Emulsifying Properties of Oat Protein/Casein Complex Prepared Using Atmospheric Cold Plasma with pH Shifting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Atmospheric Cold Plasma (ACP) and pH-Shifting Pre-Treatment
2.3. Particle Size Analysis (PSA) and Zeta Potential (ζ-Potential) Estimation
2.4. Protein Solubility and Surface Hydrophobicity (SHo)
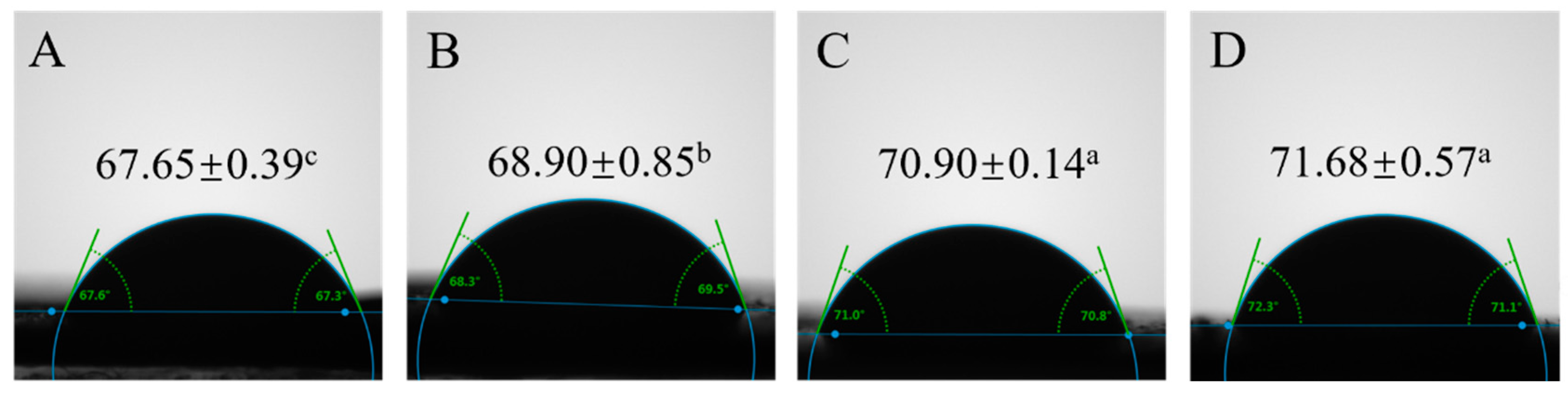
2.5. Wettability Measurement
2.6. Free Sulfhydryl Content Analysis
2.7. FTIR and Intrinsic Fluorescence Analysis
2.8. Dynamic Interfacial Pressure
2.9. Preparation of O/W Emulsions
2.10. Measurement of Emulsion Droplet Size and EAI of O/W Emulsions
2.11. Morphology of Emulsion Droplets
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
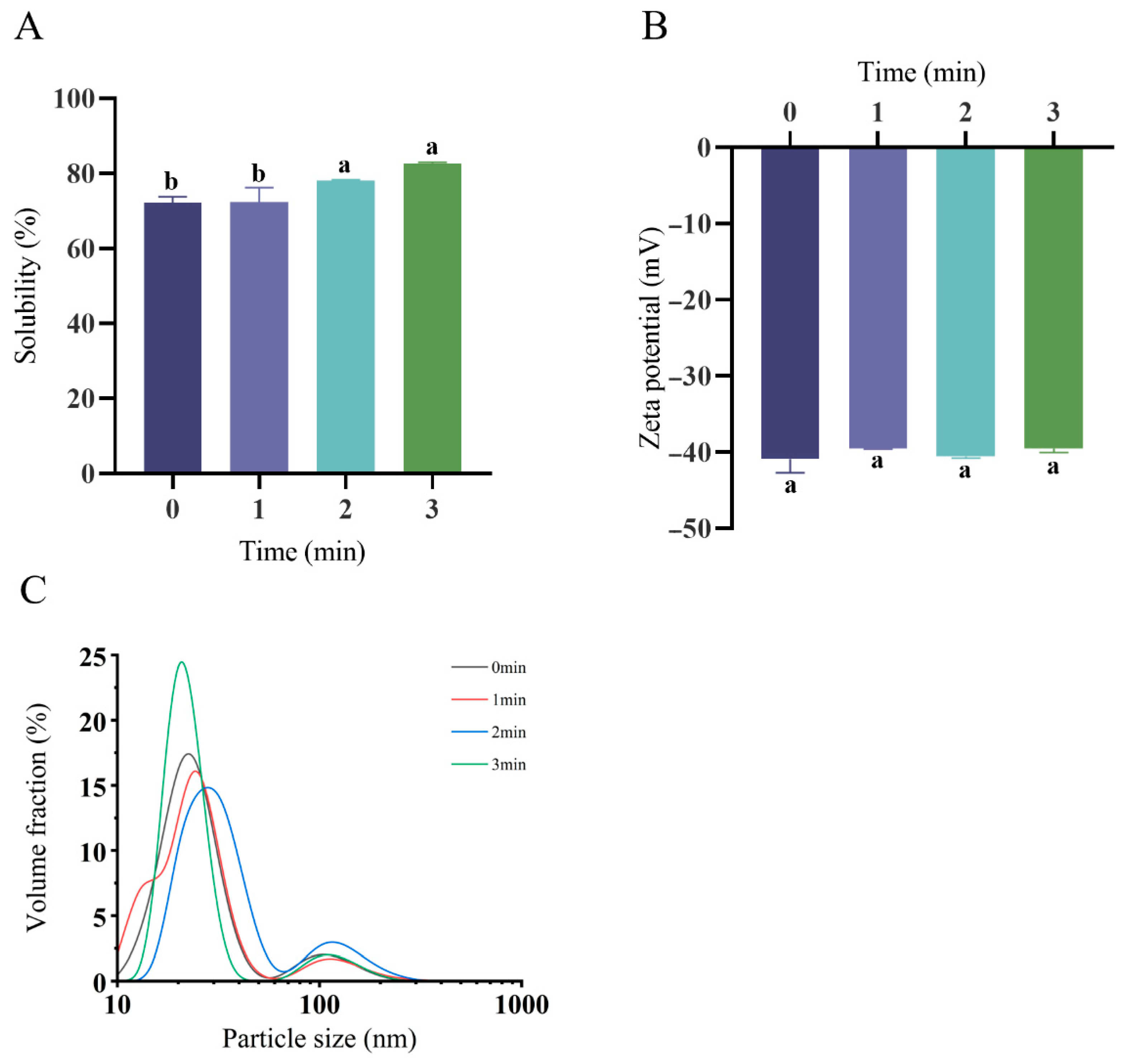
3.1. Protein Solubility, ζ-Potential, and Particle Size Distribution of OPI/Casein
3.2. Free Sulfhydryl, FTIR, and Surface Hydrophobicity Analyses
3.3. Secondary Structure of OPI/Casein
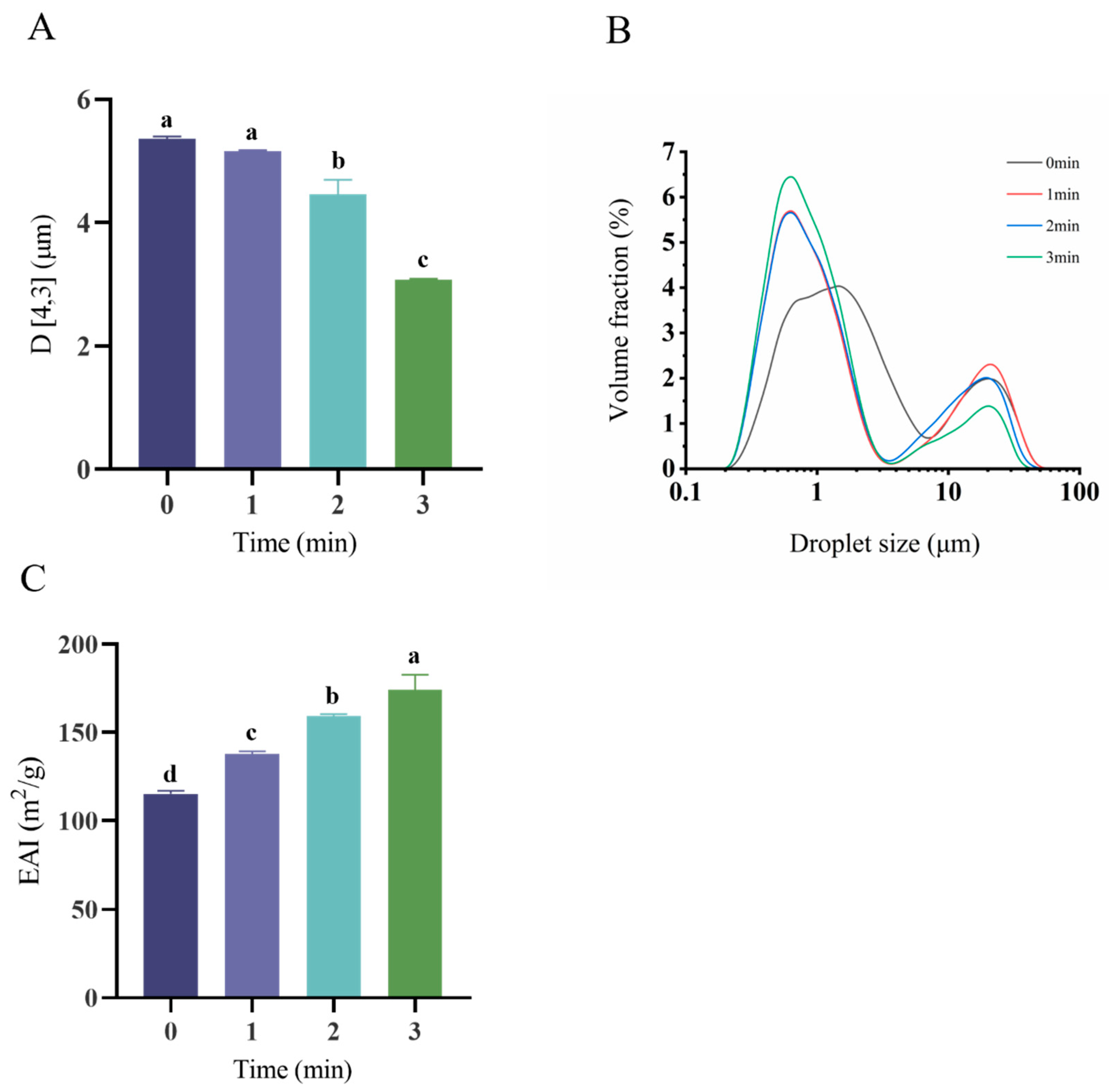
3.4. Emulsion Droplet Size Distribution and Emulsification Activity
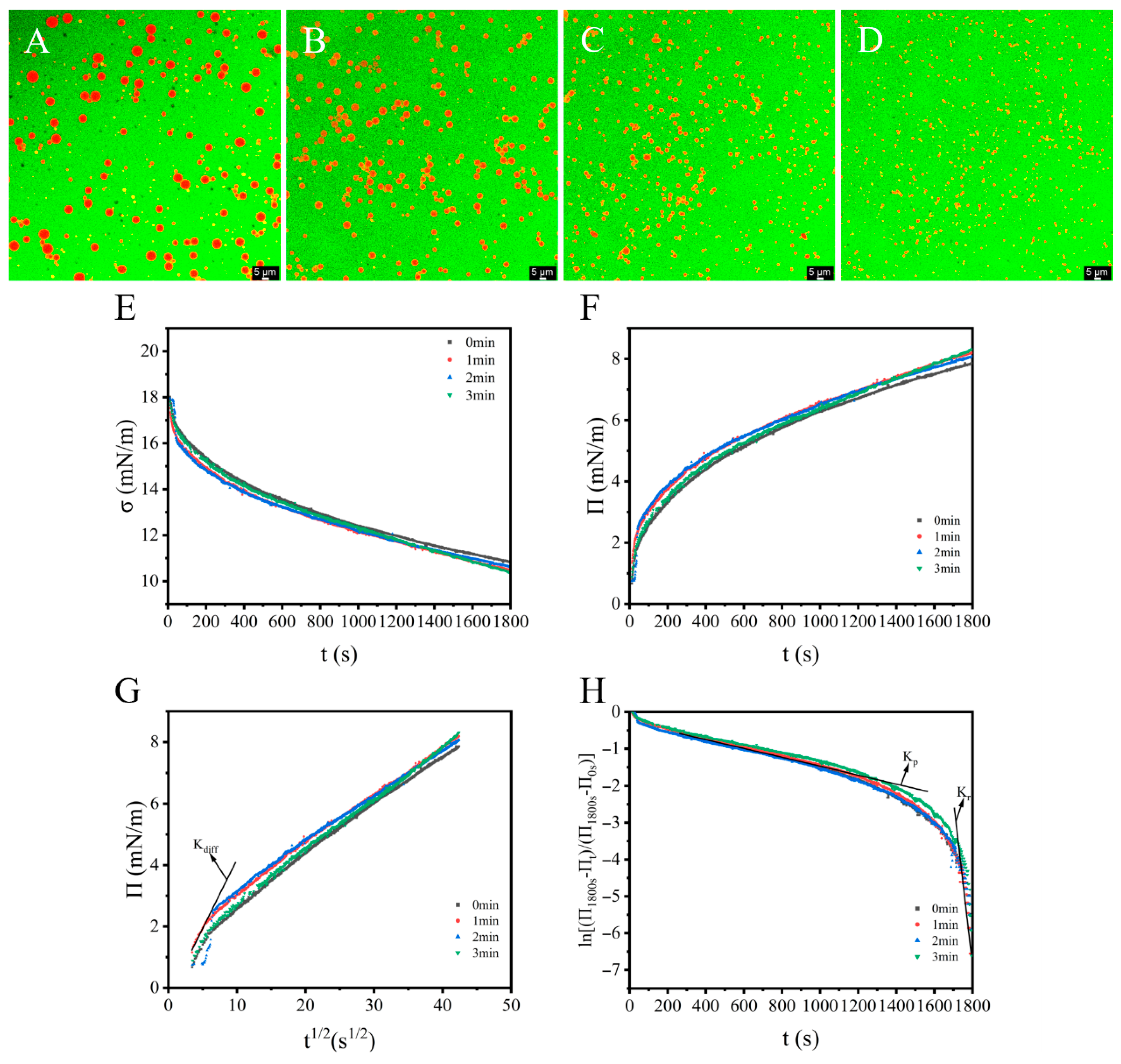
3.5. CLSM and Interfacial Property Analyses
| π1800s (mN/m) | kdiff (mN/m/s1/2) | kp (×103/s) | kr (×103/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 min | 7.86 | 0.427 | 1.00 | 66.00 |
| 1 min | 8.19 | 0.437 | 1.00 | 79.00 |
| 2 min | 8.08 | 1.36 | 1.00 | 56.00 |
| 3 min | 8.32 | 0.424 | 1.00 | 92.00 |
4. Discussion
- (I)
- Diffusion: Initial adsorption is driven by concentration gradients, exhibiting linear π vs. t 1/2 kinetics when diffusion-controlled. The slope defines the diffusion coefficient (kdiff) [54].
- (II)
- Penetration and (III) Rearrangement: Post-diffusion barriers (interfacial steric constraints/energy barriers) dominate, transitioning adsorption kinetics to penetration–rearrangement dependence [55]. This multi-stage behavior is quantifiable via first-order phenomenological modeling [41].ln[(π1800s − πt)/(π1800s − π0s)] = − ki × t
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eazhumalai, G.; Kalaivendan, R.G.T.; Annapure, U.S. Effect of atmospheric pin-to-plate cold plasma on oat protein: Structural, chemical, and foaming characteristics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 125103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eazhumalai, G.; Ranjitha Gracy, T.K.; Mishra, A.; Annapure, U.S. Atmospheric pressure nonthermal pin to plate plasma system for the microbial decontamination of oat milk. J. Food Process. Pres. 2021, 46, e16181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-B.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.-Y.; Cao, Y.; Zheng, M.-Z.; Liu, J.-S.; Wu, F. Effect of acetylation and succinylation on physicochemical properties and structural characteristics of oat protein isolate. Process Biochem. 2017, 57, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollakhalili-Meybodi, N.; Arab, M.; Zare, L. Harmful compounds of soy milk: Characterization and reduction strategies. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 3723–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.A.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, V.; Sharma, R. Milk Analog: Plant based alternatives to conventional milk, production, potential and health concerns. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3005–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brückner-Gühmann, M.; Benthin, A.; Drusch, S. Enrichment of yoghurt with oat protein fractions: Structure formation, textural properties and sensory evaluation. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 86, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, S.M.; Hassan, M.G.; Ahmed, R.B.; Abdelmontaleb, H.S. Impact of oat flour on some chemical, physicochemical and microstructure of processed cheese. J. Food Process. Pres. 2021, 45, e15761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.A.; Hamad, E.M.; Ashoush, I.S. Effect of Partial Fat Replacement by Whey Protein, Oat, Wheat Germ and Modified Starch on Sensory Properties, Viscosity and Antioxidant Activity of Reduced Fat Ice Cream. FNS 2016, 7, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zeng, Q.-H.; Liu, G.; Peng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jing Wang, J. Effects of ultrasound-assisted basic electrolyzed water (BEW) extraction on structural and functional properties of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) proteins. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 71, 105364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagliani, L.; Silva, J.V.C.; Saffon, M.; Dombrowski, J. On the foaming properties of plant proteins: Current status and future opportunities. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 118, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Sehrawat, R.; Kong, Y. Oat proteins: A perspective on functional properties. LWT 2021, 152, 112307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, M.; Tong, X.; Farid, M.S.; Chang, C.; Guo, Y.; Lian, L.; Zeng, X.; Pan, D.; Wu, Z. Enhancement of gum Arabic/casein microencapsulation on the survival of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum in the stimulated gastrointestinal conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 246, 125639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranadheera, C.S.; Liyanaarachchi, W.S.; Chandrapala, J.; Dissanayake, M.; Vasiljevic, T. Utilizing unique properties of caseins and the casein micelle for delivery of sensitive food ingredients and bioactives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 57, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Gao, A.; Xu, H.; Chen, Y. Effects of Dielectric Barrier Discharges (DBD) Cold Plasma Treatment on Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Zein Powders. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2017, 10, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekezie, F.-G.C.; Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W. Effects of atmospheric pressure plasma jet on the conformation and physicochemical properties of myofibrillar proteins from king prawn (Litopenaeus vannamei). Food Chem. 2019, 276, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizollahi, E.; Arshad, M.; Yadav, B.; Ullah, A.; Roopesh, M. Degradation of deoxynivalenol by atmospheric-pressure cold plasma and sequential treatments with heat and UV light. Food Eng. Rev. 2020, 13, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Nayak, G.; Bruggeman, P.; Annor, G.; Ismail, B.P. Impact of plasma reactive species on the structure and functionality of pea protein isolate. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavian Mehr, H.; Koocheki, A. Effect of atmospheric cold plasma on structure, interfacial and emulsifying properties of Grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 106, 105899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Nasiru, M.M.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L. Atmospheric cold plasma treatment of soybean protein isolate: Insights into the structural, physicochemical, and allergenic characteristics. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Feizollahi, E.; Roopesh, M.S.; Chen, L. Improvement of pea protein gelation at reduced temperature by atmospheric cold plasma and the gelling mechanism study. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 67, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Roopesh, M.S.; Chen, L. Pre-treatment by combining atmospheric cold plasma and pH-shifting to prepare pea protein concentrate powders with improved gelling properties. Food Res. Int. 2022, 154, 111028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhu, B.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, Y.L. Interfacial Structural Role of pH-Shifting Processed Pea Protein in the Oxidative Stability of Oil/Water Emulsions. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Du, J.; Bai, Y. Effect of pH-shifting treatment on structural and heat induced gel properties of peanut protein isolate. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhao, J.; Cao, X.; Ye, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yue, J.; Yang, L.; Jin, R.; Sun, H. Low pH-shifting treatment would improve functional properties of black turtle bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) protein isolate with immunoreactivity reduction. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krentz, A.; García-Cano, I.; Ortega-Anaya, J.; Jiménez-Flores, R. Use of casein micelles to improve the solubility of hydrophobic pea proteins in aqueous solutions via low-temperature homogenization. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.L.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, H.B.; Xiong, H. Distribution and effects of natural selenium in soybean proteins and its protective role in soybean β-conglycinin (7S globulins) under AAPH-induced oxidative stress. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, D.; Meenan, B.J. Atmospheric Dielectric Barrier Discharge Treatments of Polyethylene, Polypropylene, Polystyrene and Poly(ethylene terephthalate) for Enhanced Adhesion. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 2325–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segat, A.; Misra, N.N.; Cullen, P.J.; Innocente, N. Atmospheric pressure cold plasma (ACP) treatment of whey protein isolate model solution. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 29, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Cheng, C.; Fang, S.; McClements, D.J.; Ma, L.; Chen, X.; Zou, L.; Liang, R.; Liu, W. Study on curcumin encapsulated in whole nutritional food model milk: Effect of fat content, and partitioning situation. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 90, 104990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; True, A.D.; Sha, L.; Xiong, Y.L. Structural modification of oat protein by thermosonication combined with high pressure for O/W emulsion and model salad dressing production. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 255, 128109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, C.; Han, M.; Zhou, G.; Xu, X. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure treatment on the emulsifying behavior of myosin and its underlying mechanism. LWT 2021, 146, 111397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Tu, S.; Ghosh, S.; Nickerson, M.T. Effect of pH on the inter-relationships between the physicochemical, interfacial and emulsifying properties for pea, soy, lentil and canola protein isolates. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni-Shahri, F.S.; Housaindokht, M.R.; Bozorgmehr, M.R.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A. The influence of the flavonoid quercetin on the interaction of propranolol with human serum albumin: Experimental and theoretical approaches. J. Lumin. 2014, 154, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xiang, Q.; Liu, X.; Ding, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, Y.; Bai, Y. Inactivation of soybean trypsin inhibitor by dielectric-barrier discharge (DBD) plasma. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Liu, X.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, S.; Li, B.; Li, Y. Chitin nanofibers improve the stability and functional performance of Pickering emulsions formed from colloidal zein. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 589, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, D.; Shen, R.; Yang, X. Bacterial cellulose nanofibers improved the emulsifying capacity of soy protein isolate as a stabilizer for pickering high internal-phase emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Huang, S.; Nie, C.; Deng, Q.; Zhai, Y.; Shen, R. Effects of atmospheric pressure plasma jet on the physicochemical, functional, and antioxidant properties of flaxseed protein. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 2010–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, R.K. Effect of atmospheric pressure cold plasma treatment time and composition of feed gas on properties of skim milk. LWT 2022, 154, 112747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y. Multi-scenario simulation on the impact of China’s electricity bidding policy based on complex networks model. Energ. Policy 2021, 158, 112573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhao, Y.; Nitta, Y.; Yagioka, A.; Komatsuzaki, M. Performance of a No-tillage Seeder with Different Cover Crop Species and Residue Management for Sweet Sorghum for Sustainable Biofuel Production. Eng. Agric. Environ. Food 2013, 6, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-H.; Sun, X. Physicochemical and Structural Properties of 8S and/or 11S Globulins from Mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] with Various Polypeptide Constituents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 6395–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, E.; Kitamura, T.; Kuwabara, J.; Ikawa, S.; Yoshizawa, S.; Shiraki, K.; Kawasaki, H.; Arakawa, R.; Kitano, K. Chemical modification of amino acids by atmospheric-pressure cold plasma in aqueous solution. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 285403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.N.; Park, C.W.; Hahn, J.W. Detection of OH(A2σ+) and O(1D) emission spectrum generated in a pulsed corona plasma. BKCS 2000, 21, 228–232. [Google Scholar]
- Bußler, S.; Rumpold, B.A.; Fröhling, A.; Jander, E.; Rawel, H.M.; Schlüter, O.K. Cold atmospheric pressure plasma processing of insect flour from Tenebrio molitor: Impact on microbial load and quality attributes in comparison to dry heat treatment. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 36, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Han, F.; Peng, S.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Y. Behavioral Solubilization of Peanut Protein Isolate by Atmospheric Pressure Cold Plasma (ACP) Treatment. Food Bioprod. Process 2019, 12, 2018–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Zhuang, J.; Zong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Bazaka, K.; Ostrikov, K. Interaction of Atmospheric-Pressure Air Microplasmas with Amino Acids as Fundamental Processes in Aqueous Solution. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Gao, A.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.-t.; Chen, Y. Characterization of physicochemical and structural properties of atmospheric cold plasma (ACP) modified zein. Food Bioprod. Process 2017, 106, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Wang, J.-m.; Cheng, L.-m.; Lu, Y.-l.; Li, S.-h.; Chen, Y. Behavior of Zein in Aqueous Ethanol under Atmospheric Pressure Cold Plasma Treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7352–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alston, R.W.; Lasagna, M.; Grimsley, G.R.; Scholtz, J.M.; Reinhart, G.D.; Pace, C.N. Peptide Sequence and Conformation Strongly Influence Tryptophan Fluorescence. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 2280–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callis, P.R.; Liu, T. Quantitative Prediction of Fluorescence Quantum Yields for Tryptophan in Proteins. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 4248–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundo, J.L.M.; Zhou, H.; Tan, Y.; Liu, J.; McClements, D.J. Enhancing emulsion functionality using multilayer technology: Coating lipid droplets with saponin-polypeptide-polysaccharide layers by electrostatic deposition. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Du, L.; Zhan, F.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Z.; Pan, D. Phenolic structure dependent interaction onto modified goose liver protein enhanced by pH shifting: Modulations on protein interfacial and emulsifying properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, A.A.; Carrara, C.R.; Sánchez, C.C.; Santiago, L.G.; Rodríguez Patino, J.M. Interfacial dynamic properties of whey protein concentrate/polysaccharide mixtures at neutral pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Pan, C.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Pei, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, W. Interfacial behavior of coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) globulins at different pH: Relation to emulsion stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 108958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, G. Insight into the oil polarity impact on interfacial properties of myofibrillar protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 128, 107563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment Time (min) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particle size (nm) | 149.70 ± 1.73 c | 157.40 ± 2.85 b | 178.30 ± 1.13 a | 151.96 ± 0.99 c |
| Sample | Alpha Helix (%) | Beta Sheet (%) | Turn (%) | Unordered Coil (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 min | 12.16 | 28.29 | 42.16 | 17.40 |
| 1 min | 12.46 | 28.27 | 41.75 | 17.51 |
| 2 min | 12.75 | 28.18 | 42.16 | 16.91 |
| 3 min | 12.80 | 26.95 | 43.13 | 17.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teng, Y.; Ou, M.; Wu, J.; Jiang, T.; Zheng, K.; Guo, Y.; Pan, D.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Z. Emulsifying Properties of Oat Protein/Casein Complex Prepared Using Atmospheric Cold Plasma with pH Shifting. Foods 2025, 14, 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152702
Teng Y, Ou M, Wu J, Jiang T, Zheng K, Guo Y, Pan D, Zhang T, Wu Z. Emulsifying Properties of Oat Protein/Casein Complex Prepared Using Atmospheric Cold Plasma with pH Shifting. Foods. 2025; 14(15):2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152702
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeng, Yang, Mingjuan Ou, Jihuan Wu, Ting Jiang, Kaige Zheng, Yuxing Guo, Daodong Pan, Tao Zhang, and Zhen Wu. 2025. "Emulsifying Properties of Oat Protein/Casein Complex Prepared Using Atmospheric Cold Plasma with pH Shifting" Foods 14, no. 15: 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152702
APA StyleTeng, Y., Ou, M., Wu, J., Jiang, T., Zheng, K., Guo, Y., Pan, D., Zhang, T., & Wu, Z. (2025). Emulsifying Properties of Oat Protein/Casein Complex Prepared Using Atmospheric Cold Plasma with pH Shifting. Foods, 14(15), 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152702






