Aroma Formation, Release, and Perception in Aquatic Products Processing: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Aroma Formation in Aquatic Product Processing
2.1. Aroma Formation Pathways
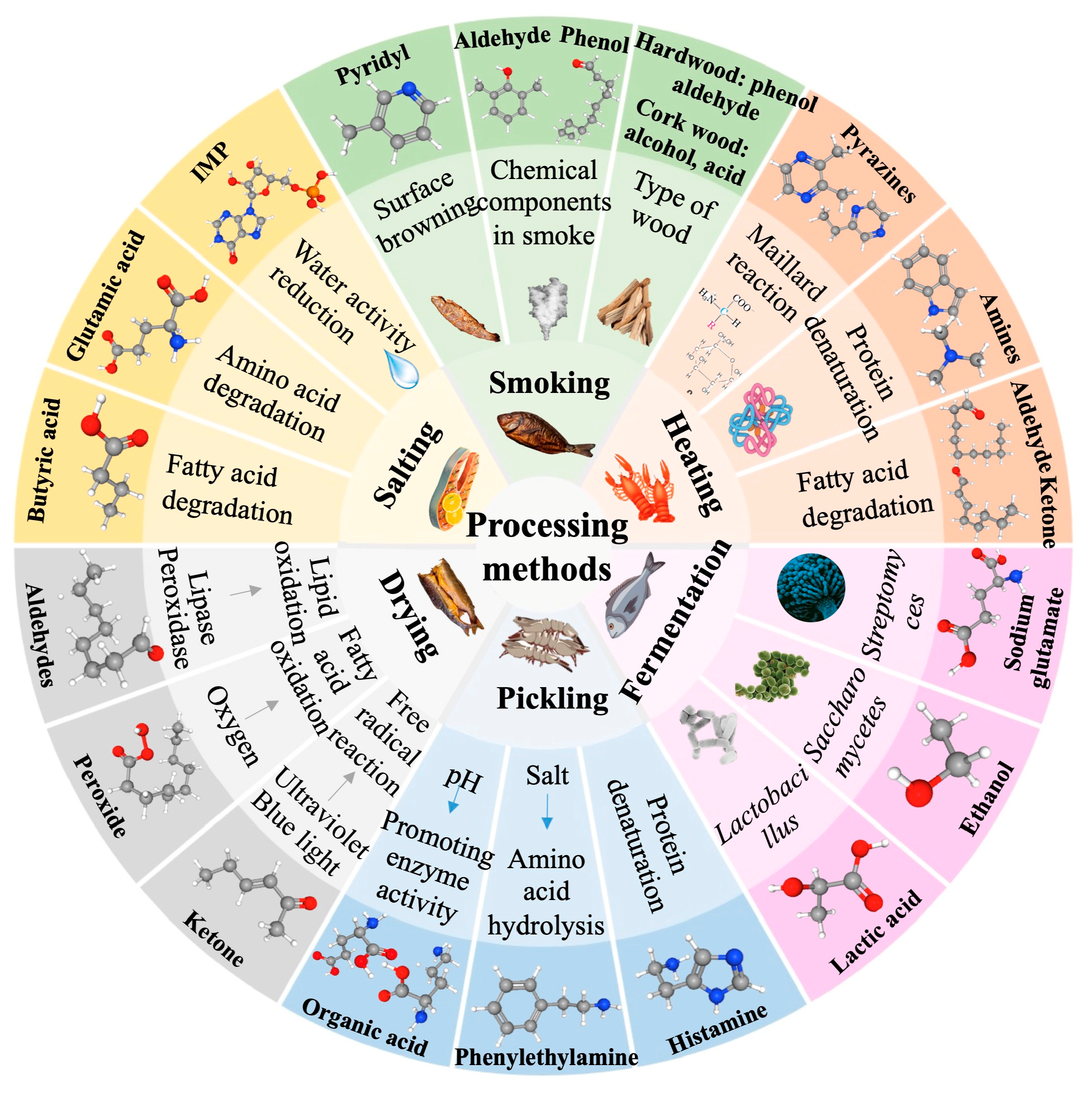
2.2. Effects of Processing Methods on the Aroma of Aquatic Products
2.2.1. Effects of Heating on the Aroma of Aquatic Products
2.2.2. Effects of Salting and Drying on the Aroma of Aquatic Products
2.2.3. Effects of Smoking on the Aroma of Aquatic Products
2.2.4. Effects of Pickling on the Aroma of Aquatic Products
2.2.5. Effects of Fermentation on the Aroma of Aquatic Products
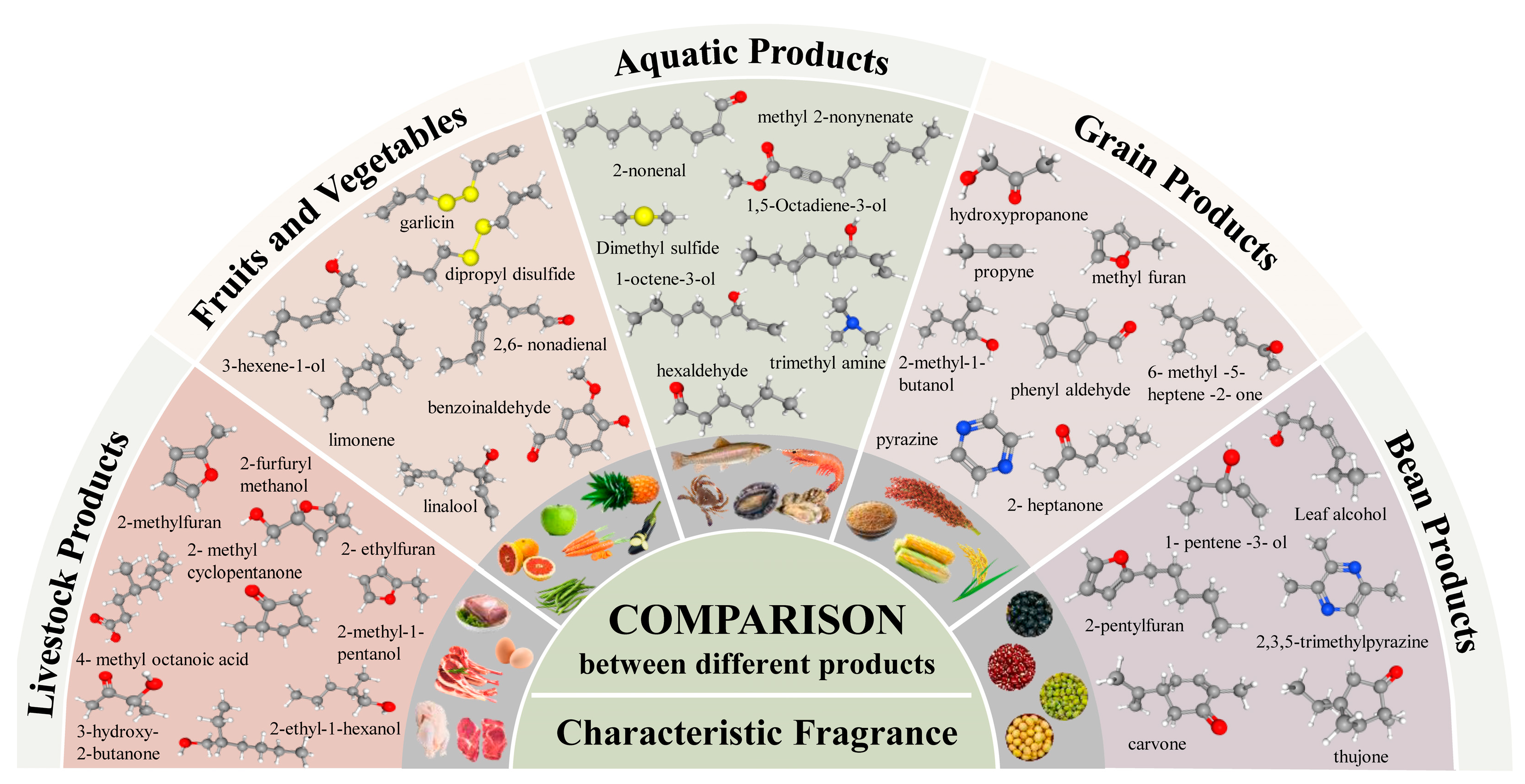
2.3. Characteristic Volatile Compounds in Aquatic Products
2.3.1. Carbonyl Compounds
2.3.2. Alcohols
2.3.3. Nitrogen Compounds
2.3.4. Sulfur Compounds
2.3.5. Hydrocarbons
3. Identification Techniques for Volatile Compounds
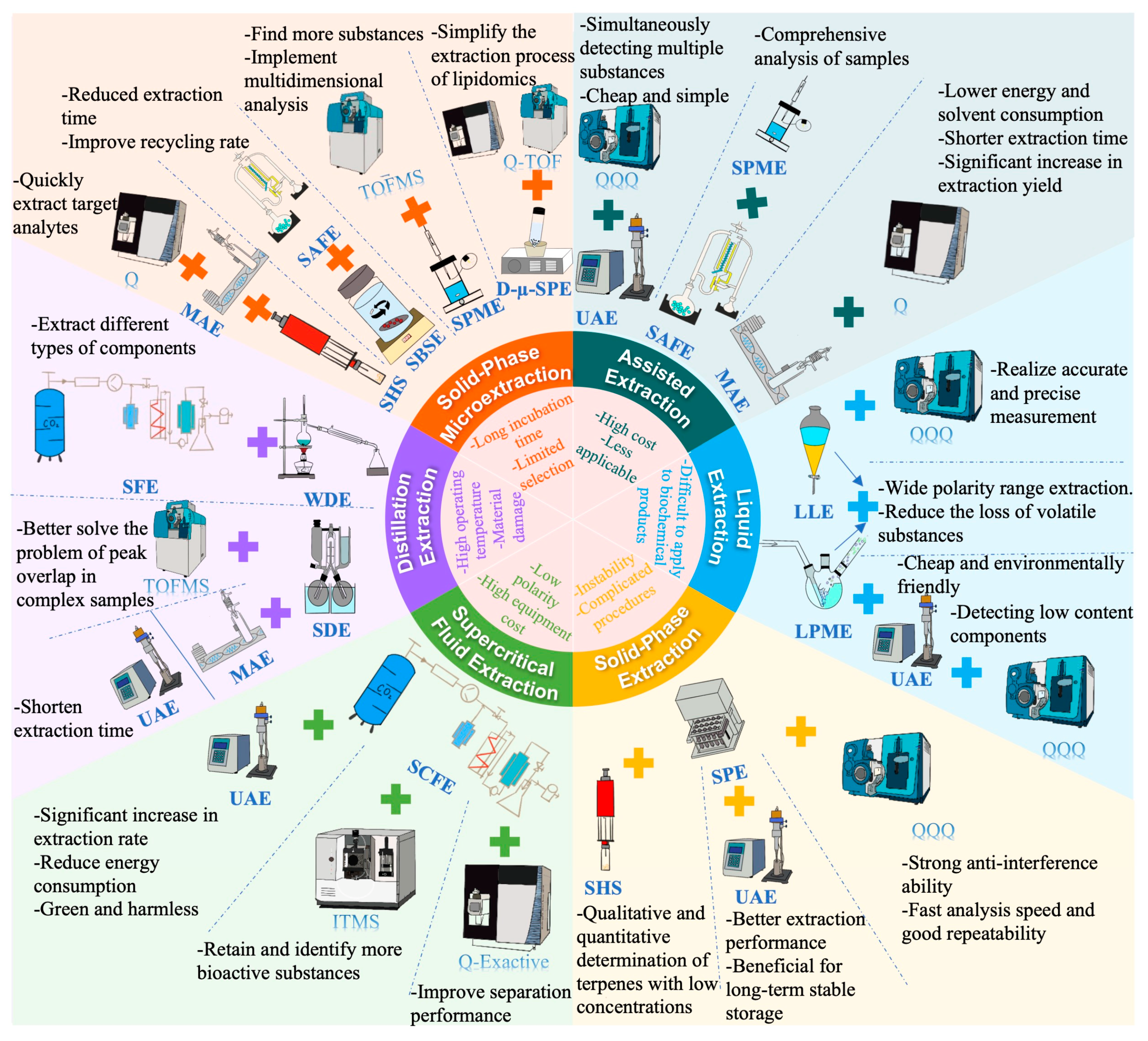
3.1. Extraction of Volatile Compounds
3.1.1. Solvent Extraction
3.1.2. Headspace Extraction
3.2. Identification of Volatile Compounds
3.2.1. Gas Chromatography–Olfaction (GC–O)
3.2.2. Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography
3.2.3. Chiral Gas Chromatography
3.2.4. High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
3.2.5. Chemical Ionization (CI) Mass Spectrometry
3.2.6. Proton Transfer Reaction–Mass Spectrometry (PTR–MS)
3.3. Quantitative Analysis of Volatile Compounds
3.3.1. Normalization Method
3.3.2. External Standard Method
3.3.3. Internal Standard Method
4. Odorant Release of Aquatic Products
4.1. Effects of the Composition of Aquatic Products on Odorants Release
4.1.1. Effects of Lipids on Volatile Compound Release
4.1.2. Effects of Carbohydrates on Volatile Compound Release
4.1.3. Effects of Protein on Volatile Compounds Release
4.2. Effects of Oral Processing on Volatile Compound Release
4.3. Physicochemical Models of Volatile Compound Release
5. Aroma Perception of Aquatic Products
5.1. Nasal Metabolism and Olfactory Perception
5.2. Research Progress on Aquatic Products Aroma Perception by ORs
6. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, K.; Gaines, S.D.; García Molinos, J.; Zhang, M.; Xu, J. Effect of trade on global aquatic food consumption patterns. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, G.L.; Langellotti, A.L.; Torrieri, E.; Masi, P. Emerging technologies in seafood processing: An overview of innovations reshaping the aquatic food industry. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F 2024, 23, e13281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. The state of world fisheries and aquaculture. In Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, J. Progress on odor deterioration of aquatic products: Characteristic volatile compounds, analysis methods, and formation mechanisms. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yang, P.; Song, H.; Guan, X. Research progress in comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and its combination with olfactometry systems in the flavor analysis field. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, N.; Sintang, M.D.; Zaini, H.; Munsu, E.; Matajun, P.; Pindi, W. Applications of protein crosslinking in food products. Int. Food Res. J. 2022, 29, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yu, S.; Xiaowei, F.; Jingyi, L.; Junyi, S.; Jie, X.; Xue, C. Effect of lipid oxidation on quality attributes and control technologies in dried aquatic animal products: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2024, 64, 10397–10418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, M.; Xu, X. Research progress of fishy odor in aquatic products: From substance identification, formation mechanism, to elimination pathway. Food Res. Int. 2024, 178, 113914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.; Yimeng, S.; Juan, W.; Baoguo, S.; Youqiang, X.; Wangang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Recent trends in aroma release and perception during food oral processing: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2024, 64, 3441–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, P.; Zhu, B.; Gu, Q. Current research on the extraction, functional properties, interaction with polyphenols, and application evaluation in delivery systems of aquatic-based proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 11844–11859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikeçligil, G.N.; Gottfried, J.A. What does the human olfactory system do, and how does it do it? Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2024, 75, 155–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Xu, M.; Dong, J.; Cui, W.; Yuan, S. The structure and function of olfactory receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 45, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, W.; Shi, Q.; Mao, J.; Xie, J.; Chai, G.; Zhang, C. Deciphering olfactory receptor binding mechanisms: A structural and dynamic perspective on olfactory receptors. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2025, 11, 1498796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Badar, I.H.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Xu, B. Odor and taste characteristics, transduction mechanism, and perceptual interaction in fermented foods: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2024, 65, 3947–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Sun, H.; Ma, G.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Pei, H.; Li, X.; Gao, L. Insights into flavor and key influencing factors of Maillard reaction products: A recent update. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 973677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Gan, R.; Feng, Q.; Shang, W.; He, Y.; Li, C.; Shen, X.; Li, Y. Flavor formation of tilapia byproduct hydrolysates in Maillard reaction. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 1554–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, A.; Zhang, C.; Xie, J.; Yang, X. Maillard reaction chemistry in formation of critical intermediates and flavour compounds and their antioxidant properties. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, F.; Zeng, C.; Yang, Y.; Xu, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, S. Sensory attributes and functional properties of Maillard reaction products derived from the crassosotrea gigas (Ostrea rivularis gould) enzymatic hydrolysate and xylose system. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, R.; Ma, L.; Liu, R.; Huang, X.; Fu, B.; Dong, X.; Qin, L. Contribution of lipids to the flavor of mussel (Mytilus edulis) Maillard reaction products. Foods 2022, 11, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Meng, N.; Song, Y.; Fan, X.; Jiang, X.; Cong, P.; Liu, Y.; Xue, C.; Xu, J. Insight into the mechanism of Maillard reaction and lipids mutually contribute to the flavor release of squid fillets during the drying process. Food Chem. 2025, 468, 142435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Tang, N.; Liu, R.; Gong, M.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, M. The relationship between flavor formation, lipid metabolism, and microorganisms in fermented fish products. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 5685–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Tan, J.; He, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Fang, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; et al. Effect of lipase and lipoxygenase on lipid metabolism and the formation of main volatile flavour compounds in fermented fish products: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 1248–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Hossain, A. Role of lipids in food flavor generation. Molecules 2022, 27, 5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Y.X.; Dong, M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Huang, X.H.; Qin, L. Flavor enhancement during the drying of scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) as revealed by integrated metabolomic and lipidomic analysis. Food Chem. 2024, 432, 137218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Duan, R.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Li, C.; Shen, X.; Li, Y. Effects of different drying temperatures on the profile and sources of flavor in semi-dried golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus). Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Lian, R.; Wang, Y. Innovative packaging materials and methods for flavor regulation of prepared aquatic products: Mechanism, classification and future prospective. Food Innov. Adv. 2023, 2, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewe, F.B.; Kudre, T.G.; Bettadaiah, B.K.; Narayan, B. Effects of ultrasound-assisted heating on aroma profile, peptide structure, peptide molecular weight, antioxidant activities and sensory characteristics of natural fish flavouring. Ultrason. Sonochem 2020, 65, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, R. Fish flavors. Food Rev. Int. 1990, 6, 437–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, K.; Kubota, K.; Aishima, T. Comparison of aroma characteristics of 16 fish species by sensory evaluation and gas chromatographic analysis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Piao, C.; Ju, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Cui, F.; Li, G.; Cui, M. Effects of low salt on lipid oxidation and hydrolysis, fatty acids composition and volatiles flavor compounds of dry-cured ham during ripening. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 187, 115347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, V.M.; Vasconi, M.; Caprino, F.; Bellagamba, F. Fatty acid profiles and volatile compounds formation during processing and ripening of a traditional salted dry fish product. J. Food Process Pres. 2017, 41, e13133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara, H.; Ide, J.; Yanai, T.; Yajima, I.; Hayashi, K. Volatile flavor compounds of some kinds of dried and smoked fish. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1990, 54, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibara, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Yajima, I.; Hayashi, K. Flavor constituents of dried bonito (katsuobushi). Food Rev. Int. 1990, 6, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlet, V.; Knockaert, C.; Prost, C.; Serot, T. Comparison of odor-active volatile compounds of fresh and smoked salmon. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3391–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Dai, Z.; Yin, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H. The volatile flavor compounds of Shanghai smoked fish as a special delicacy. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josephson, D.B.; Lindsay, R.C.; Stuiber, D.A. Influence of processing on the volatile compounds characterizing the flavor of pickled fish. J. Food Sci. 1987, 52, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Zheng, H.; Han, X.; Cao, L.; Sui, J. Development of a highly sensitive HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of eight biogenic amines in aquatic products. Acta Chromatogr. 2021, 33, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xiao’e, C.; Xubo, F.; Lili, J.; Fang, T.; Hui, Y.; Chen, Y. Isolation and identification of aroma-producing yeast from mackerel fermentation broth and its fermentation characteristics. J. Aquat. Food Prod. T 2021, 30, 1264–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Cai, X.; Cong, L.; Hu, Y.; Liu, R.; Xiong, S.; Hu, X. Quality improvement of zhayu, a fermented fish product in China: Effects of inoculated fermentation with three kinds of lactic acid bacteria. Foods 2022, 11, 2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triqui, R.; Reineccius, G.A. Flavor development in the ripening of anchovy (Engraulis encrasicholus L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Good Scents Company Information System. 2021. Available online: https://www.thegoodscentscompany.com/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Burdock, G.A. Fenaroli’s Handbook of Flavor Ingredients; CRC Press: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Josephson, D.B.; Lindsay, R.C.; Stuiber, D.A. Identification of compounds characterizing the aroma of fresh whitefish (Coregonus clupeaformis). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1983, 31, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Sakaguchi, M. Fish flavor. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 1996, 36, 257–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qian, L.; Yulong, B.; Yuqing, T.; René, L.; Hui, H.; Luo, Y. Recent advances on characterization of protein oxidation in aquatic products: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2024, 64, 1572–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora, R.; Hidalgo, F.J. Formation of heterocyclic aromatic amines with the structure of aminoimidazoazarenes in food products. Food Chem. 2020, 313, 126128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Peng, H.; Chen, Q.; Jiao, X.; Jia, J.; Pan, Z.; Cheng, J.; Wang, L. Effects of cooking processes on protein nutritional values and volatile flavor substances of Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Foods 2023, 12, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.C.; Rocker, M.M.; Keast, R.S.J.; Callahan, D.L.; Redmond, H.J.; Smullen, R.P.; Francis, D.S. Systematic review of the odorous volatile compounds that contribute to flavour profiles of aquatic animals. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1418–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Karoui, R. Quality evaluation of fish and other seafood by traditional and nondestructive instrumental methods: Advantages and limitations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2017, 57, 1976–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phong, W.N.; Gibberd, M.R.; Payne, A.D.; Dykes, G.A.; Coorey, R. Methods used for extraction of plant volatiles have potential to preserve truffle aroma: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1677–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, M.A.A.; Buettner, A. Characterisation of aroma-active and off-odour compounds in German rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Part II: Case of fish meat and skin from earthen-ponds farming. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, D.; Xu, Z.; Sun, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y. Advances in food aroma analysis: Extraction, separation, and quantification techniques. Foods 2025, 14, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, B.R.; Yesiltas, B.; Sørensen, A.D.M.; Hermund, D.B.; Glastrup, J.; Jacobsen, C. Comparison of three methods for extraction of volatile lipid oxidation products from food matrices for GC–MS analysis. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2016, 93, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Dan, M.; Zhao, G.; Wang, D. Recent advances in chromatography-mass spectrometry and electronic nose technology in food flavor analysis and detection. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zheng, F.; Chen, H.; Huang, M.; Xie, J.; Chen, F.; Sun, B. Analysis of volatiles in Dezhou Braised Chicken by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/high resolution-time of flight mass spectrometry. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zeng, Y.; Ye, Z.K.; Li, H.K.; Li, Y.Z.; Dong, B.; Su, Q.Z.; Lin, Q.B.; Xiao, J.; Zhong, H.N. Analysis of volatile organic compounds and potential odour compounds in food contact paperboard using headspace two-dimensional GC-QTOF-MS. Food Addit. Contam. A 2023, 40, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommers, J.; van der Wal, S. Column selection and optimization for comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography: A review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 51, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Du, M.; Dong, X.P.; Qin, L.; Zhu, B.W. Fresh and grilled eel volatile fingerprinting by e-Nose, GC-O, GC-MS and GC x GC-QTOF combined with purge and trap and solvent-assisted flavor. Food Res. Int. 2019, 115, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phetsang, H.; Panpipat, W.; Panya, A.; Phonsatta, N.; Cheong, L.Z.; Chaijan, M. Chemical characteristics and volatile compounds profiles in different muscle part of the farmed hybrid catfish (Clarias macrocephalus × Clarias gariepinus). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 57, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosandl, A. Enantioselective capillary gas chromatography and stable isotope ratio mass spectrometry in the authenticity control of flavors and essential oils. Food Rev. Int. 1995, 11, 597–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Ye, N.; Qiu, X.; Qian, J.; Wang, D.; Yue, W.; Zuo, Z.; Chen, M. Identification and comparison of oligopeptides during withering process of White tea by ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-orbitrap ultra-high resolution mass spectrometry. Food Rev. Int. 2019, 121, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.; Xiong, S.; Qian, Y.; Qian, M.C. In vivo and in vitro aroma release in surimi gel with different cross-linking degrees by proton transfer reaction-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrhovsek, U.; Lotti, C.; Masuero, D.; Carlin, S.; Weingart, G.; Mattivi, F. Quantitative metabolic profiling of grape, apple and raspberry volatile compounds (VOCs) using a GC/MS/MS method. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 966, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crump, A.M.; Sefton, M.A.; Wilkinson, K.L. Microwave-assisted deuterium exchange: The convenient preparation of isotopically labelled analogues for stable isotope dilution analysis of volatile wine phenols. Food Chem. 2014, 162, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Qian, Y.L.; Alcazar Magana, A.; Xiong, S.; Qian, M.C. Comparative characterization of aroma compounds in silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix), Pacific whiting (Merluccius productus), and Alaska pollock (Theragra chalcogramma) surimi by aroma extract dilution analysis, odor activity value, and aroma recombination studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 10403–10413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seuvre, A.M.; Voilley, A. Physico-chemical interactions in the flavor-release process. In Springer Handbook of Odor; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 35–36. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, C.; You, J.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, S.; Yin, T.; Huang, Q. Capacity of myofibrillar protein to adsorb characteristic fishy-odor compounds: Effects of concentration, temperature, ionic strength, pH and yeast glucan addition. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J. Food oral processing: Recent developments and challenges. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2017, 28, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ployon, S.; Morzel, M.; Canon, F. The role of saliva in aroma release and perception. Food Chem. 2017, 226, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, O.; Silcock, P.; Beauchamp, J.; Buettner, A.; Everett, D. Tongue pressure and oral conditions affect volatile release from liquid systems in a model mouth. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9918–9927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.J.; Beauchamp, J.D.; Langford, V.S. Non-destructive and high-throughput—APCI-MS, PTR-MS and SIFT-MS as methods of choice for exploring flavor release. In Dynamic Flavor: Capturing Aroma Using Real-Time Mass Spectrometry; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Kuwata, M.; Liu, Y. Wall loss of semi-volatile organic compounds in a Teflon bag chamber for the temperature range of 262–298 K: Mechanistic insight on temperature dependence. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2024, 17, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGann, J.P. Poor human olfaction is a 19th-century myth. Science 2017, 356, eaam7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mérignac-Lacombe, J.; Kornbausch, N.; Sivarajan, R.; Boichot, V.; Berg, K.; Oberwinkler, H.; Saliba, A.E.; Loos, H.M.; Ehret Kasemo, T.; Scherzad, A.; et al. Characterization of a human respiratory mucosa model to study odorant metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 12696–12706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornbausch, N.; Debong, M.W.; Buettner, A.; Heydel, J.M.; Loos, H.M. Odorant metabolism in humans. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Hazotte, A.; Faure, P.; Ménétrier, F.; Folia, M.; Schwartz, M.; Le Quéré, J.L.; Neiers, F.; Thomas-Danguin, T.; Heydel, J.M. Nasal odorant competitive metabolism is involved in the human olfactory process. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8385–8394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, X.H.; Ayed, C.; Fu, B.S.; Dong, X.P.; Fisk, I.; Qin, L. Dynamic release and perception of key odorants in grilled eel during chewing. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francia, S.; Lodovichi, C. The role of the odorant receptors in the formation of the sensory map. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glusman, G.; Yanai, I.; Rubin, I.; Lancet, D. The complete human olfactory subgenome. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 685–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkel, A.; Steinhaus, M.; Kotthoff, M.; Nowak, B.; Krautwurst, D.; Schieberle, P.; Hofmann, T. Nature’s chemical signatures in human olfaction: A foodborne perspective for future biotechnology. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7124–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouquier, S.; Taviaux, S.; Trask, B.J.; Brand-Arpon, V.; van den Engh, G.; Demaille, J.; Giorgi, D. Distribution of olfactory receptor genes in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 1998, 18, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clowney, E.J.; LeGros, M.A.; Mosley, C.P.; Clowney, F.G.; Markenskoff-Papadimitriou, E.C.; Myllys, M.; Barnea, G.; Larabell, C.A.; Lomvardas, S. Nuclear aggregation of olfactory receptor genes governs their monogenic expression. Cell 2012, 151, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serizawa, S.; Miyamichi, K.; Nakatani, H.; Suzuki, M.; Saito, M.; Yoshihara, Y.; Sakano, H. Negative feedback regulation ensures the one receptor-one olfactory neuron rule in mouse. Science 2003, 302, 2088–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, N.E.; Eberwine, J.; Dotson, R.; Jackson, J.; Ulrich, P.; Restrepo, D. Expression of mRNAs encoding for two different olfactory receptors in a subset of olfactory receptor neurons. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainland, J.D.; Li, Y.R.; Zhou, T.; Liu, W.L.L.; Matsunami, H. Human olfactory receptor responses to odorants. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, G.; Zak, J.D.; Vergassola, M.; Murthy, V.N. Antagonism in olfactory receptor neurons and its implications for the perception of odor mixtures. Elife 2018, 7, e34958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malnic, B.; Hirono, J.; Sato, T.; Buck, L.B. Combinatorial receptor codes for odors. Cell 1999, 96, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Li, H.; Guo, J.; Xu, Y. Advances in artificial intelligence for olfaction and gustation: A comprehensive review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2025, 58, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, S.S.; Saxena, A.K. Efficiency of homology modeling assisted molecular docking in G-protein coupled receptors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 269–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ahmed, L.; Zhang, R.; Pan, Y.; Matsunami, H.; Burger, J.L.; Block, E.; Batista, V.S.; Zhuang, H. Smelling sulfur: Copper and silver regulate the response of human odorant receptor OR2T11 to low-molecular-weight thiols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 13281–13288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Wu, S.; Huang, L.; Qin, D.; Hao, Q.; Gao, L. Texture, nutrition, and flavor of different freshwater fish muscles: Comparative study and molecular docking. Foods 2025, 14, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Li, Q.; Niu, Y.; She, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, R.; Zhu, J. Mechanism of the interaction between olfactory receptors and characteristic aroma compounds in sweet orange juice. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 207, 116660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Huang, Q.; Tian, M.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, F.; Li, X. Elucidation of formation and development of warmed-over flavor in precooked surimi products as affected by reheating methods. Food Chem. 2025, 480, 143859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Classification | Name | Molecular Formula | Flavor Description | Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonyl Compounds | Butanedioic acid diethyl ester | CH3CH2OCO(CH2)2COOCH2CH3 | Characteristic odor | 100.0000 |
| Ethyl Formate | HCOOC2H5 | Fruity, sharp, rum-liker odor | 90.9000 | |
| 3-Pentanone | CH3CH2COCH2CH3 | Acetone odor | 3.0000 | |
| Heptanal | C7H14O | Penetrating fruity odor | 2.7000 | |
| 2-Acetone | C3H6O | Fragrant, mint-like odor | 2.0000 | |
| Methyl palmitate | C17H34O2 | Fruit, sweet, slightly fatty odor | 2.0000 | |
| 2-Methyl-propanoic acid | (CH3)2CHCOOH | Sharp, butter-fat-like odor | 1.5000 | |
| 2-Butanone | C4H8O | Moderately sharp, fragrant, mint or acetone-like odor | 1.3000 | |
| Propanoic acid | CH3CH2COOH | Pungent, disagreeable, rancid odor | 1.0000 | |
| Benzaldehyde | C6H5CHO | Odor resembling oil of bitter almond | 0.7510 | |
| Butyl butyrate | C8H16O2 | Fruity, pineapple-like odor | 0.4000 | |
| Hexanal | C6H12O | Fatty-green, fruity odor | 0.2300 | |
| Octanoic acid-methyl ester | C9H18O2 | Powerful, winey, fruity, orange-like odor | 0.2000 | |
| 3,5-Octadien-2-one | C8H12O | Pungent herbaceous odor | 0.1500 | |
| Butyric acid | CH3CH2CH2COOH | Penetrating and obnoxious odor | 0.1450 | |
| (E, E)-2,4-Heptadienal | C7H10O | Fatty, green odor | 0.0570 | |
| 2-Octanone | C8H16O | Fatty, green cheese, fruity odor | 0.0502 | |
| 2-Nonanone | C9H18O | Fruity, floral, fatty, herbaceous odor | 0.0320 | |
| 3-Octanone | C8H16O | Mild fruity odor | 0.0214 | |
| Acetic acid | CH3COOH | Sour, vinegar-like odor | 0.0130 | |
| Methyl butanoate | C5H10O2 | Apple-like odor | 0.0059 | |
| 2-Undecanone | C11H22O | Citrus, fatty, rue-like odor | 0.0055 | |
| 1-Hexanone | C6H12O | Sharp, fruity, green grass odor | 0.0050 | |
| Decanoic acid ethyl ester | C12H24O2 | Oily brandy-like odor | 0.0050 | |
| Decanal | C10H20O | Fatty, floral-orange odor | 0.0030 | |
| Heptanal | C7H14O | Penetrating fruity, fatty, pungent odor | 0.0028 | |
| Dodecalactone | C12H22O2 | Fruity, peach-like, pear-like odor | 0.0004 | |
| Nonyl acetate | C11H22O2 | Mushroom and gardenia aroma and scent | 0.0002 | |
| Alcohols | 2-Ethyl-1-hexanol | CH3(CH2)3CH(CH2CH3)CH2OH | Mild, oily, sweet, slightly floral odor | 0.8000 |
| (Z)-2-Penten-1-ol | C5H10O | Green diffusive odor | 0.7200 | |
| Ethanol | CH3CH2OH | Pleasant, fragrant, weak, vinous odor | 0.6200 | |
| Phenylethyl alcohol | C6H5CH2CH2OH | Characteristic rose-like odor | 0.5642 | |
| n-Butanol | CH3(CH2)3OH | Rancid, sweet, mildly alcoholic odor | 0.4800 | |
| 1-Hexanol | CH3(CH2)4CH2OH | Sweet alcohol, aromatic, pleasant odor | 0.0056 | |
| 3-Methyl-1-butanol | (CH3)2CHCH2CH2OH | Disagreeable odor | 0.0040 | |
| 2-Methyl-1-butanol | CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2OH | Cooked roasted odor with fruity or alcoholic undertones | 0.0040 | |
| 1-Octen-3-ol | C8H16O | Sweet earthy odor | 0.0015 | |
| Nitrogen Compounds | Methyl-pyrazine | C5H6N2 | Nutty, cocoa-like odor | 30.0000 |
| Ethyl-pyrazine | C6H8N2 | Musty, nutty, peanut butter odor | 4.0000 | |
| 2,5-Dimethyl-pyrazine | C6H8N2 | Earthy, potato-like odor | 1.7500 | |
| 2,3-Dimethyl-pyrazine | C6H8N2 | Nutty, cocoa-like odor | 0.8800 | |
| Trimethylamine | (CH3)3N | Fishy, amine odor | 0.6300 | |
| 1-Butanamine | C4H11N | Fishy, ammonia-like odor | 0.5100 | |
| Trimethyl-pyrazine | C7H10N2 | Roasted nut, baked potato odor | 0.3500 | |
| 2,3-Dimethyl-5-ethyl-pyrazine | C8H12N2 | Deep roasted cocoa-like aroma | 0.2000 | |
| 2-Ethyl-6-methyl-pyrazine | C6H8N2 | Roasted baked potato odor | 0.0400 | |
| 2-Ethyl-5-methyl-pyrazine | C7H10N2 | Nutty, roasted, grassy odor | 0.0160 | |
| Sulfur Compounds | Methanethiol | CH4S | Powerful, decayed cabbage odor | 0.0010 |
| Hydrocarbons | 1,2-Dimethylbenzene | C8H10 | Aromatic odor | 0.4500 |
| 1,2,4,5-Tetramethyl-benzene | C10H14 | Camphor-like odor | 0.0870 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, W.; Che, X.; Ma, P.; Chen, M.; Huang, X. Aroma Formation, Release, and Perception in Aquatic Products Processing: A Review. Foods 2025, 14, 2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152651
Fan W, Che X, Ma P, Chen M, Huang X. Aroma Formation, Release, and Perception in Aquatic Products Processing: A Review. Foods. 2025; 14(15):2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152651
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Weiwei, Xiaoying Che, Pei Ma, Ming Chen, and Xuhui Huang. 2025. "Aroma Formation, Release, and Perception in Aquatic Products Processing: A Review" Foods 14, no. 15: 2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152651
APA StyleFan, W., Che, X., Ma, P., Chen, M., & Huang, X. (2025). Aroma Formation, Release, and Perception in Aquatic Products Processing: A Review. Foods, 14(15), 2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152651





