Multi-Omics Characterization of Quality Attributes in Pigeon Meat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Sample Collection
2.2. Free Amino Acid Analysis
2.3. Flavored Nucleotide Analysis
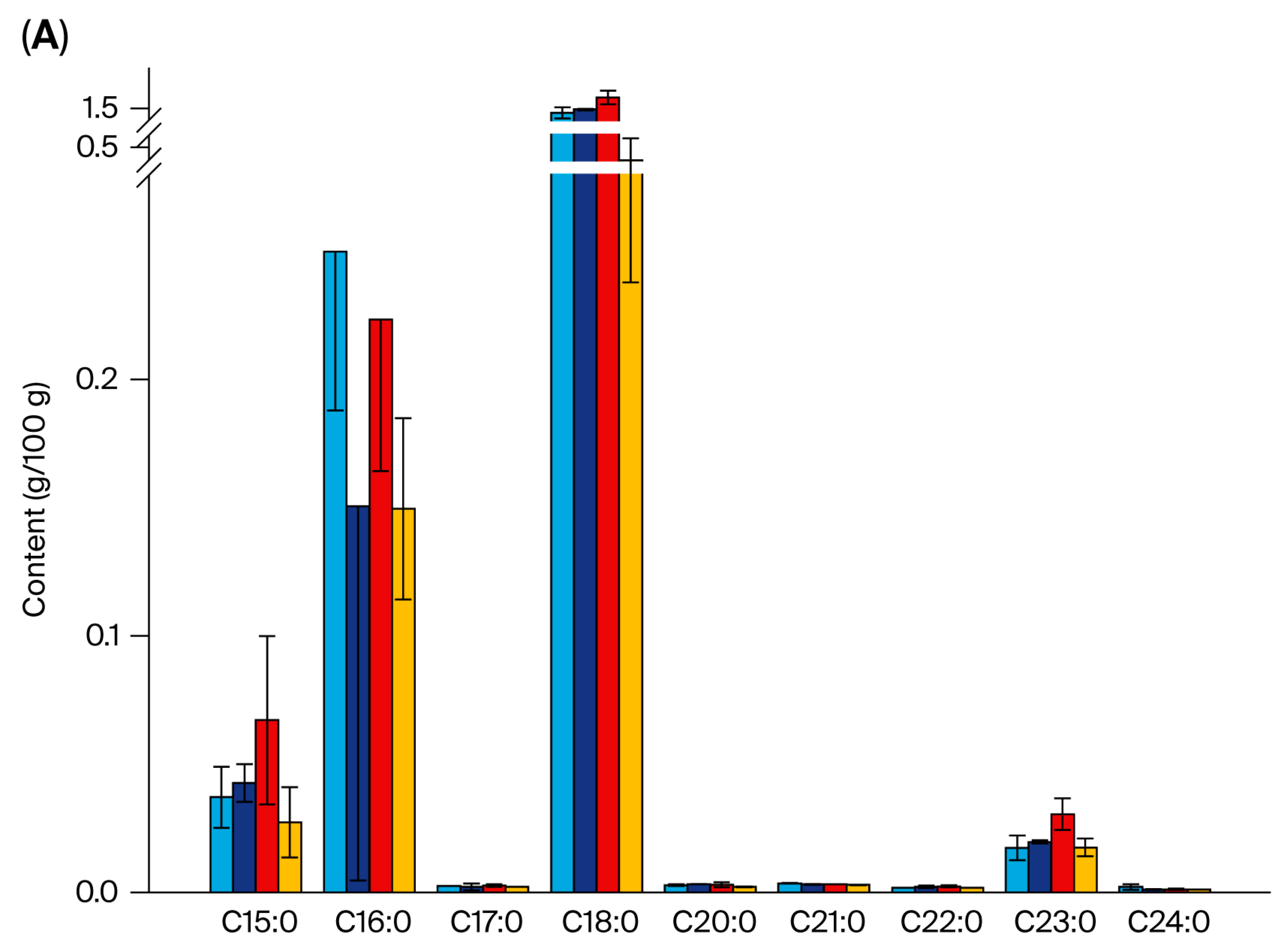
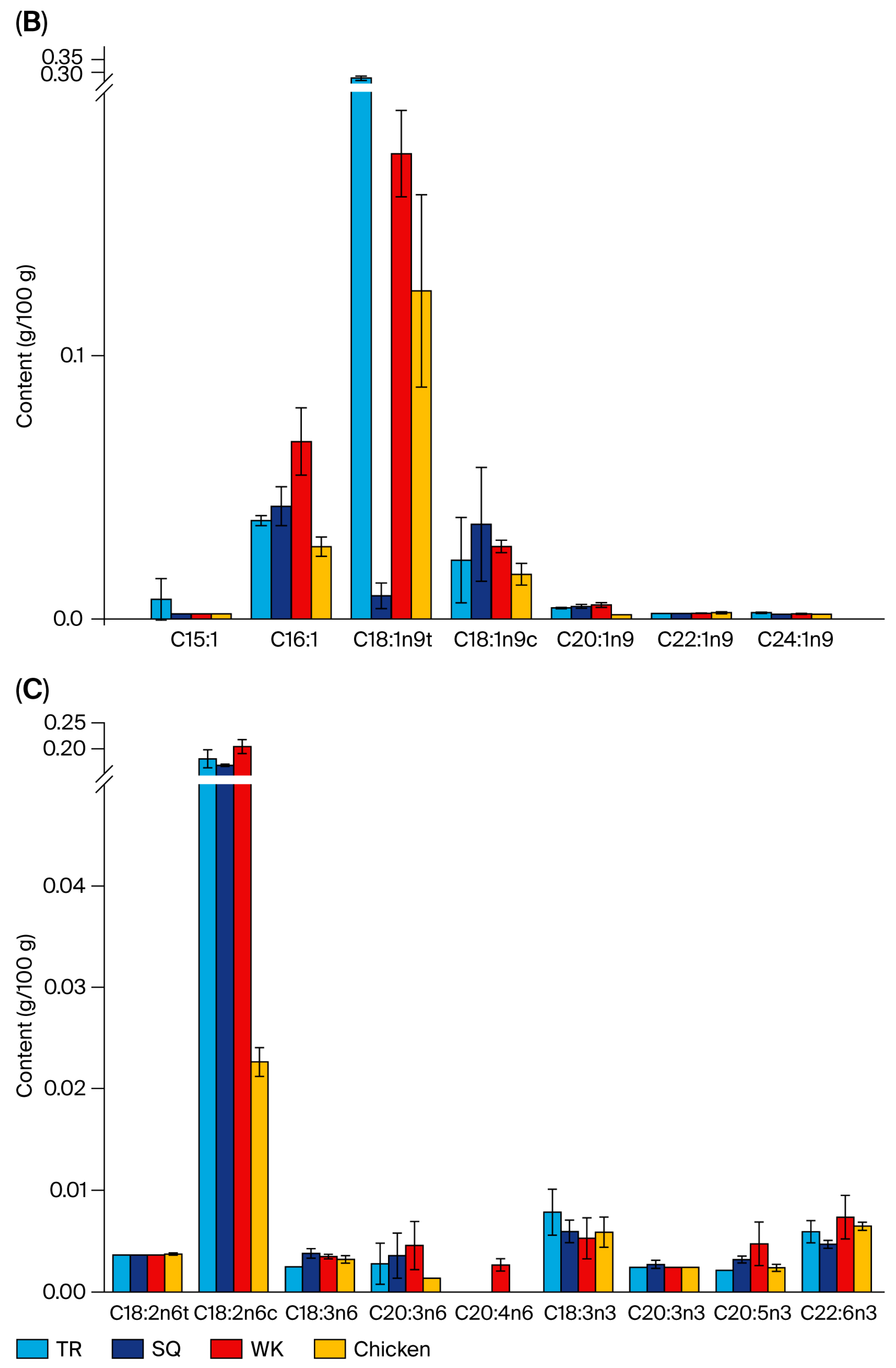
2.4. Fatty Acid Analysis
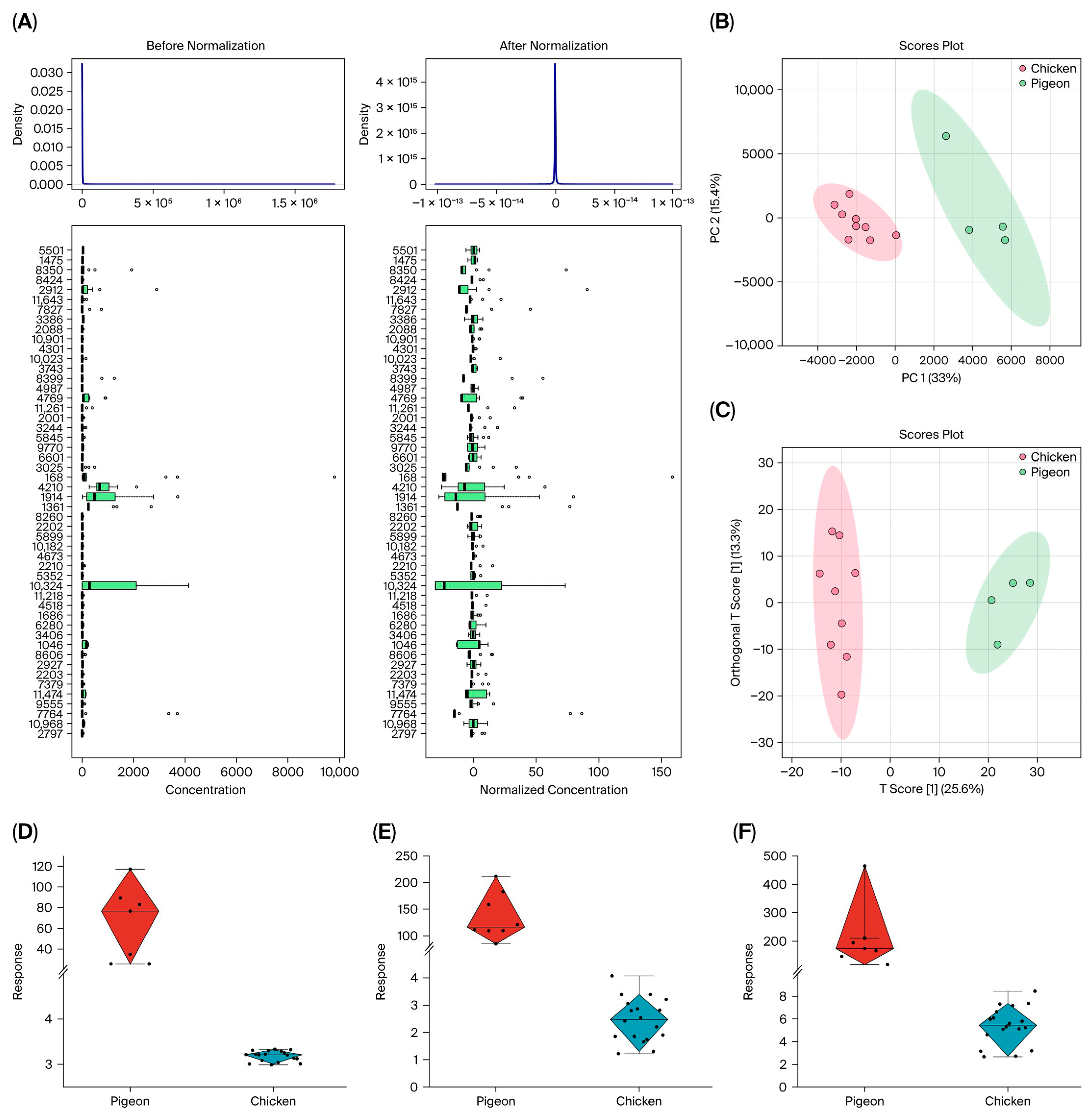
2.5. Metabolomics Analysis
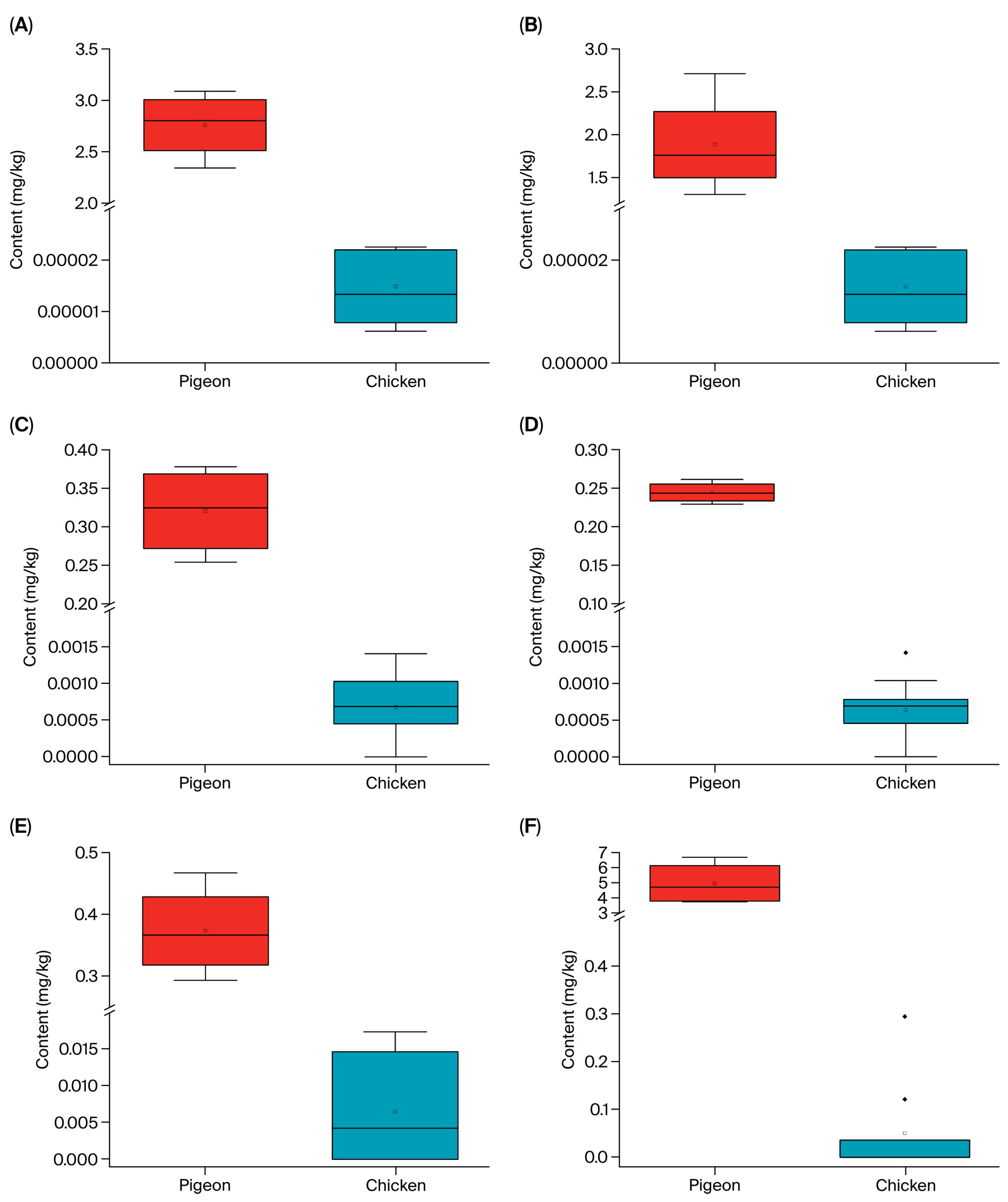
2.6. Lipidomics Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Free Amino Acid
3.2. Flavored Nucleotides
3.3. Fatty Acid
3.4. Metabolomics Analysis
3.5. Lipid Composition Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Glu | Glutamate |
| Ala | Alanine |
| Asp | Aspartate |
| Gly | Glycine |
| Tyr | Tyrosine |
| Phe | Phenylalanine |
| Leu | Leucine |
| Lys | Lysine |
| Thr | Threonine |
| Val | Valine |
| Ile | Isoleucine |
| Met | Methionine |
| Ser | Serine |
| Arg | Arginine |
| His | Histidine |
| Pro | Proline |
| IMP | Inosine monophosphate |
| GMP | Guanosine monophosphate |
| AMP | Adenosine monophosphate |
| I | Inosine |
| Hx | Hypoxanthine |
| CMP | Cytosine monophosphate |
| UMP | Uridine monophosphate |
| GP | Glycerophospholipid |
| FA | Fatty acid |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| Cer | Ceramide |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| DG | Diglyceride |
| LNAPE | N-Acylphosphatidylethanotamine |
| HexCer | Hexosylceramide |
| PI | Phosphatidylinositol |
| PEtOH | Phosphatidylethanol |
| PS | Phosphatidylserine |
| PG | Phosphatidylglycerol |
| LPS | Lyso-phosphatidylserine |
| LPE | Lyso-phosphatidylethanolamine |
| LPC | Lyso-phosphatidylcholine |
| SMGDG | Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol |
| PA | Phosphatidic acid |
| DGGA | Diacylglyceryl-α-D-glucuronide |
| BMP | Bis (monoacylglycero)phosphate |
| CAR | Constitutive Androstane Receptor |
| Hex2Cer | Hexosylceramides |
| PMeOH | Phosphatidylmethanol |
| LPG | Lyso-phosphatidylglycerol |
| LPI | Lyso-phosphatidylinositol |
| CerP | Ceramides phosphate |
| SL | Saccharolipid |
| C15:0 | Pentadecanoic acid |
| C15:1 | cis-10-Pentadecenoic acid |
| C16:0 | Palmitic acid |
| C16:1 | Palmitoleic acid |
| C17:0 | Heptadecanoic acid |
| C18:0 | Stearic acid |
| C18:1n9t | Elaidic acid |
| C18:1n9c | Oleic acid |
| C18:2n6t | Linolelaidic acid |
| C18:2n6c | Linoleic acid |
| C20:0 | Arachidic acid |
| C18:3n6 | γ-Linolenic acid |
| C20:1n9 | cis-11-Eicosenoic acid |
| C18:3n3 | α-Linolenic acid |
| C21:0 | Heneicosanoic acid |
| C20:2 | cis-11,14-Eicosadienoic acid |
| C22:0 | Behenic acid |
| C20:3n6 | cis-8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic acid |
| C22:1n9 | Erucic acid |
| C20:3n3 | cis-11,14,17-Eicasatrienoic acid |
| C20:4n6 | Arachidonic acid |
| C23:0 | Tricosanoic acid |
| C22:2n6 | cis-13,16-Docosadienoic acid |
| C24:0 | Lignoceric acid |
| C20:5n3 | cis-5,8,11,14,17-Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| C24:1n9 | Nervonic acid |
| C22:6n3 | cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-Docosahexaenoic acid |
References
- Jiang, S.G.; Pan, N.X.; Chen, M.J.; Wang, X.Q.; Yan, H.C.; Gao, C.Q. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with dl-Methionine and dl-Methionyl-dl-Methionine in Breeding Pigeons on the Carcass Characteristics, Meat Quality and Antioxidant Activity of Squabs. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Yang, C.; Hou, H.; Lv, W.; Bao, A.; Zhao, W.; Wang, X. Comparison of production characteristics and nutritional components between European meat pigeon line II and Tarim pigeon. Acta Agric. Shanghai 2022, 38, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Chang, L.; Qiu, H.; Bu, Z.; Tang, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhang, R.; Fu, S.; Mu, C. Comparative Evaluation of Meat Quality and Main Nutritional Components of Breast Muscle from Different Squab Breeds. Meat Res. 2019, 33, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, W.; Zeng, X.; Bai, W.; Xiao, G. Effects of different breeds and ages of meat pigeons on quality and flavor of pigeon soup. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Gao, Q.; Cao, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, D. Study on formation of nutrients and characteristic flavors during stewing process of domestic pigeons. Food Ferment. Ind. 2023, 49, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.; Shao, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Xie, S.; Li, J.; Ma, T.; Wang, Z. Riboflavin improves meat quality, antioxidant capacity, muscle development, and lipids composition of breast muscle in pigeon. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 104856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Fu, S.; Mu, C.; Shen, X.; Bu, Z. Evaluation of Meat Quality of Local Pigeon Varieties in China. Animals 2023, 13, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Fu, S.; Mu, C.; Zhang, R.; Bu, Z. Comparative analysis of quality and main nutrition components between European pigeon and other livestock and poultry meat. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2017, 8, 2035–2040. [Google Scholar]
- Balkir, P.; Kemahlioglu, K.; Yucel, U. Foodomics: A new approach in food quality and safety. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Qi, L.; Zhang, S.; Peng, H.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Nie, Q.; Luo, W. Metabolomic, lipidomic, and proteomic profiles provide insights on meat quality differences between Shitou and Wuzong geese. Food Chem. 2024, 438, 137967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Cai, W.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, D.; Hou, C.; Zhu, J. Characterization of the relationship between metabolites and elements of meat from four Tibetan sheep breeds through untargeted metabolomics and multi-element analysis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 134, 106583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Gai, K.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Qi, X.; Xing, K.; Wang, X.; Xiao, L.; Ni, H.; et al. HPLC-QTRAP-MS-based metabolomics approach investigates the formation mechanisms of meat quality and flavor of Beijing You chicken. Food Chem. X 2023, 17, 100550. [Google Scholar]
- Si, R.; Ming, L.; Yun, X.; He, J.; Yi, L.; Na, Q.; Ji, R.; Dong, T. Proteomics integrated with metabolomics: Analysis of the internal mechanism underlying changes in meat quality in different muscles from bactrian camels. Food Chem. X 2025, 26, 102230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Shang, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhang, X.; Bai, D.; Hu, C.; Xu, Z.; Gu, L. Metabolomics and transcriptomics profiling of the breast muscle reveals variations in the meat quality of Jiaji ducks at days 50 and 90. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 215, 117176. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Cai, D.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, B.; Yang, X.; Kong, S.; Wu, R.; Lin, D.; Yuan, R.; Mo, Y.; et al. Metabolomic, lipidomic and transcriptomic reveal meat quality differences among hybrid, indigenous and commercial broiler. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 209, 116765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, D.; Gao, K.; Dai, Y.; Liang, S.; Cai, W.; Li, Z.; Guo, Z.; Hu, J.; et al. Dietary riboflavin supplementation improves meat quality, antioxidant capacity, fatty acid composition, lipidomic, volatilomic, and proteomic profiles of breast muscle in Pekin ducks. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, R.; Yang, M.; Niu, N.; Wu, J.; Shu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Shi, L.; Zhao, F.; Wang, L.; et al. Metabolomics and lipidomics profiles related to intramuscular fat content and flavor precursors between Laiwu and Yorkshire pigs. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zou, Y.; Liao, G.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, G. Identification of characteristic flavor compounds and small molecule metabolites during the ripening process of Nuodeng ham by GC-IMS, GC–MS combined with metabolomics. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Hui, T.; Zheng, X.; Li, S.; Wei, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z. Characterization of key lipids for binding and generating aroma compounds in roasted mutton by UPLC-ESI-MS/MS and Orbitrap Exploris GC. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.most.gov.cn/xxgk/xinxifenlei/fdzdgknr/fgzc/gfxwj/gfxwj2010before/201712/t20171222_137025.html (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- CAC/RCP 41-1993; International Code of Practice for Slaughtering Animals. Codex Alimentarius Commission: Rome, Italy, 1993.
- ISO/TS 34700: 2016; Animal Welfare Management—General Requirements and Guidance for Organizations in the Food Supply Chain. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Dong, M.; Qin, L.; Xue, J.; Du, M.; Lin, S.; Xu, X.; Zhu, B. Simultaneous quantification of free amino acids and 5′-nucleotides in shiitake mushrooms by stable isotope labeling-LC-MS/MS analysis. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, G.; Yin, X.; Ge, C.; Liao, G. Effects of different cooking methods on free fatty acid profile, water-soluble compounds and flavor compounds in Chinese Piao chicken meat. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Wu, W.; Soladoye, O.P.; Aluko, R.E.; Bak, K.H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Maillard reaction of food-derived peptides as a potential route to generate meat flavor compounds: A review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 151, 110823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, M.; Ventanas, S.; Heinonen, M. Formation of Strecker aldehydes between protein carbonyls–α-Aminoadipic and γ-glutamic semialdehydes–and leucine and isoleucine. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heres, A.; Yokoyama, I.; Gallego, M.; Toldrá, F.; Arihara, K.; Mora, L. Antihypertensive potential of sweet Ala-Ala dipeptide and its quantitation in dry-cured ham at different processing conditions. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwang, N.; Marupanthorn, K.; Krutthai, N.; Wattanakul, W.; Jaturasitha, S.; Arjin, C.; Sringarm, K.; Setthaya, P. Assessment of nucleic acid content, amino acid profile, carcass, and meat quality of Thai native chicken. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 103067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Gagaoua, M.; Barba, F.J.; Zhang, W.; Lorenzo, J.M. A Comprehensive Review on Lipid Oxidation in Meat and Meat Products. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ji, H.; Liu, S.; Shi, W.; Lu, Y. Shrimp lipids improve flavor by regulating characteristic aroma compounds in hot air-dried shrimp. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 142065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katemala, S.; Molee, A.; Thumanu, K.; Yongsawatdigul, J. A comparative study of meat quality and vibrational spectroscopic properties of different chicken breeds. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, Q.; Xing, J.; Li, P.; Gao, P.; Hamid, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Gong, H. Exploring the formation and retention of aroma compounds in ready-to-eat roasted pork from four thermal methods: A lipidomics and heat transfer analysis. Food Chem. 2024, 431, 137100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Lu, C. Comparative proteomic analysis reveals the effects of different fatty acid forms on high-fat diet mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Tan, J.; Zhang, N.; Chen, A.; Feng, Z.; Qian, Y.; Xu, Z. Lipidomics and metabolomics reveal the enhanced mutton quality of Tan sheep under a standardized feeding regimen. Agric. Commun. 2023, 1, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, L.; Si, R.; Li, L.; Ji, R.; He, J. Meat quality and lipid transformation profiling of Bactrian camel during postmortem chilled aging. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 143, 107511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| SQ (mg/100 g) | WK (mg/100 g) | TR (mg/100 g) | Chicken (mg/100 g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino acids | Glu # | 27.70 ± 6.39 a | 27.06 ± 20.95 a | 12.46 ± 2.70 a | 14.27 ± 6.81 a |
| Ala # | 16.59 ± 3.42 a | 20.19 ± 7.04 a | 19.30 ± 3.88 a | 21.81 ± 3.71 a | |
| Asp # | 7.98 ± 2.16 a | 9.95 ± 5.04 a | 9.59 ± 4.65 a | 12.08 ± 4.08 a | |
| Gly # | 7.12 ± 1.51 a | 8.89 ± 2.54 a | 13.35 ± 5.86 a | 12.84 ± 1.73 a | |
| Tyr # | 7.05 ± 1.47 a | 9.39 ± 7.73 a | 4.72 ± 2.03 a | 3.52 ± 1.20 a | |
| Phe *,# | 5.33 ± 1.12 a | 8.49 ± 4.09 a | 4.92 ± 1.69 a | 3.12 ± 1.30 a | |
| Leu * | 12.26 ± 2.33 a | 16.08 ± 6.81 a | 8.97 ± 3.56 a | 6.11 ± 2.47 a | |
| Lys * | 10.04 ± 3.18 a | 13.65 ± 6.78 a | 7.86 ± 1.92 a | 6.66 ± 3.12 a | |
| Thr * | 9.01 ± 2.25 a | 11.74 ± 3.59 a | 8.33 ± 1.61 a | 8.11 ± 2.52 a | |
| Val * | 7.99 ± 1.72 a | 10.78 ± 4.91 a | 5.63 ± 1.85 ab | 4.28 ± 1.28 b | |
| Ile * | 5.42 ± 1.18 a | 9.34 ± 3.9 a | 4.12 ± 1.53 ab | 2.64 ± 1.07 b | |
| Met * | 3.62 ± 0.69 a | 5.79 ± 2.07 a | 2.84 ± 1.75 ab | 1.64 ± 0.56 b | |
| Ser | 12.58 ± 2.48 a | 17.34 ± 5.42 a | 17.32 ± 6.19 a | 10.91 ± 5.56 a | |
| Arg | 10.55 ± 2.64 a | 13.47 ± 5.93 a | 8.63 ± 1.47 a | 8.19 ± 3.40 a | |
| His | 6.77 ± 1.67 a | 8.80 ± 4.09 a | 4.65 ± 1.04 a | 5.17 ± 1.18 a | |
| Pro | 5.40 ± 2.19 a | 5.92 ± 2.87 a | 4.66 ± 1.45 a | 5.32 ± 3.46 a | |
| Essential amino acid | 60.43 ± 12.76 a | 82.67 ± 35.34 a | 47.32 ± 13.74 ab | 37.76 ± 10.88 b | |
| Umami amino acid | 71.77 ± 14.58 a | 83.97 ± 42.69 a | 64.35 ± 14.27 a | 67.65 ± 12.37 a | |
| Total | 150.00 ± 30.72 a | 194.88 ± 87.79 a | 137.35 ± 26.88 a | 126.70 ± 30.63 a | |
| Nucleotides | IMP | 124.76 ± 30.00 a | 49.26 ± 14.49 b | 86.83 ± 13.10 a | 49.92 ± 14.72 b |
| GMP | 4.47 ± 0.26 a | 3.72 ± 1.84 a | 2.14 ± 2.35 a | 2.94 ± 2.29 a | |
| AMP | 6.12 ± 1.35 a | 3.97 ± 0.62 a | 2.57 ± 0.47 a | 2.76 ± 0.85 a | |
| I | 17.01 ± 4.52 c | 41.94 ± 11.11 a | 26.71 ± 4.05 b | 33.07 ± 6.64 b | |
| Hx | 7.76 ± 0.38 c | 10.77 ± 0.96 b | 15.23 ± 1.28 a | 10.12 ± 1.58 b | |
| CMP | 0.26 ± 0.07 c | 1.24 ± 0.20 a | 0.57 ± 0.08 b | 0.57 ± 0.02 b | |
| UMP | 0.72 ± 0.12 a | 0.35 ± 0.11 c | 0.56 ± 0.05 b | 0.55 ± 0.05 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhou, J.; Wang, M. Multi-Omics Characterization of Quality Attributes in Pigeon Meat. Foods 2025, 14, 3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183230
Wang X, Hu Y, Liu Y, Li C, Wang Z, Liu M, Zhou J, Wang M. Multi-Omics Characterization of Quality Attributes in Pigeon Meat. Foods. 2025; 14(18):3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183230
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xinran, Yunyun Hu, Yan Liu, Cheng Li, Zheng Wang, Meiyu Liu, Jinhui Zhou, and Meng Wang. 2025. "Multi-Omics Characterization of Quality Attributes in Pigeon Meat" Foods 14, no. 18: 3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183230
APA StyleWang, X., Hu, Y., Liu, Y., Li, C., Wang, Z., Liu, M., Zhou, J., & Wang, M. (2025). Multi-Omics Characterization of Quality Attributes in Pigeon Meat. Foods, 14(18), 3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183230






