Pterostilbene Eliminates MRSA Independent of Metabolic State and Effectively Prevents Biofilm Formation in Milk Matrices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Compounds and Bacterial Strains
2.2. Growth Curve Analysis
2.3. Bacterial Lysis Assay and Time–Kill Assay
2.4. MRSA Persisters
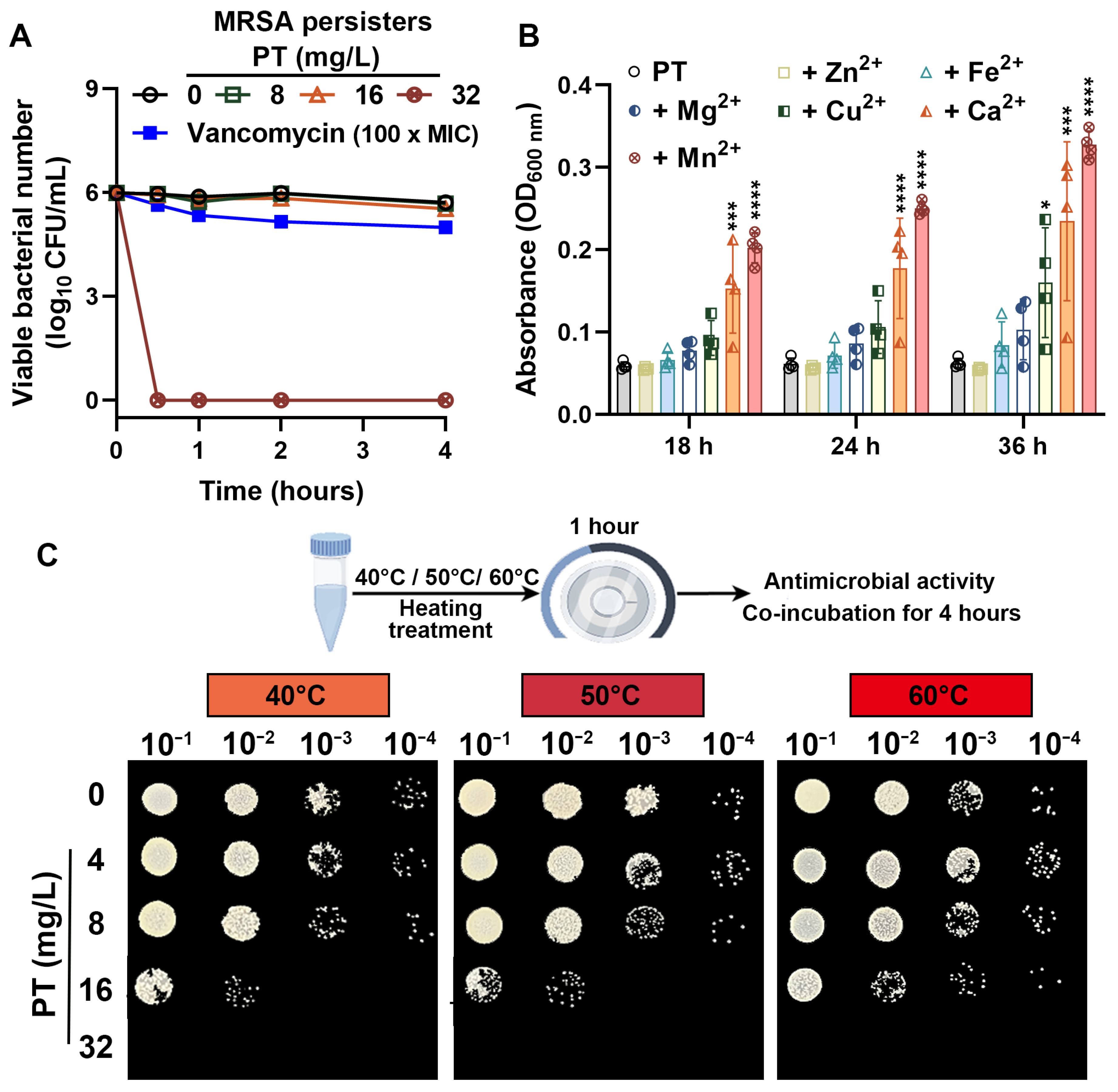
2.5. Effects of Metal Ions on the Anti-MRSA Activity of PT
2.6. Thermostability of PT Against MRSA
2.7. Measurement of Total ROS
2.8. Nitric Oxide
2.9. Lipid Peroxidation Measurement
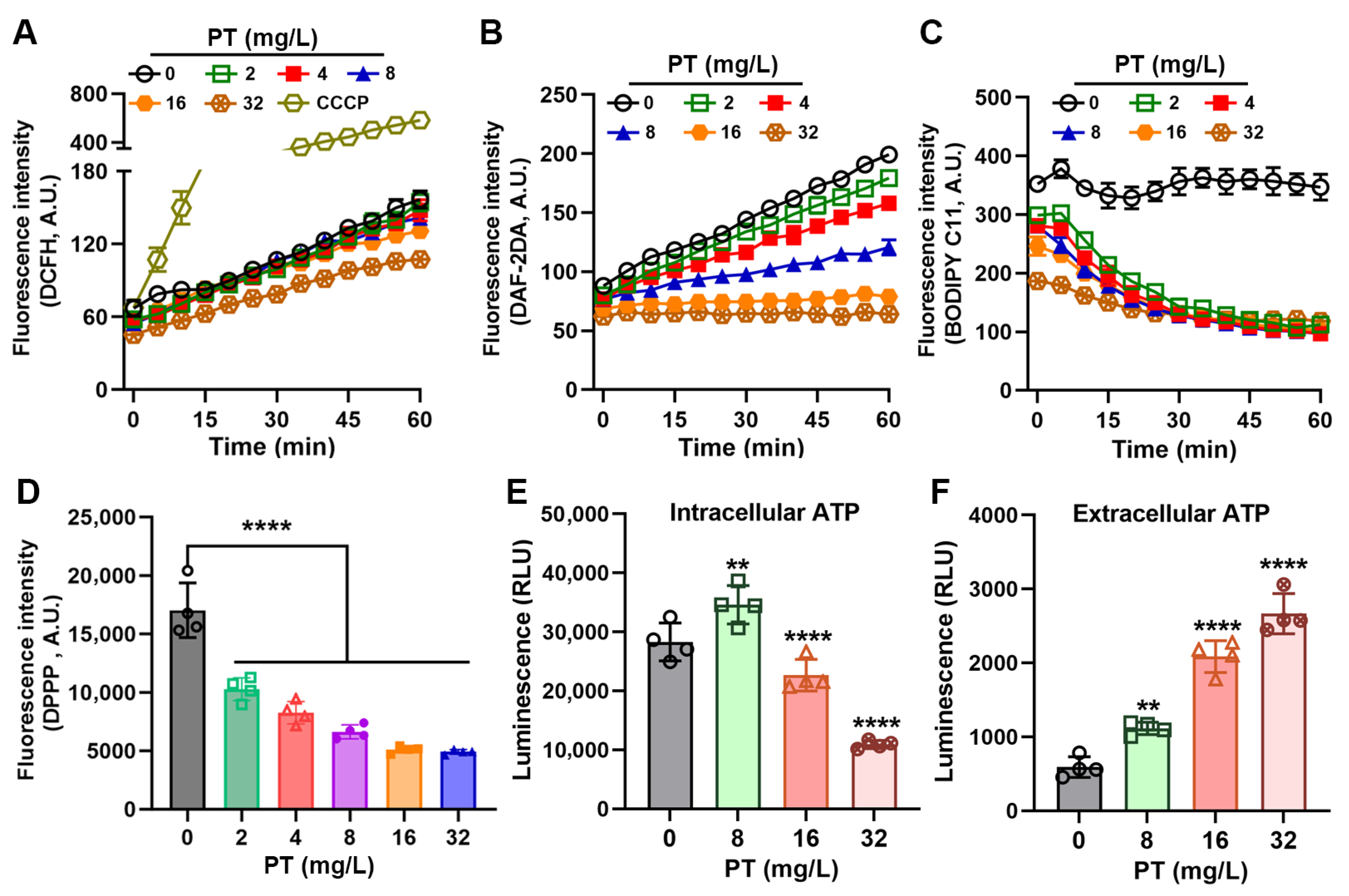
2.10. ATP Detection
2.11. Intracellular pH and Membrane Potential Detection
2.12. Membrane Permeability
2.13. Phospholipid Supplementation Assays
2.14. Analysis of Sliding Motility
2.15. Disinfectant Efficacy Against MRSA on Tableware Surfaces
2.16. Biofilm Assays
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
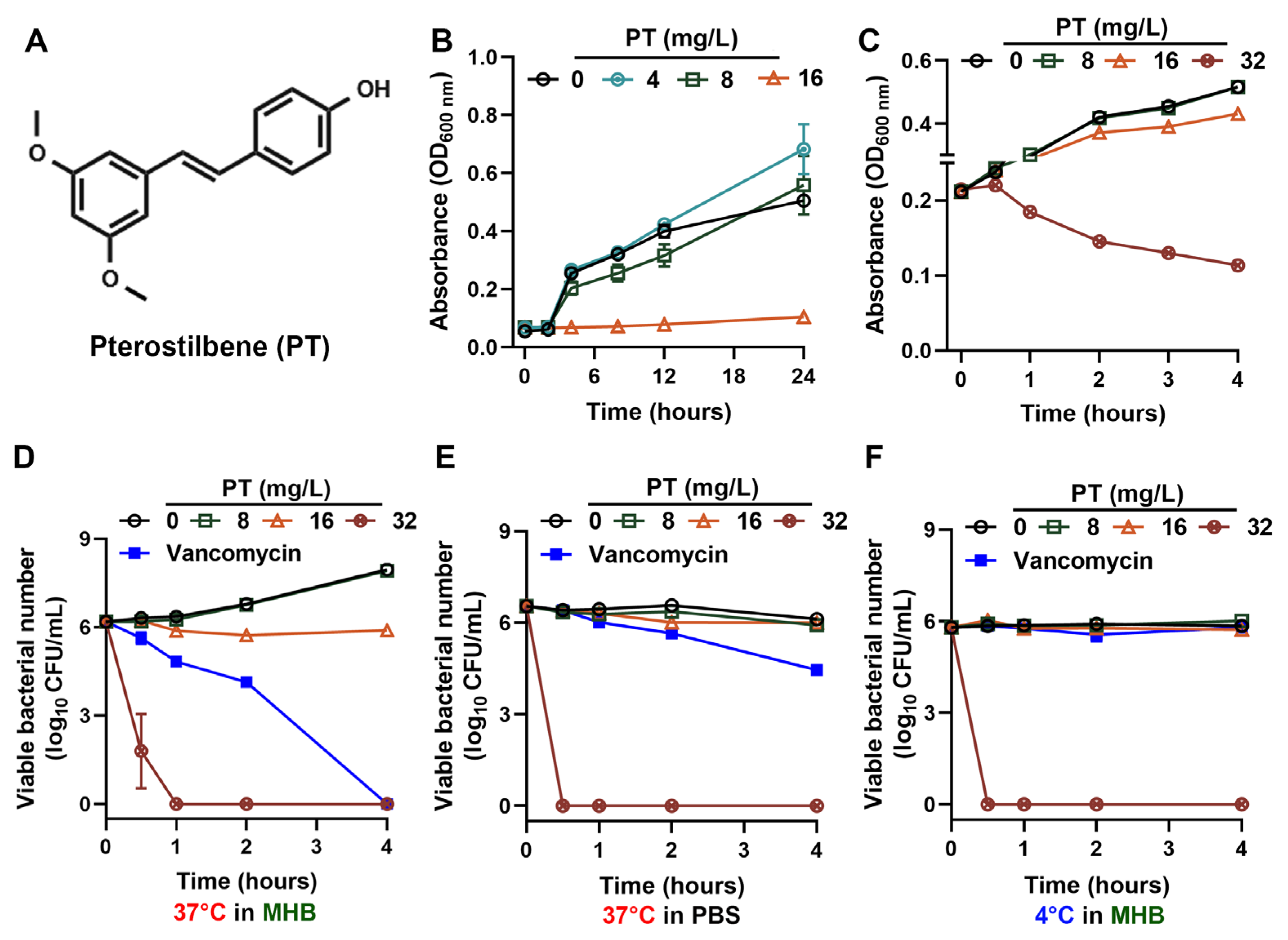
3.1. PT Exerts Potent Bactericidal Activity Independent of MRSA Physiological State
3.2. PT Eradicates MRSA Persisters and Maintains Efficacy Across Environmental Conditions
3.3. PT Inhibits Oxidative Stress in MRSA
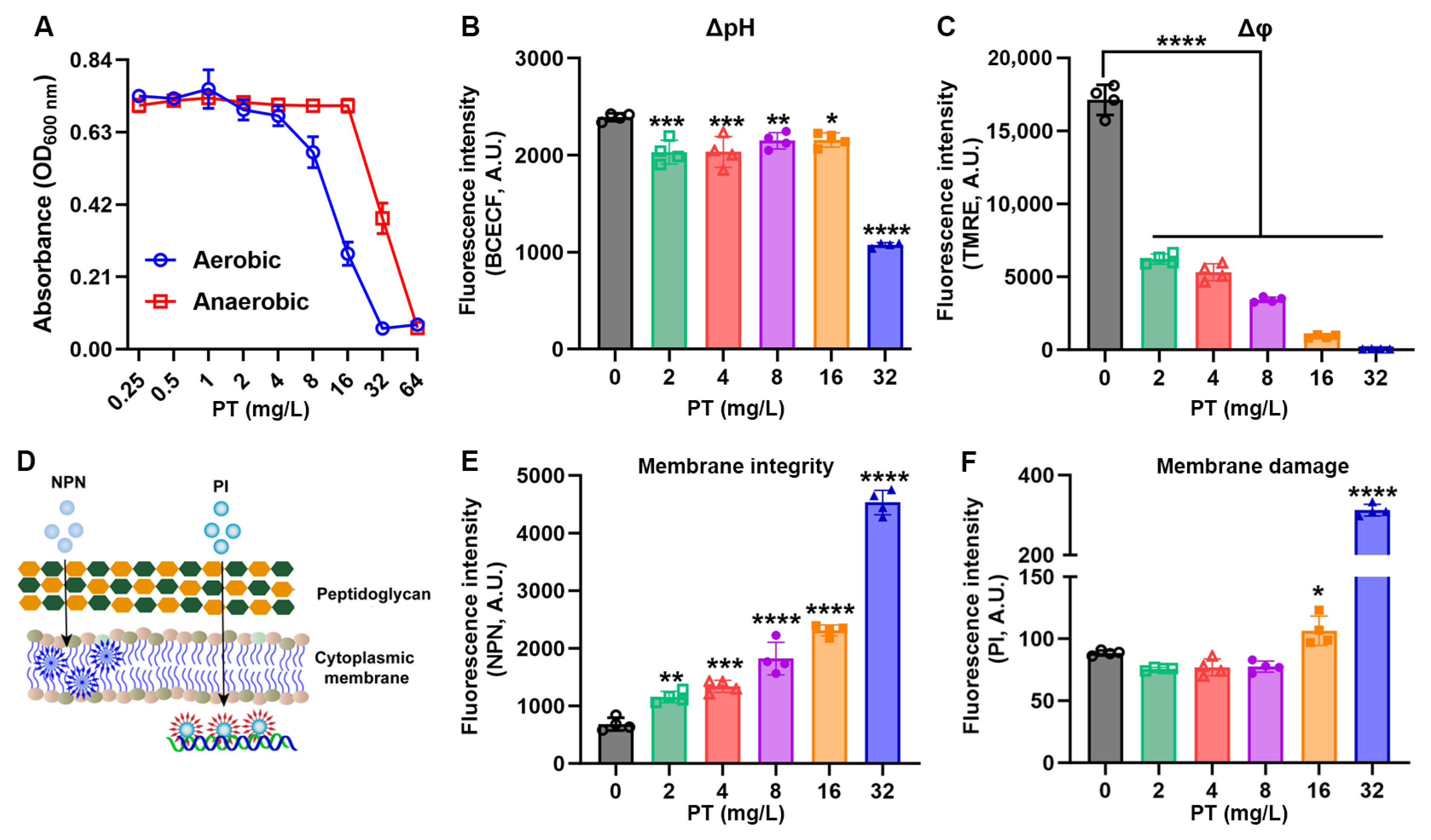
3.4. PT Disrupts Metabolic Gradients and Membrane Integrity
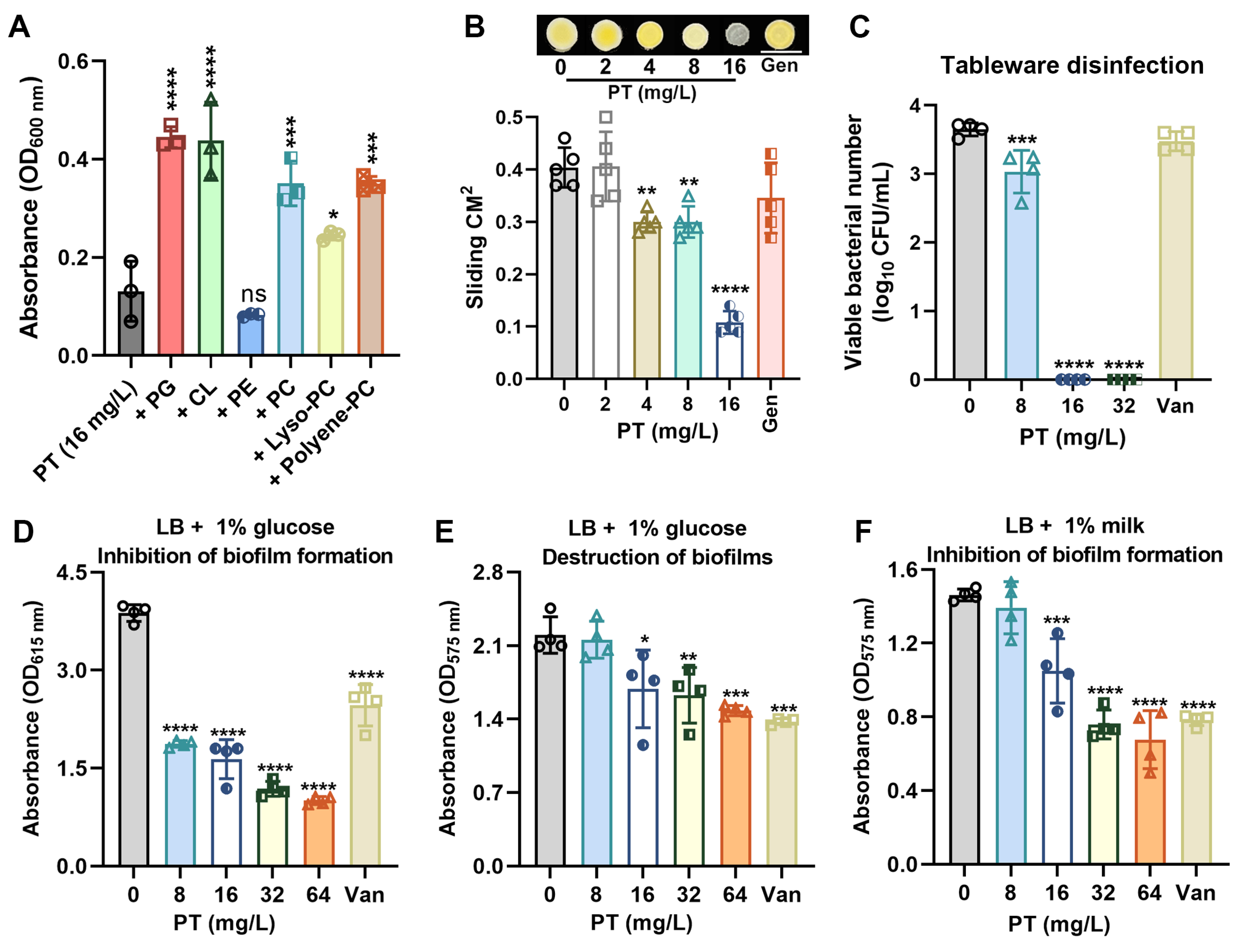
3.5. PT Targets Membrane Phospholipids and Inhibits Biofilm Formation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, R.; Wei, G.; Lin, R.; Lin, W.; Aweya, J.J.; Liang, D.; Weng, W.; Yang, S. Efficacy of Larimichthys crocea TASOR protein-derived peptide FAM286 against Staphylococcus aureus. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2025, 10, 100998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaifan, G.A.; Alhogail, S.; Zourob, M. Rapid and low-cost biosensor for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exel, C.E.; Tamminga, S.M.; Man-Bovenkerk, S.; Temming, A.R.; Hendriks, A.; Spaninks, M.; van Sorge, N.M.; Benedictus, L. Wall teichoic acid glycosylation of bovine-associated Staphylococcus aureus strains. Vet. Microbiol. 2025, 302, 110403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhou, T.; Chen, D.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Stability and emetic activity of enterotoxin like X (SElX) with high carrier rate of food poisoning Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 404, 110352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, G.A.R. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990–2021: A systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschner, F.; Mostert, D.; Daniel, J.M.; Voltz, A.; Schneider, D.C.; Khangholi, N.; Bartel, J.; Pessanha de Carvalho, L.; Brauer, M.; Gorelik, T.E.; et al. Natural products chlorotonils exert a complex antibacterial mechanism and address multiple targets. Cell Chem. Biol. 2025, 32, 586–602.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossiter, S.E.; Fletcher, M.H.; Wuest, W.M. Natural Products as Platforms To Overcome Antibiotic Resistance. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12415–12474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.R.; LeBlanc, A.R.; Wuest, W.M. From Natural Products to Small Molecules: Recent Advancements in Anti-MRSA Therapeutics. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2025, 16, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Li, B.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, D.; Han, Y. Eco-friendly bacteria-killing by nanorods through mechano-puncture with top selectivity. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 15, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Hao, Z.; Ding, S.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Zhu, K.; Shen, J. Plant Natural Flavonoids Against Multidrug Resistant Pathogens. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2100749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Fan, A.; Wu, M.; Xu, N.; Zhu, K.; Lin, W. Marine-derived new peptaibols with antibacterial activities by targeting bacterial membrane phospholipids. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2025, 15, 2764–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, H.; Han, L.; Xing, H.; Zhao, D.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y. Phase I Metabolism of Pterostilbene, a Dietary Resveratrol Derivative: Metabolite Identification, Species Differences, Isozyme Contribution, and Further Bioactivation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.S.; Leland, J.V.; Ho, C.T.; Pan, M.H. Occurrence, Bioavailability, Anti-inflammatory, and Anticancer Effects of Pterostilbene. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 12788–12799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.; Aswar, U.; Vyas, N. Pterostilbene ameliorates type-2 diabetes mellitus—Induced depressive-like behavior by mitigating insulin resistance, inflammation and ameliorating HPA axis dysfunction in rat brain. Brain Res. 2023, 1817, 148494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Tang, W.; Xiang, K.; Li, G. Pterostilbene in the treatment of inflammatory and oncological diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1323377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Chang, Y.T.; Cheng, Y.H.; Pranata, R.; Hsu, H.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Chen, R.J. Pterostilbene Protects against Osteoarthritis through NLRP3 Inflammasome Inactivation and Improves Gut Microbiota as Evidenced by In Vivo and In Vitro Studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 9150–9163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Ji, S.; Jia, P.; Wang, T. Pterostilbene Prevents Tunicamycin-Induced Intestinal Barrier Damage by Targeting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Oxidative Stress, Autophagy, and Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13661–13675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.H.; Tsai, P.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Pranata, R.; Chen, R.J. Assessment of the Antibacterial Mechanism of Pterostilbene against Bacillus cereus through Apoptosis-like Cell Death and Evaluation of Its Beneficial Effects on the Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 12219–12229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.C.; Tseng, C.H.; Wang, P.W.; Lu, P.L.; Weng, Y.H.; Yen, F.L.; Fang, J.Y. Pterostilbene, a Methoxylated Resveratrol Derivative, Efficiently Eradicates Planktonic, Biofilm, and Intracellular MRSA by Topical Application. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.X.; Basri, D.F.; Ghazali, A.R. Bactericidal Effect of Pterostilbene Alone and in Combination with Gentamicin against Human Pathogenic Bacteria. Molecules 2017, 22, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.D.; Zhang, R.L.; Zou, Y.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, E.S.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.Y. The Structure-Activity Relationship of Pterostilbene Against Candida albicans Biofilms. Molecules 2017, 22, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, N.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Niu, X.; Deng, X.; Wang, J. Pterostilbene restores carbapenem susceptibility in New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-producing isolates by inhibiting the activity of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 4548–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, T.; Li, H.; Tang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Deng, X. Pterostilbene, a Potential MCR-1 Inhibitor That Enhances the Efficacy of Polymyxin B. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kašparová, P.; Vaňková, E.; Brázdová, L.; Lokočová, K.; Maťátková, O.; Masák, J. Antibiofilm agent pterostilbene is able to enhance antibiotics action against Staphylococcus epidermidis. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 152, 104632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, Q.; Yun, S.; Guo, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Sun, Z. Zn(II) enhances the antimicrobial effect of chloroxine and structural analogues against drug-resistant ESKAPE pathogens in vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 229, 116482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, H.Y.; Zou, G.; Baek, S.; Kim, J.S.; Mylonakis, E.; Ausubel, F.M.; Gao, H.; Kim, W. A Methylazanediyl Bisacetamide Derivative Sensitizes Staphylococcus aureus Persisters to a Combination of Gentamicin And Daptomycin. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2306112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Ren, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Sun, Z. Copper(II) enhances the antibacterial activity of nitroxoline against MRSA by promoting aerobic glycolysis. Biophys. Chem. 2025, 320–321, 107419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Das, A.; Ganguly, D.; Chakraborty, P.; Paul, P.; Das, S.; Maity, A.; Malik, M.; Tribedi, P. Cuminaldehyde synergistically enhances the antimicrobial and antibiofilm potential of gentamicin: A direction towards an effective combination for the control of biofilm-linked threats of Staphylococcus aureus. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2025, 56, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, G.; Yepes, A.; Förstner, K.U.; Wermser, C.; Stengel, S.T.; Modamio, J.; Ohlsen, K.; Foster, K.R.; Lopez, D. Evolution of resistance to a last-resort antibiotic in Staphylococcus aureus via bacterial competition. Cell 2014, 158, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.A.; Wang, B.; Sidarta, M.; Cornejo, F.A.; Wijnheijmer, J.; Rani, R.; Gamba, P.; Turgay, K.; Wenzel, M.; Strahl, H.; et al. Membrane depolarization kills dormant Bacillus subtilis cells by generating a lethal dose of ROS. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wang, X.; Drlica, K.; Zhao, X. Post-stress bacterial cell death mediated by reactive oxygen species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 10064–10071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Fernández, E.; Koch, G.; Wagner, R.M.; Fekete, A.; Stengel, S.T.; Schneider, J.; Mielich-Süss, B.; Geibel, S.; Markert, S.M.; Stigloher, C.; et al. Membrane Microdomain Disassembly Inhibits MRSA Antibiotic Resistance. Cell 2017, 171, 1354–1367.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohlenkamp, C.; Geiger, O. Bacterial membrane lipids: Diversity in structures and pathways. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 133–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamudio-Chávez, L.; Suesca, E.; López, G.D.; Carazzone, C.; Manrique-Moreno, M.; Leidy, C. Staphylococcus aureus Modulates Carotenoid and Phospholipid Content in Response to Oxygen-Restricted Growth Conditions, Triggering Changes in Membrane Biophysical Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Soetaert, K.; Ravon, F.; Vandeput, M.; Bald, D.; Kauffmann, J.M.; Mathys, V.; Wattiez, R.; Fontaine, V. Isoniazid Bactericidal Activity Involves Electron Transport Chain Perturbation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01841-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.; Dick, T. Mycobacterial Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors Cause Lethal ATP Burst. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciofu, O.; Moser, C.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Høiby, N. Tolerance and resistance of microbial biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grein, F.; Müller, A.; Scherer, K.M.; Liu, X.; Ludwig, K.C.; Klöckner, A.; Strach, M.; Sahl, H.G.; Kubitscheck, U.; Schneider, T. Ca(2+)-Daptomycin targets cell wall biosynthesis by forming a tripartite complex with undecaprenyl-coupled intermediates and membrane lipids. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolouchová, I.; Maťátková, O.; Paldrychová, M.; Kodeš, Z.; Kvasničková, E.; Sigler, K.; Čejková, A.; Šmidrkal, J.; Demnerová, K.; Masák, J. Resveratrol, pterostilbene, and baicalein: Plant-derived anti-biofilm agents. Folia Microbiol. 2018, 63, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerca, N.; Martins, S.; Cerca, F.; Jefferson, K.K.; Pier, G.B.; Oliveira, R.; Azeredo, J. Comparative assessment of antibiotic susceptibility of coagulase-negative staphylococci in biofilm versus planktonic culture as assessed by bacterial enumeration or rapid XTT colorimetry. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, J.D.; Ghaskadbi, S.S. Protective effect of Pterostilbene against free radical mediated oxidative damage. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimando, A.M.; Nagmani, R.; Feller, D.R.; Yokoyama, W. Pterostilbene, a new agonist for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha-isoform, lowers plasma lipoproteins and cholesterol in hypercholesterolemic hamsters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 3403–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.W.; Yang, S.C.; Tseng, C.H. Design, Synthesis, and Anti-Bacterial Evaluation of Triazolyl-Pterostilbene Derivatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4564. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, C.; Yan, S.; Ren, X.; Sun, Z. Pterostilbene Eliminates MRSA Independent of Metabolic State and Effectively Prevents Biofilm Formation in Milk Matrices. Foods 2025, 14, 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183236
Huang X, Yang H, Wang C, Yan S, Ren X, Sun Z. Pterostilbene Eliminates MRSA Independent of Metabolic State and Effectively Prevents Biofilm Formation in Milk Matrices. Foods. 2025; 14(18):3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183236
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xiaoyong, Huiting Yang, Chenli Wang, Shiqi Yan, Xiaomin Ren, and Zilong Sun. 2025. "Pterostilbene Eliminates MRSA Independent of Metabolic State and Effectively Prevents Biofilm Formation in Milk Matrices" Foods 14, no. 18: 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183236
APA StyleHuang, X., Yang, H., Wang, C., Yan, S., Ren, X., & Sun, Z. (2025). Pterostilbene Eliminates MRSA Independent of Metabolic State and Effectively Prevents Biofilm Formation in Milk Matrices. Foods, 14(18), 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183236




