Abstract
C. macrophylla and C. tangutorum, collectively known as Shigecai in Chinese, are consumed as special and nutritious vegetables by the Tibetan, Qiang, and Yi communities in China. However, due to the insufficient knowledge of their phytochemical compositions and health benefits, the industrial utilization of these species in the food sector remains limited. Although Shigecai leaves contain substantial pectic polysaccharides, their chemical structures and biological activities remain unknown, which ultimately restricts their industrial utilization. Thus, to address this gap, this study systematically analyzed the chemical characteristics and biological functions of rhamnogalacturonan-I (RG-I)- enriched pectin from C. tangutorum (CTHDP) and C. macrophylla (CMHDP) leaves. The results demonstrate that Shigecai leaves are promising sources of RG-I-enriched pectin, with yields of 57.63–65.21 mg/g dry weight. In addition, both CTHDP and CMHDP exhibited highly similar chemical and structural properties, dominated by RG-I and homogalacturonan (HG) pectin regions, with RG-I ratios of 60.14–63.33 mol%. Furthermore, both samples demonstrated notable antioxidant ability, antiglycation activity, prebiotic potency, and immunoregulatory effects, which were strongly linked to their bound polyphenol content, uronic acid content, and molecular weight. These findings support the industrial utilization of Shigecai and establish Shigecai-derived RG-I-enriched pectin as a promising functional food ingredient.
1. Introduction
Pectin, a structurally diverse heteropolysaccharide, serves as a fundamental structural composition of plant cell walls, which is abundantly found in vegetables and fruits [1,2,3]. Its content varies significantly across plant tissues, accounting for approximately 35% of dicotyledonous cell walls, 2–10% of grasses, and 5% of woody tissues [3]. Structurally, pectin comprises three mainly distinctive domains within plant cell walls, including homogalacturonan (HG, about 60–65%), rhamnogalacturonan-I (RG-I, about 20–35%), and rhamnogalacturonan-II (RG-II, about 2–10%) [2,3,4]. HG typically comprises linearly polymerized α-1,4-linked D-galacturonic acid residues, where carboxyl groups may undergo C-6 methylation and/or O-2/O-3 acetylation. Based on the degree of esterification (DE), HG can be classified as high methyl-esterified (DE > 50%) pectin and low methyl-esterified (DE < 50%) pectin. RG-I features a repeating disaccharide backbone of galacturonic acid and rhamnose units, with the latter bearing neutral side chains (e.g., galactan, arabinan, or arabinogalactan). Similar to HG, RG-I’s galacturonic acid residues may also be acetylated at the O-2/O-3 positions [2,3,4]. Pectin exhibits excellent functional properties, such as gelation capacity, emulsification performance, and film-forming ability. These characteristics have led to its wide utilization in the food and agricultural industries as a gelling component, thickener, emulsifier, and composite film material [5,6]. Moreover, pectin demonstrates remarkable health-promoting properties, such as an intestinal prebiotic effect, immunomodulatory activity, anti-cancer effect, anti-inflammatory effect, the enhancement of immune barriers, the regulation of blood glucose and lipid metabolism, and wound healing ability [2,3,5,7,8]. These beneficial biological properties have enabled its potential applications in healthcare, particularly in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering biomaterials, healthcare products for regulating blood glucose, lipids, and cholesterol, and pectin-based pharmaceuticals [2,3,5]. Furthermore, the functional and health-promoting properties of pectin are largely determined by its structural characteristics, such as HG/RG-I ratio, molar mass, sidechain composition, degree of esterification, and uronic acid content [2,5,9]. Notably, RG-I-enriched pectin demonstrates enhanced biological activities, particularly in prebiotic function, immunomodulation, and anti-cancer effect [6,10]. These superior biological properties have driven growing research interest in the discovery of edible plant sources rich in the RG-I pectin domain [3,4,6].
Cardamine tangutorum O.E. Schulz and Cardamine macrophylla Willd., collectively known as Shigecai in Chinese, have long been utilized as both edible and medicinal plants among ethnic minority groups in China, such as the Tibetan, Qiang, and Lisu peoples [11,12]. Typically, the young stems and leaves of both C. tangutorum and C. macrophylla are also consumed as special and nutritious vegetables among the Tibetan, Qiang, and Yi communities on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau [11,12]. Several studies have identified flavonoids as one of the mainly bioactive compounds in both C. tangutorum and C. macrophylla [11,12,13]. However, due to the insufficient knowledge about their phytochemicals and health benefits, the industrial utilization of these species in food and pharmaceutical sectors remains limited. In fact, our preliminary analysis revealed that both C. tangutorum and C. macrophylla contain substantial amounts of pectic polysaccharides (approximately 5–6%, w/w). However, the structural characteristics and biological properties of these pectic polysaccharides in both C. tangutorum and C. macrophylla have never been studied and compared, which significantly hinders their potential industrial applications.
Therefore, to promote the industrial utilization of C. tangutorum and C. macrophylla and their derived pectin molecules, this study systematically characterized the structural and biological properties of pectins isolated from both C. tangutorum and C. macrophylla. The findings can provide valuable insights for developing these pectins as functional ingredients in nutraceutical and pharmaceutical applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Reagents
The tender leaves of Shigecai (C. macrophylla Willd. and C. tangutorum O. E. Schulz) were harvested from the Aba Tibetan and Qiang Autonomous Prefecture and the Ganzi Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in Sichuan Province on 16 June 2024. The specimens were authenticated by Professor Yuan Liu from Southwest Minzu University and stored in the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau Ethnic Medicinal Resources Protection and Utilization Key Laboratory of National Ethnic Affairs Commission of the People’s Republic of China. All samples were lyophilized via vacuum freeze–drying for 48 h, and then pulverized and sieved through a 60-mesh sieve.
Enzymes utilized for removing proteins and starch during the preparation of RG-I-enriched pectin from Shigecai leaves, including pancreatin (≥4000 U/g), heat-stable α-amylase (≥40,000 U/g), and amyloglucosidase (≥100,000 U/g), were purchased from the supplier Solarbio (Beijing, China). Chemical reagents utilized for the extraction and characterization of RG-I-enriched pectin from Shigecai leaves, including choline chloride, ethylene glycol, ethanol, standardized monosaccharides, 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone (PMP), potassium bromide (KBr), deuterium oxide (D2O), and sodium chloride (NaCl), were collected from the supplier Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). In addition, reagents utilized for the evaluation of biological properties, including aminoguanidine (AG), DMEM medium, MTT, 2,2′-azino-bis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS), TAK-242, TLR2-IN-C29, and commercial ELISA kits, were obtained from the suppliers Sigma, MCE China (Shanghai, China), and Elabscience (Wuhan, China). Four probiotics, including Bifidobacterium adolescentis, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus fermentum, and Lactobacillus rhamnosus, were obtained from the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (Beijing, China) and the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA).
2.2. Preparation of RG-I-Enriched Pectin from Shigecai Leaves
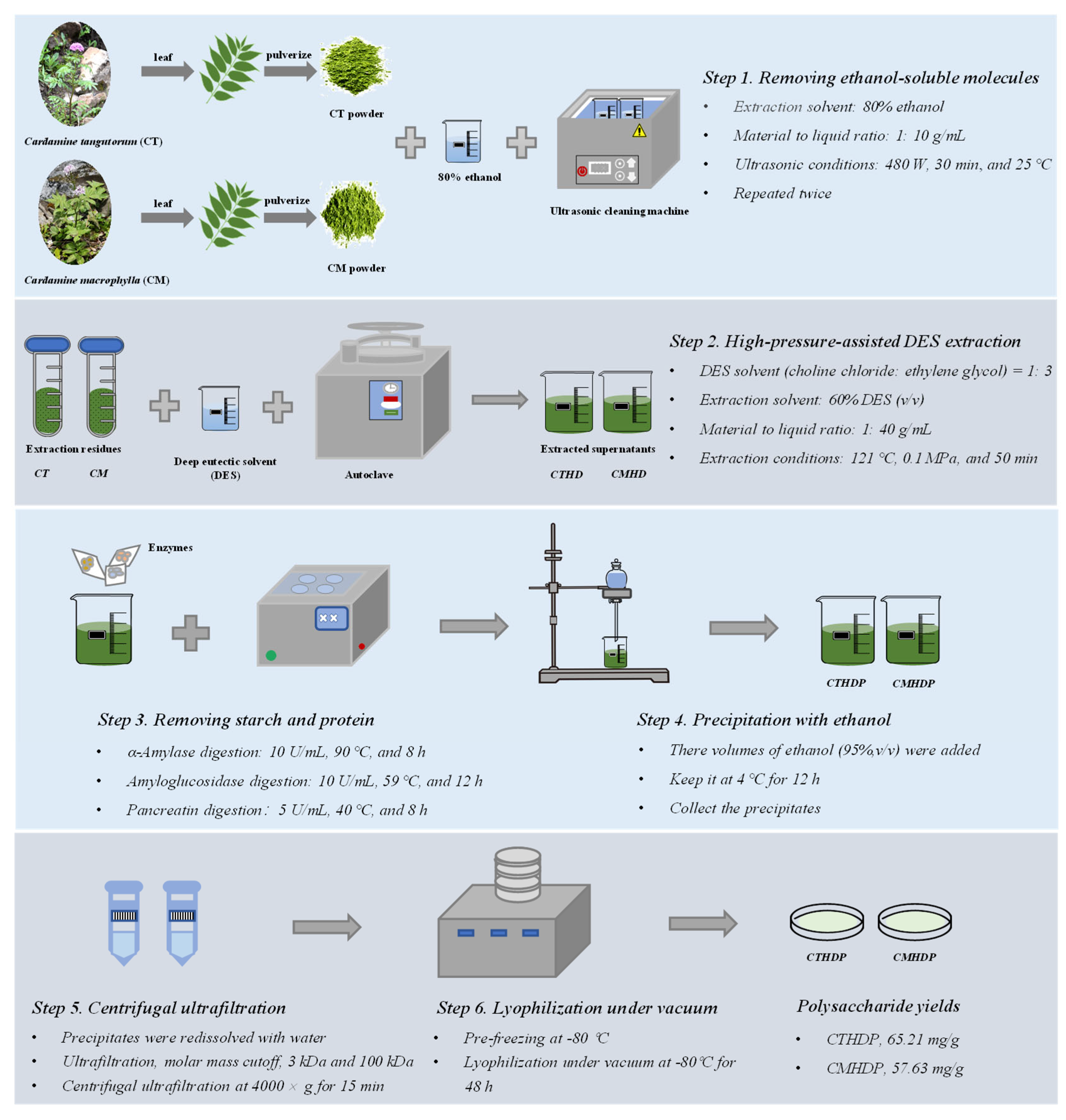
Previous studies have revealed that high-pressure-assisted deep eutectic solvent (DES) extraction (HPDEE) can efficiently and selectively extract pectic polysaccharides with enhanced biological functions [14,15]. Therefore, RG-I-enriched pectin was extracted from Shigecai leaves using the HPDEE method, following formerly developed protocols with modifications [14,15]. The detailed procedure, outlined in Figure 1, consists of six steps: (1) ultrasonic-assisted ethanol extraction to remove ethanol-soluble components (conditions: 80% ethanol, 1: 10 g/mL, 480 W, 30 min, and 25 °C); (2) high-pressure-assisted DES extraction for RG-I-enriched pectin extraction (conditions: 60% (v/v) DES solution (choline chloride: ethylene glycol, 1:3 molar ratio), 1: 40 g/mL, 121 °C, 0.1 MPa, and 50 min); (3) sequential enzymatic digestion to eliminate starch and protein (α-amylase digestion, 10 U/mL, 90 °C, and 8 h; amyloglucosidase digestion, 10 U/mL, 59 °C, and 12 h; pancreatin digestion, 5 U/mL, 40 °C, and 8 h), (4) ethanol precipitation of RG-I-enriched pectin with three volumes of ethanol; (5) isolation of RG-I-enriched pectin by centrifugal ultrafiltration (molar mass cutoffs: 100 kDa and 3 kDa); (6) lyophilization of RG-I-enriched pectin under vacuum (−80 °C, 48 h). Finally, the partially purified RG-I-enriched pectin molecules of C. tangutorum and C. macrophylla were designated as CTHDP and CMHDP, respectively.
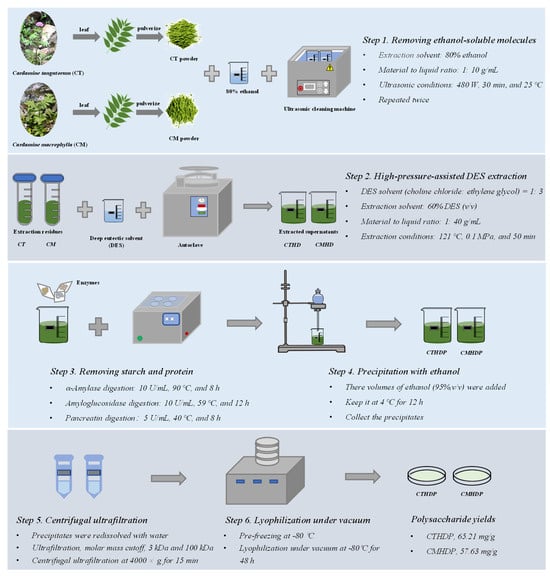
Figure 1.
Flowchart for the extraction and purification of RG-I-enriched pectin from Shigecai leaves. CTHDP and CMHDP indicate RG-I-enriched pectins isolated from C. tangutorum and C. macrophylla, respectively.
2.3. Chemical and Structural Characterization of RG-I-Enriched Pectin from Shigecai Leaves
The chemical and structural characteristics of CTHDP and CMHDP were characterized. Briefly, chemical composition analysis of CTHDP and CMHDP was performed using established colorimetric methods: total polysaccharide content (phenol–sulfuric acid method), total uronic acid content (m-hydroxyphenyl assay), total protein content (Bradford’s assay), and total bound polyphenol content (Folin–Ciocalteu’s method) [16,17,18,19]. Molecular weight distributions of CTHDP and CMHDP were determined using an established protocol involving high-performance size exclusion chromatography collected with multi-angle laser light scattering and refractive index detection (HPSEC-MALLS-RID, Wyatt Technology Co., Santa Barbara, CA, USA) [14]. Separation was performed on a Shodex OHpak SB-804 HQ column (8.0 × 300 mm) with 0.9% NaCl mobile phase in isocratic mode (0.5 mL/min and 30 °C). Samples (~1.0 mg/mL) were injected (100 μL), with data acquisition and analysis conducted using Astra software (v7.1.3). High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC, Shimadzu, Tokyo, Japan) following acid hydrolysis and PMP derivatization was employed for quantifying monosaccharides released from CTHDP and CMHDP, following a formerly reported procedure [14]. Each sample (~6.0 mg/mL) underwent acid hydrolysis (4 M TFA, 95 °C, and 12 h), followed by PMP derivatization (0.6 M NaOH, 0.5 M PMP, 70 °C, and 100 min). PMP derivatives were separated isocratically on a ZORBAX Eclipse XDB-C18 column (4.6 × 250 mm, 5 µm) with acetonitrile–phosphate buffer (17: 83 (v/v), 1.0 mL/min, and 30 °C) and detected at 245 nm (20 µL injection). A mixed standard containing mannose, rhamnose, glucuronic acid, galacturonic acid, glucose, galactose, xylose, and arabinose was used to identify monosaccharide compositions in samples. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA) was employed for profiling functional groups and determining degree of esterification (DE) of CTHDP and CMHDP [14]. Each sample (~1.0 mg) was mixed with KBr (100 mg), pressed into pellets, and scanned from 4000 to 400 cm−1. The level of DE was calculated using the signals at ~1744.8 cm−1 and 1623.1 cm−1. Finally, a Bruker Ascend 600 MHz nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrometer (Bruker, Rheinstetten, Germany) was employed for profiling glycosidic linkage patterns of CTHDP and CMHDP [14]. Each sample (~40.0 mg) was added into 1.0 mL of D2O overnight and subjected to NMR analysis at 600.13 MHz (1H) and 150.90 MHz (13C). More detailed procedures of each method are supplied in the Supplementary Materials (Section S1).
2.4. Evaluation of Biological Properties of RG-I-Enriched Pectin from Shigecai Leaves
To assess the biological activities of CTHDP and CMHDP from Shigecai leaves, in vitro antioxidant ability, antiglycation activity, prebiotic effect, and immunostimulatory effect of both samples were studied. Specifically, their ABTS free radical scavenging capacity and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) were measured to evaluate antioxidant capacity, following reported procedures [14,20]. For FRAP evaluation, 100 µL of sample solutions (2.0–10.0 mg/mL) was combined with 100 µL of 1% (w/v) potassium ferricyanide, heated at 50 °C (20 min), then treated with 100 µL of 10% (w/v) trichloroacetic acid and centrifuged. After adding 300 µL of ultrapure water and 60 µL of 0.1% (w/v) ferric chloride, the absorbance was detected at 700 nm. ABTS radical scavenging capacity was assessed by mixing 20 μL of sample solutions (2.0–10.0 mg/mL) with 200 μL of ABTS working solution in 96-well plates. After incubation (37 °C, 6 min), the absorbance was detected at 734 nm. IC50 values (mg/mL) were calculated using logarithmic regression. In addition, their inhibitory effects on advanced glycosylation end product (AGE) formation were analyzed to determine antiglycation activity, following a formerly established protocol [21]. The sample group contained sodium azide (0.5%, w/v), BSA (3%, w/v), glucose (500 mM), and sample solutions (0.25–4.0 mg/mL). After 14-day incubation at 37 °C in the dark, the fluorescence intensity was detected at λex/λem = 370/440 nm. Moreover, their growth-promoting effects on selected probiotics (Bifidobacterium adolescentis, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus fermentum, and Lactobacillus rhamnosus) were tested to assess prebiotic potential, according to a published method [21]. Each sample (10 mg/mL) was added to carbohydrate-free MRS medium, followed by inoculation with respective strains. L. plantarum and B. adolescentis were cultivated anaerobically at 37 °C for 48 h, L. fermentum anaerobically at 30 °C (48 h), and L. rhamnosus aerobically at 37 °C (48 h). OD600 was then measured for all cultures. Finally, their modulatory effects on mediator/cytokine production in RAW 264.7 macrophages were examined to evaluate immunostimulatory activity, following prior procedures [21]. RAW 264.7 macrophages were seeded in 24-well plates (1 × 105 cells/well) and incubated at 37 °C/5% CO2 for 16 h. After supernatant removal, cells were treated with samples (100–400 μg/mL, 1.0 mL) for 48 h, using culture medium (blank control) and 1 μg/mL LPS (positive control). Supernatants were reacted with Griess’s reagent (I + II, RT) and absorbance measured at 540 nm, with NaNO2 standards quantifying nitric oxide (NO). Cytokine levels were detected by commercial ELISA kits (Elabscience, Wuhan, China) per manufacturer’s protocol. Additionally, the influence of specific TLR4 inhibitor (TAK-242) and TLR2 inhibitor (TLR2-IN-C29) on CTHDP- and CMHDP-induced mediator/cytokines production in RAW 264.7 macrophages was investigated to clarify whether these pectin molecules enhance immune responses via TLR4/TLR2-mediated signaling pathways. More detailed procedures of each method are supplied in the Supplementary Materials (Section S2).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
All data are presented as mean ± deviation from three independent replicates. Statistical analyses were performed using Origin 9.0 software, with significance (p < 0.05) evaluated through two-tailed Student’s t-test or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical and Structural Characteristics of CTHDP and CMHDP
3.1.1. Primary Chemical Properties of CTHDP and CMHDP
The biological properties of pectin molecules, such as antioxidant and immunoregulatory effects, are strongly influenced by their primary chemical properties, particularly total uronic acid content and bound polyphenol content [5,22,23]. However, these parameters are still unknown in Shigecai pectin, which ultimately restricts their applications in the food industry. Hence, to facilitate their industrial utilization, the primary chemical properties of CTHDP and CMHDP were investigated. Table 1 presents the yields and primary chemical properties of CTHDP and CMHDP. Notably, CTHDP and CMHDP, confirmed as RG-I-enriched pectin through later composition monosaccharide and NMR analysis (Section 3.1.3) yielded 65.21 mg/g and 57.63 mg/g, respectively. The extraction yields of pectin molecules in Shigecai leaves (about 5.75–6.52%, w/w) are comparable to those of mulberry leaves (about 5.32–6.92%, w/w) [24,25], and are markedly higher than sweet tea leaves (about 3.65–4.64%, w/w) [15] and lotus leaves (about 0.97–2.65%, w/w) [26,27]. These results demonstrate that Shigecai leaves are potential resources for extracting RG-I-enriched pectin molecules. In addition, CTHDP and CMHDP exhibited extremely high total polysaccharide contents (90.16–92.51 mg/100 mg) and relatively low total protein contents (1.28–1.8 mg/100 mg). Furthermore, both CTHDP and CMHDP contained relatively high levels of total uronic acids, ranging from 24.91 mg/100 mg (CMHDP) to 31.68 mg/100 mg (CTHDP), suggesting that these polysaccharides contained pectic polysaccharides, similar to previous reports [14,20,27]. Notably, a higher uronic acid content is linked to enhanced biological activity due to increased binding sites and interaction potentials, probably leading to stronger immunomodulatory and antioxidant effects [5,23]. Moreover, despite the sequential extraction, precipitation, and centrifugal ultrafiltration conducted to remove polyphenols (Figure 1), trace amounts of bound polyphenols (8.21–9.82 mg GAE/g) remained in both CTHDP and CMHDP. These residual polyphenols probably enhance the antioxidant capacity of the pectin molecules [23]. Collectively, the results indicate that Shigecai leaves are a promising source for extracting RG-I-enriched pectin, with CTHDP and CMHDP exhibiting minimal variations in their primary chemical properties.

Table 1.
Extraction yields and physicochemical characteristics of RG-I-enriched pectin from Shigecai leaves.
3.1.2. Molecular Weights and Functional Groups of CTHDP and CMHDP
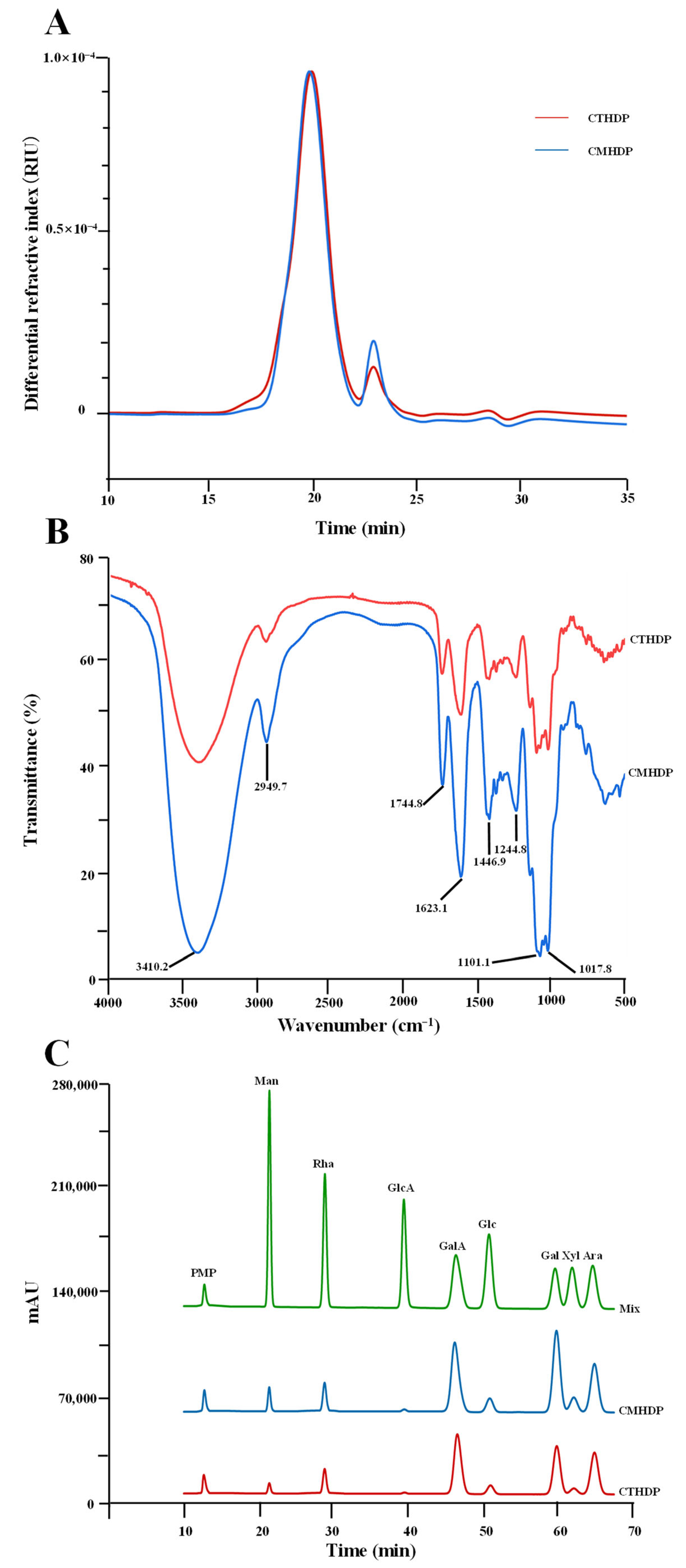
Apart from the primary chemical properties, the biological properties of pectin molecules, such as antioxidant ability, immunoregulatory activity, and anti-inflammatory effect, are also affected by their molecular weight distribution and degree of esterification (DE) [2,5,9]. Nevertheless, the molecular weights and functional groups of CTHDP and CMHDP have not yet been systematically characterized. To address this gap, we conducted an in-depth investigation of the molecular weights and functional group profiles of CTHDP and CMHDP in this study. Figure 2A displays the comparable HPSEC elution curves of CTHDP and CMHDP. Notably, CTHDP and CMHDP exhibited nearly identical symmetrical elution patterns, with similar elution time, suggesting comparable molecular weight distributions. Quantitatively, their molecular weights ranged from 3.33 × 104 Da (CTHDP) to 4.12 × 104 Da (CMHDP), with polydispersity indexes of 2.52 (CTHDP) and 2.21 (CMHDP), respectively. These values align with RG-I-enriched pectin from jujube fruits (about 2.88 × 104–4.09 × 104 Da) and sweet leaves (about 4.268 × 104–4.472 × 104 Da) [20,28], but are markedly lower than those reported for lotus leaves (about 4.476 × 104–1.04 × 105 Da) [26], wolfberry (about 8.638 × 104–9.277 × 104 Da) [29], young apple (about 5.92 × 105–1.787 × 106 Da) [30], and citrus peel (about 9.506 × 104–2.813 × 105 Da) [31]. Generally, the lower molecular weight pectins are more easily absorbed and metabolized by biological systems, thereby potentially enhancing their bioactivity [5].
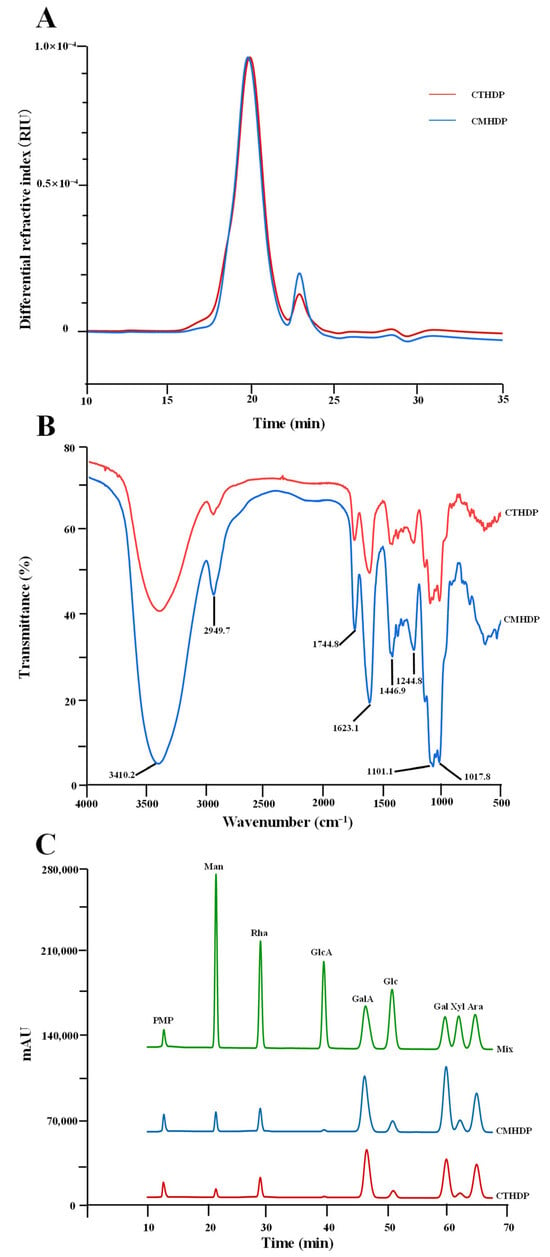
Figure 2.
Size exclusion chromatographic elution curves (A), FT-IR spectra (B), and HPLC elution curves of constituent monosaccharides (C) of CTHDP and CMHDP. CTHDP and CMHDP indicate RG-I-enriched pectins isolated from C. tangutorum and C. macrophylla, respectively; the codes for individual monosaccharides are the same as in Table 1.
Figure 2B displays the comparable FT-IR spectra of CTHDP and CMHDP, which exhibited nearly identical profiles and characteristic absorption bands, indicating similar functional group compositions. Both samples showed characteristic signals corresponding to pectin molecules, including 3410.2, 2949.7, 1744.8, 1623.1, 1446.9, 1244.8, 1101.1, and 1017.8 cm−1, consistent with previously reported RG-I-enriched pectin values [14,20,30,32,33,34]. In particular, the characteristic peaks at 1744.8 cm−1 and 1623.1 cm−1 can be utilized for the estimation of the relative DE value [20,28]. Based on their peak area calculations, the relative DE values were determined to be 35.91% for CTHDP and 33.01% for CMHDP, indicating both as low-methoxyl pectins. Generally, pectin with lower DE levels typically contained more free carboxyl groups, leading to improved solubility and enhanced bioactivity [21,28].
3.1.3. Monosaccharide Compositions and Glycosidic Linkage Patterns of CTHDP and CMHDP
The galacturonic acid ratio, the HG/RG-I domain ratio, the side chain pattern, and the branching degree of pectin largely determine its functionality and bioactivity [2,5,7,9]. Therefore, to elucidate the chemical structures of CTHDP and CMHDP, we conducted comprehensive monosaccharide composition and glycosidic linkage pattern analyses. Figure 2C displays comparable HPLC profiles of compositional monosaccharides released from CTHDP and CMHDP, exhibiting nearly identical elution patterns that suggest similar monosaccharide compositions. Quantitatively, as summarized in Table 1, galacturonic acid (31.66–35.29 mol%), galactose (23.23–28.12 mol%), arabinose (18.48–22.40 mol%), and rhamnose (6.77–8.85 mol%) were identified as major components in both CTHDP and CMHDP, similar to previously reported RG-I-enriched pectin values [20,26,28,30,31,35]. Based on the molar percentages of these monosaccharides [26,29], it could be inferred that CTHDP and CMHDP had comparable molar percentages of RG-I (60.14–63.33 mol%) and HG (24.89–26.44 mol%) domains (Table 1). Furthermore, the degrees of RG-I branching of CTHDP and CMHDP were calculated as (Gal + Ara)/Rha, with calculated ratios of 5.16 and 6.88 for CTHDP and CMHDP, indicating highly branched side chains in both pectins.
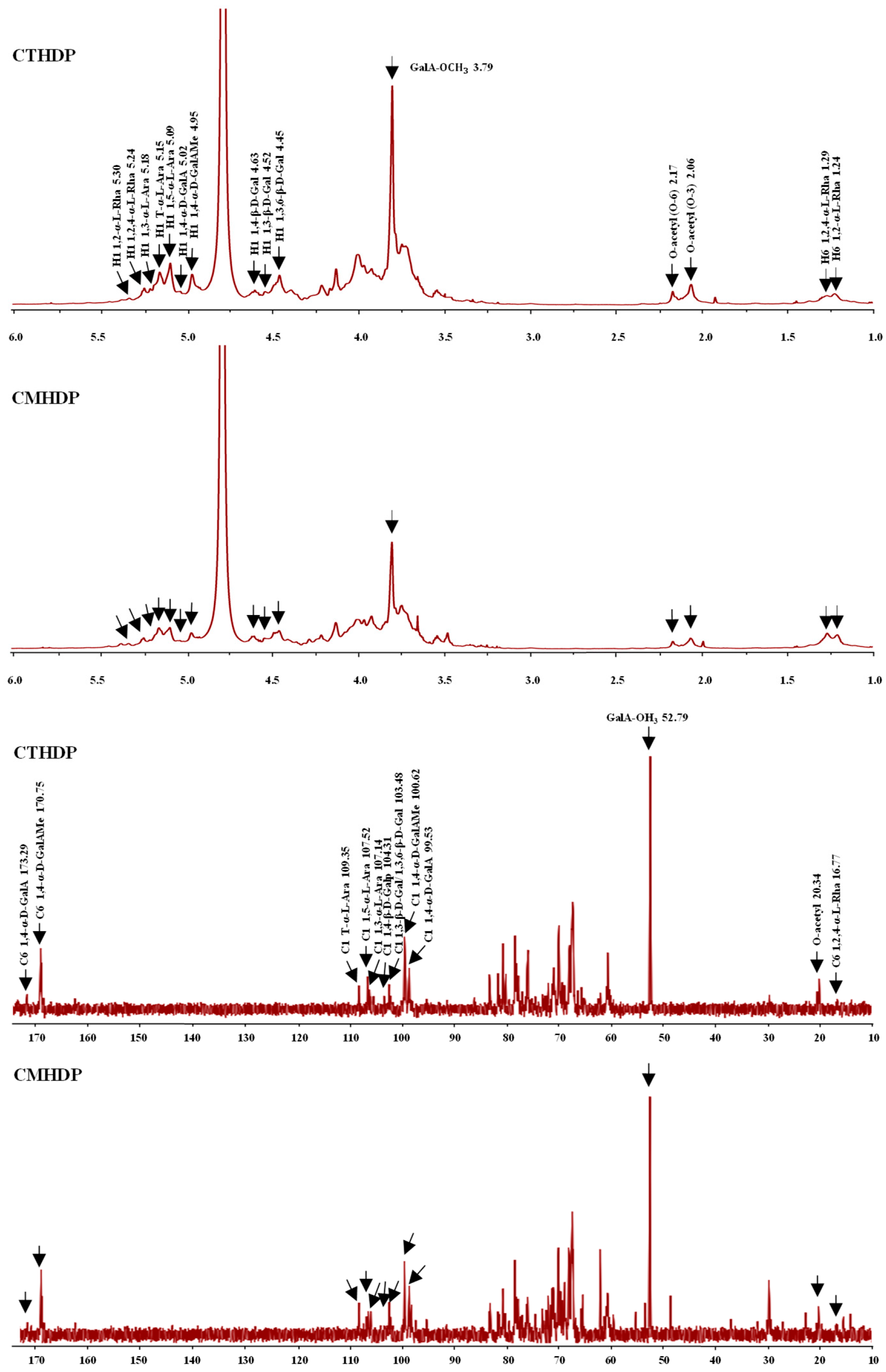
Furthermore, to elucidate the glycosidic linkage patterns of CTHDP and CMHDP, 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy analyses were conducted. As presented in Figure 3, the NMR spectra of both samples exhibited highly similar profiles, suggesting closely related glycosidic linkage patterns. Notably, characteristic signals for the main chains and branched chains of HG and RG-I pectin regions were identified in CTHDP and CMHDP, further confirming their structural similarity. For instance, the distinct chemical shifts at 5.02 (H-1)/99.53 (C-1)/173.26 ppm (C-6), 4.95 (H-1)/100.62 (C-1)/170.75 ppm (C-6), 5.30 (H-1)/1.24 (H-6), and 5.24 (H-1)/1.29 (H-6)/16.77 ppm (C-6), probably corresponded to 1,4-α-D-GalAp, 1,4-α-D-GalAMep, 1,2-α-L-Rhap, and 1,2,4-α-L-Rhap, respectively, which represented the backbones of HG and RG-I pectin regions in both CTHDP and CMHDP [20,28,36,37,38]. In addition, the distinct chemical shifts at 4.52 (H-1)/103.48 ppm (C-1), 4.45 (H-1)/103.48 ppm (C-1), 4.63 (H-1)/104.31 ppm (C-1), 5.15 (H-1)/109.35 ppm (C-1), 5.18 (H-1)/107.14 ppm (C-1), and 5.09 (H-1)/107.52 ppm (C-1), probably corresponded to 1,3-β-D-Galp, 1,3,6-β-D-Galp, 1,4-β-D-Galp, T-α-L-Araf, 1,3-α-L-Araf, and 1,5-α-L-Araf, respectively, which represented the sidechains of RG-I pectin region in both samples [20,28,36,37,38]. Furthermore, the distinct chemical shifts at 3.79/52.79 ppm and 2.06/2.17/20.34 ppm indicated the methyl- and acetyl-esterified groups in both CTHDP and CMHDP [20,38]. Taken together, these results infer that CTHDP and CMHDP possess comparable glycosidic linkage patterns, mainly composed of HG and RG-I pectin domains with arabinogalactan and arabinan branched chains.
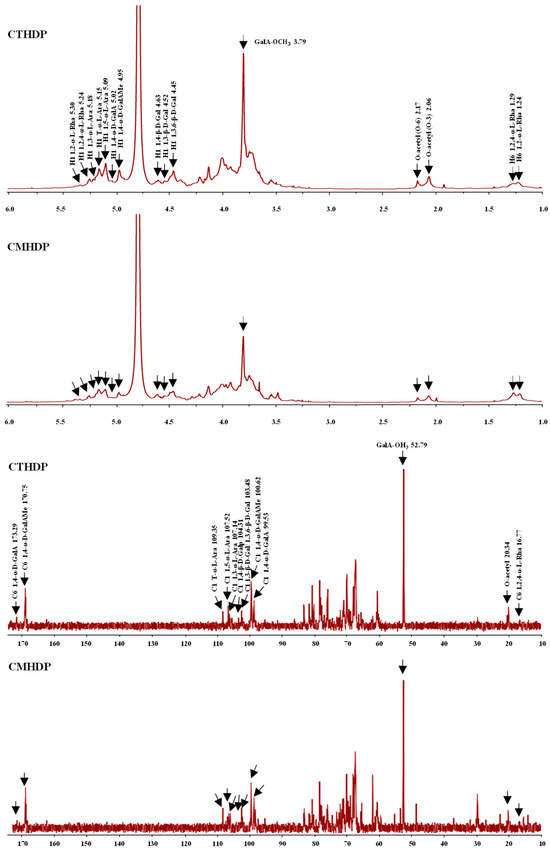
Figure 3.
1H and 13C NMR spectra of CTHDP and CMHDP. CTHDP and CMHDP indicate RG-I-enriched pectins isolated from C. tangutorum and C. macrophylla, respectively.
3.2. Antioxidant and Antiglycation Effects of CTHDP and CMHDP
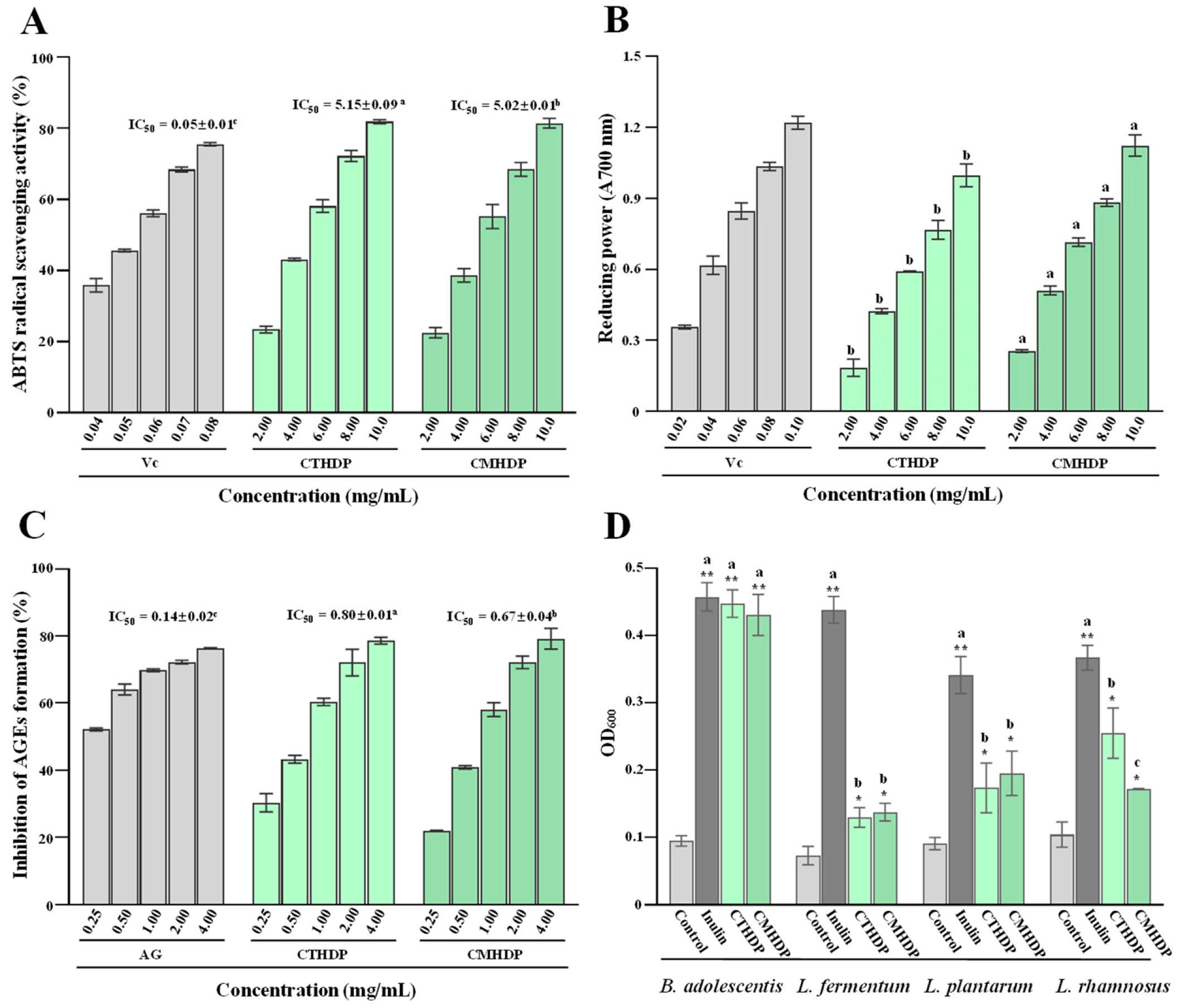
Pectin demonstrates remarkable antioxidant activity by effectively scavenging free radicals, chelating metal ions, and inhibiting reactive oxygen species production, which is closely intertwined with its structural properties [5,6]. Therefore, to advance the application potential of Shigecai and its derived RG-I-enriched pectin, the antioxidant and antiglycation effects of CTHDP and CMHDP were systematically characterized. As displayed in Figure 4A,B, both CTHDP and CMHDP exhibited dose-dependent ABTS radical scavenging ability and reducing power (FRAP value). Notably, CMHDP demonstrated superior antioxidant activity over CTHDP. The IC50 values of the ABTS scavenging ability for CTHDP and CMHDP were 5.15 mg/mL and 5.02 mg/mL, respectively. CMHDP exhibited significantly higher reducing power across all tested concentrations than that of CTHDP, particularly at 10.0 mg/mL (absorbance at 700 nm, 1.12 for CMHDP and 1.01 for CTHDP). Additionally, Shigecai-derived RG-I-enriched pectin exhibits antioxidant potency comparable to reported sources: hawthorn pectin (reducing power at 10 mg/mL ranged from 0.315 to 0.349) [39], citrus peel pectin (ABTS IC50 ranged from 2.06 to 9.11 mg/mL) [40], and black mulberry pectin (ABTS scavenging rate at 4.0 mg/mL ranged from 27.82% to 56.58%) [41]. This demonstrates its potential as a natural antioxidant for industrial food applications.
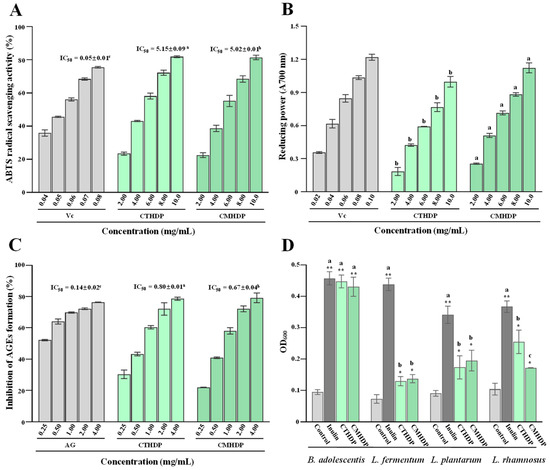
Figure 4.
In vitro antioxidant (A,B), antiglycation (C), and prebiotic effects (D) of CTHDP and CMHDP. CTHDP and CMHDP indicate RG-I-enriched pectins isolated from C. tangutorum and C. macrophylla, respectively; the error bars are standard deviations; significant differences (p < 0.05) between CTHDP and CMHDP are shown by data bearing different letters; significant differences in the growth rates of individual probiotics between samples and negative control are shown by * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
Furthermore, pectin scavenges radicals or inhibits their formation via metal chelation. Pectin’s antioxidant potency is strongly linked to its bound polyphenol content, uronic acid content, DE value, and molecular weight, with bound polyphenols being the most critical factor [23]. These bound polyphenols significantly contribute to pectin’s antioxidant activity, enabling the scavenging of DPPH and ABTS radicals [23]. Recent studies have confirmed that pectin’s antioxidant activity positively correlates with bound polyphenol content [14,23], but negatively correlates with DE value [21,28]. Thus, taken together, the superior antioxidant activity of CMHDP compared with CTHDP is likely primarily attributed to the combined effects of its bound polyphenol content, DE value, and uronic acid content.
To assess the antiglycation potency of CTHDP and CMHDP, we evaluated their inhibitor effects on advanced glycation end product (AGE) formation. Figure 4C compares their inhibitory effects on AGE formation. Both samples exerted marked antiglycation activity, with CMHDP (IC50 value, 0.67 mg/mL) outperforming CTHDP (IC50 value, 0.80 mg/mL). Notably, the antiglycation activity trend of both samples paralleled their antioxidant activity, suggesting a strong correlation between these two activities. In fact, pectin can scavenge free radicals and active dicarbonyl components during AGE formation owing to its free radical scavenging capacity [42]. Thus, this suggests that the antiglycation effect of Shigecai-derived RG-I-enriched pectin is closely linked to its antioxidant activity.
3.3. Prebiotic Effects of CTHDP and CMHDP
Pectin resists digestion in the upper gastrointestinal tract (mouth, stomach, and small intestine), but is metabolized and utilized by gut microbiota in the colon, thereby regulating intestinal microbial composition and microbial metabolites to demonstrate prebiotic activity [2,3,5,6]. Particularly, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium spp. are best understood for their applications as probiotics [43]. Therefore, to evaluate the prebiotic potential of CTHDP and CMHDP, we assessed their growth-promoting effects on four individual probiotic strains in vitro, including Lactobacillus fermentum, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, and Bifidobacterium adolescentis.
As presented in Figure 4D, both samples demonstrated marked prebiotic potential by enhancing the growth rates of different probiotic strains (Lactobacillus fermentum, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, and Bifidobacterium adolescentis), with particularly pronounced effects on B. adolescentis. The promotive effects of both samples on B. adolescentis growth were comparable to that of inulin (a representative commercial prebiotic), indicating that RG-I-enriched pectin derived from Shigecai exhibits excellent potential for the development as a targeted prebiotic for B. adolescentis. Notably, Bifidobacterium spp. strains are established as safe and effective probiotics [44], and B. adolescentis represents one of the most abundant species within this genus in the healthy human intestinal microbiota. Collectively, these results suggest that Shigecai-derived RG-I-enriched pectin holds good potential for development as a prebiotic targeting Bifidobacterium spp. Nevertheless, animal studies are required to confirm their prebiotic effect on intestinal microbial composition in future, given the limitations of in vitro systems.
3.4. Immunostimulatory Effects of CTHDP and CMHDP
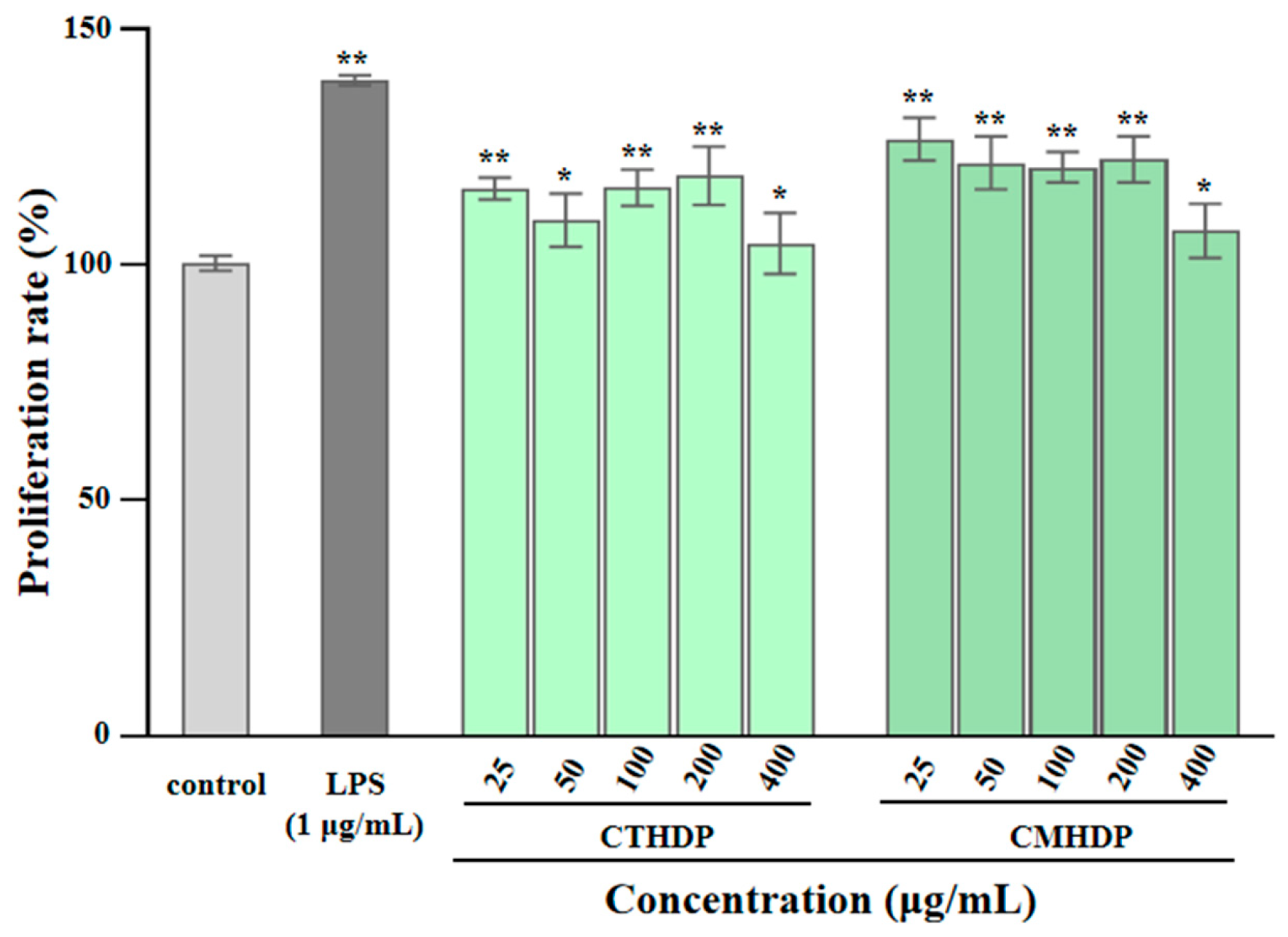
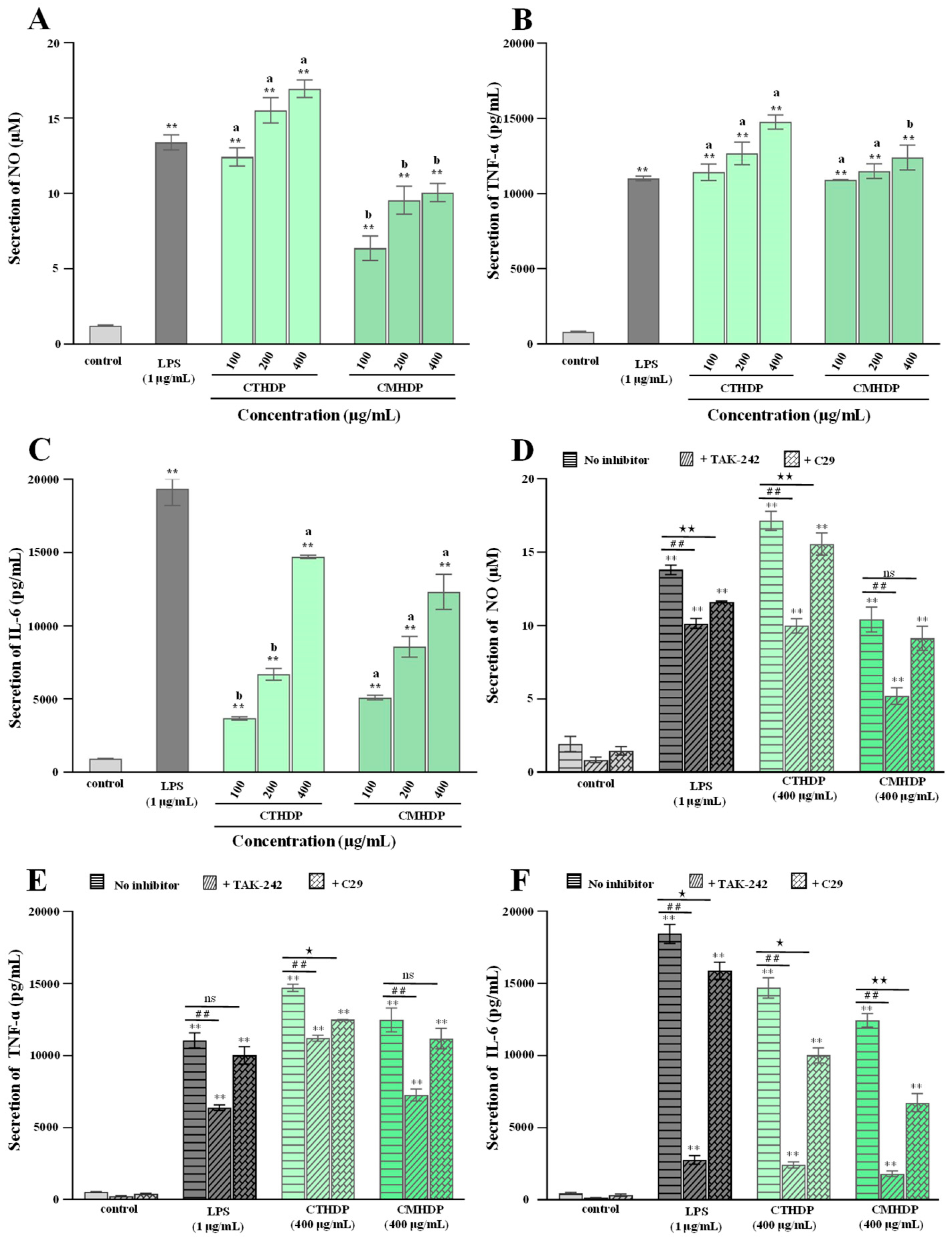
Pectin molecules, particularly RG-I-enriched pectin derived from vegetables and fruits, exhibit notable immunoregulatory activity towards macrophages, lymphocytes, and the complement system [5,6,10]. Macrophages, particularly RAW 264.7 cells, have been widely applied to evaluating in vitro immunoregulatory effects [22]. Therefore, to evaluate their potential applications as natural immune modulators, we assessed the immunostimulatory effects of RG-I-enriched pectin derived from Shigecai leaves on RAW 264.7 macrophages. As presented in Figure 5, neither CTHDP nor CMHDP exhibited toxicity towards RAW 264.7 macrophages at any tested concentration. Figure 6A–C demonstrate the regulator effects of both samples on NO production (Figure 6A), TNF-α secretion (Figure 6B), and IL-6 secretion (Figure 6C) in macrophages. Notably, both samples significantly enhanced the production of NO, TNF-α, and IL-6, indicating a potent immunoenhancing effect. In particular, at a concentration of 400 μg/mL, CTHDP exhibited superior immunoenhancing effects compared with CMHDP, with higher levels of NO (16.97 μM vs. 10.07 μM), TNF-α (14,768.6 pg/mL vs. 12,411.4 pg/mL), and IL-6 (14,710 pg/mL vs. 12,322.5 pg/mL). Generally, the immunoregulatory effects of pectins strongly associate with their chemical and structural properties. These effects exhibit negative correlations toward molecular weight and DE level [28,45,46], but positive correlations toward uronic acid content and RG-I domain abundance [10,14,47]. Thus, taken together, the superior immunoregulatory effect of CTHDP might be partially attributed to the synergistic contributions of its higher uronic acid content, lower molecular weight, and greater RG-I domain ratio. Nevertheless, due to its indigestibility in the upper GI tract, animal studies are needed to confirm whether CTHDP and CMHDP exert immunostimulatory effects via gut microbiota modulation in future.
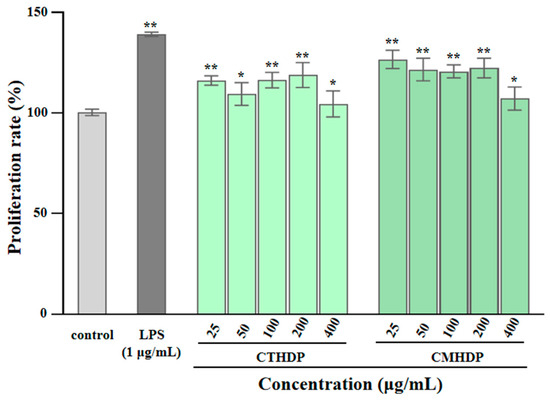
Figure 5.
Effects of CTHDP and CMHDP on the proliferation of RAW 264.7 macrophages. CTHDP and CMHDP indicate RG-I-enriched pectins isolated from C. tangutorum and C. macrophylla, respectively; the error bars are standard deviations; significant differences between sample groups and control group are shown by * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01.
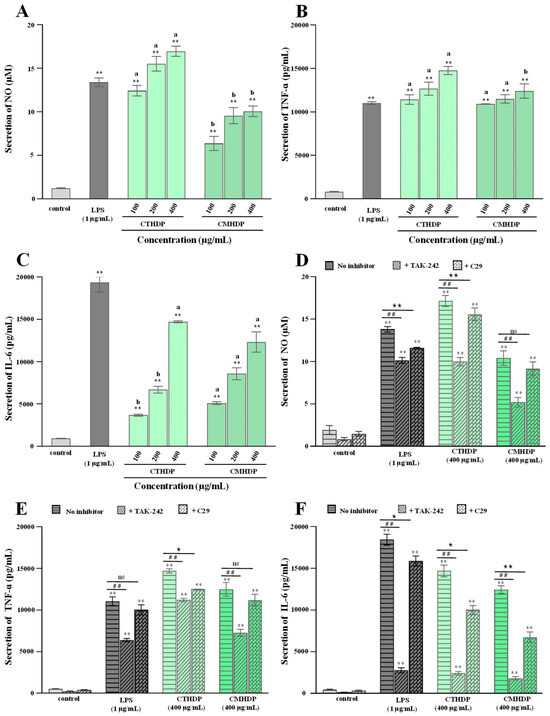
Figure 6.
Immunoregulatory effects (A–C) of CTHDP and CMHDP and effects of selective inhibitors (D–F) on their immune responses induced by CTHDP and CMHDP. (A–C) indicate the nitric oxide (NO) production, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) secretion, and interleukin-6 (IL-6) secretion in macrophages induced by CTHDP and CMHDP; D, E, and F indicate the impacts of selective inhibitors (TAK-242 and C29) on the production of NO, TNF-α, and IL-6 in macrophages induced by CTHDP and CMHDP. CTHDP and CMHDP indicate RG-I-enriched pectins isolated from C. tangutorum and C. macrophylla, respectively; the error bars are standard deviations; significant differences (p < 0.05) between CTHDP and CMHDP are shown by data bearing different letters (a–b); significant differences between sample groups and negative control group are shown by ** p < 0.01. Significant differences between samples treated with TAK-242 and without TAK-242 are shown by ## p < 0.01. Significant differences between samples treated with C29 and without C29 are shown by ★ p < 0.05 and ★★ p < 0.01. ‘ns’ indicates no significant difference.
Pectin activates macrophages and enhances immune responses through recognition using pattern recognition receptors, such as toll-like receptors (TLRs) [5,46]. So, to further elucidate the possible mechanism of CTHDP- and CMHDP-mediated macrophage activation, we assessed the effects of selective TLR4 and TLR2 inhibitors (TAK-242 and C29, respectively) on their immunoregulatory activity. Figure 6D–F display the effects of TAK-242 and C29 on NO, TNF-α, and IL-6 release in macrophages. Notably, both TAK-242 (1 μM) and C29 (1 μM) inhibitors markedly inhibited the immune responses induced by CTHDP and CMHDP (Figure 6D–F). In particular, TAK-242 exhibited a stronger inhibitory effect than C29, indicating that the immunoregulatory effects of both samples depend more crucially on TLR4 than TLR2, similar to reported results [46,48].
4. Conclusions
The present findings suggest that Shigecai leaves are promising sources of RG-I-enriched pectin. Both CTHDP and CMHDP exhibited highly similar chemical and structural properties, dominated by the RG-I pectin region (60.14–63.33 mol%). Furthermore, both CTHDP and CMHDP demonstrated remarkable antioxidant, antiglycation, prebiotic, and immunoregulatory effects, closely linked to their bound polyphenol content, uronic acid level, and molecular weight. These findings provide good evidence for the development of RG-I-enriched pectin from Shigecai as a functional food ingredient. However, further studies using animal models are needed to validate these beneficial effects, due to the inherent limitations of in vitro assays. Additionally, fine structural characterization and modification are required to elucidate the precise structure–function relationships of these RG-I-enriched pectic polysaccharides.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/foods14132340/s1, Section S1: Chemical and structural characteristics of RG-I-enriched pectin from Shigecai leaves (CTHDP and CMHDP); Section S2: Evaluation of antioxidant, antiglycation, prebiotic, and immunoregulatory effects of RG-I-enriched pectin from Shigecai leaves (CTHDP and CMHDP).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.-T.W. and W.-B.L.; methodology, D.-T.W. and W.-B.L.; validation, B.L., J.F., and J.W.; formal analysis, M.-M.Q.M., B.L., D.-T.W., J.F., and W.-B.L.; investigation, M.-M.Q.M.; resources, Y.W. and Y.L.; data curation, M.-M.Q.M. and D.-T.W.; writing—original draft preparation, M.-M.Q.M. and B.L.; writing—review and editing, D.-T.W., J.L., Y.W., Y.L., and W.-B.L.; supervision, D.-T.W. and W.-B.L.; funding acquisition, D.-T.W. and W.-B.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Scientific Research Fund Project of the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province (No. 2024NSFSC0363), the Scientific and Technological Innovation Team for Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau Research in Southwest Minzu University (No. 2024CXTD04), the Science and Technology Development Fund, Macau SAR (No. 001/2023/ALC), and the Macao Centre for Research and Development in Chinese Medicine, University of Macau (No. MCRDCM-OP-202501).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tang, X.; de Vos, P. Structure-function effects of different pectin chemistries and its impact on the gastrointestinal immune barrier system. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 65, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Xu, F.; He, Z.; Du, Y.; Lian, Y.; Wu, P.; Sun-Waterhouse, D. Recent advances in utilization of pectins in biomedical applications: A review focusing on molecular structure-directing health-promoting properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 3386–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Li, T.; Li, S. Preparation and structure-function relationships of homogalacturonan-rich and rhamnogalacturonan-I rich pectin: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 304, 140775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.; Wu, D.; Wei, C.; Tao, W.; Ye, X.; Linhardt, R.J.; Orfila, C.; Chen, S. Reconsidering conventional and innovative methods for pectin extraction from fruit and vegetable waste: Targeting rhamnogalacturonan I. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 94, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Ding, K. An in-depth review: Unraveling the extraction, structure, bio-functionalities, target molecules, and applications of pectic polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 343, 122457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, H.; Dou, Z.; Hou, K.; Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Fu, X. A critical review of RG-I pectin: Sources, extraction methods, structure, and applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 8911–8931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, F.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Lü, X. Structural features and anticancer mechanisms of pectic polysaccharides: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.-Y.; Li, M.-Y.; Huang, R.-M.; Wu, X.-Y.; Sun, Y.-M.; Xu, Z.-L. Structural features and anti-inflammatory properties of pectic polysaccharides: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 107, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Ye, X.; Linhardt, R.J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, K.; Yu, C.; Ding, T.; Liu, D.; He, Q.; Chen, S. Dietary pectic substances enhance gut health by its polycomponent: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2015–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zheng, J.; Mao, G.; Hu, W.; Ye, X.; Linhardt, R.J.; Chen, S. Rethinking the impact of RG-I mainly from fruits and vegetables on dietary health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2938–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Cai, X.; Hailai, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y. Quality evaluation of Cardamine macrophylla Willd as an edible and medicinal herb of Tibetan and Qiang ethnic groups. Med. Plant 2024, 15, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Su, H.; Li, W.; Liu, Y. Optimizing of ultrasonic-enzymatic extraction of total flavonoids from Cardamine tangutorum O. E. Schulz by response surface methodology and content determination. Med. Plant 2020, 11, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.-S.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.-L. A new acylated flavonol glycoside from the aerial parts of Cardamine tangutorum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 14, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Luo, X.; Qu Mo, M.-M.; Feng, J.; Li, W.-B.; Yan, H.; Hu, Y.-C.; Zou, L.; Wu, D.-T. Structural properties and biological effects of pectic polysaccharides extracted from Tartary buckwheat sprouts by high pressure-assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 203, 116397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Li, W.; Fu, M.-X.; Wang, A.-Q.; Wu, D.-T.; Guo, H.; Hu, Y.-C.; Gan, R.-Y.; Zou, L.; Liu, Y. Pressurized hot water extraction, structural properties, biological effects, and in vitro microbial fermentation characteristics of sweet tea polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 3215–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenkrantz, N.; Asboe-Hansen, G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal. Biochem. 1973, 54, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Luo, X.; Li, B.; Yang, X.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.-W.; Hu, Y.-C.; Zou, L.; Wu, D.-T. Chemical structures, antioxidant capacities, and immunostimulatory activities of pectic polysaccharides from jujube fruits collected from different producing areas. Food Biosci. 2025, 68, 106485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Feng, J.; Luo, X.; Qu Mo, M.-M.; Li, W.-B.; Huang, J.-W.; Wang, S.; Hu, Y.-C.; Zou, L.; Wu, D.-T. Potential structure–function relationships of pectic polysaccharides from quinoa microgreens: Impact of various esterification degrees. Food Res. Int. 2024, 187, 114395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Xu, J.; Wu, W.; Wen, Y.; Lu, S.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Zhao, C. Structure–immunomodulatory activity relationships of dietary polysaccharides. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, P.A.R.; Coimbra, M.A. The antioxidant activity of polysaccharides: A structure-function relationship overview. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 314, 120965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.-Y.; Wan, Y.; Xu, J.-Y.; Wu, G.-H.; Li, L.; Yao, X.-H. Ultrasound extraction of polysaccharides from mulberry leaves and their effect on enhancing antioxidant activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Santhanam, R.K.; Xue, Z.; Guo, Q.; Gao, X.; Chen, H. Effect of different drying methods on the physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of mulberry leaves polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhao, M. Lotus leaf polysaccharides prepared by alkaline water, deep eutectic solvent and high pressure homogenization-assisted dual enzyme extraction: A comparative study of structural features, prebiotic activities and functionalities. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 143, 108870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-R.; Han, A.-R.; Park, S.-G.; Cho, C.-W.; Rhee, Y.-K.; Hong, H.-D. Effect of enzyme-assisted extraction on the physicochemical properties and bioactive potential of lotus leaf polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-J.; Feng, J.; Deng, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, H.-Y.; Liang, Q.; Hu, Y.-C.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Zou, L.; Wu, D.-T. The degree of esterification influences the bioactivity of pectic polysaccharides isolated from Lithocarpus Litseifolius. Food Chem. X 2025, 27, 102462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Lin, L.; Zhao, M. Demonstration of feasibility and effectiveness of deep eutectic solvent-water system extraction of RG-I type pectin from wolfberry based on target polysaccharide, solvent and their interactions. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 109027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, D.; Xia, W.; Guo, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xue, J. Physicochemical and functional properties of RG-I enriched pectin extracted from thinned-young apples. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 236, 123953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Cheng, H.; Wu, D.; Chen, J.; Ye, X.; Chen, S. Enhanced extraction assisted by pressure and ultrasound for targeting RG-I enriched pectin from citrus peel wastes: A mechanistic study. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 107778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cai, J. Preparation of branched RG-I-rich pectin from red dragon fruit peel and the characterization of its probiotic properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 299, 120144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Hou, C.; Yan, Y.; Shi, M.; Liu, Y. Comparison of structural characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) fruit. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Yan, Y.; Hou, C.; Shi, M.; Liu, Y. Structural characterization of a galacturonic acid-rich polysaccharide from Ziziphus Jujuba cv. Muzao. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Zhou, T.; Xu, F.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Wu, P. Physicochemical, structural and emulsifying properties of RG-I enriched pectin extracted from unfermented or fermented cherry pomace. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovchenko, V.V.; Khlopin, V.A.; Patova, O.A.; Feltsinger, L.S.; Bilan, M.I.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Shashkov, A.S. Pectin from leaves of birch (Betula pendula Roth.): Results of NMR experiments and hypothesis of the RG-I structure. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 284, 119186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zheng, J.; Hu, W.; Zheng, X.; He, Q.; Linhardt, R.J.; Ye, X.; Chen, S. Structure-activity relationship of Citrus segment membrane RG-I pectin against Galectin-3: The galactan is not the only important factor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Du, Y.; Fu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wu, P.; Ai, S.; Sun-Waterhouse, D. Structural, rheological and emulsifying properties of RG-I enriched pectins from sweet and sour cherry pomaces. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 139, 108442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qi, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Q. Effect of ultrasound on the properties and antioxidant activity of hawthorn pectin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Zhao, P.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Comparison of characterization and antioxidant activity of different citrus peel pectins. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, X.; Bao, X.; Gao, L.; Tao, Y. Extraction of polysaccharides from black mulberry fruit and their effect on enhancing antioxidant activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Guo, A.; Zhang, R.; Shi, L. Mechanism of natural antioxidants regulating advanced glycosylation end products of Maillard reaction. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhai, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Hill, C. Gut colonization mechanisms of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium: An argument for personalized designs. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 213–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E.; Merenstein, D.J.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: From biology to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Aipire, A.; Yang, Y.; Wei, X.; Fu, C.; Zhou, F.; Mahabati, M.; Li, J.; Li, J. Comparison of the structural characteristics and immunostimulatory activities of polysaccharides from wild and cultivated Pleurotus feruleus. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 72, 104050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tao, Y.; Lai, C.; Huang, C.; Ling, Z.; Yong, Q. Influence of glycosyl composition on the immunological activity of pectin and pectin-derived oligosaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-R.; Han, A.-R.; Lim, T.-G.; Lee, E.-J.; Hong, H.-D. Isolation, purification, and characterization of novel polysaccharides from lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) leaves and their immunostimulatory effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Q.; Mao, J.-B.; Zhou, M.-Q.; Jin, Y.-W.; Lou, C.-H.; Dong, Y.; Shou, D.; Hu, Y.; Yang, B.; Jin, C.-Y.; et al. Polysaccharide from Phellinus Igniarius activates TLR4-mediated signaling pathways in macrophages and shows immune adjuvant activity in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).