Green Extraction of Tea Polysaccharides Using Ultrasonic-Assisted Deep Eutectic Solvents and an Analysis of Their Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. DES System Preparation
2.3. Selection of DES and Molar Ratio of HBA to HBD in DES System
2.4. Optimization of UADES Extraction
2.4.1. Single-Factor Experiments
2.4.2. Box–Behnken Design (BBD) Experiments
2.5. Determination of Proteins, Uronic Acid, and Mw of Tea Polysaccharides
2.6. HW Extraction of Tea Polysaccharides
2.7. Charicterization of Tea Polysaccharides
2.8. Anti-Oxidant Activity Assay
2.9. Cell Culture and Cell Viability
2.10. Protective Effect on H2O2-Induced Oxidative Injury Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
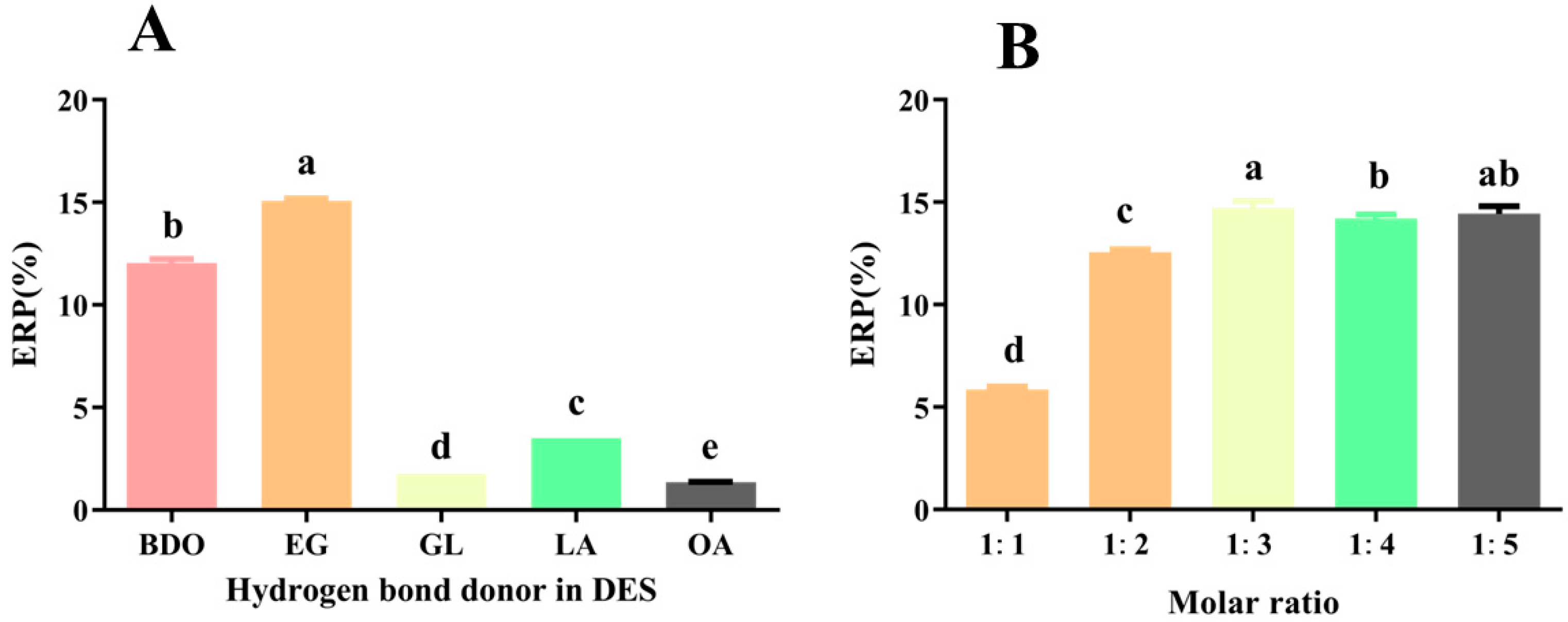
3.1. Effect of DES Type and the Ratio of HBAs to HBDs on EPR
3.2. Effect of the Water Content of DES and the Extraction Temperature, Extracting Time and Ultrasonic Power on ERP
3.3. Response Surface Optimization
3.4. Comparison of UADESTP and HWTP
3.5. Characterization of UADESTP
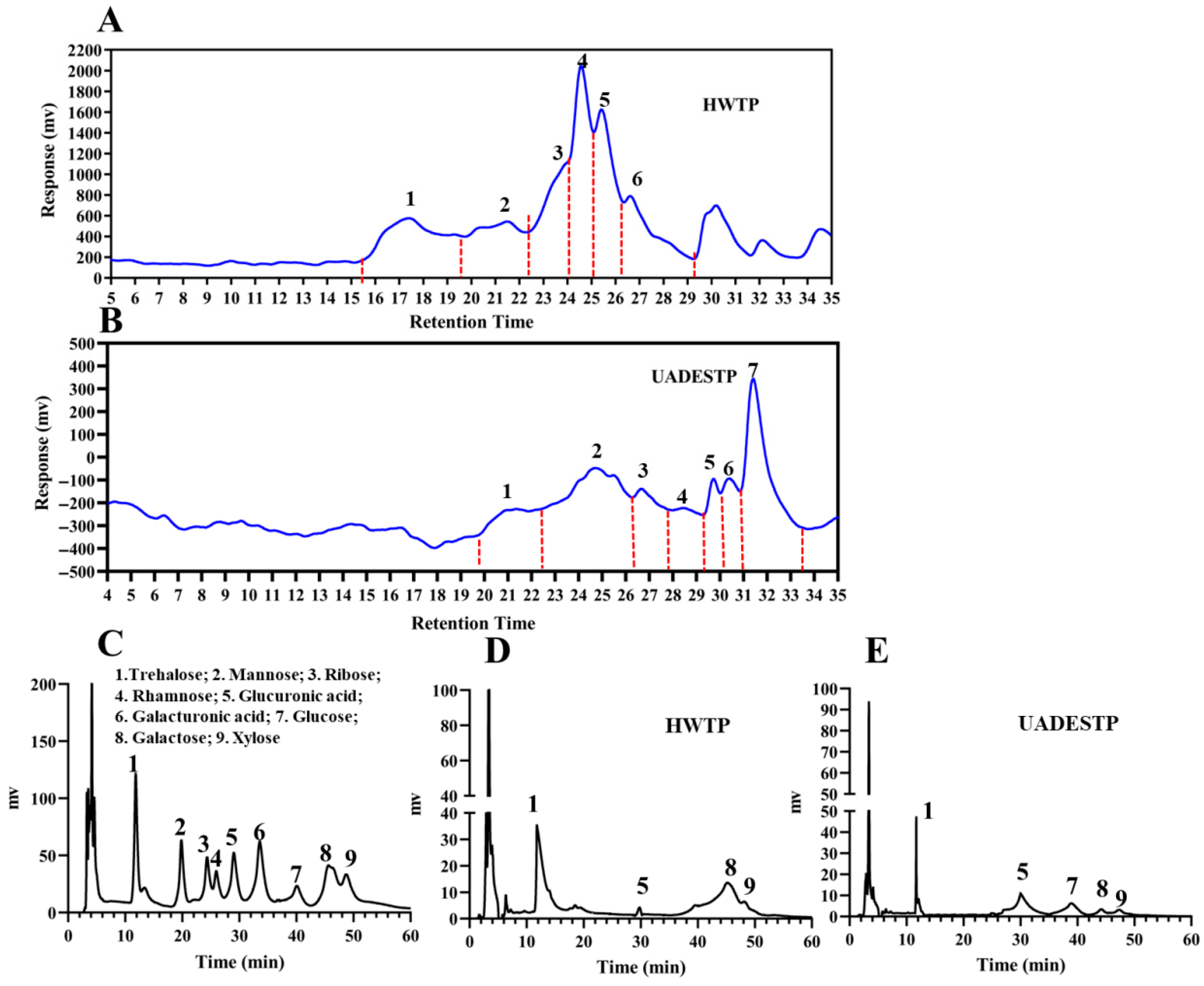
3.5.1. Mw and Monosaccharide Composition
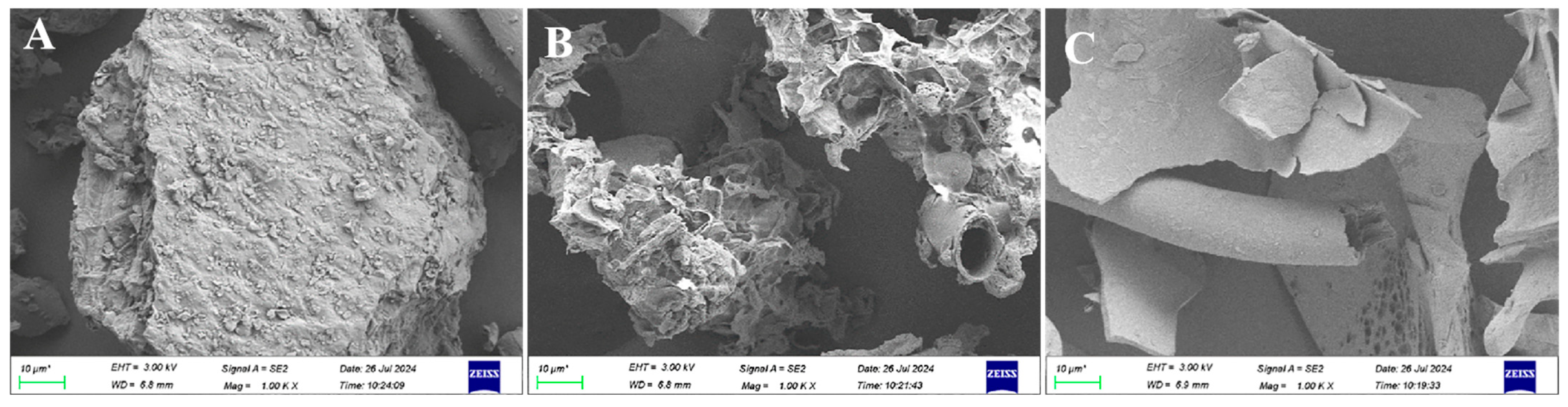
3.5.2. Microstructure
3.5.3. UV and FT-IR
3.6. Anti-Oxidant Activity of UADESTP
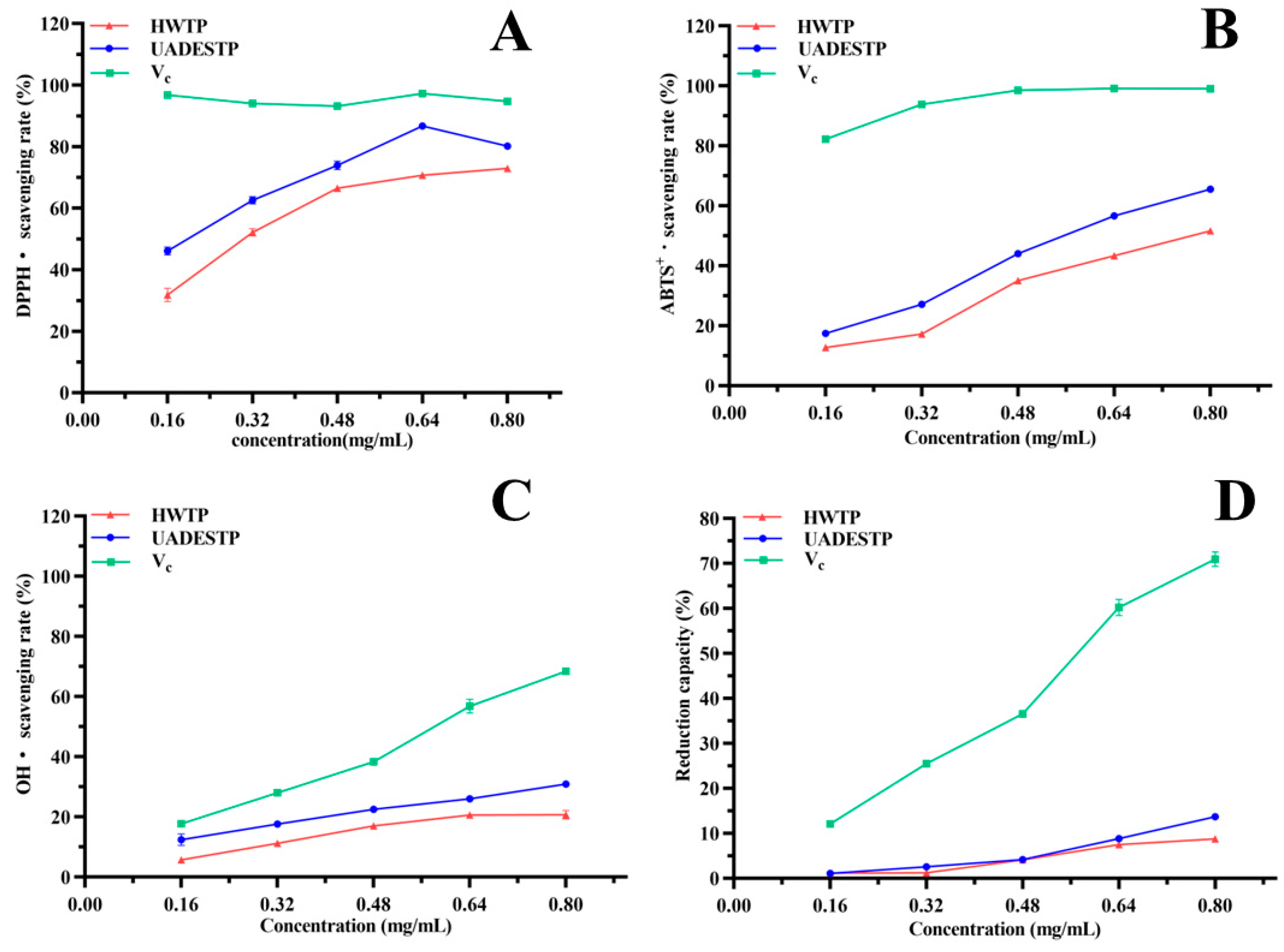
3.6.1. Free Radical Scavenging and Reduction Abilities of UADESTP
3.6.2. UADESTP Attenuates H2O2-Induced Oxidative Injury
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBD | Box–Behnken design |
| CAT | catalase |
| CC | choline chloride |
| ERP | extraction rate of polysaccharide |
| EG | ethylene glycol |
| FT-IR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| GSH-Px | glutathione peroxidase |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| HPGPC | high-performance gel permeation chromatography |
| HW | hot water |
| HBD | hydrogen bond donors |
| HWTP | hot water extracted tea polysaccharides |
| HBA | hydrogen bond acceptors |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| LA | lactic acid |
| OA | oxalic acid |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| UADESTP | ultrasonic-assisted DES extracted tea polysaccharides |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| UADES | ultrasonic-assisted deep eutectic solvents |
References
- Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Han, N.; Song, C.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ren, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, T. Effects of Fu brick tea polysaccharides on gut microbiota and fecal metabolites of HFD/STZ-Induced type 2 diabetes rats. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 10910–10923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Liang, X.; Hu, J.; Li, C.; Hu, W.; Li, K.; Chang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; et al. Feeding tea polysaccharides affects lipid metabolism, antioxidant capacity and immunity of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1074198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Yu, H. Extraction methods, chemical compositions, molecular structure, health functions, and potential applications of tea polysaccharides as a promising biomaterial: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Yang, W.; Huang, G.; Huang, H. Ultrasonic-Assisted extraction, characteristics and activity of Ipomoea batatas polysaccharide. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 96, 106420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Pu, L.; Dong, B.; Zhu, D.; Wu, W.; Yang, Q. Effects of ultrasonic degradation on physicochemical and antioxidant properties of Gleditsia sinensis seed polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 2024, 545, 109272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Duan, Z.; Xia, G.; Xin, T.; Yang, L.; Liu, F.; Xie, H. Ultrasonic-Assisted extraction and gastrointestinal digestion characteristics of polysaccharides extracted from Mallotus oblongfolius. Foods 2024, 13, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, N.; Mohamed, A.H.; Sajid, M.; Zain, N.N.M.; Liao, P.C.; Chew, K.W. Deep eutectic solvents as sustainable extraction media for extraction of polysaccharides from natural sources: Status, challenges and prospects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 338, 122199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Lin, L.; Zhao, M. Demonstration of feasibility and effectiveness of deep eutectic Solvent-Water system extraction of RG-I type pectin from wolfberry based on target polysaccharide, solvent and their interactions. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 109027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenutti, L.; Zielinski, A.A.F.; Ferreira, S.R.S. Subcritical water extraction (SWE) modified by deep eutectic solvent (DES) for pectin recovery from a Brazilian berry By-Product. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2022, 189, 105729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Liang, L.; Zhu, X.P.; Jiang, X.; Du, M.; Wang, Z. Optimization of enzymatic extraction, characterization and bioactivities of Se-Polysaccharides from Se-Enriched Lentinus edodes. Food Biosci. 2023, 51, 102346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, S.; Ran, C.; Wang, L.; Kan, J. Extraction, characterization and antioxidant activity of Water-Soluble polysaccharides from Tuber huidongense. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Fu, M.X.; Zhao, Y.X.; Li, H.; Li, H.B.; Wu, D.T.; Gan, R.Y. The chemical, structural, and biological properties of crude polysaccharides from sweet tea (Lithocarpus litseifolius (Hance) Chun) based on different extraction technologies. Foods 2021, 10, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Huang, L.; Teng, J.; Wei, B.; Xia, N.; Ye, Y. Purification, characterization, and bioactivity of Liupao tea polysaccharides before and after fermentation. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yan, X.; Chen, X.; Jiang, X.; Ye, K.; Xiong, Q.; Kong, J.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Xu, T.; et al. A mild and efficient extraction method for polysaccharides from Sinonovacula constricta and study of their structural characteristic and antioxidant activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Qiu, H.; Liang, L.; Weng, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, L.; Meng, F. The antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Armillaria gallica. Front. Nutr. 2024, 10, 1277877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jia, X.; Yang, R.; Qin, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Kong, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Deep eutectic solvents boosting solubilization and Se-Functionalization of heteropolysaccharide: Multiple hydrogen bonds modulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 284, 119159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achkar, T.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. Basics and properties of deep eutectic solvents: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, Q. Study on extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Radix Bupleuri by natural deep eutectic solvents combined with Ultrasound-Assisted enzymolysis. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 30, 100877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Wu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Dong, Q.; Yang, H.; Dai, C. An efficient approach for extraction of polysaccharide from abalone (Haliotis discus hannai Ino) viscera by natural deep eutectic solvent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.T.; Fu, M.X.; Guo, H.; Hu, Y.C.; Zheng, X.Q.; Gan, R.Y.; Zou, L. Microwave-Assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction, structural characteristics, and biological functions of polysaccharides from sweet tea (Lithocarpus litseifolius) leaves. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Liu, B.; Bai, M. Two green approaches for extraction of dihydromyricetin from Chinese vine tea using β-Cyclodextrin-Based and ionic Liquid-Based Ultrasonic-Assisted extraction methods. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Li, Q.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, S.; Chen, Y.; Shi, R. Optimization of Ultrasonic-Assisted deep eutectic solvent for the extraction of polysaccharides from Indocalamus tessellatus leaves and their biological studies. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 30, 100855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Huang, G.; Huang, H. The Ultrasonic-Assisted enzymatic extraction, characteristics and antioxidant activities of lychee nuclear polysaccharide. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 110, 107038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Liang, L.; Kang, Y.; Yu, R.; Wang, J.; Fan, D. Preparation, characterization, and property evaluation of Hericium erinaceus Peptide-Calcium chelate. Front. Nutr. 2024, 10, 1337407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L. Optimization of ultrasonic extraction of polysaccharides from Lentinus Edodes based on enzymatic treatment. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2015, 39, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.T.; Feng, K.L.; Huang, L.; Gan, R.Y.; Hu, Y.C.; Zou, L. Deep eutectic Solvent-Assisted extraction, partially structural characterization, and bioactivities of acidic polysaccharides from Lotus Leaves. Foods 2021, 10, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, H.; Yu, C.; Han, Z.; Shao, S.; Hu, X.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y. Effects of extraction methods on physicochemical properties and hypoglycemic activities of polysaccharides from coarse green tea. Glycoconj. J. 2020, 37, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Mu, G.; Qian, F. Novel insights into whey protein peptideiron chelating agents: Structural characterization, in vitro stability and functional properties. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Zhu, J.; Qian, Y.; Yue, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Gao, X.; He, H.; Wang, D. Effect of purity of tea polysaccharides on its antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Hu, M.; Jiang, T.; Xiao, P.; Duan, J.-A. Insights into the molecular mechanisms, Structure-Activity relationships and application prospects of polysaccharides by regulating Nrf2-Mediated antioxidant response. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 333, 122003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, M.; Xie, M.; Wan, P.; Chen, D.; Hu, B.; Ye, H.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Z. Evaluation of chemical property, cytotoxicity and antioxidant activity in vitro and in vivo of polysaccharides from Fuzhuan brick teas. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Ren, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, H.; Han, Y.; Hu, J. A polysaccharide from green tea (Camellia sinensis L.) protects human retinal endothelial cells against hydrogen Peroxide-Induced oxidative injury and apoptosis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Abbreviation | Combination | Mole Ratio | Water Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCB | Choline chloride:1,4-butanediol | 4:1 | 30 |
| CCEG | Choline chloride:Ethylene glycol | 2:1 | 30 |
| CCG | Choline chloride:Glycerol | 2:1 | 30 |
| CCLA | Choline chloride:Lactic acid | 1:1 | 30 |
| CCOA | Choline chloride:Oxalic acid | 1:1 | 30 |
| Number | A (Water Content/%) | B (Temperature/°C) | C (Time/min) | ERP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | 60 | 60 | 15.04 |
| 2 | 40 | 60 | 60 | 14.87 |
| 3 | 30 | 60 | 80 | 13.06 |
| 4 | 40 | 60 | 60 | 15.38 |
| 5 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 13.15 |
| 6 | 40 | 50 | 80 | 13.19 |
| 7 | 50 | 70 | 60 | 13.51 |
| 8 | 40 | 70 | 80 | 13.27 |
| 9 | 40 | 70 | 40 | 13.55 |
| 10 | 40 | 60 | 60 | 15.17 |
| 11 | 50 | 50 | 60 | 13.33 |
| 12 | 40 | 50 | 40 | 13.36 |
| 13 | 30 | 50 | 60 | 13.19 |
| 14 | 30 | 70 | 60 | 13.56 |
| 15 | 50 | 60 | 40 | 12.89 |
| 16 | 30 | 60 | 40 | 12.94 |
| 17 | 40 | 60 | 60 | 15.27 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 13.14 | 9 | 1.46 | 39.29 | <0.0001 |
| A | 1.823 × 10−3 | 1 | 1.823 × 10−3 | 0.049 | 0.8310 |
| B | 0.084 | 1 | 0.084 | 2.26 | 0.1768 |
| C | 5.426 × 10−4 | 1 | 5.426 × 10−4 | 0.015 | 0.9072 |
| AB | 8.927 × 10−3 | 1 | 8.927 × 10−3 | 0.24 | 0.6390 |
| AC | 5.327 × 10−3 | 1 | 5.327 × 10−3 | 0.14 | 0.7162 |
| BC | 2.915 × 10−3 | 1 | 2.915 × 10−3 | 0.079 | 0.7862 |
| A2 | 4.54 | 1 | 4.54 | 122.29 | <0.0001 |
| B2 | 2.12 | 1 | 2.12 | 57.14 | 0.0001 |
| C2 | 5.05 | 1 | 5.05 | 135.90 | <0.0001 |
| Residual | 0.26 | 7 | 0.037 | ||
| Lack of fit | 0.099 | 3 | 0.033 | 0.81 | 0.5490 |
| Pure error | 0.16 | 4 | 0.040 | ||
| Cor Total | 13.40 | 16 | |||
| R2 = 0.9806, Radjusted = 0.9556, C.V. = 1.40 | |||||
| HWE | UADES | |
|---|---|---|
| EPR (%) | 4.41± 0.08% b | 15.89 ± 0.13% a |
| Total polysaccharides (%) | 74.08± 2.51% a | 75.47 ± 1.35% a |
| Protein (%) | 20.99 ± 2.11% a | 12.91 ± 4.58% b |
| Uronic acid (%) | 7.22 ± 0.19 % b | 8.35 ± 0.26% a |
| Polysaccharides | Item | Component 1 | Component 2 | Component 3 | Component 4 | Component 5 | Component 6 | Component 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HWTP | Mw (Da) | 2.84 × 105 | 1.52 × 104 | 3.20 × 103 | 1.62 × 103 | 986 | 539 | - |
| Mass fraction (%) | 17.25 | 11.76 | 15.72 | 24.50 | 20.47 | 10.29 | - | |
| UADESTP | Mw (Da) | 1.19 × 104 | 1.80 × 103 | 555 | 322 | 229 | 190 | 149 |
| Mass fraction (%) | 11.13 | 33.38 | 10.28 | 4.81 | 5.19 | 7.24 | 27.97 |
| Monosaccharide | Ratio of HWTP | Ratio of UADESTP |
|---|---|---|
| Trehalose | 32 | 8 |
| Glucuronic acid | 4 | 16 |
| Galactose | 36 | 1 |
| Xylose | 1 | 1 |
| Glucose, | - | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, H.; Liang, L.; Wei, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, B. Green Extraction of Tea Polysaccharides Using Ultrasonic-Assisted Deep Eutectic Solvents and an Analysis of Their Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties. Foods 2025, 14, 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152601
Gu H, Liang L, Wei Y, Wang J, Ma Y, Shi J, Li B. Green Extraction of Tea Polysaccharides Using Ultrasonic-Assisted Deep Eutectic Solvents and an Analysis of Their Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties. Foods. 2025; 14(15):2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152601
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Haofeng, Lei Liang, Yang Wei, Jiahao Wang, Yibo Ma, Jiaxin Shi, and Bao Li. 2025. "Green Extraction of Tea Polysaccharides Using Ultrasonic-Assisted Deep Eutectic Solvents and an Analysis of Their Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties" Foods 14, no. 15: 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152601
APA StyleGu, H., Liang, L., Wei, Y., Wang, J., Ma, Y., Shi, J., & Li, B. (2025). Green Extraction of Tea Polysaccharides Using Ultrasonic-Assisted Deep Eutectic Solvents and an Analysis of Their Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties. Foods, 14(15), 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152601






