Determining the Benzo[a]pyrene Degradation, Tolerance, and Adsorption Mechanisms of Kefir-Derived Bacterium Bacillus mojavensis TC-5
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical
2.2. BaP-Degrading Bacteria Screen and Identification
2.3. BaP Removal Analysis
2.3.1. HPLC Analysis of BaP Biodegradation
2.3.2. Optimization of the Degradation Performance of BaP-Degrading Bacteria
2.3.3. HPLC Analysis for BaP Removal
2.4. Whole Genome Sequencing of Bacillus mojavensis TC-5
2.5. Transcriptomics Analysis
2.6. Analysis of Degradation Products Using GC-MS
2.7. Data Processing and Statistical
3. Results and Discussion
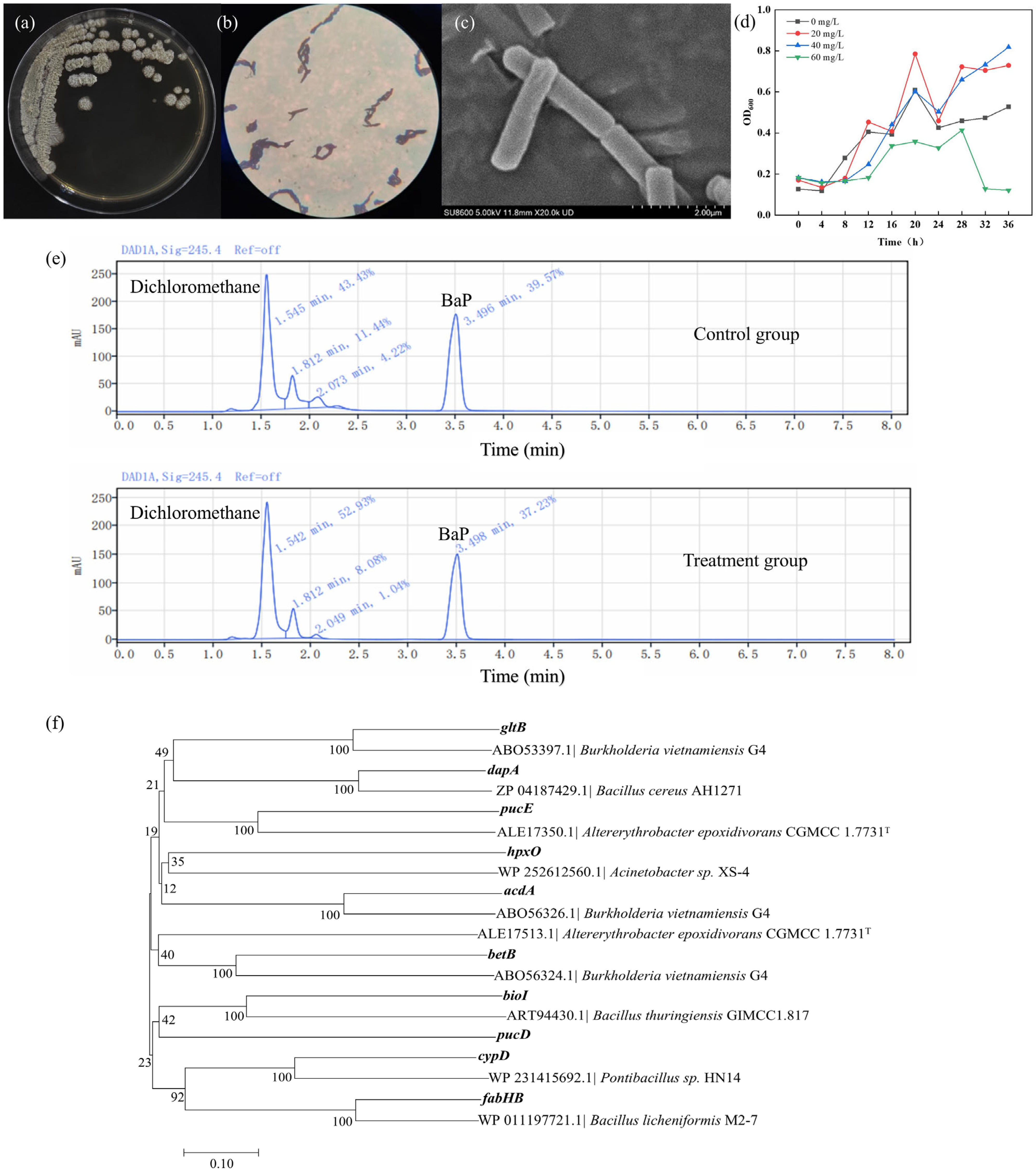
3.1. Screen and Characterization of BaP-Degrading Bacteria
3.2. Genomic Analysis of Bacillus Mojavensis TC-5
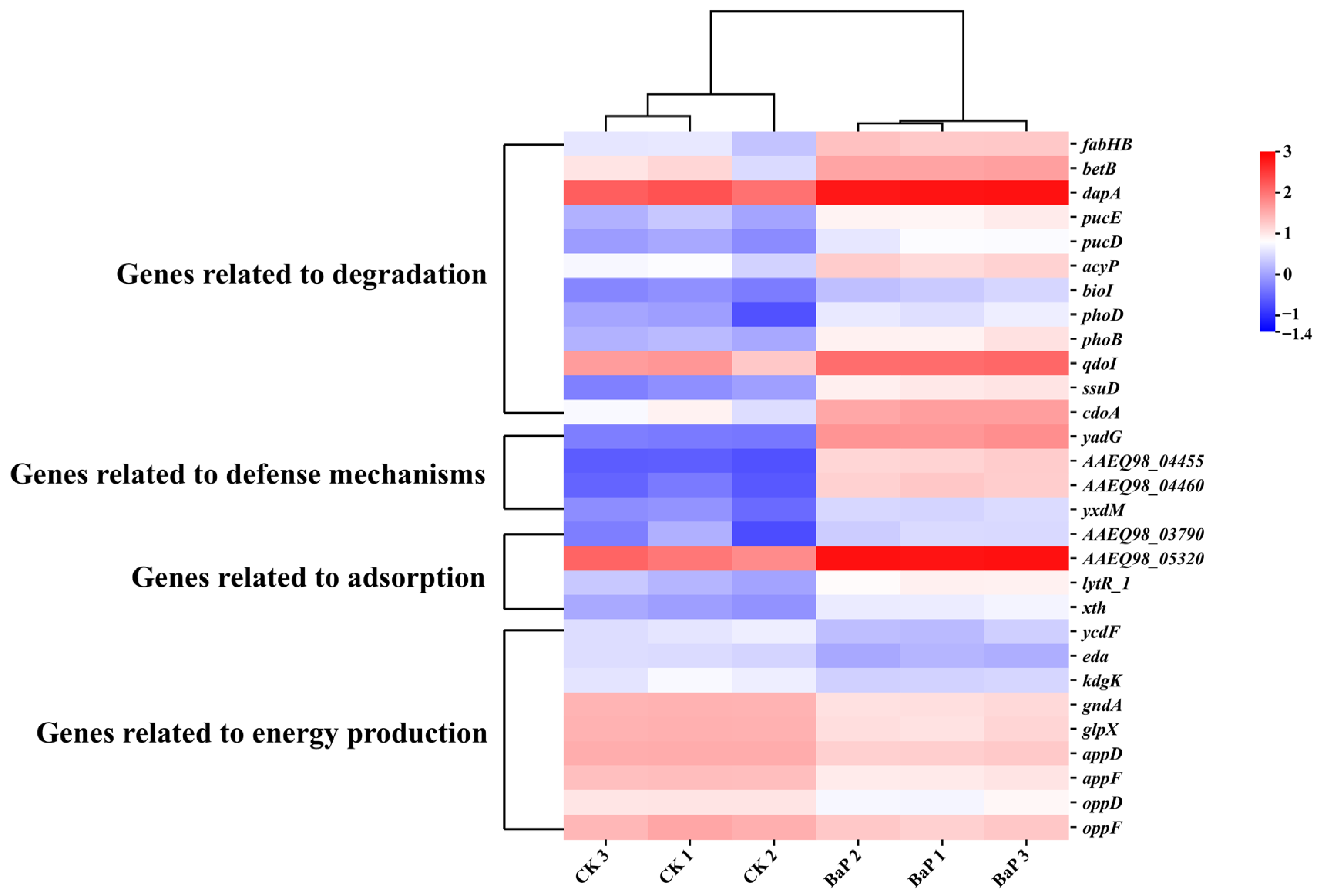
3.3. Differentially Expressed Genes of Bacillus mojavensis TC-5 Under BaP Stress
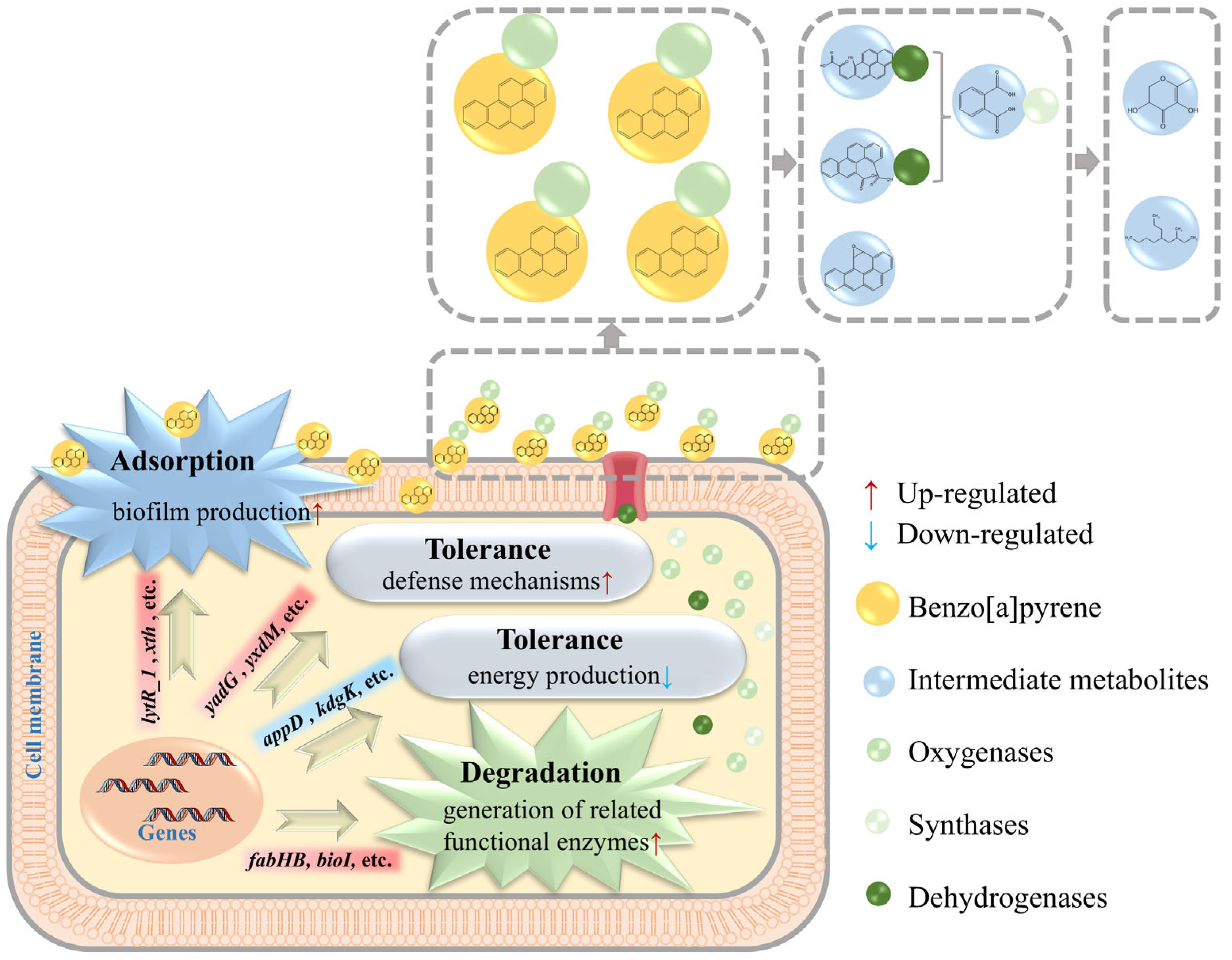
3.3.1. In-Depth Analysis: Mechanism of BaP Degradation by Strain TC-5
3.3.2. In-Depth Analysis: Mechanisms of Adsorption and Tolerance of BaP by Strain TC-5
3.4. Intermediate Metabolites and Unique Metabolic Pathways of BaP
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, J.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, J.; Tang, Z.W. Concentrations and distributions of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in vegetables and animal-based foods before and after grilling: Implication for human exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.N.; Wang, R.; Feng, X.R.; Cai, K.Z.; Zhou, H.; Xu, B.C. Composite starch films as green adsorbents for removing benzo[a]pyrene from smoked sausages. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.Q.; Yan, K.; Wu, S.M.; Gong, G.Y. Occurrence, spatial distribution and impact factors of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in milks from nine countries. Food Control 2020, 113, 107197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, K.; Sivasantosh, S.; Sathiyaseelan, A.; Sankaranarayanan, A.; Naveen, K.V.; Zhang, X.; Jamla, M.; Vijayasarathy, S.; Priya, V.V.; MubarakAli, D.; et al. Impact of benzo[a]pyrene with other pollutants induce the molecular alternation in the biological system: Existence, detection, and remediation methods. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 304, 119207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadighara, P.; Abedini, A.H.; Mahvi, A.H.; Esrafili, A.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Tarahomi, A.; Yousef, M. Benzo(a)pyrene in infant foods: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and health risk assessment. Rev. Environ. Health 2023, 39, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punetha, A.; Saraswat, S.; Rai, J.P.N. An insight on microbial degradation of benzo[a]pyrene: Current status and advances in research. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.; Mahadevan, V.; Jerina, D.; Yogi, H.; Yeh, H. Oxidation of the carcinogens benzo[a]pyrene and benzo[a]anthracene to dihydrodiols by a bacterium. Science 1975, 189, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lily, M.K.; Bahuguna, A.; Dangwal, K.; Garg, V. Degradation of Benzo[a]Pyrene by a novel strain Bacillus subtilis BMT4i (MTCC 9447). Braz. J. Microbiol. 2009, 40, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qian, Z.H.; Peng, T.; Huang, T.W.; Hu, Z. Oxidization of benzo[a]pyrene by CYP102 in a novel PAHs-degrader Pontibacillus sp. HN14 with potential application in high salinity environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.H.; Yang, H.C.; Li, J.; Peng, T.; Huang, T.W.; Hu, Z. The unique biodegradation pathway of benzo[a]pyrene in moderately halophilic Pontibacillus chungwhensis HN14. Chemosphere 2024, 354, 141705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goveas, L.C.; Selvaraj, R.; Vinayagam, R.; Sajankila, S.P.; Pugazhendhi, A. Biodegradation of benzo(a)pyrene by Pseudomonas strains, isolated from petroleum refinery effluent: Degradation, inhibition kinetics and metabolic pathway. Chemosphere 2023, 321, 138066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamilet, G.B.M.; Daniel, J.T.R.; Alberto, J.E.H.; Carlos, O.P.; Jeiry, T.J.; Ángel, M.R.B.; Erubiel, T.H.; Augusto, R.A.; Yanet, R.R. The catE gene of Bacillus licheniformis M2-7 is essential for growth in benzopyrene, and its expression is regulated by the Csr system. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotoky, R.; Pandey, P. The genomic attributes of Cd-resistant, hydrocarbonoclastic Bacillus subtilis SR1 for rhizodegradation of benzo(a)pyrene under co-contaminated conditions. Genomics 2021, 113, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauduro, G.P.; Leal, A.L.; Lopes, T.F.; Marmitt, M.; Valiati, V.H. Differential Expression and PAH Degradation: What Burkholderia vietnamiensi G4 Can Tell Us? Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 8831331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Liu, N.; Ren, Y.; Cui, T.B. Transcriptomic and biochemical analysis of metabolic remodeling in Bacillus subtilis MSC4 under Benzo[a]pyrene stress. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Q.; Xu, J.T.; Zhao, W.J.; Wang, J.F.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.Q.; Tian, Y. Benzo[a]pyrene might be transported by a TonB-dependent transporter in Novosphingobium pentaromativorans US6-1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.F.; Zhou, F.; Qi, Y.Q.; Piotr, D.; Bai, F.L.; Piotr, W.; Zhang, B.L. Screening of Lactobacillus strains for their ability to bind Benzo(a)pyrene and the mechanism of the process. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, O.; Lee, S.; Seo, H.; Mahmud, H.; Kim, S.; Seo, A. Biodegradation and removal of PAH by Bacillus velezensis isolated from fermented food. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Fan, F.Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, X.; Ding, A.Z.; Dou, J.F. Comparative proteomic analysis and characterization of benzo(a)pyrene removal by Microbacterium sp. strain M. CSW3 under denitrifying conditions. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 40, 1825–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Shao, D.Q.; Liu, H.Y.; Feng, J.; Feng, B.H.; Song, X.M.; Zhao, Q.; Chu, M.; Jiang, C.T.; Huang, W.; et al. Metabolomics analysis reveals that benzo[a]pyrene, a component of PM2.5, promotes pulmonary injury by modifying lipid metabolism in a phospholipase A2-dependent manner in vivo and in vitro. Redox Biol. 2017, 13, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hu, M.; Yin, L.Q.; Qin, W.; Hu, X.Y.; Lyu, S.M.; Dou, J.F. Multi-omics analyses reveal metabolic pathways of benzo[a]pyrene biodegradation under sole or mixed carbon sources. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2023, 184, 105665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.S.; Su, Q.; Yi, Q.W.; Guo, L.; Chen, D.Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.C.; Li, J. Determining the degradation mechanism and application potential of benzopyrene-degrading bacterium Acinetobacter XS-4 by screening. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 456, 131666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Zhao, X.H.; Yao, J.H.; Lu, Q.; Feng, X.J.; Wu, S.M. Biodegradation and adsorption of benzo[a]pyrene by fungi-bacterial coculture. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2024, 283, 116811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, M.; Kafilzadeh, F.; Sabokbar, A. Biodegradation of Phenanthrene Polluted Soil through Native Strains in the Darkhouvin Oil Field. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2023, 43, 5158–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, C.N.; Zhu, Y.P.; Li, J.L.; Li, X.T. Biodegradation of seven phthalate esters by Bacillus mojavensis B1811. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 132, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.F.; Tursun, D.; Tan, L.R.; Yang, Z.N.; Duo, Z.X.; Qin, Y.N.; Zhang, R. Whole genome sequencing and analysis of benzo(a)pyrene-degrading bacteria Bacillus cereus M72-4. Genome 2025, 68, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luang-In, V.; Deeseenthum, S. Exopolysaccharide-producing isolates from Thai milk kefir and their antioxidant activities. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Long, Y.; Liang, X.J.; He, B.Y.; Yu, L.H.; Ye, J.S. Benzo(a)pyrene degradation by cytochrome P450 hydroxylase and the functional metabolism network of Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Huo, Y.Y.; Cheng, H.; Wang, C.S.; Xu, X.W. Complete genome sequence of a benzo[a]pyrene-degrading bacterium Altererythrobacter epoxidivorans CGMCC 1.7731T. Mar. Genom. 2016, 25, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouanneau, Y.; Meyer, C.; Duraffourg, N.; Duraffourg, N. Dihydroxylation of four- and five-ring aromatic hydrocarbons by the naphthalene dioxygenase from Sphingomonas CHY-1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.N.; Yin, H.; Chang, J.J.; Peng, H.; Dang, Z. Physiology and bioprocess of single cell of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in bioremediation of co-existed benzo[a]pyrene and copper. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 32, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Aparicio, A.; Hernández-Eligio, J.; Toribio-Jiménez, J.; Rodríguez-Barrera, M.; Castellanos-Escamilla, M.; RomeroRamírez, Y. Research Article Genetic expression of pobA and fabHB in Bacillus licheniformis M2-7 in the presence of benzo[a]pyrene. Genet. Mol. Res. 2018, 17, 16039916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.W.; Lima, B.P.; Herbomel, G.G.; Gopinath, T.; McDonald, L.; Shyne, M.T.; Lee, J.K.; Kreth, J.; Ross, K.F.; Veglia, G.; et al. An intramembrane sensory circuit monitors sortase A–mediated processing of streptococcal adhesins. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaas9941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesankar, P.J.; Pal, M.; Patil, A.; Qureshi, A. Microbial exopolymeric substances and biosurfactants as ‘bioavailability enhancers’ for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons biodegradation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 20, 5823–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, H.C.; Lynch, S.G.; Ryall, G.J. A Metabolic Roadmap for Somatic Stem Cell Fate. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 1052–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiza, L.; Hussain, F.M.M.; Samiah, A.; Muhammad, M.; Urooj, H.; Hussain, I.S.; Muhammad, A.; Seok, H.K.; Che, S.; Liu, Q. Reprisal of Schima superba to Mn stress and exploration of its defense mechanism through transcriptomic analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1022686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.Q.; Aslam, M.; Liu, X.J.; Du, H.; Xie, X.H.; Jia, H.J.; Huang, N.; Tang, K.M.; Yang, Y.Q.; Li, P. Impact of Pb on Chlamydomonas reinhardtii at Physiological and Transcriptional Levels. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritash, A.K.; Kaushik, C.P. Biodegradation aspects of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Arab, A.A.K.; Abou-Bakr, S.; Maher, R.A.; El-Hendawy, H.H.; Awad, A.A. Degradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons as Affected by Some Lactic Acid Bacteria. Am. J. Sci. 2010, 6, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene Name | Accession No. | Predicted Function |
|---|---|---|
| fabHB | AAEQ98_05520 | beta-ketoacyl-ACP synthase III FabHB [EC:2.3.1.180] |
| betB | AAEQ98_15130 | betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase [EC:1.2.1.8] |
| dapA | AAEQ98_09030 | 4-hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate synthase [EC:4.3.3.7] |
| pucE | AAEQ98_15870 | xanthine dehydrogenase subunit E [EC:1.17.1.4] |
| pucD | AAEQ98_15875 | xanthine dehydrogenase subunit D [EC:1.17.1.4] |
| acyP | AAEQ98_04155 | acylp1.3.13.3hosphatase [EC:3.6.1.7] |
| bioI | AAEQ98_14610 | cytochrome P450 [EC:1.14.14.46] |
| phoD | AAEQ98_01630 | alkaline phosphatase PhoD [EC:3.1.3.1] |
| phoB | AAEQ98_03160 | alkaline phosphatase PhoB [EC:3.1.3.1] |
| qdoI | AAEQ98_19870 | quercetin 2,3-dioxygenase [EC:1.13.11.24] |
| ssuD | AAEQ98_04825 | alkanesulfonate monooxygenase [EC:1.14.14.5 1.14.14.34] |
| cdoA | AAEQ98_15170 | cysteine dioxygenase family protein [EC:1.13.11.20] |
| Name | CAS | RT (min) | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Molecular Formula | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-methyl-5-propylnonane | 31081-18-2 | 12.871 | 184.36 | C13H28 | <0.0001 |
| 4H-Pyran-4-one,2,3-dihydro-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl | 28564-83-2 | 5.71 | 144.13 | C6H8O4 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duo, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Jin, A.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Qin, Y. Determining the Benzo[a]pyrene Degradation, Tolerance, and Adsorption Mechanisms of Kefir-Derived Bacterium Bacillus mojavensis TC-5. Foods 2025, 14, 2727. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152727
Duo Z, Li H, Wang Z, Zhang Z, Yang Z, Jin A, Zhang M, Zhang R, Qin Y. Determining the Benzo[a]pyrene Degradation, Tolerance, and Adsorption Mechanisms of Kefir-Derived Bacterium Bacillus mojavensis TC-5. Foods. 2025; 14(15):2727. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152727
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuo, Zhixian, Haohao Li, Zeyu Wang, Zhiwei Zhang, Zhuonan Yang, Aofei Jin, Minwei Zhang, Rui Zhang, and Yanan Qin. 2025. "Determining the Benzo[a]pyrene Degradation, Tolerance, and Adsorption Mechanisms of Kefir-Derived Bacterium Bacillus mojavensis TC-5" Foods 14, no. 15: 2727. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152727
APA StyleDuo, Z., Li, H., Wang, Z., Zhang, Z., Yang, Z., Jin, A., Zhang, M., Zhang, R., & Qin, Y. (2025). Determining the Benzo[a]pyrene Degradation, Tolerance, and Adsorption Mechanisms of Kefir-Derived Bacterium Bacillus mojavensis TC-5. Foods, 14(15), 2727. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152727







