Effect of Raspberry (Rubus indeaus L.) Juice Fermented by Limosilactobacillus fermentum FUA033 on the Human Gut Microbiota Cultured In Vitro: A Multi-Omics Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Raspberry Juice Preparation and Its Probiotic Fermentation
2.3. Fecal Donors
2.4. In Vitro Fermentation
2.5. Determination of SCFAs
2.6. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.7. Nontargeted Metabolomics
2.8. Data Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects on the Gut Microbiota Structure
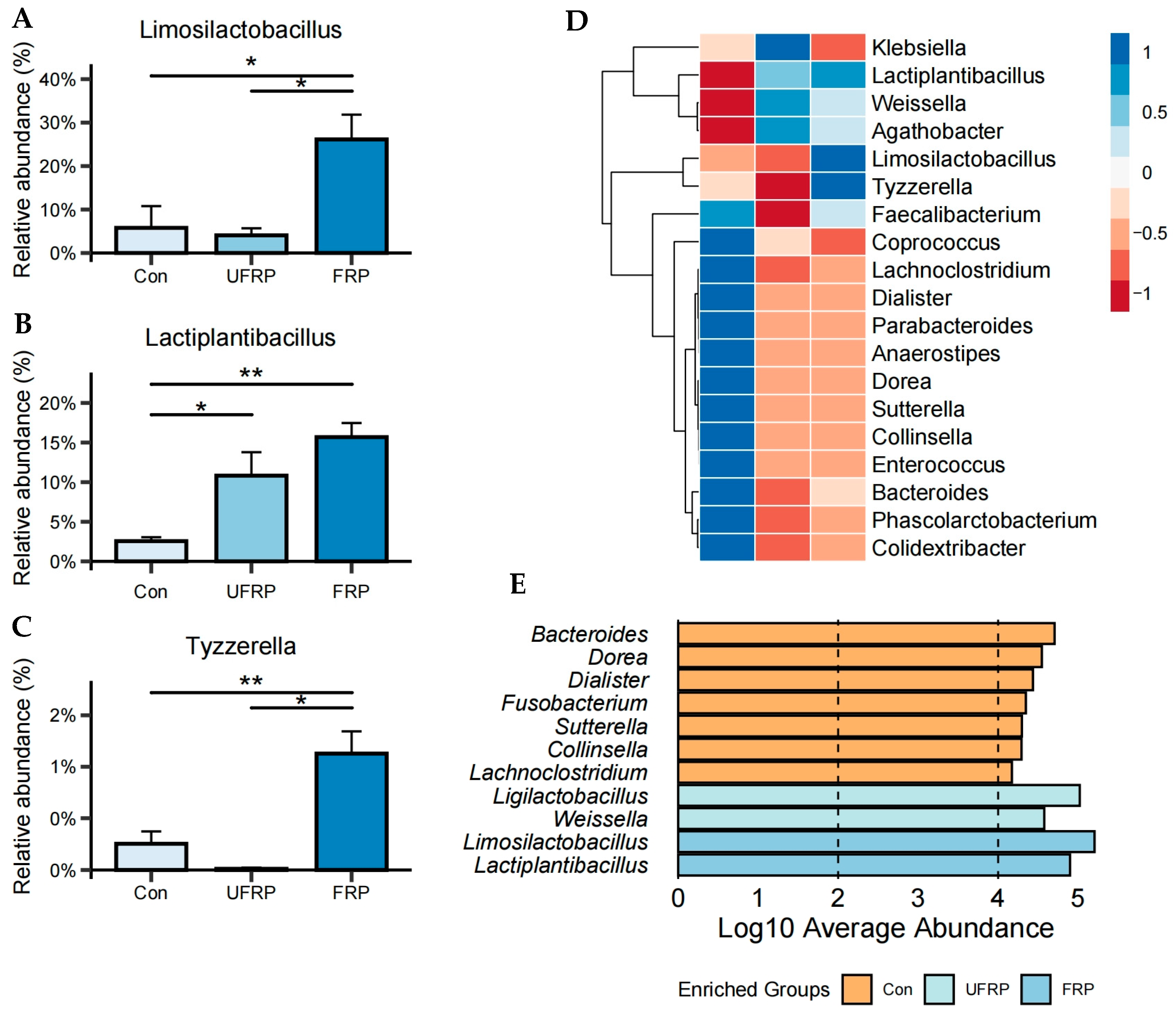
3.2. Changes in the Microbiota at the Genus Level
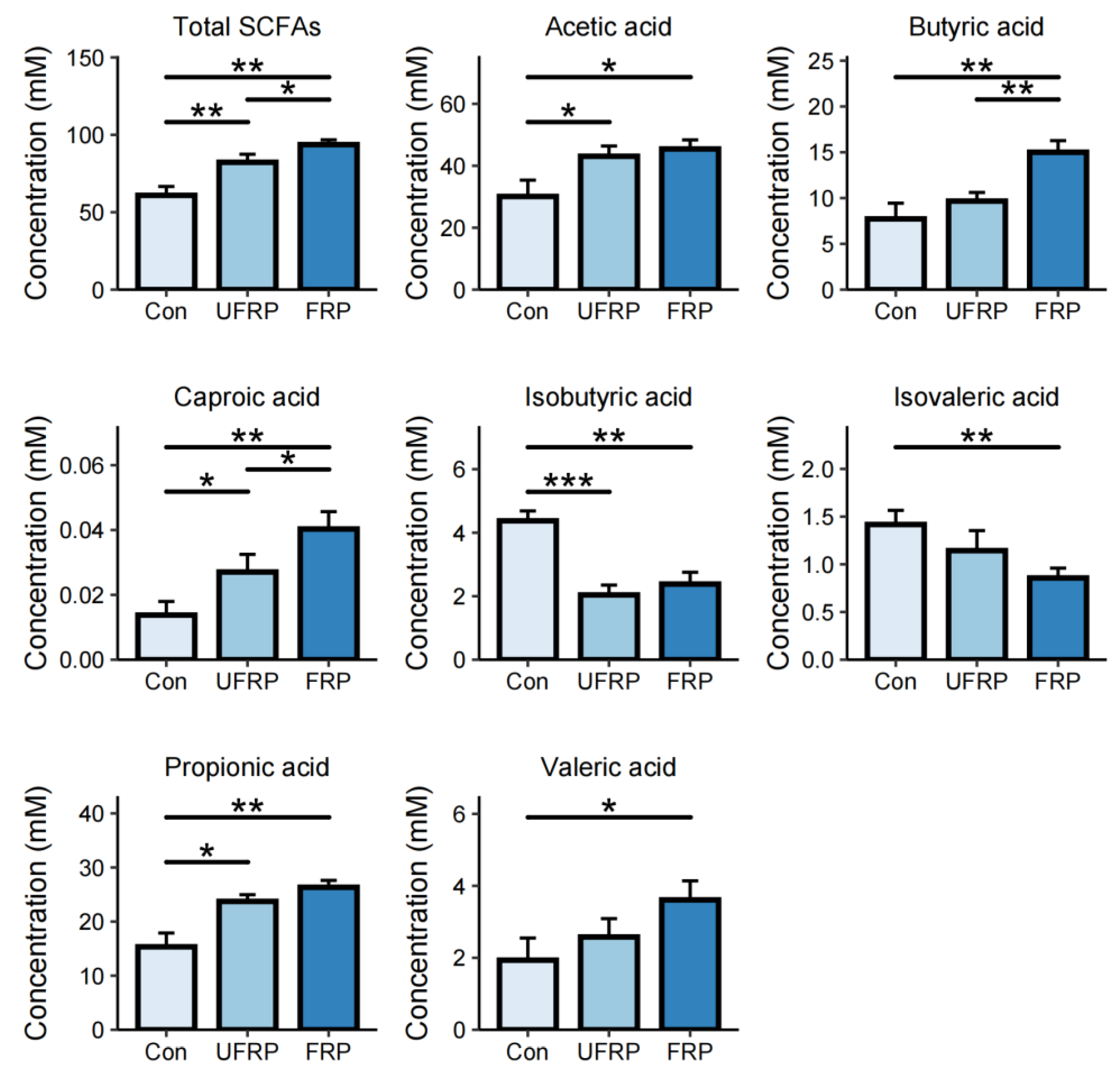
3.3. Effects on SCFA Production
3.4. Effects on Metabolic Profiles
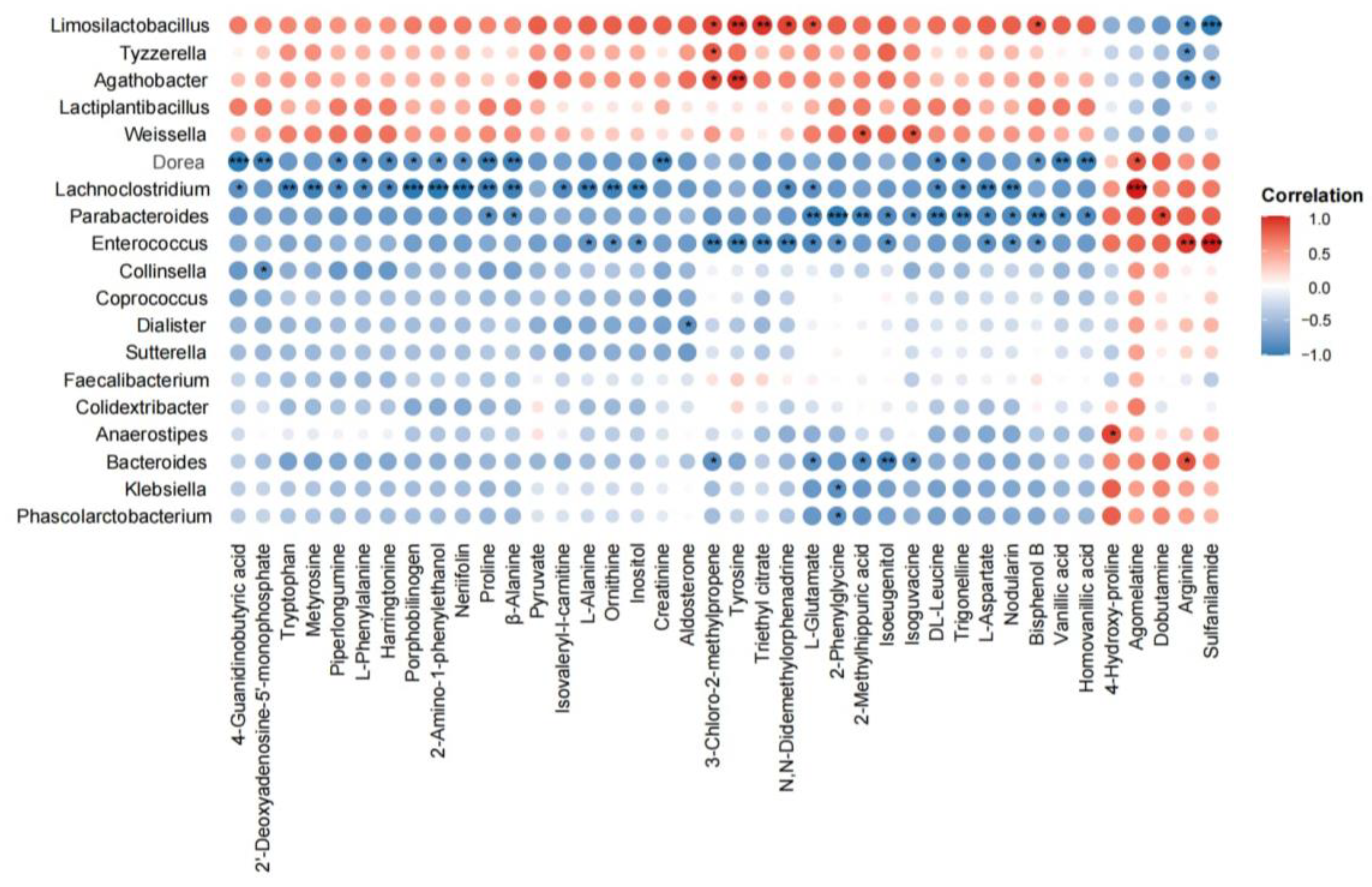
3.5. Correlations Between the Gut Microbiota Composition and Associated Metabolic Profiles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clemente, J.C.; Ursell, L.K.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: An integrative view. Cell 2012, 148, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiome and health: Mechanistic insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Xing, X.; Gupta, M.; Keber, F.C.; Lopez, J.G.; Lee, Y.-C.J.; Roichman, A.; Wang, L.; Neinast, M.D.; Donia, M.S. Gut bacterial nutrient preferences quantified in vivo. Cell 2022, 185, 3441–3456.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Liao, M.; Zhou, N.; Bao, L.; Ma, K.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, J. Parabacteroides distasonis alleviates obesity and metabolic dysfunctions via production of succinate and secondary bile acids. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 222–235.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambrova, M.; Latkovskis, G.; Kuka, J.; Strele, I.; Konrade, I.; Grinberga, S.; Hartmane, D.; Pugovics, O.; Erglis, A.; Liepinsh, E. Diabetes is associated with higher trimethylamine N-oxide plasma levels. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2016, 124, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmora, N.; Suez, J.; Elinav, E. You are what you eat: Diet, health and the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumerle, S.; Sarill, M.; Saponaro, M.; Colucci, M.; Contu, L.; Lazzarini, E.; Sartori, R.; Pezzini, C.; Rinaldi, A.; Scanu, A. Targeting senescence induced by age or chemotherapy with a polyphenol-rich natural extract improves longevity and healthspan in mice. Nat. Aging 2024, 4, 1231–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksono, W.A.; Cernava, T.; Wassermann, B.; Abdelfattah, A.; Soto-Giron, M.J.; Toledo, G.V.; Virtanen, S.M.; Knip, M.; Hyöty, H.; Berg, G. The edible plant microbiome: Evidence for the occurrence of fruit and vegetable bacteria in the human gut. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2258565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwibedi, C.; Axelsson, A.S.; Abrahamsson, B.; Fahey, J.W.; Asplund, O.; Hansson, O.; Ahlqvist, E.; Tremaroli, V.; Bäckhed, F.; Rosengren, A.H. Effect of broccoli sprout extract and baseline gut microbiota on fasting blood glucose in prediabetes: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Nat. Microbiol. 2025, 10, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Corona, A.V.; Valencia-Espinosa, I.; González-Sánchez, F.A.; Sánchez-López, A.L.; Garcia-Amezquita, L.E.; Garcia-Varela, R. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic activity of phenolic compound family extracted from raspberries (Rubus idaeus): A general review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sandhu, A.; Edirisinghe, I.; Burton-Freeman, B. An exploratory study of red raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.)(poly) phenols/metabolites in human biological samples. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Yang, J.; Cui, J.; Fan, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Y. Stability and mechanism of phenolic compounds from raspberry extract under in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Lwt 2021, 139, 110552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zogona, D.; Zongo, A.W.-S.; Elkhedir, A.E.; Salah, M.; Tao, M.; Li, R.; Wu, T.; Xu, X. Red raspberry supplementation mitigates alcohol-induced liver injury associated with gut microbiota alteration and intestinal barrier dysfunction in mice. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1209–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotschki, B.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Jurgoński, A.; Sójka, M. Fructo-oligosaccharides and pectins enhance beneficial effects of raspberry polyphenols in rats with nonalcoholic fatty liver. Nutrients 2021, 13, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsdottir, G.; Blanco, N.; Xu, J.; Ahrné, S.; Molin, G.; Sterner, O.; Nyman, M. Formation of Short-Chain Fatty Acids, Excretion of Anthocyanins, and Microbial Diversity in Rats Fed Blackcurrants, Blackberries, and Raspberries. J. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 2013, 202534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogal, A.; Valdes, A.M.; Menni, C. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between gut microbiota and diet in cardio-metabolic health. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1897212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marnpae, M.; Balmori, V.; Kamonsuwan, K.; Nungarlee, U.; Charoensiddhi, S.; Thilavech, T.; Suantawee, T.; Sivapornnukul, P.; Chanchaem, P.; Payungporn, S. Modulation of the gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acid production by gac fruit juice and its fermentation in in vitro colonic fermentation. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 3640–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Bian, Y.; Lu, F.; Liu, S.; Ma, W.; Chen, T.; Feng, J.; Xia, Y.; Fang, Y. Changes in Antioxidant and Flavor Profiles of Raspberry, Blackberry, and Mulberry Juices Fermented by Urolithin A-Producing Limosilactobacillus fermentum FUA033. Food Biosci. 2025, 65, 106131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Wu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Jennifer, T.G.; Zhao, D.; Fang, Y. Essential roles of ellagic acid-to-urolithin converting bacteria in human health and health food industry: An updated review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 151, 104622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Hua, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hou, X.; Yang, G.; Liu, S.; Fang, Y. Improvement of urolithin A yield by in vitro cofermentation of Streptococcus thermophilus FUA329 with human gut microbiota from different urolithin metabotypes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 3008–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, K.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Da, S.; Ciren, D.; Tang, H. In vitro digestion and fermentation combined with microbiomics and metabolomics reveal the mechanism of superfine yak bone powder regulating lipid metabolism by altering human gut microbiota. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culp, E.J.; Goodman, A.L. Cross-feeding in the gut microbiome: Ecology and mechanisms. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menéndez, G.G.; Sichel, L.; López, M.D.C.; Hernández, Y.; Arteaga, E.; Rodríguez, M.; Fleites, V.; Fernández, L.T.; Cano, R.D.J. From colon wall to tumor niche: Unraveling the microbiome’s role in colorectal cancer progression. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0311233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tett, A.; Pasolli, E.; Masetti, G.; Ercolini, D.; Segata, N. Prevotella diversity, niches and interactions with the human host. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The changing face of the family Enterobacteriaceae (Order:“Enterobacterales”): New members, taxonomic issues, geographic expansion, and new diseases and disease syndromes. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e00174-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Yang, Z.; Yan, H.; Chen, G.; Zhong, S.; Chen, P.; Zhong, H.; Yang, H.; Jia, Y.; Yin, Z. Gut proinflammatory bacteria is associated with abnormal functional connectivity of hippocampus in unmedicated patients with major depressive disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djukovic, A.; Garzón, M.J.; Canlet, C.; Cabral, V.; Lalaoui, R.; García-Garcerá, M.; Rechenberger, J.; Tremblay-Franco, M.; Peñaranda, I.; Puchades-Carrasco, L. Lactobacillus supports Clostridiales to restrict gut colonization by multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.E.; Kim, M.S.; Shim, K.W.; Kim, Y.-I.; Chu, J.; Kim, B.-K.; Choi, I.S.; Kim, J.Y. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum Q180 on postprandial lipid levels and intestinal environment: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Yang, N.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Li, Q.; Jin, H.; Zheng, L.; Sun, Z.; Zuo, K. Effect of the probiotic strain, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum P9, on chronic constipation: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 191, 106755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Bai, M.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Zhong, Z.; Sun, Z. The intricate symbiotic relationship between lactic acid bacterial starters in the milk fermentation ecosystem. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 65, 728–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, N.; Mizukoshi, E.; Yamashita, T.; Yutani, M.; Seishima, J.; Wang, Z.; Arai, K.; Okada, H.; Yamashita, T.; Sakai, Y. Chronic liver disease enables gut Enterococcus faecalis colonization to promote liver carcinogenesis. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 1039–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seishima, J.; Iida, N.; Kitamura, K.; Yutani, M.; Wang, Z.; Seki, A.; Yamashita, T.; Sakai, Y.; Honda, M.; Yamashita, T. Gut-derived Enterococcus faecium from ulcerative colitis patients promotes colitis in a genetically susceptible mouse host. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.Q.; Li, T.; Nakatsu, G.; Chen, Y.-X.; Yau, T.O.; Chu, E.; Wong, S.; Szeto, C.H.; Ng, S.C.; Chan, F.K. A novel faecal Lachnoclostridium marker for the non-invasive diagnosis of colorectal adenoma and cancer. Gut 2020, 69, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Cai, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Bao, W.; Fan, H.; Wu, S. A high-fat diet increases the characteristics of gut microbial composition and the intestinal damage associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N. Sex difference of gut microbiota. In Sex/Gender-Specific Medicine in the Gastrointestinal Diseases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 363–377. [Google Scholar]
- Bezerra, M.; Ribeiro, M.; Cosme, F.; Nunes, F.M. Overview of the distinctive characteristics of strawberry, raspberry, and blueberry in berries, berry wines, and berry spirits. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Cai, X.; Fei, W.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, C. The role of short-chain fatty acids in immunity, inflammation and metabolism. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Long, Y.; Tan, B.; Li, Q.X.; Dong, Z.; Wan, X. Dietary fiber and polyphenols from whole grains: Effects on the gut and health improvements. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 4682–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, E.R.; Lam, Y.K.; Uhlig, H.H. Short-chain fatty acids: Linking diet, the microbiome and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, J.; Murphy, K.G.; Frost, G.; Chambers, E.S. Short-chain fatty acids as potential regulators of skeletal muscle metabolism and function. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Bao, L.; Qiu, M.; Wu, K.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, L.; Xiang, K.; Zhang, N.; Hu, X.; Fu, Y. Commensal cow Roseburia reduces gut-dysbiosis-induced mastitis through inhibiting bacterial translocation by producing butyrate in mice. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Covian, D.; González, S.; Nogacka, A.M.; Arboleya, S.; Salazar, N.; Gueimonde, M.; De Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G. An overview on fecal branched short-chain fatty acids along human life and as related with body mass index: Associated dietary and anthropometric factors. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre, M.; Eck, A.; Koenen, M.E.; Savelkoul, P.H.; Budding, A.E.; Venema, K. Diet drives quick changes in the metabolic activity and composition of human gut microbiota in a validated in vitro gut model. Res. Microbiol. 2016, 167, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Prabhakaran, P.; Zhou, W.; Han, Y.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Li, D.; Li, F. Sesamin Alleviates Allergen-Induced Diarrhea by Restoring Gut Microbiota Composition and Intestinal Barrier Function. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 1965–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baenas, N.; Nunez-Gomez, V.; Navarro-Gonzalez, I.; Sanchez-Martinez, L.; Garcia-Alonso, J.; Periago, M.J.; Gonzalez-Barrio, R. Raspberry dietary fibre: Chemical properties, functional evaluation and prebiotic in vitro effect. Lwt 2020, 134, 110140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Zimmermann-Kogadeeva, M.; Wegmann, R.; Goodman, A.L. Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature 2019, 570, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, N.; Robbins, T.W.; Rowe, J.B. The role of noradrenaline in cognition and cognitive disorders. Brain 2021, 144, 2243–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, A.; Tang, Y.; Kuang, J.; Li, M.; Chen, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H. Gut bacteria-driven homovanillic acid alleviates depression by modulating synaptic integrity. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 1000–1012.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, B.; Elliott-Sale, K.; Artioli, G.G.; Swinton, P.A.; Dolan, E.; Roschel, H.; Sale, C.; Gualano, B. β-alanine supplementation to improve exercise capacity and performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, G.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, H.; Guan, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, P. Proline uptake promotes activation of lymphoid tissue inducer cells to maintain gut homeostasis. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 1953–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, B.D.; Funabashi, M.; Adame, M.D.; Wang, Z.; Boktor, J.C.; Haney, J.; Wu, W.-L.; Rabut, C.; Ladinsky, M.S.; Hwang, S.-J. A gut-derived metabolite alters brain activity and anxiety behaviour in mice. Nature 2022, 602, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.V.; Markussen, K.H.; Jakobsen, E.; Schousboe, A.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Aldana, B.I. Glutamate metabolism and recycling at the excitatory synapse in health and neurodegeneration. Neuropharmacology 2021, 196, 108719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forzano, I.; Avvisato, R.; Varzideh, F.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Cioppa, A.; Mone, P.; Salemme, L.; Kansakar, U.; Tesorio, T.; Trimarco, V. L-Arginine in diabetes: Clinical and preclinical evidence. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanetti, R.J.; Ng, Y.S.; Errington, L.; Blain, A.P.; Mcfarland, R.; Gorman, G.S. l-Arginine in mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes: A systematic review. Neurology 2022, 98, e2318–e2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossmann, D.; Müller, C.; Park, S.; Ryback, B.; Colombi, M.; Ritter, N.; Weißenberger, D.; Dazert, E.; Coto-Llerena, M.; Nuciforo, S. Arginine reprograms metabolism in liver cancer via RBM39. Cell 2023, 186, 5068–5083.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, Z.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mao, T.; Xv, R.; Pan, M.; Hu, Y.; Liu, S.; Fang, Y. Effect of Raspberry (Rubus indeaus L.) Juice Fermented by Limosilactobacillus fermentum FUA033 on the Human Gut Microbiota Cultured In Vitro: A Multi-Omics Approach. Foods 2025, 14, 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101796
Hua Z, Lv Y, Zhang H, Mao T, Xv R, Pan M, Hu Y, Liu S, Fang Y. Effect of Raspberry (Rubus indeaus L.) Juice Fermented by Limosilactobacillus fermentum FUA033 on the Human Gut Microbiota Cultured In Vitro: A Multi-Omics Approach. Foods. 2025; 14(10):1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101796
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Ziyan, Yunfan Lv, Han Zhang, Tianyi Mao, Ruyu Xv, Mingxuan Pan, Yadong Hu, Shu Liu, and Yaowei Fang. 2025. "Effect of Raspberry (Rubus indeaus L.) Juice Fermented by Limosilactobacillus fermentum FUA033 on the Human Gut Microbiota Cultured In Vitro: A Multi-Omics Approach" Foods 14, no. 10: 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101796
APA StyleHua, Z., Lv, Y., Zhang, H., Mao, T., Xv, R., Pan, M., Hu, Y., Liu, S., & Fang, Y. (2025). Effect of Raspberry (Rubus indeaus L.) Juice Fermented by Limosilactobacillus fermentum FUA033 on the Human Gut Microbiota Cultured In Vitro: A Multi-Omics Approach. Foods, 14(10), 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101796





