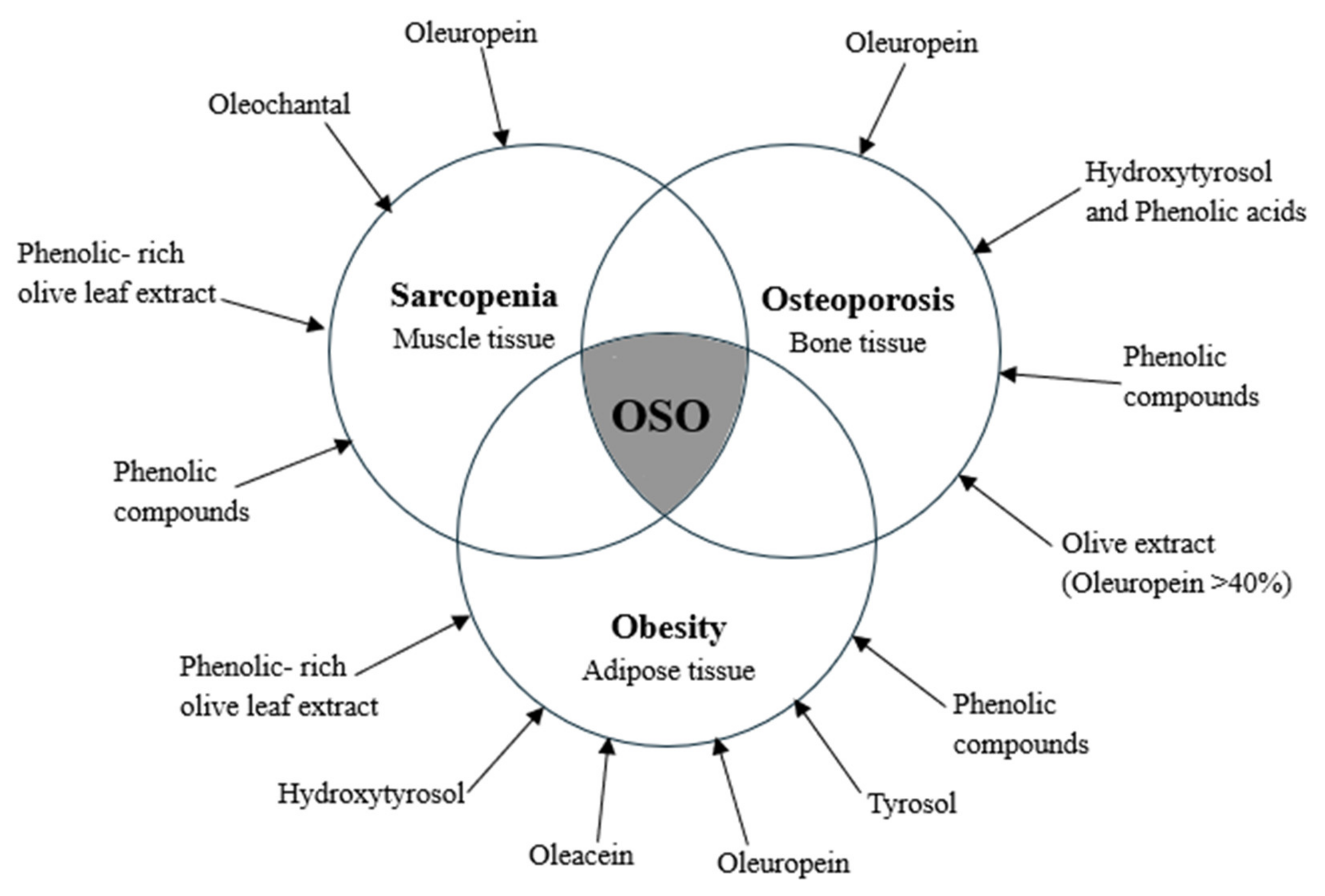
The Role of Olive Oil Polyphenols in Osteosarcopenic Obesity-Related Biological Domains: A Systematic Review of Current Evidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Risk of Bias Assessment
4. Results
4.1. Effects on Adipose Tissue
4.2. Effects on Bone Tissue
4.3. Effects on the Skeletal Muscle Tissue
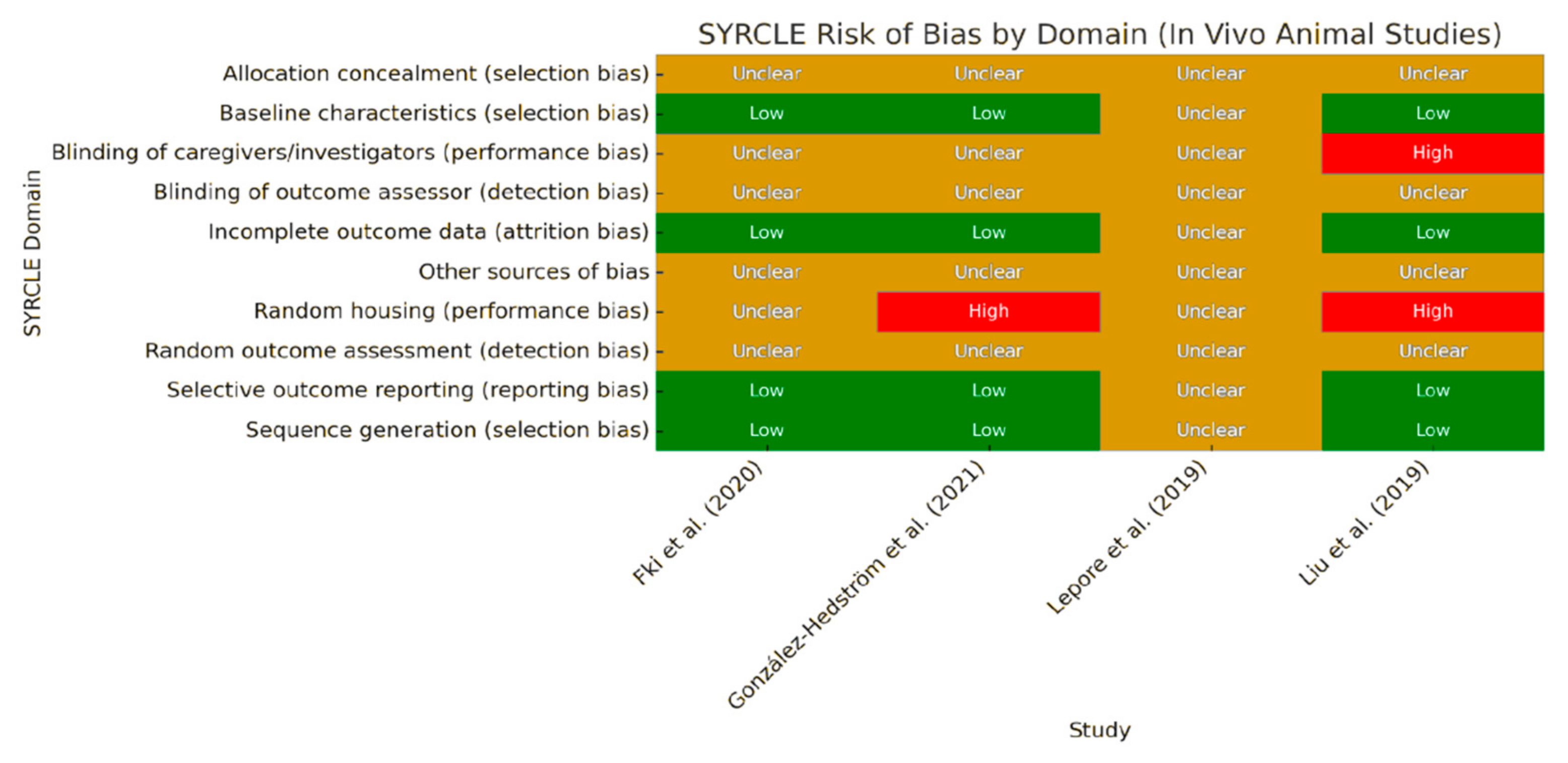
4.4. Risk of Bias Assessment for In Vivo Studies
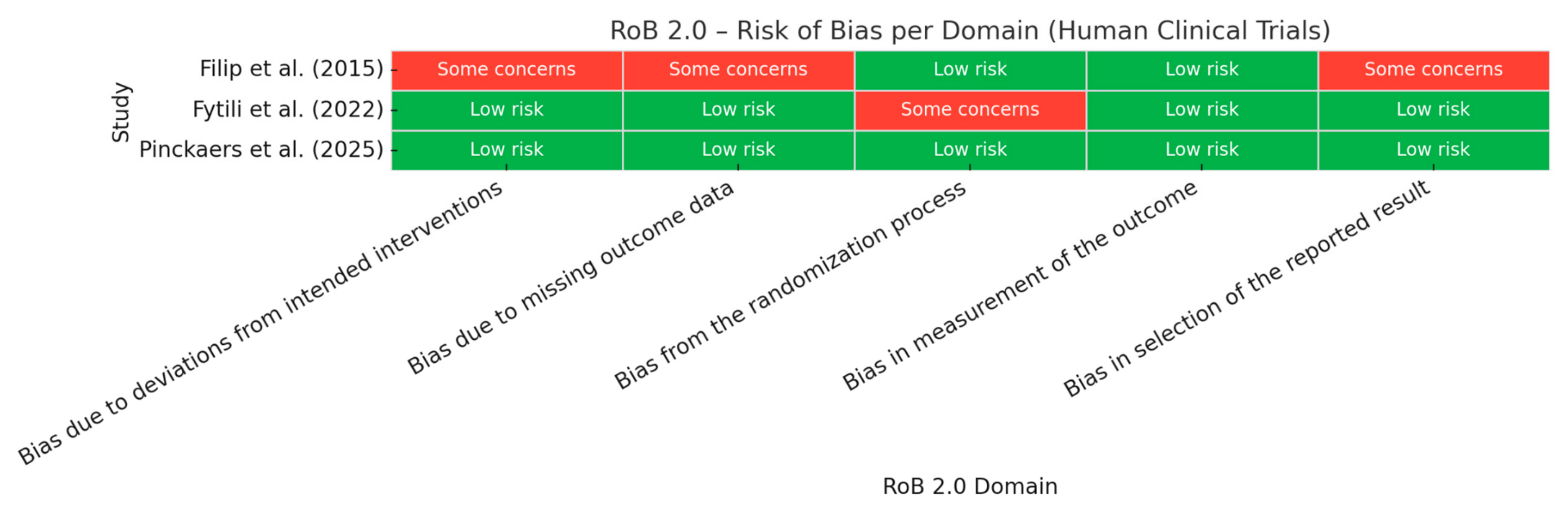
4.5. Risk of Bias Assessment for in Humans Studies
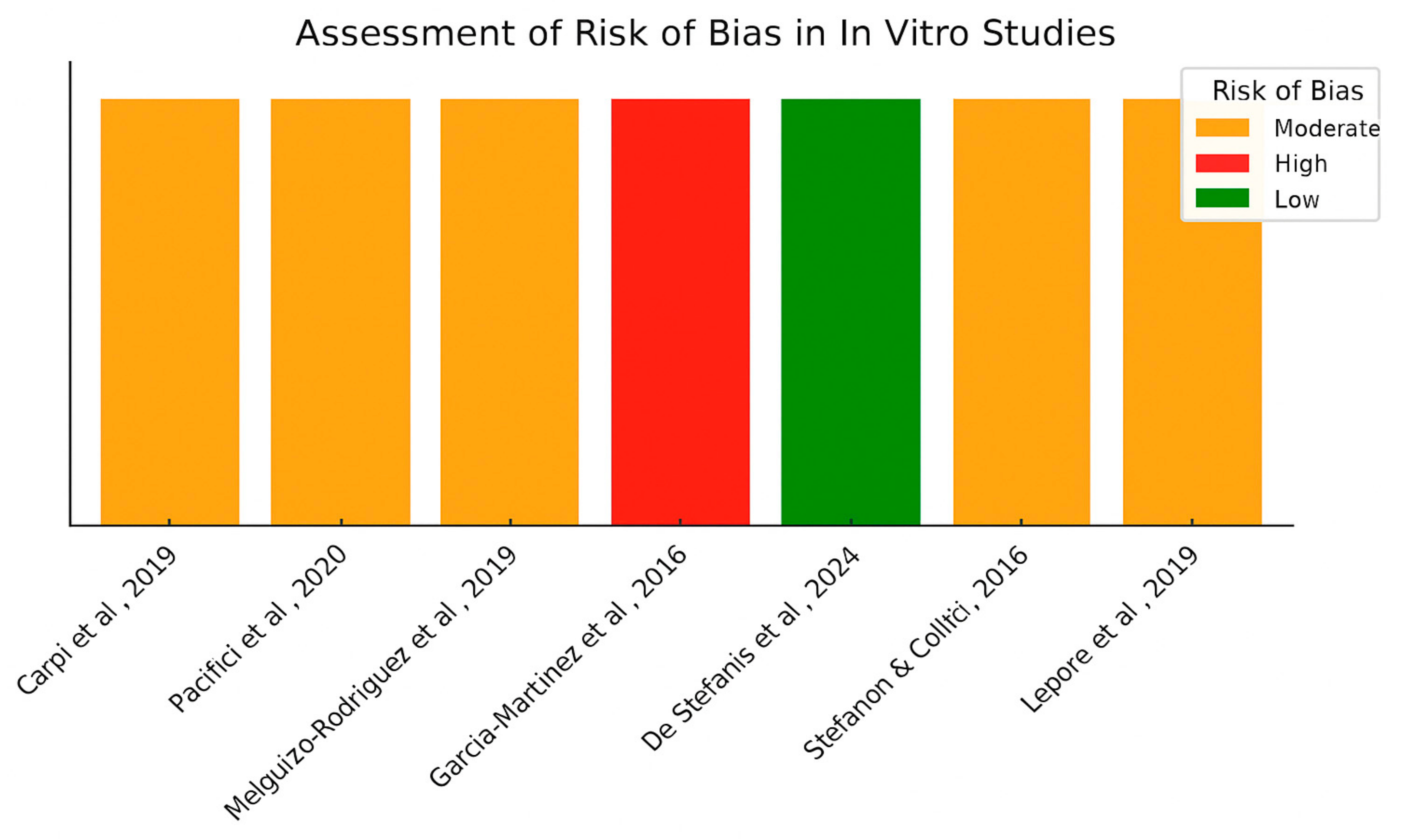
4.6. Risk of Bias Assessment for In Vitro Studies
5. Discussion
6. Limitations
7. Practical Applications
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hita-Contreras, F.; Martínez-Amat, A.; Cruz-Díaz, D.; Pérez-López, F.R. Osteosarcopenic Obesity and Fall Prevention Strategies. Maturitas 2015, 80, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilich, J.Z.; Kelly, O.J.; Inglis, J.E.; Panton, L.B.; Duque, G.; Ormsbee, M.J. Interrelationship among Muscle, Fat, and Bone: Connecting the Dots on Cellular, Hormonal, and Whole Body Levels. Ageing Res. Rev. 2014, 15, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ormsbee, M.J.; Prado, C.M.; Ilich, J.Z.; Purcell, S.; Siervo, M.; Folsom, A.; Panton, L. Osteosarcopenic Obesity: The Role of Bone, Muscle, and Fat on Health. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2014, 5, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilich, J.Z.; Kelly, O.J.; Inglis, J.E. Osteosarcopenic Obesity Syndrome: What Is It and How Can It Be Identified and Diagnosed? Curr. Gerontol. Geriatr. Res. 2016, 2016, 7325973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Hao, Q.; Wu, J. Global Prevalence of Osteosarcopenic Obesity amongst Middle Aged and Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Osteoporos. 2023, 18, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, G.; Keshtkar, A.; Soltani, A.; Ahadi, Z.; Larijani, B.; Heshmat, R. Prevalence of Sarcopenia in the World: A Systematic Review and Meta- Analysis of General Population Studies. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2017, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Lim, S.; Yoon, J.W.; Kang, S.M.; Kim, K.W.; Lim, J.Y.; Cho, N.H.; Jang, H.C. Sarcopenia and Obesity: Gender-Different Relationship with Functional Limitation in Older Persons. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2013, 28, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, S.; Spadaccini, D.; Nichetti, M.; Avanzato, I.; Faliva, M.A.; Rondanelli, M. Osteosarcopenic Visceral Obesity and Osteosarcopenic Subcutaneous Obesity, Two New Phenotypes of Sarcopenia: Prevalence, Metabolic Profile, and Risk Factors. J. Aging Res. 2018, 2018, 6147426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, O.J.; Gilman, J.C.; Boschiero, D.; Ilich, J.Z. Osteosarcopenic Obesity: Current Knowledge, Revised Identification Criteria and Treatment Principles. Nutrients 2019, 11, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, R.; Anwar, F.; Alkharfy, K.M.; Gilani, A.-H.; Saari, N. Valuable Nutrients and Functional Bioactives in Different Parts of Olive (Olea europaea L.)—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3291–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serreli, G.; Deiana, M. Biological Relevance of Extra Virgin Olive Oil Polyphenols Metabolites. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupo, R.; Castellana, F.; Lisco, G.; Corbo, F.; Crupi, P.; Sardone, R.; Panza, F.; Lozupone, M.; Rondanelli, M.; Clodoveo, M.L. Dietary Intake of Polyphenols and All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Metabolites 2024, 14, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clodoveo, M.L.; Crupi, P.; Muraglia, M.; Corbo, F. Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Polyphenols from Ripe Carob Pods (Ceratonia siliqua L.): Combined Designs for Screening and Optimizing the Processing Parameters. Foods 2022, 11, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupo, R.; Castellana, F.; Crupi, P.; Desantis, A.; Rondanelli, M.; Corbo, F.; Clodoveo, M.L. Olive Oil Polyphenols Improve HDL Cholesterol and Promote Maintenance of Lipid Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufino-Palomares, E.E.; Pérez-Jiménez, A.; García-Salguero, L.; Mokhtari, K.; Reyes-Zurita, F.J.; Peragón-Sánchez, J.; Lupiáñez, J.A. Nutraceutical Role of Polyphenols and Triterpenes Present in the Extracts of Fruits and Leaves of as Antioxidants, Anti-Infectives and Anticancer Agents on Healthy Growth. Molecules 2022, 27, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, A.; Ieri, F.; Urciuoli, S.; Noce, A.; Marrone, G.; Nediani, C.; Bernini, R. Health Effects of Phenolic Compounds Found in Extra-Virgin Olive Oil, By-Products, and Leaf of L. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piroddi, M.; Albini, A.; Fabiani, R.; Giovannelli, L.; Luceri, C.; Natella, F.; Rosignoli, P.; Rossi, T.; Taticchi, A.; Servili, M.; et al. Nutrigenomics of Extra-Virgin Olive Oil: A Review. Biofactors 2017, 43, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Rovers, M.M.; de Vries, R.B.M.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Langendam, M.W. SYRCLE’s Risk of Bias Tool for Animal Studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepore, S.M.; Maggisano, V.; Bulotta, S.; Mignogna, C.; Arcidiacono, B.; Procopio, A.; Brunetti, A.; Russo, D.; Celano, M. Oleacein Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Adiposity and Ameliorates Some Biochemical Parameters of Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, A.; Huang, Y.; Hou, A.; Miao, W.; Hong, L.; Deng, N.; Fan, Y. Efficacy and Mechanisms of Oleuropein in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Comput. Math Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 9767113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fki, I.; Sayadi, S.; Mahmoudi, A.; Daoued, I.; Marrekchi, R.; Ghorbel, H. Comparative Study on Beneficial Effects of Hydroxytyrosol- and Oleuropein-Rich Olive Leaf Extracts on High-Fat Diet-Induced Lipid Metabolism Disturbance and Liver Injury in Rats. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1315202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Hedström, D.; Priego, T.; Amor, S.; de la Fuente-Fernández, M.; Martín, A.I.; López-Calderón, A.; Inarejos-García, A.M.; García-Villalón, Á.L.; Granado, M. Olive Leaf Extract Supplementation to Old Wistar Rats Attenuates Aging-Induced Sarcopenia and Increases Insulin Sensitivity in Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Muscle. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fytili, C.; Nikou, T.; Tentolouris, N.; Tseti, I.K.; Dimosthenopoulos, C.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Simos, D.; Kokkinos, A.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Katsilambros, N.; et al. Effect of Long-Term Hydroxytyrosol Administration on Body Weight, Fat Mass and Urine Metabolomics: A Randomized Double-Blind Prospective Human Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinckaers, P.J.; Petrick, H.L.; Horstman, A.M.; Moreno-Asso, A.; De Marchi, U.; Hendriks, F.K.; Kuin, L.M.; Fuchs, C.J.; Grathwohl, D.; Verdijk, L.B.; et al. Oleuropein Supplementation Increases Resting Skeletal Muscle Fractional Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Activity but Does Not Influence Whole-Body Metabolism: A Randomized, Double-Blind, and Placebo-Controlled Trial in Healthy, Older Males. J. Nutr. 2025, 155, 1373–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filip, R.; Possemiers, S.; Heyerick, A.; Pinheiro, I.; Raszewski, G.; Davicco, M.-J.; Coxam, V. Twelve-Month Consumption of a Polyphenol Extract from Olive (Olea europaea) in a Double Blind, Randomized Trial Increases Serum Total Osteocalcin Levels and Improves Serum Lipid Profiles in Postmenopausal Women with Osteopenia. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2015, 19, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, K.; Schwarz, M.; Burkholder, I.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Edler, L.; Kinsner-Ovaskainen, A.; Hartung, T.; Hoffmann, S. “ToxRTool”, a New Tool to Assess the Reliability of Toxicological Data. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 189, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanon, B.; Colitti, M. Original Research: Hydroxytyrosol, an Ingredient of Olive Oil, Reduces Triglyceride Accumulation and Promotes Lipolysis in Human Primary Visceral Adipocytes during Differentiation. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, S.; Scoditti, E.; Massaro, M.; Polini, B.; Manera, C.; Digiacomo, M.; Esposito Salsano, J.; Poli, G.; Tuccinardi, T.; Doccini, S.; et al. The Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Polyphenols Oleocanthal and Oleacein Counteract Inflammation-Related Gene and miRNA Expression in Adipocytes by Attenuating NF-κB Activation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifici, F.; Farias, C.L.A.; Rea, S.; Capuani, B.; Feraco, A.; Coppola, A.; Mammi, C.; Pastore, D.; Abete, P.; Rovella, V.; et al. Tyrosol May Prevent Obesity by Inhibiting Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 4794780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; Manzano-Moreno, F.J.; Illescas-Montes, R.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; de Luna-Bertos, E.; Ruiz, C.; García-Martínez, O. Bone Protective Effect of Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds by Modulating Osteoblast Gene Expression. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martínez, O.; De Luna-Bertos, E.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; Ruiz, C.; Milia, E.; Lorenzo, M.L.; Jimenez, B.; Sánchez-Ortiz, A.; Rivas, A. Phenolic Compounds in Extra Virgin Olive Oil Stimulate Human Osteoblastic Cell Proliferation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefanis, D.; Balestrini, A.; Costelli, P. Oleocanthal Protects C2C12 Myotubes against the Pro-Catabolic and Anti-Myogenic Action of Stimuli Able to Induce Muscle Wasting. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, M.; Baldelli, S.; Ciriolo, M.R.; Costanzo, P.; Procopio, A.; Colica, C. Oleuropein Aglycone Peracetylated (3,4-DHPEA-EA(P)) Attenuates HO-Mediated Cytotoxicity in C2C12 Myocytes via Inactivation of P-JNK/p-c-Jun Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2020, 25, 5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, N.; Ma, Y.; Wen, D. Hydroxytyrosol Improves Obesity and Insulin Resistance by Modulating Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, A.A.; Boyles, A.L.; Wolfe, M.S.; Bucher, J.R.; Thayer, K.A. Systematic Review and Evidence Integration for Literature-Based Environmental Health Science Assessments. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| A | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author, Year | Model | Compound | Sample | Dose | Mechanism of Action | Key Findings |
| Stefanon & Colitti, 2016 [27] | In vitro | Hydroxytyrosol | Human adipocytes | 5–70 mg/mL | ↓ Triglycerides, ↑ apoptosis | Anti-adipogenic, pro-lipolytic |
| Pacifici et al., 2020 [29] | In vitro | Tyrosol | 3T3-L1 cells | 300–500 μM | ↓ Adipogenesis, ↑ lipolysis | AMPK-ATGL-HSL pathway activation |
| Carpi et al., 2019 [28] | In vitro | Oleocanthal, Oleacein | Human preadipocytes | 25 μmol/L | ↓ NF-κB activation, ↓ miRNA | Anti-inflammatory |
| De Stefanis et al., 2024 [32] | In vitro | Oleocanthal | C2C12 myotubes | 10 μM | ↓ Atrogin-1, MuRF1 | Myotube preservation |
| Nardi et al., 2020 [33] | In vitro | Oleuropein (aglycone) | C2C12 myocytes | 10 μM | ↓ Oxidative stress | ↑ MyoD, anti-atrophic |
| Liu et al., 2022 [20] | In vivo | Oleuropein | OVX rats | 200 μg/kg | ↑ BMD, ↓ IL-6/TNF-α | Bone remodeling via OPG/RANKL |
| Liu et al., 2019 [34] | In vivo | Hydroxytyrosol | Mice | 50 mg/kg | Modulation of gut microbiota | Anti-obesogenic effect |
| Fytili et al., 2022 [23] | Human | Hydroxytyrosol | Overweight women | 5–15 mg/day | ↓ Adipogenesis gene expression | ↓ Visceral fat |
| Pinckaers et al., 2025 [24] | Human | Oleuropein | Older males | 100 mg/day | ↑ PDH activity | Muscle metabolism support |
| B | ||||||
| Author, Year | Model | Extract Type | Sample | Dose | Mechanism of Action | Key Findings |
| Lepore et al., 2019 [19] | In vitro/in vivo | Oleacein (from olive extract) | 3T3-L1 cells, mice | 10–100 µM; 20 mg/kg | ↓ Lipid accumulation, ↑ adiponectin | ↓ Fat mass, anti-inflammatory |
| Melguizo-Rodríguez et al., 2019 [30] | In vitro | EVOO phenolics | MG63 osteoblasts | 10−6 M | ↑ TGFβ1, BMP2, BMP7 | Osteogenic effect |
| Garcia-Martínez et al., 2016 [31] | In vitro | EVOO phenolics | MG63 cells | Various | ↑ ALP, ↑ proliferation | Variety-dependent effect |
| González-Hedström et al., 2021 [22] | In vivo | Olive Leaf Extract (OLE) | Aged rats | 100 mg/kg | ↓ IL-6, ↑ myogenin | Anti-sarcopenic, ↑ insulin sensitivity |
| Fki et al., 2020 [21] | In vivo | HT- and Oleuropein-rich extracts | Rats | 16 mg/kg | ↓ adipogenesis, ↑ lipid metabolism | Hepatoprotective effects |
| Filip et al., 2015 [25] | Human | Polyphenol extract (oleuropein >40%) | Osteopenic women | 250 mg/day | ↑ Osteocalcin, ↑ BMD | Improved bone/lipid profile |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zupo, R.; Castellana, F.; Clodoveo, M.L.; Lisco, G.; Mazzola, G.; Rondanelli, M.; Cantù, A.; Riso, P.; Perna, S. The Role of Olive Oil Polyphenols in Osteosarcopenic Obesity-Related Biological Domains: A Systematic Review of Current Evidence. Foods 2025, 14, 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162766
Zupo R, Castellana F, Clodoveo ML, Lisco G, Mazzola G, Rondanelli M, Cantù A, Riso P, Perna S. The Role of Olive Oil Polyphenols in Osteosarcopenic Obesity-Related Biological Domains: A Systematic Review of Current Evidence. Foods. 2025; 14(16):2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162766
Chicago/Turabian StyleZupo, Roberta, Fabio Castellana, Maria Lisa Clodoveo, Giuseppe Lisco, Giuseppe Mazzola, Mariangela Rondanelli, Alice Cantù, Patrizia Riso, and Simone Perna. 2025. "The Role of Olive Oil Polyphenols in Osteosarcopenic Obesity-Related Biological Domains: A Systematic Review of Current Evidence" Foods 14, no. 16: 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162766
APA StyleZupo, R., Castellana, F., Clodoveo, M. L., Lisco, G., Mazzola, G., Rondanelli, M., Cantù, A., Riso, P., & Perna, S. (2025). The Role of Olive Oil Polyphenols in Osteosarcopenic Obesity-Related Biological Domains: A Systematic Review of Current Evidence. Foods, 14(16), 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162766









