Physical Aspects, Phytochemical Profiles, and Nutritional Properties of Lemon (Citrus limon) Slices Under Different Drying Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Fruit and Sample Preparations
2.3. Analysis of Color Parameters and Browning Degree
2.4. Analysis of Basic Components
2.5. Analysis of Aroma Compounds
2.5.1. Electronic Nose (E-Nose) Analysis
2.5.2. GC-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) Analysis
2.6. Analysis of Bioactive Compounds
2.6.1. Synephrine Content
2.6.2. Limonoid Contents
2.6.3. Fraction and Profile Assays of Phenols
2.7. Analysis of Active Ingredients and Antioxidant Activities of Lemon Brewed Beverages
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Color Parameters and Browning Degree
3.2. Basic Components
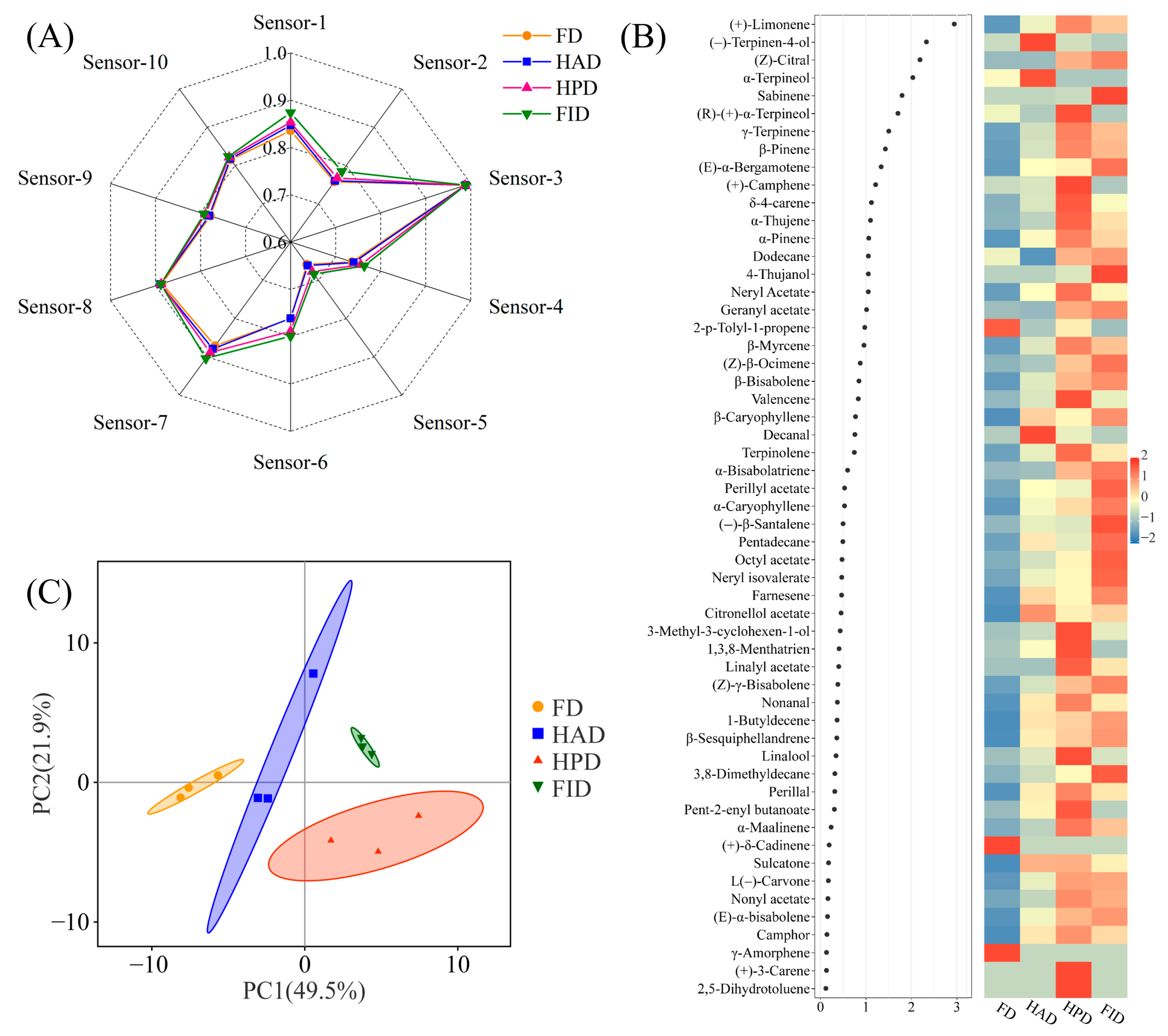
3.3. Aroma Compounds
3.4. Bioactive Compounds
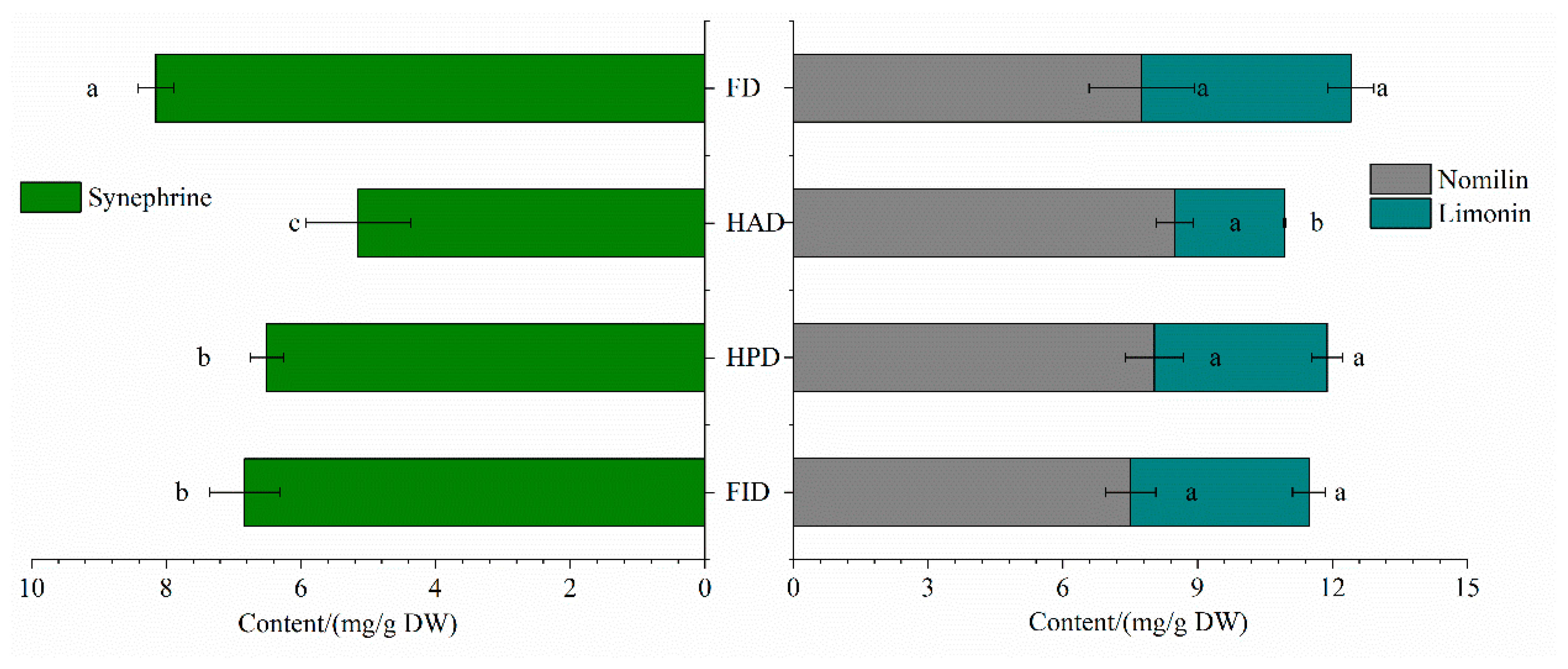
3.4.1. Synephrine
3.4.2. Limonoids
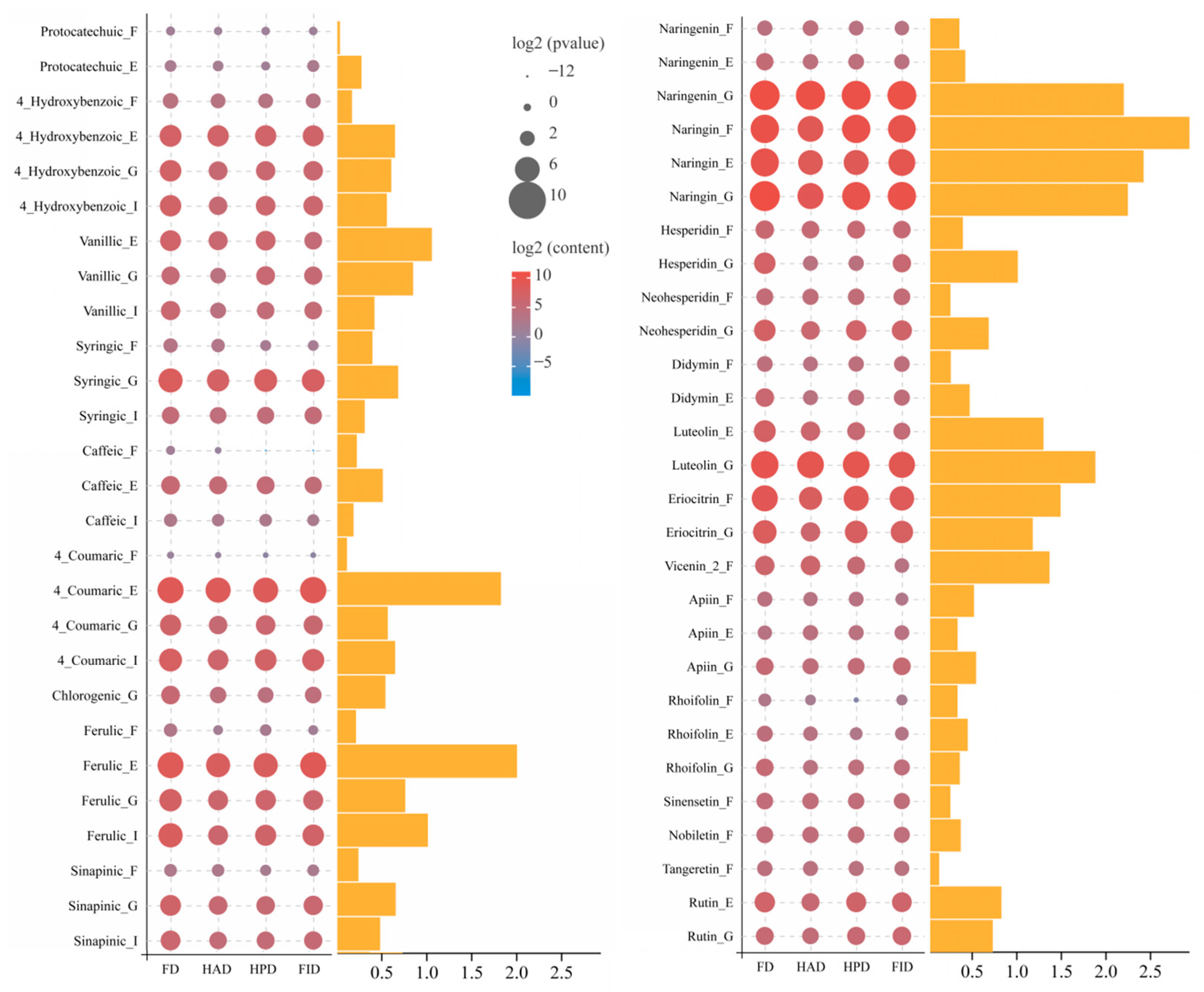
3.4.3. Phenolic Compounds
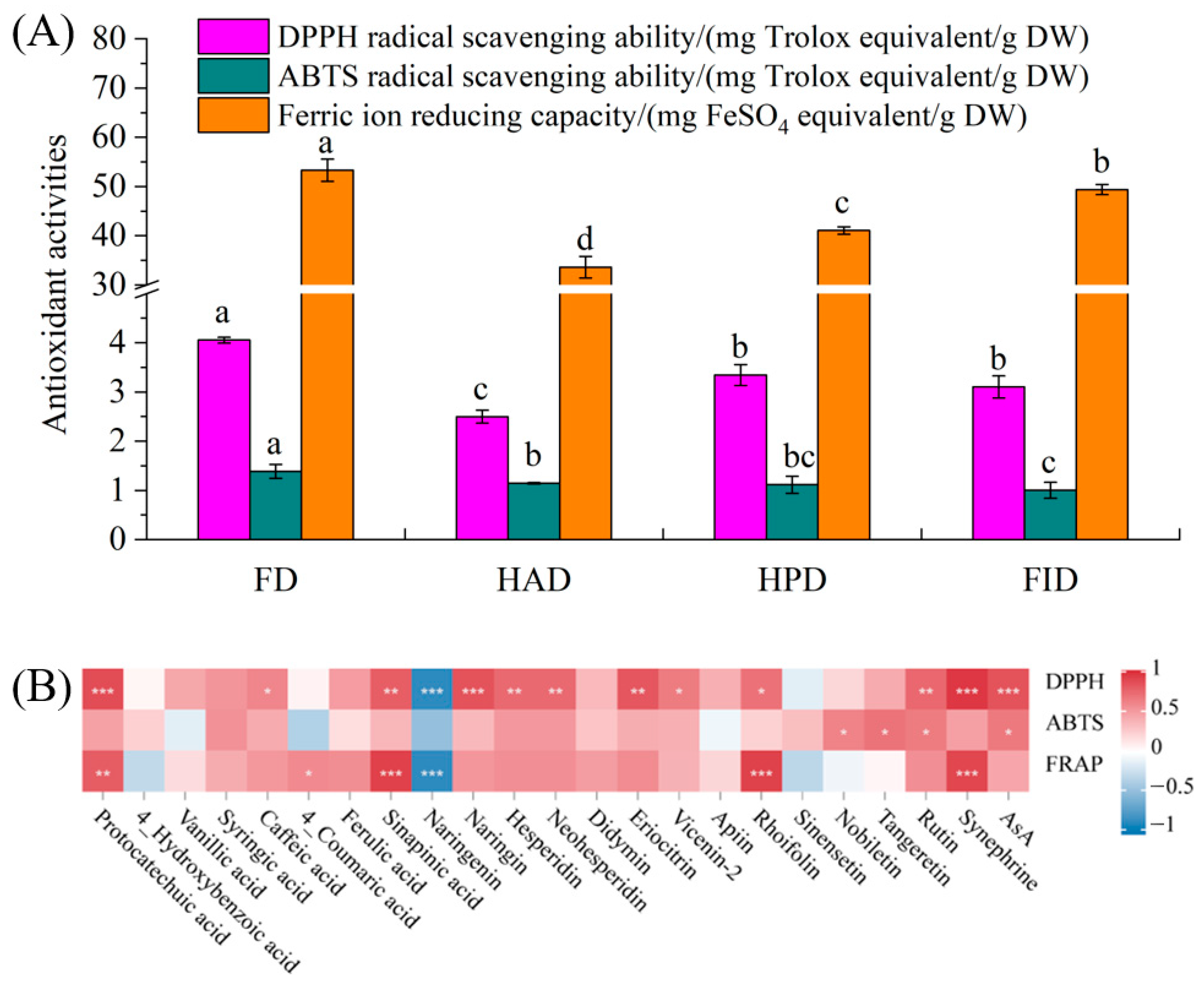
3.5. Active Ingredients and Antioxidant Activities of Lemon Brewed Beverages
3.6. Summary of Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.; Li, S.; Ho, C.-T. Dietary bioactives and essential oils of lemon and lime fruits. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uçan, F.; Ağçam, E.; Akyildiz, A. Bioactive compounds and quality parameters of natural cloudy lemon juices. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Xiao, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Ben, A.; Wang, Y. Dynamic changes in volatile and non-volatile flavor compounds in lemon flavedo during freeze-drying and hot-air drying. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 175, 114510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Cao, J.; Jiang, W. An advance on nutritional profile, phytochemical profile, nutraceutical properties, and potential industrial applications of lemon peels: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 124, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Nicolas, J.J.; Núñez-Gómez, D.; Lidón, V.; Martínez-Font, R.; Melgarejo, P.; Hernández, F.; Legua, P. Physico-chemical attributes of lemon fruits as affected by growing substrate and rootstock. Foods 2022, 11, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Cao, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, R.; Bai, F.; Wei, P. Effect of hydroalcohol extract of lemon (Citrus limon) peel on a rat model of type 2 diabetes. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 17, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjadmand, F.; Karimpour-Razkenari, E.; Nabavi, S.M.; Ardekani, M.R.S.; Saeedi, M. Plant polyphenols: Natural and potent UV-protective agents for the prevention and treatment of skin disorders. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maalik, S.; Moosa, A.; Zulfiqar, F.; Aslam, M.N.; Mahmood, T.; Siddique, K.H.M. Endophytic Bacillus atrophaeus CHGP13 and salicylic acid inhibit blue mold of lemon by regulating defense enzymes. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1184297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Pan, H.; Shui, Y.; Xing, Y.; Wu, L.; Zheng, F.; Fan, X.; Bi, X. Effect of different drying technologies on the characteristics and quality of lemon slices. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 2980–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Ou, S.; Shan, Y. Effect of drying temperature on the sugars, organic acids, limonoids, phenolics, and antioxidant capacities of lemon slices. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Law, C.-L.; Nema, P.K.; Zhao, J.-H.; Liu, Z.-L.; Deng, L.-Z.; Gao, Z.-J.; Xiao, H.-W. Pulsed vacuum drying enhances drying kinetics and quality of lemon slices. J. Food Eng. 2018, 224, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.Y.W.; Chong, C.H.; Chua, B.L.; Figiel, A. Influence of drying methods on the antibacterial, antioxidant and essential oil volatile composition of herbs: A review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 450–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benestante, A.; Chalapud, M.C.; Baümler, E.; Carrín, M.E. Physical and mechanical properties of lemon (Citrus lemon) seeds. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2023, 22, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, E.; Gocmen, D. The influences of drying method and metabisulfite pre-treatment on the color, functional properties and phenolic acids contents and bioaccessibility of pumpkin flour. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhao, R.; Liu, C.; Wu, Y.; Duan, X.; Hu, J.; Yang, F.; Wang, H. Dynamic changes in volatile flavor compounds, amino acids, organic acids, and soluble sugars in lemon juice vesicles during freeze-drying and hot-air drying. Foods 2022, 11, 2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M’hiri, N.; Ghali, R.; Nasr, I.B.; Boudhrioua, N. Effect of different drying processes on functional properties of industrial lemon byproduct. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 116, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhong, T.; Mei, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, G.; Rao, S.; Zheng, X.; Yang, Z. Comparison of different drying technologies for brocade orange (Citrus sinensis) peels: Changes in color, phytochemical profile, volatile, and biological availability and activity of bioactive compounds. Food Chem. 2023, 425, 136539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazewski, C.; Liang, K.; de Mejia, E.G. Comparison of the effect of chemical composition of anthocyanin-rich plant extracts on colon cancer cell proliferation and their potential mechanism of action using in vitro, in silico, and biochemical assays. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhong, T.; Chen, X.; Yang, B.; Du, M.; Wang, K.; Zalán, Z.; Kan, J. Potential of volatile organic compounds emitted by Pseudomonas fluorescens ZX as biological fumigants to control citrus green mold decay at postharvest. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragull, K.; Breksa, A.P., III; Cain, B. Synephrine content of juice from Satsuma mandarins (Citrus unshiu Marcovitch). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8874–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhong, T.; Li, B.; Yang, Q.; Du, M.; Zalán, Z.; Kan, J. Bioeffector Pseudomonas fluorescens ZX elicits biosynthesis and accumulation of functional ingredients in citrus fruit peel: A promising strategy for a more sustainable crop. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 13810–13820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Ding, F.; Sun, D.; Ma, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, J. Content changes of bitter compounds in “Guoqing No. 1” Satsuma mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.) during fruit development of consecutive 3 seasons. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Guo, Z.; Feng, X.; Huang, P.; Du, M.; Zalán, Z.; Kan, J. Distribution and natural variation of free, esterified, glycosylated, and insoluble-bound phenolic compounds in brocade orange (Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck) peel. Food Res. Int. 2022, 153, 110958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Mei, X.; Chen, X.; Rao, S.; Ju, T.; Li, J.; Yang, Z. Extraction and recovery of bioactive soluble phenolic compounds from brocade orange (Citrus sinensis) peels: Effect of different extraction methods thereon. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 173, 114337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, B.; Chen, X.; Huang, P.; Chen, K.; Ma, Y.; Agarry, I.E.; Kan, J. Optimization and comparison of non-conventional extraction techniques for soluble phenolic compounds from brocade orange (Citrus sinensis) peels. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 4917–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ying, T.J. Kinetic model on surface color in tomato fruits during the postharvest storage and its application. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2001, 17, 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Papoutsis, K.; Pristijono, P.; Golding, J.B.; Stathopoulos, C.E.; Bowyer, M.C.; Scarlett, C.J.; Vuong, Q.V. Effect of vacuum-drying, hot air-drying and freeze-drying on polyphenols and antioxidant capacity of lemon (Citrus limon) pomace aqueous extracts. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, M.C.; Petit, J.; Zimmer, D.; Djantou, E.B.; Scher, J. Effects of drying and grinding in production of fruit and vegetable powders: A review. J. Food Eng. 2016, 188, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, A.; Wojdyło, A.; Lech, K.; Łysiak, G.P.; Figiel, A. Physicochemical properties of whole fruit plum powders obtained using different drying technologies. Food Chem. 2016, 207, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suharta, S.; Hunaef, D.; Wijaya, C.H. Changes in volatiles and aroma profle of andaliman (Zanthoxylum acanthopodium DC.) upon various drying techniques. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, D.; Gao, H. Kinetics, physicochemical properties, and antioxidant activities of Angelica keiskei processed under four drying conditions. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 98, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, J.A.; Norton, T.; Alagusundaram, K.; Tiwari, B.K. Novel drying techniques for the food industry. Food Eng. Rev. 2014, 6, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Hong, Q.; Kan, J. Assessment of fresh star anise (Illicium verum Hook.f.) drying methods for influencing drying characteristics, color, flavor, volatile oil and shikimic acid. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahato, N.; Sharma, K.; Koteswararao, R.; Sinha, M.; Baral, E.R.; Cho, M.H. Citrus essential oils: Extraction, authentication and application in food preservation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2017, 59, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Li, X.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, O.; Huang, L.; Guo, L.; Gao, W. A review of chemical constituents and health-promoting effects of citrus peels. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 13058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasquez-Gomez, K.L.; Mori-Mestanza, D.; Caetano, A.C.; Idrogo-Vasquez, G.; Culqui-Arce, C.; Auquiñivin-Silva, E.A.; Cas-tro-Alayo, E.M.; Cruz-Lacerna, R.; Perez-Ramos, H.A.; Balcázar-Zumaeta, C.R.; et al. Exploring chemical properties of essential oils from citrus peels using green solvent. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ma, M.-L.; Luo, S.; Zhang, R.-M.; Han, P.; Hu, W. Metabolic responses to ethanol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using a gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry-based metabolomics approach. Int. J. Biochem. Cell B. 2012, 44, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahmandfar, R.; Tirgarian, B.; Dehghan, B.; Nemati, A. Changes in chemical composition and biological activity of essential oil from Thomson navel orange (Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck) peel under freezing, convective, vacuum, and microwave drying methods. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 8, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Tu, H.; Wan, J.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Luo, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H. Spatio-temporal distribution and natural variation of metabolites in citrus fruits. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manners, G.D. Citrus limonoids: Analysis, bioactivity, and biomedical prospects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8285–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Mitra, I.; Batuta, S.; Alam, M.N.; Roy, K.; Begum, N.A. Design, synthesis and exploring the quantitative structure-activity relationship of some antioxidant flavonoid analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5050–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Yi, J.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Bi, J. Systematic review of phenolic compounds in apple fruits: Compositions, distribution, absorption, metabolism, and processing stability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Ge, S.; Lin, S. Review of distribution, extraction methods, and health benefits of bound phenolics in food plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 68, 3330–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z. The maturity degree, phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of Eureka lemon [Citrus limon (L.) Burm. f.]: A negative correlation between total phenolic content, antioxidant capacity and soluble solid content. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 243, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Shan, Y.; Ding, S. Impact of dehydration methods on the phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of lemon slices. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 19, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Morita, T.; Akiyoshi, T.; Sato, R.; Uekusa, Y.; Katayama, K.; Yajima, K.; Imaoka, A.; Sugimoto, Y.; Kiuchi, F.; Ohtani, H. Citrus fruit-derived flavanone glycoside narirutin is a novel potent inhibitor of organic anion-transporting polypeptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 14182–14191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Zhou, X.; Long, C.; Du, Y.; Li, J.; Yue, J.; Pan, S. Variations of flavonoid composition and antioxidant properties among different cultivars, fruit tissues and developmental stages of citrus fruits. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e1900690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Treatment | Peel | Flesh | Browning Degree | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | Hue Angle | Chroma | Saturation | L* | a* | b* | Hue Angle | Chroma | Saturation | ||
| FD | 78.91 ± 4.35a | 2.09 ± 0.37b | 72.26 ± 4.17a | 88.35 ± 0.24a | 72.30 ± 4.18a | 0.92 ± 0.05b | 47.30 ± 3.12a | −1.04 ± 0.17d | 21.60 ± 2.87a | 87.21 ± 0.61d | 21.62 ± 2.87b | 0.46 ± 0.07c | 28.33 ± 2.34d |
| HAD | 54.50 ± 3.72b | 16.06 ± 1.22a | 55.07 ± 3.86b | 73.70 ± 1.29b | 57.38 ± 3.84b | 1.06 ± 0.08a | 24.17 ± 2.42b | 4.29 ± 0.56b | 25.43 ± 2.66a | 80.42 ± 0.61a | 25.79 ± 2.70ab | 1.08 ± 0.18b | 38.04 ± 3.07c |
| HPD | 52.35 ± 4.59b | 16.22 ± 2.59a | 50.20 ± 5.06b | 71.97 ± 3.46b | 52.84 ± 4.77b | 1.01 ± 0.07ab | 12.80 ± 2.05c | 12.44 ± 1.80a | 23.49 ± 3.29a | 61.77 ± 5.27b | 26.69 ± 2.86a | 2.13 ± 0.15a | 48.73 ± 0.81b |
| FID | 52.08 ± 2.15b | 13.79 ± 1.83a | 54.31 ± 4.67b | 75.60 ± 2.74b | 56.09 ± 4.29b | 1.08 ± 0.08a | 0.00 ± 0.00d | −7.73 ± 0.98c | −9.04 ± 1.51b | 49.23 ± 4.21c | 11.92 ± 1.58c | / | 62.06 ± 1.14a |
| Parameter | Available Compound | Available Amount of Compound (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FD | HAD | HPD | FID | FD | HAD | HPD | FID | |
| Phenols (μg/g DW) | ||||||||
| Protocatechuic acid | 2.81 ± 0.22a | 1.53 ± 0.13c | 1.69 ± 0.12bc | 1.82 ± 0.10b | 47.75 ± 3.72a | 31.79 ± 2.71b | 43.84 ± 3.06a | 30.10 ± 1.70b |
| 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | 4.98 ± 0.62a | 5.12 ± 0.15a | 4.98 ± 0.47a | 3.69 ± 0.25b | 1.52 ± 0.19c | 2.69 ± 0.08a | 2.29 ± 0.22b | 1.71 ± 0.11 |
| Vanillic acid | 6.33 ± 0.33b | 5.01 ± 0.31c | 8.54 ± 0.48a | 6.20 ± 0.76b | 3.75 ± 0.20b | 6.37 ± 0.40a | 6.34 ± 0.36a | 6.44 ± 0.79a |
| Syringic acid | 37.27 ± 1.54a | 29.88 ± 1.29b | 25.39 ± 1.80c | 25.99 ± 3.22bc | 15.15 ± 0.63b | 19.67 ± 0.85a | 14.25 ± 1.01b | 14.67 ± 1.82b |
| Caffeic acid | 10.12 ± 1.64a | 6.30 ± 0.02c | 7.76 ± 0.30b | 6.55 ± 1.51bc | 19.95 ± 2.22a | 15.85 ± 0.04b | 20.70 ± 0.79a | 21.76 ± 2.01a |
| 4-Coumaric acid | 25.41 ± 0.65b | 21.55 ± 1.18c | 21.44 ± 0.46c | 33.67 ± 3.28a | 4.18 ± 0.11c | 5.44 ± 0.30a | 4.89 ± 0.10b | 6.08 ± 0.59a |
| Ferulic acid | 80.52 ± 0.17a | 71.97 ± 3.62b | 77.50 ± 5.06b | 76.80 ± 2.61b | 11.60 ± 0.02c | 21.47 ± 1.08a | 20.20 ± 1.32a | 14.60 ± 0.50b |
| Sinapinic acid | 33.65 ± 0.52a | 21.30 ± 2.65c | 23.47 ± 1.00c | 30.01 ± 2.15b | 22.34 ± 0.35b | 28.46 ± 3.54a | 30.89 ± 1.31a | 31.72 ± 2.27a |
| Naringenin | 9.89 ± 1.06c | 19.64 ± 1.44a | 16.46 ± 1.34b | 14.09 ± 2.14b | 0.68 ± 0.07c | 1.58 ± 0.12a | 1.43 ± 0.12ab | 1.28 ± 0.19b |
| Naringin | 749.04 ± 30.35a | 168.16 ± 10.48c | 709.30 ± 49.00a | 305.23 ± 41.63b | 22.12 ± 0.90b | 13.31 ± 0.83c | 32.64 ± 2.26a | 13.12 ± 1.79c |
| Hesperidin | 4.93 ± 0.32a | 3.30 ± 0.50b | 3.64 ± 0.13b | 3.39 ± 0.21b | 2.79 ± 0.18c | 6.34 ± 0.97a | 6.21 ± 0.22a | 3.93 ± 0.24b |
| Neohesperidin | 49.30 ± 3.26a | 33.05 ± 3.06b | 36.44 ± 1.29b | 33.87 ± 2.10b | 30.91 ± 2.04b | 44.20 ± 6.76a | 30.96 ± 1.10b | 29.38 ± 1.82b |
| Didymin | 21.64 ± 2.85a | 16.97 ± 1.98b | 13.48 ± 1.79c | 18.47 ± 1.78ab | 29.74 ± 3.91c | 60.56 ± 7.07a | 35.90 ± 4.77c | 45.19 ± 4.36b |
| Eriocitrin | 119.32 ± 3.26a | 80.47 ± 8.41c | 101.23 ± 6.98b | 83.42 ± 7.07c | 16.69 ± 0.46c | 29.53 ± 3.09a | 18.56 ± 1.28b | 17.68 ± 1.50bc |
| Vicenin-2 | 8.34 ± 0.91a | 6.07 ± 0.66b | 6.43 ± 0.81b | 5.42 ± 0.22c | 11.86 ± 1.29c | 8.45 ± 0.92d | 15.99 ± 2.01b | 43.26 ± 1.79a |
| Apiin | 13.52 ± 1.55ab | 11.48 ± 2.02b | 14.83 ± 1.30a | 13.13 ± 0.74ab | 21.22 ± 2.12b | 23.02 ± 2.05ab | 25.87 ± 2.26a | 21.94 ± 1.24b |
| Rhoifolin | 7.58 ± 0.40a | 2.83 ± 0.52c | 4.14 ± 0.60b | 7.12 ± 0.65a | 11.91 ± 0.64c | 9.49 ± 1.05d | 15.94 ± 2.31b | 21.12 ± 1.93a |
| Sinensetin | 6.44 ± 0.81ab | 6.87 ± 0.49a | 5.34 ± 0.92b | 4.80 ± 1.05b | 24.18 ± 3.06ab | 28.24 ± 2.01a | 22.30 ± 3.84b | 21.72 ± 3.73b |
| Nobiletin | 15.65 ± 0.86a | 14.07 ± 1.18a | 7.05 ± 0.22b | 3.59 ± 0.70c | 57.18 ± 3.15a | 59.62 ± 4.98a | 27.42 ± 0.86b | 17.25 ± 1.35c |
| Tangeretin | 13.76 ± 1.27a | 9.97 ± 0.89b | 8.55 ± 1.31b | 2.25 ± 0.14c | 55.20 ± 2.32a | 47.47 ± 4.22b | 40.13 ± 4.44b | 10.93 ± 0.66c |
| Rutin | 73.09 ± 8.51a | 26.61 ± 3.60b | 22.18 ± 4.00bc | 18.77 ± 1.98c | 54.41 ± 6.33a | 38.48 ± 3.21b | 17.11 ± 2.08c | 14.30 ± 0.51d |
| Total | 1293.61 ± 37.97a | 562.16 ± 16.37d | 1119.85 ± 63.65b | 698.291 ± 56.51c | 13.58 ± 0.40b | 10.86 ± 0.32c | 17.19 ± 0.82a | 10.43 ± 0.84c |
| Other compounds (mg/g DW) | ||||||||
| Synephrine | 0.94 ± 0.03a | 0.28 ± 0.004c | 0.57 ± 0.03b | 0.60 ± 0.08b | 11.59 ± 0.43a | 5.36 ± 0.71c | 8.75 ± 0.53b | 8.72 ± 0.74b |
| AsA | 0.80 ± 0.07a | 0.55 ± 0.04c | 0.71 ± 0.04b | 0.55 ± 0.07c | 32.54 ± 2.77d | 45.94 ± 3.24b | 37.46 ± 2.08c | 65.26 ± 6.37a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Fu, Q.; Hao, G.; Gu, Y.; Sun, T.; Gao, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Zheng, X.; Yang, Z.; et al. Physical Aspects, Phytochemical Profiles, and Nutritional Properties of Lemon (Citrus limon) Slices Under Different Drying Technologies. Foods 2025, 14, 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152586
Wang Z, Fu Q, Hao G, Gu Y, Sun T, Gao L, Wang B, Wang S, Zheng X, Yang Z, et al. Physical Aspects, Phytochemical Profiles, and Nutritional Properties of Lemon (Citrus limon) Slices Under Different Drying Technologies. Foods. 2025; 14(15):2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152586
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhirong, Qingqing Fu, Guijie Hao, Yuanwei Gu, Tianqi Sun, Lu Gao, Bo Wang, Shuai Wang, Xiangfeng Zheng, Zhenquan Yang, and et al. 2025. "Physical Aspects, Phytochemical Profiles, and Nutritional Properties of Lemon (Citrus limon) Slices Under Different Drying Technologies" Foods 14, no. 15: 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152586
APA StyleWang, Z., Fu, Q., Hao, G., Gu, Y., Sun, T., Gao, L., Wang, B., Wang, S., Zheng, X., Yang, Z., & Rao, S. (2025). Physical Aspects, Phytochemical Profiles, and Nutritional Properties of Lemon (Citrus limon) Slices Under Different Drying Technologies. Foods, 14(15), 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152586






