Impact of Brown Rice as Adjunct on Beer Brewing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Beer Brewing Process
2.2.1. Grain Preparation
2.2.2. Wort Preparation
2.2.3. Fermentation
2.3. Determination of Indicators
2.3.1. Basic Physicochemical Characteristics
2.3.2. Antioxidant Properties
2.3.3. Volatile Compounds
- 1.
- HS-SPME pre-treatment
- 2.
- GC-MS analysis conditions
2.3.4. Sensory Analysis
2.3.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Physicochemical Indicators and Antioxidant Properties
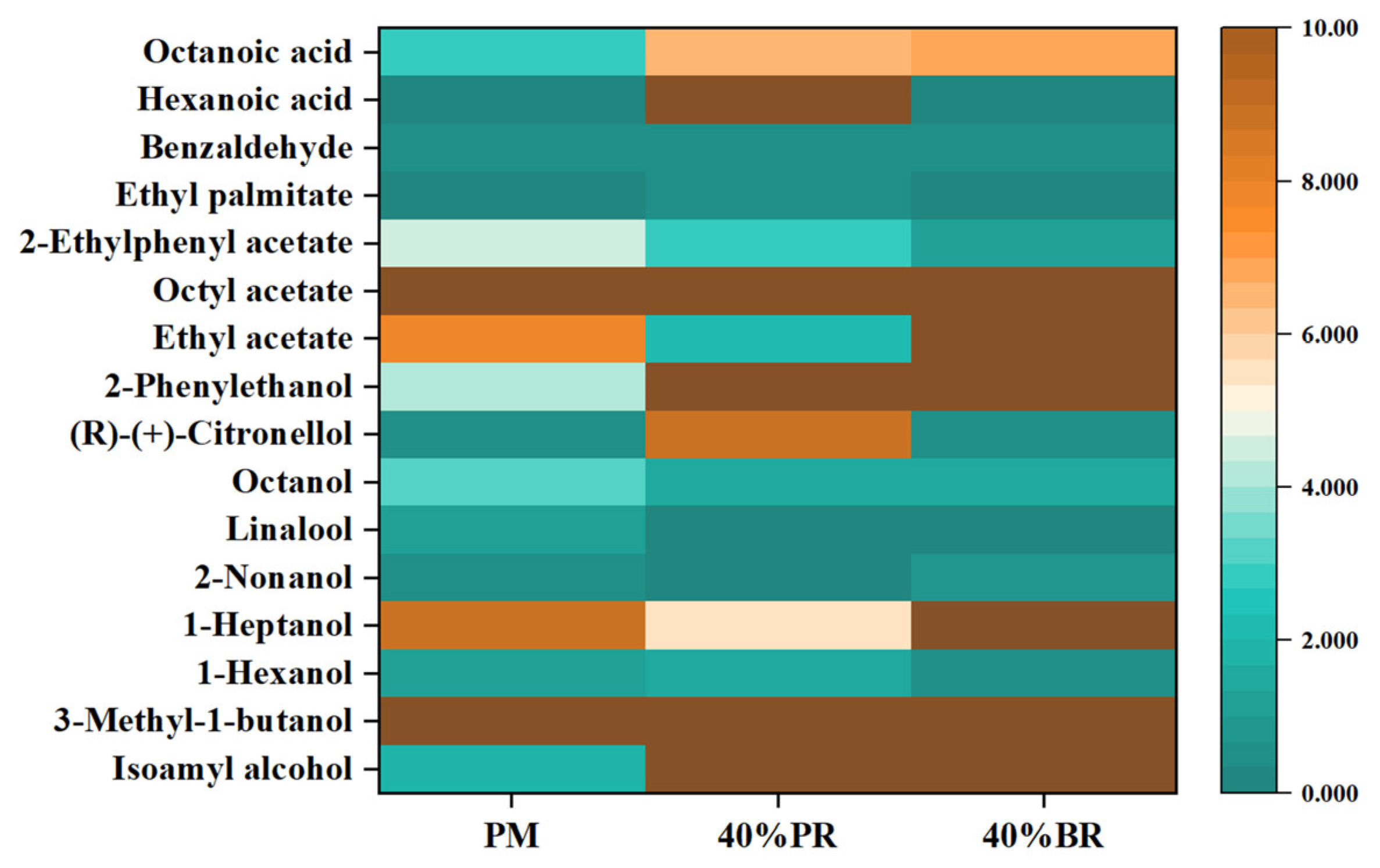
3.2. Volatile Compounds in Beer Samples
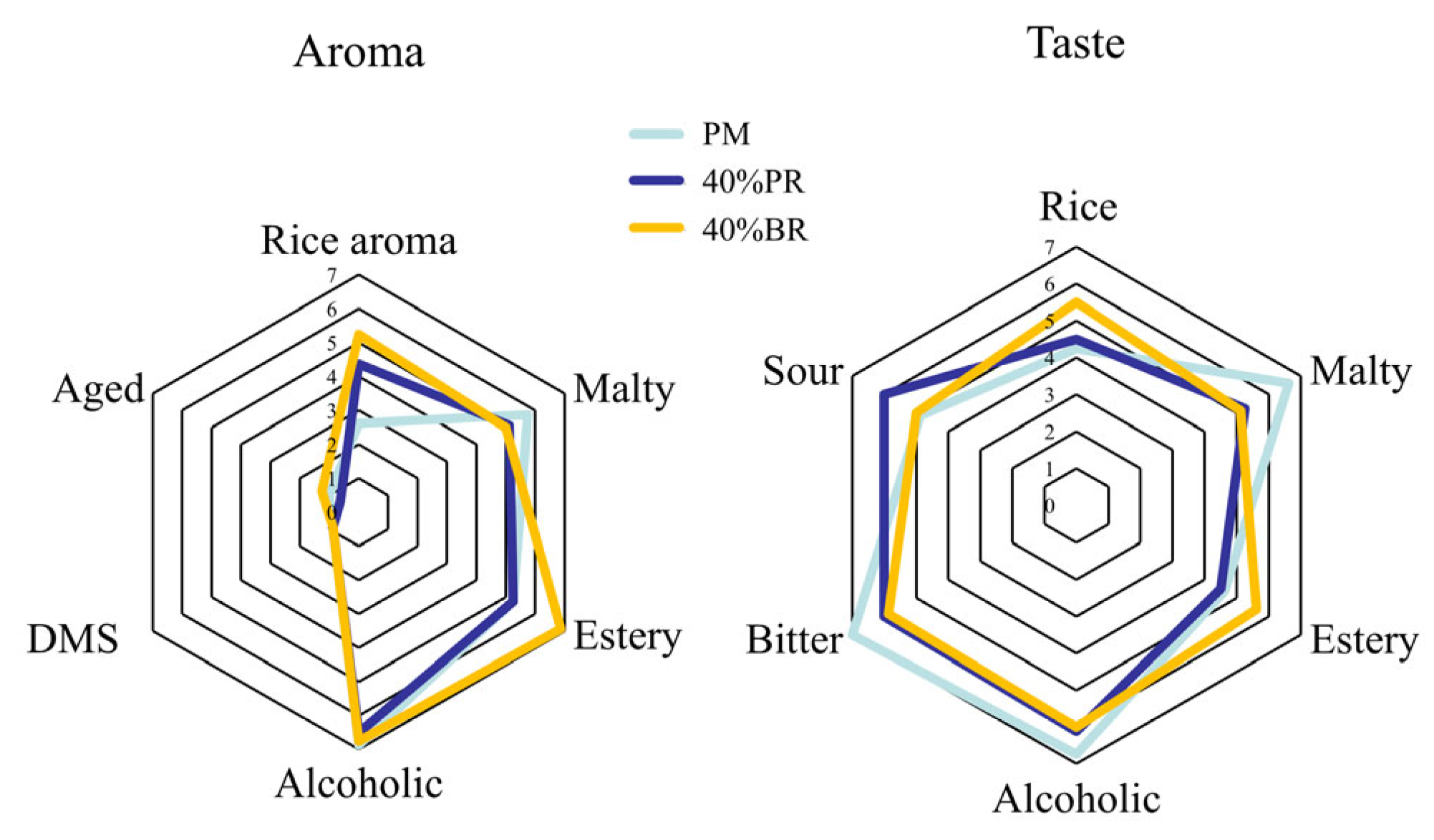
3.3. Sensory Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, B.L.; Shahin, F.; Selim, A.; Berjanskii, M.; Torres-Calzada, C.; Kovur, P.; Mandal, R.; Wishart, D.S. Automated beer analysis by NMR spectroscopy. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 5, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Delmond, A.R.; Nti, F.K. Dynamic analysis of source-based preferences: The case of imported beer in China. Bri. Food J. 2021, 123, 362–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczyński, P.; Iwaniuk, P.; Hrynko, I.; Łuniewski, S.; Łozowicka, B. The effect of the multi-stage process of wheat beer brewing on the behavior of pesticides according to their physicochemical properties. Food Control 2024, 160, 110356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirado-Kulieva, V.A.; Hernandez-Martinez, E.; Minchan-Velayarce, H.H.; Pasapera-Campos, S.E.; Luque-Vilca, O.M. A comprehensive review of the benefits of drinking craft beer: Role of phenolic content in health and possible potential of the alcoholic fraction. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanță, L.C.; Coldea, T.E.; Ignat, M.V.; Pop, C.R.; Tofană, M.; Mudura, E.; Borșa, A.; Pasqualone, A.; Zhao, H. Non-alcoholic and craft beer production and challenges. Processes 2020, 8, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brožová, M.; Matoulková, D.; Mikyška, A.; Kyselová, L. Barley malt substitutes—Their role today and in near future. Part 1—Sugar adjuncts and barley, corn and rice as cereal adjuncts. Kvasny Prumysl 2022, 68, 602–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, Y.J.; Ye, L.; Muller, J.; Ow, D.S.; Bi, X. Brewing with malted barley or raw barley: What makes the difference in the processes? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadini, G.; Porretta, S. Uncovering patterns of consumers’ interest for beer: A case study with craft beers. Food Res. Int. 2017, 91, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, P.; Kordialik-Bogacka, E. Alternatives to malt in brewing. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 65, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabija, A.; Ciocan, M.E.; Chetrariu, A.; Codină, G.G. Maize and sorghum as raw materials for brewing, A review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, H.B.; Song, M. Rice as an alternative feed ingredient in swine diets. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, A.S.; Wang, P.; Wang, N.; Yang, L.; Xiao, Z. Brown rice versus white rice: Nutritional quality, potential health benefits, development of food products, and preservation technologies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1070–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, S.A.; Shah, M.A.; Bosco, S.J.D.; Sunooj, K.V.; Farooq, S. A review on nutritional properties, shelf life, health aspects, and consumption of brown rice in comparison with white rice. Cereal Chem. 2020, 97, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, G.H.; Kringel, D.H.; Acunha, T.d.S.; Ferreira, C.D.; Dias, Á.R.G.; Zavareze, E.d.R.; de Oliveira, M. Cake of brown, black and red rice: Influence of transglutaminase on technological properties, in vitro starch digestibility and phenolic compounds. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, C.; Cunha, S.; Debyser, W.; Cook, D. Impacts of adjunct incorporation on flavor stability metrics at early stages of beer production. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2023, 81, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, H.; Marconi, O.; Regnicoli, G.F.; Perretti, G.; Fantozzi, P. Production of a saccharifying rice malt for brewing using different rice varieties and malting parameters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5369–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EBC. European Brewery Convention Analytica–EBC; Fachverlag Hans Carl: Nürnberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Yin, Y.; Fang, W.; Yang, Z. Potential of germinated brown rice in beer brewing. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 114, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, Z.; Liu, X.; Yin, Y.; Yang, Z.; Fang, W. Effects of crystal malts as adjunct on the quality of craft beers. J. Food Process. Pres. 2022, 46, e16684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, H.; Ceccaroni, D.; Marconi, O.; Sileoni, V.; Perretti, G.; Fantozzi, P. Development of an all rice malt beer: A gluten free alternative. LWT 2016, 67, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.K.; Kimi, L.; Haripriya, S.; Kang, N. Effects of polishing on proximate composition, physico-chemical characteristics, mineral composition and antioxidant properties of pigmented rice. Rice Sci. 2017, 24, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordialik-Bogacka, E.; Bogdan, P.; Pielech-Przybylska, K.; Michalowska, D. Suitability of unmalted quinoa for beer production. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 5027–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha dos Santos Mathias, T.; Moreira Menezes, L.; Camporese Sérvulo, E.F. Effect of maize as adjunct and the mashing proteolytic step on the brewer wort composition. Beverages 2019, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; He, L.; Wen, J.; Li, L. Impact of Qingke (Hulless barley) application on antioxidant capacity and flavor compounds of beer. J. Cereal Sci. 2022, 109, 103624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.E.; Stewart, G.G. Free amino nitrogen in brewing. Fermentation 2019, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błażewicz, J.; Zembold-Guła, A. Milled Corn products in worts production. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2007, 57, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Cadenas, R.; Caballero, I.; Nimubona, D.; Blanco, C.A. Brewing with starchy adjuncts: Its influence on the sensory and nutritional properties of beer. Foods 2021, 10, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, H.Y.; Chung, H.J.; Oh, S.-K. Starch structure of raw materials with different amylose contents and the brewing quality characteristics of Korean rice beer. Foods 2023, 12, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.; Zhao, H.; Lei, H.; Zhao, M. Effects of nitrogen composition on fermentation performance of brewer’s yeast and the absorption of peptides with different molecular weights. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiels, P.; Debyser, W.; Courtin, C.; Langenaeken, N. Filtration enzymes applied during mashing affect beer composition and viscosity. J. Inst. Brew. 2023, 129, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorke, J.; Cook, D.; Ford, R. Brewing with unmalted cereal adjuncts: Sensory and analytical impacts on beer quality. Beverages 2021, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trummer, J.; Watson, H.; De Clippeleer, J.; Poreda, A. Brewing with 10% and 20% malted lentils—Trials on laboratory and pilot scales. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humia, B.V.; Santos, K.S.; Schneider, J.K.; Leal, I.L.; de Abreu Barreto, G.; Batista, T.; Machado, B.A.S.; Druzian, J.I.; Krause, L.C.; da Costa Mendonca, M.; et al. Physicochemical and sensory profile of Beauregard sweet potato beer. Food Chem. 2020, 312, 126087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, J.C.O.; Pereira de Gusmão, R.; Tejo Cavalcanti, M.; de Luna Freire, K.R.; Moreira de Carvalho, L.; Sousa Galvão, M.; Madruga, M.S.; Abrantes da Silva Souza, T.; Lisboa, H.M.; Nascimento, A.P.S. The role of red rice in craft beer: A sensory and nutritional evaluation. Cereal Chem. 2024, 102, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccaroni, D.; Sileoni, V.; Marconi, O.; De Francesco, G.; Lee, E.G.; Perretti, G. Specialty rice malt optimization and improvement of rice malt beer aspect and aroma. LWT 2019, 99, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Fan, W.; Xu, Y. Changes in Volatile Compounds of Chinese rice wine wheat Qu during fermentation and storage. J. Inst. Brew. 2009, 115, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniran, A.O.; Hiralal, L.; Mokoena, M.P.; Pillay, B. Flavour-active volatile compounds in beer: Production, regulation and control. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 123, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, H.E.; Santos, I.C.; Hildenbrand, Z.L.; Schug, K.A. A review of the analytical methods used for beer ingredient and finished product analysis and quality control. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1085, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jia, J.; Meng, Q.; Song, H.; Qiu, R. Characterization of key odor-active compounds in Chinese-style traditional craft beer “Li”. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 134, 106575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, L.; Schieberle, P. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in an American Bourbon whisky by quantitative measurements, aroma recombination, and omission studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5820–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. Black rice addition prompted the beer quality by the extrusion as pretreatment. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 3664–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Nam, P.W.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, K.G. Volatile compounds isolated from rice beers brewed with three medicinal plants. J. Inst. Brew. 2013, 119, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; He, Y.; Ma, C.; Li, H. Improvement of beer flavour with extruded rice as adjunct. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 123, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladokun, O.; Tarrega, A.; James, S.; Smart, K.; Hort, J.; Cook, D. The impact of hop bitter acid and polyphenol profiles on the perceived bitterness of beer. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Indicators | PM | PR | BR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture (g/100 g) | 8.25 ± 0.27 b | 13.00 ± 0.12 a | 14.24 ± 0.10 a |
| Fat (%) | 1.97 ± 0.04 b | 2.02 ± 0.13 a | 3.38 ± 0.05 a |
| Protein (%) | 12.09 ± 0.11 a | 4.12 ± 0.63 c | 6.85 ± 0.11 b |
| Starch (%) | 63.65 ± 0.73 c | 78.99 ± 0.91 a | 72.92 ± 1.36 b |
| Ash (%) | 1.85 ± 0.05 a | 0.14 ± 0.05 c | 1.04 ± 0.13 b |
| Extract (%) | 75.90 ± 0.14 a | 68.26 ± 0.23 b | 72.43 ± 0.65 a |
| Indicators | PM | 40% PR | 40% BR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colour (EBC) | 11.82 ± 0.05 a | 9.35 ± 0.011 b | 11.22 ± 0.04 a |
| pH | 5.77 ± 0.17 a | 6.02 ± 0.13 a | 5.85 ± 0.10 a |
| Viscosity (mm2/s) | 1.63 ± 0.26 a | 1.11 ± 0.05 b | 1.51 ± 0.13 a |
| Mashing time (min) | <15 | 30~45 | 30~45 |
| Extract (g/100 g) | 13.65 ± 0.14 a | 11.08 ± 0.10 b | 13.23 ± 0.15 a |
| FAN (mg/L) | 304.12 ± 0.12 a | 144.12 ± 0.03 c | 243.60 ± 0.17 b |
| Reducing sugar (g/100 mL) | 8.13 ± 0.24 a | 8.24 ± 0.21 a | 8.28 ± 0.12 a |
| Indicators | PM | 40% PR | 40% BR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original extract (°P) | 10.80 ± 0.05 a | 9.77 ± 0.05 c | 10.18 ± 0.22 b |
| Real extract (%) | 4.65 ± 0.05 b | 4.83 ± 0.05 b | 5.38 ± 0.22 a |
| Alcohol (%vol) | 3.96 ± 0.10 a | 3.18 ± 0.02 b | 3.08 ± 0.05 b |
| Fermentation degree (%) | 58.33 ± 0.26 a | 51.88 ± 0.26 b | 48.50 ± 1.03 c |
| Viscosity (mm2/s) | 1.53 ± 0.11 a | 1.30 ± 0.09 b | 1.45 ± 0.11 a |
| Colour (EBC) | 11.25 ± 0.03 a | 7.01 ± 0.10 b | 7.40 ± 0.09 b |
| pH | 4.02 ± 0.01 b | 4.66 ± 0.04 a | 3.98 ± 0.18 b |
| Bitterness (IBU) | 17.75 ± 0.04 a | 17.35 ± 0.24 a | 17.15 ± 0.11 a |
| DPPH (mmol TE/L) | 0.50 ± 0.15 a | 0.12 ± 0.05 b | 0.55 ± 0.11 a |
| ABTS (mmol TE/L) | 0.78 ± 0.28 a | 0.40 ± 0.05 b | 0.75 ± 0.30 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Zhu, J.; Yin, Y.; Yang, Z. Impact of Brown Rice as Adjunct on Beer Brewing. Foods 2025, 14, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122019
Wang Y, Zhao X, Liu S, Zhu J, Yin Y, Yang Z. Impact of Brown Rice as Adjunct on Beer Brewing. Foods. 2025; 14(12):2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122019
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yufeng, Xinyi Zhao, Suya Liu, Jiangyu Zhu, Yongqi Yin, and Zhengfei Yang. 2025. "Impact of Brown Rice as Adjunct on Beer Brewing" Foods 14, no. 12: 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122019
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhao, X., Liu, S., Zhu, J., Yin, Y., & Yang, Z. (2025). Impact of Brown Rice as Adjunct on Beer Brewing. Foods, 14(12), 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122019







