Process Optimization for Polyphenol Extraction from Macroalgae Residues and Assessment of Their Compositions, Antioxidant Activities, and Glycosidase Inhibition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.1.1. Samples
2.1.2. Reagents and Equipment
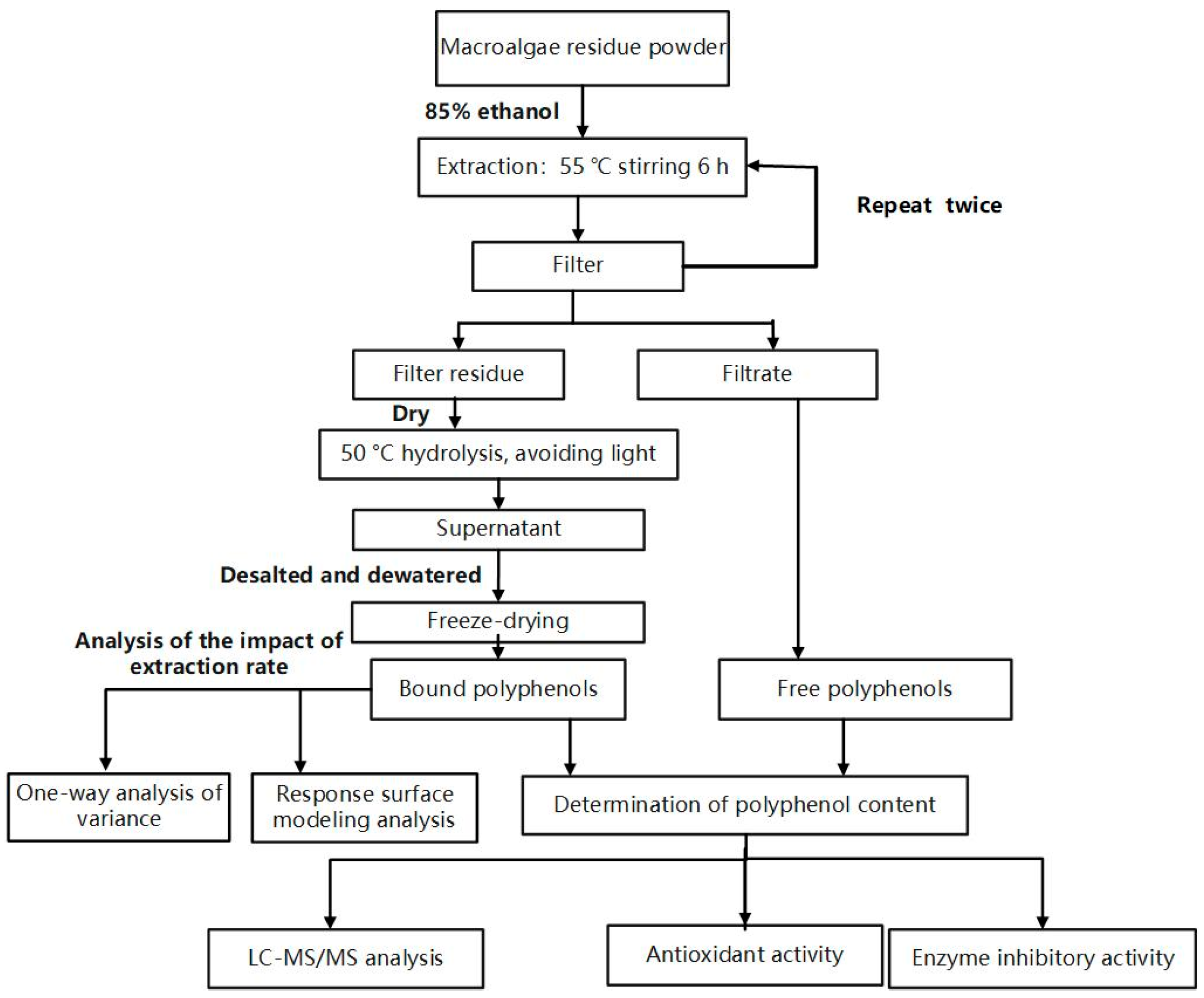
2.2. Extraction of FPs
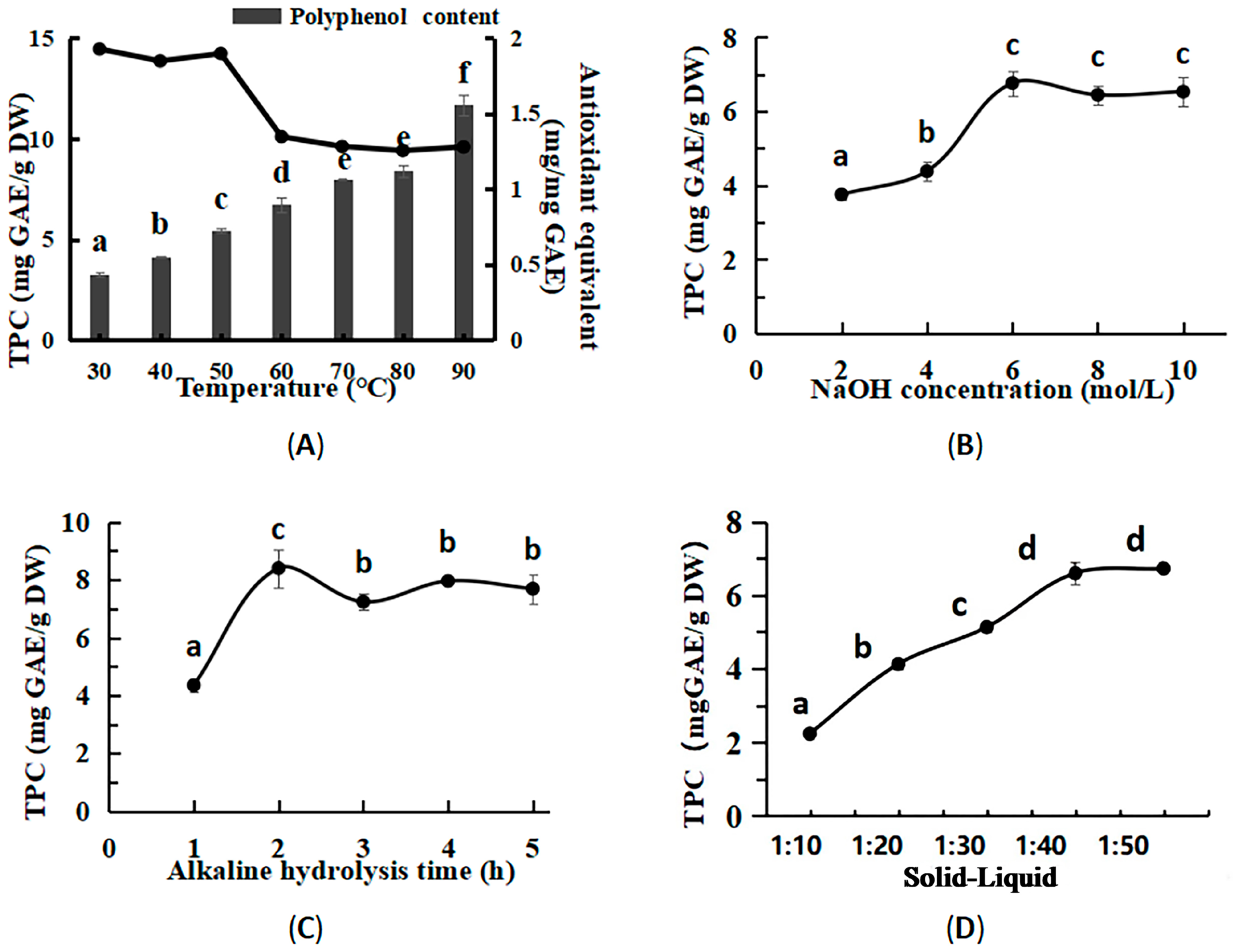
2.3. Single-Factor Extraction Experiments for BPs
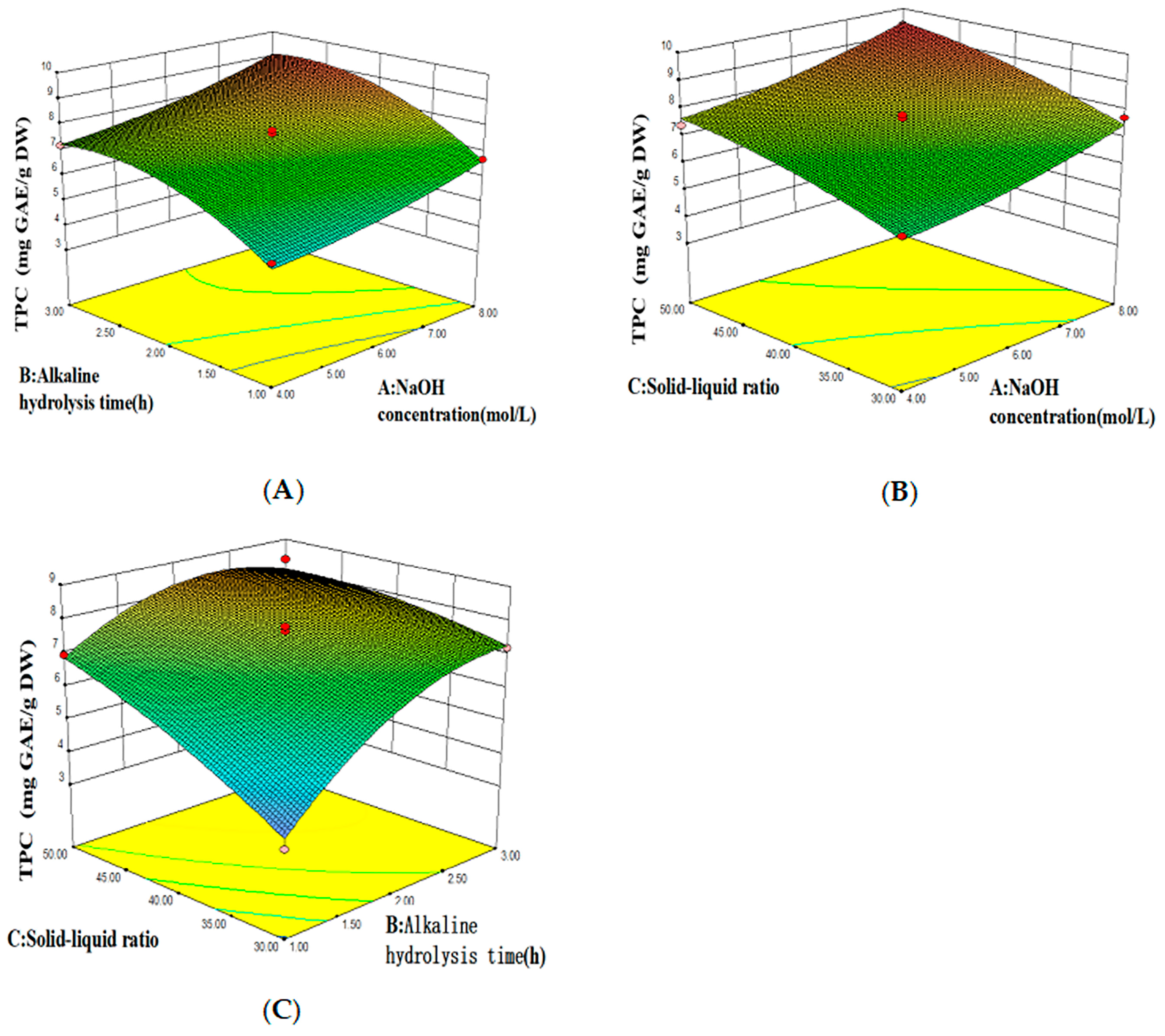
2.4. Optimization of Extraction Conditions and Quantification of Total Phenolic Contents
2.5. Qualitative Analysis of Phenolic Compounds by HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS
2.6. Antioxidant Activity and Glycosidase Activity Inhibition Assay
2.6.1. Antioxidant Activity Assay
2.6.2. Glycosidase Activity Inhibition Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Quantification of Free Polyphenols from the Macroalgae Residue
3.2. Optimized Conditions for Bound Polyphenols
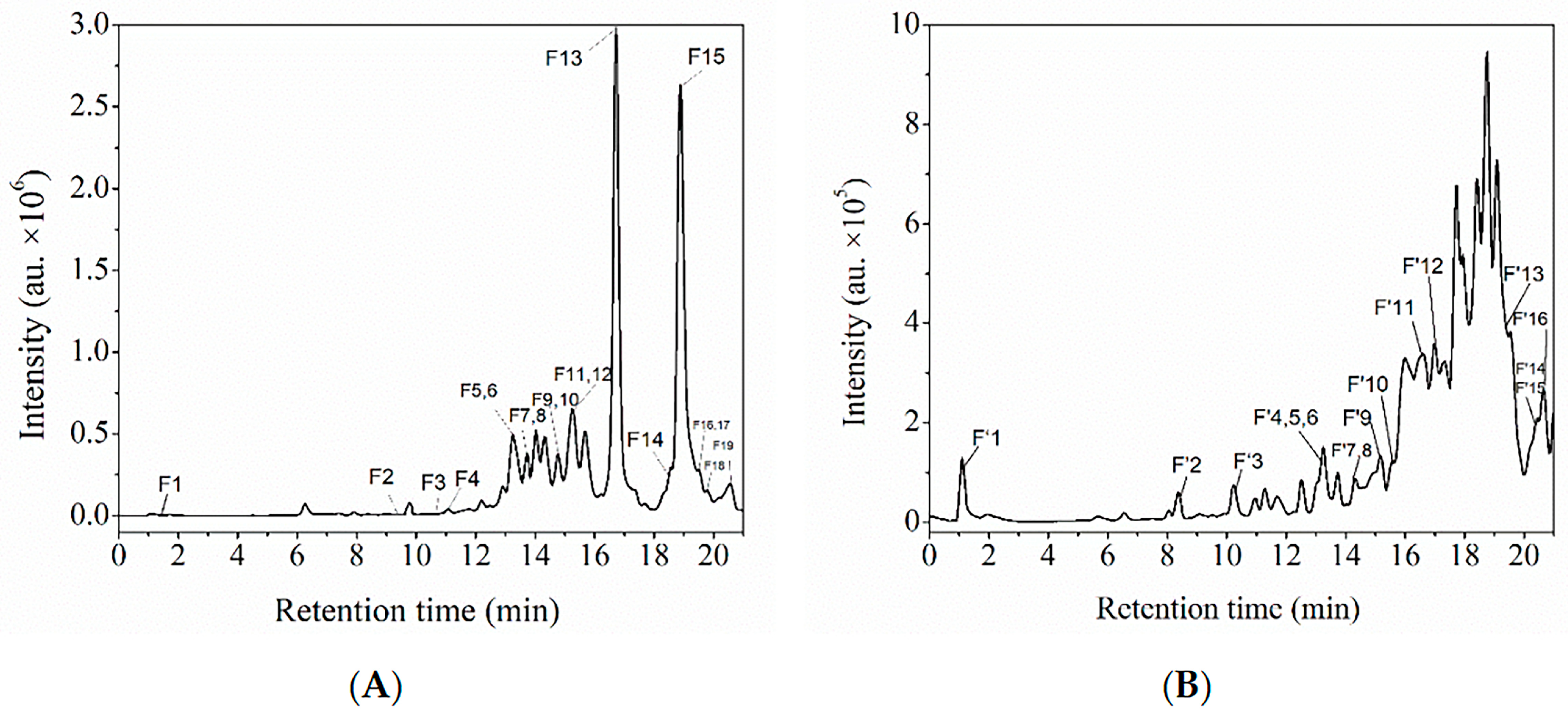
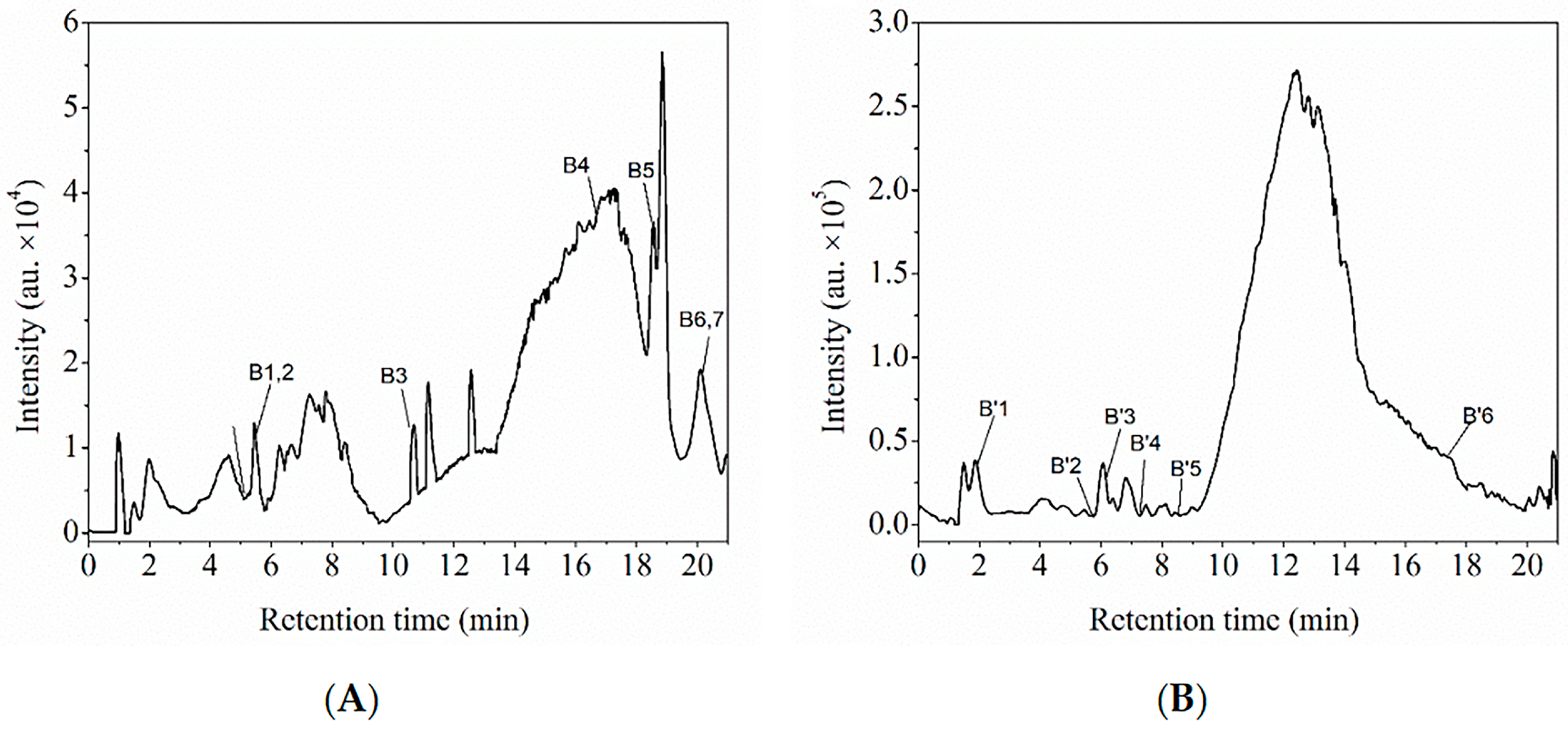
3.3. Characterization of the Two Polyphenol Extracts
Characterization of Polyphenol Extracts by HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS and Comparison with MSn Data from an Online Database
3.4. Antioxidant Activity and Inhibitory Effect on Glycosidase Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Besednova, N.N.; Andryukov, B.G.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Kryzhanovsky, S.P.; Kuznetsova, T.A.; Fedyanina, L.N.; Makarenkova, I.D.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. Algae Polyphenolic Compounds and Modern Antibacterial Strategies: Current Achievements and Immediate Prospects. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, A.; Garima; Bharadvaja, N. A Comprehensive Review on Algal Nutraceuticals as Prospective Therapeutic Agent for Different Diseases. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Silva, J.; Pinteus, S.; Gaspar, H.; Alpoim, M.C.; Botana, L.M.; Pedrosa, R. From Marine Origin to Therapeutics: The Antitumor Potential of Marine Algae-Derived Compounds. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbalace, M.C.; Malaguti, M.; Giusti, L.; Lucacchini, A.; Hrelia, S.; Angeloni, C. Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Marine Algae in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo-Shady, A.M.; Gheda, S.F.; Ismail, G.A.; Cotas, J.; Pereira, L.; Abdel-Karim, O.H. Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Activity of Algae. Life 2023, 13, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Yu, Q.; Liao, W.; Liu, S.; He, Z.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Nie, S.; Xie, M. Composition of Bound Polyphenols from Carrot Dietary Fiber and Its in Vivo and in Vitro Antioxidant Activity. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, K.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Tan, L.; Liu, S.; Dong, R.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, Q. Optimization and Identification of Non-Extractable Polyphenols in the Dietary Fiber of Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam.) Pulp Released by Alkaline, Acid and Enzymatic Hydrolysis: Content, Composition and Antioxidant Activities. LWT 2021, 138, 110400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, S.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Dong, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Xie, J.; Hu, X.; Yu, Q. Antioxidant, α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activities of Bound Polyphenols Extracted from Mung Bean Skin Dietary Fiber. LWT 2020, 132, 109943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwal, S.; Perreault, V.; Marciniak, A.; Tamigneaux, É.; Deslandes, É.; Bazinet, L.; Jacques, H.; Beaulieu, L.; Doyen, A. Effects of High Hydrostatic Pressure and Polysaccharidases on the Extraction of Antioxidant Compounds from Red Macroalgae, Palmaria Palmata and Solieria Chordalis. J. Food Eng. 2019, 252, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjana, K.; Arunkumar, K. Brown Algae Biomass for Fucoxanthin, Fucoidan and Alginate; Update Review on Structure, Biosynthesis, Biological Activities and Extraction Valorisation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.L. Algae: The World’s Most Important “Plants”—An Introduction. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2013, 18, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlgaeBase. Available online: https://www.algaebase.org/ (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Zheng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, L. A Bioactive Substance Derived from Brown Seaweeds: Phlorotannins. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Arceo, M.; Gómez-Zorita, S.; Aguirre, L.; Portillo, M.P. Effect of Microalgae and Macroalgae Extracts on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.; Dordevic, A.L.; Ryan, L.; Bonham, M.P. An Emerging Trend in Functional Foods for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes: Marine Algal Polyphenols. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1342–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotas, J.; Leandro, A.; Monteiro, P.; Pacheco, D.; Figueirinha, A.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Da Silva, G.J.; Pereira, L. Seaweed Phenolics: From Extraction to Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.P.; Woodman, T.J.; Chuck, C.J. An Integrated Biorefinery to Produce 5-(Hydroxymethyl)Furfural and Alternative Fuel Precursors from Macroalgae and Spent Coffee Grounds. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2021, 5, 6189–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sahoo, D. A Comprehensive Analysis of Alginate Content and Biochemical Composition of Leftover Pulp from Brown Seaweed Sargassum Wightii. Algal Res. 2017, 23, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L. Macroalgae. Encyclopedia 2021, 1, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, Y.I.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents | American Journal of Enology and Viticulture. Available online: https://www.ajevonline.org/content/16/3/144 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Marić, B.; Abramović, B.; Ilić, N.; Bodroža-Solarov, M.; Pavlić, B.; Oczkowski, M.; Wilczak, J.; Četojević-Simin, D.; Šarić, L.; Teslić, N. UHPLC-Triple-TOF-MS Characterization, Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Antiproliferative Activity of Raspberry (Rubus Idaeus L.) Seed Extracts. Foods 2022, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, M.; Kitamura, Y.; Nagano, H.; Kawatsu, J.; Gotoh, H. DPPH Measurements and Structure—Activity Relationship Studies on the Antioxidant Capacity of Phenols. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, N.; Wang, Y.-D.; Li, G.-R.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Feng, J.; Qiao, C.-L.; Zhang, H.-F. Ultrasound-Microwave Combined Extraction of Novel Polysaccharide Fractions from Lycium Barbarum Leaves and Their In Vitro Hypoglycemic and Antioxidant Activities. Molecules 2023, 28, 3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Jia, W.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, D.; Tao, J.; Yue, H.; et al. Inhibitory Activities and Rules of Plant Gallotannins with Different Numbers of Galloyl Moieties on Sucrase, Maltase and α-Amylase In Vitro and In Vivo. Phytomedicine 2023, 120, 155063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Gong, Y.; Wang, D.; Fan, L.; Zhao, X. Changes in Phenols, Antioxidant Ability, in Vitro Hypoglycemic Activity of Flos Sophorae Immaturus During Different Drying Methods. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 8540–8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Gu, C.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Li, M.; Guan, W.; Kong, Y.; Gao, H. The Research on Metabolomics Mechanism of Calcium Ion-Induced Whole Black Bean Polyphenols and Biological Activities. LWT 2024, 195, 115851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emire, S.A.; Hagos, A.D.; Eun, J.B.; Dadi, D.W. Effect of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Moringa Stenopetala Leaves on Bioactive Compounds and Their Antioxidant Activity. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 57, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Yang, X.; Zhou, C.; Mei, X.; Yang, X.; Fu, Q.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yang, C. Optimization of the Extraction Process of Polyphenols from Allium Cepa Using Response Surface Methodology and Assessment of Its Antioxidant and Lipid-Lowering Action. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.S.; Kanan, M.K.A.; Ahmed, J.; Hossain, M.A.; Akter, M.S.; Ahmed, K.S.; Hossain, H.; Alam, M.; Mozumder, N.H.M.R.; Ahmed, M. Free and Insoluble-Bound Phenolic Compounds in Parboiled and Non-Parboiled Rice (Oryza sativa L): Impact of Hydrothermal Treatments. LWT 2025, 228, 118091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Dai, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, S.; Dai, Q.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Xia, T. Evaluation of Astringent Taste of Green Tea through Mass Spectrometry-Based Targeted Metabolic Profiling of Polyphenols. Food Chem. 2020, 305, 125507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Singhal, S.; Tarafdar, A.; Pharande, A.; Ganesan, M.; Badgujar, P.C. Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Selected Edible Macroalgae: Effect on Antioxidant Activity and Quantitative Assessment of Polyphenols by Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Algal Res. 2020, 52, 102114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Shao, F.; Zhang, J.; Long, Y.; Dong, W. The Composition and Bioactivity of Bound Polyphenols from Coffee Dietary Fiber During in Vitro Simulating Digestion. Food Res. Int. 2025, 199, 115390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpf, J.; Burger, R.; Schulze, M. Statistical Evaluation of DPPH, ABTS, FRAP, and Folin-Ciocalteu Assays to Assess the Antioxidant Capacity of Lignins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Mao, F.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yamamoto, K. Interaction of Dietary Polyphenols with Bovine Milk Proteins: Molecular Structure–Affinity Relationship and Influencing Bioactivity Aspects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, P.K.; Subramanian, A.; Manjusha, W.A. Phytochemical Screening and Evaluation of Antidiabetic Activity of the Marine Microalgae: Nannochloropsis Sp.: Life Sciences-Marine Biology for Medical Therapy. Int. J. Life Sci. Pharma Res. 2022, 10, L36–L40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Xie, F.; Wang, G.; Yuan, C.; Huang, S.; Zhou, T.; Song, Z.; Ai, L. The Inhibitory Effects of Free and Bound Phenolics from Phyllanthus Emblica Linn. on α-Amylase: A Comparison Study. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 9719–9728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Liquid–Solid Ratio | NaOH Concentration (mol/L) | Alkaline Hydrolysis Time (h) | Alkaline Hydrolysis Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1:40 | 4 | 1 | 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 |
| 2 | 1:40 | 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 | 1 | 50 |
| 3 | 1:40 | 4 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 | 50 |
| 4 | 1:10, 1:20, 1:30, 1:40, 1:50 | 4 | 2 | 50 |
| Level | A: NaOH Concentration (mol/L) | B: Alkaline Hydrolysis (h) | C: Liquid–Solid Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 4 | 1 | 1:30 |
| 0 | 6 | 2 | 1:40 |
| 1 | 8 | 3 | 1:50 |
| No. | NaOH Concentration | Alkaline Hydrolysis Time (B) | Liquid–Solid Ratio (C) | Total Polyphenol Content (Y) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 (−1) | 1 (−1) | 40 (0) | 5.27 |
| 2 | 8 (1) | 1 (−1) | 40 (0) | 6.69 |
| 3 | 4 (−1) | 3 (1) | 40 (0) | 7.18 |
| 4 | 8 (1) | 3 (1) | 40 (0) | 8.88 |
| 5 | 4 (−1) | 2 (0) | 30 (−1) | 5.98 |
| 6 | 8 (1) | 2 (0) | 30 (−1) | 7.72 |
| 7 | 4 (−1) | 2 (0) | 50 (1) | 7.38 |
| 8 | 8 (1) | 2 (0) | 50 (1) | 9.38 |
| 9 | 6 (0) | 1 (−1) | 30 (−1) | 3.57 |
| 10 | 6 (0) | 3 (1) | 30 (−1) | 7.20 |
| 11 | 6 (0) | 1 (−1) | 50 (1) | 6.94 |
| 12 | 6 (0) | 3 (1) | 50 (1) | 8.35 |
| 13 | 6 (0) | 2 (0) | 40 (0) | 7.49 |
| 14 | 6 (0) | 2 (0) | 40 (0) | 7.67 |
| 15 | 6 (0) | 2 (0) | 40 (0) | 7.80 |
| 16 | 6 (0) | 2 (0) | 40 (0) | 7.60 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | Significant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 28.27 | 9 | 3.14 | 39.54 | 0.0001 | ** |
| A | 5.87 | 1 | 5.87 | 73.86 | 0.0001 | ** |
| B | 10.44 | 1 | 10.44 | 131.48 | <0.0001 | ** |
| C | 7.19 | 1 | 7.19 | 90.54 | <0.0001 | ** |
| AB | 0.019 | 1 | 0.019 | 0.24 | 0.6409 | |
| AC | 0.016 | 1 | 0.016 | 0.21 | 0.6646 | |
| BC | 1.23 | 1 | 1.23 | 15.47 | 0.0077 | ** |
| A2 | 0.22 | 1 | 0.22 | 2.73 | 0.1496 | * |
| B2 | 3.02 | 1 | 3.02 | 37.98 | 0.0008 | ** |
| C2 | 0.26 | 1 | 0.26 | 3.33 | 0.1178 | |
| Residual | 0.48 | 6 | 0.079 | |||
| Lack of fit | 0.43 | 3 | 0.14 | 8.67 | 0.0547 | |
| Pure error | 0.049 | 3 | 0.016 | |||
| Cor. total | 28.74 | 15 |
| Identity | Formula | Retention Time (min) | Addition Ion | m/z | Reference (m/z) | Peak |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free Polyphenols | ||||||
| Polyhydroxybenzene | ||||||
| 5-{8(Z),11(Z)-pentadecadienyl}resorcinol | C21H32O2 | 14.0939 | [M−H]− | 315.3153 | 315.3175 | F′8 |
| Flavonoids | ||||||
| 6,8-dihydroxy-2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-7-(3-methylbutanoyl)-9-(2-methylpropyl)-9H-xanthene-1,3-dione | C26H34O6 | 20.41 | [M−H]− | 441.3863 | 441.3867 | F′15 |
| 5-O-methylgenistein | C16H12O5 | 16.68 | [M−H]− | 283.3203 | 283.3212 | F′11 |
| Epiafzelechin (2R,3R)(-) | C15H14O5 | 9.148 | [M−H]− | 273.1768 | 273.1747 | F′2 |
| 5-hydroxy-2′,4′,7,8-tetramethoxyflavone | C19H18O7 | 20.18 | [M−H]− | 339.3171 | 339.3141 | F′14 |
| 7,4′-dimethoxysoflavone | C17H14O4 | 20.65 | [M−H]− | 281.3031 | 281.2998 | F′16 |
| Catechin | C15H14O6 | 1.25 | [M−H]− | 289.127 | 289.1219 | F′1 |
| 3-[(Z)-heptadec-10-enyl]benzene-1,2-diol | C23H38O2 | 15.65 | [M−H]− | 345.2745 | 345.2799 | F′10 |
| Neobavaisoflavone | C20H18O4 | 10.64 | [M+H]+ | 345.1133 | 345.11 | F3 |
| 2′′-O-rhamnosyl icariside II | C33H40O14 | 15.4 | [M+H]+ | 683.2292 | 683.23 | F12 |
| Others | ||||||
| Fraxin | C16H18O10 | 14.82 | [M+H]+ | 409.0553 | 409.0532 | F10 |
| α-Tochopherol | C29H50O2 | 15.33 | [M−H]− | 429.3738 | 429.3738 | F′9 |
| Esculin | C15H16O9 | 1.4 | [M+H]+ | 363.0636 | 363.06 | F1 |
| 2-hydroxy-6-pentadecylbenzoic acid | C22H36O3 | 13.53 | [M−H]− | 347.2638 | 347.258 | F′6 |
| Bound polyphenols | ||||||
| Flavonoids | ||||||
| 2′,5′-dihydroxy-4-methoxychalcone | C16H14O4 | 8.52 | [M−H]− | 269.1664 | 269.1674 | B′5 |
| 5-O-methylgenistein | C16H12O5 | 17.35 | [M−H]− | 283.3191 | 283.3212 | B′6 |
| Quercetin 3,7-dimethyl ether | C17H14O7 | 1.88 | [M−H]− | 329.0576 | 329.062 | B′7 |
| Licoflavone A | C20H18O4 | 10.69 | [M+Na]+ | 345.1138 | 345.11 | B3 |
| Licoricidin | C26H32O5 | 20.79 | [M+H]+ | 447.2125 | 447.21 | B7 |
| Others | ||||||
| Juglone | C10H6O3 | 5.03 | [M+H]+ | 212.9939 | 212.9949 | B1 |
| Alpha-estradiol | C18H24O2 | 5.58 | [M+H]+ | 255.1714 | 255.1744 | B2 |
| 3-methoxy-2-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-5-pentylphenol | C17H26O2 | 6.15 | [M−H]− | 261.1752 | 261.1783 | B′3 |
| Atalaphylline | C23H25NO4 | 7.28 | [M−H]− | 378.2395 | 378.2336 | B′4 |
| Identity | Addition Ion | Measured Mass (m/z) | MS/MS Fragment Detected (m/z) | Algae Source | Peak |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free polyphenols | |||||
| Fuhalols | |||||
| 2-(1) | [M+H]+ | 267.2 | 141 | Sargassum fusiforme | F5 |
| 3-(1) | [M+H]+ | 391.3 | 125 | Sargassum fusiforme | F6 |
| 5-(1) | [M+H]+ | 639.3 | 388 | Sargassum fusiforme | F17 |
| 5-(2) | [M+H]+ | 655.3 | 527, 389 | Sargassum fusiforme | F8 |
| 6-(3) | [M+H]+ | 795.3 | 667 | Sargassum fusiforme | F14 |
| Dihydroxytetrafuhalol | [M+H]+ | 547.4 | 529 | Sargassum muticum | F11 |
| Dihydroxypentafuhalol | [M+H]+ | 671.3 | 625, 623, 607, 527, 465, 402, 341, and 263 | Sargassum muticum | F4 |
| Dihydroxyhexafuhalol | [M+H]+ | 795.3 | 777, 749, 731, 653, and 465 | Sargassum muticum | F14 |
| Pentafuhalol | [M+H]+ | 639.3 | 621, 513, 385, and 373 | Sargassum muticum | F15 |
| Hydroxytetrafuhalol | [M+H]+ | 655.3 | 637, 527, and 389 | Sargassum muticum | F8 |
| Bifuhalol trimer | [M+H]+ | 795.3 | 515 | Carpophyllum flexuosum | F14 |
| Octafuhalol | [M+H]+ | 1011.7 | 621 | Sargassum muticum | F7 |
| nd | [M+H]+ | 653.3 | 607 and 465 | Laminaria digitata | F16 |
| nd | [M+H]+ | 653.3 | 607 and 465 | Laminaria digitata | F18 |
| Dihydroxypentafuhalol | [M−H]− | 669.6 | 625 | Sargassum muticum | F′13 |
| Dihydroxyhexafuhalol | [M−H]− | 793.6 | 465 | Sargassum muticum | F′12 |
| Hydroxytrifuhalol | [M−H]− | 405.2 | 154 | Carpophyllum flexuosum | F′3 |
| Eckols | |||||
| 3-(1) | [M+H]+ | 389.2 | 329, 245, and 123 | Sargassum fusiforme | F2 |
| Eckol | [M−H]− | 371.2 | 335 | Sargassum fusiforme | F′7 |
| Eckol derivative | [M−H]− | 401.3 | 371 | Fucus vesiculosus | F′5 |
| Others | |||||
| Tetramer | [M+H]+ | 499.4 | 481 and 233 | Fucus vesiculosus | F9 |
| Fucol | [M+H]+ | 623.3 | 495, 479, 461, 373, and 355 | Laminaria digitata | F13 |
| Pentaphlorethol | [M+H]+ | 623.3 | 603 and 493 | Sargassum muticum | F19 |
| Pentamer | [M+H]+ | 623.3 | 605, 497, 434, and 356 | Fucus vesiculosus | F13 |
| Phlorethol | [M−H]− | 745.5 | 477 | Laminaria digitata | F′4 |
| Bound polyphenols | |||||
| Fuhalols | |||||
| 3-(1) | [M+H]+ | 391.3 | 123 | Sargassum fusiforme | B5 |
| 6-(3) | [M+H]+ | 795.5 | 667 and 389 | Sargassum fusiforme | B6 |
| Dihydroxyhexafuhalol | [M+H]+ | 795.5 | 777, 749, 731, 513, 511, 485, 483, and 385 | Sargassum muticum | B6 |
| Trifuhalol | [M+H]+ | 391.3 | 251 | Sargassum muticum | B5 |
| Bifuhalol trimer | [M+H]+ | 795.5 | 515 and 261 | Carpophyllum flexuosum | B6 |
| Eckols | |||||
| 6-(3) | [M+H]+ | 793.5 | 747 and 385 | Sargassum fusiforme | B4 |
| 2-(1) | [M−H]− | 263.2 | 245 and 219 | Sargassum fusiforme | B′2 |
| Others | |||||
| Fucol | [M+H]+ | 623.3 | 477 and 371 | Fucus vesiculosus | B4 |
| Fucophlorethol | [M+H]+ | 623.3 | 461, 373, and 355 | Fucus vesiculosus | B4 |
| Pentaphlorethol | [M+H]+ | 623.3 | 493 | Sargassum muticum | B4 |
| 5 | [M+H]+ | 623.3 | 605, 373, 356, 355, and 340 | Sargassum muticum | B4 |
| Polyphenol Type | DPPH (μg TE/mg) | FRAP (μg TE/mg) | Anti-Amylase (mg AE/mg) | Anti-Glucosidase (μg AE/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 3.03 | 19.40 | 0.11 | 21.53 |
| Bound | 1.79 | 7.43 | 0.01 | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, X.; Chen, H.; Mi, J.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Dong, X. Process Optimization for Polyphenol Extraction from Macroalgae Residues and Assessment of Their Compositions, Antioxidant Activities, and Glycosidase Inhibition. Foods 2025, 14, 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173055
Luo X, Chen H, Mi J, Li X, Wu Z, Jiang Y, Dong X. Process Optimization for Polyphenol Extraction from Macroalgae Residues and Assessment of Their Compositions, Antioxidant Activities, and Glycosidase Inhibition. Foods. 2025; 14(17):3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173055
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Xianxian, Hao Chen, Jiayi Mi, Xinyan Li, Ziheng Wu, Yan Jiang, and Xiufang Dong. 2025. "Process Optimization for Polyphenol Extraction from Macroalgae Residues and Assessment of Their Compositions, Antioxidant Activities, and Glycosidase Inhibition" Foods 14, no. 17: 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173055
APA StyleLuo, X., Chen, H., Mi, J., Li, X., Wu, Z., Jiang, Y., & Dong, X. (2025). Process Optimization for Polyphenol Extraction from Macroalgae Residues and Assessment of Their Compositions, Antioxidant Activities, and Glycosidase Inhibition. Foods, 14(17), 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173055





