Formation Mechanisms and Kinetic Modeling of Key Aroma Compounds During Qidan Tea Roasting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Tea Samples
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Determination of Free Amino Acid Content
2.4. Descriptive Sensory Evaluation Methods
2.5. Model Reactions
2.6. Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME)
2.7. GC×GC–MS Analysis
2.8. Carbon Module Labeling (CAMOLA) Experiment
2.9. Kinetic Studies Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
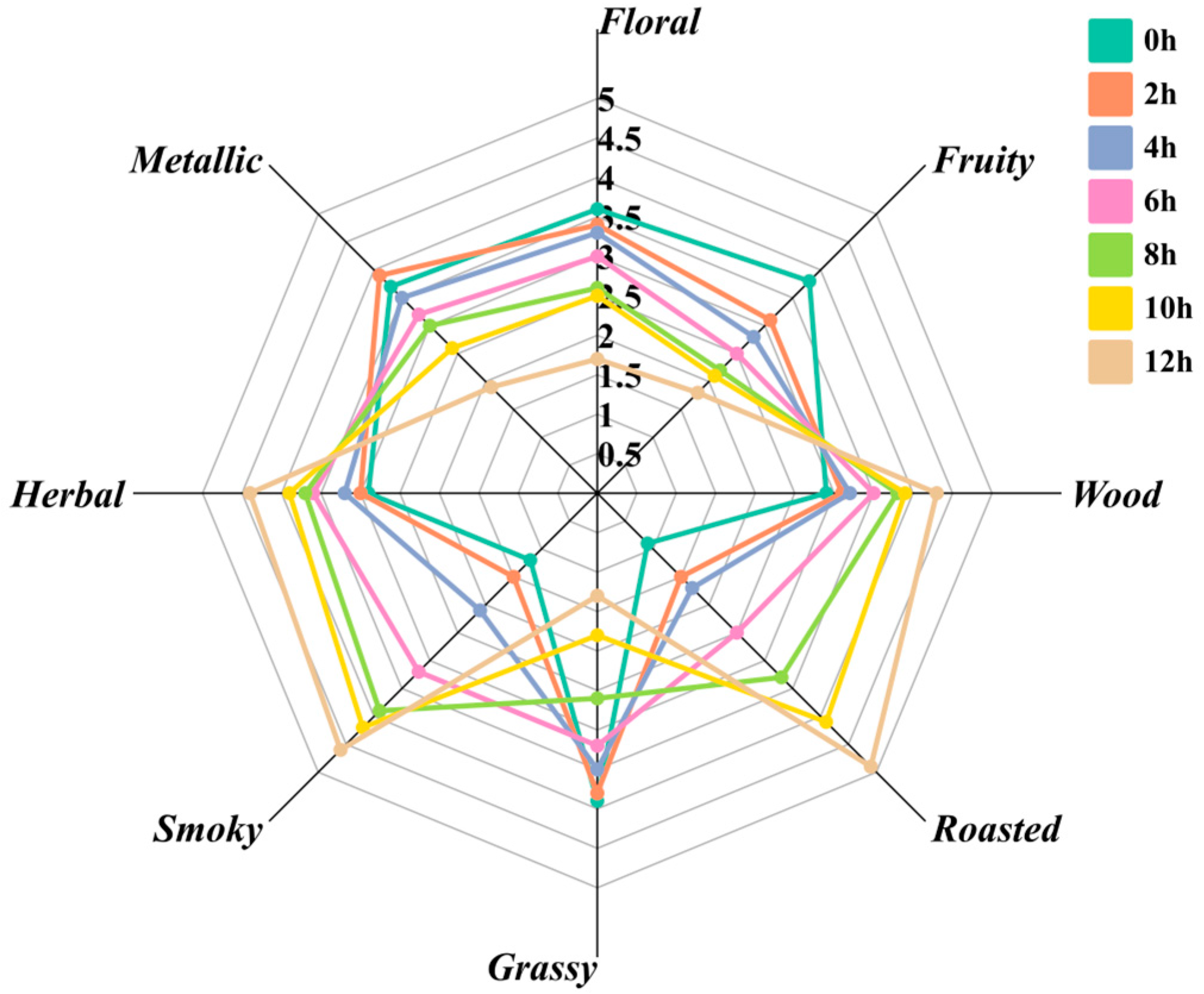
3.1. Analysis of Descriptive Sensory Evaluation Results of Different Roasting Time of Qidan
3.2. Determination and Analysis of Amino Acid Content
3.3. Labeling Glucose to Infer the Source of Aroma Compounds
3.4. Establishment of Maillard Reaction Model and Kinetic Equation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, X.; Ho, C.-T.; Wan, X.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Q.; Wen, Z. Changes of Volatile Compounds and Odor Profiles in Wuyi Rock Tea during Processing. Food Chem. 2021, 341, 128230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Yu, M.; Raza, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, H.; Xu, Y. Effect of Roasting Time on Aroma Quality of Shuixian Wuyi Rock Tea (Camellia sinensis). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 135, 106662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, F.; Sun, J.; Ni, L. Dynamic Changes of Volatile and Phenolic Components during the Whole Manufacturing Process of Wuyi Rock Tea (Rougui). Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.; Zheng, X.; Li, S. Tea Aroma Formation. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2015, 4, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P. Formation Pathway of Key Aroma-Active Compounds Generated by Maillard Reaction During Roasting of Wuyi Rock Tea. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Technology and Business University, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Liu, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Shan, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Yu, W.; Yang, Z.; Yu, X. Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis Reveals Dynamic Changes of Volatile and Non-Volatile Metabolites during Oolong Tea Manufacture. Food Res. Int. 2020, 128, 108778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, C.; Schieberle, P. Characterization of the Key Aroma Compounds in the Beverage Prepared from Darjeeling Black Tea: Quantitative Differences between Tea Leaves and Infusion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Song, H.; Lin, Y.; Guo, T.; Wang, L.; Granvogl, M.; Xu, Y. Differences of Characteristic Aroma Compounds in Rougui Tea Leaves with Different Roasting Temperatures Analyzed by Switchable GC-O-MS and GC × GC-O-MS and Sensory Evaluation. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4797–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Boekel, M.A.J.S. Formation of Flavour Compounds in the Maillard Reaction. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, Y.; Luo, S.; Wickremasinghe, R.L.; Yamanishi, T. Botany. Food Rev. Int. 1995, 11, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigematsu, H.; Kurata, T.; Kato, H.; Fujimaki, M. Volatile Compounds Formed on Roasting Dl-α-Alanine with d-Glucose. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1972, 36, 1631–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaylayan, V.A. Recent Advances in the Chemistry of Strecker Degradation and Amadori Rearrangement: Implications to Aroma and Color Formation. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2003, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, A.; Zhao, H.; Luo, D.; Luo, X.; Zhang, W. Quality and Flavor of Kiwifruit with Storage Using Kinetic Modeling and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS). Anal. Lett. 2025, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.K. The Kinetics of Thermal Generation of Flavour. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Diao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, G.; Gu, Y.; Ren, D.; Li, S.; Dong, W.; Yi, L. Sulfury/Roasty Fading Indicators in Roasted Coffees: Their Contribution and Applicability in Coffee Freshness Perception and Prediction. LWT 2025, 218, 117469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Song, H. Dynamic Changes in Qidan Aroma during Roasting: Characterization of Aroma Compounds and Their Kinetic Fitting. Foods 2024, 13, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 18745-2006; Product of Geographical Indication—Wuyi Rock-Essence Tea. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Gao, X.; Yu, M.; Han, X.; Song, H.; Pan, W.; Chen, W.; Xiong, W. Characterization of Odor-Active Compounds in Liuzhou River Snail Rice Noodles Soup by Sensory-Directed Flavor Analysis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 131, 106276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 23776-2018; Methodology for Sensory Evaluation of Tea. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Yang, P.; Wang, H.; Cao, Q.; Song, H.; Xu, Y.; Lin, Y. Aroma-Active Compounds Related to Maillard Reaction during Roasting in Wuyi Rock Tea. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 115, 104954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Bai, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, L.; Mu, Y.; Shakoor, A.; Fan, B.; Wang, F. The Number and Position of Unsaturated Bonds in Aliphatic Aldehydes Affect the Cysteine-Glucose Maillard Reaction: Formation Mechanism and Comparison of Volatile Compounds. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Li, T.; Wan, S.; Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; Raza, A.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, H. Study of Aroma Generation Pattern during Boiling of Hot Pot Seasoning. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.V.; Bowyer, M.C.; Roach, P.D. L-Theanine: Properties, Synthesis and Isolation from Tea. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qu, F.; Wang, P.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Han, Y.; Zhang, X. Characterization Analysis of Flavor Compounds in Green Teas at Different Drying Temperature. LWT 2022, 161, 113394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, Q. A Review on Formation Mechanism, Determination and Safety Assessment of Furfural and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) in Foods. Food Sci. 2012, 33, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.; Rappert, S. Pyrazines: Occurrence, Formation and Biodegradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ho, C.-T.; Schwab, W.; Song, C.; Wan, X. Aroma Compositions of Large-Leaf Yellow Tea and Potential Effect of Theanine on Volatile Formation in Tea. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhong, Q.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yao, W. Kinetic Study on the Generation of Furosine and Pyrraline in a Maillard Reaction Model System of D-Glucose and l-Lysine. Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, M.; Osorio, J.; Heeres, H.J.; Chejne, F. Kinetic Studies on Cocoa Roasting Including Volatile Characterization. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnavi, F.; Alizadeh, S.R.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.A. Pyrrolopyrazine Derivatives: Synthetic Approaches and Biological Activities. Med. Chem. Res. 2021, 30, 1981–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No | Amino Acids | Molecular Weight | Standard Curve | R2 | Concentration (mg/mL) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 2 h | 4 h | 6 h | 8 h | 10 h | 12 h | |||||
| 1 | Asp | 133.1 | y = 106.13x + 2.263 | 0.9926 | 28.35 ± 3.14 a | 29.11 ± 4.21 a | 23.19 ± 3.14 b | 20.42 ± 2.41 b | 16.27 ± 0.14 c | 18.13 ± 3.14 c | 23.43 ± 6.27 b |
| 2 | Glu | 147.1 | y =186.24x − 1.652 | 0.9947 | 59.99 ± 10.24 a | 48.54 ± 2.93 b | 42.29 ± 3.52 b | 41.79 ± 3.57 b | 34.93 ± 1.47 c | 23.75 ± 9.11 d | 16.83 ± 0.42 e |
| 3 | Ser | 105.1 | y = 129.82x − 4.001 | 0.9736 | 26.07 ± 6.31 a | 27.37 ± 4.53 a | 24.40 ± 4.17 a | 21.02 ± 6.07 a | 14.13 ± 2.86 b | 14.25 ± 3.13 b | 10.20 ± 2.14 b |
| 4 | His | 155.2 | y = 244.16x + 2.171 | 0.9947 | 21.11 ± 3.18 b | 23.06 ± 1.12 b | 28.31 ± 13.21 a | 23.94 ± 1.59 b | 14.41 ± 11.12 c | 22.66 ± 12.71 b | 12.17 ± 3.18 c |
| 5 | Gly | 75.1 | y = 173.12x + 0.806 | 0.9867 | 2.64 ± 0.25 a | 1.94 ± 0.51 b | 1.01 ± 0.08 b | - | - | - | - |
| 6 | Thr | 119.1 | y = 118.05x − 0.813 | 0.9946 | 10.18 ± 2.13 a | 12.68 ± 1.09 a | 12.20 ± 4.36 a | 6.10 ± 0.04 b | 5.29 ± 1.52 b | 6.84 ± 0.57 b | 3.24 ± 0.04 c |
| 7 | Arg | 174.2 | y = 272.84x − 3.179 | 0.9892 | 8.82 ± 2.98 b | 13.90 ± 4.38 a | 14.41 ± 6.38 a | 9.30 ± 1.73 b | 10.10 ± 4.79 b | 5.48 ± 1.98 c | - |
| 8 | Ala | 89.1 | y = 150.76x + 3.308 | 0.9878 | 11.99 ± 3.82 a | 12.67 ± 4.43 a | 10.90 ± 2.16 a | 7.36 ± 1.71 b | 3.21 ± 1.36 c | 4.77 ± 1.07 c | 3.12 ± 0.78 c |
| 9 | Tyr | 181.2 | y = 269.11x − 1.592 | 0.9831 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 10 | Cys | 121.2 | y = 193.99x + 0.254 | 0.9885 | 13.72 ± 1.77 a | 15.75 ± 4.11 a | 10.61 ± 4.36 b | 9.18 ± 365.49 b | 3.40 ± 0.44 c | 2.47 ± 1.31 c | 1.20 ± 0.09 c |
| 11 | Val | 117.2 | y = 111.16x − 1.667 | 0.9972 | 7.02 ± 3.53 b | 12.78 ± 1.03 a | 10.96 ± 2.35 a | 8.13 ± 2.74 b | 5.44 ± 4.43 c | 2.54 ± 0.82 d | 1.43 ± 0.62 d |
| 12 | Met | 149.2 | y = 198.02x − 0.456 | 0.9906 | 3.13 ± 0.97 a | 2.65 ± 1.11 b | 5.00 ± 1.88 a | 3.89 ± 0.13 a | 1.21 ± 0.40 b | 0.23 ± 0.07 c | 0.58 ± 0.01 c |
| 13 | Phe | 165.2 | y = 168.98x + 4.169 | 0.9953 | 14.50 ± 5.03 a | 15.39 ± 1.53 a | 11.21 ± 7.54 b | 5.96 ± 3.08 c | 6.16 ± 4.17 c | 2.66 ± 0.44 d | 1.75 ± 0.22 d |
| 14 | Ile | 131.2 | y = 196.92x − 1.296 | 0.9882 | 5.13 ± 0.89 a | 5.80 ± 1.98 a | 3.78 ± 0.33 b | 3.28 ± 0.97 b | 5.94 ± 0.09 a | 3.80 ± 1.32 b | 4.63 ± 1.31 b |
| 15 | Leu | 131.2 | y = 189.35x + 1.067 | 0.9743 | 1.74 ± 0.13 a | 0.47 ± 0.124 b | - | - | - | - | - |
| 16 | Lys | 146.2 | y = 153.69x − 0.885 | 0.9877 | 8.63 ± 2.43 a | 6.42 ± 1.88 b | 5.40 ± 1.92 b | 5.52 ± 0.25 b | 3.47 ± 1.129 c | 3.65 ± 1.69 c | 1.93 ± 0.13 d |
| 17 | The | 174.2 | y = 120.98x − 17.923 | 0.9913 | 261.12 ± 11.24 a | 264.12 ± 21.35 a | 184.18 ± 11.24 b | 141.92 ± 4.13 c | 121.12 ± 11.75 c | 80.19 ± 7.13 d | 60.34 ± 11.21 d |
| No. | Compounds | m/z a | Molecular Formula | System b | 13C-Labeled | Relative Distributions of Isotopologues (%) c | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | M + 1 | M + 2 | M + 3 | M + 4 | M + 5 | M + 6 | M + 7 | ||||||
| 1 | 3-Methylbutyraldehyde | 86 | C5H10O | A | all | 100 | |||||||
| half | 100 | ||||||||||||
| 2 | Furfuryl alcohol | 98 | C5H6O2 | A | all | 40 | 60 | ||||||
| half | 40 | 20 | 40 | ||||||||||
| 3 | Hexanal | 100 | C6H12O | A | all | 41 | 59 | ||||||
| half | 40 | 30 | 30 | ||||||||||
| 4 | Furfural | 96 | C5H4O2 | A | all | 100 | |||||||
| half | 32 | 32 | 36 | ||||||||||
| 5 | Benzaldehyde | 106 | C7H6O | A | all | 100 | |||||||
| half | 100 | ||||||||||||
| 6 | 5-Methylfurfural | 110 | C6H6O2 | A | all | 50 | 50 | ||||||
| half | 100 | ||||||||||||
| 7 | 2,3-Butanedione | 86 | C4H6O2 | A | all | 100 | |||||||
| half | 33 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 37 | ||||||||
| 8 | Pyrazine | 80 | C4H4N2 | A | all | 100 | |||||||
| half | 30 | 50 | 20 | ||||||||||
| 9 | 2-Methylpyrazine | 94 | C5H6N2 | A | all | 100 | |||||||
| half | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | |||||||||
| 10 | 2,5-Dimethylpyrazine | 108 | C6H8N2 | A | all | 100 | |||||||
| half | 23 | 50 | 27 | ||||||||||
| 11 | 2,3-Dimethylpyrazine | 108 | C6H8N2 | A | all | 100 | |||||||
| half | 33 | 46 | 21 | ||||||||||
| 12 | 2-Vinylpyrazine | 106 | C6H6N2 | A | all | 40 | 30 | 30 | |||||
| half | 40 | 30 | 30 | ||||||||||
| 13 | 2-Pyrrolecarboxaldehyde | 95 | C5H5NO | A | all | 46 | 54 | ||||||
| half | 20 | 26 | 10 | 30 | 14 | ||||||||
| 14 | 2-Acetylpyrrole | 109 | C6H7NO | A | all | 100 | |||||||
| half | 30 | 70 | |||||||||||
| 15 | 2-Acetylfuran | 110 | C6H6O2 | A | all | 70 | 30 | ||||||
| half | 50 | 50 | 30 | ||||||||||
| 16 | 2,5-dimethyl-1-propyl-1H-pyrrole | 137 | C9H15N | A | all | 30 | 70 | ||||||
| half | 25 | 10 | 40 | 7 | 8 | 10 | |||||||
| 17 | N-ethylacetamide | 87 | C4H9NO | A | all | 29 | 71 | ||||||
| half | 100 | ||||||||||||
| 18 | Nonanoic acid | 158 | C9H18O2 | A | all | 100 | |||||||
| half | 100 | ||||||||||||
| No. | Compounds | m/z a | Molecular Formula | D5-Labeled | Relative Distributions of Isotopologues (%) b | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | M + 1 | M + 2 | M + 3 | M + 4 | M + 5 | |||||
| 1 | Furfuryl alcohol | 98 | C5H6O2 | all | 100 | |||||
| half | 100 | |||||||||
| 2 | Hexanal | 100 | C6H12O | all | 100 | |||||
| half | 100 | |||||||||
| 3 | Furfural | 96 | C5H4O2 | all | 100 | |||||
| half | 100 | |||||||||
| 4 | 2-Methylfuran | 82 | C5H6O | all | 80 | 20 | ||||
| half | 90 | 10 | ||||||||
| 5 | 1-Ethyl-1H-pyrrole | 95 | C6H9N | all | 100 | |||||
| half | 100 | |||||||||
| No. | Compounds | CAS | Reaction Temperature (°C) | Fitted Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 100 | y = 0.2379x − 0.00247 | 0.9149 |
| 110 | y = 0.41551e0.01314x + 0.03794 | 0.9148 | |||
| 120 | y = 0.13824e0.01326x + 0.31244 | 0.9384 | |||
| 2 | 2-Methylpyrazine | 109-08-0 | 100 | y = 0.06502x − 4.52855 | 0.8195 |
| 110 | y = 0.08362x − 4.14681 | 0.9526 | |||
| 120 | y = 0.13029x − 0.59493 | 0.8984 | |||
| 3 | 2,6-Dimethylpyrazine | 108-50-9 | 100 | y = 0.41071x − 0.25 | 0.995 |
| 110 | y = 0.49107x + 0.41071 | 0.9938 | |||
| 120 | y = 2.83929x − 2.86429 | 0.9984 | |||
| 4 | 2-Methylfuran | 534-22-5 | 100 | y = 0.00616x − 0.31015 | 0.915 |
| 110 | y = 0.12865e0.01288x − 0.14638 | 0.9018 | |||
| 120 | y = 0.61399e0.0133x − 0.20183 | 0.9584 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Song, H. Formation Mechanisms and Kinetic Modeling of Key Aroma Compounds During Qidan Tea Roasting. Foods 2025, 14, 2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122125
Gao X, Wang S, Wang Y, Song H. Formation Mechanisms and Kinetic Modeling of Key Aroma Compounds During Qidan Tea Roasting. Foods. 2025; 14(12):2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122125
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xing, Siyuan Wang, Ying Wang, and Huanlu Song. 2025. "Formation Mechanisms and Kinetic Modeling of Key Aroma Compounds During Qidan Tea Roasting" Foods 14, no. 12: 2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122125
APA StyleGao, X., Wang, S., Wang, Y., & Song, H. (2025). Formation Mechanisms and Kinetic Modeling of Key Aroma Compounds During Qidan Tea Roasting. Foods, 14(12), 2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122125





