Heterologous Expression of Recombinant Ginseng Tetradecapeptide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Evaluation of Its Biological Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Media
2.2. Reagents and DNA Manipulation Techniques
2.3. Molecular Construction and Transformation of S. cerevisiae
2.4. Expression of 7RS14α in Flasks
2.5. Protein Detection and Purification
2.6. Cell Culture, Treatment, and Activity Assay
2.7. Adipogenic Differentiation of Cells, Oil Red O Staining Observation, and Insulin-Resistant Cell Model Establishment
2.8. The Insulin Synergistic Effect on the Insulin-Resistant Cell Model Cells Was Assessed
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Engineering, Heterologous Expression, and Purification of Recombinant Ginseng Polypeptide
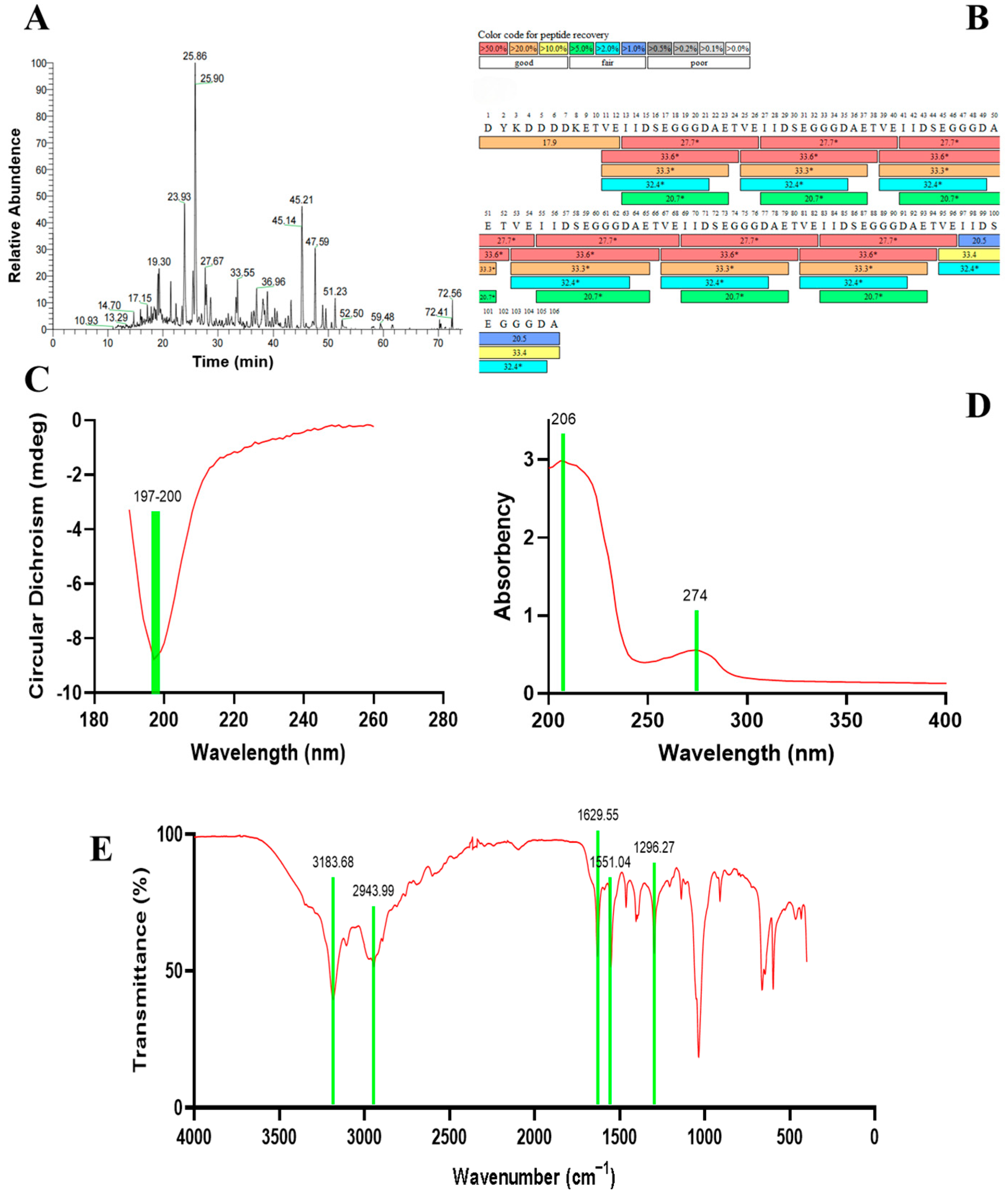
3.2. Characterization of Recombinant Ginseng Polypeptides
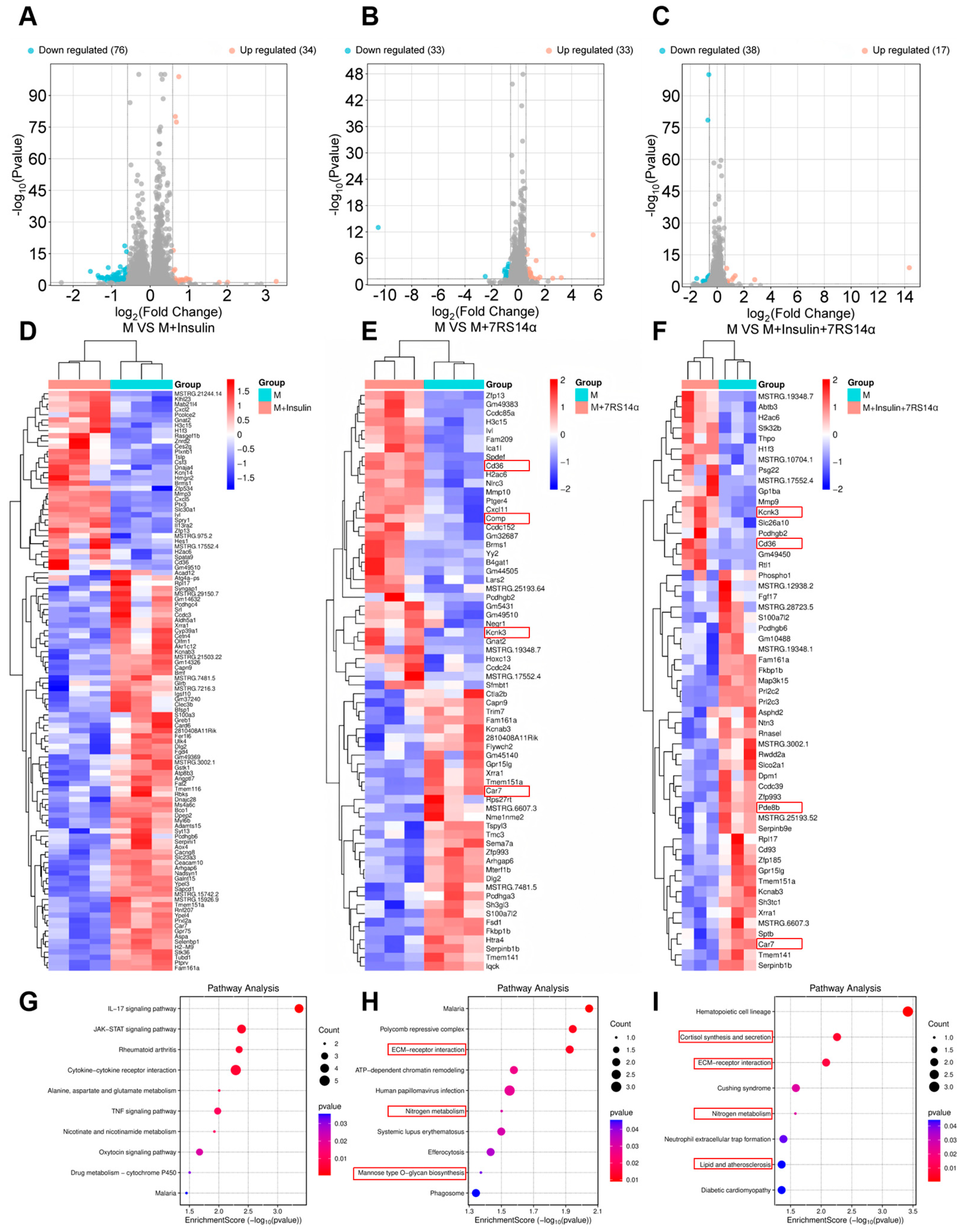
3.3. Evaluation of the Biological Activity of Recombinant Ginseng Tetradecapeptide
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAM | Complementary and Alternative Medicine |
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
| GRAS | Generally Recognized as Safe |
| YPD | Yeast Extract Peptone Dextrose Medium |
| SD-Ura | Synthetic Dropout Medium-Uracil |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-PolyAcrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| OD | Optical Density |
| LC-MS | Liquid Chromatograph Mass Spectrometer |
| WB | Western Blot |
| CD | Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy |
| CDNN | Cluster-based Discriminative Neural Networks |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| FTIR | Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| TIC | Total I on Chromatogram |
| Dex | Dexamethasone |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| FC | FoldChange |
| DEGs | Differentially Expressed Genes |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| CNY | Chinese Yuan |
References
- Cojic, M.; Kocic, R.; Klisic, A.; Kocic, G. The Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on Metabolic and Oxidative Stress Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A 6-Month Follow-Up Randomized Controlled Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 610893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rein, M.; Ben-Yacov, O.; Godneva, A.; Shilo, S.; Zmora, N.; Kolobkov, D.; Cohen-Dolev, N.; Wolf, B.-C.; Kosower, N.; Lotan-Pompan, M.; et al. Effects of Personalized Diets by Prediction of Glycemic Responses on Glycemic Control and Metabolic Health in Newly Diagnosed T2DM: A Randomized Dietary Intervention Pilot Trial. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Szarek, M.; Pitt, B.; Cannon, C.P.; Leiter, L.A.; McGuire, D.K.; Lewis, J.B.; Riddle, M.C.; In Zucchi, S.E.; Kosiborod, M.N.; et al. Sotagliflozin in Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Yang, X.; Meng, X.; Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Huang, D.; Wang, Z.; et al. Discovery of Novel PTP1B Inhibitors with Once—Weekly Therapeutic Potential for Type 2 Diabetes: Design, Synthesis, and In Vitro and In Vivo Investigations of BimBH3 Peptide Analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 3030–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naufel, M.F.; Telles, M.M.; Hachul, A.C.L.; Santamarina, A.B.; Oyama, L.M.; Coelho, F.M.S.; Ribeiro, E.B.; Pedroso, A.P. Bioactive Natural Products for the Prevention and Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2020, 67, 161–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquah, C.; Kodzu Vor, C.K.; Tosh, S.; Agyei, D. Anti-Diabetic Effects of Bioactive Peptides: Recent Advances and Clinical Implications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zeng, Y.; Hou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Luo, X.; Xi, W.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, M. The Soybean Peptide Aglycin Regulates Glucose Homeostasis in Type 2 Diabetic Mice via IR/IRS1 Pathway. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Lv, C.-N.; Lu, J. Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for Organ Fibrosis Disease. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, C. Recent Advances in Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer as a Herb for Anti-Fatigue: An Effects and Mechanisms Review. Foods 2021, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, S.; Kam, A.; Dutta, B.P.; Zhang, X.; Feng, N.; Sze, S.K.; Liu, C.-F.; Wang, X.; Tam, J.P. Broad-spectrum ginsentides are principal bioactives in unraveling the cure—All effects of ginseng. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, Y.-B.; Wang, Z.; Li, W. Research Progress on Chemical Constituents and Transformation Mechanism of Ginseng. Jilin Nongye Daxue Xuebao 2023, 45, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Muraoka, T.; Yamasaki, N.; Okuda, H. Preparation of Anti–lipolytic Substance from Panax ginseng. Planta Med. 1980, 38, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajiwara, H.; Aso, H.; Okubo, A.; Yamazaki, S. Inhibition of Adrenaline—Induced Lipolysis by Ginseng Polypeptide and Its Modified Peptides. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1998, 62, 2065–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, C.; Duan, Z.; Ma, P.; Ma, X.; Fan, D. Network Pharmacological Analysis Combined with Experimental Verification to Explore the Effect of Ginseng Polypeptide on the Improvement of Diabetes Symptoms in db/db Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 18537–18551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-H.; Jin, M.-H.; Hu, R.-Y.; Tang, S.; Li, K.-K.; Gong, X.-J.; Sun, Y.-S.; Wang, Y.-P.; Wang, Z.; Li, W. Exploring the Mechanism of Active Components from Ginseng to Manage Diabetes Mellitus Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Tan, D.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Shi, L. Gypenoside Ameliorates Insulin Resistance and Hyperglycemia via the AMPK—Mediated Signaling Pathways in the Liver of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, J.P.; Nguyen, G.K.T.; Loo, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, D.W.; Kam, A. Ginsentides: Cysteine and Glycine-rich Peptides from the Ginseng Family with Unusual Disulfide Connectivity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Yan, X.; Xu, Z.Z.; Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Z.H.; Wang, P.P. Pathway elucidation of bioactive rhamnosylated ginsenosides in Panax ginseng and their de novo high-level production by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Z.; Shi, G. Microbial production of small peptide: Pathway engineering and synthetic biology. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 2257–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandi, A.; Adam, D.; Zare, A.; Trinh, V.T.; Schaefer, S.L.; Burt, M.; Erb, T.J. Cell-free Biosynthesis Combined with Deep Learning Accelerates De Novo-development of Antimicrobial Peptides. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatwa, A.; Wang, W.; Hassan, Y.I.; Abraham, N.; Li, X.-Z.; Zhou, T. Challenges Associated With the Formation of Recombinant Protein Inclusion Bodies in Escherichia coli and Strategies to Address Them for Industrial Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2021, 9, 630551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.D.; Tong, Y.; Li, Y.; Tao, J.; Rao, S.Q.; Li, J.H.; Zhou, J.W.; Liu, S. Autoinduction AND Gate inhibits cell lysis to enhance protein production in Bacillus subtilis controlled by population density and cell physiological state. ACS Synth. Biol. 2023, 12, 2742–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goffeau, A.; Barrell, B.G.; Bussey, H.; Davis, R.W.; Dujon, B.; Feldmann, H.; Oliver, S.G. The Genome Sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A Platform for Functional Genomics. Science 1996, 274, 546–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrzanowski, G. Saccharomyces Cerevisiae—An Interesting Producer of Bioactive Plant Polyphenolic Metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, C.; Lage, P.; Vilela, A.; Mendes–Faia, A.; Mendes-Ferreira, A. Phenotypic and Metabolic Traits of Commercial Saccharomyces cerevisiae Yeasts. AMB Express 2014, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprodu, I.; Bunea, A.; Socaci, S.A.; Vodnar, D.C. Protease as a Tool for Regulating the Antioxidant Activity and Function of Brewer’s Yeast Protein. Molecules 2024, 29, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, N.A.; Suter, B.; Müller, S.; Rudolph, C. Development and optimisation of a defined high cell density yeast medium. Yeast 2020, 37, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippelt, A.; Nett, M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae as host for the recombinant production of polyketides and nonribosomal peptides. Microb. Cell Fact. 2021, 20, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.S.; Ferreira, C.; Pereira, J.O.; Pintado, M.E.; Carvalho, A.P. Spent brewer’s yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) as a potential source of bioactive peptides: An overview. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Qu, L.; Lei, H.; Duan, Z.; Zhu, C.; Yuwen, W.; Ma, X.; Fan, D. Expression of Multicopy Tandem Recombinant Ginseng Hexapeptide in Bacillus subtilis and the Evaluation of Antiaging Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 7266–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, S.D.; Fleming, C.; Berry, D.R.; Johnston, J.R. An improved lithium acetate method for yeast transformation. Biotechnol. Tech. 1991, 5, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, C.; Rigaud, C.; Chanteclaire, E.; Blandais, C.; Tassy-Freches, E.; Rico, C.A.; Javaud, C. PCR on yeast colonies: An improved method for glyco-engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paciello, L.; De Alteriis, E.; Mazzoni, C.; Palermo, V.; Zueco, J.; Parascandola, P. Performance of the auxotrophic Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741 as host for the production of IL-1β in aerated fed-batch reactor: Role of ACA supplementation, strain viability, and maintenance energy. Microb. Cell Fact. 2009, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Wan, X.; Yu, M.T.; He, Y.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, T.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Sun, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, W.J.; et al. A novel whole blood purifier for efficient capture and separation of circulating tumor cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 232, 115292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.F.; Chen, B.; Luo, Q.; Zao, X.R.; Liu, H.Z.; Li, Y.Q. Hulless barley polyphenol extract inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells and obesity related-enzymes. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 933068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sörmann, J.; Schewe, M.; Proks, P.; Jouen-Tachoire, T.; Rao, S.; Riel, E.B.; Agre, K.E.; Begtrup, A.; Dean, J.; Descartes, M. Gain-of-function mutations in KCNK3 cause a developmental disorder with sleep apnea. Nat Genet. 2022, 54, 1534–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H. Lipolysis engages CD36 to promote ZBP1—Mediated necroptosis—Impairing lung regeneration in COPD. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, R.; Georgiadis, C.; Syed, F.U.; Zhan, H.; Etuk, A.; Gkazi, S.A.; Preece, R.; Ottaviano, G.; Braybrook, T.; Chu, J.; et al. Base-Edited CAR7 T Cells for Relapsed T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nersisyan, S.; Novosad, V.; Giba Ryan, N.E.; Ushkaryov, Y.; Nikulin, S.; Tonevitsky, A. ECM–Receptor Regulatory Network and Its Prognostic Role in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 782699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Lee, Z.; Jeong, E.; Kim, S.; Seo, J.S.; Um, T.; Shim, J.S. Signaling Pathways Underlying Nitrogen Transport and Metabolism in Plants. BMB Rep. 2023, 56, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.F.; Aoki, K.; Akase, S.; Ishihara, M.; Liu, Y.S.; Yang, G.; Kizuka, Y.; Mizumoto, S.; Tiemeyer, M.; Gao, X.D.; et al. Global Mapping of Glycosylation Pathways in Human—Derived Cells. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 1195–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson-Manning, C. Elaboration of the Corticosteroid Synthesis Pathway in Primates through a Multistep Enzyme. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 2257–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khojasteh Malek Mohammad, K.; Bezsonov, E.E.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Role of Lipid Accumulation and Inflammation in Atherosclerosis: Focus on Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 707529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Narwal, S.; Kumar, V.; Prakash, O. α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Plants: A Natural Approach to Treat Diabetes. Pharmacogn Rev. 2011, 5, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, G.J.; Lee, S.H.; Park, K.S. Therapeutic potential of ginseng and its components for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.W.; Jiang, J.L.; Zou, J.J. Therapeutic potential of ginsenosides on diabetes: From hypoglycemic mechanism to clinical trials. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Strain or Plasmid | Description | Source/ Reference |
|---|---|---|
| BY4741 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C-derivative laboratory strain, MATa his3Δ1 leu2Δ0 met15Δ0 ura3Δ0 | lab stock |
| DH5α | Escherichia coli cloning strain | lab stock |
| pYES2 | plasmid E. coli–S. cerevisiae shuttle vector, AmpR for E. coli | lab stock |
| pET28-7RS14 | E. coli vector, AmpR, pET28 carrying seven replicate fragments of ginseng tetradecapeptide and FLAG tag. | Sagon |
| Name | Protein Secondary Structure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helix | Beta-Pleated Sheet | Beta-Turn | Rndm. Coil | ||
| Antiparallel | Parallel | ||||
| 7RS14α | 8.5% | 39.5% | 3.1% | 19.6% | 29.4% |
| Name | Microbial Synthesis | Plant Extraction | Chemical Synthesis |
|---|---|---|---|
| material cost | CNY 50 | CNY 2000 | CNY 2000 |
| time | a week | more than a week | more than a week |
| yield | 10–20 mg recombinant ginseng peptide | 2 mg ginseng peptide | 20 mg ginseng peptide |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, Y.; Ma, P.; Wang, P.; Zhu, C. Heterologous Expression of Recombinant Ginseng Tetradecapeptide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Evaluation of Its Biological Activity. Foods 2025, 14, 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122049
Qi Y, Ma P, Wang P, Zhu C. Heterologous Expression of Recombinant Ginseng Tetradecapeptide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Evaluation of Its Biological Activity. Foods. 2025; 14(12):2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122049
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Yi, Pei Ma, Pan Wang, and Chenhui Zhu. 2025. "Heterologous Expression of Recombinant Ginseng Tetradecapeptide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Evaluation of Its Biological Activity" Foods 14, no. 12: 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122049
APA StyleQi, Y., Ma, P., Wang, P., & Zhu, C. (2025). Heterologous Expression of Recombinant Ginseng Tetradecapeptide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Evaluation of Its Biological Activity. Foods, 14(12), 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122049





