Lipidomic Profiling of Edible Japanese Sea Urchins by LC–MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
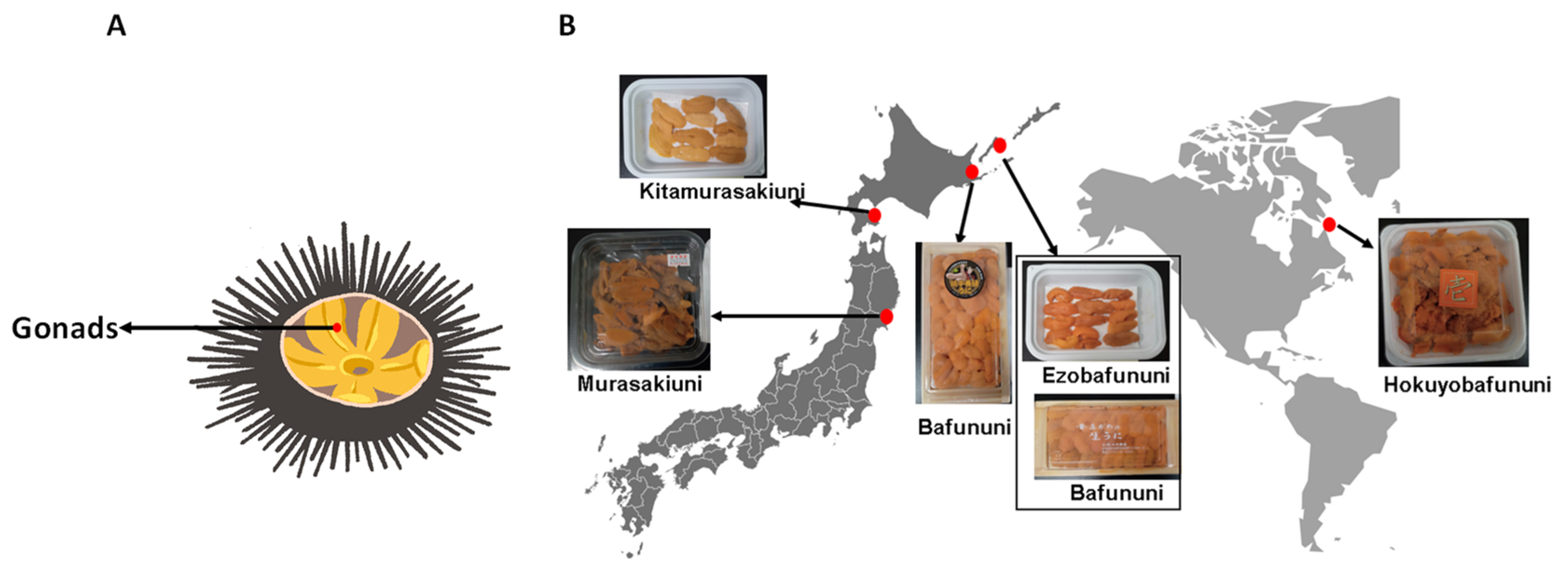
2.2. Sea Urchin Samples
2.3. Lipid Extraction
2.4. LC/MS Analysis
2.5. Determination of Total Lipid Percentage
2.6. Calculation of Nutritional Indices of Sea Urchins
3. Results and Discussion
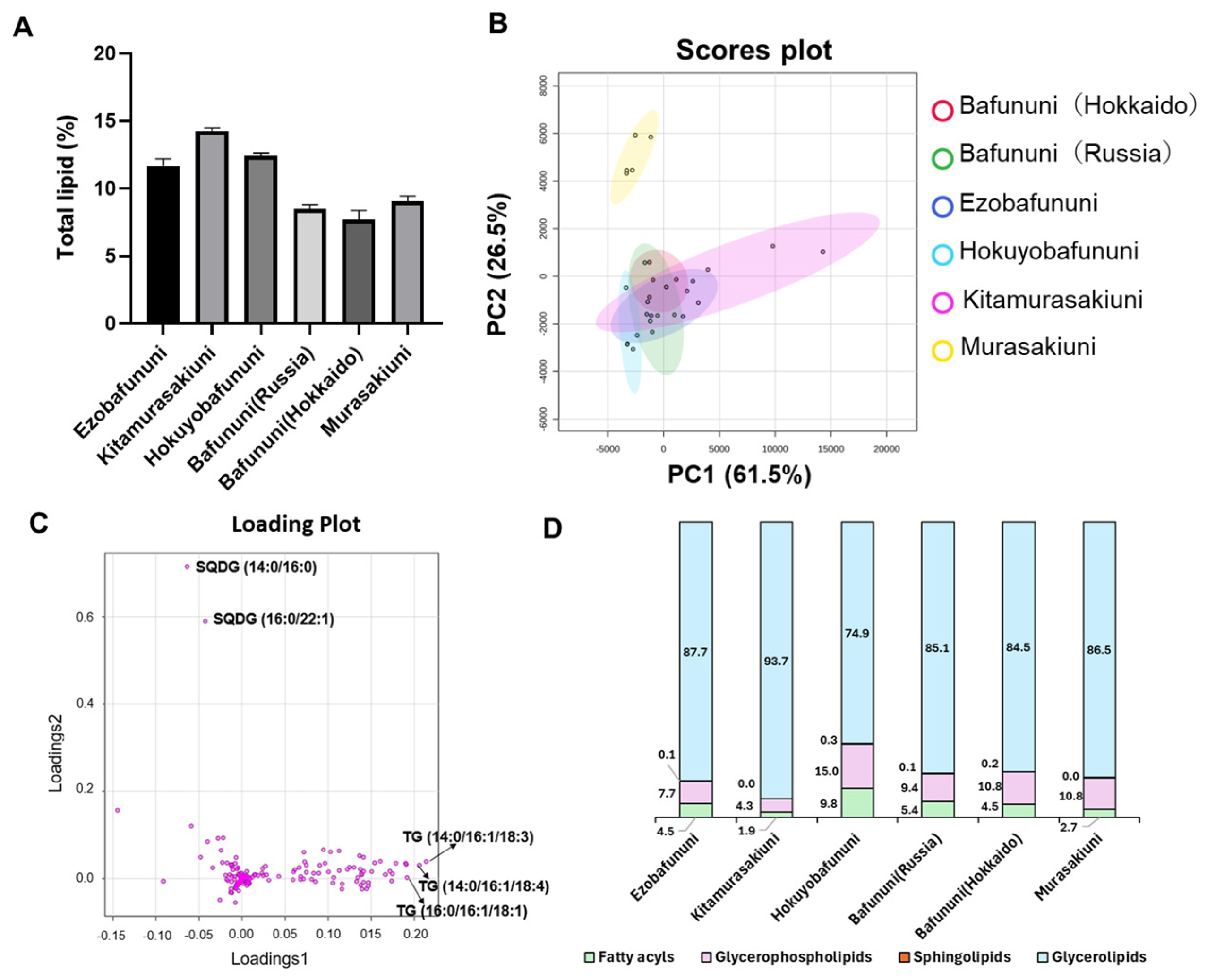
3.1. The Distribution of the Amount of Lipids in Sea Urchins Based on Lipid Classes
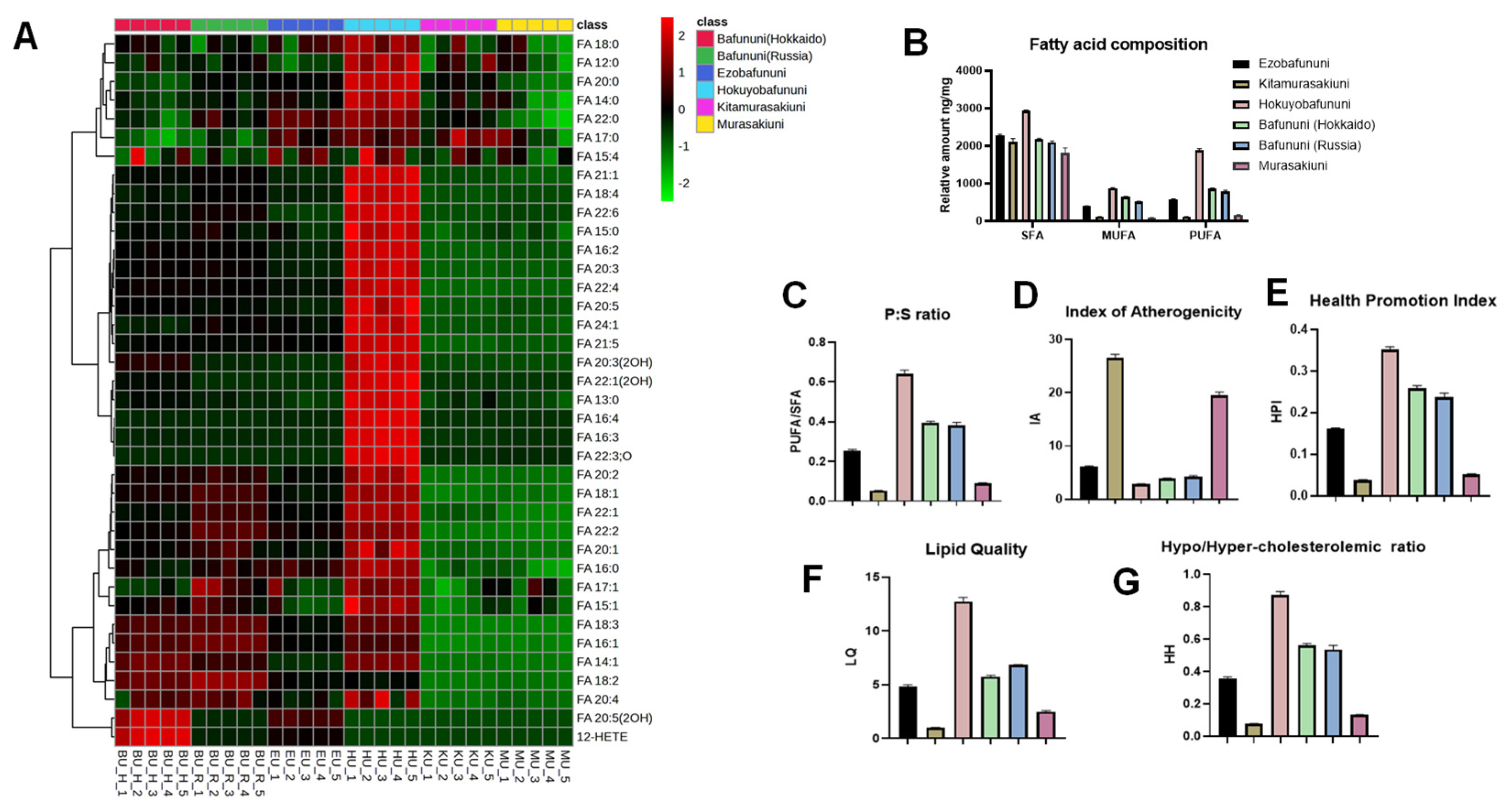
3.2. Hierarchical Cluster Correlation Analysis and Composition of Free Fatty Acid
3.3. Analysis of Nutritional Indices of Sea Urchin Samples
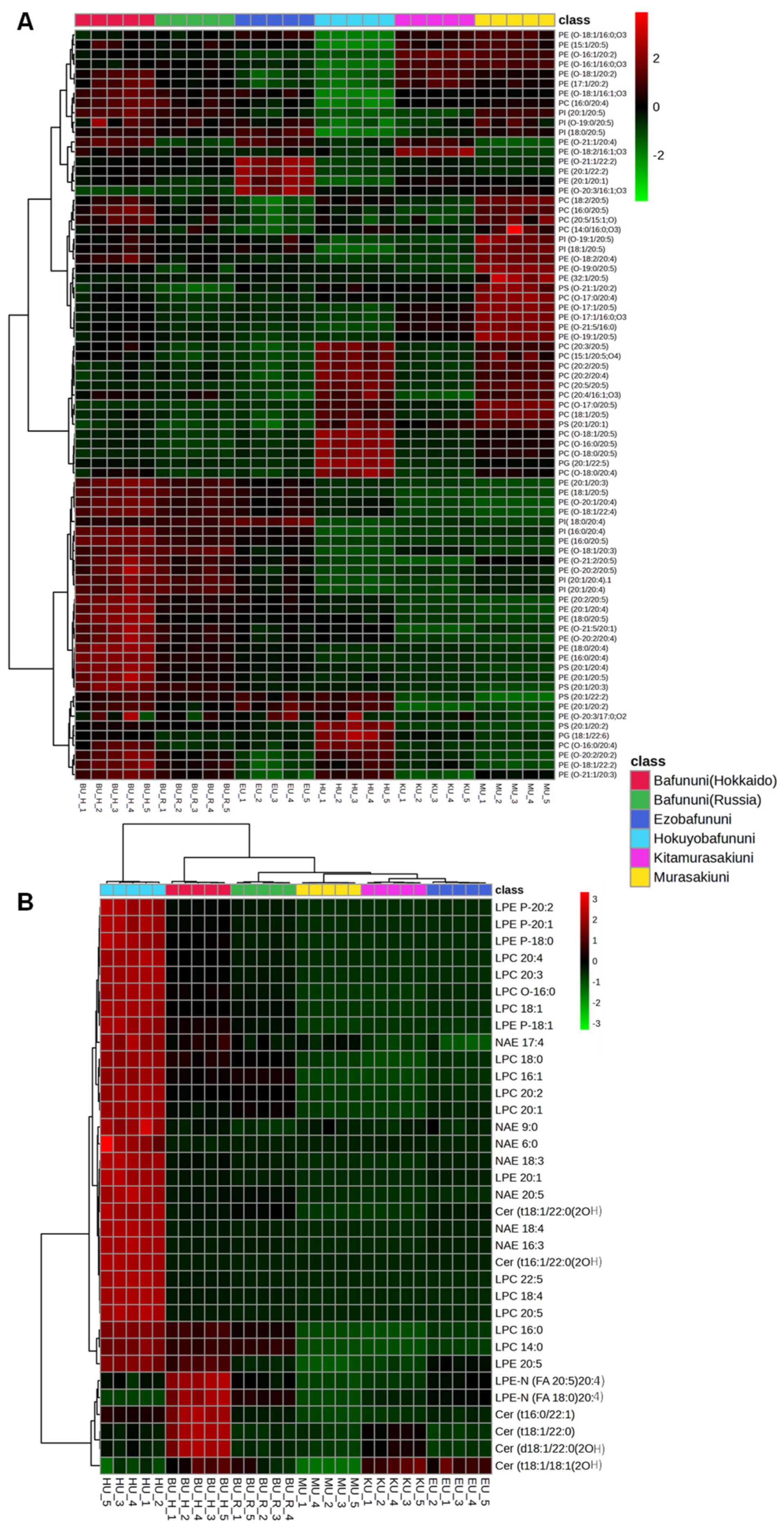
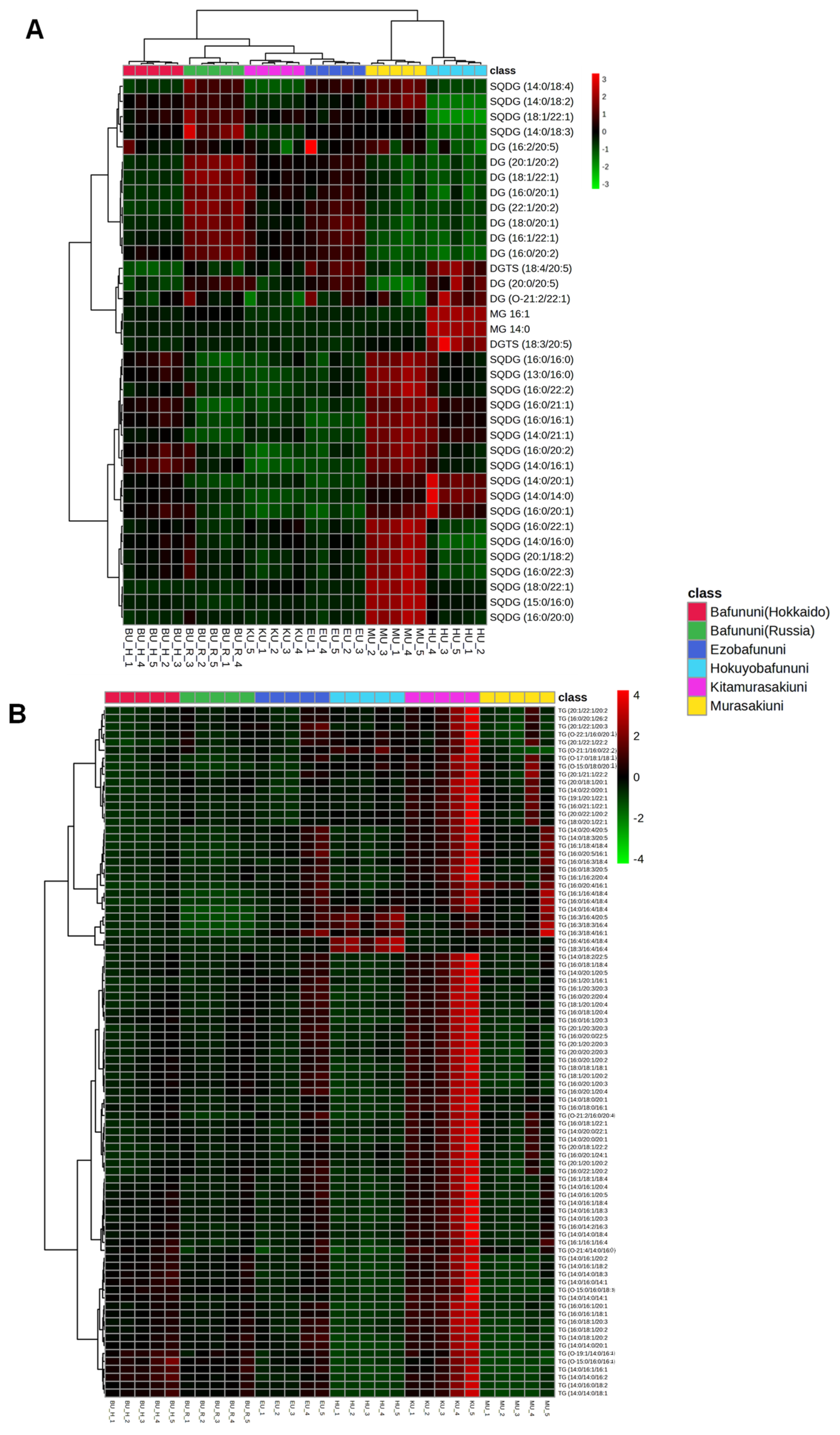
3.4. Hierarchical Correlation Analysis of Complex Lipids Analyzed in Sea Urchins
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | arachidonic acid |
| CAD | coronary artery disease |
| Cer | ceramide |
| DG | diacylglycerol |
| DGTS | diacylglyceryl trimethylhomoserine |
| DHA | docosahexaenoic acid |
| EPA | eicosapentaenoic fatty acid |
| FA | fatty acid |
| FLQ | fish lipid quality |
| FW | fresh weight |
| HH ratio | hypo/hypercholesterolemic ratio |
| HPI | health promotion index |
| IA | index of atherogenicity |
| LC-MS | liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| LPC | lysophophatidylcholine |
| LPE | lysophosphatidylethanolamine |
| LPE-N | n-acyl-lysophosphatidylethanolamine |
| LQ | lipid quality |
| MG | monoacylglycerol |
| MUFA | mono-unsaturated fatty acid |
| NAEs | n-acyl ethanolamines |
| PC | phosphatidylcholines |
| PE | phosphatidylethanolamine |
| PS | phosphatidylserine |
| PUFA | polyunsaturated fatty acid |
| SFA | saturated fatty acid |
| SQDG | sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol |
| TG | triacylglycerol |
| UFA | unsaturated fatty acid |
References
- Costello, C.; Cao, L.; Gelcich, S.; Cisneros-Mata, M.Á.; Free, C.M.; Froehlich, H.E.; Golden, C.D.; Ishimura, G.; Maier, J.; Macadam-Somer, I.; et al. The Future of Food from the Sea. Nature 2020, 588, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidira, M.; Agriopoulou, S.; Smaoui, S.; Varzakas, T. Omics-Integrated Approach (Metabolomics, Proteomics and Lipidomics) to Assess the Quality Control of Aquatic and Seafood Products. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agatsuma, Y. Ecological Studies on the Population Dynamics of Sea Urchins Associated with the Communities of Marine Algae. Nippon. Suisan Gakkaishi 2011, 77, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Ding, B.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Zuo, R.; Chang, Y.; Ding, J. Comparative Lipidomics Profiling of the Sea Urchin, Strongylocentrotus Intermedius. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 40, 100900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Cong, Y.; et al. The Multifaceted Role of Gut Microbiota in Sea Urchin Digestion: Diversity, Function, Symbiosis, and Carbohydrate Degradation. Aquac. Res. 2024, 2024, 7363987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefánsson, G.; Kristinsson, H.; Ziemer, N.; Hannon, C.; James, P. Markets for Sea Urchins: A Review of Global Supply and Markets. 2017. Available online: https://matis.is/media/matis/utgafa/10-17-Sea-Urchin-Market-Report.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Chen, G.; Xiang, W.-Z.; Lau, C.-C.; Peng, J.; Qiu, J.-W.; Chen, F.; Jiang, Y. A Comparative Analysis of Lipid and Carotenoid Composition of the Gonads of Anthocidaris Crassispina, Diadema Setosum and Salmacis Sphaeroides. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.-K.-H.; Nguyen, P.-H.; Phuong, D.L.; Dang, T.-P.-L.; Quan, P.M.; Dao, T.-K.-D.; Grigorchuk, V.P.; Long, P.Q. Component and Content of Lipid Classes and Phospholipid Molecular Species of Eggs and Body of the Vietnamese Sea Urchin Tripneustes Gratilla. Molecules 2023, 28, 3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, R.; Minami, H.; Matsusaki, H.; Sakashita, M.; Morita, N.; Nishimiya, O.; Tsutsumi, N.; Hosokawa, M.; Itabashi, Y.; Matsui, T.; et al. Consumption of the Edible Sea Urchin Mesocentrotus Nudus Attenuates Body Weight Gain and Hepatic Lipid Accumulation in Mice. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell, J.D.; Kennedy, E.J.; Robinson, S.M.C.; Parsons, G.J.; Blair, T.J.; Gonzalez-Duran, E. Effect of Dietary Lipids on Fatty Acid Composition and Metabolism in Juvenile Green Sea Urchins (Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis). Aquaculture 2004, 242, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.; Shang, X.; Dong, Q.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H.; Lu, X. Polysaccharide Constituents of Three Types of Sea Urchin Shells and Their Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5882–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbs, A.B.; Ermolenko, E.V.; Grigorchuk, V.P.; Sikorskaya, T.V.; Velansky, P.V. Current Progress in Lipidomics of Marine Invertebrates. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asokapandian, S.; Sreelakshmi, S.; Rajamanickam, G. Lipids and Oils: An Overview. In Food Biopolymers: Structural, Functional and Nutraceutical Properties; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 389–411. [Google Scholar]
- Fahy, E.; Cotter, D.; Sud, M.; Subramaniam, S. Lipid Classification, Structures and Tools. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2011, 1811, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietel, Z.; Hammann, S.; Meckelmann, S.W.; Ziv, C.; Pauling, J.K.; Wölk, M.; Würf, V.; Alves, E.; Neves, B.; Domingues, M.R. An Overview of Food Lipids toward Food Lipidomics. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 4302–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Liu, X.; Gang, D.; Zuo, R.; Han, L.; Chang, Y.; Ding, J. Comparative Lipidome and Transcriptome Provide Novel Insight Into Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Metabolism of the Sea Urchin. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 777341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, V.; Turco, V.L.; Licata, P.; Panayotova, V.; Peycheva, K.; Fazio, F.; Rando, R.; Di Bella, G.; Potortì, A.G. Determination of Fatty Acid Profile in Processed Fish and Shellfish Foods. Foods 2023, 12, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibiya, A.; Jeyavani, J.; Sivakamavalli, J.; Ravi, C.; Divya, M.; Vaseeharan, B. Bioactive Compounds from Various Types of Sea Urchin and Their Therapeutic Effects—A Review. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeropoulos, N.; Mikellidi, A.; Nomikos, T.; Chiou, A. Screening of Macro- and Bioactive Microconstituents of Commercial Finfish and Sea Urchin Eggs. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archana, A.; Babu, K.R. Nutrient Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Gonads of Sea Urchin Stomopneustes Variolaris. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Cong, P.; Xu, J.; Xue, C. Lipidomics Approach in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis Dyslipidemia Hamsters: Alleviation Using Ether-Phospholipids in Sea Urchin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 9167–9177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, P.L.; Thompson, J.W.; Foster, M.W.; Moseley, M.A.; Byrne, M.; Wray, G.A. A Comparative Analysis of Egg Provisioning Using Mass Spectrometry during Rapid Life History Evolution in Sea Urchins. Evol. Dev. 2019, 21, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, S.G.B.; Yifan, C.; Gowda, D.; Tsuboi, Y.; Chiba, H.; Hui, S.-P. Analysis of Antioxidant Lipids in Five Species of Dietary Seaweeds by Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, S.G.B.; Minami, Y.; Gowda, D.; Chiba, H.; Hui, S.-P. Detection and Characterization of Lipids in Eleven Species of Fish by Non-Targeted Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Lu, T.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.-X.; Hu, X.-P.; Zhang, J.-H.; Shahidi, F. Characterization of Lipids in Three Species of Sea Urchin. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Stanley, G.H.S. A Simple Method for the Isolation and Purification of Total Lipides from Animal Tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, S.G.B.; Gao, Z.-J.; Chen, Z.; Abe, T.; Hori, S.; Fukiya, S.; Ishizuka, S.; Yokota, A.; Chiba, H.; Hui, S.-P. Untargeted Lipidomic Analysis of Plasma from High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Rats Using UHPLC–Linear Trap Quadrupole–Orbitrap MS. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, H. Nutritional Indices for Assessing Fatty Acids: A Mini-Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Shang, Z.; Lv, X.; Du, M.; Ma, L.; Hou, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Zhao, F. Structure Elucidation and Antitumor Activity of a Water Soluble Polysaccharide from Hemicentrotus Pulcherrimus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 292, 119718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkarem, F.M.; Assaf, H.K.; Mostafa, Y.A.; Mahdy, A.; Hussein, M.F.; Ross, S.A.; Mohamed, N.M. Antiviral Activity of Sulphated Specialized Metabolites from Sea Urchin Clypeaster Humilis: In Vitro and in Silico Studies. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 14185–14193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Cong, P.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Meng, N.; Fan, X.; Xu, J.; Xue, C. Comprehensive Lipid Profile of Eight Echinoderm Species by RPLC–Triple TOF-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 8230–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N.; Laakso, I.; Seppänen-Laakso, T.; Makarenko, I.E.; Faustova, N.M.; Makarova, M.N.; Makarov, V.G. Bioactivity and Chemical Characterization of Gonads of Green Sea Urchin Strongylocentrotus Droebachiensis from Barents Sea. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 17, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komprda, T. Eicosapentaenoic and Docosahexaenoic Acids as Inflammation-Modulating and Lipid Homeostasis Influencing Nutraceuticals: A Review. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, E.L.; Holub, B.J. Effects of a Liquid Egg Product Containing Fish Oil on Selected Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: A Randomized Crossover Trial. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Huertas, E. Health Effects of Oleic Acid and Long Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids (EPA and DHA) Enriched Milks. A Review of Intervention Studies. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 61, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, K.C.; Van Elswyk, M.E.; McCarthy, D.; Seeley, M.A.; Veith, P.E.; Hess, S.P.; Ingram, K.A.; Halvorson, J.J.; Calaguas, E.M.; Davidson, M.H. Lipid Responses in Mildly Hypertriglyceridemic Men and Women to Consumption of Docosahexaenoic Acid-Enriched Eggs. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2003, 73, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, G.; Litrenta, F.; Pino, S.; Tropea, A.; Potortì, A.G.; Nava, V.; Lo Turco, V. Variations in Fatty Acid Composition of Mediterranean Anchovies (Engraulis encrasicolus) after Different Cooking Methods. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 2285–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.J.; Shin, M.S.; Park, J.N.; Lee, S.S. The Effects of Polyunsaturated:Saturated Fatty Acids Ratios and Peroxidisability Index Values of Dietary Fats on Serum Lipid Profiles and Hepatic Enzyme Activities in Rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 94, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabiee Rad, M.; Ghasempour Dabaghi, G.; Darouei, B.; Amani-Beni, R. The Association of Atherogenic Index of Plasma with Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özbey, F. Fatty Acid Composition, Lipid Quality Indices, and Textural Profile of Traditional Kargı Tulum PDO Cheese. Prog. Nutr. 2023, 25, e2023021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudicella, V.A.; Beveridge, C.; Carboni, S.; Franco, S.C.; Doherty, M.K.; Long, N.; Mitchell, E.; Stanley, M.S.; Whitfield, P.D.; Hughes, A.D. Lipidomics Analysis of Juveniles’ Blue Mussels (Mytilus edulis L. 1758), a Key Economic and Ecological Species. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0223031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili Tilami, S.; Sampels, S. Nutritional Value of Fish: Lipids, Proteins, Vitamins, and Minerals. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2018, 26, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R. The Effect of Diet on Cardiovascular Disease and Lipid and Lipoprotein Levels; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Arita, K.; Kobuchi, H.; Utsumi, T.; Takehara, Y.; Akiyama, J.; Horton, A.A.; Utsumi, K. Mechanism of Apoptosis in HL-60 Cells Induced by n-3 and n-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2001, 62, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Wei, Y.; Kan, X.; Liu, X.; Han, X.; Zhao, Z.; An, T.; Fang, Z.-Z.; et al. Abdominal Obesity in Youth: The Associations of Plasma Lysophophatidylcholine Concentrations with Insulin Resistance. Pediatr. Res. 2024, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coderch, L.; López, O.; de la Maza, A.; Parra, J.L. Ceramides and Skin Function. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2003, 4, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilátová, M.B.; Solárová, Z.; Mezencev, R.; Solár, P. Ceramides and Their Roles in Programmed Cell Death. Adv. Med. Sci. 2023, 68, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, D.N. Chapter 6 Metabolism of Triacylglycerols. In New Comprehensive Biochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 171–203. [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi, H.; Watanabe, H.; Onizawa, K.; Nagao, T.; Gotoh, N.; Yasukawa, T.; Tsushima, R.; Shimasaki, H.; Itakura, H. Double-Blind Controlled Study on the Effects of Dietary Diacylglycerol on Postprandial Serum and Chylomicron Triacylglycerol Responses in Healthy Humans. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2000, 19, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveeva, V.A.; Shulgina, L.V.; Prikhodko, Y.V.; Shulgin, Y.P.; Madej, K.; Piekoszewski, W. Nutritional Value of Sea Urchin Roe (Strongylocentrotidae)—Study of Composition and Storage Conditions. Separations 2021, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amai, S.; Yuki, K.; Gowda, S.G.B.; Gowda, D.; Hui, S.-P. Lipidomic Profiling of Edible Japanese Sea Urchins by LC–MS. Foods 2025, 14, 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132268
Amai S, Yuki K, Gowda SGB, Gowda D, Hui S-P. Lipidomic Profiling of Edible Japanese Sea Urchins by LC–MS. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132268
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmai, Sahana, Kisara Yuki, Siddabasave Gowda B. Gowda, Divyavani Gowda, and Shu-Ping Hui. 2025. "Lipidomic Profiling of Edible Japanese Sea Urchins by LC–MS" Foods 14, no. 13: 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132268
APA StyleAmai, S., Yuki, K., Gowda, S. G. B., Gowda, D., & Hui, S.-P. (2025). Lipidomic Profiling of Edible Japanese Sea Urchins by LC–MS. Foods, 14(13), 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132268







