Inhibitory Effect and Potential Mechanism of Trans-2-Hexenal Treatment on Postharvest Rhizopus Rot of Peach Fruit
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fruit Materials and Treatment
2.2. Disease Incidence and Lesion Diameter Assessment
2.3. Measurement of Firmness, Yield of Juice, and Total Soluble Solids (TSS)
2.4. Determination of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content and Total Phenolic Content
2.5. Determination of Chitinase (CHI) and β-1,3-Glucanase (GLU) Activities
2.6. Assays of Phenylpropanoid Metabolism-Related Enzyme Activities
2.7. Determination of ROS Parameters
2.8. Assays of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) and Catalase (CAT) Activities
2.9. Determination of Ascorbate-Glutathione (AsA-GSH) Cycle-Related Parameters
2.10. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
2.11. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
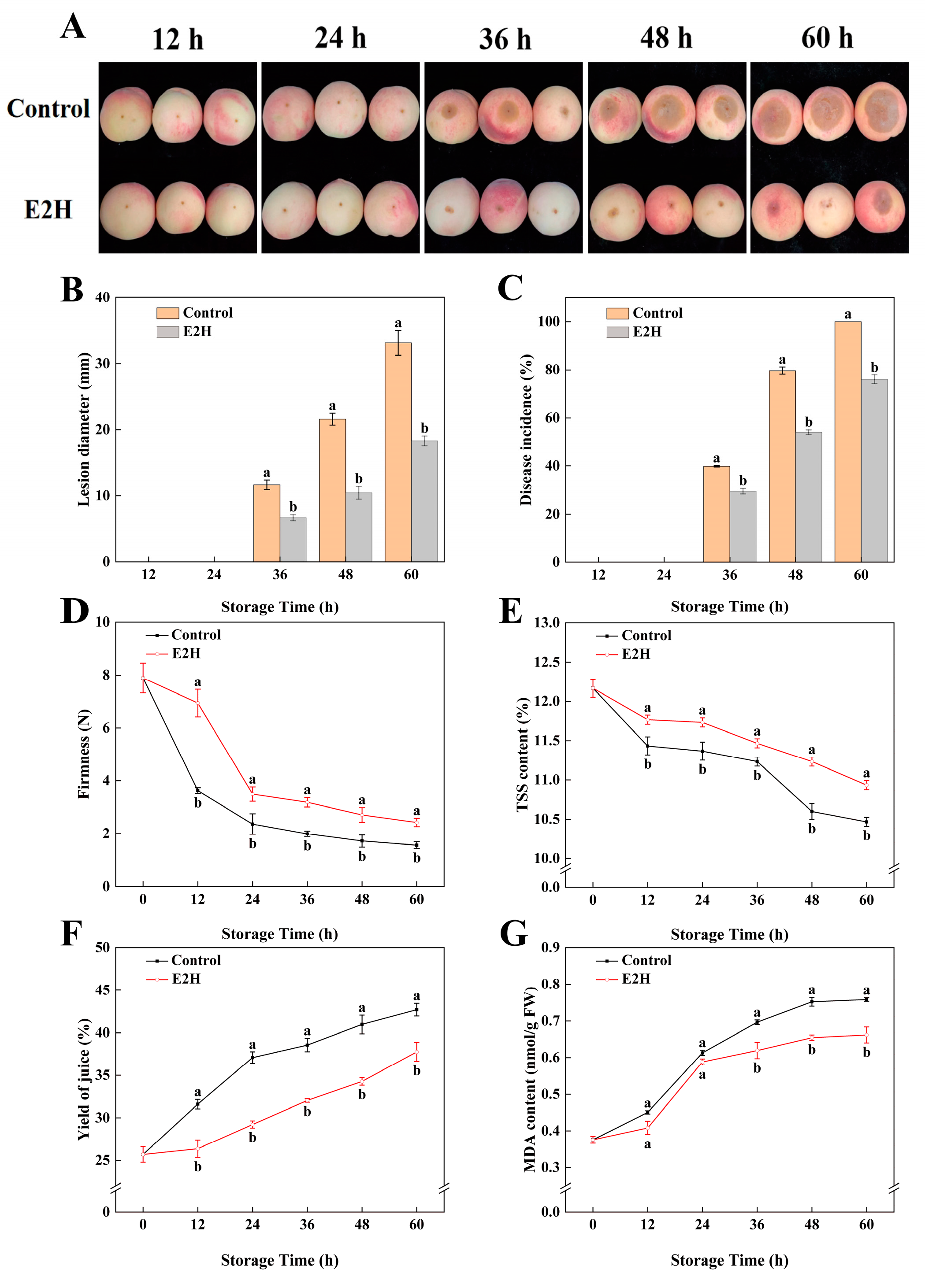
3.1. Effects of E2H Treatment on Postharvest Rhizopus Rot Development and Fruit Quality in Peach
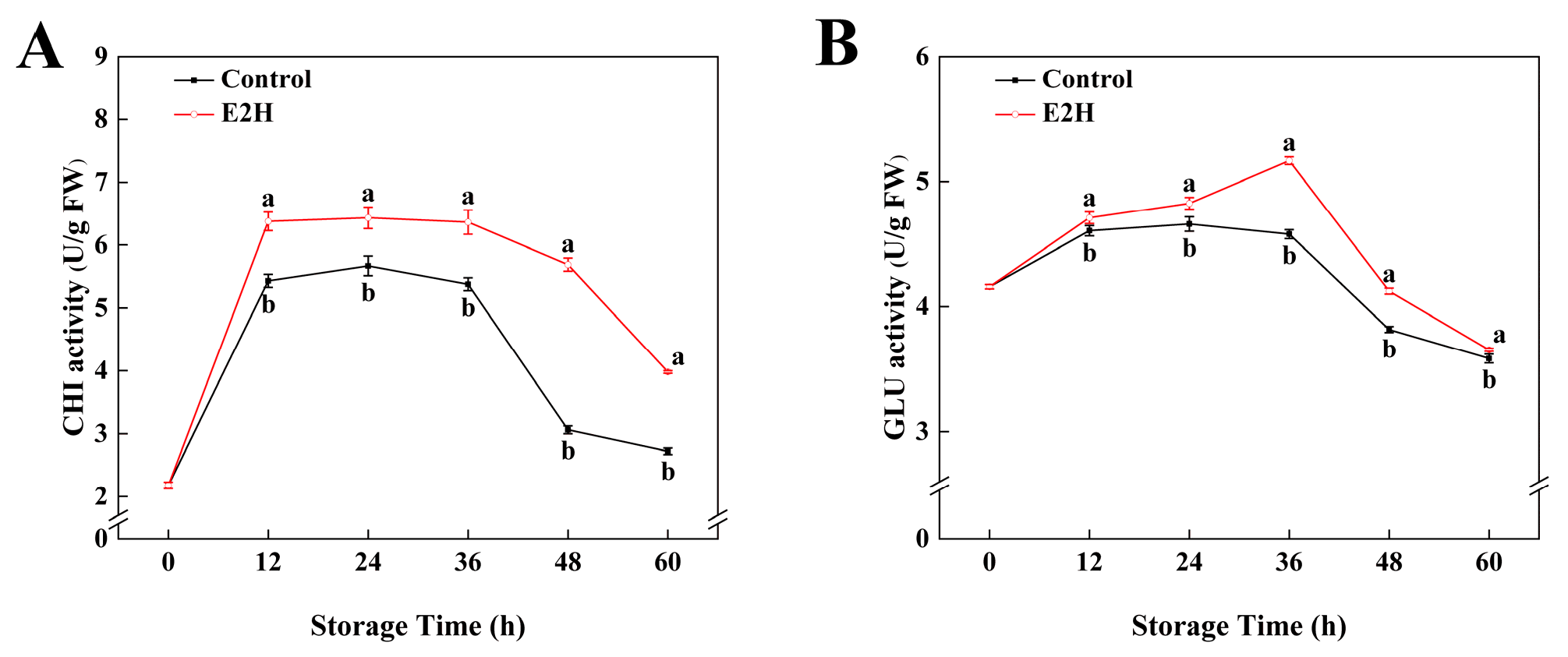
3.2. Effects of E2H Treatment on CHI and GLU Activities in Postharvest Peach Fruit
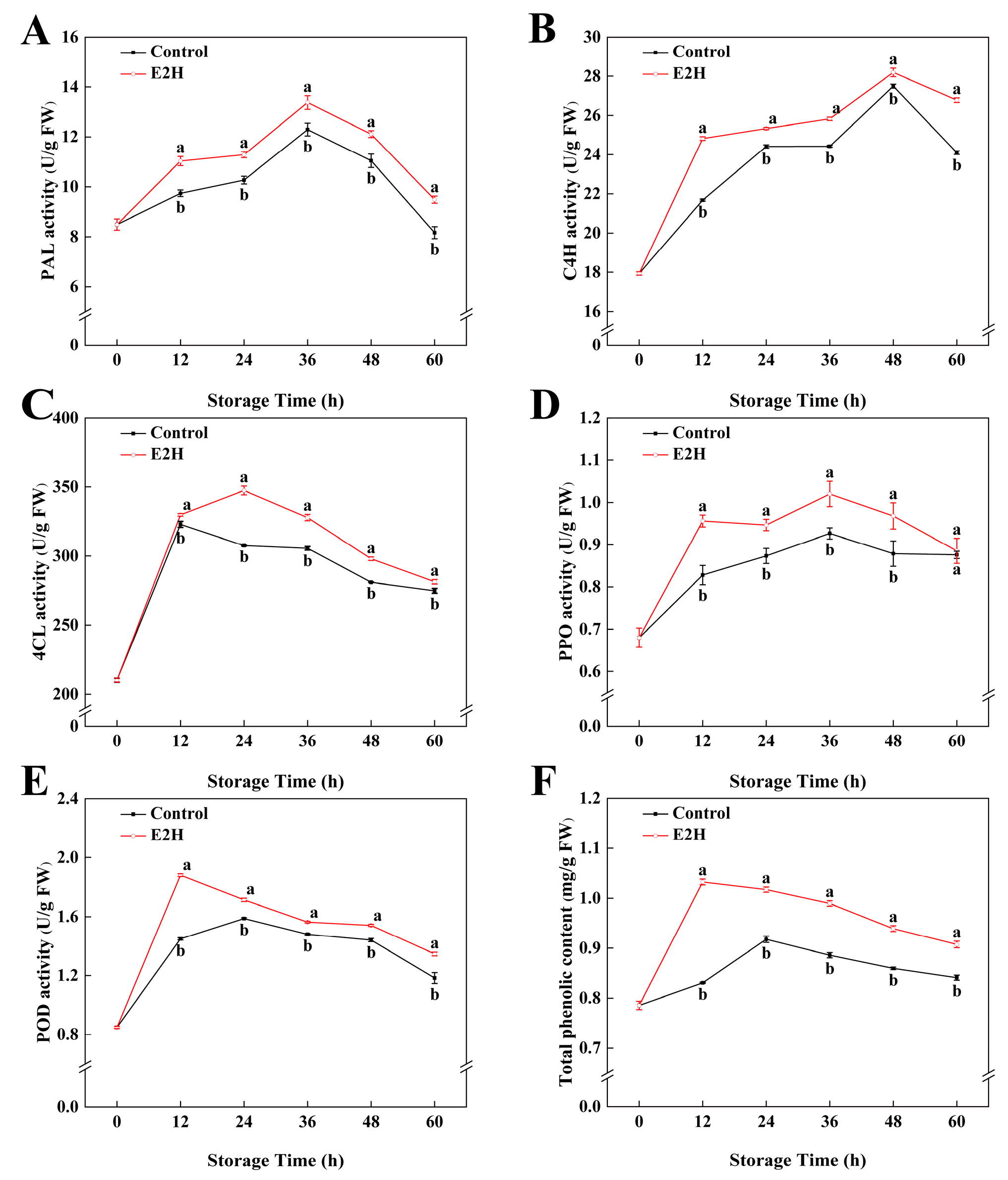
3.3. Effects of E2H Treatment on Phenylpropanoid Metabolism in Peach Fruit
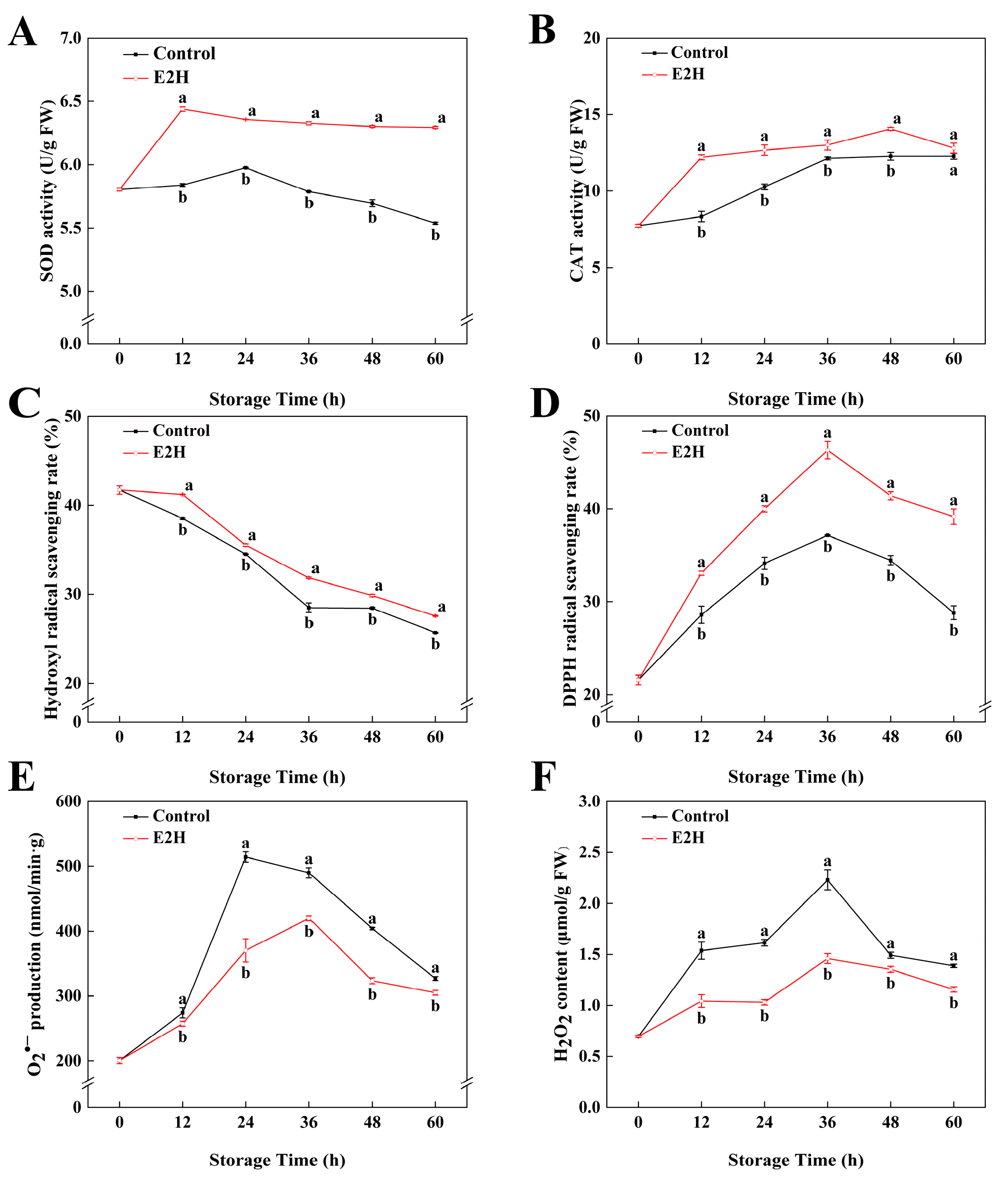
3.4. Effects of E2H Treatment on ROS Metabolic Pathways
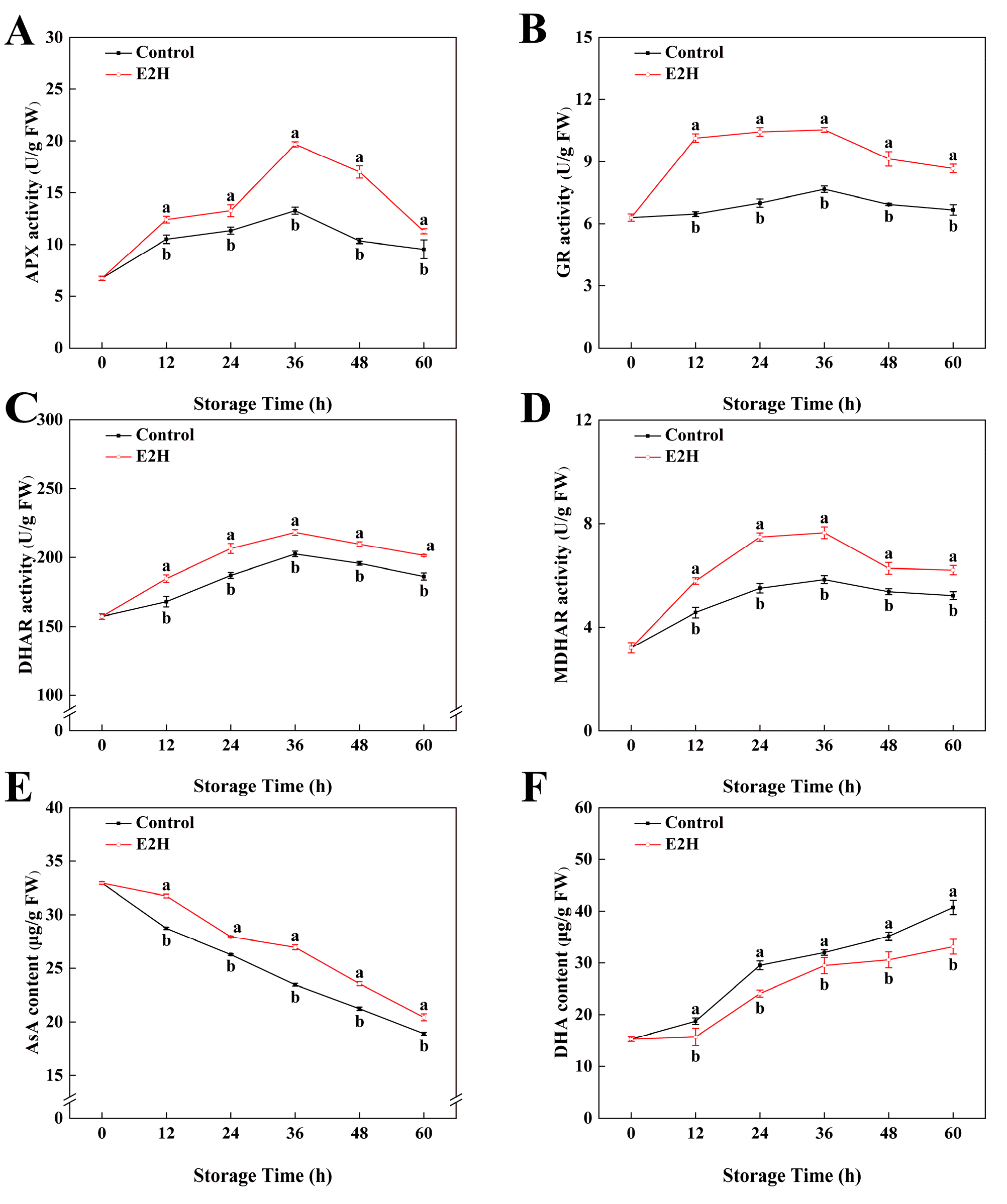
3.5. Effects of E2H Treatment on AsA-GSH Cycle
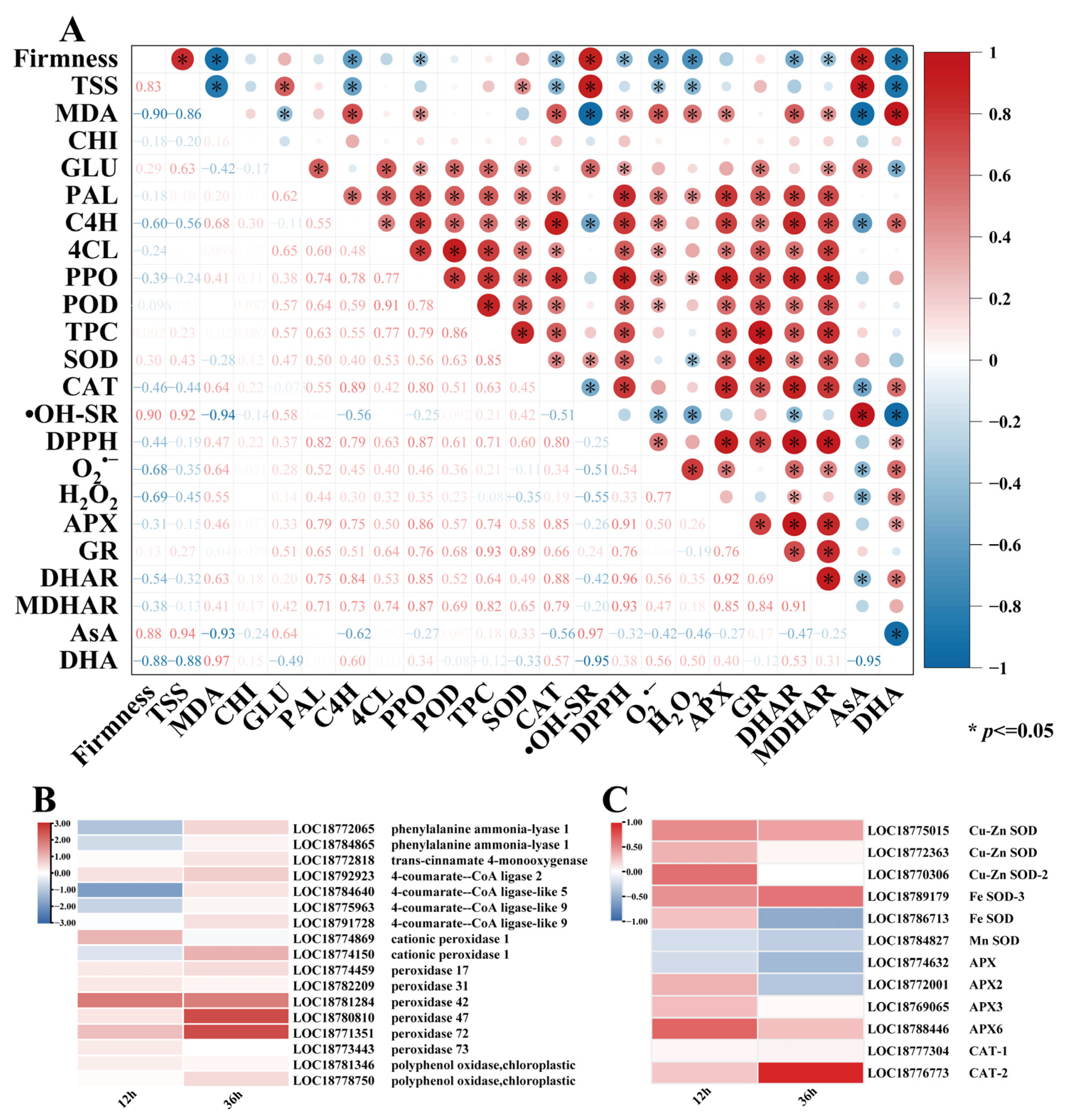
3.6. Effects of E2H Treatment on Differential Gene Expression in ROS and Phenylpropanoid Metabolism Pathways and Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| E2H | Trans-2-hexenal |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| PAL | Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase |
| C4H | Cinnamate 4-hydroxylase |
| 4CL | 4-coumarate-CoA ligase |
| PPO | Polyphenol oxidase |
| POD | Peroxidase |
| CHI | Chitinase |
| GLU | β-1,3-glucanase |
| AsA | Ascorbic acid |
| DHA | Dehydroascorbic acid |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| PR | Pathogenesis-related protein |
| HR | Hypersensitive response |
| PCD | Programmed cell death |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| APX | Ascorbate peroxidase |
| GR | Glutathione reductase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| GABA | γ-aminobutyric acid |
| PDA | Potato dextrose agar |
| TSS | Total soluble solids |
| N | Newtons |
| TBA | Thiobarbituric acid method |
| TCA | Trichloroacetic acid |
| DMAB | P-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde |
| •OH | Hydroxyl radical |
| O2•− | Superoxide anion |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| MDHAR | Monodehydroascorbate reductase |
| DHAR | Dehydroascorbate reductase |
| GLM | generalized linear model |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| Fig. | Figure |
| TPC | Total phenolic content |
| •OH-SR | hydroxyl radical scavenging rate |
| ASM | Acibenzolar-S-methyl |
References
- Wang, L.; Shan, T.M.; Xie, B.; Ling, C.; Shao, S.; Jin, P.; Zheng, Y.H. Glycine betaine reduces chilling injury in peach fruit by enhancing phenolic and sugar metabolisms. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.Y.; Gong, L.; Dong, Q.F.; Kang, Y.F.; Osako, K.; Li, L. Characterization of PLA-P3,4HB active film incorporated with essential oil: Application in peach preservation. Food Chem. 2020, 313, 126134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.Q.; Dhanasekaran, S.; Chen, X.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, X.Z.; Wu, M.Y.; Song, Y.D.; Zhang, H.Y. Study on the control effect and physiological mechanism of Wickerhamomyces anomalus on primary postharvest diseases of peach fruit. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 413, 110575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.H.; Bassi, D.; Corre, M.N.; Lino, L.O.; Signoret, V.; Quilot-Turion, B.; Cirilli, M. Phenotyping brown rot susceptibility in stone fruit: A literature review with emphasis on peach. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, X.R.; He, Y.; Han, X.D.; Song, Z.Y.; Shi, J.Y. The volatile components from Bacillus cereus N4 can restrain brown rot of peach fruit by inhibiting sporulation of Monilinia fructicola and inducing disease resistance. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 210, 112755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, S.S.; De Mio, L.L.M.; Amorim, L. Comparative analysis of Monilinia fructicola and M-laxa isolates from Brazil: Monocyclic components of peach brown rot. Cienc. Rural. 2017, 47, e20160300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanazzi, G.; Sanzani, S.M.; Bi, Y.; Tian, S.P.; Martínez, P.G.; Alkan, N. Induced resistance to control postharvest decay of fruit and vegetables. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 122, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.E.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhou, H.J.; Wang, L.F.; Zhou, L.; Mao, J.X.; Zhang, S.Y.; Shen, S.L.; Zheng, X.L.; Huan, C. Control efficiency and potential mechanisms of chlorogenic acid against postharvest gray mold caused by Botrytis cinerea on peach fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 218, 113134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Xu, F.; Wang, J.; Jin, P.; Zheng, Y.H. Bacillus cereus AR156 induces resistance against Rhizopus rot through priming of defense responses in peach fruit. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.T.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, K.P.; Xu, Q.; Yao, Y.; Gao, H. Biocontrol of postharvest Rhizopus decay of peaches with Pichia caribbica. Curr. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Hamada, M.S.; Hahn, M.; Li, G.Q.; Luo, C.X. Fungicide resistance of Botrytis cinerea from strawberry to procymidone and zoxamide in Hubei, China. Phytopathol. Res. 2019, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.Y.; Du, X.L.; Lu, X.F.; Lu, Y.; Li, G.P.; Li, J.L. Component analysis and antifungal activity of three Chinese herbal essential oils and their application of postharvest preservation of peach fruit. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gura, W.P.; Gelain, J.; Sikora, E.J.; Vinson, E.L.; Brannen, P.M.; Schnabel, G. Low frequency of resistance to thiophanate-methyl in Monilinia fructicola populations from southeastern United States peach orchards. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 197, 105642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Michailides, T.J.; Xiao, C.L. Fungicide resistance profiling in Botrytis cinerea populations from blueberry in California and Washington and their impact on control of gray mold. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 2087–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Shahwar, D.; Hassan, F.E.; Ahmed, Z.F.R. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of date palm fruit (Phoenix dactylifera L.) in response to postharvest application with natural elicitors. Acta Hortic. 2023, 1364, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OuYang, Q.L.; Okwong, R.O.; Chen, Y.P.; Tao, N.G. Synergistic activity of cinnamaldehyde and citronellal against green mold in citrus fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 162, 111095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.D.; Wang, B.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.B.; Sun, Y.Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; He, J. Mushroom alcohol treatment inhibited the growth of Alternaria tenuissima and reduced the incidence of postharvest diseases of fresh wolfberry fruit. Food Control. 2025, 175, 111283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.R.; Feng, J.Z.; Zhang, P.Y.; Jia, L.Y.; Chen, K.S. Postharvest treatment with trans-2-hexenal induced resistance against Botrytis cinerea in tomato fruit. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2015, 44, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.; Lee, J.G.; Yang, K.Y.; Lim, S.; Lee, E.J. Postharvest fumigation of (E)-2-hexenal on kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis cv. ‘Haegeum’) enhances resistance to Botrytis cinerea. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 187, 111854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.B.; Zhao, L.L.; Xie, Y.L. Inhibitory effect of (E)-2-hexenal as a potential natural fumigant on Aspergillus flavus in stored peanut seeds. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 107, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.X.; Meng, K.X.; Shi, S.W.; Wu, Y.Y.B.; Chen, X.M.; OuYang, Q.L.; Tao, N.G. Trans-2-hexenal inhibits the growth of imazalil-resistant Penicillium digitatum Pdw03 and delays green mold in postharvest citrus. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 199, 112304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francesco, A.; Martini, C.; Mari, M. Biological control of postharvest diseases by microbial antagonists: How many mechanisms of action? Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 145, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sels, J.; Mathys, J.; De Coninck, B.M.A.; Cammue, B.P.A.; De Bolle, M.F.C. Plant pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins: A focus on PR peptides. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 46, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeles, F.B.; Bosshart, R.P.; Forrence, L.E.; Habig, W.H. Preparation and purification of glucanase and chitinase from bean leaves. Plant Physiol. 1971, 47, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.H.; Duan, B.; Li, C.Y.; Tang, Q.; Li, X.; Wei, M.L.; Chen, Y.R.; Li, J.R. γ-Aminobutyric acid delays senescence of blueberry fruit by regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolism and phenylpropanoid pathway. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 240, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Li, C.Y.; Jinyue, R.X.; Xu, H.P.; Ge, Y.H. Acibenzolar-S-methyl activates phenylpropanoid pathway to enhance resistance against Alternaria alternata in pear fruit. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wei, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Ye, J.F.; Xu, F.; Lou, Y.J.; Ding, P.B.; Ouaziz, M.; Shao, X.F. Agaro-oligosaccharides enhanced the Monilinia fructicola resistance of peach fruit by regulating antioxidative and phenylpropanoid metabolism. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 217, 113126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.F.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, S.M.; Xu, Y.Q.; Luo, Z.S. Postharvest MeJA maintains the shelf quality of kiwifruit after cold storage by regulating antioxidant capacity and activating the disease resistance. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 211, 112827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Dai, Y.; Li, M.Q.; Zhang, H.W. Natamycin and potassium sorbate synergistically enhance resistance to Botrytis cinerea by activating the phenylpropanoid metabolism in harvested strawberry. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 222, 113361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.J.; Lin, H.T.; Lin, M.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y.X.; Shi, J.; Lin, Y.F. A novel chitosan formulation treatment induces disease resistance of harvested litchi fruit to Peronophythora litchii in association with ROS metabolism. Food Chem. 2018, 266, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.N.; Yu, H.; Zhou, J.M.; Smith, S.M.; Li, J.Y. Malate circulation: Linking chloroplast metabolism to mitochondrial ROS. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.T.; Li, L.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, W.D.; Guo, M.R.; Chen, G.G. MeJA and MeSA alleviate black rot in winter jujube caused by Alternaria tenuissima by regulating membrane lipid and reactive oxygen metabolism. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 219, 113275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.C.; Liu, S.; Duan, X.W.; Pan, X.J.; Dong, B.Y. MAPK cascade and ROS metabolism are involved in GABA-induced disease resistance in red pitaya fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 200, 112324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Zhu, J.F.; Wei, H.; Ding, Z.P.; Li, X.R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.B.; Wang, Y.P. Biological control efficacy of Bacillus licheniformis HG03 against soft rot disease of postharvest peach. Food Control. 2023, 145, 109402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.M.; Jin, P.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.P.; Wang, X.L.; Zheng, Y.H. Exogenous glycine betaine treatment enhances chilling tolerance of peach fruit during cold storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 114, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Limwachiranon, J.; Li, L.; Du, R.X.; Luo, Z.S. Involvement of energy metabolism to chilling tolerance induced by hydrogen sulfide in cold-stored banana fruit. Food Chem. 2016, 208, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, D.J.; Gao, X.X.; Yue, Z.Y.; Zhou, H.L. Exogenous caffeic acid and epicatechin enhance resistance against Botrytis cinerea through activation of the phenylpropanoid pathway in apples. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 268, 109348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.J.; Yu, H.T.; Dai, X.M.; Yu, M.L.; Yu, Z.F. Effect of methyl jasmonate on the quality and antioxidant capacity by modulating ascorbate-glutathione cycle in peach fruit. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 303, 111216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Zheng, Y.H.; Jin, P. Effects of CaCl2 Treatment Alleviates Chilling Injury of Loquat Fruit (Eribotrya japonica) by Modulating ROS Homeostasis. Foods 2021, 10, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.X.; Cao, S.F.; Jia, W.R.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Jin, P.; Zheng, Y.H. Near-saturated relative humidity alleviates chilling injury in zucchini fruit through its regulation of antioxidant response and energy metabolism. Food Chem. 2021, 351, 129336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexieva, V.; Sergiev, I.; Mapelli, S.; Karanov, E. The effect of drought and ultraviolet radiation on growth and stress markers in pea and wheat. Plant Cell Environ. 2001, 24, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Q.; Hu, S.Q.; Chen, G.F.; Zheng, Y.H.; Jin, P. Cold shock treatment alleviates chilling injury in peach fruit by regulating antioxidant capacity and membrane lipid metabolism. Food Qual. Saf. 2022, 6, fyab026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, P.; Huang, Y.P.; Shan, T.M.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Zheng, Y.H. Effect of hot water combined with glycine betaine alleviates chilling injury in cold-stored loquat fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 118, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumyam, A.; Shank, L.; Faiyue, B.; Uthaibutra, J.; Saengnil, K. Effects of chlorine dioxide fumigation on redox balancing potential of antioxidative ascorbate-glutathione cycle in ‘Daw’ longan fruit during storage. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 222, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ding, T.; Zuo, J.H.; Gao, L.P.; Fan, L.L. Amelioration of postharvest chilling injury in sweet pepper by glycine betaine. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 112, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.C.; Wang, G.X.; Zhu, J.M.; Mu, W.; Dou, D.L.; Liu, F. Green leaf volatile trans-2-hexenal inhibits the growth of Fusarium graminearum by inducing membrane damage, ROS accumulation, and cell dysfunction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 5646–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, F.T.; Moreno, J.; Daza, P.; Boianova, L.; Romero, F. Antifungal activity of strawberry fruit volatile compounds against Colletotrichum acutatum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5701–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Tian, H.; Sun, H.L.; Wang, X.Y. Antifungal activity of trans-2-hexenal against Penicillium cyclopium by a membrane damage mechanism. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 41, e12289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto, M.A.; Butassi, E.; Ribas, J.C.; Svetaz, L.A.; Cortés, J.C.G. Natural products targeting the synthesis of β(1,3)-D-glucan and chitin of the fungal cell wall. Existing drugs and recent findings. Phytomedicine 2021, 88, 153556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzelepis, G.; Karlsson, M. Killer toxin-like chitinases in filamentous fungi: Structure, regulation and potential roles in fungal biology. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2019, 33, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.W.; Qin, Z.; Zhou, P.; Wang, R.M.; Yan, Q.J.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Yang, S.Q. Structural insights into the substrate recognition and catalytic mechanism of a fungal glycoside hydrolase family 81 β-1,3-glucanase. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2022, 153, 109948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Wang, M.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, S.R.; Xu, H.P.; Ge, Y.H. Activation of the calcium signaling, mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade and phenylpropanoid metabolism contributes to the induction of disease resistance in pear fruit upon phenylalanine treatment. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 210, 112782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, M.; Xu, H.P.; Zhang, S.R.; Liu, J.Q.; Jin, Y.R.X.; Ge, Y.H. Postharvest caffeic acid dipping enhances disease resistance and storage capacity of ‘Zaosu’ pear fruit via regulating phenylpropanoid metabolism. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 209, 112716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Huang, M.M.; Peng, Y.; Yang, W.T.; Shi, J.Y. Antifungal activity of 1-octen-3-ol against Monilinia fructicola and its ability in enhancing disease resistance of peach fruit. Food Control 2022, 135, 108804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.X.; Song, R.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.Y.; Jiao, L.; Yuan, S.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Chen, L.; Meng, D.M. Para-coumaric acid and cinnamic acid enhance resistance of Agaricus bisporus s mushrooms to Brown blotch disease caused by Pseudomonas tolaasii. Food Control 2025, 168, 110859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.C.; Li, W.H.; Han, X.D.; Wu, B.; Song, Z.Y.; Shi, J.Y. Plant glycerol suppresses brown rot of peach fruit by enhancing disease resistance. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 129, 102204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sui, Y.; Wisniewski, M.; Droby, S.; Tian, S.P.; Norelli, J.; Hershkovitz, V. Effect of heat treatment on inhibition of Monilinia fructicola and induction of disease resistance in peach fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2012, 65, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, D.C.; Chen, T.; Li, B.Q.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Qin, G.Z.; Tian, S.P. Production, signaling, and scavenging mechanisms of reactive oxygen species in fruit-pathogen interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.Q.; Chen, T.; Tian, S.P. Reactive oxygen species: A generalist in regulating development and pathogenicity of phytopathogenic fungi. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 3344–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, N.G.; Fan, F.; Jia, L.; Zhang, M.L. Octanal incorporated in postharvest wax of Satsuma mandarin fruit as a botanical fungicide against Penicillium digitatum. Food Control 2014, 45, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.L.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Xue, H.L.; Bi, Y.; Yang, X.; Zong, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.G.; Chen, J.Y.; Prusky, D. TrPLD1 and TrPLD2 modulate reactive oxygen species production and pathogenicity in Trichothecium roseum infected apple fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 199, 112222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xue, H.L.; Liu, Z.G.; Liu, Q.L.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Nan, M.N. The effects of different ambient pH on the pathogenicity of Fusarium sulphureum and reactive oxygen species metabolism in F. sulphureum inoculation muskmelon fruits. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 122, 101893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Y.; Huang, D.D.; Chen, C.B.; Zhu, S.H.; Gao, J.G. Regulation of ascorbate-glutathione cycle in peaches via nitric oxide treatment during cold storage. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 247, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.L.; Ge, Y.H.; Li, C.Y.; Han, X.; Qin, S.C.; Chen, Y.R.; Tang, Q.; Li, J.R. G6PDH regulated NADPH production and reactive oxygen species metabolism to enhance disease resistance against blue mold in apple fruit by acibenzolar-S-methyl. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 148, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Ling, Y.; Deng, L.L.; Yao, S.X.; Zeng, K.F. Effect of L-cysteine treatment to induce postharvest disease resistance of Monilinia fructicola in plum fruits and the possible mechanisms involved. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 191, 105367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, X.; Xiang, W.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Shen, X.; Bao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jin, P. Inhibitory Effect and Potential Mechanism of Trans-2-Hexenal Treatment on Postharvest Rhizopus Rot of Peach Fruit. Foods 2025, 14, 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132265
Cai X, Xiang W, Zhao L, Liu Z, Li Y, Zeng Y, Shen X, Bao Y, Zheng Y, Jin P. Inhibitory Effect and Potential Mechanism of Trans-2-Hexenal Treatment on Postharvest Rhizopus Rot of Peach Fruit. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132265
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Xuanyi, Wen Xiang, Liangyi Zhao, Ziao Liu, Ye Li, Yuan Zeng, Xinyan Shen, Yinqiu Bao, Yonghua Zheng, and Peng Jin. 2025. "Inhibitory Effect and Potential Mechanism of Trans-2-Hexenal Treatment on Postharvest Rhizopus Rot of Peach Fruit" Foods 14, no. 13: 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132265
APA StyleCai, X., Xiang, W., Zhao, L., Liu, Z., Li, Y., Zeng, Y., Shen, X., Bao, Y., Zheng, Y., & Jin, P. (2025). Inhibitory Effect and Potential Mechanism of Trans-2-Hexenal Treatment on Postharvest Rhizopus Rot of Peach Fruit. Foods, 14(13), 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132265






