Metabolomics Analysis of the Spoilage Characteristics of Pseudomonas fragi and Aeromonas salmonicida Co-Culture in Refrigerated Grass Carp
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Preparation of Grass Carp
2.3. Bacterial Enumeration
2.4. Microbial Composition Determination
2.5. Determination of TVB-N
2.6. Determination of TBARs
2.7. Texture Determination
2.8. Metabolomics Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microbial Analysis
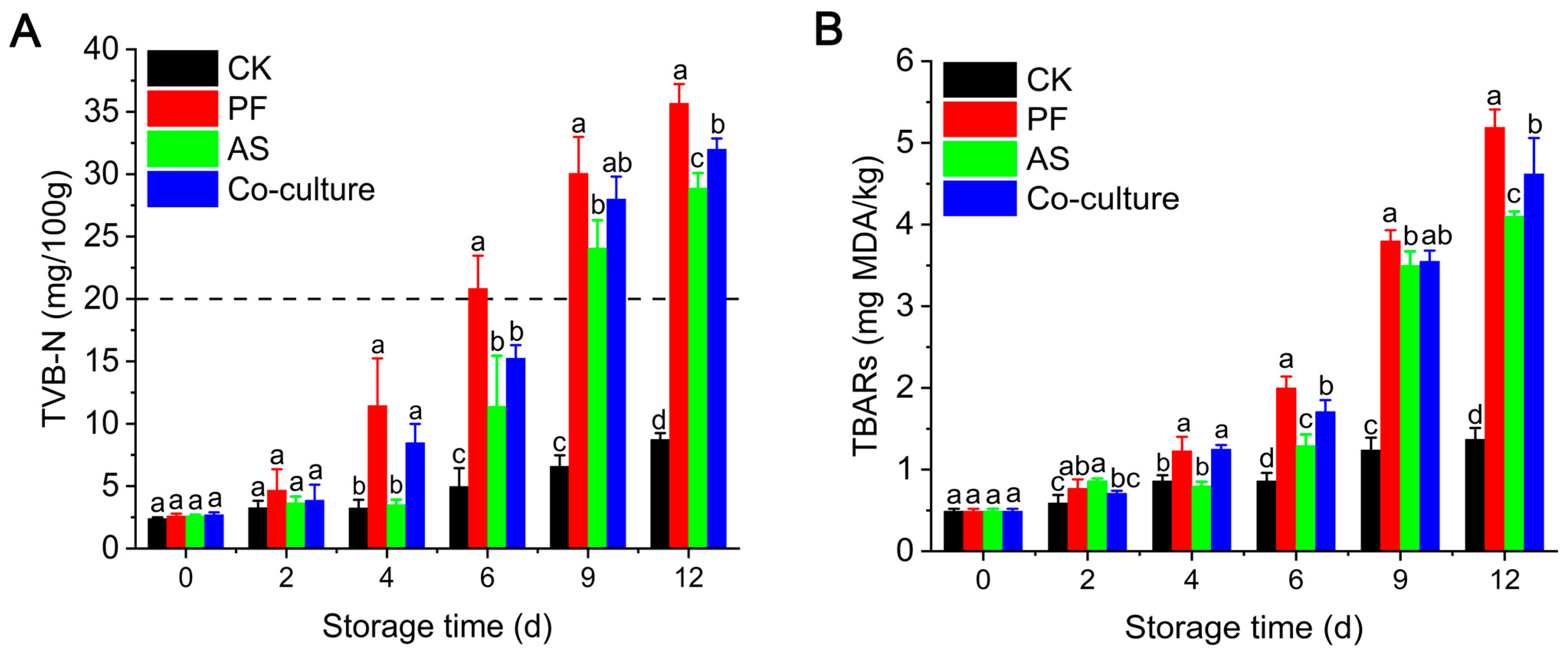
3.2. TVB-N Analysis
3.3. TBARs Analysis
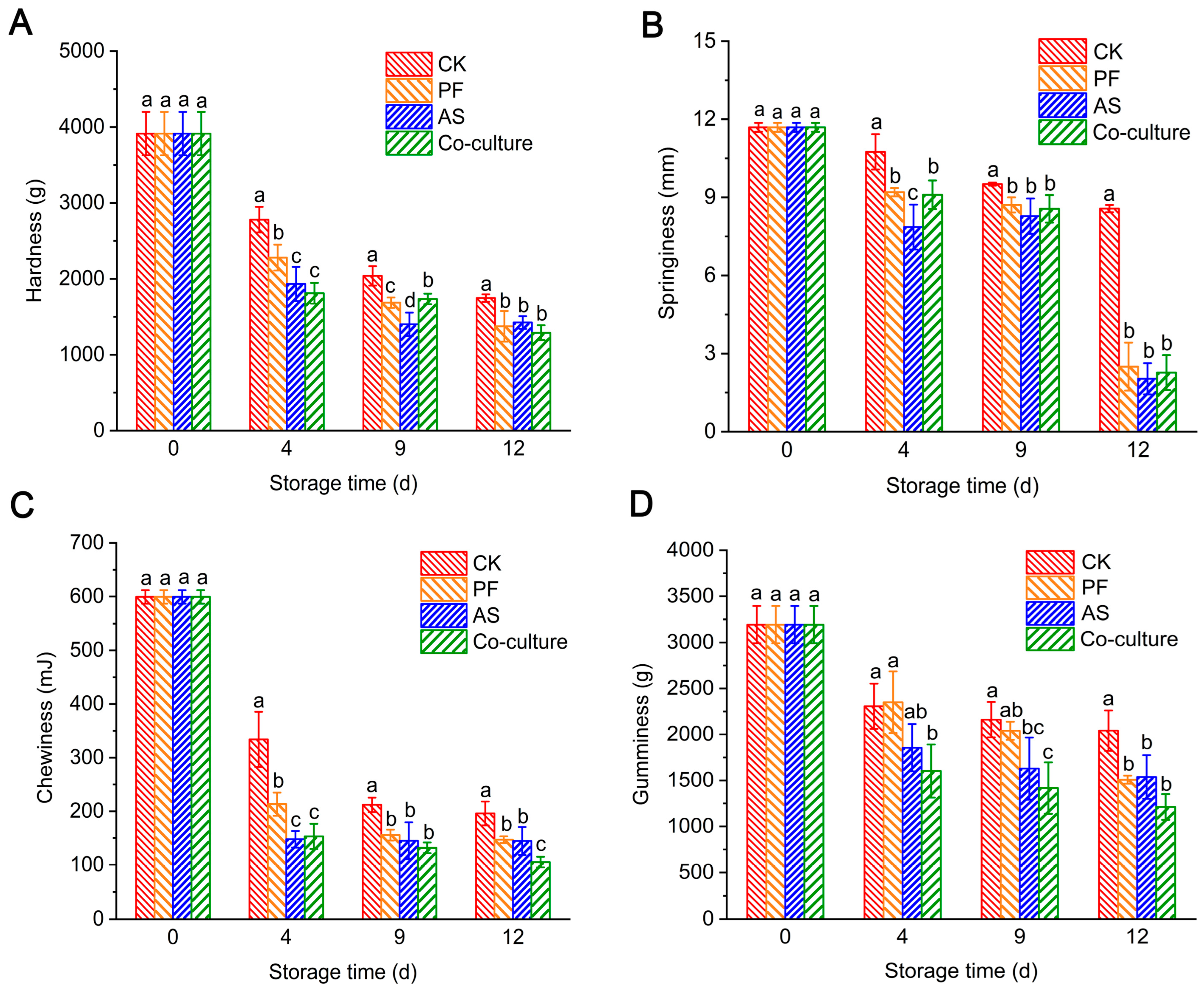
3.4. Changes in Texture of Fish
3.5. Metabolomic Analysis
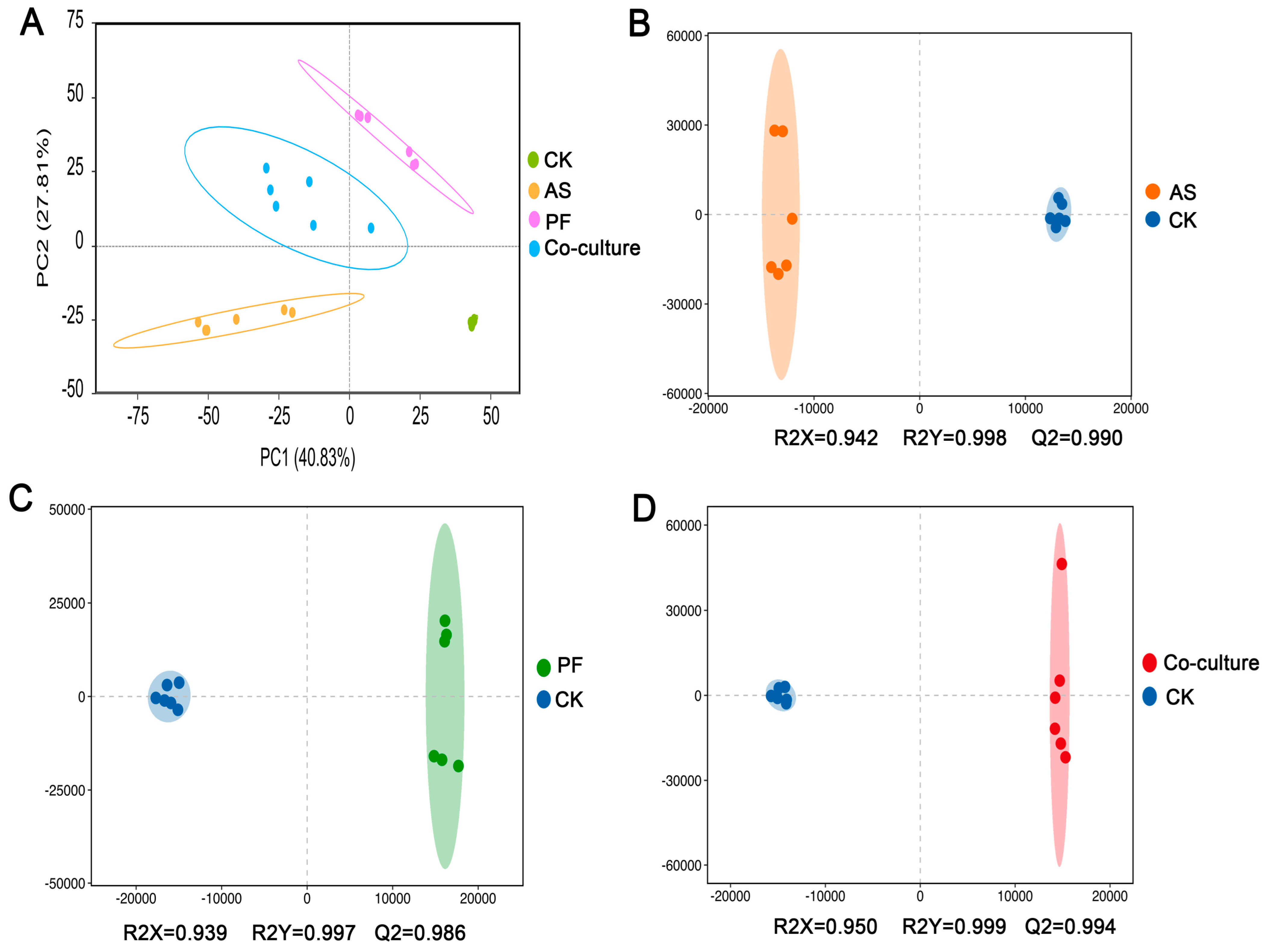
3.5.1. Multivariate Analysis
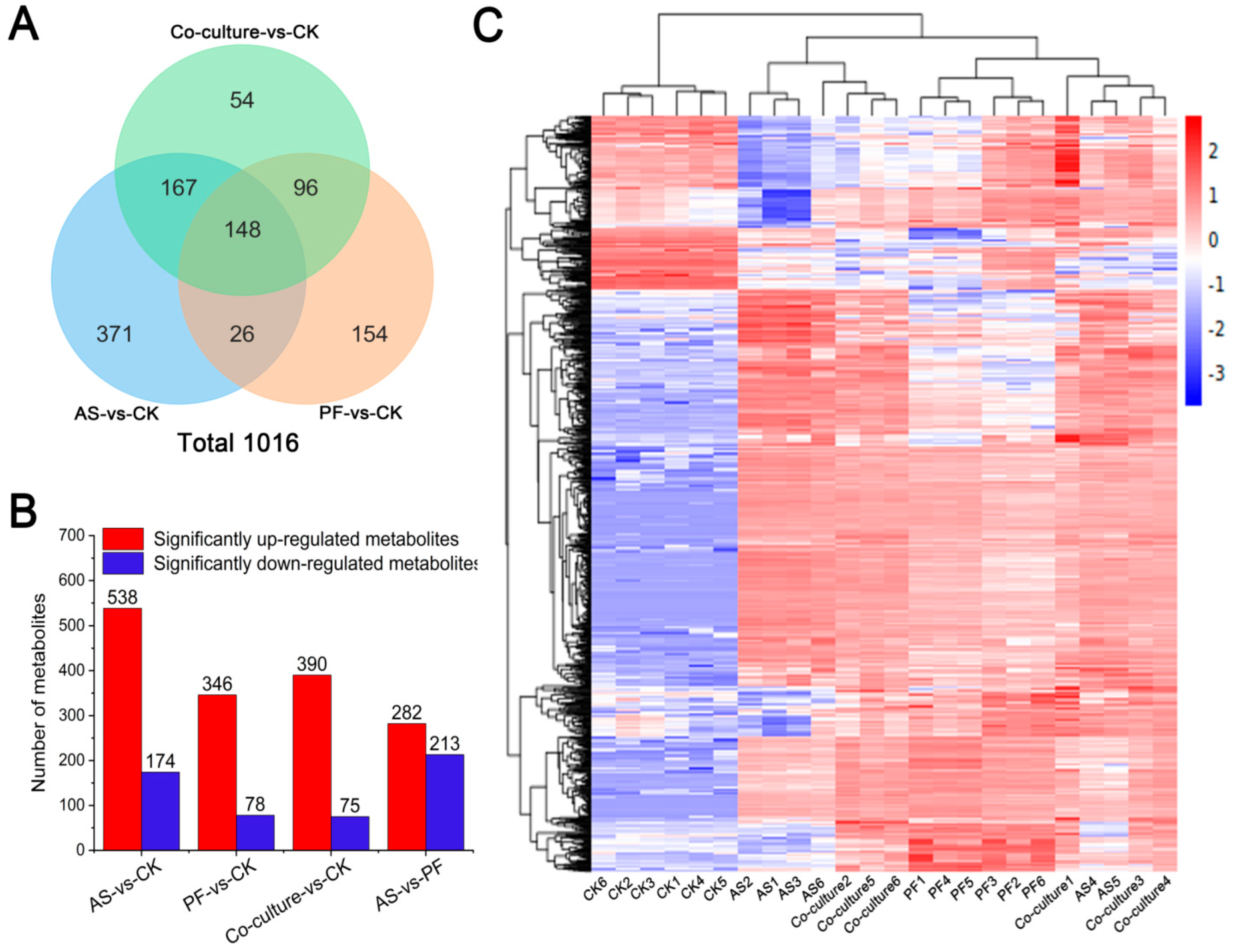
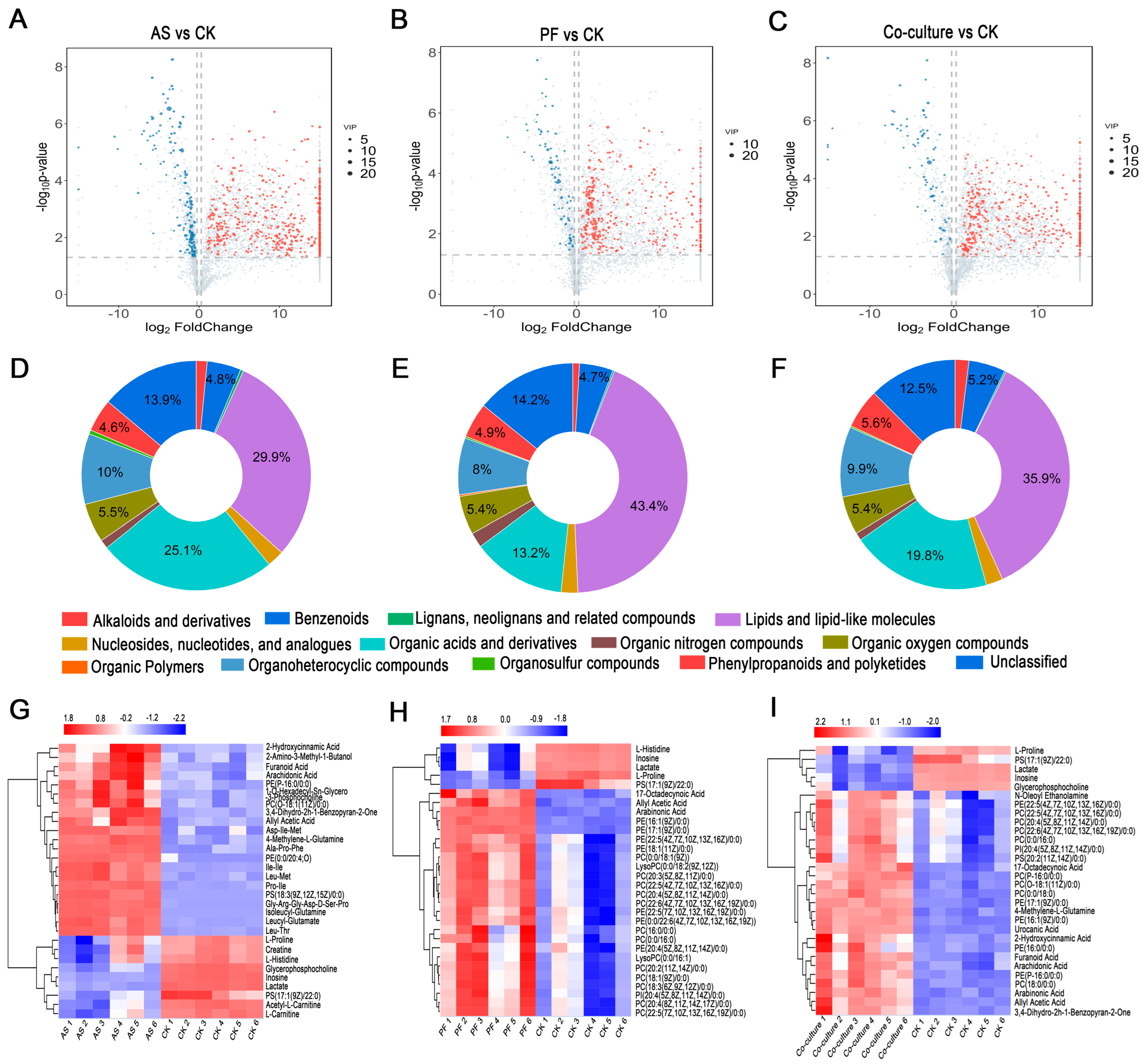
3.5.2. Differential Metabolites Analysis
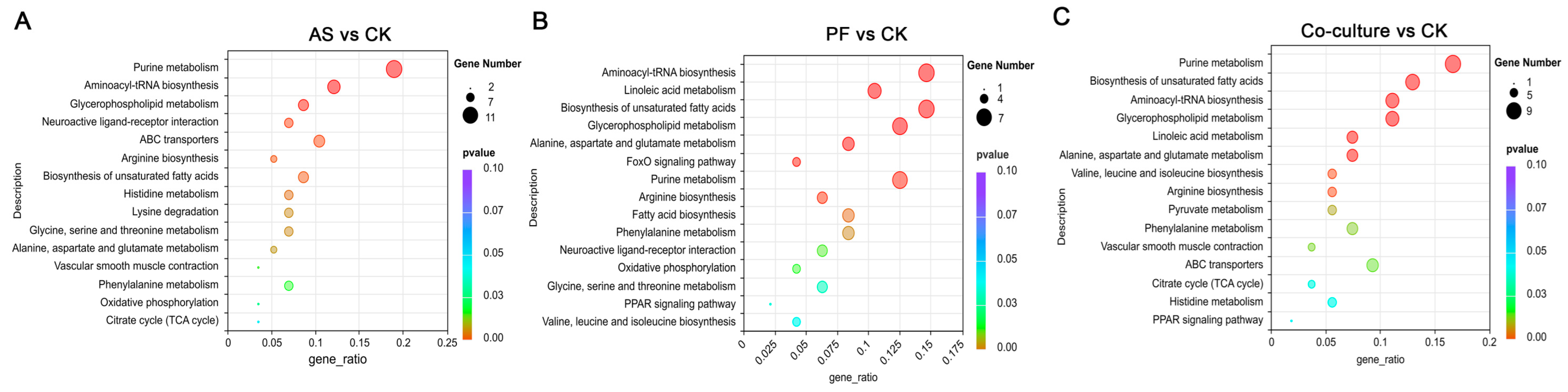
3.5.3. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
3.5.4. Potential Spoilage Biomarkers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TVB-N | Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen |
| TBARs | Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances |
References
- Bureau of Fisheries of the Ministry of Agriculture. China Fisheries Statistical Yearbook; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Hong, H.; Jia, S.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y. Effects of phytic acid and lysozyme on microbial composition and quality of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) fillets stored at 4 °C. Food Microbiol. 2020, 86, 103313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, R.; Gui, M.; Jiang, Z.; Li, P. Identification of the specific spoilage organism in farmed sturgeon (Acipenser baerii) fillets and its associated quality and flavour change during ice storage. Foods 2021, 10, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Huang, Z.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y. Application of Illumina-MiSeq high throughput sequencing and culture-dependent techniques for the identification of microbiota of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) treated by tea polyphenols. Food Microbiol. 2018, 76, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, F.; Jatt, A.-N.; Liu, H.; Niu, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Characterization of co-culture of Aeromonas and Pseudomonas bacterial biofilm and spoilage potential on refrigerated grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 71, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, H.; Lu, T.; Mou, Z. A transcriptome analysis focusing on splenic immune-related mciroRNAs of rainbow trout upon Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida infection. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2019, 91, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Xie, Z.; Xu, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhao, X.; Yang, H. Effect of slightly acid electrolysed water ice on metabolite and volatilome profile of shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) during cold storage. Food Control 2023, 145, 109421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Jiao, X.; Yan, B.; Zhang, N.; Huang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Fan, D. Changes in physicochemical properties of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) surimi during chilled storage: The roles of spoilage bacteria. Food Chem. 2022, 87, 132847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmid, N.A.; Heising, J.; Fogliano, V.; Dekker, M. Packaging design using mustard seeds as a natural antimicrobial: A study on inhibition of Pseudomonas fragi in liquid medium. Foods 2020, 9, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternisa, M.; Klancnik, A.; Mozina, S.S. Spoilage Pseudomonas biofilm with Escherichia coli protection in fish meat at 5 °C. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2019, 99, 4635–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Li, T. Effects of deletion of siderophore biosynthesis gene in Pseudomonas fragi on quorum sensing and spoilage ability. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 396, 110196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeyemi, O.A.; Alegbeleye, O.O.; Strateva, M.; Stratev, D. Understanding spoilage microbial community and spoilage mechanisms in foods of animal origin. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolívar, A.; Tarlak, F.; Costa, J.C.C.P.; Cejudo-Gómez, M.; Bover-Cid, S.; Zurera, G.; Pérez-Rodríguez, F. A new expanded modelling approach for investigating the bioprotective capacity of Latilactobacillus sakei CTC494 against Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat fish products. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, T.J.; Queller, D.C.; Strassmann, J.E. Context dependence in the symbiosis between Dictyostelium discoideum and Paraburkholderia. Evol. Lett. 2022, 6, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Ren, F.; Huang, Q.; Cheng, H.; Cun, Y.; Ni, Y.; Wu, W.; Xu, B.; Yang, Q.; Yang, L. Characterization and interactions of spoilage of Pseudomonas fragi C6 and Brochothrix thermosphacta S5 in chilled pork based on LC-MS/MS and screening of potential spoilage biomarkers. Food Chem. 2024, 444, 138562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Dou, H.; Teng, S.; Ye, K. Pseudomonas fragi and Pseudomonas lundensis drove the co-spoilage in chilled pork: Insights from the metabolome. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Huang, H.; Xu, Q. Microbial succession of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) filets during storage at 4 °C and its contribution to biogenic amines’ formation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 190, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, P.; Lanaridi, O.; Warth, B.; Ansari, K.M. Metabolomics as an emerging approach for deciphering the biological impact and toxicity of food contaminants: The case of mycotoxins. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2023, 64, 9859–9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Zhu, W.; Chen, S.; Zou, Y.; Xia, X. Studies on quality deterioration and metabolomic changes in oysters induced by spoilage bacteria during chilled storage. Foods 2025, 14, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Zhai, D.; Yang, H. Changes of metabolite profiles of fish models inoculated with Shewanella baltica during spoilage. Food Control 2021, 123, 107697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H.; Xu, Q.; Shi, C.; Luo, Y. Spoilage potential of three different bacteria isolated from spoiled grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) fifillets during storage at 4 °C. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zhang, D.; Morton, J.; Wang, S.; Chai, X.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, W.; Hou, C. Contribution of mono- and co-culture of Pseudomonas paralactis, Acinetobacter MN21 and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia to the spoilage of chill-stored lamb. Food Res. Int. 2024, 186, 114313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, S.; Wu, H.; Jatt, A.N.; Pan, Y.; Zeng, M. Quorum sensing involved in the spoilage process of the skin and flesh of vacuum-packaged farmed turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) stored at 4 °C. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, M2776–M2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Liao, M.; Han, Y. An effective deep learning fusion method for predicting the TVB-N and TVC contents of chicken breasts using dual hyperspectral imaging systems. Food Chem. 2024, 456, 139847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Xu, T.; Yan, Q.; Karsli, B.; Li, D.; Xie, J. Effect of temperature fluctuations on large yellow croaker fillets (Larimichthys crocea) in cold chain logistics: A microbiological and metabolomic analysis. J. Food Eng. 2025, 386, 112290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Wen, X.; Chen, L.; Shu, W.; Wang, Y.; Hoang, T.; Yang, H. Changes in texture, rheology and volatile compounds of golden pomfret sticks inoculated with Shewanella baltica during spoilage. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Guo, Z.; Qiao, R.; Liu, L.; Jatt, A.-N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C. Understanding the spoilage mechanism of refrigerated turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) using high-throughput sequencing combined with untargeted metabolomics. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 228, 118072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Xiao, X.; Cai, W.; Ding, Z.; Ma, J.; Lv, W.; Yang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, W. Unraveling the spoilage characteristics of refrigerated pork using high-throughput sequencing coupled with UHPLC-MS/MS-based non-targeted metabolomics. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Lei, Y.; Regenstein, J.M.; Luo, Y. Characterization of the microbial composition and quality of lightly salted grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) fillets with vacuum or modified atmosphere packaging. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 293, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xie, J.; Mei, J. Research progress regarding psychrotrophic Pseudomonas in aquatic products: Psychrophilic characteristics, spoilage mechanisms, detection methods, and control strategies. Foods 2025, 14, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, M.A.D.; Santana, T.N.D.; Pena, L.A.; Duarte, A.M.; dos Santos, L.C.; Alves, S.J.F.; Dias, R.M.; Oliveira, A.V.D.; Machado, S.G.; Eller, M.R. A comprehensive review on the prevalence and issues caused by Pseudomonas spp. in food. Food Control 2025, 177, 111428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Li, L.; Shen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, M. Effects of tea polyphenol treatments on the quality and microbiota of crisp grass carp fillets during storage at 4 °C. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Feng, L.; Lu, H.; Zhu, J. Metabolomics reveals spoilage characteristics and interaction of Pseudomonas lundensis and Brochothrix thermosphacta in refrigerated beef. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickramasinghe, N.N.; Ravensdale, J.; Coorey, R.; Chandry, S.P.; Dykes, G.A. The predominance of psychrotrophic Pseudomonads on aerobically stored chilled red meat. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1622–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romruen, O.; Karbowiak, T.; Auras, R.; Rawdkuen, S. Smart bilayer film: Quality monitoring for freshness of fish and minced pork delights. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2024, 44, 101299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, Y.; Wang, H.; Han, Y.; Hou, W. Changes in physicochemical properties, moisture distribution and volatile flavor compounds of yellow catfish: The roles of dominant spoilage bacteria. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ye, X.; Yang, Y. Spoilage potential characterization of Shewanella and Pseudomonas isolated from spoiled large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 2733-2015; National food safety standard - Fresh and frozen animalistic aquatic products. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Bekhit, A.E.D.A.; Holman, B.W.B.; Giteru, S.G.; Hopkins, D.L. Total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) and its role in meat spoilage: A review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 109, 280–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Yang, J.; Holman, B.W.B.; Tassou, C.C.; Papadopoulou, O.S.; Luo, X.; Zhu, L.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Exploration of the shelf-life difference between chilled beef and pork with similar initial levels of bacterial contamination. Meat Sci. 2024, 213, 109480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shao, L.; Gong, J.; Sheng, J.; Ning, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, H. Discovery of a temperature-dependent protease spoiling meat from Pseudomonas fragi: Target to myofibrillar and sarcoplasmic proteins rather than collagen. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 140155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milijasevic, J.B.; Milijasevic, M.; Lilic, S.; Djinovic-Stojanovic, J.; Nastasijevic, I.; Geric, T.; Del Nobile, M.A. Effect of vacuum and modified atmosphere packaging on the shelf life and quality of gutted rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during refrigerated storage. Foods 2023, 12, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Du, X.; Shen, Y.; Lao, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, L.; Du, Z. Evaluation of the distribution of adipose tissues in fish using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Aquaculture 2015, 448, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Yi, L.; Cheng, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, S. Lipidomics analysis reveals new insights into crisp grass carp associated with meat texture. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Gong, J.; Dong, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, H. Hydrolyzing collagen by extracellular protease Hap of Aeromonas salmonicida: Turning chicken by-products into bioactive resources. Food Chem. 2025, 471, 142778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solinho, J.; Santos, J.; Vázquez, M.; Pinheiro, R. Comparative study of preservation techniques for refrigerated Atlantic bonito fillets: Effects of modified atmosphere packaging, vacuum packaging, and alginate coating on shelf life and quality. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2025, 50, 101556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Q.; Tappi, S.; Braschi, G.; Picone, G.; Rocculi, P.; Laghi, L. Comparative metabolomic analysis of minced grey mullet (Mugil cephalus) pasteurized by high hydrostatic pressure (HHP) during chilled storage. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Shang, B.; Yang, W.; Duan, X.; Sun, H. Metabolomic analysis reveals insights into deterioration of rice quality during storage. Foods 2022, 11, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacaria, J.; Delamare, A.P.L.; Costa, S.O.P.; Echeverrigaray, S. Diversity of extracellular proteases among Aeromonas determined by zymogram analysis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Dong, Y.; Chen, S.; Sheng, J.; Cai, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, H. Revealing extracellular protein profile and excavating spoilage-related proteases of Aeromonas salmonicida based on multi-omics investigation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 130916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, J.; Tu, M.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Rao, Y.; Rao, L.; Gui, M. Complete genome sequence provides information on quorum sensing related spoilage and virulence of Aeromonas salmonicida GMT3 isolated from spoiled sturgeon. Food Res. Int. 2024, 196, 115039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prediger, K.C.; Surek, M.; Dallagassa, C.B.; Assis, F.E.A.; Piantavini, M.S.; Souza, E.M.; Pedrosa, F.O.; Farah, S.M.S.S.; Alberton, D.; Fadel-Picheth, C.M.T. Utilization of carbon sources by clinical isolates of Aeromonas. Can. J. Microbio. 2017, 63, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Zhang, L.; Meng, Z.; Di, W.; Han, X.; Yi, H.; Cui, Y. Lipolytic psychrotrophic bacteria and lipase heat-resistant property in bovine raw milk of North China. J. Food Process. Pres. 2017, 41, e13289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmohan, S.; Dodd, C.E.R.; Waites, W.M. Enzymes from isolates of Pseudomonas fluorescens involved in food spoilage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 93, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, G.; Li, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhang, B.; Wu, W.; Lv, C.; Sun, T.; Zhou, T.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Characterization of Pseudomonas spp. contamination and in situ spoilage potential in pasteurized milk production process. Food Res. Int. 2024, 188, 114463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Tiwari, S.K. Plantaricin LD1: A bacteriocin produced by food isolate of Lactobacillus plantarum LD1. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2014, 172, 3354–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Gao, P.; Meng, A.; Fu, Y.; Chen, H.; Huang, M. The spoilage characteristics and key metabolites of Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus plantarum in ready-to-eat chicken feet. Food Res. Int. 2025, 214, 116689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.; Hughes, J.; Piyasiri, U.; Zhang, Y.; Kaur, M.; Li, Y.; Mellor, G.; Stark, J. Volatile and non-volatile metabolite changes in 140-day stored vacuum packaged chilled beef and potential shelf life markers. Meat Sci. 2020, 161, 108016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Song, S.; Wang, Z.; Kong, C.; Luo, Y. The role of microorganisms in the degradation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in chill-stored common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fillets. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, G.; Xue, P.; Dong, X.; Xia, Y.; Regenstein, J.; Du, M.; Sun, L. Spoilage microbes’ effect on freshness and IMP degradation in sturgeon fillets during chilled storage. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 101008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Xie, J. Coculture of Acinetobacter johnsonii and Shewanella putrefaciens contributes to the ABC transporter that impacts cold adaption in the aquatic food storage environment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 10605–10615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Y.; Luo, L. LC-MS/MS-based peptidomics and metabolomics reveal different metabolic patterns of common spoilage bacteria in grass carp flesh. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, G.; Sun, S.; Fan, C.; Feng, X.; Xiong, P. Biosynthetic pathway and metabolic engineering of succinic acid. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2022, 10, 843887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Jo, C. A non-destructive predictive model for estimating the freshness/spoilage of packaged chicken meat using changes in drip metabolites. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 419, 110738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peifer, S.; Barduhn, T.; Zimmet, S.; Volmer, D.A.; Heinzle, E.; Schneider, K. Metabolic engineering of the purine biosynthetic pathway in Corynebacterium glutamicum results in increased intracellular pool sizes of IMP and hypoxanthine. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Guo, S.; Xue, R.; Liu, L.; Jatt, A.-N.; Zhang, C. Metabolomics Analysis of the Spoilage Characteristics of Pseudomonas fragi and Aeromonas salmonicida Co-Culture in Refrigerated Grass Carp. Foods 2025, 14, 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183228
Liu Y, Guo S, Xue R, Liu L, Jatt A-N, Zhang C. Metabolomics Analysis of the Spoilage Characteristics of Pseudomonas fragi and Aeromonas salmonicida Co-Culture in Refrigerated Grass Carp. Foods. 2025; 14(18):3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183228
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yanlong, Shuya Guo, Ruyan Xue, Li Liu, Abdul-Nabi Jatt, and Caili Zhang. 2025. "Metabolomics Analysis of the Spoilage Characteristics of Pseudomonas fragi and Aeromonas salmonicida Co-Culture in Refrigerated Grass Carp" Foods 14, no. 18: 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183228
APA StyleLiu, Y., Guo, S., Xue, R., Liu, L., Jatt, A.-N., & Zhang, C. (2025). Metabolomics Analysis of the Spoilage Characteristics of Pseudomonas fragi and Aeromonas salmonicida Co-Culture in Refrigerated Grass Carp. Foods, 14(18), 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183228




