Dielectric Properties and Heating Rates of Egg Components Associated with Radio Frequency and Microwave Pasteurization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.1.1. Egg Samples
2.1.2. Egg White, Yolk, and Eggshell Samples
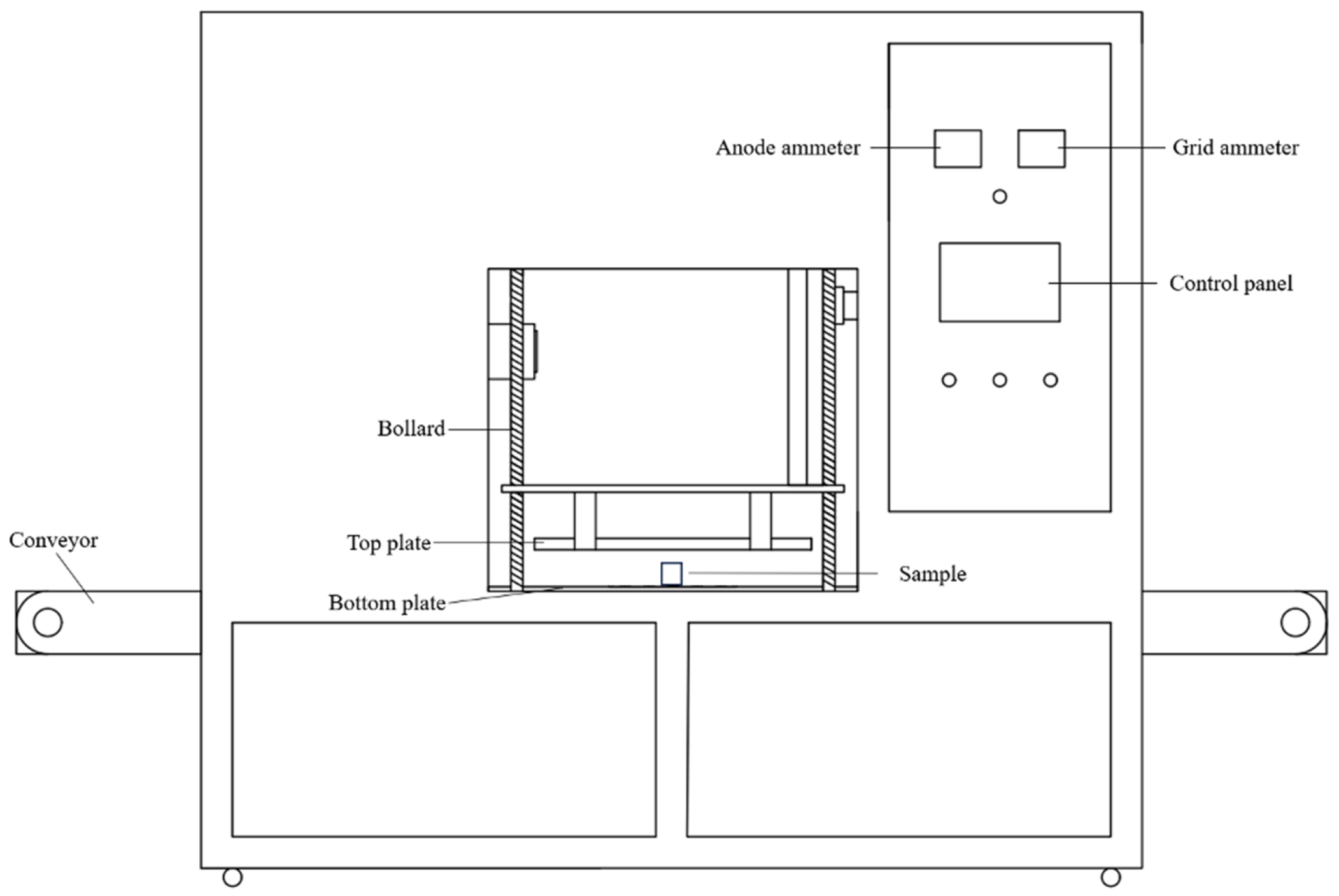
2.2. Dielectric Properties Measurement System
2.3. Determination of Penetration Depth
2.4. Regression Models for Dielectric Properties
2.5. RF and MW Treatments
2.5.1. RF Treatments
2.5.2. MW Treatments
2.6. Determination of Heating Rates of Egg White, Yolk, and Eggshell
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Frequency and Temperature on Dielectric Properties
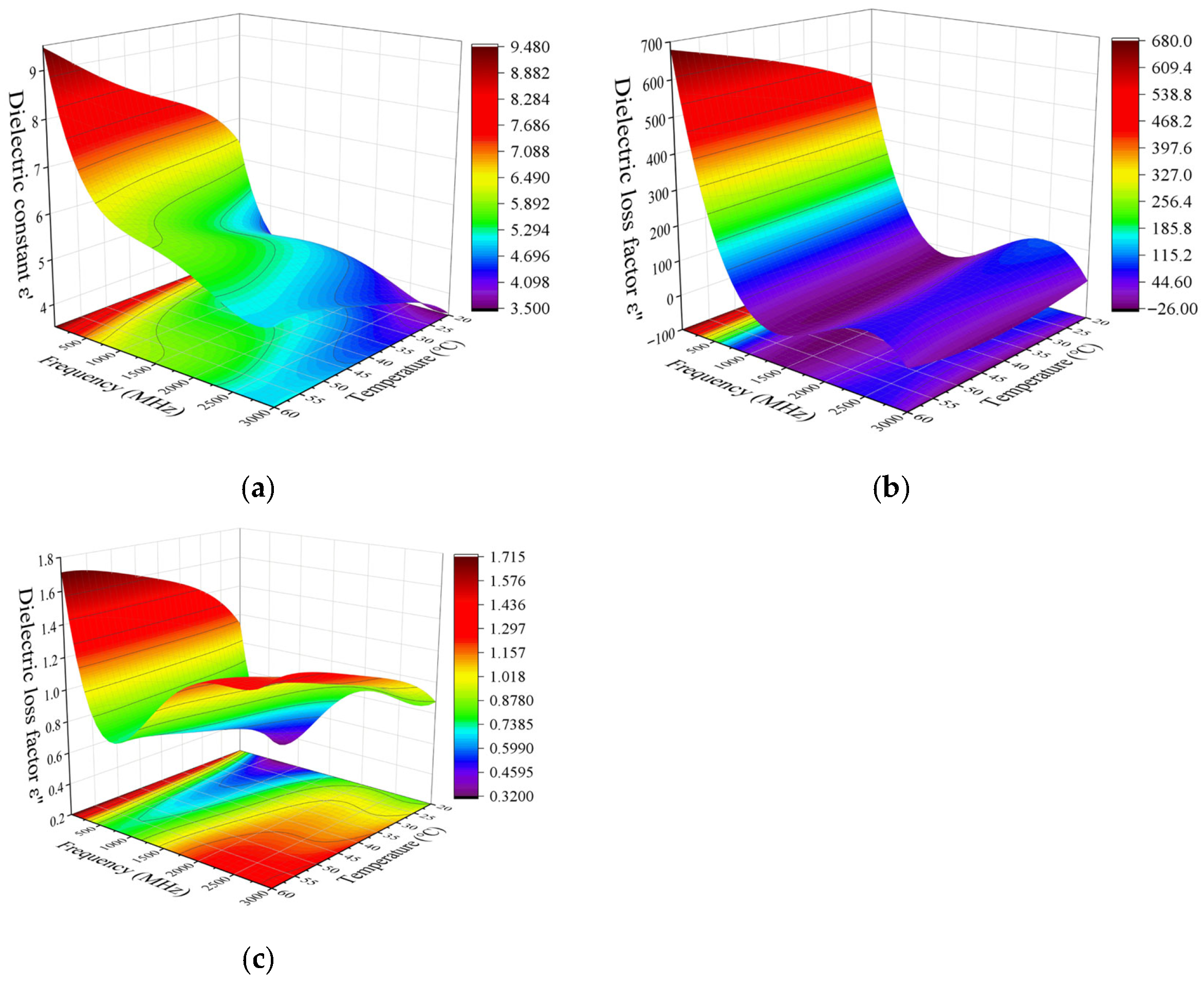
3.1.1. Effects of Frequency and Temperature on Dielectric Constant
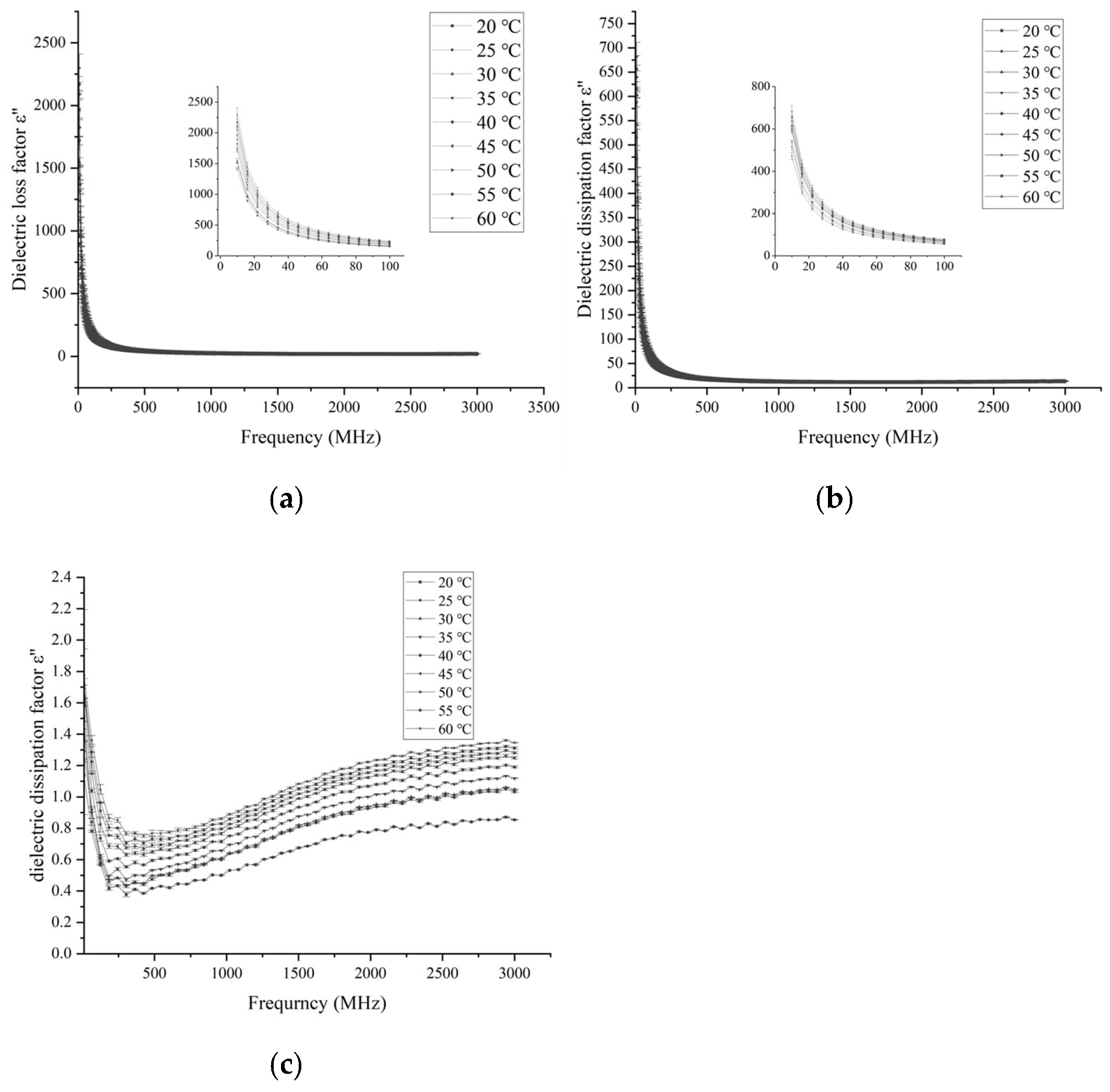
3.1.2. Effects of Frequency and Temperature on Loss Factor
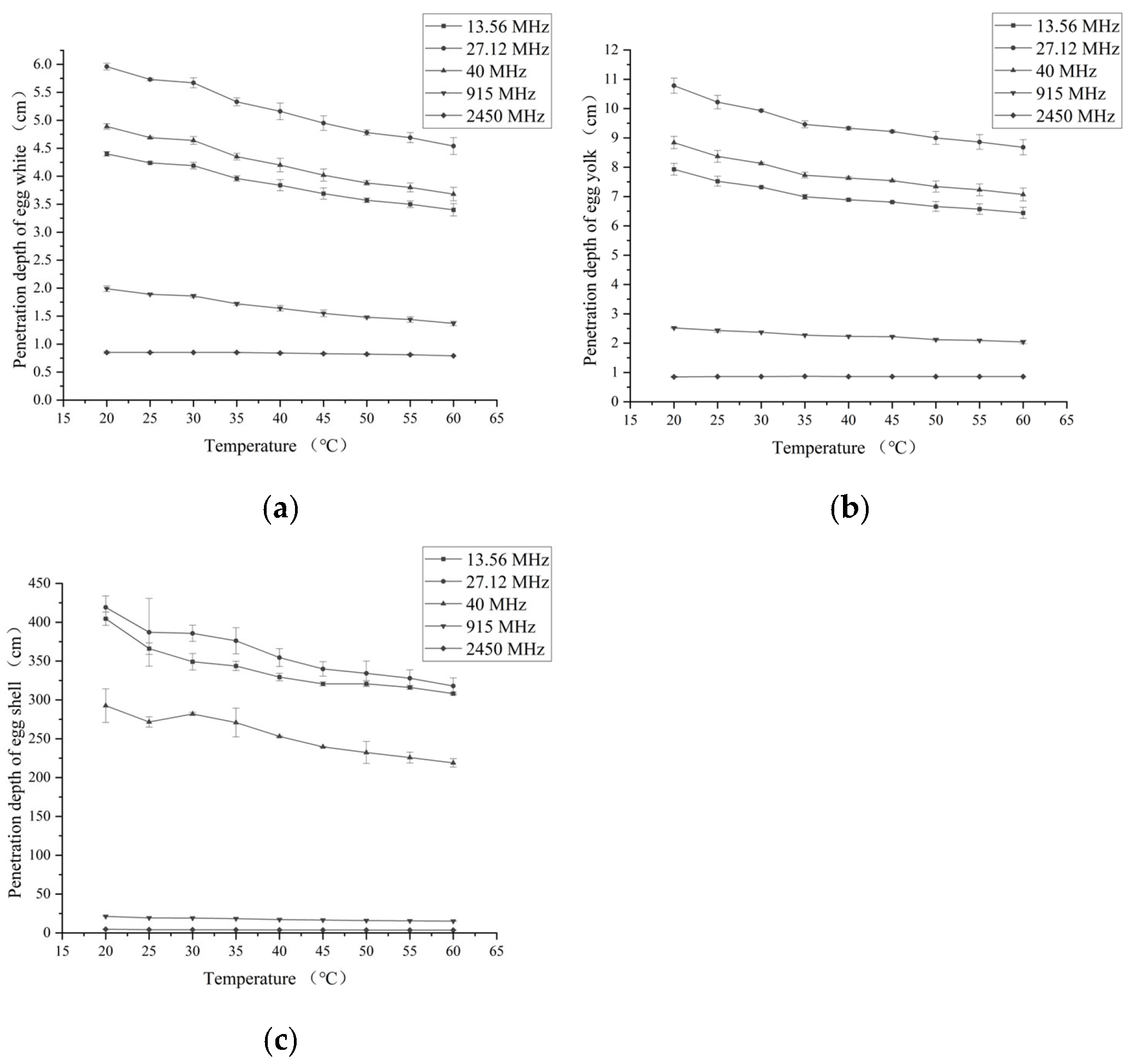
3.2. Penetration Depth
3.3. Regression Models for Dielectric Properties of Egg White, Yolk, and Eggshell
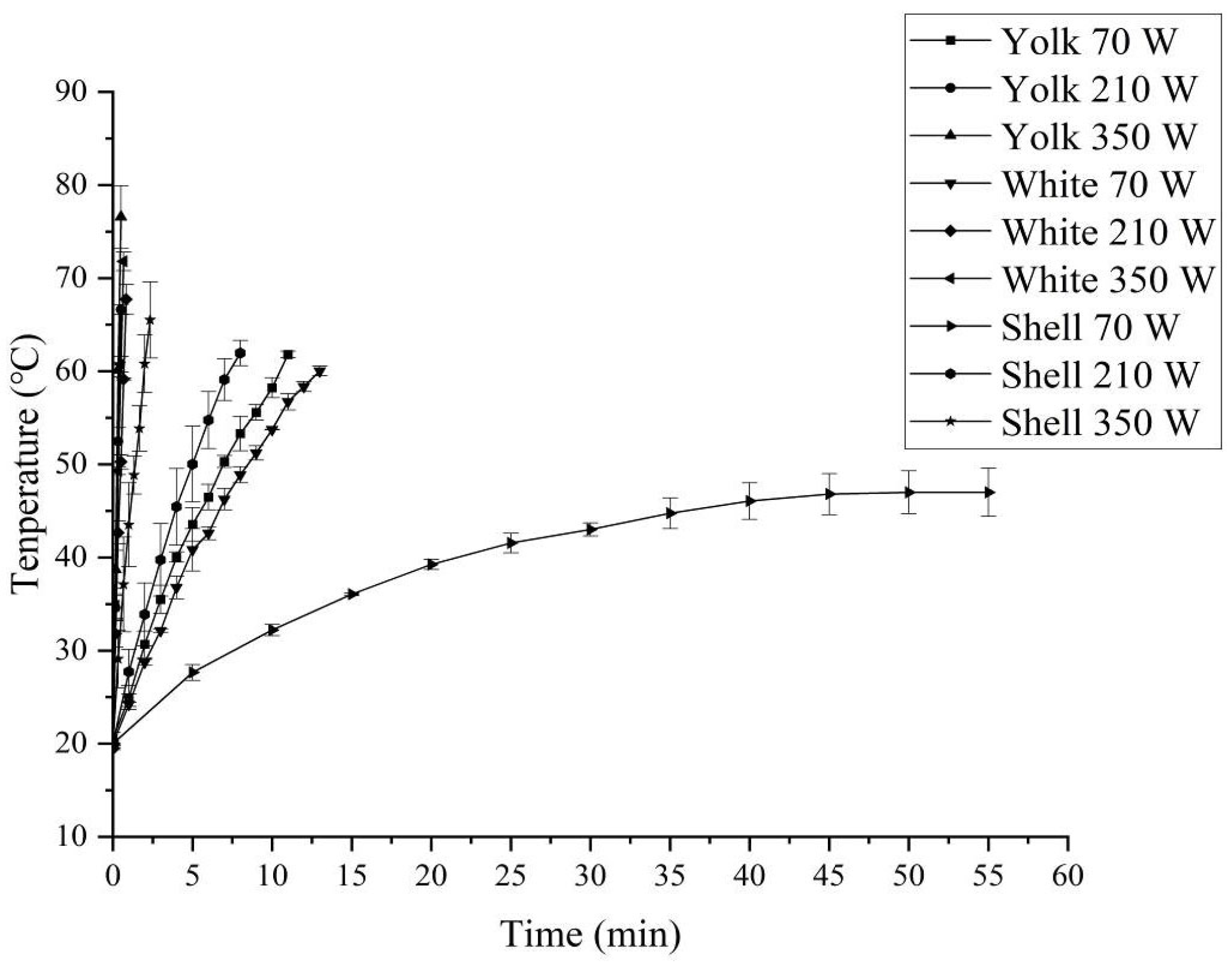
3.4. Heating Rates of Egg White, Yolk, and Eggshell Induced by RF and MW Treatments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, D.M.; Li, R.; Li, Y.K.; Gao, X.; Fan, X.K.; Du, Q.; Zhou, C.L. Effects of manual washing with three alkaline sterilizing agent solutions on egg quality during storage. Food Chem. 2022, 396, 133733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAOSTAT. Food and Agriculture Organization Corporate Statistical Database. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL/ (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Kataoka, N.; Kawahara, D.; Sekiguchi, M. Uniform irradiation of table eggs in the shell with low-energy electron beams. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2023, 202, 110553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/eggs-09-24/ (accessed on 6 September 2024).
- Yang, Y.S.; Geveke, D.J. Shell egg pasteurization using radio frequency in combination with hot air or hot water. Food Microbiol. 2020, 85, 103281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Cheng, T.; Hong, Y.K.; Wei, L.A.; Tang, J.M. The effect of dry headspace on the thermal resistance of bacteria in peanut oil and peanut butter in thermal treatments. Food Control 2022, 137, 108851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geveke, D.J.; Gurtler, J.B.; Jones, D.R.; Bigley, A.B.W. Inactivation of Salmonella in shell eggs by hot water immersion and its effect on quality. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhao, P.Y.; Yao, Z.Q.; Li, T.H.; Zhu, M.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Huang, L.L.; Niyazi, G.; Liu, D.X.; Rong, M.Z. Inactivation of Salmonella enteritidis on the surface of eggs by air activated with gliding arc discharge plasma. Food Control 2023, 148, 109662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, M.; Wiacek, C.; Weihe, T.; Ehlbeck, J.; Weltmann, K.D.; Braun, P.G. Effect of cold atmospheric pressure plasma treatment of eggshells on the total bacterial count inoculated Salmonella Enteritidis and selected quality parameters. Plasma Process. Polym. 2021, 18, e2000061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geveke, D.J.; Bigley, A.B.W.; Brunkhorst, C.D. Pasteurization of shell eggs using radio frequency heating. J. Food Eng. 2017, 193, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geveke, D.J.; Bigley, A.B.W.; Brunkhorst, C.D.; Jones, D.R.; Tilman, E.D. Improvement in the radio frequency method to pasteurize shell eggs by automation and cost reduction. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2500–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.Y.; Xu, Y.M.; Li, R.; Cheng, T.; Wang, S.J. Development of a radio frequency pasteurisation process for Acidovorax citrulli control in watermelon seeds. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 243, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.K.; Zhou, L.F.; Chen, J.J.; Subbiah, J.; Chen, X.W.; Fu, H.F.; Wang, Y.Y. Dielectric properties of chili powder in the development of radio frequency and microwave pasteurization. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 20, S3373–S3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Ma, H.L.; Wang, S.J. Pasteurization mechanism of S. aureus ATCC 25923 in walnut shells using radio frequency energy at lab level. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 143, 111129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.Y.; Wang, P.Z.; Shi, H.; Li, F.; Jiao, Y. Radio frequency inactivation of E. coli O157: H7 and Salmonella Typhimurium ATCC 14028 in black pepper (piper nigrum) kernels: Thermal inactivation kinetic study and quality evaluation. Food Control 2022, 132, 108553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgett, R.E. Electrical properties of foods. In Engineering Properties of Foods; Rizvi, S.S.H., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 398–410. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Tang, B.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Cheng, T.; Wang, S.; Guan, X.; Lu, X. Improving radio-frequency heating uniformity to ensure food safety. J. Food Eng. 2025, 405, 112783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinbun, W.; Rattanadecho, P. An investigation of the dielectric and thermal properties of frozen foods over a temperature from −18 to 80 °C. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Rasco, B.; Kong, F.B.; Wang, S.J. Dielectric properties of salmon fillets as a function of temperature and composition. J. Food Eng. 2008, 87, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Brodie, G.; Jacob, M.V.; Antunes, E. Dielectric properties of chickpea, red and green lentil in the microwave frequency range as a function of temperature and moisture content. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energy 2018, 52, 198–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Xie, W.; Wang, F.; Yang, D. Investigation on dielectric heterogeneity and radio frequency differential heating of corn kernels based on multicomponent structure. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 146, 111360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, K.L.; Amkondan, S. An automatic system for measuring dielectric properties of foods: Albumen, yolk, and shell of fresh eggs. J. Food Eng. 2017, 223, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Swanson, B. Dielectric properties of egg whites and whole eggs as influenced by thermal treatments. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Z.X.; Liu, Y.P. Effect of salt and sucrose content on the dielectric properties of salted duck egg white protein relevant to radio frequency dying. Dry. Technol. 2014, 35, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.X.; Hao, Y.J.; Guan, X.Y.; Wang, P.H.; Wang, S.J. Temperature and moisture dependent dielectric and thermal properties of walnut components associated with radio frequency and microwave pasteurization. Foods 2022, 11, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, D.W.; Xie, Y.K.; Jia, Z.H.; Sun, W.L.; Peng, Z.K.; Liu, Y.H. Dielectric properties of in-shell peanuts with radio frequency and microwave heating treatment and RF heating performance. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 211, 112800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, F.; Tang, J.M.; Koral, T.; Jiao, Y. Influence of composition, temperature, and frequency on dielectric properties of selected saltwater and freshwater fish. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1920–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.Y.; Wang, S.J. Dielectric properties, heating rate, and heating uniformity of wheat flour with added bran associated with radio frequency treatments. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 60, 102290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, S.R.S.; Raghavan, G.S.V.; Gariepy, Y. Dielectric properties of egg components and microwave heating for in-shell pasteurization of eggs. J. Food Eng. 2008, 86, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boreddy, S.R.; Subbiah, J. Temperature and moisture dependent dielectric properties of egg white powder. J. Food Eng. 2016, 168, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.H.; Guo, W.C.; Wu, X.L.; Wang, S.J. Dielectric properties of chestnut flour relevant to drying with radio-frequency and microwave energy. J. Food Eng. 2012, 113, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Holy, M.; Wang, Y.F.; Tang, J.; Rasco, B. Dielectric properties of salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) and sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus) caviar at radio frequency (RF) and microwave (MW) pasteurization frequencies. J. Food Eng. 2005, 70, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Gao, Y.Y.; Fan, X.Q.; Zhao, K.S. Broadband dielectric properties of honey: Effects of temperature. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1656–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.Y.; Han, J.P.; Lagnika, C.; Jiang, N.; Qian, C.L.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, D.J.; Tao, Y.; Yu, Z.F.; Wang, L.B.; et al. Dielectric properties of edible fungi powder related to radio-frequency and microwave drying. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2021, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhou, X.J.; Cui, Y.; Jiao, S.S.; Shi, X.M. Development of a pasteurization method based on radio frequency heating to ensure microbiological safety of liquid egg. Food Control 2021, 123, 107035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| 13.56 MHz | 27.12 MHz | 40 MHz | 915 MHz | 2450 MHz | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ε′ | ε″ | ε′ | ε″ | ε′ | ε″ | ε′ | ε″ | ε′ | ε″ | ||
| Egg white | a0 | 116.87 | 994.66 | 94.285 | 573.02 | 86.153 | 399.85 | 56.678 | 23.505 | 53.906 | 20.43 |
| a1 | −2.0969 | 8.909 | −0.7221 | −10.762 | −0.3462 | −7.3228 | 2.0436 | −0.2574 | 2.0877 | −0.837 | |
| a2 | 0.0832 | 0.8329 | 0.0259 | 0.4754 | 0.0086 | 0.3268 | −0.971 | 0.0119 | −0.0992 | 0.001 | |
| a3 | −0.0014 | −0.0066 | −0.0005 | −0.0037 | −0.0002 | −0.0026 | 0.0017 | −9 × 10−5 | 0.0018 | 3 × 10−6 | |
| a4 | 9 × 10−6 | 4 × 10−6 | 2 × 10−6 | 1 × 10−5 | −1 × 10−5 | ||||||
| R2 | 0.9934 | 0.9956 | 0.9874 | 0.9955 | 0.9837 | 0.9955 | 0.9854 | 0.9958 | 0.9829 | 0.9665 | |
| Yolk | a0 | 81.739 | 95.578 | 73.246 | 59.928 | 68.552 | 44.514 | 41.102 | 8.2363 | 35.419 | 11.414 |
| a1 | −2.9118 | 14.791 | −2.7951 | 8.4916 | −2.7553 | 5.9678 | −1.2593 | 0.2579 | −1.018 | 0.0981 | |
| a2 | 0.1331 | −0.2664 | 0.1255 | −0.1531 | 0.1229 | −0.1078 | 0.0595 | −0.0045 | 0.0507 | −0.0028 | |
| a3 | −0.0025 | 0.0019 | −0.0023 | 0.0011 | −0.0022 | 0.0008 | −0.0011 | 3 × 10−5 | −0.001 | 2 × 10−5 | |
| a4 | 2 × 10−5 | 1 × 10−5 | 1 × 10−5 | 8 × 10−6 | 7 × 10−6 | ||||||
| R2 | 0.9887 | 0.9950 | 0.9393 | 0.9951 | 0.9043 | 0.9951 | 0.9233 | 0.9974 | 0.9644 | 0.9020 | |
| Eggshell | a0 | 9.8177 | 0.5054 | 6.9896 | 0.9156 | 6.6067 | 1.8662 | −3.8040 | 0.2618 | −2.7466 | 0.1931 |
| a1 | −0.3857 | 0.0416 | −0.27764 | −0.009 | −0.2962 | −0.09012 | 0.8216 | 0.0133 | 0.6532 | 0.0415 | |
| a2 | −0.01355 | −0.0006 | 0.01496 | 8 × 10−4 | 0.1604 | 0.00276 | −0.0298 | −6 × 10−5 | −0.0232 | −5.9 × 10−4 | |
| a3 | −1.4 × 10−4 | 4.7 × 10−6 | −0.00025 | −7.6 × 10−6 | −2.7 × 10−4 | −2.3 × 10−5 | 5 × 10−4 | 5.8 × 10−8 | 3.9 × 10−4 | 3.4 × 10−6 | |
| a4 | 2.6 × 10−7 | 1.4 × 10−6 | 1.6 × 10−6 | −3 × 10−6 | −2.4 × 10−6 | ||||||
| R2 | 0.9912 | 0.9820 | 0.9836 | 0.9970 | 0.9972 | 0.9886 | 0.9933 | 0.9972 | 0.9927 | 0.9936 | |
| Egg White | Yolk | Eggshell | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ε′ | ε″ | ε′ | ε″ | ε′ | ε″ | |
| a0 | 347.7161 | 7919.58866 | 62.85377 | 283.4594 | −2.24302 | −1.09470 |
| a1 | −26.73673 | −800.33164 | 0.940589 | 12.49945 | 0.835286 | 0.01216 |
| a2 | −0.112731 | −2.79984 | −7.9989 × 10−2 | −0.87386 | −6.97 × 10−3 | 2.502 × 10−3 |
| a12 | −1.324 × 10−3 | −4.2245 × 10−2 | −3.13 × 10−4 | −8.74 × 10−3 | −3.5 × 10−5 | −3.3 × 10−3 |
| a11 | 1.14605 | 34.6736 | −2.0246 × 10−2 | −0.146662 | −2.7204 × 10−2 | −6.749 × 10−3 |
| a22 | 9.7 × 10−5 | 2.563 × 10−3 | 5 × 10−5 | 6.28 × 10−4 | 7.55381 × 10−6 | 3.30809 × 10−6 |
| a112 | 5.31364 × 10−6 | 3.1 × 10−4 | 8.58045 × 10−7 | 4 × 10−5 | 1.30068 × 10−6 | 4.55551 × 10−7 |
| a122 | 6.25052 × 10−7 | 1.6 × 10−5 | 6.01474 × 10−8 | 1.26969 × 10−6 | −1.90438 × 10−8 | 7.62115 × 10−9 |
| a111 | −2.0507 × 10−2 | −0.620937 | 1.65 × 10−4 | 8.62 × 10−4 | 4.07 × 10−4 | 1.01 × 10−4 |
| a222 | −3.25677 × 10−8 | −8.70530 × 10−7 | −9.21494 × 10−9 | −1.20518 × 10−7 | −2.93614 × 10−9 | −1.37577 × 10−9 |
| a1122 | 1.64497 × 10−9 | 1.9443 × 10−8 | 1.9815 × 10−10 | −5.58362 × 10−11 | ||
| a1112 | −1.04689 × 10−7 | −3.30906 × 10−6 | −1.72482 × 10−8 | −2.09252 × 10−9 | ||
| a1222 | −1.24201 × 10−10 | −2.76264 × 10−9 | 1.94927 × 10−12 | −3.1911 × 10−13 | ||
| a1111 | 1.33 × 10−4 | 3.993 × 10−3 | −2.18433 × 10−6 | −5.71768 × 10−7 | ||
| a2222 | 3.83130 × 10−12 | 1.01493 × 10−10 | 3.93449 × 10−13 | 1.86083 × 10−13 | ||
| R2 | 1 | 1 | 0.9912 | 0.9897 | 0.9998 | 0.9997 |
| Variances and R2 | Egg White | Yolk | Eggshell |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | <0.0001 | 0.4953 | <0.0001 |
| F | <0.0001 | 0.2463 | 0.1138 |
| TF | 0.0073 | 0.0737 | 0.0056 |
| T2 | <0.0001 | 0.8262 | 0.8927 |
| F2 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0002 |
| T2F | <0.0001 | 0.7940 | 0.0020 |
| TF2 | <0.0001 | 0.2411 | <0.0001 |
| T3 | <0.0001 | 0.7396 | 0.0007 |
| F3 | <0.0001 | - a | <0.0001 |
| T2F2 | <0.0001 | - | 0.0009 |
| T3F | 0.0640 | - | 0.0263 |
| TF3 | <0.0001 | - | 0.2480 |
| T4 | <0.0001 | - | 0.0392 |
| F4 | <0.0001 | - | <0.0001 |
| Model | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| R2 | 1 | 0.9912 | 0.9998 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, F.; Hu, J.; Li, H.; Tang, X.; Xiang, Q.; Guan, X.; Sun, W.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, T. Dielectric Properties and Heating Rates of Egg Components Associated with Radio Frequency and Microwave Pasteurization. Foods 2025, 14, 3287. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193287
Yang F, Hu J, Li H, Tang X, Xiang Q, Guan X, Sun W, Li P, Zhang H, Cheng T. Dielectric Properties and Heating Rates of Egg Components Associated with Radio Frequency and Microwave Pasteurization. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3287. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193287
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Feixue, Jianhang Hu, Huijia Li, Xinyu Tang, Qisen Xiang, Xiangyu Guan, Wenhao Sun, Ping Li, Haiyan Zhang, and Teng Cheng. 2025. "Dielectric Properties and Heating Rates of Egg Components Associated with Radio Frequency and Microwave Pasteurization" Foods 14, no. 19: 3287. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193287
APA StyleYang, F., Hu, J., Li, H., Tang, X., Xiang, Q., Guan, X., Sun, W., Li, P., Zhang, H., & Cheng, T. (2025). Dielectric Properties and Heating Rates of Egg Components Associated with Radio Frequency and Microwave Pasteurization. Foods, 14(19), 3287. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193287





