The Metabolic Network of Chilled Yak Meat During Storage Was Constructed Based on Metabolomics Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Determination of the Total Viable Count (TVC), Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N), and Metabolites of Yak Meat
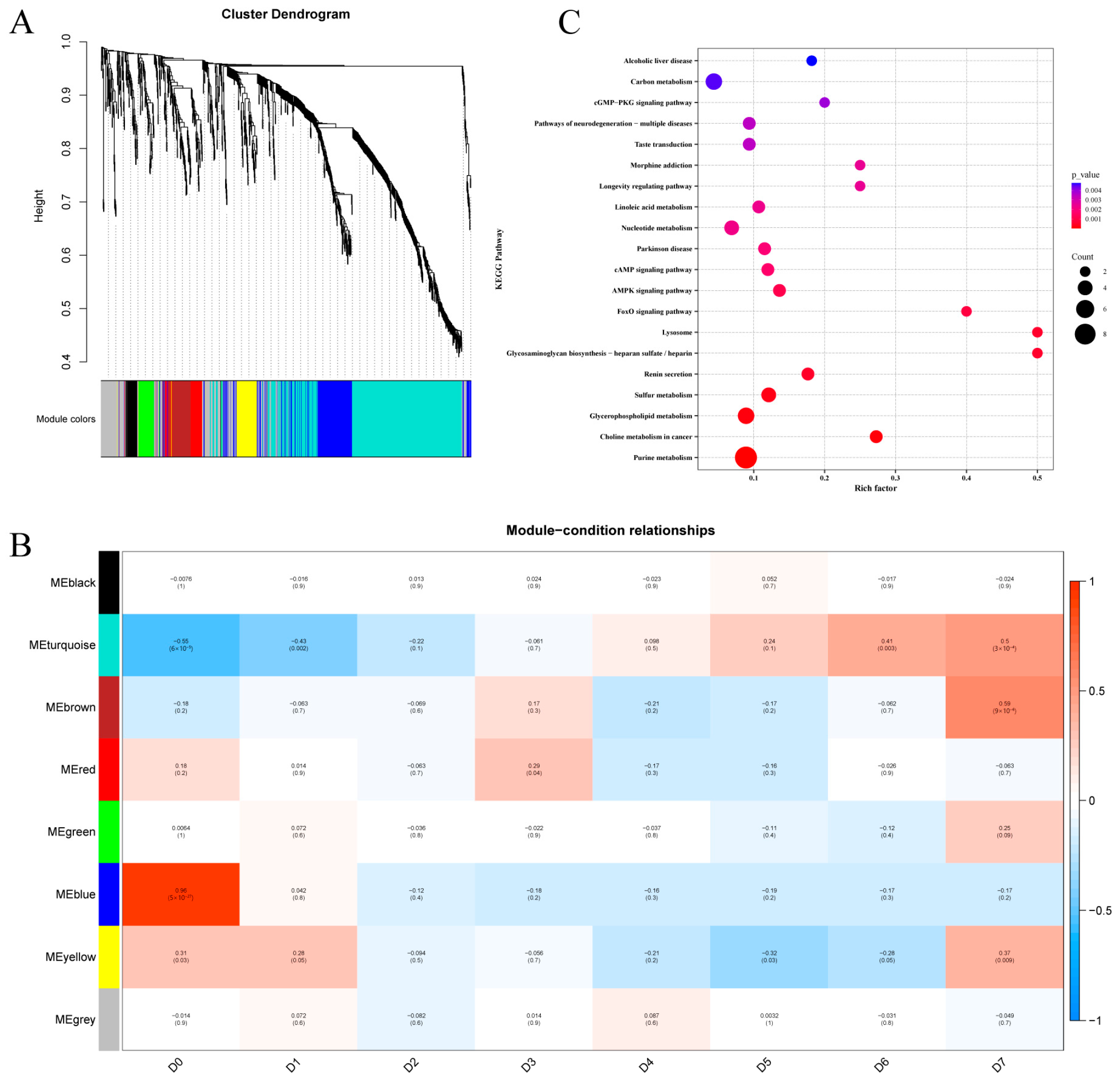
2.4. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
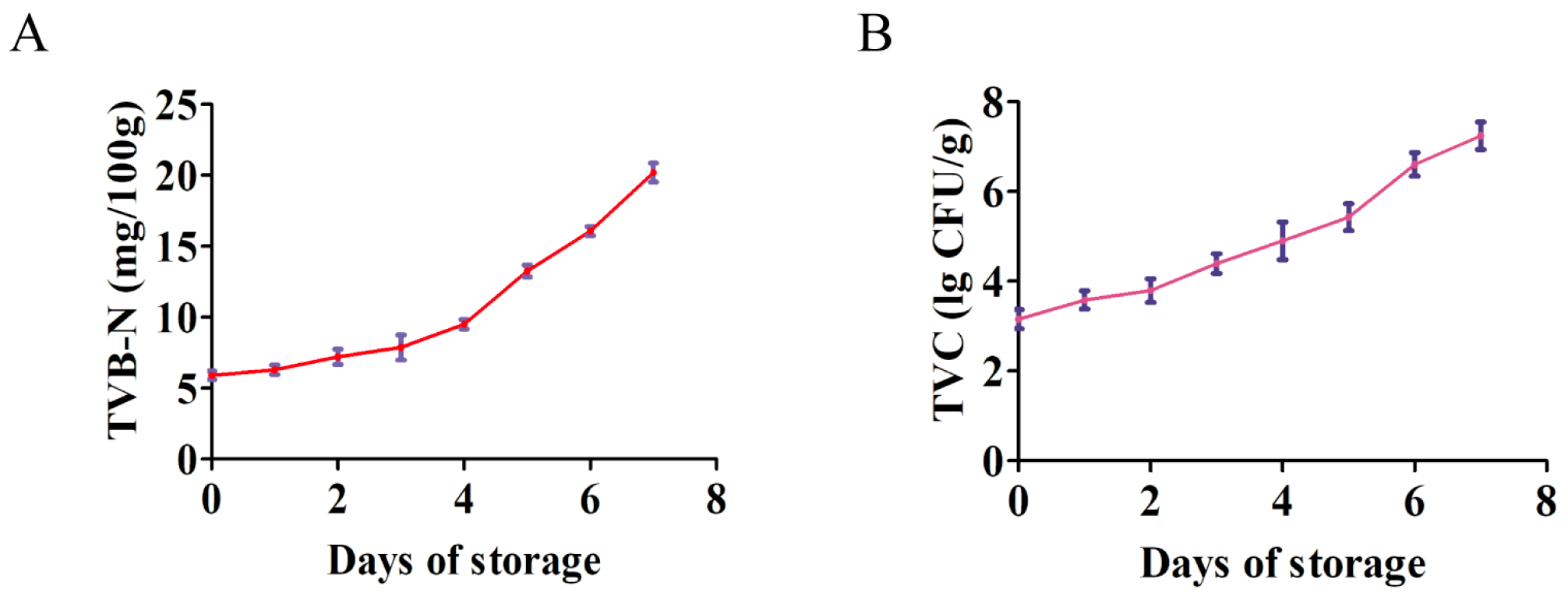
3.1. Changes in the TVB-N and TVC of Yak Meat During 4 °C Storage
3.2. LC-MS/MS Analysis of the Non-Volatile Metabolites in the Yak Meat Stored at 4 °C
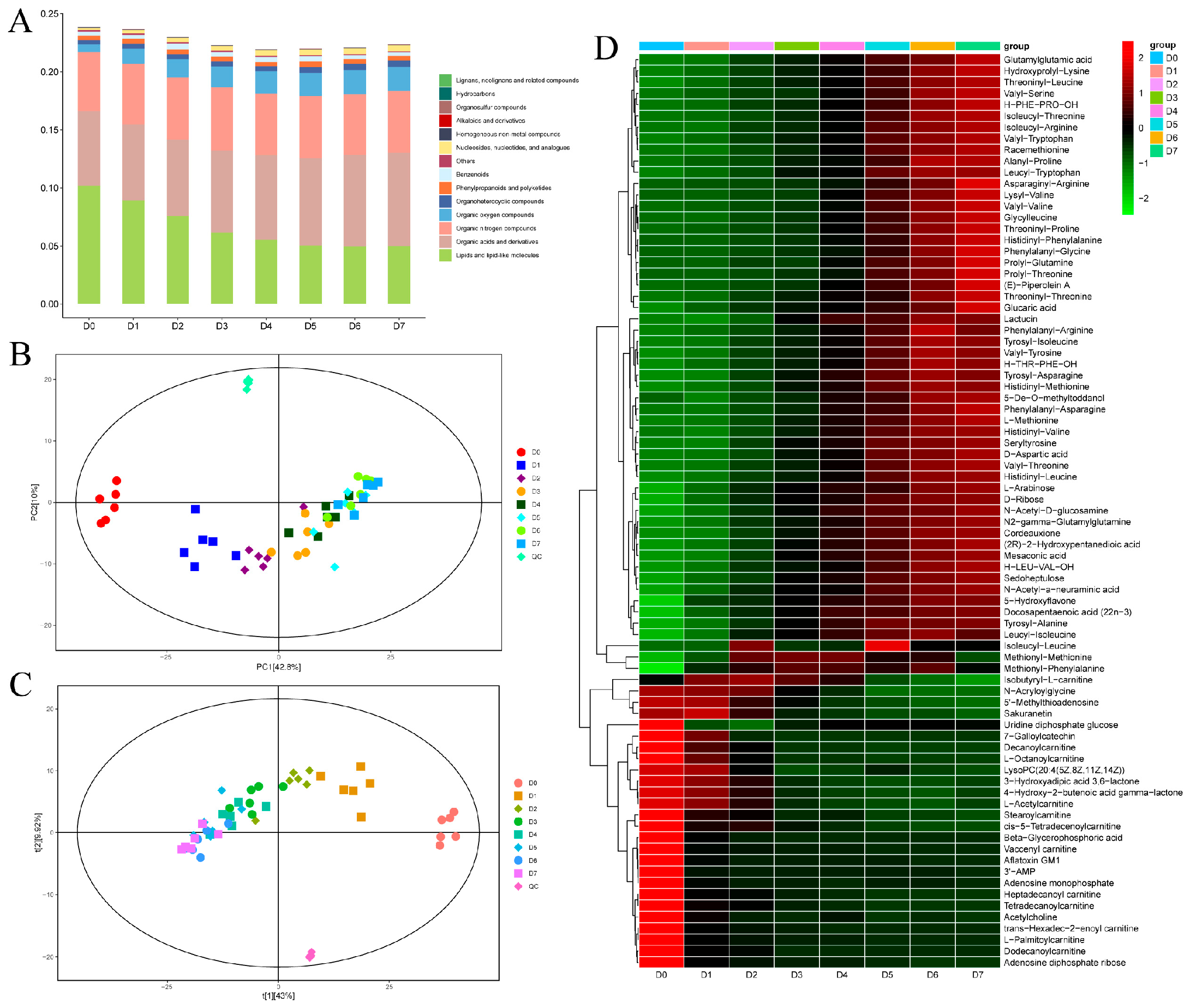
3.2.1. Storage Time-Dependent Non-Volatile Metabolite Profiles of the Yak Meat Stored at 4 °C
3.2.2. PCA and PLS-DA
3.2.3. Changes in the Levels of Non-Volatile Metabolites in Chilled Yak Meat
3.3. HS-GC-IMS Analysis of the VOCs in the Yak Meat Stored at 4 °C
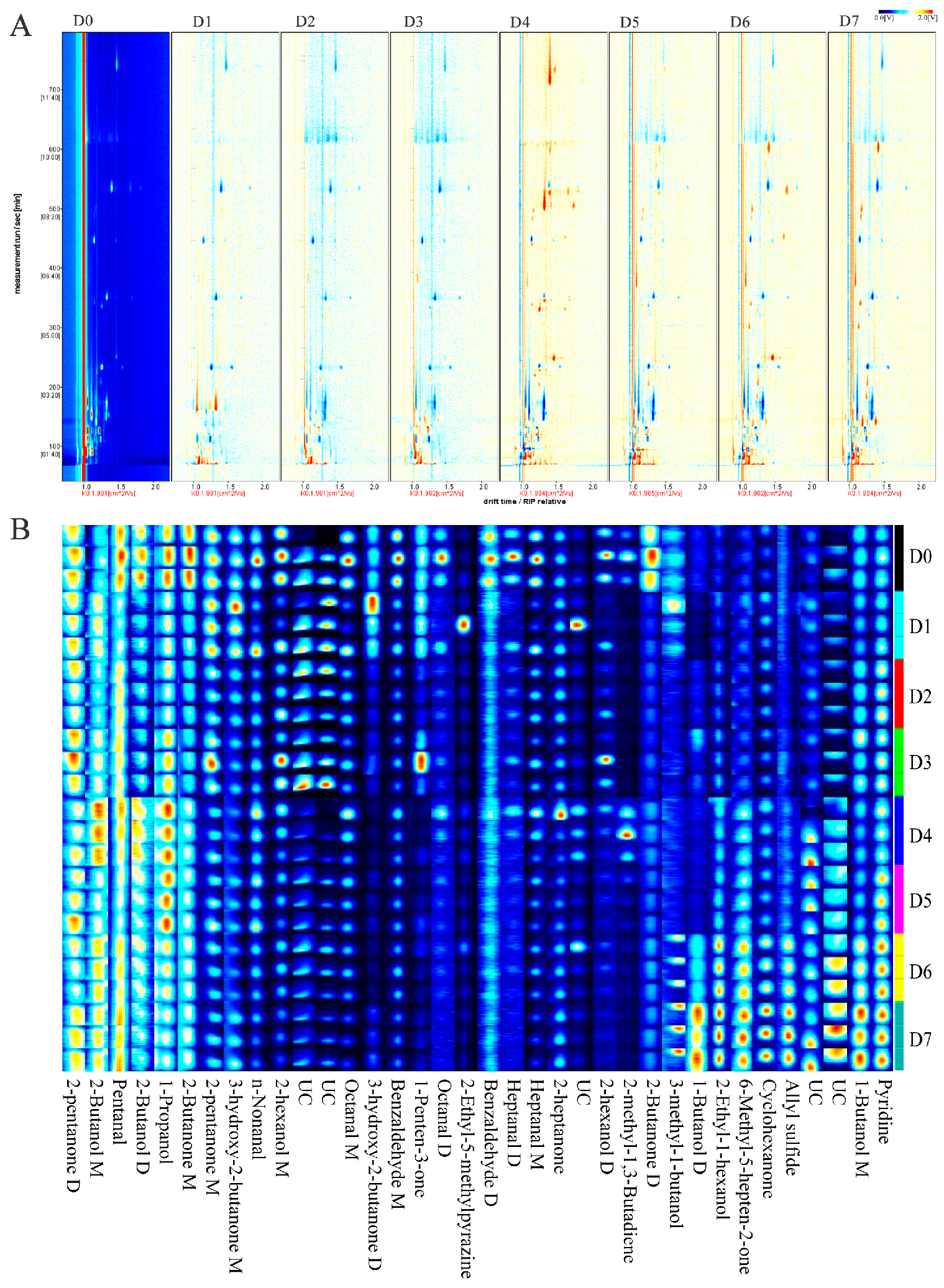
3.3.1. Storage Time-Dependent Topographic Plots of Chilled Yak Meat
3.3.2. VOC Variations in Chilled Yak Meat
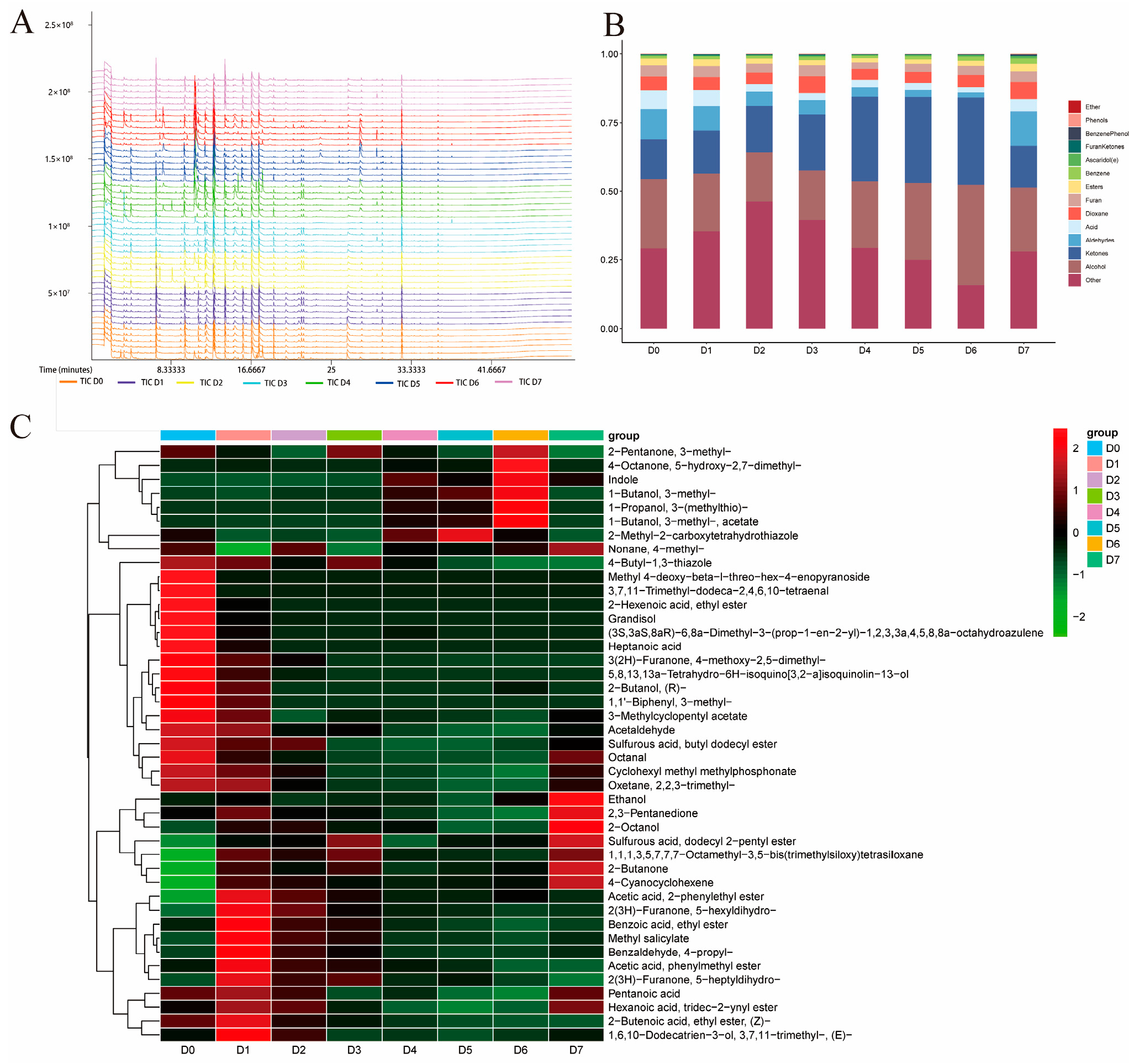
3.4. GC-MS Analysis of the VOCs in Chilled Yak Meat
3.5. WGCNA
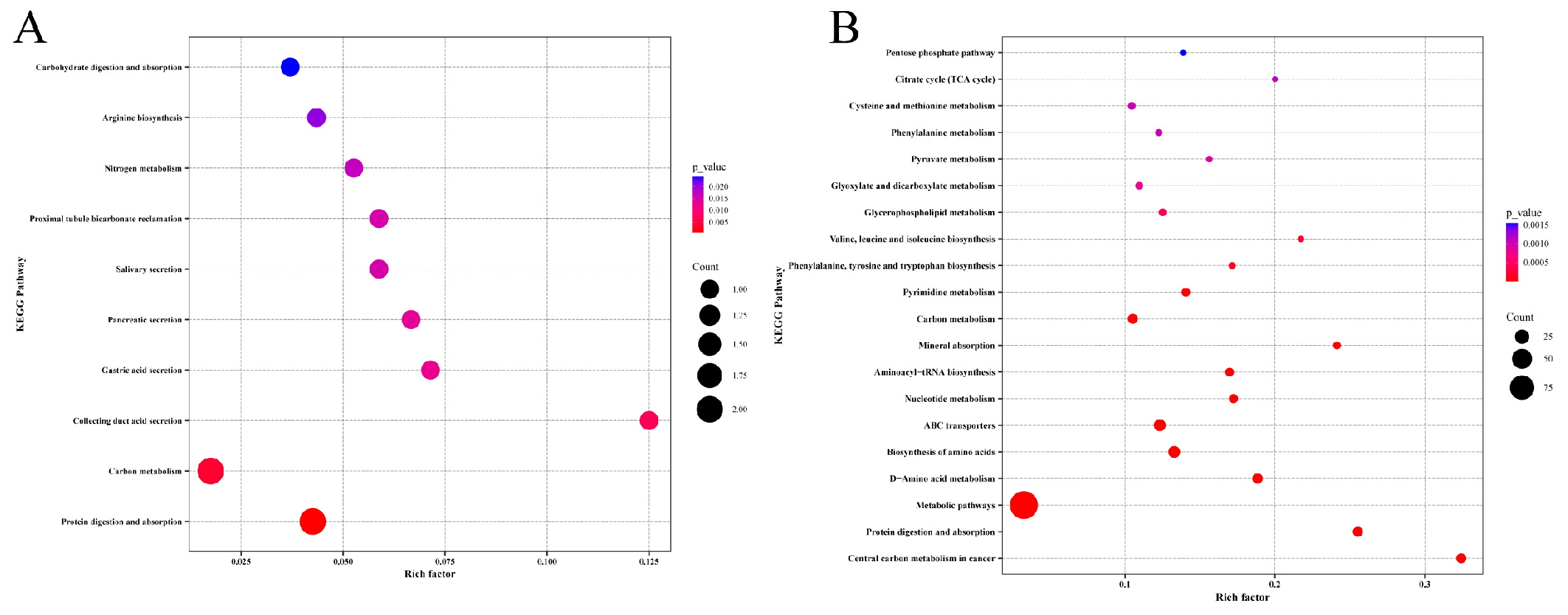
3.6. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Storage Time-Specific Modules
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, H.; Yu, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Mei, C.; Abbas Raza, S.H.; Cheng, G.; Zan, L. Comprehensive Analysis of Transcriptome and Metabolome Reveals Regulatory Mechanism of Intramuscular Fat Content in Beef Cattle. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 2911–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, G.; Paul, V.; Biswas, T.K.; Chouhan, V.S.; Das, P.J.; Sejian, V. Adaptation strategies of yak to seasonally driven environmental temperatures in its natural habitat. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2018, 62, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zong, W.; Zhao, S.; Qie, M.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y. Nutrition and edible characteristics, origin traceability and authenticity identification of yak meat and milk: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 139, 104133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.P.; Krishnan, G.; Doley, J.; Bhattacharya, D.; Deb, S.M.; Chakravarty, P.; Das, P.J. Establishing gene Amelogenin as sex-specific marker in yak by genomic approach. J. Genet. 2019, 98, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pei, J.; Bao, P.; Cao, M.; Guo, S.; Song, R.; Song, W.; Liang, C.; Yan, P.; Guo, X. Mitogenomic diversity and phylogeny analysis of yak (Bos grunniens). BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wan, M.; Yan, H.; Chang, X.; Liu, J. Comparative study on the meat nutritional and sensory quality characteristics of Maiwa yak and Simmental cattle. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2021, 53, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Gao, X.; Shi, B.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Luo, Y. Sequence and haplotypes of ankyrin 1 gene (ANK1) and their association with carcass and meat quality traits in yak. Mamm. Genome 2021, 32, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Guo, S.; Jiang, A. Study on New Preserving Method of Chilled Chicken. Meat Res. 2009, 23, 81–83. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y. Nondestructive measurement of total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) in pork meat by integrating near infrared spectroscopy, computer vision and electronic nose techniques. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Dong, K.; Wang, Q.; Huang, X.; Wang, G.; An, F.; Luo, Z.; Luo, P. Changes in volatile flavor of yak meat during oxidation based on multi-omics. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parastar, H.; Weller, P. Feature selection and extraction strategies for non-targeted analysis using GC-MS and GC-IMS: A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1343, 343635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, P.; Liao, L.; Qin, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y. Characteristic fingerprints and volatile flavor compound variations in Liuyang Douchi during fermentation via HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Lv, X.; Ma, J.; Lei, M.; Feng, C.; Lu, W.; Ji, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Volatile-compound fingerprinting and discrimination of positional isomers in stamp-pad ink tracing using HS-GC-IMS combined with multivariate statistical analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Cai, F.; Luo, B.X.; Gu, R.; Ahmed, S.; Long, C. Variation of Microbiological and Biochemical Profiles of Laowo Dry-Cured Ham, an Indigenous Fermented Food, during Ripening by GC-TOF-MS and UPLC-QTOF-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 8925–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, C.; Ye, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Xu, B. Evolution of Volatile Compounds and Spoilage Bacteria in Smoked Bacon during Refrigeration Using an E-Nose and GC-MS Combined with Partial Least Squares Regression. Molecules 2018, 23, 3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mey, E.; De Klerck, K.; De Maere, H.; Dewulf, L.; Derdelinckx, G.; Peeters, M.C.; Fraeye, I.; Vander Heyden, Y.; Paelinck, H. The occurrence of N-nitrosamines, residual nitrite and biogenic amines in commercial dry fermented sausages and evaluation of their occasional relation. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 19477-2018; Operating Procedures of Slaughtering for Livestock and Poultry—Cattle. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB 4789.2-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Microbiological Examination of Food—Enumeration of Total Aerobic Bacterial Count. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.228-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Volatile Base Nitrogen in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Kang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiong, L.; Pei, J.; Ding, Z.; Guo, S.; Cao, M.; Bao, P.; Wu, X.; Chu, M. Application of GC-IMS, GC-MS, and LC-MS/MS techniques to a comprehensive systematic study on the flavor characteristics of different muscles in the yak. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, S. Study on the nutrient and flavor of Datong yak meat. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 35, 106–110+113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pophiwa, P.; Webb, E.C.; Frylinck, L. A review of factors affecting goat meat quality and mitigating strategies. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 183, 106035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhit, A.A.-O.; Giteru, S.A.-O.; Holman, B.A.-O.; Hopkins, D.A.-O. Total volatile basic nitrogen and trimethylamine in muscle foods: Potential formation pathways and effects on human Health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 3620–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, X.; Cao, M.; Wu, X.; Xiong, L.; Bao, P.; Chu, M.; Liang, C.; Yan, P.; Pei, J.; et al. The transcriptome-wide N6-methyladenosine (m(6)A) map profiling reveals the regulatory role of m(6)A in the yak ovary. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, B.W.B.; Bekhit, A.E.A.; Waller, M.; Bailes, K.L.; Kerr, M.J.; Hopkins, D.L. The association between total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) concentration and other biomarkers of quality and spoilage for vacuum packaged beef. Meat Sci. 2021, 179, 108551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, D.; Xu, W.; Yu, Q. Research on growth of Yersinia enterocolitica in chilled chicken. Food Ferment. Ind. 2016, 42, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.G.; Yoon, Y.; Park, J.N.; Han, I.J.; Song, B.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, W.G.; Hwang, H.J.; Han, S.B.; Lee, J.W. Effects of gamma irradiation and electron beam irradiation on quality, sensory, and bacterial populations in beef sausage patties. Meat Sci. 2010, 85, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ai, Q.; Zhang, D. Changes in Microflora on Fresh Mutton during Chilled Storage. Food Sci. 2015, 36, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ji, Z.; Liu, X.; Shi, C.; Yang, X. Non-destructive determination of chemical and microbial spoilage indicators of beef for freshness evaluation using front-face synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, B.; Qiao, X.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Qu, C. Changes in Volatile Components of Fresh Beef during Cold Storage. Meat Res. 2016, 30, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhan, J.; Tang, X.; Li, T.; Duan, S. Characterization and identification of pork flavor compounds and their precursors in Chinese indigenous pig breeds by volatile profiling and multivariate analysis. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, A. A metabolomics-based approach investigates volatile flavor formation and characteristic compounds of the Dahe black pig dry-cured ham. Meat Sci. 2019, 158, 107904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Xi, B.; He, X.; Yang, X.; Li, W. Analysis of volatile compounds and flavor fingerprint in Jingyuan lamb of different ages using gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS). Meat Sci. 2021, 175, 108449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Luan, H.; Bu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Changes in taste substances during fermentation of fish sauce and the correlation with protease activity. Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.J.; Schieber, A.; Gänzle, M.G. Formation of taste-active amino acids, amino acid derivatives and peptides in food fermentations—A review. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Yang, X.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, B.G.; Chen, H.T.; Sun, Y. Comparison of non-volatile umami components in chicken soup and chicken enzymatic hydrolysate. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Jo, C.; Tariq, M.R. Meat flavor precursors and factors influencing flavor precursors—A systematic review. Meat Sci. 2015, 110, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbowicz, K.; Liu, Z.; Alseekh, S.; Tieman, D.; Taylor, M.; Kuhalskaya, A.; Ofner, I.; Zamir, D.; Klee, H.J.; Fernie, A.R.; et al. Quantitative Trait Loci Analysis Identifies a Prominent Gene Involved in the Production of Fatty Acid-Derived Flavor Volatiles in Tomato. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 1147–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Cui, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, J.; Liu, L.; Wen, J.; Zhao, G. Fatty acid metabolism-related genes are associated with flavor-presenting aldehydes in Chinese local chicken. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 902180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldrá, F.; Flores, M. The role of muscle proteases and lipases in flavor development during the processing of dry-cured ham. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1998, 38, 331–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Liang, D.; Hu, Y.; Xue, Q. Volatile Flavor Components of Sanchuan Ham and Air-Dried Ham. Meat Res. 2021, 35, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Bai, L.; Feng, X.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhang, D.; Yao, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y. Characterization of Jinhua ham aroma profiles in specific to aging time by gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS). Meat Sci. 2020, 168, 108178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, G.A.-O.; Murphy, R.; Butts, C.; Brough, L.; Whelan, K.; Coad, J. Habitual dietary fibre intake influences gut microbiota response to an inulin-type fructan prebiotic: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over, human intervention study. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, M.; Jiao, L.; Sun, P.; Betancor, M.B.; Tocher, D.R.; Zhou, Q. Modification of nutritional values and flavor qualities of muscle of swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus): Application of a dietary lipid nutrition strategy. Food Chem. 2020, 308, 125607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Rubin, L.J.; D’Souza, L.A. Meat flavor volatiles: A review of the composition, techniques of analysis, and sensory evaluation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1986, 24, 141–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timón, M.L.; Ventanas, J.; Carrapiso, A.I.; Jurado, A.; García, C. Subcutaneous and intermuscular fat characterisation of dry-cured Iberian hams. Meat Sci. 2001, 58, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migita, K.; Iiduka, T.; Tsukamoto, K.; Sugiura, S.; Tanaka, G.; Sakamaki, G.; Yamamoto, Y.; Takeshige, Y.; Miyazawa, T.; Kojima, A.; et al. Retort beef aroma that gives preferable properties to canned beef products and its aroma components. Anim. Sci. J. 2017, 88, 2050–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Long, J.; Liu, J.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. Fermentation Characteristics, Antinutritional Factor Level and Flavor Compounds of Soybean Whey Yogurt. Foods 2024, 13, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliani, M.; Farmer, L.J.; Kennedy, J.T.; Moss, B.W.; Gordon, A. Post-slaughter changes in ATP metabolites, reducing and phosphorylated sugars in chicken meat. Meat Sci. 2013, 94, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Erasmus, S.; Yang, P.; Huang, F.; Zhang, C.; van Ruth, S. Establishing the relations of characteristic aroma precursors and volatile compounds for authenticating Tibetan pork. Food Chem. 2023, 427, 136717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Xiao, M.; Hu, H.; Yu, S.; Xie, F. Metabolic profiles and potential antioxidant mechanisms of hawk tea. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Bassey, A.P.; Zhou, G. Molecular Changes of Meat Proteins During Processing and Their Impact on Quality and Nutritional Values. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 14, 85–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Guo, S.; Xiong, L.; Wu, X.; Bao, P.; Kang, Y.; Cao, M.; Ding, Z.; Hu, L.; Liang, C.; et al. The Metabolic Network of Chilled Yak Meat During Storage Was Constructed Based on Metabolomics Technology. Foods 2025, 14, 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183173
Wang X, Guo S, Xiong L, Wu X, Bao P, Kang Y, Cao M, Ding Z, Hu L, Liang C, et al. The Metabolic Network of Chilled Yak Meat During Storage Was Constructed Based on Metabolomics Technology. Foods. 2025; 14(18):3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183173
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xingdong, Shaoke Guo, Lin Xiong, Xiaoyun Wu, Pengjia Bao, Yandong Kang, Mengli Cao, Ziqiang Ding, Liyan Hu, Chunnian Liang, and et al. 2025. "The Metabolic Network of Chilled Yak Meat During Storage Was Constructed Based on Metabolomics Technology" Foods 14, no. 18: 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183173
APA StyleWang, X., Guo, S., Xiong, L., Wu, X., Bao, P., Kang, Y., Cao, M., Ding, Z., Hu, L., Liang, C., Pei, J., & Guo, X. (2025). The Metabolic Network of Chilled Yak Meat During Storage Was Constructed Based on Metabolomics Technology. Foods, 14(18), 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183173




