Effects of Partial Freezing and Superchilling Storage on the Quality of Beef: A Kinetic Modelling Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and Chemicals
2.2. Superchilling Process–Experimental Design
2.3. Measuring of Temperature During Partial Freezing and Superchilling Storage
2.4. Characterization of the Quality Parameters
2.4.1. Determination of Drip Loss
2.4.2. Texture Analysis
2.4.3. Measurement of pH
2.4.4. Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB−N) Compounds
2.4.5. Thiobarbituric Acid−Reactive Substances (TBARS) Content
2.4.6. Colour Measurement
2.5. Kinetic Analysis
2.5.1. Kinetic Modelling for Quality Parameters
2.5.2. The Relationship Between Kinetic Rate and Storage Temperature
2.5.3. Validation of Kinetic Models
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Temperature Fluctuations During Superchilled Storage
3.2. Characterization of Quality Parameters of Beef
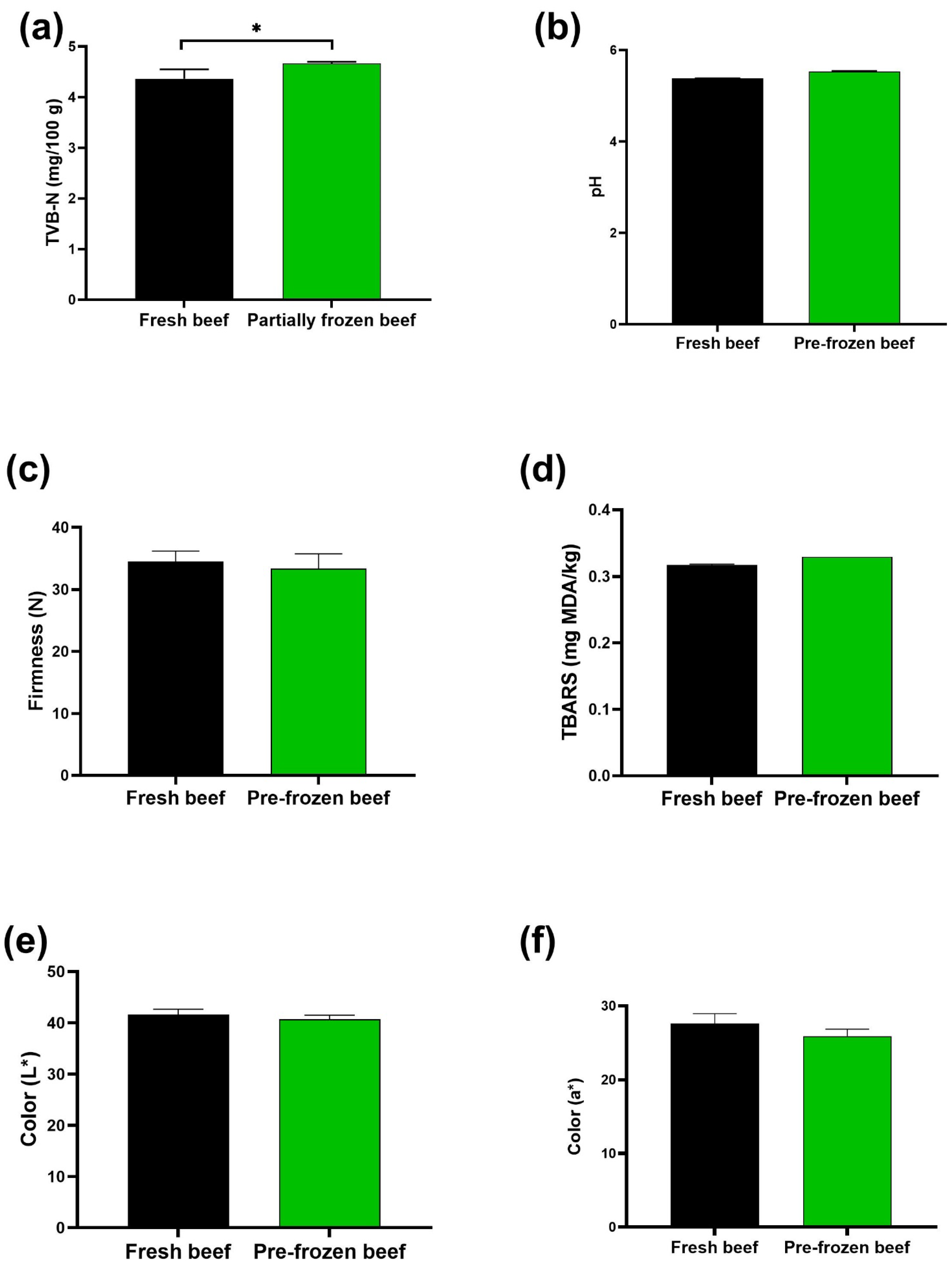
3.2.1. Effect of Partial Freezing
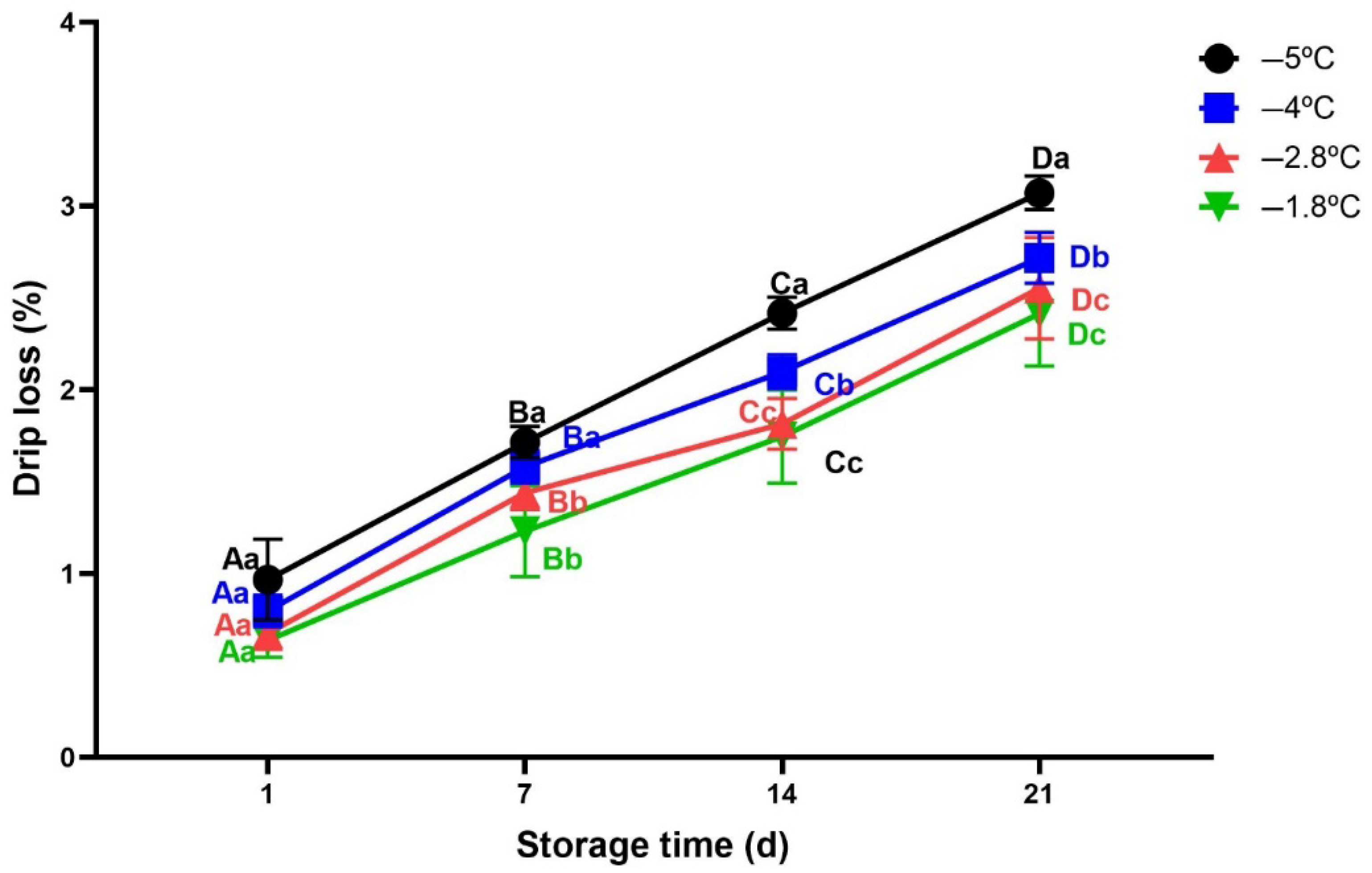
3.2.2. Drip Loss
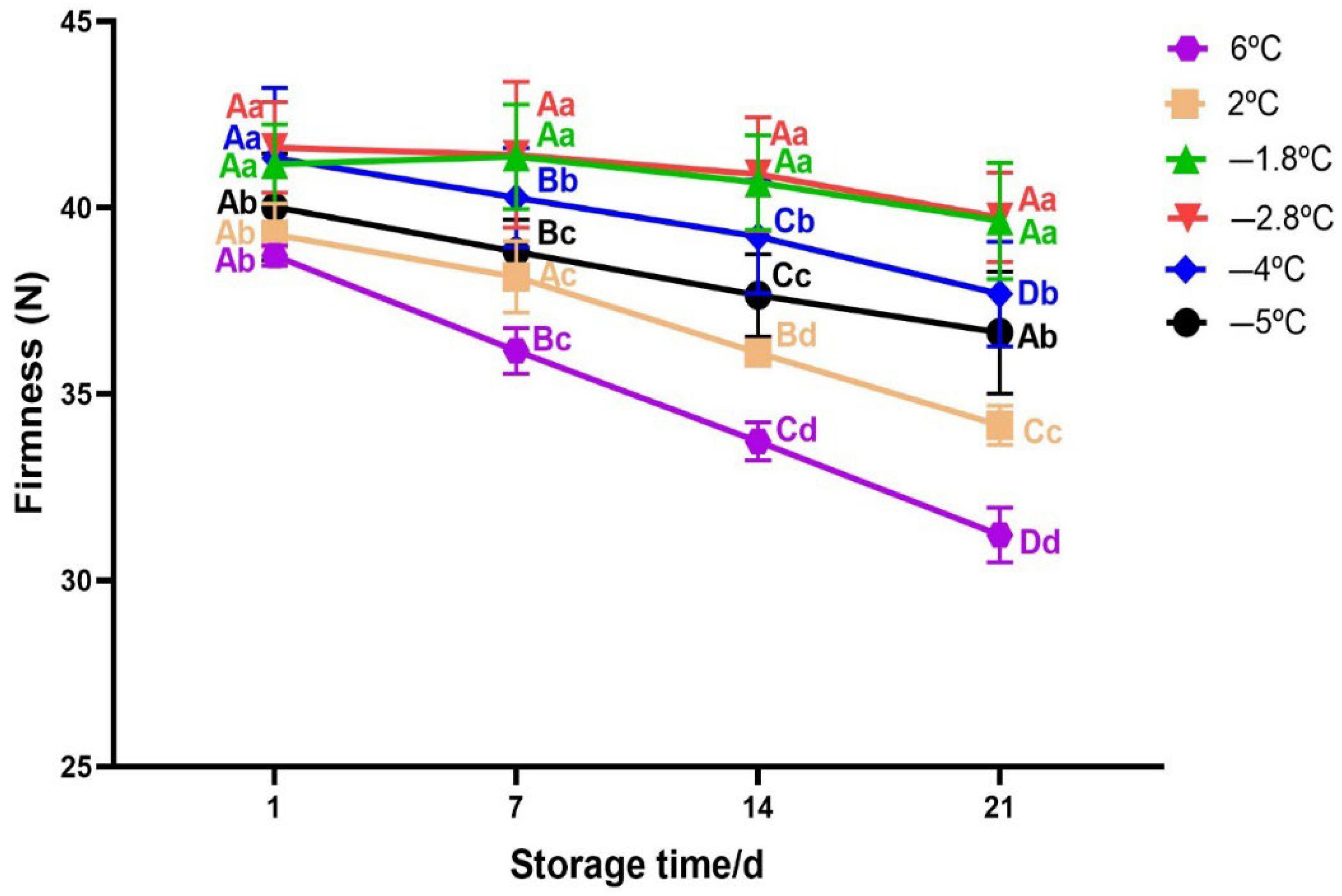
3.2.3. Texture Change
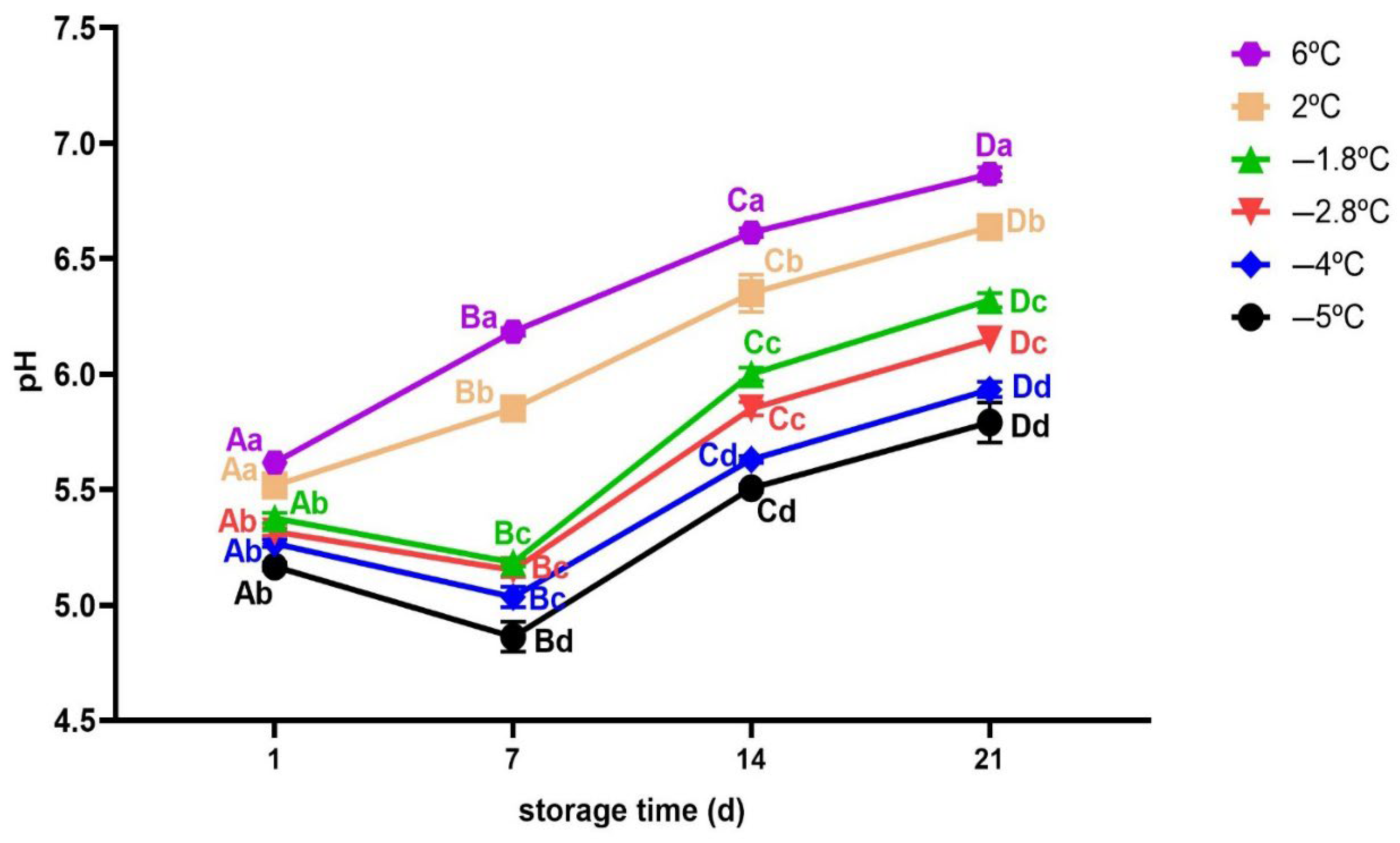
3.2.4. pH Measurement
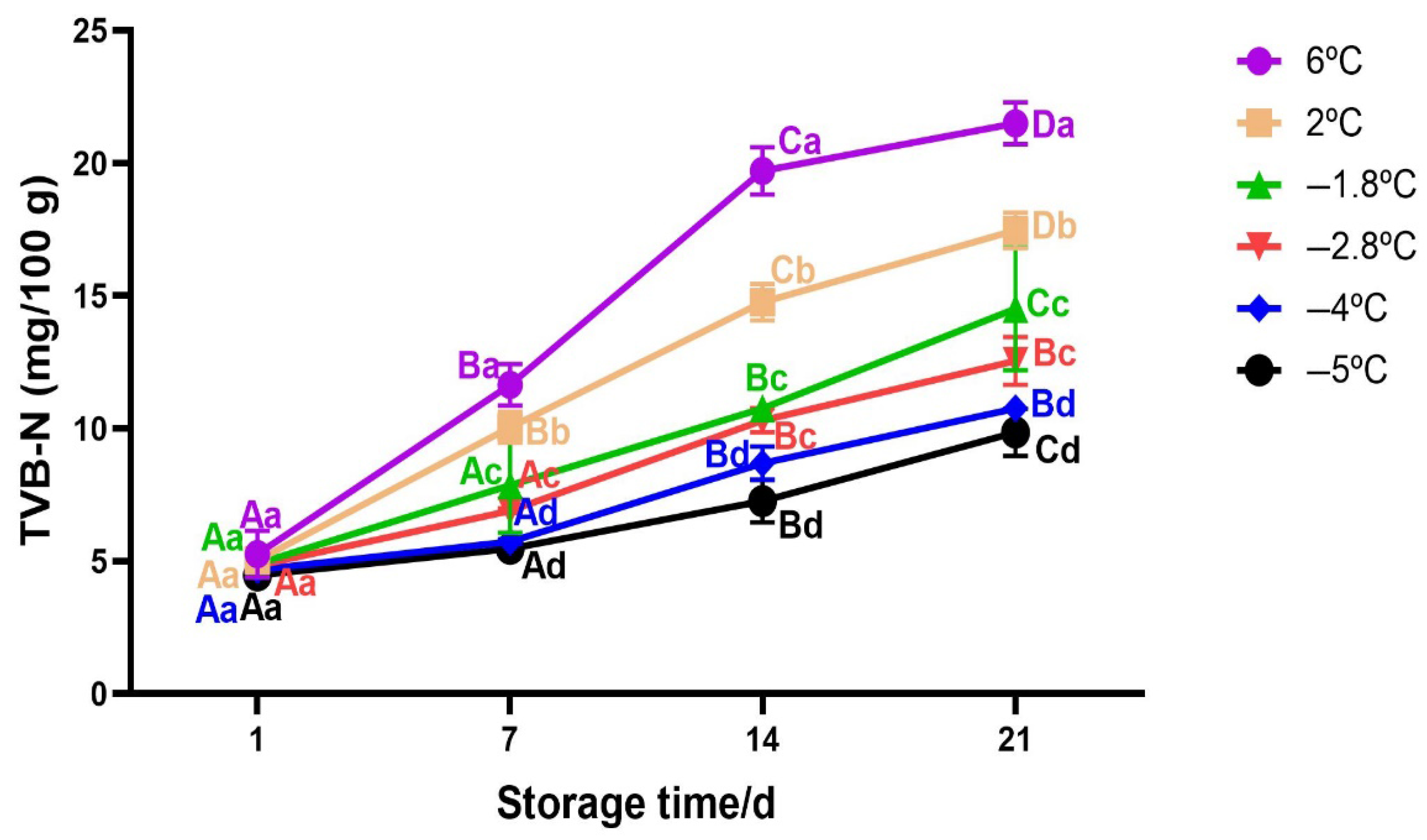
3.2.5. Changes in TVB−N of Beef During Storage
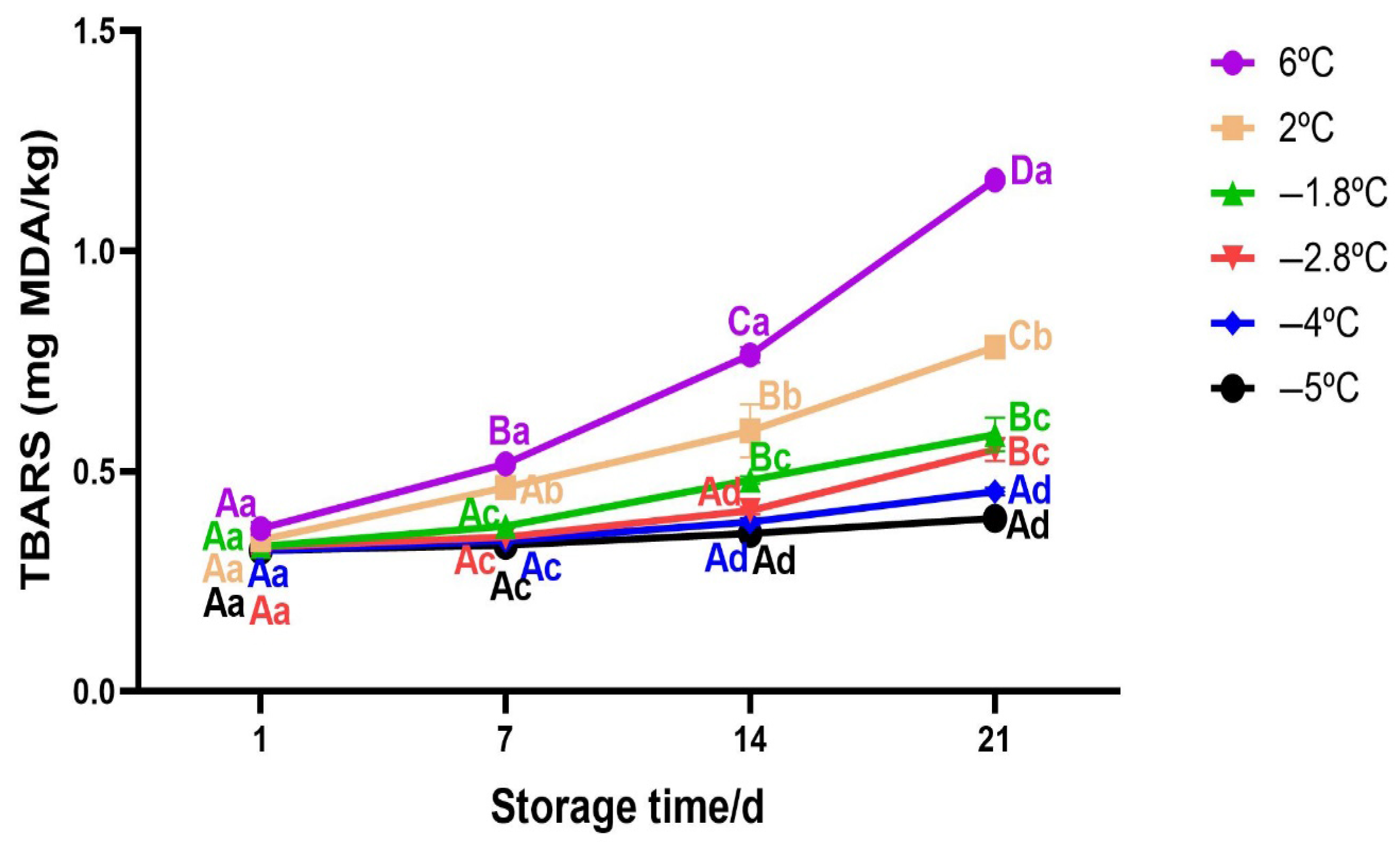
3.2.6. Changes in TBARS of Beef During Storage
3.2.7. Changes in Colour
3.3. Kinetic Modelling of Quality Change
3.3.1. Kinetic Model Parameters
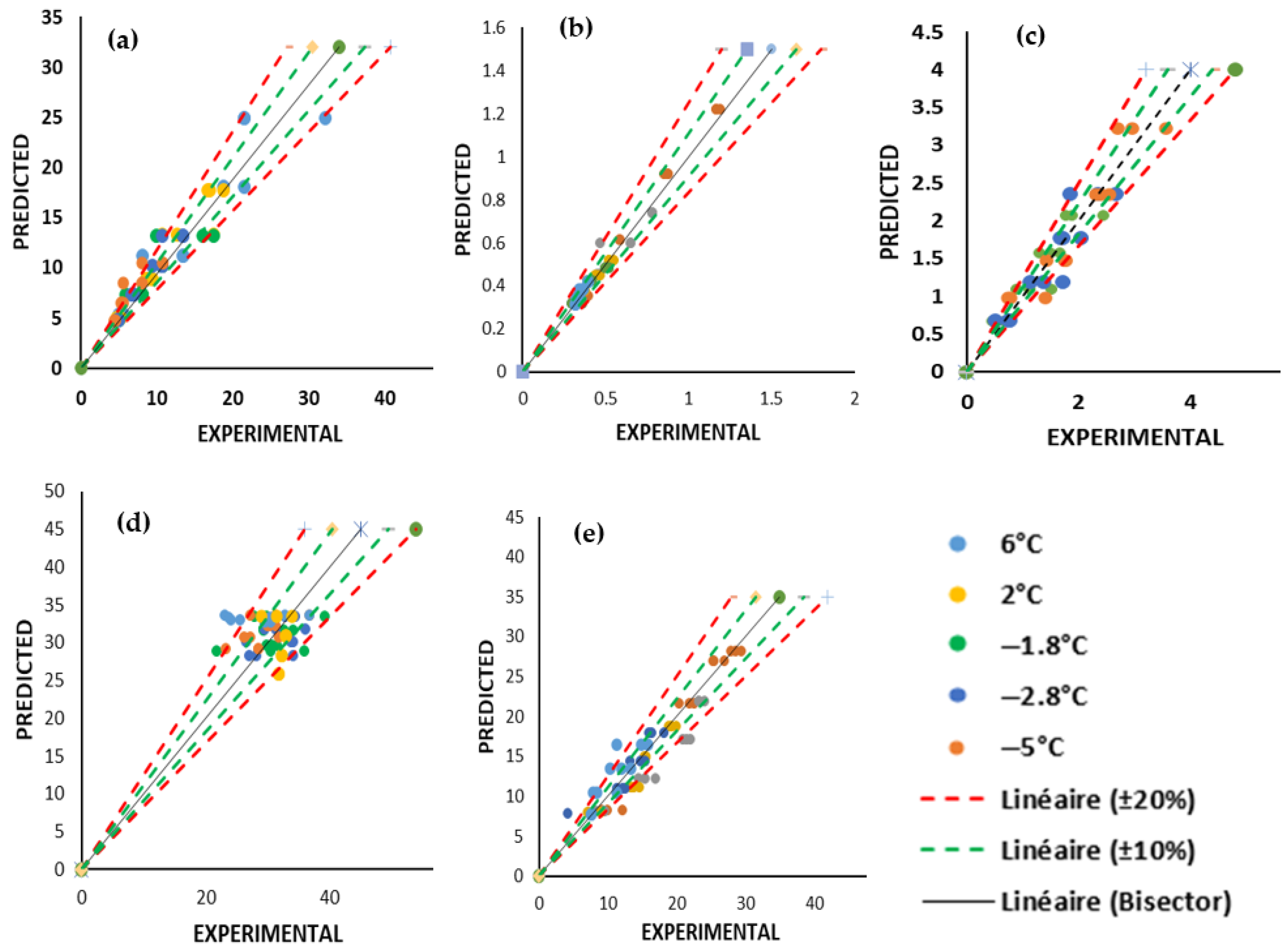
3.3.2. Model Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Activation energy (J | |
| k | Kinetic rate constant for quality change |
| n | Number of observations |
| C | Measured value of quality parameter at time t |
| Initial value of quality parameter | |
| Observed value of quality parameter at each time point | |
| Predicted value for each observation | |
| R | Universal gas constant (8.314 J) |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| MAPE | Mean absolute percentage error |
| t | Storage time (day) |
| T | Temperature (K) |
| GDP | Gross domestic product |
| Partial freezing time (seconds) | |
| Initial freezing point in °C | |
| Air temperature in °C | |
| Density of beef (kg/m3) | |
| Latent heat of fusion of water (333.6 kJ/kg) | |
| P | Shape factor (16 for infinite cylinder) |
| Q | Shape factor (4 for infinite cylinder) |
| Heat transfer coefficient (W/m2K) | |
| K | Thermal conductivity (W/mK) |
| L* | CIE coordinate for lightness of beef |
| a* | CIE coordinate for redness of beef |
| b* | CIE coordinate for yellowness of beef |
| TBARS | Thiobarbituric acid−reactive substances content |
| TVB−N | Total volatile nitrogen basic compounds |
| TBA | Thiobarbituric acid |
| TCA | Trichloroacetic acid |
References
- Ramanathan, R.; Hunt, M.C.; Price, T.; Mafi, G.G. Chapter Five—Strategies to limit meat wastage: Focus on meat discoloration. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Toldrá, F., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2021; Volume 95, pp. 183–205. [Google Scholar]
- Muth, M.K.; Birney, C.; Cuéllar, A.; Finn, S.M.; Freeman, M.; Galloway, J.N.; Gee, I.; Gephart, J.; Jones, K.; Low, L.; et al. A systems approach to assessing environmental and economic effects of food loss and waste interventions in the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 1240–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, N. Meeting the demand: An estimation of potential future greenhouse gas emissions from meat production. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 67, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD/FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2021–2030; OECD Publishing: Paris, French, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, D.L.; Thompson, J.M. Factors contributing to proteolysis and disruption of myofibrillar proteins and the impact on tenderisation in beef and sheep meat. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2002, 53, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colle, M.J.; Richard, R.P.; Killinger, K.M.; Bohlscheid, J.C.; Gray, A.R.; Loucks, W.I.; Day, R.N.; Cochran, A.S.; Nasados, J.A.; Doumit, M.E. Influence of extended aging on beef quality characteristics and sensory perception of steaks from the gluteus medius and longissimus lumborum. Meat Sci. 2015, 110, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coombs, C.E.O.; Holman, B.W.B.; Friend, M.A.; Hopkins, D.L. Long-term red meat preservation using chilled and frozen storage combinations: A review. Meat Sci. 2017, 125, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, S.; Salsi, M.; Tiburzi, M.; Rafaghelli, R.; Tessi, M.; Coutaz, V. Spoilage microflora in fresh chicken breast stored at 4 C: Influence of packaging methods. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 83, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaritzky, N.E. Frozen Storage. In Frozen Food Science and Technology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 224–247. [Google Scholar]
- Zennoune, A.; Latil, P.; Flin, F.; Perrin, J.; Weitkamp, T.; Scheel, M.; Geindreau, C.; Benkhelifa, H.; Ndoye, F.-T. Investigating the influence of freezing rate and frozen storage conditions on a model sponge cake using synchrotron X-rays micro-computed tomography. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer, A.; Özalp, B.; Dalmış, Ü.; Bilgin, V. Effects of freezing temperature and duration of frozen storage on lipid and protein oxidation in chicken meat. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulomb, D. Refrigeration and cold chain serving the global food industry and creating a better future: Two key IIR challenges for improved health and environment. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaale, L.D.; Eikevik, T.M.; Bardal, T.; Kjorsvik, E.; Nordtvedt, T.S. The effect of cooling rates on the ice crystal growth in air-packed salmon fillets during superchilling and superchilled storage. Int. J. Refrig. 2013, 36, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaale, L.D.; Eikevik, T.M.; Rustad, T.; Kolsaker, K. Superchilling of food: A review. J. Food Eng. 2011, 107, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Kang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, X. The effect of super-chilled preservation on shelf life and quality of beef during storage. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e73222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Luo, X.; Hopkins, D.L. Effect of superchilled storage on shelf life and quality characteristics of M. longissimus lumborum from Chinese Yellow cattle. Meat Sci. 2019, 149, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, R.; Kong, B.H.; Zhang, Y.G. Effect of superchilling storage on quality characterizes of beef as compared with chilled and frozen preservation. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 554, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Shang, Y.; Song, Y.; Dong, Q. Changes in the quality of super chilled rabbit meat stored at different temperatures. Meat Sci. 2016, 117, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duun, A.S.; Hemmingsen, A.K.T.; Haugland, A.; Rustad, T. Quality changes during superchilled storage of pork roast. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 2136–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, E.; Palacio, F.; Nuin, M.; Zárate, A.G.D.; Juarros, A.; Gómez, J.M.; Marco, S. RFID smart tag for traceability and cold chain monitoring of foods: Demonstration in an intercontinental fresh fish logistic chain. J. Food Eng. 2009, 93, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Karim, N.; Jiang, F.; Hu, H.; Chen, W. Assessment of quality deviation of pork and salmon due to temperature fluctuations during superchilling. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B 2022, 23, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Ye, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Dou, H. Effect of temperature fluctuation during superchilling storage on the microstructure and quality of raw pork. Meat Sci. 2023, 198, 109096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Abdi, N.; Alvarez, G.; Ndoye, F. Studying the effects of superchilling storage conditions on the microstructure and quality of chicken breast meat. J. Food Eng. 2025, 393, 112504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Xu, R.; Lu, B.; Song, X.; Liu, B. Effects of temperature fluctuations on the meat quality and muscle microstructure of frozen beef. Int. J. Refrig. 2020, 116, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Han, Y.; Gao, T.; Ye, K.; Liu, J. Effect of temperature fluctuation during frozen storage on beef quality. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Mehmood, W.; Zhang, C.; Blecker, C. Effects of frozen storage temperature and duration on changes in physicochemical properties of beef myofibrillar protein. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 8836749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taoukis, P.S.; Labuza, T.P. Applicability of time-temperature indicators as shelf life monitors of food products. J. Food Sci. 1989, 54, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Wang, Z. Using oxidation kinetic models to predict the quality indices of rabbit meat under different storage temperatures. Meat Sci. 2020, 162, 108042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Lin, H.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Meng, J.; Guan, W.; Liu, B. Modeling of chilled/supercooled pork storage quality based on the entropy weight method. Animal 2022, 12, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, J.; Paula, M.; Tanaka, M.; Filho, R.; Ramos, A.; Ramos, E. Kinetic modeling of proteolysis, tenderness, and microbial growth during beef accelerated aging by the freeze/thaw process. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Honikel, K.O. Reference methods for the assessment of physical characteristics of meat. Meat Sci. 1998, 49, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.G. Manuals of food quality control. 3. Commodities. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. FAO. Food Nutr. Pap. 1979, 14, iii-xi, 1–409. [Google Scholar]
- Ribero, G.; Rubiolo, A.; Zorrilla, S. Initial freezing point of Mozzarella cheese. J. Food Eng. 2007, 81, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnelli, M.E.; Mascheroni, R.H. Quality evaluation of foodstuffs frozen in a cryomechanical freezer. J. Food Eng. 2002, 52, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, O.; Salmerón, J.; Guillén, M.D.; Casas, C. Texture profile analysis of meat products treated with commercial liquid smoke flavourings. Food Control 2004, 15, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewthong, P.; Pomponio, L.; Carrascal, J.R.; Knøchel, S.; Wattanachant, S.; Karlsson, A.H. Changes in the quality of chicken breast meat due to superchilling and temperature fluctuations during storage. J. Poult. Sci. 2019, 56, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, E.J.; Byrne, A. An absorption apparatus for the micro-determination of certain volatile substances: The micro-determination of ammonia. Biochem. J. 1933, 27, 419–429. [Google Scholar]
- Lo Fiego, D.P.; Santoro, P.; Macchioni, P.; Mazzoni, D.; Piattoni, F.; Tassone, F.; De Leonibus, E. The effect of dietary supplementation of vitamins C and E on the α-tocopherol content of muscles, liver and kidney, on the stability of lipids, and on certain meat quality parameters of the longissimus dorsi of rabbits. Meat Sci. 2004, 67, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdougall, D.B. 13—Colour measurement of food: Principles and practice. In Colour Measurement; Gulrajani, M.L., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Stockton, UK, 2010; pp. 312–342. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, R.R.B.; Patel, A.; Patil, G. Kinetics of colour and texture changes in Gulabjamun balls during deep-fat frying. Lwt—Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratkowsky, D.A.; Olley, J.; McMeekin, T.; Ball, A. Relationship between temperature and growth rate of bacterial cultures. J. Bacteriol. 1982, 149, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakourou, M.; Taoukis, P. Kinetic modelling of vitamin C loss in frozen green vegetables under variable storage conditions. Food Chem. 2003, 83, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenjiao, F.; Yongkui, Z.; Yunchuan, C.; Junxiu, S.; Yuwen, Y. TBARS predictive models of pork sausages stored at different temperatures. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Lu, W.; Shen, H.; Luo, Y. Quality predictive models of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) at different temperatures during storage. Food Control 2011, 22, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leygonie, C.; Britz, T.J.; Hoffman, L.C. Impact of freezing and thawing on the quality of meat: Review. Meat Sci. 2012, 91, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yang, F.W.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.H.; Xie, X.L. [Effects of Freezing and Thawing Treatments on Beef Protein Secondary Structure Analyzed with ATR-FTIR]. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi 2016, 36, 3542–3546. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30198667/ (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Jiang, Q.; Jia, R.; Nakazawa, N.; Hu, Y.; Osako, K.; Okazaki, E. Changes in protein properties and tissue histology of tuna meat as affected by salting and subsequent freezing. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ertbjerg, P. On the origin of thaw loss: Relationship between freezing rate and protein denaturation. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolbe, E.; Kramer, D. Planning for Seafood Freezing. In Alaska Sea Grant College Program; University of Alaska Fairbanks: Fairbanks, AK, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Turan, H.; Kaya, Y.; Erkoyuncu, İ. Effects of glazing, packaging and phosphate treatments on drip loss in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss W., 1792) during frozen storage. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2003, 3, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Duun, A.; Rustad, T. Quality of superchilled vacuum packed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fillets stored at −1.4 °C and −3.6 °C. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Hu, F.; Mehmood, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Blecker, C. The rise of thawing drip: Freezing rate effects on ice crystallization and myowater dynamics changes. Food Chem. 2021, 373, 131461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, P.; Sun, D.-W.; Du, C.-J.; Allen, P.; Downey, G. Prediction of beef eating quality from colour, marbling and wavelet texture features. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Quinn, T.G.; Legako, J.F.; Brooks, J.C.; Miller, M.F. Evaluation of the contribution of tenderness, juiciness, and flavor to the overall consumer beef eating experience. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2018, 2, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Hao, R.; Guo, Z.; Han, L.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, W. Combined effects of superchilling and natural extracts on beef preservation quality. LWT 2022, 153, 112520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahuaud, D.; Mørkøre, T.; Langsrud, Ø.; Sinnes, K.; Veiseth, E.; Ofstad, R.; Thomassen, M. Effects of −1.5 °C super-chilling on quality of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) pre-rigor fillets: Cathepsin activity, muscle histology, texture and liquid leakage. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Yan, L.; Xiao, S.; Hou, B.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Bai, T.; Zhu, K.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J. Effects of different low-temperature storage methods on the quality and processing characteristics of fresh beef. Foods 2023, 12, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Niu, Y.; Wei, H.; Lin, Y.; Lu, X.; Yamashita, T.; Yu, K.; Takaki, K.; Yuan, C. Effect of super-chilling storage on maintenance of quality and freshness of the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Food Qual. Saf. 2023, 7, fyad008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Zhou, C.; Ge, X.; Ye, K.; Wang, P.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, G. The effect of different degrees of superchilling on shelf life and quality of pork during storage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelidis, B.; Haas, D.; Grieshaber, M. Extracellular and intracellular acid-base status with regard to the energy metabolism in the oyster crassostrea gigas during exposure to air. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2005, 78, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Calleja, J.M.; García-López, M.-L.; Santos, J.A.; Otero, A. Development of the aerobic spoilage flora of chilled rabbit meat. Meat Sci. 2005, 70, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Holman, B.W.B.; Giteru, S.G.; Hopkins, D.L. Total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) and its role in meat spoilage: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 280–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dong, P.; Li, K.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X.; Mao, Y.; Niu, L.; Hopkins, D.L.; Luo, X.; Liang, R.; et al. Effect of the combination of superchilling and super-chilled storage on shelf-life and bacterial community dynamics of beef during long-term storage. Meat Sci. 2022, 192, 108910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kwon, J.A.; Kim, M.; Lee, Y.E.; Ryu, M.; Jo, C. Effect of supercooling on storage ability of different beef cuts in comparison to traditional storage methods. Meat Sci. 2023, 199, 109137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, X.; Xie, B.; Sun, Z. Inhibitory effects of lotus seedpod procyanidins against lipid and protein oxidation and spoilage organisms in chilled-storage beef. LWT 2022, 160, 113247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganhão, R.; Estévez, M.; Morcuende, D. Suitability of the TBA method for assessing lipid oxidation in a meat system with added phenolic-rich materials. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegg, R.B.; Shahidi, F. Off Flavors and Rancidity in Foods. In Handbook of Meat, Poultry and Seafood Quality; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 127–139. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral, A.B.; Silva, M.V.D.; Lannes, S.C.D.S. Lipid oxidation in meat: Mechanisms and protective factors–A review. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.; Juncher, D.; Henckel, P.; Karlsson, A.; Bertelsen, G.; Skibsted, L.H. Oxidative stability of chilled pork chops following long term freeze storage. Meat Sci. 2004, 68, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, R.; Lambert, L.; Nair, M.N.; Morgan, B.; Feuz, R.; Mafi, G.; Pfeiffer, M. Economic Loss, Amount of Beef Discarded, Natural Resources Wastage, and Environmental Impact Due to Beef Discoloration. Meat Muscle Biol. 2022, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, B.; Graiver, N.; Califano, A.; Zaritzky, N. Physicochemical characteristics and quality parameters of a beef product subjected to chemical preservatives and high hydrostatic pressure. Meat Sci. 2015, 100, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, D.F.; Bambicha, R.; Laporte, G.; Cárdenas, F.C.; Mestorino, N. Kinetics of colour and texture changes of beef during storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Duan, X.; Holman, B.W.B.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X.; Hopkins, D.L.; Luo, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y. The retail color characteristics of vacuum-packaged beef m. longissimus lumborum following long-term superchilled storage. Meat Sci. 2023, 196, 109050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremiah, L.E.; Gibson, L.L. The influence of storage temperature and storage time on color stability, retail properties and case-life of retail-ready beef. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Hanna, M.A. Kinetics of drip loss, cooking loss and color degradation in frozen ground beef during storage. J. Food Eng. 1989, 9, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeldaiem, M.H.; Ali, H.G.M.; Foda, M.I. Improving the quality of minced beef by using mulberry leaves extract. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, C.; Guan, W.; Blecker, C. Effect of sub-freezing storage (−6, −9 and −12 °C) on quality and shelf life of beef. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2129–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Hua, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, W. Rapid evaluation of mutton quality by near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2018, 9, 2734–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leducq, D.; Alvarez, G.; Evans, J.; Verboven, P.; Widell, K.N. Food Supply Assessment Tool Including Renewable Energy Sources; Deliverable D4.1, ENOUGH Project, Grant Agreement No. 101036588; INRAE: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]

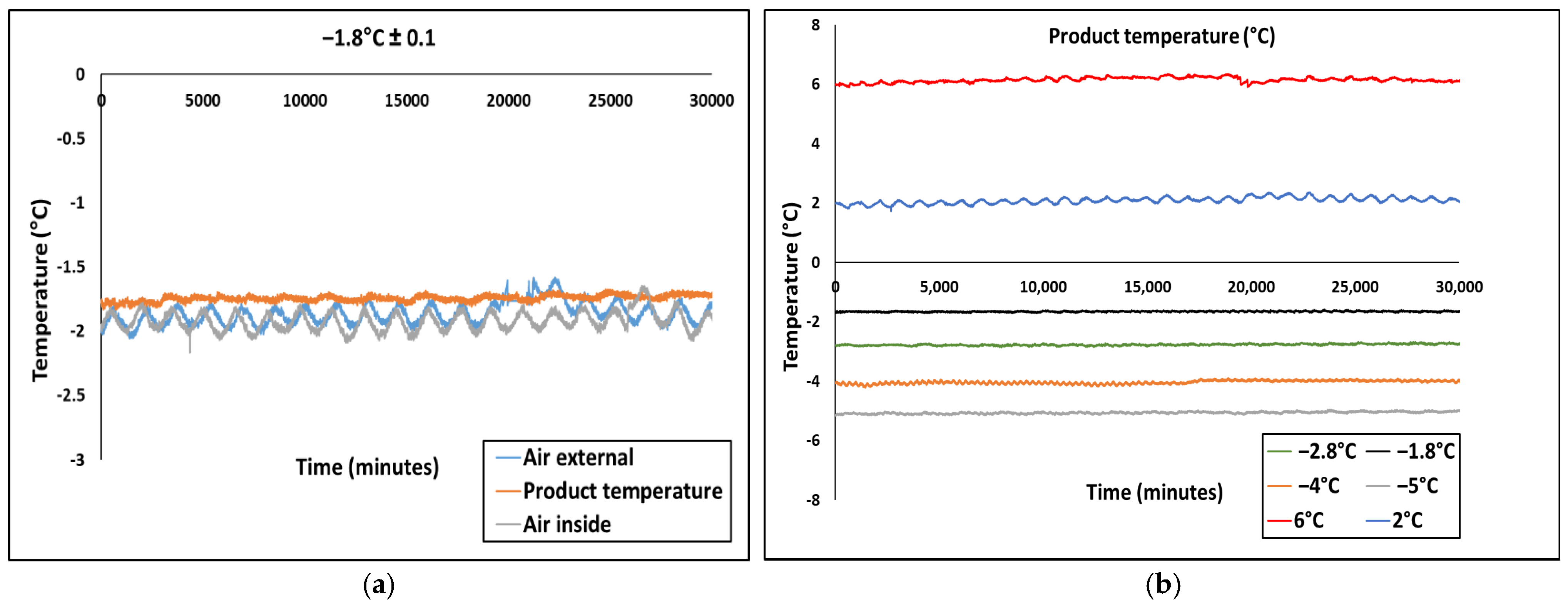


| Set Temperature (°C) | Measured Temperature (°C) | Average Measured Temperature (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 21 | ||
| −5 | −5.1 | −5.1 | −4.7 | −5.1 | −5.1 ± 0.2 |
| −4 | −4.2 | −4.2 | −4.1 | −4.1 | −4.2 ± 0.1 |
| −2.8 | −2.75 | −2.9 | −2.85 | −2.8 | −2.8 ± 0.1 |
| −1.8 | −1.76 | −1.7 | −1.8 | −1.79 | −1.8 ± 0.1 |
| +2 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 2.1 ± 0.2 |
| +6 | 5.8 | 6.2 | 6.1 | 6.1 | 6.1 ± 0.2 |
| Storage Time/Days | Storage Temperature (°C) | Colour Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | ||
| 1 | 6.0 | 36.06 ± 0.34 Aa | 20.24 ± 0.91 Aa | 14.77 ± 0.40 Aa |
| 2.0 | 37.24± 0.15 Aa | 20.81 ± 0.35 Aa | 15.42 ± 0.36 Aa | |
| −1.8 | 38.48± 0.56 Ab | 21.65± 0.34 Ab | 15.26± 0.55 Aa | |
| −2.8 | 39.63 ± 0.76 Ab | 22.27± 0.91 Ab | 16.25± 0.52 Ab | |
| −4.0 | 40.65 ± 0.18 Ab | 22.86 ± 0.24 Aab | 16.74 ± 0.18 Ab | |
| −5.0 | 41.15 ± 1.34 Ab | 23.34 ± 1.06 Ac | 17.29 ± 0.98 Ab | |
| 7 | 6.0 | 29.24 ± 0.36 Ba | 12.03 ± 0.49 Ba | 11.05 ± 0.57 Ba |
| 2.0 | 33.50 ± 1.06 Bb | 16.66 ± 0.28 Bb | 11.90 ± 0.28 Ba | |
| −1.8 | 34.38 ± 0.41 Bb | 17.62 ± 0.74 Bb | 14.49 ± 0.14 Bb | |
| −2.8 | 35.60 ± 0.61 Ab | 18.58 ± 0.13 Bb | 13.73± 0.72 Bb | |
| −4.0 | 37.57 ± 0.18 Bc | 18.75 ± 0.77 Bb | 14.32 ± 0.23 Bb | |
| −5.0 | 38.89 ± 0.13 Bc | 19.64 ± 1.11 Bc | 14.80 ± 0.38 Bb | |
| 14 | 6.0 | 27.86 ± 0.74 Ca | 8.69 ± 0.40 Ca | 9.39 ± 0.15 Ca |
| 2.0 | 31.40 ± 0.94 Bb | 11.71 ± 0.26 Cb | 10.32 ± 0.42 Bb | |
| −1.8 | 34.01 ± 0.40 Bc | 16.54 ± 0.24 Cc | 13.32 ± 0.72 Bb | |
| −2.8 | 34.89 ± 0.08 Bc | 17.10 ± 0.71 Bc | 13.49± 0.60 Bb | |
| −4.0 | 35.27 ± 0.05 Cc | 17.81 ± 0.67 Bc | 14.34 ± 0.66 Bb | |
| −5.0 | 36.16 ± 0.26 Cc | 18.14 ± 0.81 Bc | 14.99 ± 0.88 Bb | |
| 21 | 6.0 | 25.78 ± 0.27 Da | 7.44 ± 0.23 Da | 6.52 ± 0.06 Da |
| 2.0 | 30.01 ± 0.57 Bb | 10.03 ± 0.27 Db | 8.67 ± 0.02 Cb | |
| −1.8 | 31.79 ± 0.59 Cb | 13.10 ± 0.22 Db | 12.67 ± 0.27 Cc | |
| −2.8 | 34.28 ± 0.81 Bc | 13.78 ± 0.46 Cb | 13.97 ± 0.55 Bc | |
| −4.0 | 34.94 ± 0.31 Cc | 14.67 ± 0.75 Cb | 13.29 ± 0.62 Cc | |
| −5.0 | 36.12 ± 0.21 Cd | 16.07 ± 1.57 Cc | 14.57 ± 0.47 Bc | |
| Quality Indicator | Storage Temperature (°C) | Kinetic Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | (kJ/mol) | ) | ||||
| Drip loss | −1.8 | 0.068 | 0.9946 | 110.111 | 0.9974 | 4.4 × |
| −2.8 | 0.085 | 0.9887 | ||||
| −5 | 0.1238 | 0.989 | ||||
| Texture | 6 | 0.019 | 0.9744 | 52.870 | 0.7439 | 1.4 × |
| 2 | 0.015 | 0.9711 | ||||
| −1.8 | 0.007 | 0.9627 | ||||
| −2.8 | 0.006 | 0.9782 | ||||
| −5 | 0.002 | 0.9703 | ||||
| TVB−N | 6 | 0.985 | 0.9988 | 68.553 | 0.9923 | 6.6 × |
| 2 | 0.604 | 0.9921 | ||||
| −1.8 | 0.441 | 0.9978 | ||||
| −2.8 | 0.378 | 0.9977 | ||||
| −5 | 0.280 | 0.9808 | ||||
| TBARS | 6 | 0.0409 | 0.9984 | 119.480 | 0.9458 | 9.9 × |
| 2 | 0.0218 | 0.9916 | ||||
| −1.8 | 0.0125 | 0.9978 | ||||
| −2.8 | 0.0098 | 0.9561 | ||||
| −5 | 0.004 | 0.9713 | ||||
| Colour difference | 6 | 0.9864 | 0.9508 | 47.301 | 0.9906 | 7.0 × |
| 2 | 0.7334 | 0.9499 | ||||
| −1.8 | 0.5372 | 0.9295 | ||||
| −2.8 | 0.4818 | 0.9311 | ||||
| −5 | 0.4424 | 0.9559 | ||||
| Quality Parameter | Source | RMSE | MAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TVB−N | Present work | 0.49 | 6.98 |
| [55] | 0.81 | 8.17 | |
| [76] | 1.52 | 7.03 | |
| TBARS | Present work | 0.07 | 2.79 |
| [55] | 0.13 | 6.7 | |
| Drip loss | Present work | 0.47 | 5.03 |
| [77] | 0.61 | 16.31 | |
| Texture | Present work | 0.26 | 0.77 |
| Colour difference | Present work | 1.4 | 10.67 |
| [72] | 1.13 | 16.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mwakosya, A.W.; Alvarez, G.; Ndoye, F.T. Effects of Partial Freezing and Superchilling Storage on the Quality of Beef: A Kinetic Modelling Approach. Foods 2025, 14, 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152687
Mwakosya AW, Alvarez G, Ndoye FT. Effects of Partial Freezing and Superchilling Storage on the Quality of Beef: A Kinetic Modelling Approach. Foods. 2025; 14(15):2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152687
Chicago/Turabian StyleMwakosya, Anjelina William, Graciela Alvarez, and Fatou Toutie Ndoye. 2025. "Effects of Partial Freezing and Superchilling Storage on the Quality of Beef: A Kinetic Modelling Approach" Foods 14, no. 15: 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152687
APA StyleMwakosya, A. W., Alvarez, G., & Ndoye, F. T. (2025). Effects of Partial Freezing and Superchilling Storage on the Quality of Beef: A Kinetic Modelling Approach. Foods, 14(15), 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152687







