Saponins from Solanum nigrum L. Fruit: Extraction Optimization, Structural Characterization, and Dual-Functional Efficacy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Determination of Total Saponin Content
2.3. Optimization of the Extraction Process of Crude Saponins
2.4. Isolation and Purification of Saponins
2.5. Analysis and Characterization of Purified Substance
2.5.1. Thin-Layer Chromatography
2.5.2. Liquid Chromatography
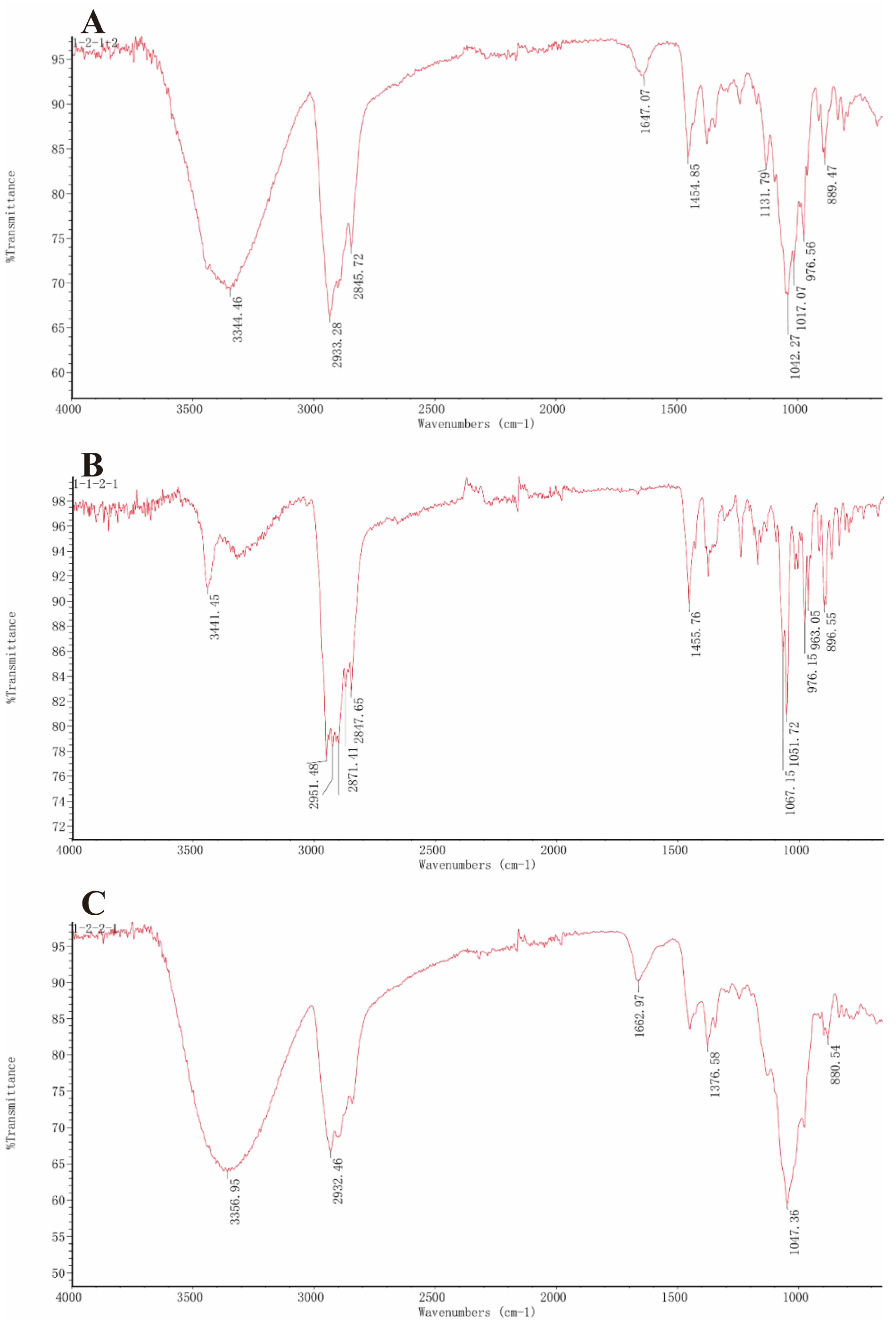
2.5.3. Infrared Spectroscopy
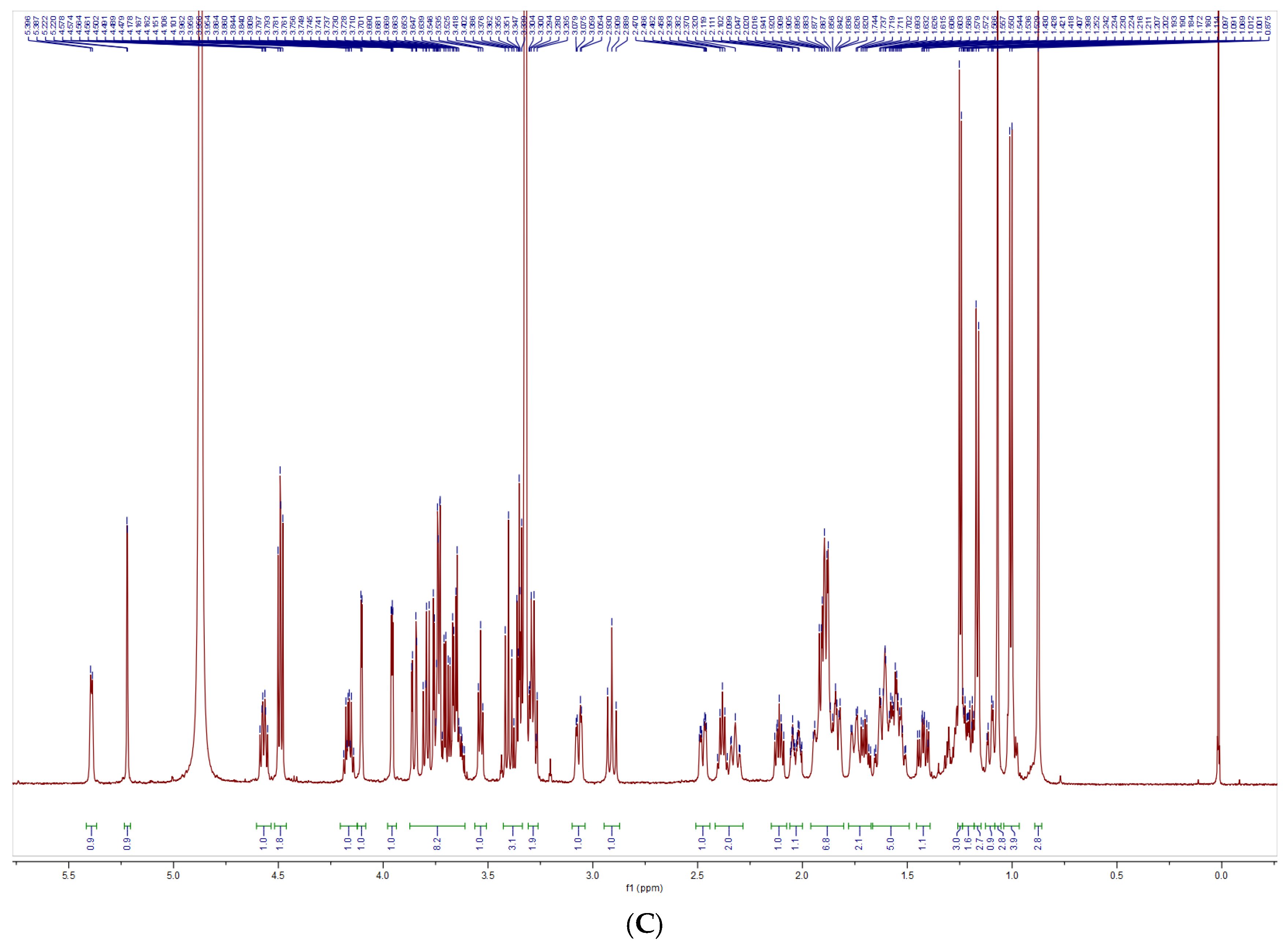
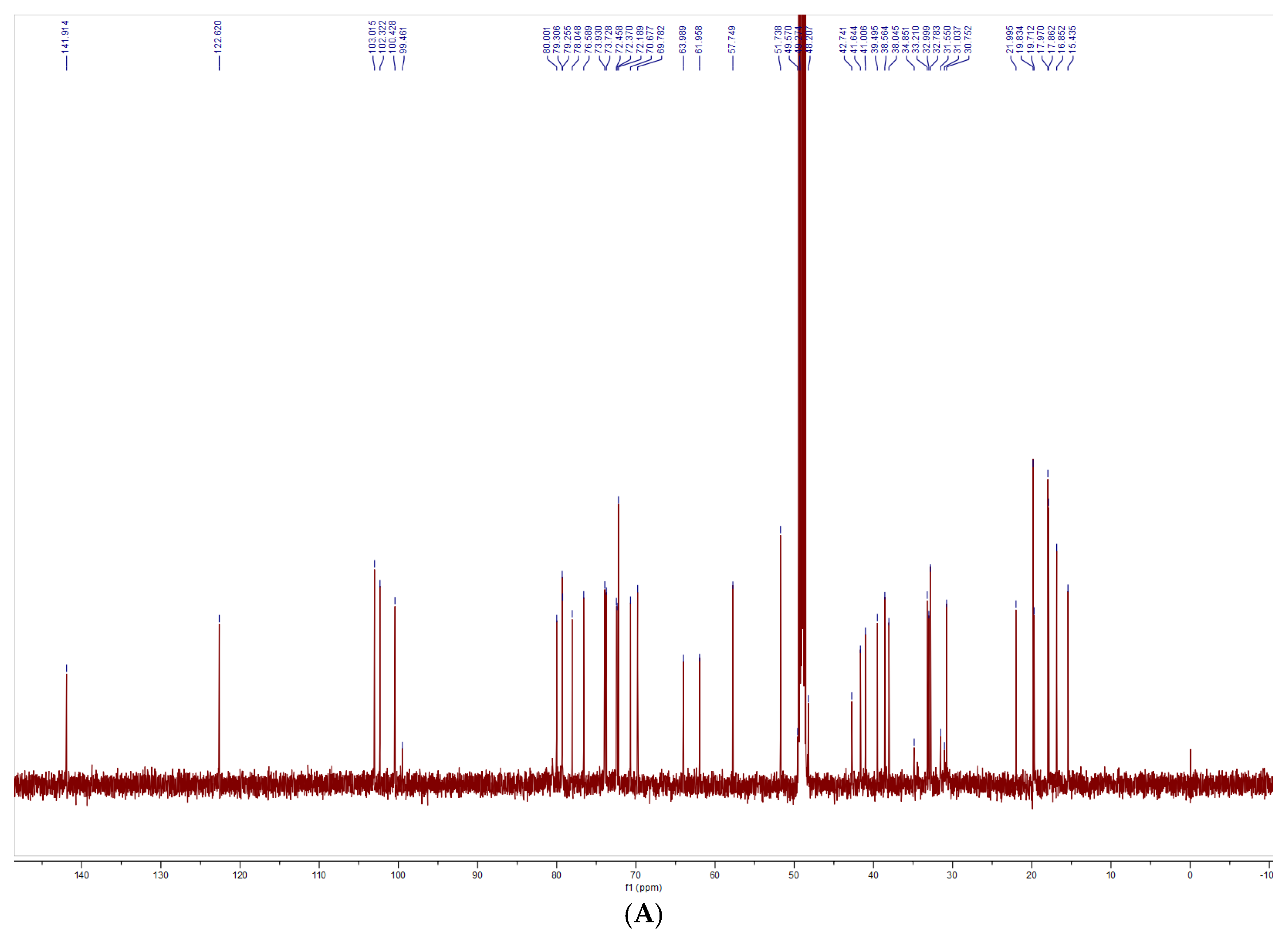
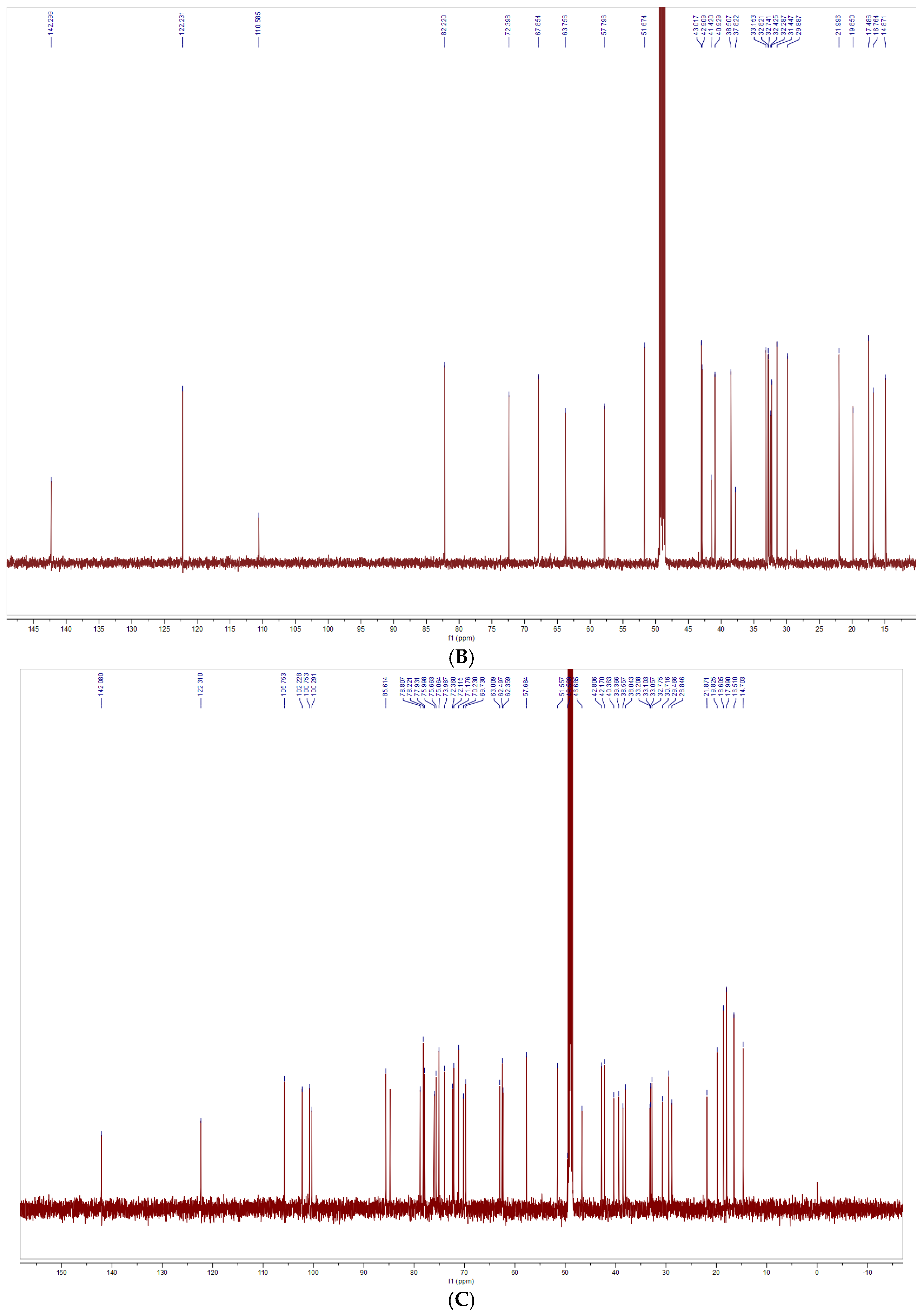
2.5.4. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectra
2.5.5. Mass Spectrometry
2.6. Determination of S. nigrum Extract Antioxidant Activity
2.6.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.6.2. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity
2.6.3. ABTS Free Radical Scavenging Activity
2.6.4. Superoxide Anion Radical Scavenging Activity
2.6.5. Ferric Ion Chelating Activity
2.7. Measurement of Antimicrobial Activity of S. nigrum Extracts
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of the Crude Saponin Extraction Process
3.2. Separation and Purification of Saponins for Identification of Results
3.2.1. Thin-Layer Chromatography Analysis Results
3.2.2. Liquid Chromatography Analysis Results
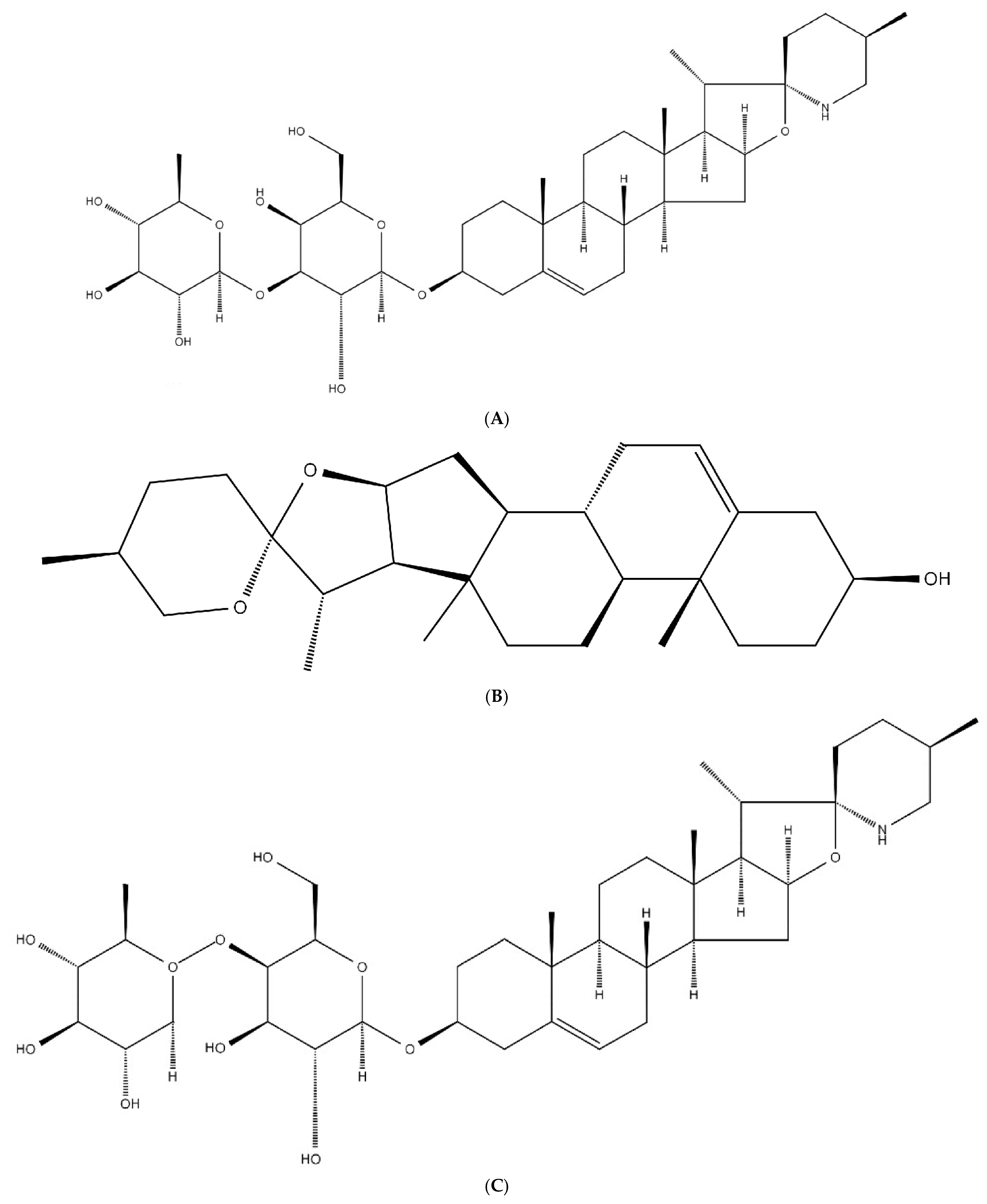
3.3. Structural Characterization Results of Saponins
3.3.1. Structural Identification of the Saponin SNL1
3.3.2. Structural Identification of the Saponin SNL2
3.3.3. Structural Identification of the Saponin SNL3
3.4. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity Analysis of Extracts
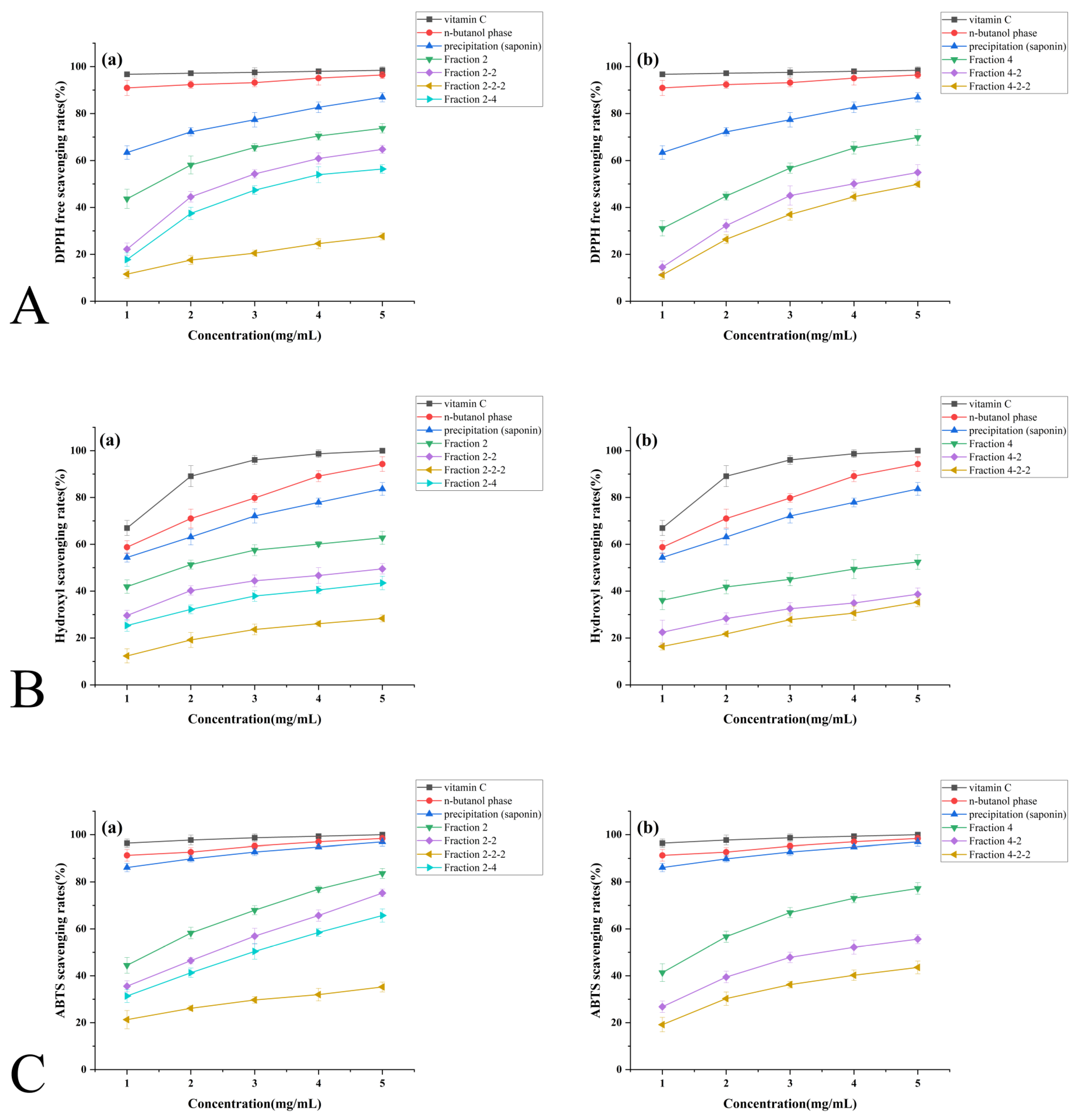
3.4.1. DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Capacity
3.4.2. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Capacity
3.4.3. ABTS Free Radical Scavenging Capacity
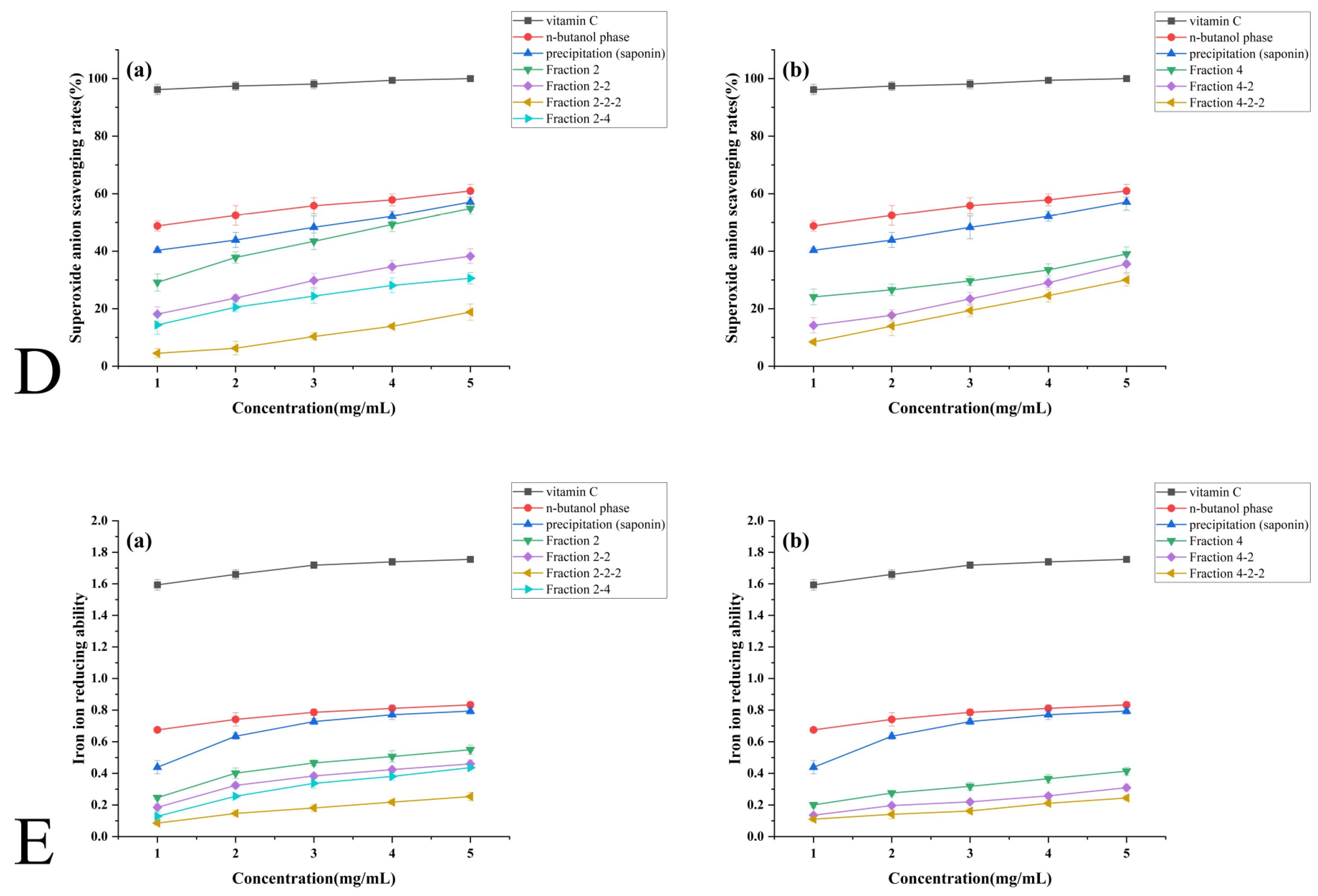
3.4.4. Superoxide Anion Radical Scavenging Capacity
3.4.5. Ferric Ion Reducing Power Capacity
3.5. Antimicrobial Activity of S. nigrum Extracts
3.5.1. Bacteriostatic Effect on Escherichia coli
3.5.2. Bacteriostatic Effect on Candida albicans
3.5.3. Bacteriostatic Effect on Shigella flexneri
3.5.4. Bacteriostatic Effect on Salmonella paratyphi B
3.5.5. Bacteriostatic Effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa
3.5.6. Bacteriostatic Effect on Staphylococcus aureus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, L.; He, X. Synergistic Combination of the Total Steroidal Saponins from the Berries of Black Nightshade and Adriamycin to Overcome Leukemia Multidrug Resistance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 3315–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yi, X.; He, X. Steroidal alkaloid glycosides and phenolics from the immature fruits of Solanum nigrum. Fitoterapia 2019, 137, 104268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dai, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, L.; He, X.; Gong, G. Solanum nigrum Linn.: An Insight into Current Research on Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 918071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, G.K. A review of the ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacological relevance of the South African weed Solanum sisymbriifolium Lam. (Solanaceae). Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2017, 21, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.-H.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Bai, M.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.-X.; Huang, X.-X.; Song, S.-J. Chemical constituents from the fruits of Solanum nigrum and their chemotaxonomic significance. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2022, 103, 104452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-W.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Gao, W.-K.; Zhang, L.-H.; Yu, H.-Y.; Wu, H.-H. Steroidal constituents from Solanum nigrum. Fitoterapia 2023, 169, 105603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Wang, L.; Tang, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Sun, C.; Wu, X.; Xu, D. Two novel polysaccharides from Solanum nigrum L. exert potential prebiotic effects in an in vitro fermentation model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elizalde-Romero, C.A.; Montoya-Inzunza, L.A.; Contreras-Angulo, L.A.; Heredia, J.B.; Gutiérrez-Grijalva, E.P. Solanum Fruits: Phytochemicals, Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability, and Their Relationship With Their Health-Promoting Effects. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 790582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Kumar, R.; Dubey, R.C.; Kumar, P. Studies on phytochemical constituents and antimicrobial activities of leaves, fruits and stems of Solanum nigrum L. Asian J. Plant Sci. Res. 2016, 6, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Jia, Q.; Wu, M.-S.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, G.; Zou, C.-Y.; Tang, Q.; Lu, J.; Huang, G.; et al. Degalactotigonin, a Natural Compound from Solanum nigrum L. Inhibits Growth and Metastasis of Osteosarcoma through GSK3β Inactivation-Mediated Repression of the Hedgehog/Gli1 Pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Liu, S.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wen, S.; Qiu, R.; Li, Y.; Fan, H. Extract of Astragali Radix and Solanum nigrum Linne regulates microglia and macrophage polarization and inhibits the growth and infiltration of C6 glioblastoma. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moenga, M.N.; Mogwasi, R.; Okemwa, E.K.; Olale, K.O. Determination of Essential Minerals in the Indigenous Vegetables Solanum nigrum (Stout Shade) and Gynandropsis gynandra (Spider Plant) from Two Agroecological Zones in Kisii County, Kenya. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 203, 2365–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Ou, X.; Shi, H.; Huang, W.; Song, L.; Zhu, J.; Yu, R. Isolation, structures and biological activities of medicinal glycoproteins from natural resources: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öner, A.C.; Yur, F.; Fethullah, M.N. Antioxidant and Antihyperlipidemic Effect of Solanum Nigrum Extract in Experimental Diabetes Model. Van Vet. J. 2023, 34, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, P.M.; Critzer, F.J.; Taylor, T.M. Naturally Occurring Antimicrobials for Minimally Processed Foods. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 163–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.-p.; Yu, H.; Guo, Y.-h.; Cheng, Y.-l.; Xie, Y.-f.; Yao, W.-r. Antibacterial activity of Sapindus saponins against microorganisms related to food hygiene and the synergistic action mode of Sapindoside A and B against Micrococcus luteus in vitro. Food Control 2021, 130, 108337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro del Hierro, J.; Herrera, T.; García-Risco, M.R.; Fornari, T.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. Ultrasound-assisted extraction and bioaccessibility of saponins from edible seeds: Quinoa, lentil, fenugreek, soybean and lupin. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.-Q.; Dong, X.; Yin, X.; Fan, Y.; Fan, Y.; Mao, C.; Zhou, W. A mass spectrometry database for identification of saponins in plants. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1625, 461296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randriamamonjy, T.H.; Ontiveros, J.F.; Andrianjafy, M.T.; Samiez, P.; Berlioz-Barbier, A.; Nardello-Rataj, V.; Aubry, J.-M.; Ramanandraibe, V.; Lemaire, M. Comparative study on the amphiphilicity, emulsifying and foaming properties of saponins extracted from Furcraea foetida. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 653, 129923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Luan, F.; Zou, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, B.; Xin, B.; Sun, J.; Guo, D.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y. Traditional uses, phytochemical constituents, pharmacological properties, and quality control of Pseudostellaria heterophylla (Miq.) Pax. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 337, 118871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szliszka, E.; Czuba, Z.P.; Domino, M.; Mazur, B.; Zydowicz, G.; Krol, W. Ethanolic Extract of Propolis (EEP) Enhances the Apoptosis- Inducing Potential of TRAIL in Cancer Cells. Molecules 2021, 14, 738–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, C.L.; Salminen, H.; Weiss, J. QuillajaSaponin Characteristics and Functional Properties. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado Gonzalez, P.; Sörensen, P.M. Characterization of saponin foam from Saponaria officinalis for food applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Tyagi, A.; Bhansali, P.; Pareek, S.; Singh, V.; Ilyas, A.; Mishra, R.; Poddar, N.K. Saponins: Extraction, bio-medicinal properties and way forward to anti-viral representatives. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 150, 112075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, X.; Liu, F.; Mao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W.; Cui, S. Sources, metabolism, health benefits and future development of saponins from plants. Food Res. Int. 2024, 197, 115226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yi, X.; He, X. Anti-inflammatory steroidal glycosides from the berries of Solanum nigrum L. (European black nightshade). Phytochemistry 2018, 148, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiang, L.; Yi, X.; He, X. Potential Anti-inflammatory Steroidal Saponins from the Berries of Solanum nigrum L. (European Black Nightshade). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4262–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Zhu, J.; Tian, R.; Yang, W.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Q.; Zeng, Z. Quality evaluation for Dipacus asperoides from Enshi areas and optimization extraction of saponins and organic acids and its application. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Su, S.; Zhou, H.; Yan, H.; Ye, J.; Zhao, Z.; You, L.; Fu, X. Antioxidant/antihyperglycemic activity of phenolics from sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) bagasse and identification by UHPLC-HR-TOFMS. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 101, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.-H.; Yao, L.; Zhang, J.-X.; Wang, L.-A.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.-P.; Xiao, S.-Y.; Li, C.-T.; Li, Y. Novel 2,5-Diarylcyclopentenone Derivatives from the Wild Edible Mushroom Paxillus involutus and Their Antioxidant Activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 5040–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zou, Y.; Liang, X.; Peng, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Hu, K. Encapsulation of resveratrol in zein/pectin core-shell nanoparticles: Stability, bioaccessibility, and antioxidant capacity after simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, R.; Li, Y.; Miao, J.; Liu, G.; Lan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y. HPLC fingerprint analysis of Phyllanthus emblica ethanol extract and their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 254, 112740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-x.; Zhang, C.; Pan, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Yang, K.; Zeng, X.; Tian, J. Analysis of chemical components and biological activities of essential oils from black and white pepper (Piper nigrum L.) in five provinces of southern China. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 117, 108644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.A.; Asghar, M.A. Green synthesized and characterized copper nanoparticles using various new plants extracts aggravate microbial cell membrane damage after interaction with lipopolysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atsamnia, D.; Hamadache, M.; Hanini, S.; Benkortbi, O.; Oukrif, D. Prediction of the antibacterial activity of garlic extract on E. coli, S. aureus and B. subtilis by determining the diameter of the inhibition zones using artificial neural networks. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, B. Simultaneous analysis of diosgenin and sarsasapogenin in Asparagus officinalis byproduct by thin-layer chromatography. Phytochem. Anal. 2010, 22, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Ma, B.; Wang, Y. Study on separation and identification of steroidal saponins of Dioscorea nipponica Makino. Chin. Pharm. J. 2005, 40, 1539. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L.; Hu, X.; Ren, J.; Jiao, H.; Li, P. Preparation and Study on Anti-hyperthyroidism Activities of Diosgenin. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2015, 32, 692–695. [Google Scholar]
- Mahato, S.B.; Sahu, N.P.; Ganguly, A.N.; Kasai, R.; Tanaka, O. Steroidal alkaloids from Solanum khasian um: Application of 13C NMR spectroscopy to their structural elucidation. Phytochemistry 1980, 19, 2017–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, A. Study Approach of Antioxidant Properties in Foods: Update and Considerations. Foods 2017, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcour, A.H. Outer membrane permeability and antibiotic resistance. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2009, 1794, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, G.; Giacomini, D. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities for natural and synthetic dual-active compounds. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| 1.25 mg/mL | 2.5 mg/mL | 5 mg/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n-butanol phase | 14.00 ± 1.00 ** | 14.50 ± 1.50 ** | 16.13 ± 2.37 ** |
| Precipitation (saponin) | 13.00 ± 0.50 *** | 14.25 ± 1.00 *** | 16.75 ± 1.00 ** |
| Fr. 2 | 12.25 ± 1.50 ** | 17.00 ± 0.75 *** | 17.25 ± 0.75 ** |
| Fr. 2-2 | 13.25 ± 0.50 *** | 14.50 ± 0.50 *** | 14.75 ± 1.50 ** |
| Fr. 2-2-2 | 12.75 ± 0.25 *** | 14.25 ± 0.75 *** | 14.25 ± 1.00 *** |
| Fr. 2-4 | 11.17 ± 0.83 ** | 11.67 ± 1.33 ** | 12.00 ± 0.75 *** |
| Fr. 4 | 13.17 ± 0.33 *** | 13.75 ± 0.75 *** | 14.00 ± 1.00 *** |
| Fr. 4-2 | 12.75 ± 0.75 *** | 13.50 ± 0.50 *** | 13.75 ± 0.75 *** |
| Fr. 4-2-2 | 12.25 ± 0.25 *** | 12.33 ± 0.17 *** | 12.50 ± 0.50 *** |
| 1.25 mg/mL | 2.5 mg/mL | 5 mg/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n-butanol phase | — | — | — |
| Precipitation (saponin) | — | 14.00 ± 1.25 ** | 16.25 ± 1.00 *** |
| Fr. 2 | 14.00 ± 0.75 *** | 15.00 ± 1.75 ** | 17.00 ± 1.75 ** |
| Fr. 2-2 | 12.50 ± 0.50 *** | 13.50 ± 0.75 *** | 15.75 ± 1.00 ** |
| Fr. 2-2-2 | — | — | 10.50 ± 0.50 *** |
| Fr. 2-4 | — | — | — |
| Fr. 4 | 13.25 ± 0.25 *** | 15.5 ± 0.50 *** | 16.75 ± 0.75 *** |
| Fr. 4-2 | 10.50 ± 0.50 ** | 13.00 ± 0.75 *** | 14.00 ± 1.00 ** |
| Fr. 4-2-2 | — | — | — |
| 1.25 mg/mL | 2.5 mg/mL | 5 mg/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n-butanol phase | 12.50 ± 0.50 *** | 14.50 ± 0.50 *** | 15.50 ± 1.00 ** |
| Precipitation (saponin) | 13.83 ± 1.66 ** | 15.50 ± 0.75 *** | 15.83 ± 1.66 ** |
| Fr. 2 | 15.25 ± 0.25 *** | 16.00 ± 0.75 *** | 17.00 ± 1.00 *** |
| Fr. 2-2 | 10.50 ± 0.75 ** | 14.67 ± 0.83 ** | 15.75 ± 0.75 *** |
| Fr. 2-2-2 | — | — | — |
| Fr. 2-4 | 12.50 ± 0.25 *** | 12.50 ± 0.50 *** | 12.67 ± 0.33 *** |
| Fr. 4 | 13.00 ± 0.75 *** | 15.25 ± 0.75 *** | 15.50 ± 0.50 *** |
| Fr. 4-2 | — | — | — |
| Fr. 4-2-2 | — | — | — |
| 1.25 mg/mL | 2.5 mg/mL | 5 mg/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n-butanol phase | — | — | — |
| Precipitation (saponin) | 11.00 ± 1.00 ** | 12.25 ± 0.75 *** | 12.67 ± 0.83 *** |
| Fr. 2 | 11.17 ± 1.33 * | 12.33 ± 0.67 *** | 12.75 ± 0.75 *** |
| Fr. 2-2 | 10.00 ± 0.25 *** | 10.33 ± 0.17 *** | 10.50 ± 0.25 *** |
| Fr. 2-2-2 | — | — | — |
| Fr. 2-4 | — | — | — |
| Fr. 4 | 10.00 ± 0.25 *** | 11.17 ± 0.33 *** | 11.67 ± 0.83 ** |
| Fr. 4-2 | — | — | — |
| Fr. 4-2-2 | — | — | — |
| 1.25 mg/mL | 2.5 mg/mL | 5 mg/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n-butanol phase | — | — | — |
| Precipitation (saponin) | 11.50 ± 0.25 *** | 12.50 ± 1.00 ** | 13.00 ± 0.50 *** |
| Fr.2 | — | — | — |
| Fr.2-2 | — | — | — |
| Fr.2-2-2 | — | — | — |
| Fr.2-4 | — | — | — |
| Fr.4 | — | — | — |
| Fr.4-2 | — | — | — |
| Fr.4-2-2 | — | — | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Guo, W.; Zhang, T.; Chen, J.; Huang, L.; Huang, J.; Huang, R. Saponins from Solanum nigrum L. Fruit: Extraction Optimization, Structural Characterization, and Dual-Functional Efficacy. Foods 2025, 14, 2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132370
Chen S, Guo W, Zhang T, Chen J, Huang L, Huang J, Huang R. Saponins from Solanum nigrum L. Fruit: Extraction Optimization, Structural Characterization, and Dual-Functional Efficacy. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132370
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shuyuan, Weiyun Guo, Tonghe Zhang, Jianfang Chen, Li Huang, Jihong Huang, and Ruqiang Huang. 2025. "Saponins from Solanum nigrum L. Fruit: Extraction Optimization, Structural Characterization, and Dual-Functional Efficacy" Foods 14, no. 13: 2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132370
APA StyleChen, S., Guo, W., Zhang, T., Chen, J., Huang, L., Huang, J., & Huang, R. (2025). Saponins from Solanum nigrum L. Fruit: Extraction Optimization, Structural Characterization, and Dual-Functional Efficacy. Foods, 14(13), 2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132370






