms in both screening assays. The relationship between the HK LAB and bioactivity remains unclear. Some studies have shown that excessive heating at 121 °C can significantly reduce the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of probiotics. This reduction may be attributed to a decrease in the content of metabolites that possess these beneficial activities [60].
Following screening using these biochemical assays, four strains were selected for their maximum antioxidant potential: Lacticaseibacillus paracasei D2, Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus JL, Latilactobacillus sakei F1, and Weissella cibaria JLK. Another method was used for evaluating oxidative stress tolerance is to assess cell viability in the presence of H2O2. H2O2 is considered a mild oxidant; however, it can permeate the cell membrane and generate more ROS and initiate oxidative damage [9]. Lactobacilli are known to generate O2- and H2O2 and accumulate millimolar concentrations of peroxide. Mechanisms to counteract the toxicity of ROS are crucial for survival in oxygen-rich environments. To prevent oxidative stress, all bacteria, including LAB, possess enzymatic and non-enzymatic defensive mechanisms [24]. Enzymatic mechanisms typically involve superoxide dismutase (SOD) and hydrogen peroxidase enzymes such as catalases (CAT) and peroxidases which serve as the primary defence against O2− and H2O2, respectively [61]. Specifically, SOD catalyses the conversion of superoxide anions to oxygen, helping to prevent H2O2-induced cell damage. CAT is the enzyme that catalyses the decomposition of H2O2, playing a vital role in protecting cells from oxidative damage caused by ROS. LAB generally lack CAT because they cannot synthesise heme [62]. An, et al. [63] reported that L. rhamnosus is deficient in katE and sodA/sodB genes, which matches our findings for the absence of these genes in L. rhamnosus JL. Additionally, we observed that W. cibaria JLK also lacks both katE and sodA/sodB genes. Although we found that L. paracasei D2 and L. sakei F1 contain the sodA gene, our findings did not support its active involvement in antioxidant properties, despite its well-documented role in this regard for other bacteria. We observed the downregulation of sodA in both strains across all concentrations and growth phases, suggesting that sodA does not contribute to the antioxidative properties of the tested strains. This lack of involvement may be due to strain-specific differences. Additionally, L. sakei F1 is the only strain that contains the katE gene, which exhibited upregulation in the presence of H2O2. L. sakei F1 shared other common antioxidant-related genes, including npx, tpx, trxB, gshR, sodA, as well as katE, in agreement with the study by Li, et al. [55]. They found that L. sakei MS103, isolated from pickled garlic, exhibited antioxidant activity and stress response in the presence of H2O2, with upregulated expression of the gshR2, gshR4, gpx, and npx genes. However, in our study, these genes did not show active involvement in the presence of H2O2, except for katE. Nevertheless, significant upregulation occurred in dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (5.45- fold change) at 4 mM H2O2 exposure in the F1 strain, an enzyme that does not directly neutralise ROS but indirectly contributes to antioxidant activity through influencing cellular redox balance [47].
The glutathione peroxidase system, including gshR and gpx genes, is another system that plays a crucial role in protecting against oxidative damage by oxidising glutathione disulphide, thereby reducing H2O2 levels [64]. Furthermore, the glutathione peroxidase system is involved in redox regulation [65,66]. The relationship between H2O2-induced oxidative stress and the glutathione peroxidase system in Lactobacilli has been rarely studied. However, in this study, we observed that the expression levels of gpx and gshR increased at the beginning of the stationary phase in L. paracasei D2 strain. This suggests that these enzymes also play a role in the antioxidant activity of L. paracasei D2 by regulating oxidative stress. Recent studies have reported that L. paracasei has promising antioxidant effects [67,68]. The strain L. paracasei TDM-2, isolated from a fermented dairy product, demonstrated high antioxidant capacity and tolerance against 2 mM H2O2 [69]. In addition, Yang, et al. [46] found that L. paracasei strain M11-4 isolated from fermented rice has antioxidant potential and survives under 2.5 mM H2O2. It upregulated the expression of its antioxidant enzyme systems, notably the Trx and glutathione peroxidase antioxidant pathways. The Trx system is known to respond to H2O2-induced oxidative stress in lactobacilli. In agreement with this finding, we observed elevated expression of genes associated with Trx and glutathione peroxidase pathways, indicating that both play an important role in the antioxidant activity of L. paracasei D2.
The gene npx is a well-known gene harboured by microorganisms that are involved in the scavenging of H2O2 [70]. It directly reduces H2O2 to water using NADH [55]. Strains without katE rely on npx and high intracellular manganese for peroxide scavenging [63]. In this study, we observed that npx appeared to play a role in the antioxidant activity of strain L. paracasei D2 and L. rhamnosus JL during the mid-log phase. Additionally, L. rhamnosus strains were found to possess nox and npx genes, possibly managing ROS, and often accumulate high levels of manganese, which can non-enzymatically suppress superoxides [31]. Our findings align with this prior research, as nox and npx were noticeably upregulated in the mid-log phase. Moreover, the results revealed that most antioxidant-related genes are growth phase-dependent, supporting the findings of Wu, et al. [71], who investigated the antioxidant mechanisms of L. plantarum ZJ316. The strain exhibited upregulation of the nox and npx genes by 1.72-fold and 1.41-fold, respectively, during the stationary phase under 2.5 mM H2O2 stress.
There is a limited number of studies on the antioxidant mechanisms of the W. cibaria species. Yu, et al. [72] showed that the strain W. cibaria JW15, isolated from kimchi, exhibited considerably higher free radical scavenging activity than other strains. It efficiently neutralised DPPH, ABTS, and hydroxyl radicals, and also inhibited linoleic acid peroxidation, indicating that JW15 can both prevent lipid oxidation and directly scavenge ROS [72]. Our study found that all common antioxidant-related genes in W. cibaria JLK were not upregulated under H2O2 stress, except for npx, which showed slight upregulation. The classical katE or sodA are also absent in this strain, further demonstrating that its antioxidant activity is likely to rely on non-enzymatic factors such as EPS and antioxidant metabolites [24].
5. Conclusions
In this study, four LAB strains isolated from fermented foods or raw vegetables exhibiting strong in vitro antioxidant activity were identified through a series of experimental evaluations. L. paracasei D2, L. rhamnosus JL, L. sakei F1 and W. cibaria JLK demonstrated notable tolerance to H2O2 stress and effective scavenging activity against free radicals. The three different antioxidant systems, including NADH oxidase-peroxidase, thioredoxin, and glutathione peroxidase systems, appear to play an important role in the antioxidant activity of strains D2 and JL. In contrast, the role of these systems in the antioxidant activities of strains JLK and F1 was not obvious, with only npx found to be upregulated under H2O2 stress in strain JLK. Instead, non-enzymatic antioxidant factors and indirect antioxidant pathways may be involved, as demonstrated by the significant upregulation of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase in strain F1. The catalase pathway also seems to be involved in the antioxidant activity of this strain. These findings offer new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying the antioxidant activity of LAB strains. Further studies are needed to fully elucidate the antioxidant pathways involved. Based on their antioxidative properties, these four LAB strains have promising potential as probiotic candidates for the development of functional foods with superior antioxidant benefits.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.A. and T.T.H.V.; Data curation, T.A.; Formal analysis, T.A.; Funding acquisition, T.T.H.V.; Investigation, T.A. and T.T.H.V.; Methodology, T.A., T.T.H.V., S.E. and C.S.; Project administration, T.T.H.V.; Supervision, T.T.H.V., C.P., C.B. and A.G.; Validation, T.A. and T.T.H.V.; Visualization, T.A.; Writing—original draft, T.A.; Writing—review & editing, T.T.H.V., C.P., C.B., A.G., S.E. and C.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
T.A. was supported by the RMIT Research Stipend Scholarship (RRSS), and this study was funded by the RMIT Vice-Chancellor’s Senior Research Fellowship scheme (VCRF2022).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The genome sequences of the isolates have been submitted to NCBI under the following accession numbers: Latilactobacillus sakei F1 (PRJNA1093171), Lacticaseibacillus paracasei D2 (PRJNA1251814), Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus JL(PRJNA1252288), and Weissella cibaria JLK (PRJNA1265932).
Conflicts of Interest
A.G. was employed by Edlyn Foods Pty Ltd., Epping, Victoria 3076, Australia. The company was not involved in the study design, data collection, analysis, interpretation, the writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| BHA | Butylated hydroxyanisole |
| MBP | Metal-binding proteins |
| HK | Heat-killed |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | Catalase |
References
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative stress: Harms and benefits for human health. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandimali, N.; Bak, S.G.; Park, E.H.; Lim, H.-J.; Won, Y.-S.; Kim, E.-K.; Park, S.-I.; Lee, S.J. Free radicals and their impact on health and antioxidant defenses: A review. Cell Death Discov. 2025, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, H.K.; Pereira, M.; Rajavelu, I.; Jayaraman, V.; Krishna, K.; Wang, T.; Bei, K.; Rajasekaran, J.J. Oxidative stress: Fundamentals and advances in quantification techniques. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1470458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firuzi, O.; Miri, R.; Tavakkoli, M.; Saso, L. Antioxidant therapy: Current status and future prospects. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 3871–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaretti, A.; di Nunzio, M.; Pompei, A.; Raimondi, S.; Rossi, M.; Bordoni, A. Antioxidant properties of potentially probiotic bacteria: In vitro and in vivo activities. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, U.C.; Bhol, N.K.; Swain, S.K.; Samal, R.R.; Nayak, P.K.; Raina, V.; Panda, S.K.; Kerry, R.G.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. Oxidative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders: Mechanisms and implications. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2025, 15, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Guo, Y.; Tang, W.; Chen, D.; Xue, L.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wei, S.; Wu, M.; Dai, J.; et al. Reactive oxygen species-scavenging nanomaterials for the prevention and treatment of age-related diseases. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Shah, C.; Mokashe, N.; Chavan, R.; Yadav, H.; Prajapati, J. Probiotics as potential antioxidants: A systematic review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3615–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hu, L.; Ye, S.; Jiang, L.; Liu, S. Genome-wide identification of glutathione peroxidase (GPX) gene family and their response to abiotic stress in cucumber. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hu, L.; Wu, H.; Jiang, L.; Liu, S. Genome-wide identification and transcriptional expression analysis of cucumber superoxide dismutase (SOD) family in response to various abiotic stresses. Int. J. Genom. 2017, 2017, 7243973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Several lines of antioxidant defense against oxidative stress: Antioxidant enzymes, nanomaterials with multiple enzyme-mimicking activities, and low-molecular-weight antioxidants. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 1323–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Fang, B. Structural identification of ginseng polysaccharides and testing of their antioxidant activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Bu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Meng, X. Exploring the mechanisms of the antioxidants BHA, BHT, and TBHQ in Hepatotoxicity, Nephrotoxicity, and Neurotoxicity from the Perspective of Network Toxicology. Foods 2025, 14, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Shanab, A.; Quigley, E.M. The role of the gut microbiota in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Ed-Dra, A.; Song, Y.; Elbediwi, M.; Nambiar, R.B.; Zhou, X.; Yue, M. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus alleviates intestinal inflammation and promotes microbiota-mediated protection against Salmonella fatal infections. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 973224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damholt, A.; Keller, M.; Baranowski, K.; Brown, B.; Wichmann, A.; Melsaether, C.; Eskesen, D.; Westphal, V.; Arltoft, D.; Habicht, A.; et al. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG DSM 33156 effects on pathogen defence in the upper respiratory tract: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled paediatric trial. Benef. Microbes 2022, 13, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.S.; Korber, D.R.; Tanaka, T. Influence of oxygen on NADH recycling and oxidative stress resistance systems in Lactobacillus panis PM1. AMB Express 2013, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vašková, J.; Kočan, L.; Vaško, L.; Perjési, P. Glutathione-Related Enzymes and Proteins: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Holmgren, A. The thioredoxin antioxidant system. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 66, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.M.; Poole, L.B. Catalytic mechanism of thiol peroxidase from Escherichia coli. Sulfenic acid formation and overoxidation of essential CYS61. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9203–9211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, A.; Yan, L.J.; Jana, C.K.; Das, N. Role of catalase in oxidative stress- and age-associated degenerative diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9613090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukai, T.; Ushio-Fukai, M. Superoxide dismutases: Role in redox signaling, vascular function, and diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1583–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Mei, X.; Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. Antioxidant properties of probiotic bacteria. Nutrients 2017, 9, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampemohotti, T.; Aida, G.; Christopher, P.; Charles, B.; Hao Van, T.T. Fermented vegetables: Their microbiology and impact on gut microbiota and overall health benefits. Food Rev. Int. 2025, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, S.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, Y.-C.; Choi, I.; Kim, G.-B. Effect of fermentation on the antioxidant activity in plant-based foods. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.J.; Song, M.W.; Lee, N.K.; Paik, H.D. Antioxidant effects of live and heat-killed probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum Ln1 isolated from kimchi. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 3174–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, B.H.; Ali, S.A.; Behare, P.V.; Yadav, H. Postbiotics-parabiotics: The new horizons in microbial biotherapy and functional foods. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.S.; Jung, W.J.; Lee, S.B.; Jo, S.J.; Hwang, M.H.; Park, J.H.; Venkatachalam, S.; Park, S.C. Effect of dietary heat-killed Lactiplantibacillus plantarum VSG3 on growth, immunity, antioxidant status, and immune-related gene expression in pathogen-aggravated Cyprinus carpio. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 149, 109547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maresca, D.; Zotta, T.; Mauriello, G. Adaptation to Aerobic Environment of Lactobacillus johnsonii/gasseri Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.; Wang, J. Oxidative stress tolerance and antioxidant capacity of lactic acid bacteria as probiotic: A systematic review. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1801944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batdorj, B.; Dalgalarrondo, M.; Choiset, Y.; Pedroche, J.; Métro, F.; Prévost, H.; Chobert, J.M.; Haertlé, T. Purification and characterization of two bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria isolated from Mongolian airag. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ahmadi, K.; Haboubi, K.; El Allaoui, H.; El Hammoudani, Y.; Bouhrim, M.; Eto, B.; Shahat, A.A.; Herqash, R.N. Isolation and preliminary screening of lactic acid bacteria for antimicrobial potential from raw milk. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1565016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanak, E.K.; Yilmaz, S.Ö. Identification, antibacterial and antifungal effects, antibiotic resistance of some lactic acid bacteria. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacef, M.; Chevalier, M.; Chollet, S.; Drider, D.; Flahaut, C. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for the identification of lactic acid bacteria isolated from a French cheese: The Maroilles. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 247, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Jeong, Y.; Kang, C.-H. Antioxidant activity and probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria. Fermentation 2022, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Cui, X.; Gu, S.; Yan, X.; Li, R.; Xia, S.; Chen, H.; Ge, J. Antioxidative and probiotic activities of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional artisanal milk cheese from northeast China. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 1086–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Y.; Yen, C.L. Antioxidative ability of lactic acid bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Li, D.; Niu, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Q. Antioxidant activity of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from traditional Chinese fermented foods. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niel, E.W.J.; Hofvendahl, K.; Hahn-Hägerdal, B. Formation and conversion of oxygen metabolites by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis atcc 19435 under different growth conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4350–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coil, D.; Jospin, G.; Darling, A.E. A5-miseq: An updated pipeline to assemble microbial genomes from Illumina MiSeq data. Bioinformatics 2014, 31, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Xing, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Molecular mechanisms and in vitro antioxidant effects of Lactobacillus plantarum MA2. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1642–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gong, W.; Xu, C.; Zhu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Xie, C. Probiotic assessment and antioxidant characterization of Lactobacillus plantarum GXL94 isolated from fermented chili. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 997940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dong, C.; Ren, F.; Xie, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Jin, J. Lactobacillus paracasei M11-4 isolated from fermented rice demonstrates good antioxidant properties in vitro and in vivo. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 3107–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, R.A.G.; Calil, F.A.; Feliciano, P.R.; Pinheiro, M.P.; Nonato, M.C. The dihydroorotate dehydrogenases: Past and present. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 632, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Tuo, Y.; Qian, F. Protecting Effect of Bacillus coagulans T242 on HT-29 Cells Against AAPH-Induced Oxidative Damage. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2022, 14, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Li, C.; He, Z.; Pan, F.; Pan, S.; Wang, Y. Probiotic properties and cellular antioxidant activity of Lactobacillus plantarum MA2 isolated from Tibetan kefir grains. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, T.C.; Cruz, A.G.; Pereira, E.; da Costa, W.K.A.; da Silva Rocha, R.; de Souza Pedrosa, G.T.; dos Santos Rocha, C.; Alves, J.M.; Alvarenga, V.O.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; et al. Postbiotics: An overview of concepts, inactivation technologies, health effects, and driver trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piqué, N.; Berlanga, M.; Miñana-Galbis, D. Health benefits of heat-killed (Tyndallized) probiotics: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almada, C.N.; Almada, C.N.; Martinez, R.C.R.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Paraprobiotics: Evidences on their ability to modify biological responses, inactivation methods and perspectives on their application in foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 58, 96–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floegel, A.; Kim, D.-O.; Chung, S.-J.; Koo, S.I.; Chun, O.K. Comparison of ABTS/DPPH assays to measure antioxidant capacity in popular antioxidant-rich US foods. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łepecka, A.; Szymański, P.; Okoń, A. Isolation, identification, and evaluation of the antioxidant properties of lactic acid bacteria strains isolated from meat environment. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0327225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Luan, C. Antioxidant effects and probiotic properties of Latilactobacillus sakei MS103 isolated from sweet pickled garlic. Foods 2023, 12, 4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Improved pyrogallol autoxidation method: A reliable and cheap superoxide-scavenging assay suitable for all antioxidants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6418–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.-J.; Fu, Y.-R.; Li, M.; Gao, K.-S.; Zhang, X.-G. Effect of LTA isolated from bifidobacteria on d-galactose-induced aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2009, 44, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-T.; Yang, S.J.; Paik, H.-D. Probiotic properties of novel probiotic Levilactobacillus brevis KU15147 isolated from radish kimchi and its antioxidant and immune-enhancing activities. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Qiao, Y.; Peng, Q.; Shi, B. Probiotic properties of Loigolactobacillus coryniformis NA-3 and in vitro comparative evaluation of live and heat-killed cells for antioxidant, anticancer and immunoregulatory activities. Foods 2023, 12, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Fang, B.; Hung, W.; Gao, H.; Zhao, W.; Lan, H.; Liu, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, M. Effect of thermal inactivation on antioxidant, anti-inflammatory activities and chemical profile of postbiotics. Foods 2023, 12, 3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, T.; Hassan, H.M. Role of the Mn-catalase in aerobic growth of Lactobacillus plantarum ATCC 14431. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 1, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Du, G.; Fang, F. Heme dependent catalase conditionally contributes to oxygen tolerance of Tetragenococcus halophilus strains isolated from soy sauce moromi. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Zhai, Z.; Yin, S.; Luo, Y.; Han, B.; Hao, Y. Coexpression of the Superoxide Dismutase and the Catalase Provides Remarkable Oxidative stress resistance in Lactobacillus rhamnosus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3851–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, J.; González, B.; Sempere, V.; Mas, A.; Torija, M.J.; Beltran, G. Melatonin reduces oxidative stress damage induced by hydrogen peroxide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Lu, J.; Holmgren, A. Thioredoxin 1 is inactivated due to oxidation induced by peroxiredoxin under oxidative stress and reactivated by the glutaredoxin system. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 32241–32247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-L.; Wang, C.-H.; Kuo, Y.-W.; Tsai, C.-H. Antioxidative and hepatoprotective effects of fructo-oligosaccharide in d-galactose-treated Balb/cJ mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, M.; Attri, S.; Sharma, K.; Goel, G. Lactobacillus paracasei CD4 as potential indigenous lactic cultures with antioxidative and ACE inhibitory activity in soymilk hydrolysate. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-Y.; Chen, L.-H.; Wang, M.-F.; Hsu, C.-C.; Chan, C.-H.; Li, J.-X.; Huang, H.-Y. Lactobacillus paracasei PS23 delays progression of age-related cognitive decline in senescence accelerated mouse prone 8 (SAMP8) mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Fan, X.; Li, D.; Zhao, T.; Wu, D.; Liu, Z.; Long, D.; Li, B.; Huang, X. High Antioxidant Capacity of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei TDM-2 and Pediococcus pentosaceus TCM-3 from Qinghai Tibetan Plateau and Their Function towards Gut Modulation. Foods 2023, 12, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, S.; Abe, F.; Ishibashi, N.; Miyakawa, H.; Yaeshima, T.; Araya, T.; Tomita, M. Relationship between oxygen sensitivity and oxygen metabolism of Bifidobacterium species. J. Dairy Sci. 1992, 75, 3296–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, F.; Li, P.; Gu, Q. Antioxidant properties and molecular mechanisms of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum ZJ316: A potential probiotic resource. LWT 2023, 187, 115269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.S.; Lee, N.K.; Choi, A.J.; Choe, J.S.; Bae, C.H.; Paik, H.D. Antagonistic and antioxidant effect of probiotic Weissella cibaria JW15. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).