Effect of Combining Surfactants with Potato Protein Hydrolysates on Their Emulsifying and Antioxidant Properties in Fish-Oil-in-Water Emulsions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Production of Small-Scale Emulsions
2.3. Production of Large-Scale Emulsions and Storage Experiment
2.4. Physical Stability of Emulsions
2.4.1. Emulsion Stability
2.4.2. Droplet Size Distribution
2.4.3. Zeta Potential
2.5. Oxidative Stability of Emulsions
2.5.1. Peroxide Value
2.5.2. Tocopherol Content
2.5.3. Secondary Volatile Oxidation Compounds—Dynamic Headspace Coupled with GC-MS
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of Optimal Surfactant to Protein Ratio in Small-Scale Emulsion Study
3.2. Physical Stability of the Emulsions Produced on a Large Scale with Fractions of PPH
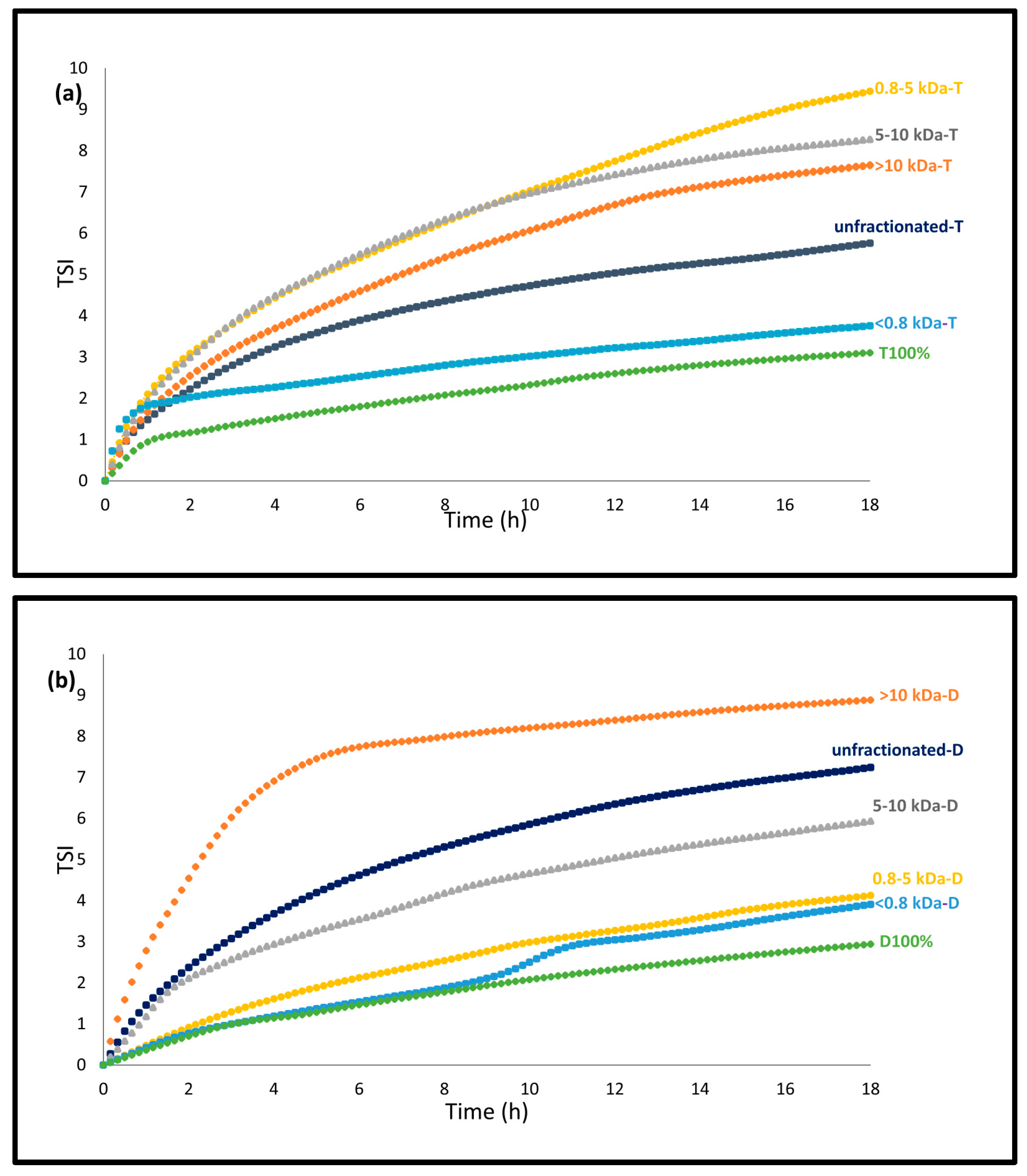
3.2.1. Emulsion Stability-TSI
3.2.2. Droplet Size Distribution and Zeta Potential
3.3. Oxidative Stability
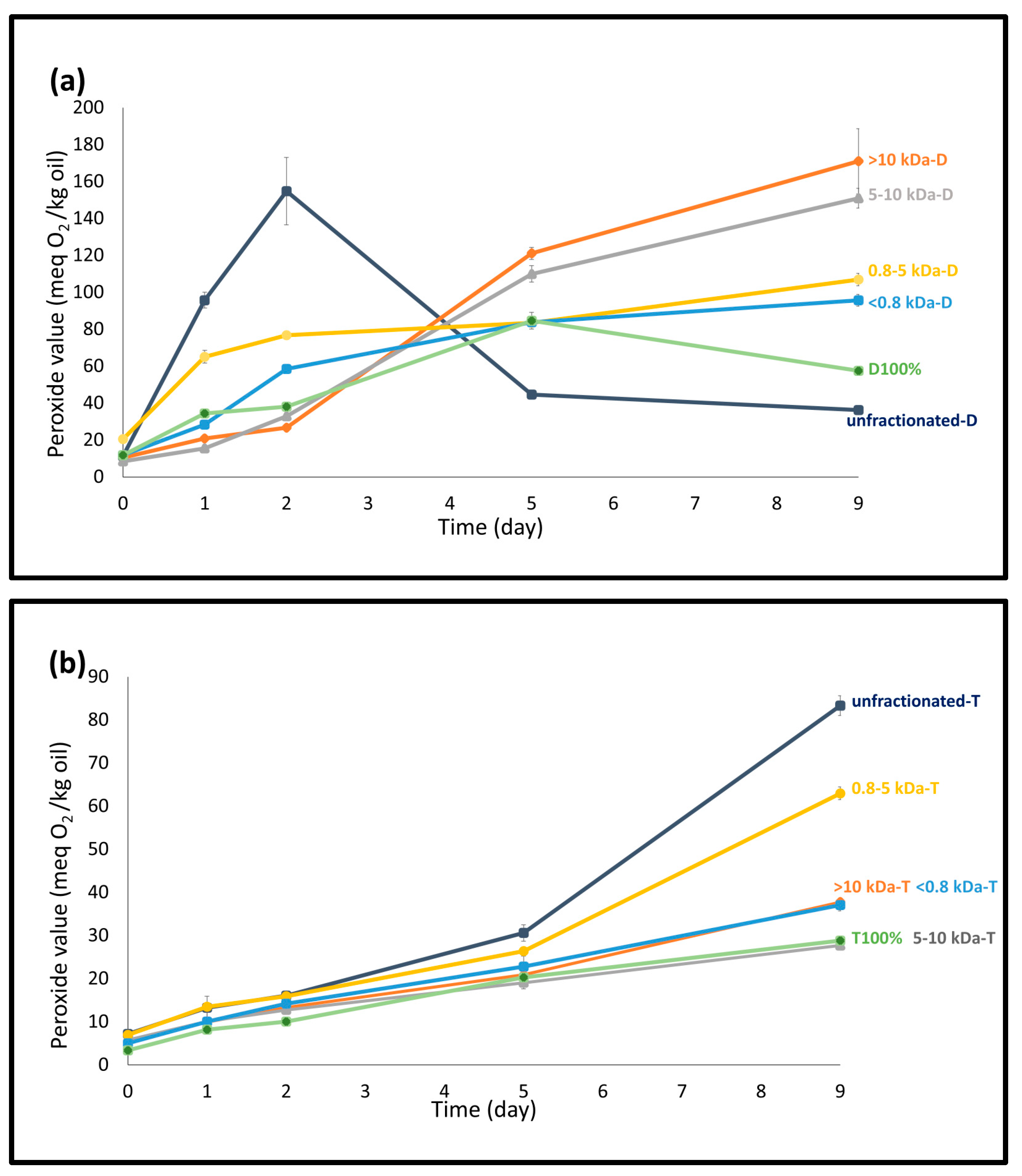
3.3.1. Formation of Hydroperoxides
3.3.2. Consumption of Tocopherols
3.3.3. Development of Secondary Oxidation Volatile Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PUFAs | Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids |
| DATEM | Diacetyl Tartaric Acid Ester of Mono- and Diglycerides |
| PPH | Potato Protein Hydrolysate |
| PV | Peroxide Value |
| TSI | Turbiscan Stability Index |
| TW20 | Tween 20 |
References
- Arab-Tehrany, E.; Jacquot, M.; Gaiani, C.; Imran, M.; Desobry, S.; Linder, M. Beneficial effects and oxidative stability of omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 25, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids, inflammation, and inflammatory diseases. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1505S–1519S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, B.; Brothersen, C.; McMahon, D.J. Fortification of Foods with Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, K.; Uemura, M. Effective Prevention of Oxidative Deterioration of Fish Oil: Focus on Flavor Deterioration. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Impact of whey protein emulsifiers on the oxidative stability of salmon oil-in-water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villeneuve, P.; Bourlieu-lacanal, C.; Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; Mcclements, D.J.; Decker, E.A.; Villeneuve, P.; Bourlieu-lacanal, C.; Durand, E. Lipid oxidation in emulsions and bulk oils: A review of the importance of micelles. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghelichi, S.; Hajfathalian, M.; Yeşiltaş, B.; Sørensen, A.; García-moreno, P.J.; Jacobsen, C. Oxidation and oxidative stability in emulsions. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 1864–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Decker, E. Interfacial Antioxidants: A Review of Natural and Synthetic Emulsifiers and Coemulsifiers That Can Inhibit Lipid Oxidation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real Hernandez, L.M.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Enzymatic Production, Bioactivity, and Bitterness of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum) Peptides. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1913–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandelli, A.; Daroit, D.J. Unconventional microbial proteases as promising tools for the production of bioactive protein hydrolysates. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 4714–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasri, M. Protein Hydrolysates and Biopeptides: Production, Biological Activities, and Applications in Foods and Health Benefits. A Review, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 81. [Google Scholar]
- Alting, A.C.; Pouvreau, L.; Giuseppin, M.L.F.; van Nieuwenhuijzen, N.H. Potato Proteins; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2011; Volume 2008. [Google Scholar]
- García-Moreno, P.J.; Gregersen, S.; Nedamani, E.R.; Olsen, T.H.; Marcatili, P.; Overgaard, M.T.; Andersen, M.L.; Hansen, E.B.; Jacobsen, C. Identification of emulsifier potato peptides by bioinformatics: Application to omega-3 delivery emulsions and release from potato industry side streams. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Moreno, P.J.; Jacobsen, C.; Marcatili, P.; Gregersen, S.; Overgaard, M.T.; Andersen, M.L.; Sørensen, A.D.M.; Hansen, E.B. Emulsifying peptides from potato protein predicted by bioinformatics: Stabilization of fish oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen Echers, S.; Jafarpour, A.; Yesiltas, B.; García-Moreno, P.J.; Greve-Poulsen, M.; Hansen, D.K.; Jacobsen, C.; Overgaard, M.T.; Hansen, E.B. Targeted hydrolysis of native potato protein: A novel workflow for obtaining hydrolysates with improved interfacial properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.M.; Damgaard, H.; Greve-Poulsen, M.; Larsen, L.B.; Hammershøj, M. Foam and emulsion properties of potato protein isolate and purified fractions. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 74, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.W.; Han, C.H.; Lee, M.H.; Hsu, F.L.; Hou, W.C. Patatin, the tuber storage protein of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.), exhibits antioxidant activity in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4389–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesiltas, B.; García-Moreno, P.J.; Mikkelsen, R.K.; Echers, S.G.; Hansen, D.K.; Greve-Poulsen, M.; Hyldig, G.; Hansen, E.B.; Jacobsen, C. Physical and Oxidative Stability of Emulsions Stabilized with Fractionated Potato Protein Hydrolysates Obtained from Starch Production Side Stream. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriades, K.; McClements, D.J. Influence of pH and Heating on Physicochemical Properties of Whey Protein-Stabilized Emulsions Containing a Nonionic Surfactant. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3936–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.B.; Yan, D.Q.; Jiang, Y.S.; Ding, C.H. Competitive displacement of interfacial soy proteins by Tween 20 and its effect on the physical stability of emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L.; Wang, R.; Lu, T.; Xue, C. Influence of diacetyl tartaric acid ester of monoglycerides on the properties of whey powder–maltodextrin emulsion. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOCS Official Method Ce 8-89; Determination of Tocopherols and Tocotrienols in Vegetable Oils and Fats by HPLC. American Oil Chemists’ Society: Champaign, IL, USA, 1998.
- Yesiltas, B.; García-Moreno, P.J.; Gregersen, S.; Olsen, T.H.; Jones, N.C.; Hoffmann, S.V.; Marcatili, P.; Overgaard, M.T.; Hansen, E.B.; Jacobsen, C. Antioxidant peptides derived from potato, seaweed, microbial and spinach proteins: Oxidative stability of 5% fish oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, O.; Heyd, B.; Broyart, B.; Castillo, R.; Maillard, M.N. Oxidative reactivity of unsaturated fatty acids from sunflower, high oleic sunflower and rapeseed oils subjected to heat treatment, under controlled conditions. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 52, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorsen, B.L.; Blomhoff, R. Determination of lipid oxidation products in vegetable oils and marine omega-3 supplements. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 55, 5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shantha, N.C.; Decker, E.A. Rapid, sensitive, iron-based spectrophotometric methods for determination of peroxide values of food lipids. J. AOAC Int. 1994, 77, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xiong, Y.L.; Chen, J. Antioxidant and emulsifying properties of potato protein hydrolysate in soybean oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, N.A.; Kennedy, D.; Hogan, S.A.; Kelly, P.M.; Thapa, K.; Murphy, K.M.; Fenelon, M.A. Emulsification properties of pea protein isolate using homogenization, microfluidization and ultrasonication. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Interfacial adsorption of peptides in oil-in-water emulsions costabilized by tween 20 and antioxidative potato peptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11575–11581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiong, Y.L.; Chen, J.; Zhou, L. Synergy of licorice extract and pea protein hydrolysate for oxidative stability of soybean oil-in-water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8204–8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Ning, J.; Zhu, Z.; Cui, L.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Impact of interfacial composition on co-oxidation of lipids and proteins in oil-in-water emulsions: Competitive displacement of casein by surfactants. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zheng, L.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, M. Desirable characteristics of casein peptides with simultaneously enhanced emulsion forming ability and antioxidative capacity in O/W emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.H.G.; Kurozawa, L.E. Improvement of the functional and antioxidant properties of rice protein by enzymatic hydrolysis for the microencapsulation of linseed oil. J. Food Eng. 2020, 267, 109761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wu, C.; Yu, C.; Bi, A.; Xu, X.; Du, M. High stability of bilayer nano-emulsions fabricated by Tween 20 and specific interfacial peptides. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesiltas, B.; Soria Caindec, A.M.; García-Moreno, P.J.; Echers, S.G.; Olsen, T.H.; Jones, N.C.; Hoffmann, S.V.; Marcatili, P.; Overgaard, M.T.; Hansen, E.B.; et al. Physical and oxidative stability of fish oil-in-water emulsions stabilized with emulsifier peptides derived from seaweed, methanotrophic bacteria and potato proteins. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 663, 131069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, A.F.; Nielsen, N.S.; Jensen, L.S.; Horsewell, A.; Jacobsen, C. The choice of homogenisation equipment affects lipid oxidation in emulsions. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padial-Domínguez, M.; Espejo-Carpio, F.J.; García-Moreno, P.J.; Jacobsen, C.; Guadix, E.M. Protein derived emulsifiers with antioxidant activity for stabilization of omega-3 emulsions. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, A.D.M.; Nielsen, N.S.; Hyldig, G.; Jacobsen, C. Influence of emulsifier type on lipid oxidation in fish oil-en riched light mayonnaise. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 1012–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, R.J.; Kellerby, S.S.; Decker, E.A. Antioxidant activity of proteins and peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, E. Lipid oxidation, 2nd ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2012; ISBN 9780953194988. [Google Scholar]
- Ospina-Quiroga, J.L.; García-Moreno, P.J.; Guadix, A.; Guadix, E.M.; Almécija-Rodríguez, M.D.C.; Pérez-Gálvez, R. Evaluation of Plant Protein Hydrolysates as Natural Antioxidants in Fish Oil-In-Water Emulsions. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falade, E.O.; Mu, T.H.; Zhang, M. Improvement of ultrasound microwave-assisted enzymatic production and high hydrostatic pressure on emulsifying, rheological and interfacial characteristics of sweet potato protein hydrolysates. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Molecular Weight of the Potato Protein Hydrolysates | Protein % |
|---|---|
| Unfractionated | 79.42 ± 1.94 |
| >10 kDa | 71.50 ± 3.09 |
| 5–10 kDa | 79.79 ± 0.19 |
| 0.8–5 kDa | 79.97 ± 0.58 |
| <0.8 kDa | 73.31 ± 4.46 |
| Emulsion Code * | D [4,3] (µm) (Day 1) | D [4,3] (µm) (Day 7) | D [3,2] (µm) (Day 1) | D [3,2] (µm) (Day 7) | Zeta Potential (mV) (Day1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unfractionated PPH100% | 5.30 ± 0.56 E,a | 18.94 ± 2.50 D,b | 0.24 ± 0.02 C,a | 0.57 ± 0.05 E,b | −56.1 ± 1.8 C |
| D33% | 1.31 ± 0.18 BC,a | 6.19 ± 0.75 C,b | 0.21 ± 0.01 BC,a | 0.36 ± 0.03 C,b | −80.0 ± 2.7 B |
| D50% | 1.06 ± 0.20 BC,a | 3.94 ± 0.75 BC,b | 0.20 ± 0.01 AB,a | 0.29 ± 0.02 B,b | −84.7 ± 1.9 B |
| D67% | 0.37 ± 0.02 A,a | 1.03 ± 0.04 A,b | 0.17 ± 0.01 A,a | 0.21 ± 0.01 A,b | −88.3 ± 5.0 AB |
| D100% | 0.35 ± 0.03 A,a | 2.91 ± 0.50 AB,b | 0.17 ± 0.01 A,a | 0.18 ± 0.01 A,a | −93.5 ± 5.3 A |
| T33% | 2.77 ± 0.15 D,a | 3.06 ± 0.36 AB,a | 0.45 ± 0.02 F,a | 0.43 ± 0.00 D,a | −26.0 ± 2.0 D |
| T50% | 1.46 ± 0.22 C,a | 1.38 ± 0.24 AB,a | 0.37 ± 0.02 E,a | 0.36 ± 0.01 C,a | −24.4 ± 1.7 D |
| T67% | 0.96 ± 0.08 ABC,a | 0.88 ± 0.04 A,a | 0.33 ± 0.02 D,a | 0.31 ± 0.01 BC,a | −20.4 ± 1.5 D |
| T100% | 0.79 ± 0.01 AB,a | 0.74 ± 0.01 A,a | 0.30 ± 0.00 D,a | 0.30 ± 0.00 BC,a | −18.2 ± 0.8 D |
| Emulsion Code * | D [4,3] (µm) (Day 1) | D [4,3] (µm) (Day 9) | Zeta Potential (mV) (Day1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| unfractionated-D | 1.189 ± 0.002 F,a | 1.309 ± 0.022 CD,b | −78.00 ± 3.07 B |
| >10 kDa-D | 2.429 ± 0.038 I,a | 2.508 ± 0.004 F,b | −84.78 ± 5.38 AB |
| 5–10 kDa-D | 0.764 ± 0.002 D,a | 0.974 ± 0.059 B,b | −85.05 ± 3.75 AB |
| 0.8–5 kDa-D | 0.389 ± 0.002 C,a | 0.472 ± 0.001 A,b | −78.43 ± 3.72 B |
| <0.8 kDa-D | 0.352 ± 0.000 BC,a | 0.354 ± 0.004 A,a | −83.26 ± 5.55 B |
| D100% | 0.279 ± 0.005 A,a | 0.276 ± 0.002 A,a | −94.08 ± 5.70 A |
| unfractionated-T | 1.051 ± 0.015 E,b | 0.947 ± 0.005 B,a | −29.03 ± 2.03 C |
| >10 kDa-T | 1.607 ± 0.021 H,a | 1.575 ± 0.118 E,a | −19.15 ± 0.80 CD |
| 5–10 kDa-T | 1.541 ± 0.011 G,b | 1.264 ± 0.071 C,a | −18.58 ± 1.59 D |
| 0.8–5 kDa-T | 1.604 ± 0.003 H,b | 1.501 ± 0.012 DE,a | −16.93 ± 0.58 D |
| <0.8 kDa-T | 1.599 ± 0.003 H,a | 1.436 ± 0.173 CDE,a | −19.80 ± 2.45 CD |
| T100% | 0.317 ± 0.001 AB,a | 0.330 ± 0.004 A,b | −14.73 ± 1.61 D |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yay, C.; Yesiltas, B.; Jacobsen, C. Effect of Combining Surfactants with Potato Protein Hydrolysates on Their Emulsifying and Antioxidant Properties in Fish-Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Foods 2025, 14, 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111974
Yay C, Yesiltas B, Jacobsen C. Effect of Combining Surfactants with Potato Protein Hydrolysates on Their Emulsifying and Antioxidant Properties in Fish-Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Foods. 2025; 14(11):1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111974
Chicago/Turabian StyleYay, Cansu, Betül Yesiltas, and Charlotte Jacobsen. 2025. "Effect of Combining Surfactants with Potato Protein Hydrolysates on Their Emulsifying and Antioxidant Properties in Fish-Oil-in-Water Emulsions" Foods 14, no. 11: 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111974
APA StyleYay, C., Yesiltas, B., & Jacobsen, C. (2025). Effect of Combining Surfactants with Potato Protein Hydrolysates on Their Emulsifying and Antioxidant Properties in Fish-Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Foods, 14(11), 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111974








