Physicochemical, Microbiological and Sensory Evaluation of Plant-Based Meat Analogs Supplemented with Phenolic Extracts from Olive Mill By-Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Reagents and Materials
2.2. Production of Plant-Based Meat Analogs
2.3. Phenolic Extract (PE) from Olive Vegetation Water (OVW)
Phenolic Composition
2.4. Physicochemical Analysis of the Meat Analog
2.4.1. Bromatological Parameters
Moisture Content
Ash Content
Lipid Content
2.4.2. pH and Water Activity
2.4.3. Texture Analysis
2.4.4. Color Analysis
2.4.5. HPLC Analysis of Phenolic Compounds from OVW
2.4.6. Antioxidant Activity
2.4.7. Total Phenols
2.5. Microbiological Analysis
2.6. Sensory Evaluations
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Bromatological and Physicochemical Characteristics
3.2. Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity
3.3. Microbiological Results
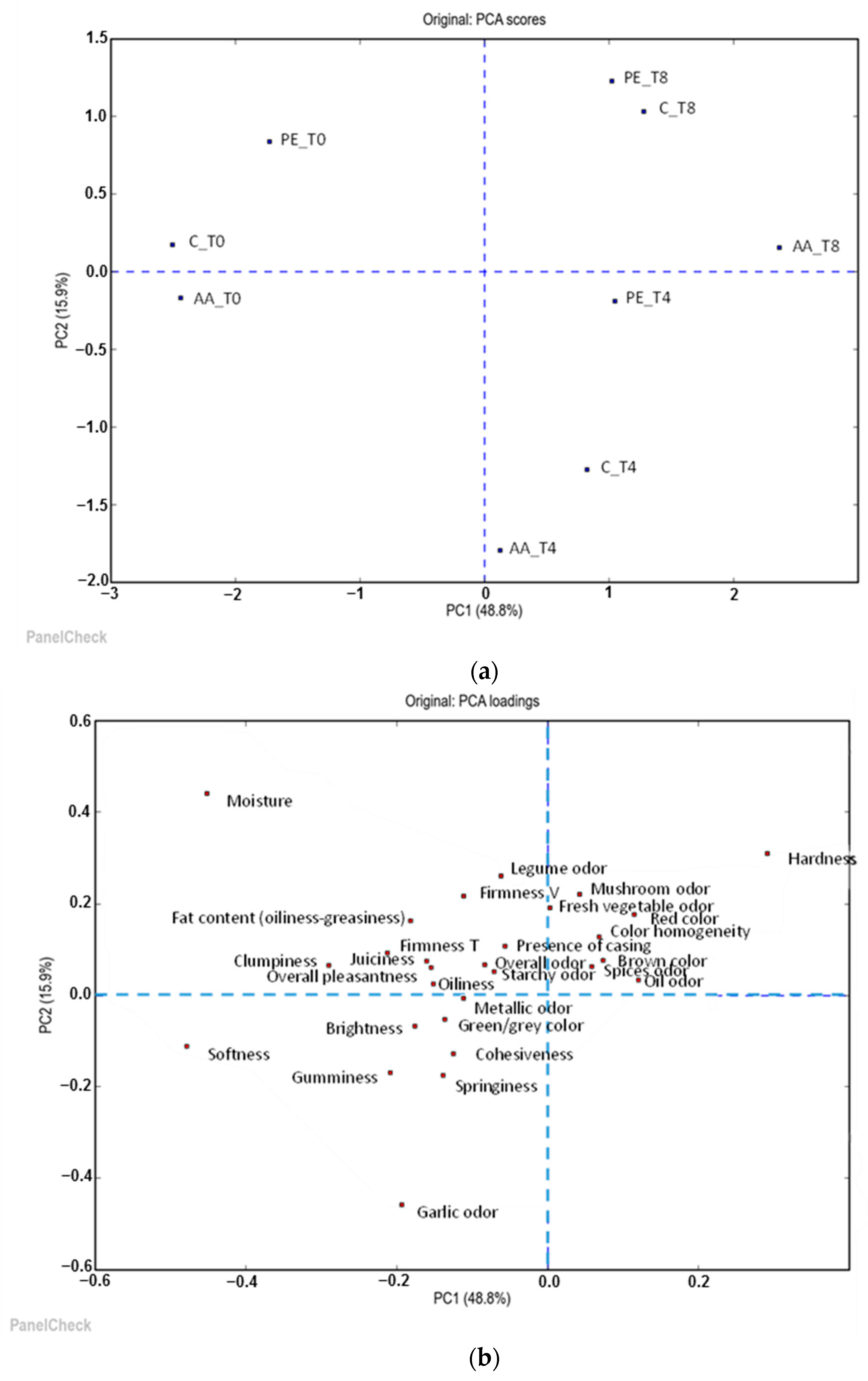
3.4. Sensory Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palvic, B.; Acimovic, M.; Sknepnek, A.; Miletic, D.; Mrkonjiv, W.; Kljakic, A.C.; Jerkovic, J.; Misan, A.; Pojic, M.; Stupar, Z.Z.; et al. Sustainable raw materials for efficient valorization and recovery of bioactive compounds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 193, 116167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, T.; Chowdhary, P.; Chaurasia, D.; Gnansounou, E.; Pandey, A.; Chaturvedi, P. Sustainable green processing of grape pomace the production of value-added products: An overview. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Ferreira, J.A.; Sirohi, R.; Sarsaiya, S.; Khoshnevisan, B.; Baladi, S.; Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A.; Juneja, A.; et al. A critical review on the development stage of biorefinery systems towards the management of apple processing-derived waste. Renew. Sustanable Energy Rev. 2021, 143, 110972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enaime, G.; Dababat, S.; Wichern, M.; Lübken, M. Olive mill wastes: From wastes to resources. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 20853–20880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, T.; Quina, M.M.J.; Martins, R.C.; Gomes, J. Olive Mill Wastewater Treatment Strategies to Obtain Quality Water for Irrigation: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grispoldi, L.; Ianni, F.; Blasi, F.; Pollini, L.; Crotti, S.; Cruciani, D.; Cenci-Goga, B.T.; Cossignani, L. Apple pomace as valuable food ingredient for enhancing nutritional and antioxidant properties of Italian salami. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiapelo, L.; Ianni, F.; Pagano, C.; Grispoldi, L.; Blasi, F.; Cenci-Goga, B.; Perioli, L.; Cossignani, L. Role of apple pomace in the formulation of a novel healthy mayonnaise. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 2835–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollini, L.; Blasi, F.; Ianni, F.; Grispoldi, L.; Moretti, S.; Di Veroli, A.; Cossignani, L.; Cenci-goga, B.T. Ultrasound-assisted extraction and characterization of polyphenols from apple pomace, functional ingredients for beef burger fortification. Molecules 2022, 27, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneziani, G.; Novelli, E.; Esposto, S.; Taticchi, A.; Servili, M. Applications of recovered bioactive compounds in food products. In Olive MIll Waste; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 231–253. [Google Scholar]
- Vignesh, A.; Amal, T.C.; Sarvalingam, A.; Vasanth, K. A review on the influence of nutraceuticals and functional foods on health. Food Chem. Adv. 2024, 5, 100749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustino, M.; Veiga, M.; Sousa, P.; Costa, E.M.; Silva, S.; Pintado, M. Agro-Food By-products as a New Source of Natural Food Additives. Molecules 2019, 24, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpicer, A.; Onopiuk, A.; Barczak, M.; Kurek, M. The optimization of a gluten-free and soy-free plant-based meat analog recipe enriched with anthocyanins microcapsules. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 168, 113849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estell, M.; Huhghes, J.; Grafenauer, S. Plant protein and plant-based meat alternatives: Consumer and nutrition professional attitudes and perception. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.T.; Khong, N.M.H.; Lim, S.S.; Hee, Y.Y.; Sim, B.I.; Lau, K.I.; Lai, O.M. A review: Modified agricultural by-products for the development and fortification of food products and nutraceuticals. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 59, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Yong, H.I.; Kim, M.; Choi, Y.S.; Jo, C. Status of meat alternatives and their potential role in the future meat market: A review. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Pan, L.; Deng, N.; Sang, M.; Cai, K.; Chen, C.; Han, J.; Ye, A. Protein digestibility of textured-wheat-protein (TWP)-based meat analogues: (I) Effects of fibrous structure. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 130, 107694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagapo, T.M. Meat analogs, the Canadian Meat Industry and the Canadian consumer. Meat Sci. 2022, 191, 108846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaghaghian, S.; McClements, D.J.; Khalesi, M.; Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Mirzapour-Kouhdasht, A. Digestibility and bioavailability of plant-based proteins intended for use in meat analogues: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 129, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Qian, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, B.; Wei, K.; Peng, B.; Yan, W. Effects of food components and processing parameters on plant-based meat texture formation and evaluation methods. J. Texture Stud. 2022, 54, 349–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, R. A review on nutritional advantages of edible mushrooms and its industrialization development situation in protein meat analogues. J. Future Foods 2022, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banovic, M.; Barone, A.M.; Asioli, D.; Grasso, S. Enabling sustainable plant-forward transition: European consumer attitudes and intention to buy hybrid products. Food Qual. Prefer. 2022, 96, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Diet, Nutrition and the Prevention of Chronic Diseases. WHO technical report series 916. Report of a Joint WHO/FAO Expert Consultation. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 33, 914–915. [Google Scholar]
- Grispoldi, L.; Karama, M.; El-Ashram, S.; Saraiva, C.; García-Díez, J.; Chalias, A.; De Gennis, M.; Vannuccini, A.; Poerio, G.; Torlai, P.; et al. A study on the application of natural extracts as alternatives to sodium nitrite in processed meat. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dranca, F.; Oroian, M. Extraction, purification and characterization of pectin from alternative sources with potential technological applications. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 327–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roila, R.; Sordini, B.; Esposto, S.; Ranucci, D.; Primavilla, S.; Valiani, A.; Taticchi, A.; Branciari, R.; Servili, M. Effect of the application of a green preservative strategy on minced meat products: Antimicrobial efficacy of olive mill wastewater polyphenolic extract in improving beef burger shelf-life. Foods 2022, 11, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnamayanti, L.; Jamhari, J.; Hanim, C.; Irawan, A. Physicochemical Properties, Oxidative Stability, and Sensory Quality of Lamb Sausage Added with Green Tea Leaves (Camelia sinensis) Powder. Trop. Anim. Sci. J. 2020, 43, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taticchi, A.; Esposto, S.; Urbani, S.; Veneziani, G.; Selvaggini, R.; Sordini, B.; Servili, M. Effect of an olive phenolic extract added to the oily phase of a tomato sauce, on the preservation of phenols and carotenoids during domestic cooking. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercatante, D.; Curró, S.; Rosignoli, P.; Cardenia, V.; Sordini, B.; Taticchi, A.; Rodriguez-Estrada, M.T.; Fabiani, R. Effects of Phenols from Olive Vegetation Water on Mutagenicity and Genotoxicity of Stored-Cooked Beef Patties. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servili, M.; Esposto, S.; Veneziani, G.; Urbani, S.; Taticchi, A.; Di Maio, I.; Selvaggini, R.; Sordini, B.; Montedoro, G.F. Improvement of bioactive phenol content in virgin olive oil with an olive-vegetation water concentrate produced by membrane treatment. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaggini, R.; Esposto, S.; Taticchi, A.; Urbani, S.; Veneziani, G.; Di Maio, I.; Sordini, B.; Servili, M. Optimization of the temperature and oxygen concentration conditions in the malaxation during the oil mechanical extraction process of four italian olive cultivars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3813–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 662; Animal and Vegetable Fats and Oils—Determination of Moisture and Volatile Matter Content, 5th ed. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- AOCS. Official Method Ba 5a-49. Official and Tratative Methods of the American oil Chemists’ Society; AOAC International: Champaign, IL, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Approved Methods of Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 16th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, VA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Miraglia, D.; Castrica, M.; Menchetti, L.; Esposto, S.; Branciari, R.; Ranucci, D.; Urbani, S.; Sordini, B.; Veneziani, G.; Servili, M. Effect of an olive vegetation water phenolic extract on the physico-chemical, microbiological and sensory traits of shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris) during the shelf life. Foods 2020, 9, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzaroli, C.; Sordini, B.; Daidone, L.; Veneziani, G.; Esposto, S.; Urbani, S.; Selvaggini, R.; Servili, M.; Taticchi, A. Recovery and valorization of food industry by-by-products through the application of Olea europaea L. leaves in kombucha tea manufacturing. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, I.G.; Apetrei, C. Analytical Methods Used in Determining Antioxidant Activity: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposto, S.; Veneziani, G.; Taticchi, A.; Urbani, S.; Selvaggini, R.; Sordini, B.; Daidone, L.; Gironi, G.; Servili, M. Chemical Composition, antioxidant activity, and sensory characterization of commercial pomegranate juices. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grispoldi, L.; Karama, M.; Sechi, P.; Iulietto, M.F.; Cenci-Goga, B.T. Effect of the Addition of Starter Cultures to Ground meat for Hamburger Preparation. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 11, 8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grispoldi, L.; Karama, M.; Sechi, P.; Iulietto, M.F.; Hadjicharalambous, C.; Cenci-Goga, B.T. Evaluation of a nitrite-free commercial preparation in the production of swine and roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) salami. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 20, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenci-Goga, B.T.; Sechi, P.; Iulietto, M.F.; Amirjalali, S.; Barbera, S.; Karama, M.; Aly, S.; Grispoldi, L. Characterization and growth under different storage temperatures of ropy slime-producing Leuconostoc mesenteroides isolated from cooked meat products. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 8586:2012; Sensory Analysis—General Guidelines for the Selection, Training and Monitoring of Selected Assessors and Expert Sensory Assessors. ISO (International Organization for Standardization): Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- EN ISO 13299:2010; Sensory Analysis—Methodology—General Guidance for Establishing a Sensory Profile. ISO (International Organization for Standardization): Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Dottori, I.; Urbani, S.; Sordini, B.; Servili, M.; Selvaggini, R.; Veneziani, G.; Ranucci, D.; Taticchi, A.; Esposto, S. Frozen ready-to-(h)eat meals: Evolution of their quality during a real-time short shelf life. Foods 2023, 12, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilgaard, M.C.; Civile, G.V.; Carr, B.T. Sensory Evaluation Techniques, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; p. 433. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. FoodData Central–About Us. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/about-us (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Varga-Visi, É.; Jócsák, I.; Kozma, V.; Lóki, K.; Ali, O.; Szabó, A. Effects of Surface Treatment with Thymol on the Lipid Oxidation Processes, Fatty Acid Profile and Color of Sliced Salami during Refrigerated Storage. Foods 2022, 11, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-González, M.; Purriños, L.; Martínez, S.; Carballo, J. Spices Affect the Biochemical Events Taking Place during the Manufacture of Galician Chorizo Sausage. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 216, 117322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Ji, J.; Mou, Y.; Chen, F.; Xiao, Z.; Liao, X.; Hu, X.; Ma, L. Polyphenol mediated non-enzymatic browning and its inhibition in apple juice. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, R.; Alvarez-Orti, M.; Pardo, J.E. Influence of the paprika type on redness loss in red line meat products. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, V.L.; Gavahian, M.; Lin, J. Textural properties of plant-based meat analogue extrudates enriched with pineapple processing by-product powder. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 60, vvae080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.M.M.; Lima, M.A.; Koksel, F.; Sato, A.C.K. Incorporation of Brewer’s Spent Grain into Plant-based Meat Analogues: Benefits to Physical and Nutritional Quality. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 3870–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahari, I.; Purhagen, J.K.; Rayner, M.; Ahlström, C.; Helstad, A.; Landers, M.; Müller, J.; Eriksson, J.; Östbring, K. Extrusion of High-Moisture Meat Analogues from Hempseed Protein Concentrate and Oat Fibre Residue. J. Food Eng. 2023, 354, 111567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, K.K.; Kang, Y.K.; Jeong, E.W.; Baek, Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, H.G. Applications of Various Natural Pigments to a Plant-Based Meat Analog. LWT 2023, 174, 114431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Berry pomace as a potential ingredient for plant-based meat analogs. Food Biomacromolecules 2024, 1, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulou, K.; Keppler, J.K.; van der Goot, A.J. Functionality of Ingredients and Additives in Plant-Based Meat Analogues. Foods 2021, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everette, J.D.; Bryant, Q.M.; Green, A.M.; Abbey, Y.A.; Wangila, G.W.; Walker, R.B. Thorough study of reactivity of various compound classes toward the Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8139–8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, G.E.; Lewers, K.S.; Medina, M.B.; Saftner, R.A. Comparative analysis of strawberry total phenolics via Fast Blue BB vs. Folin–Ciocalteu: Assay interference by ascorbic acid. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 27, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, J.; Rawel, H.M.; Rohn, S. Reactions of plant phenolics with food proteins and enzymes under special consideration of covalent bonds. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2003, 9, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, D.; Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Guo, H.; Ren, F. Interaction of plant phenols with food macronutrients: Characterisation and nutritional-physiological consequences. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2014, 27, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Toffoli, A.; Monteleone, E.; Bucalossi, G.; Veneziani, G.; Fia, G.; Servili, M.; Zanoni, B.; Pagliarine, E.; Gallina Toschi, T.; Dinnella, C. Sensory and chemical profile of a phenolic extract from olive mill waste waters in plant-base food with varied macro-composition. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichita, A.; Veneziani, G.; Sordini, B.; Dottori, I.; Butnariu, G.; Popa, M.E. Impact on quality characteristics of a plant-based analogues enriched with bioactive compounds recovered from olive mill waste water. In Scientific Papers. Series D. Animal Science, Vol. LXVIII, Proceedings of the Fourteenth Edition of the International Conference “Agriculture for Life, Life for Agriculture”, Bucharest, Romania, 5–7 June 2025; University of Agronomic Sciences and Veterinary Medicine of Bucharest: Romania, Italy, 2025; Abstract Number 152, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Obied, H.K.; Allen, M.S.; Bedgood, D.R.; Prenzler, P.D.; Robards, K. Bioactivity and analysis of biophenols recovered from olive mill waste. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel. Scientific Opinion on the Substantiation of a Health Claim Related to Polyphenols in Olive and Maintenance of Normal Blood HDL Cholesterol Concentrations (ID 1639, Further Assessment) Pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. Eur. Food Saf. Auth. J. 2012, 10, 2848. [Google Scholar]
- Leouifoudi, I.; Harnafi, H.; Zyad, A. Olive Mill Waste Extracts: Polyphenols Content, Antioxidant, and Antimicrobial Activities. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 2015, 714138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasolato, L.; Carraro, L.; Facco, P.; Cardazzo, B.; Balzan, S.; Taticchi, A.; Andrea, N.; Montemurro, F.; Elena, M.; Di, G.; et al. Agricultural by-products with bioactive effects: A multivariate approach to evaluate microbial and physicochemical changes in a fresh pork sausage enriched with phenolic compounds from olive vegetation water. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 228, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimat, V.; Skroza, D.; Tabanelli, G.; Cagalj, M.; Pasini, F.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; Fernández-Fernández, C.; Sterniša, M.; Smole Možina, S.; Ozogul, Y.; et al. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Hydroethanolic Leaf Extracts from Six Mediterranean Olive Cultivars. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Lafi, S.; Al-Natsheh, M.S.; Yaghmoor, R.; Al-Rimawi, F. Enrichment of Phenolic Compounds from Olive Mill Wastewater and In Vitro Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial Activities. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 3706915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-Guerrero, B.; Garrido-Fernández, A.; Fermoso, F.G.; Rodríguez-Gutierrez, G.; Fernández-Prior, M.; Reinhard, C.; Nyström, L.; Benítez-Cabello, A.; Arroyo-López, F.N. Antimicrobial effects of treated olive mill waste on foodborne pathogens. LWT 2022, 164, 113628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Spallarossa, A.; Comite, A.; Pagliero, M.; Guida, P.; Belotti, V.; Caviglia, D.; Schito, A.M. Valorization and Potential Antimicrobial Use of Olive Mill Wastewater (OMW) from Italian Olive Oil Production. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sar, T.; Akbas, M.Y. Antimicrobial Activities of Olive Oil Mill Wastewater Extracts against Selected Microorganisms. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, E.; Brenes, M.; Romero, C.; García, A.; de Castro, A. Main antimicrobial compounds in table olives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 9817–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menchetti, L.; Taticchi, A.; Esposto, S.; Servili, M.; Ranucci, D.; Branciari, R.; Miraglia, D. The influence of phenolic extract from olive vegetation water and storage temperature on the survival of Salmonella Enteritidis inoculated on mayonnaise. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 129, 109648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roila, R.; Valiani, A.; Ranucci, D.; Ortenzi, R.; Servili, M.; Veneziani, G.; Branciari, R. Antimicrobial efficacy of a polyphenolic extract from olive oil by-product against “Fior di latte” cheese spoilage bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 295, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, H.; Curiel, J.A.; Landete, J.M.; de las Rivas, B.; de Felipe, F.L.; Gomez-Cordoves, C.; Mancheno, J.M.; Munoz, R. Food phenolics and lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 132, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinder, M.; Kovač, M.; Mozina, S.S. Antimicrobial effects of phenolic compounds on lactic acid bacteria and their role in the quality of fermented meat products. Food Control 2021, 120, 107510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiani, M.; Cattaneo, C.; Laureati, M. Sensory properties and consumer acceptance of plant-based meat, dairy, fish and eggs analogs: A systematic review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1268068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckett, C.R.; Kuttappan, V.A.; Johnson, L.G.; Owens, C.M.; Han-Seok, S. Comparison of three instrumental methods for predicting sensory texture attributes of poultry deli meat. J. Sens. Stud. 2014, 29, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, V.T.; Mateus, N.; de Freitas, V.; Fernandes, A. Plant-Based Meat Analogues: Exploring Proteins, Fibers and Polyphenolic Compounds as Functional Ingredients for Future Food Solutions. Foods 2024, 13, 2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salejda, A.M.; Olender, K.; Zielińska-Dawidziak, M.; Mazur, M.; Szperlik, J.; Miedzianka, J.; Szmaja, A. Frankfurter-Type Sausage Enriched with Buckwheat By-Product as a Source of Bioactive Compounds. Foods 2022, 11, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsh, A.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, E.Y.; Sabikun, N.; Hwang, Y.H.; Joo, S.T. A Novel Approach for Tuning the Physicochemical, Textural, and Sensory Characteristics of Plant-Based Meat Analogs with Different Levels of Methylcellulose Concentration. Foods 2021, 10, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinali, M.; Liyanage, R.; Silva, M.; Newman, L.; Adhikari, B.; Wijesekara, I.; Chandrapala, J. Fibrous Structure in Plant-Based Meat: High-Moisture Extrusion Factors and Sensory Attributes in Production and Storage. Food Rev. Int. 2024, 40, 2940–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, O.; Negishi, Y.; Ozawa, T. Effects of food materials on removal of Allium-specific volatile sulfur compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3856–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Samples | C | AA | PE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry lentils | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| Fresh champignon mushrooms | 350 | 350 | 350 |
| Extra virgin olive oil | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Pepper | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Fresh garlic | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Paprika | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Salt | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Maltodextrin | 15 | 15 | - |
| Ascorbic acid | - | 5 | - |
| Phenolic extract | - | - | 30 |
| Phenolic Compounds | PE |
|---|---|
| Hydroxytyrosol (3,4-DHPEA) * | 6.8 ± 0.03 |
| Tyrosol (p-HPEA) | 0.9 ± 0.02 |
| Verbascoside | 2.3 ± 0.06 |
| Oleacein (3,4- DHPEA-EDA) | 17.1 ± 0.6 |
| Oleocanthal (p-HPEA-EDA) | 0.3 ± 0.01 |
| Total phenols | 27.3 ± 0.6 |
| Sample * | C | AA | PE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | 69 ± 0.7 a | 64.1 ± 0.9 b | 61.4 ± 0.5 b |
| Ash (% d.w.) | 3.1 ± 0.1 a | 3.1 ± 0.1 a | 3.9 ± 0.3 b |
| Lipid (% d.w.) | 3.2 ± 0.3 a | 3.0 ± 0.3 a | 3.0 ± 0.1 a |
| Total protein (% d.w.) | 26.8 ± 1.4 a | 26.7 ± 1.2 a | 27 ± 1.6 a |
| pH | 6.8 ± 0.0 a | 5.8 ± 0.1 b | 6.6 ± 0.1 a |
| Aw | 96.2 ± 0.5 a | 95.7 ± 0.1 a | 95.4 ± 0.1 a |
| Time (Days) * | T0 | T4 | T8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 69.0 ± 0.7 Aa | 69.0 ± 0.9 Aa | 68.4 ± 0.5 Aa |
| AA | 64.1 ± 0.7 Ba | 63.0 ± 0.6 Ba | 59.8 ± 0.4 Bb |
| PE | 61.4 ± 0.5 Ca | 61.3 ± 0.3 Ca | 54.4 ± 0.8 Cb |
| C | AA | PE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | |||
| day-0 | 6.79 ± 0.02 a | 5.82 ± 0.02 b | 6.6 ± 0.02 c |
| day-2 | 6.79 ± 0.02 a | 6.12 ± 0.02 b | 6.44 ± 0.02 c |
| day-4 | 6.81 ± 0.02 a | 6.24 ± 0.02 b | 6.53 ± 0.02 c |
| day-8 | 6.32 ± 0.02 ac | 5.82 ± 0.02 b | 6.32 ± 0.02 c |
| aw | |||
| day-0 | 0.962 ± 0.005 ab | 0.957 ± 0.001 a | 0.954 ± 0.001 b |
| day-2 | 0.955 ± 0.002 ac | 0.965 ± 0.001 b | 0.96 ± 0.001 c |
| day-4 | 0.957 ± 0.008 a | 0.955 ± 0.002 a | 0.958 ± 0.001 a |
| day-8 | 0.957 ± 0.001 a | 0.956 ± 0.004 ac | 0.952 ± 0.001 c |
| Shear force | |||
| day-0 | 3.18 ± 0.47 a | 1.72 ± 0.29 b | 2.00 ± 0.10 ab |
| day-2 | 1.12 ± 0.55 ab | 1.57 ± 0.21 a | 2.47 ± 0.20 b |
| day-4 | 4.58 ± 1.79 ab | 4.72 ± 0.28 a | 3.40 ± 0.38 b |
| day-8 | 5.28 ± 0.65 a | 9.70 ± 2.75 a | 6.35 ± 1.44 a |
| Compression | |||
| day-0 | 11.70 ± 1.21 a | 6.72 ± 1.00 b | 6.60 ± 2.04 ab |
| day-2 | 4.85 ± 0.69 a | 5.88 ± 0.26 a | 8.02 ± 2.62 a |
| day-4 | 8.37 ± 0.65 a | 17.55 ± 6.11 ab | 15.30 ± 2.22 b |
| day-8 | 30.68 ± 4.85 a | 25.78 ± 4.18 a | 33.58 ± 8.18 a |
| L* | |||
| day-0 | 52.67 ± 3.51 a | 42.67 ± 2.89 b | 44.67 ± 3.06 ab |
| day-2 | 34.33 ± 8.96 a | 41.67 ± 1.16 a | 39.33 ± 3.79 a |
| day-4 | 41.33 ± 1.16 a | 40.67 ± 5.77 a | 45.33 ± 1.53 a |
| day-8 | 56.00 ± 3.61 a | 46.33 ± 1.53 a | 40.33 ± 14.84 a |
| a* | |||
| day-0 | 3.00 ± 1.00 a | 5.33 ± 1.16 a | 4.00 ± 1.00 a |
| day-2 | 3.33 ± 1.53 a | 3.00 ± 1.00 a | 3.33 ± 0.58 a |
| day-4 | 2.67 ± 1.16 a | 4.67 ± 0.58 a | 2.67 ± 1.53 a |
| day-8 | 2.00 ± 1.73 a | 1.67 ± 1.16 a | 1.33 ± 1.53 a |
| b* | |||
| day-0 | 32.00 ± 1.73 a | 35.00 ± 2.00 a | 30.33 ± 5.03 a |
| day-2 | 26.33 ± 1.53 a | 31.33 ± 0.58 b | 31.67 ± 0.58 b |
| day-4 | 27.33 ± 3.22 a | 29.33 ± 4.73 a | 32.67 ± 4.51 a |
| day-8 | 38.67 ± 3.22 a | 35.00 ± 0.00 a | 33.00 ± 2.65 a |
| Storage Time (Days) | SEM | p | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | T0 | T4 | T8 | F | ST | F × ST | |||||
| Total phenol content (TPC) | C | 0.85 | Ca | 0.84 | Ca | 0.94 | Ca | 0.12 | <0.001 | <0.05 | <0.001 |
| AA | 4.52 | Ab | 5.34 | Aa | 4.48 | Ab | |||||
| PE | 2.75 | Ba | 2.58 | Bab | 2.19 | Bb | |||||
| Antioxidant activity (DPPH˙) | C | 1.82 | Ca | 1.39 | Ca | 1.69 | Ca | 0.67 | <0.001 | N.S. | <0.05 |
| AA | 32.13 | Aa | 33.68 | Aa | 32.64 | Aa | |||||
| PE | 10.21 | Ba | 8.72 | Bab | 7.05 | Bb | |||||
| Time (Days) * | T0 | T4 | T8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxytyrosol (3,4-DHPEA) | 240.8 ± 3.1 a | 205.2 ± 2.7 b | 183.0 ± 5.7 c |
| Tyrosol (p-HPEA) | 53.1 ± 1.1 a | 52.5 ± 2.4 a | 51.3 ± 1.9 a |
| Verbascoside | 48.6 ± 2.9 a | 46.7 ± 1.2 a | 45.7 ± 1.7 a |
| Oleacein (3,4-DHPEA-EDA) | 126.1 ± 8.0 a | 0.0 ± 0.0 b | 0.0 ± 0.0 b |
| p-HPEA-EDA | 0.0 ± 0.0 a | 0.0 ± 0.0 a | 0.0 ± 0.0 a |
| Total phenols | 468.6 ± 9.1 a | 304.4 ± 3.9 b | 280.0 ± 6.2 c |
| C | AA | PE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesophilic microbiota | |||
| day-0 | 5.92 ± 0.27 | 5.01 ± 0.11 | 5.07 ± 0.36 |
| day-2 | 6.38 ± 0.2 a | 5.83 ± 0.16 b | 5.51 ± 0.05 b |
| day-4 | 6.58 ± 0.37 | 5.37 ± 0.52 | 5.71 ± 0.46 |
| day-8 | 8.85 ± 0.00 a | 5.59 ± 0.83 b | 8.24 ± 0.09 a |
| Enterococcus spp. | |||
| day-0 | <3 | <3 | <3 |
| day-2 | 3.60 ± 0.00 | <3 | <3 |
| day-4 | 4.90 ± 0.00 | 4.74 ± 0.00 | <3 |
| day-8 | 7.09 ± 0.55 | 6.78 ± 0.00 | <3 |
| Lactococcus spp. | |||
| day-0 | 5.18 ± 0.33 | 4.95 ± 0.19 | 4.69 ± 0.02 |
| day-2 | 5.64 ± 0.06 | 5.08 ± 0.52 | 5.71 ± 0.27 |
| day-4 | 5.83 ± 0.68 | 5.85 ± 0.08 | 5.37 ± 0.09 |
| day-8 | 8.08 ± 0.00 | 7.09 ± 0.13 | 7.78 ± 0.00 |
| Lactobacillus spp. | |||
| day-0 | <3 | <3 | <3 |
| day-2 | 4.45 ± 0.00 | 3.90 ± 0.00 | 3.00 ± 0.00 |
| day-4 | 5.91 ± 0.00 ab | 6.07 ± 0.06 a | 4.57 ± 0.44 b |
| day-8 | 8.26 ± 0.00 a | 8.11 ± 0.00 a | 5.80 ± 0.06 b |
| Staphylococcus spp. | |||
| day-0 | <3 | 3.89 ± 0.58 | 3.70 ± 0.00 |
| day-2 | 4.33 ± 0.21 | 5.05 ± 0.17 | 4.57 ± 0.13 |
| day-4 | 3.00 ± 0.00 | 3.30 ± 0.00 | <3 |
| day-8 | 3.00 ± 0.00 | 3.48 ± 0.00 | 3.00 ± 0.00 |
| Pseudomonas spp. | |||
| day-0 | 4.06 ± 0.08 | 4.14 ± 0.20 | 3.89 ± 0.16 |
| day-2 | 4.13 ± 0.18 | 4.09 ± 0.13 | 4.13 ± 0.18 |
| day-4 | 6.82 ± 0.05 a | 4.60 ± 0.14 b | 5.69 ± 0.13 c |
| day-8 | 8.08 ± 0.00 | 7.90 ± 0.00 | 6.87 ± 0.04 |
| Enterobacteriaceae | |||
| day-0 | 5.30 ± 0.52 | 4.87 ± 0.15 | 4.91 ± 0.23 |
| day-2 | 5.83 ± 0.50 | 5.30 ± 0.61 | 5.79 ± 0.08 |
| day-4 | 6.78 ± 0.22 | 5.09 ± 0.55 | 6.78 ± 0.22 |
| day-8 | 8.78 ± 0.00 ab | 5.88 ± 0.36 a | 8.30 ± 0.00 b |
| Coliform organisms | |||
| day-0 | 5.20 ± 0.36 | 4.84 ± 0.17 | 4.76 ± 0.51 |
| day-2 | 5.97 ± 0.45 | 5.45 ± 0.00 | 5.12 ± 0.16 |
| day-4 | 6.21 ± 0.13 ab | 5.07 ± 0.10 c | 5.77 ± 0.21 b |
| day-8 | 8.24 ± 0.09 a | 5.00 ± 0.00 b | 7.15 ± 0.21 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nichita, A.; Sordini, B.; Al-Olayan, E.; Esposto, S.; Costanzi, E.; Cenci-Goga, B.; Popa, M.E.; Servili, M.; Veneziani, G. Physicochemical, Microbiological and Sensory Evaluation of Plant-Based Meat Analogs Supplemented with Phenolic Extracts from Olive Mill By-Products. Foods 2025, 14, 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193347
Nichita A, Sordini B, Al-Olayan E, Esposto S, Costanzi E, Cenci-Goga B, Popa ME, Servili M, Veneziani G. Physicochemical, Microbiological and Sensory Evaluation of Plant-Based Meat Analogs Supplemented with Phenolic Extracts from Olive Mill By-Products. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193347
Chicago/Turabian StyleNichita, Adina, Beatrice Sordini, Ebtsam Al-Olayan, Sonia Esposto, Egidia Costanzi, Beniamino Cenci-Goga, Mona Elena Popa, Maurizio Servili, and Gianluca Veneziani. 2025. "Physicochemical, Microbiological and Sensory Evaluation of Plant-Based Meat Analogs Supplemented with Phenolic Extracts from Olive Mill By-Products" Foods 14, no. 19: 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193347
APA StyleNichita, A., Sordini, B., Al-Olayan, E., Esposto, S., Costanzi, E., Cenci-Goga, B., Popa, M. E., Servili, M., & Veneziani, G. (2025). Physicochemical, Microbiological and Sensory Evaluation of Plant-Based Meat Analogs Supplemented with Phenolic Extracts from Olive Mill By-Products. Foods, 14(19), 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193347







