Influence of Electrohydrodynamics on Drying Characteristics, Physicochemical Properties, and Texture Characteristics of Potato
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Material
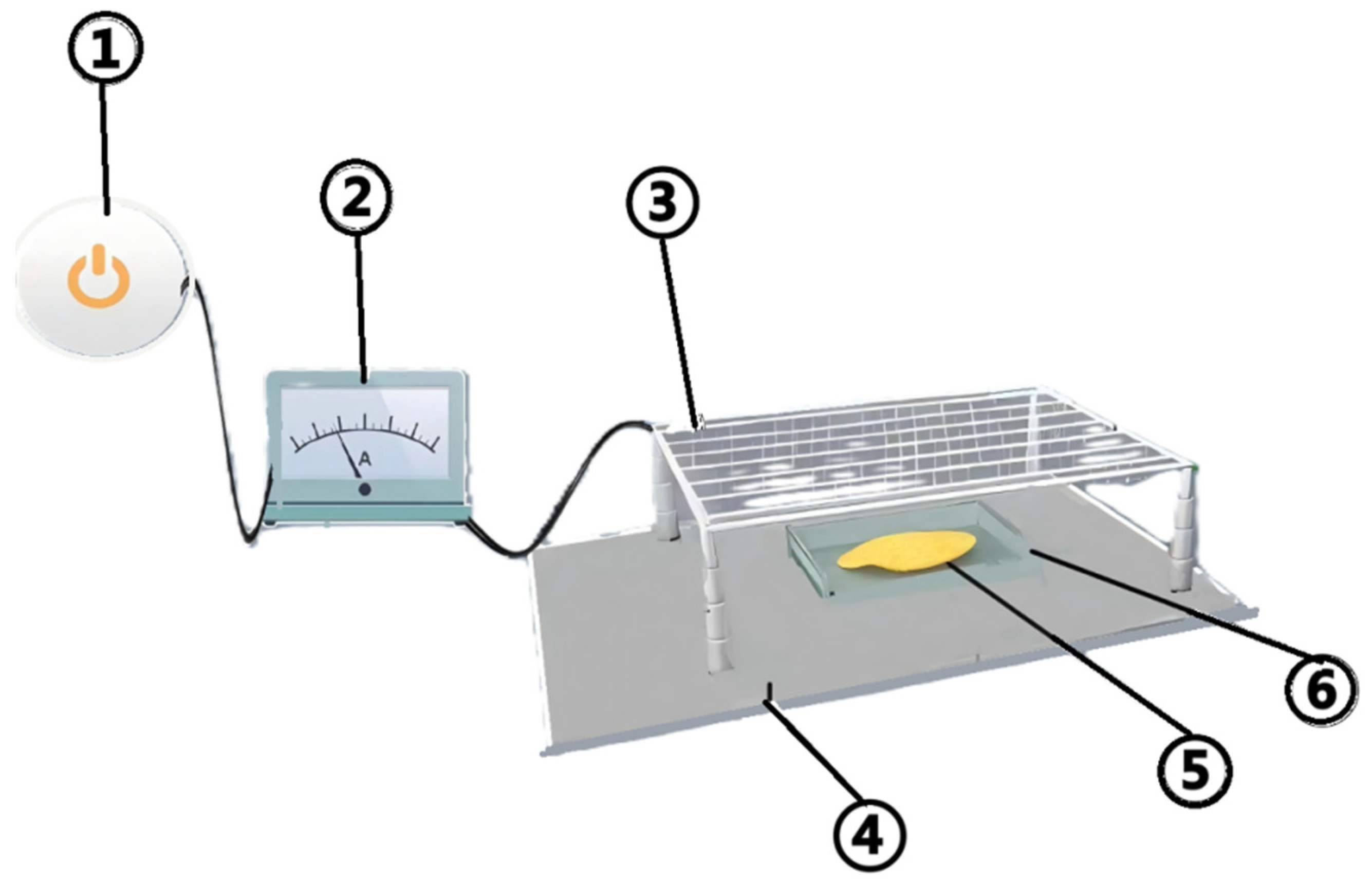
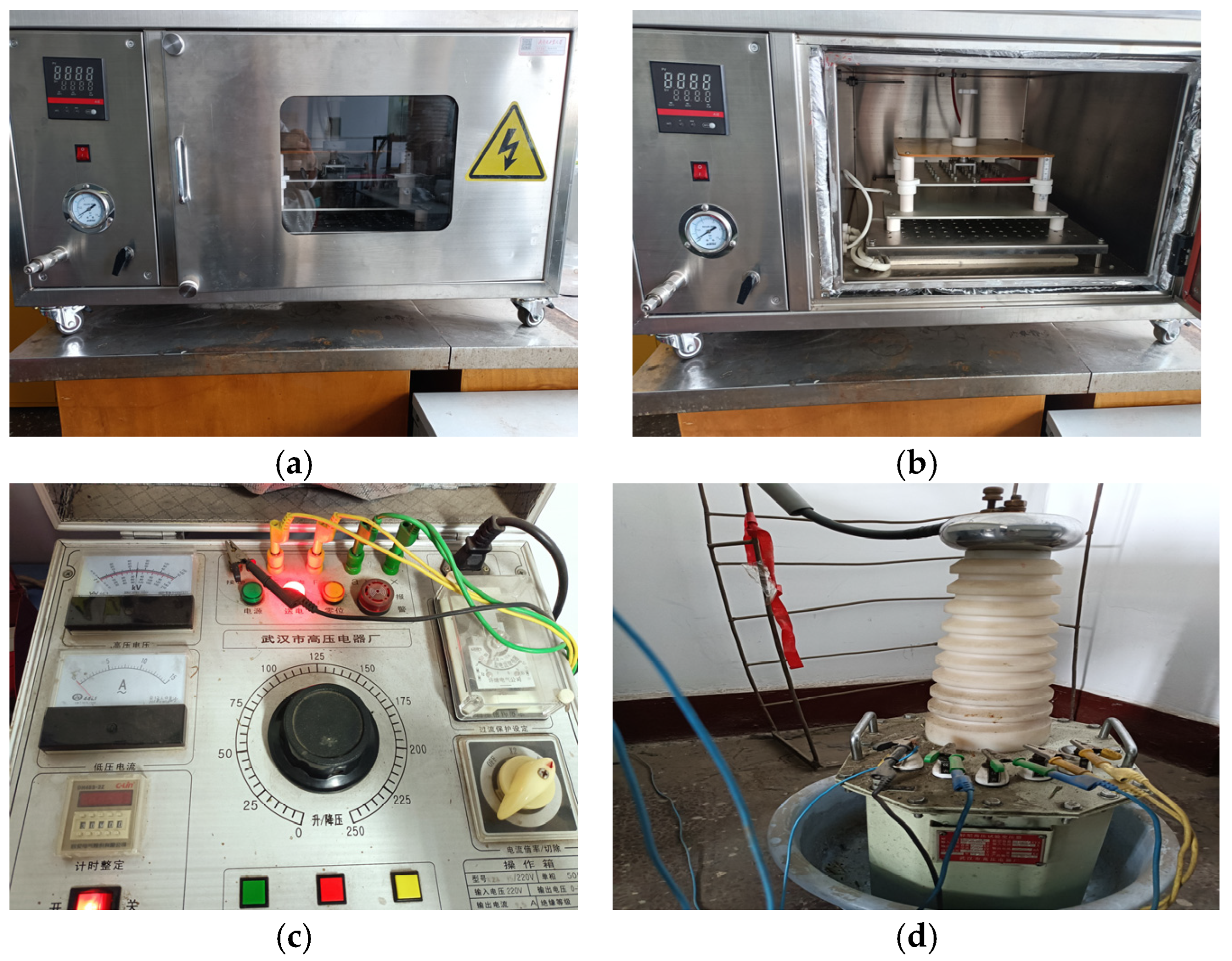
2.2. Experimental Setups
2.3. Experimental Methods
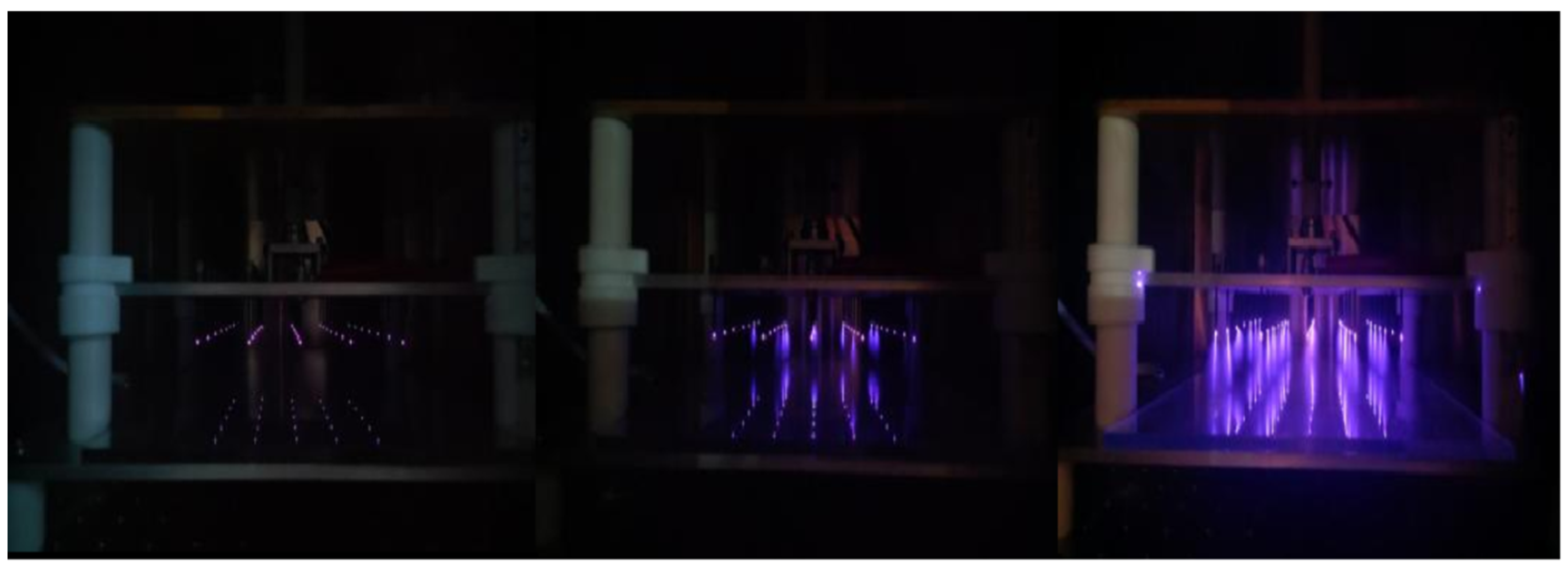
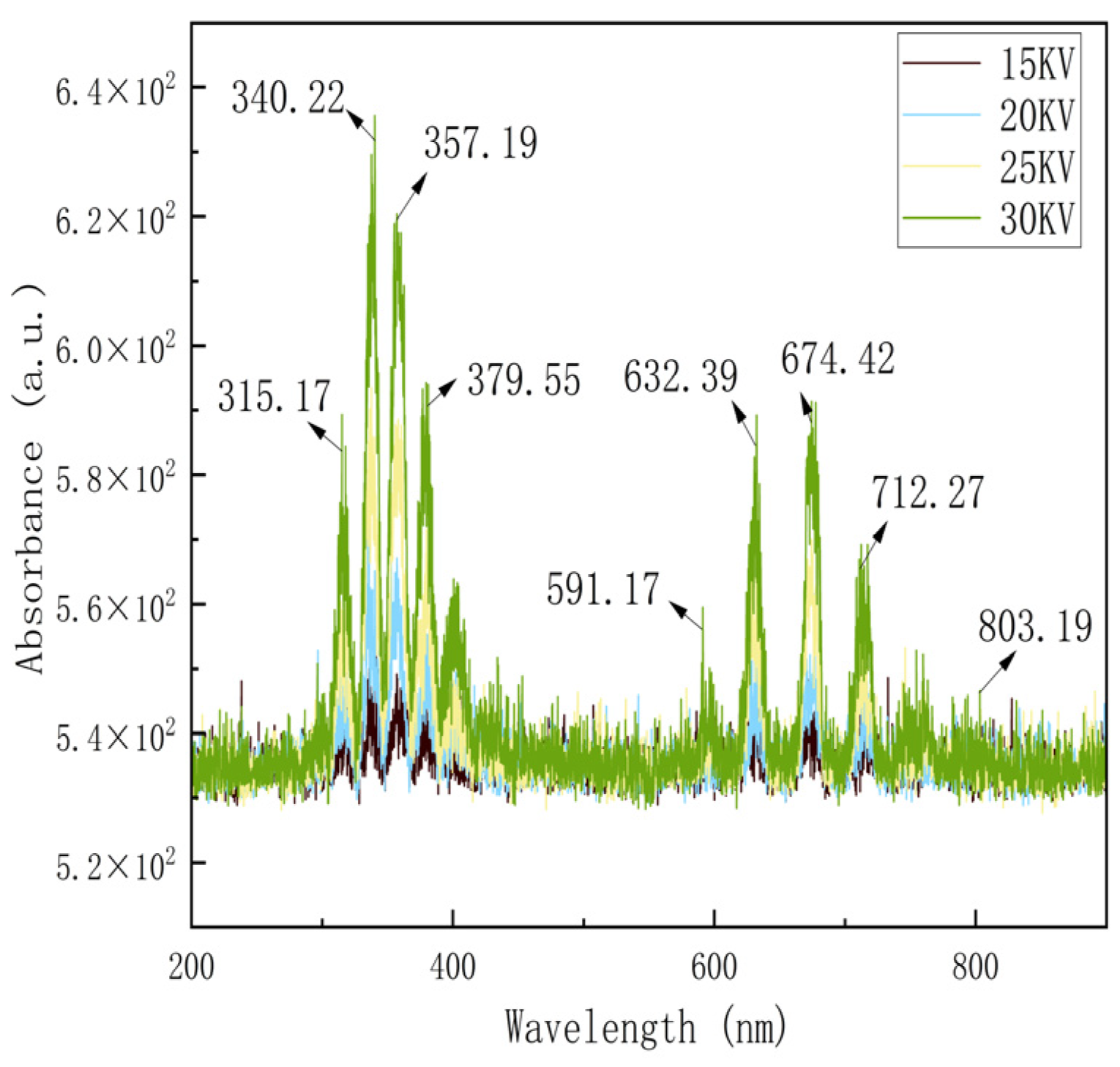
2.4. Measurement of Electric Field Discharge Characteristics
2.5. Moisture Content
2.6. Drying Rate
2.7. Effective Water Diffusion Coefficient
2.8. Shrinkage Rate
2.9. Rehydration Rate
2.10. Sample Color Difference
2.11. Infrared Spectrum
2.12. Protein Secondary Structures
2.13. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.14. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR)
2.15. Texture Properties
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Discharge Characteristics of EHD Systems
3.2. Drying Characteristics
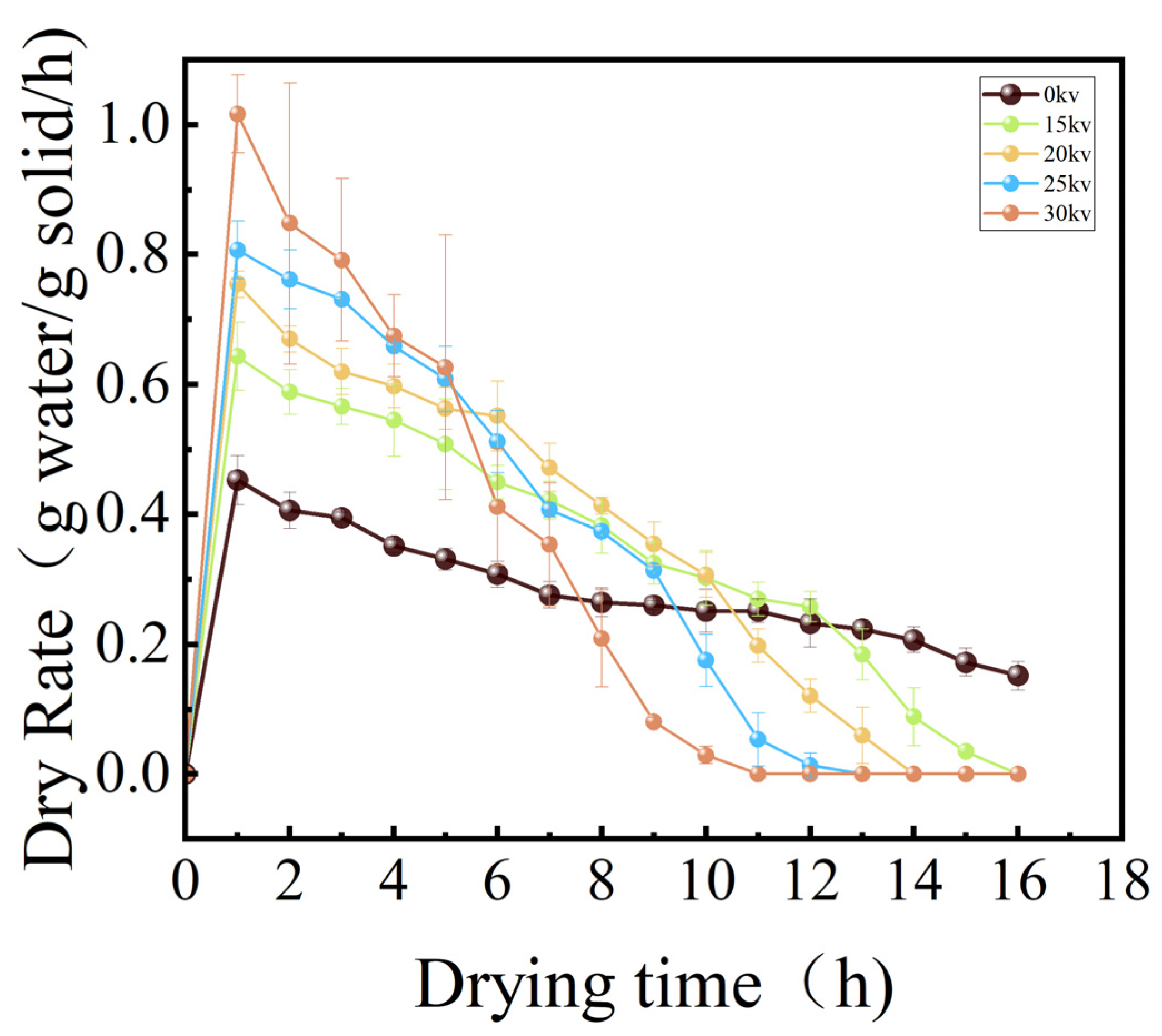
3.2.1. Drying Moisture Content, Drying Rate, and Drying Time Analysis
3.2.2. Analysis of Effective Water Diffusion Coefficient
3.3. Quality Analysis
3.3.1. Color Analytics
3.3.2. Volume Shrinkage
3.3.3. Rehydration Performance Analysis
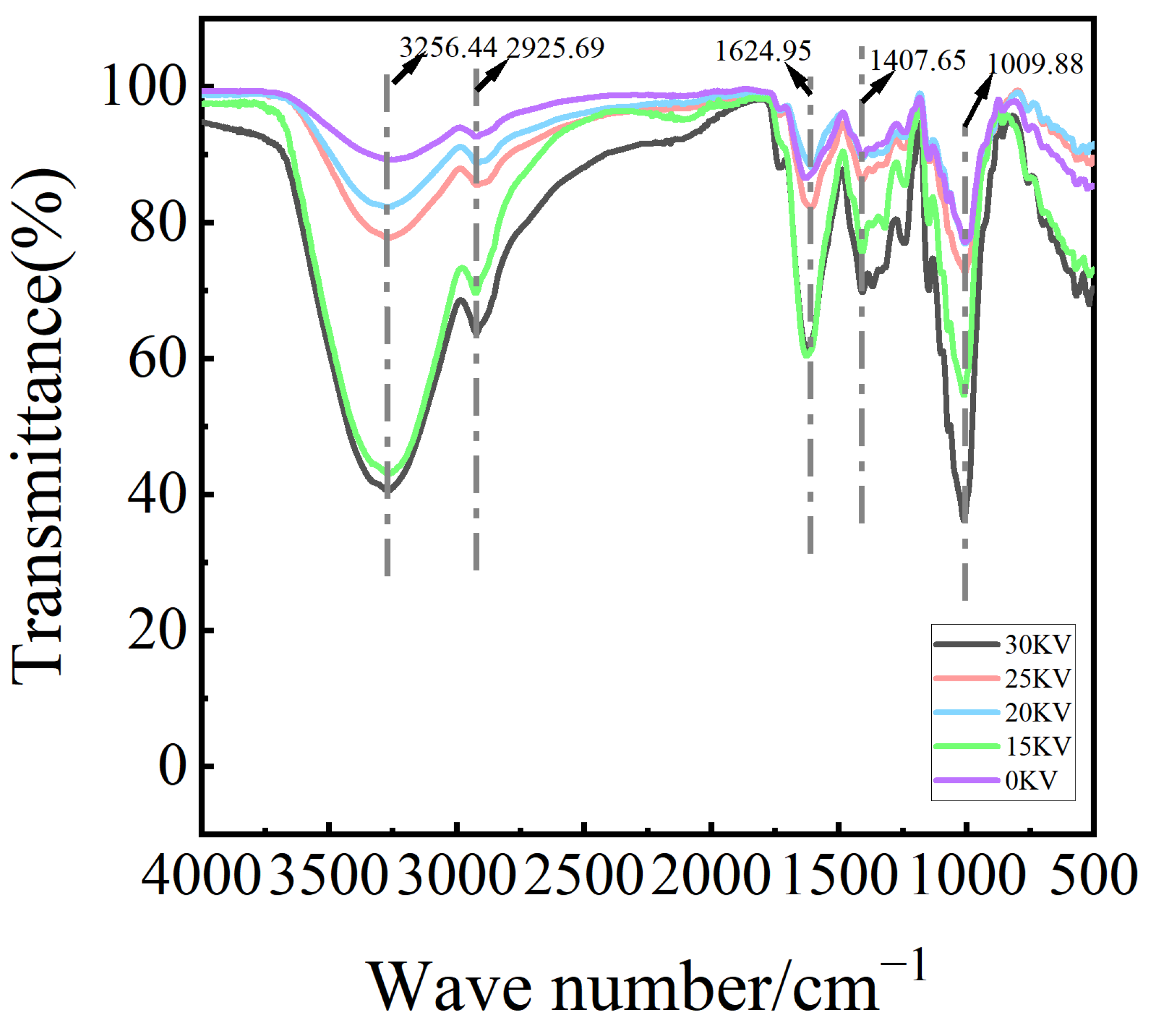
3.4. Infrared Spectral Analysis
3.5. Protein Secondary Structure
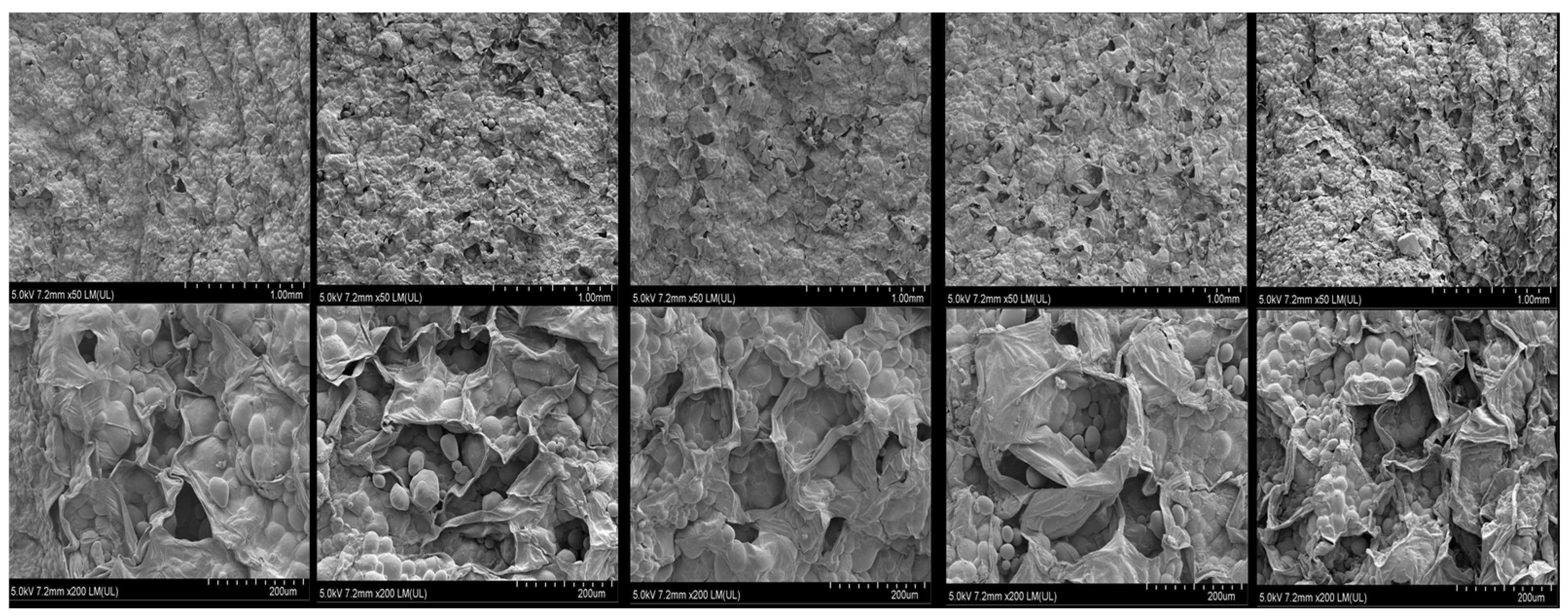
3.6. Microstructure Analysis
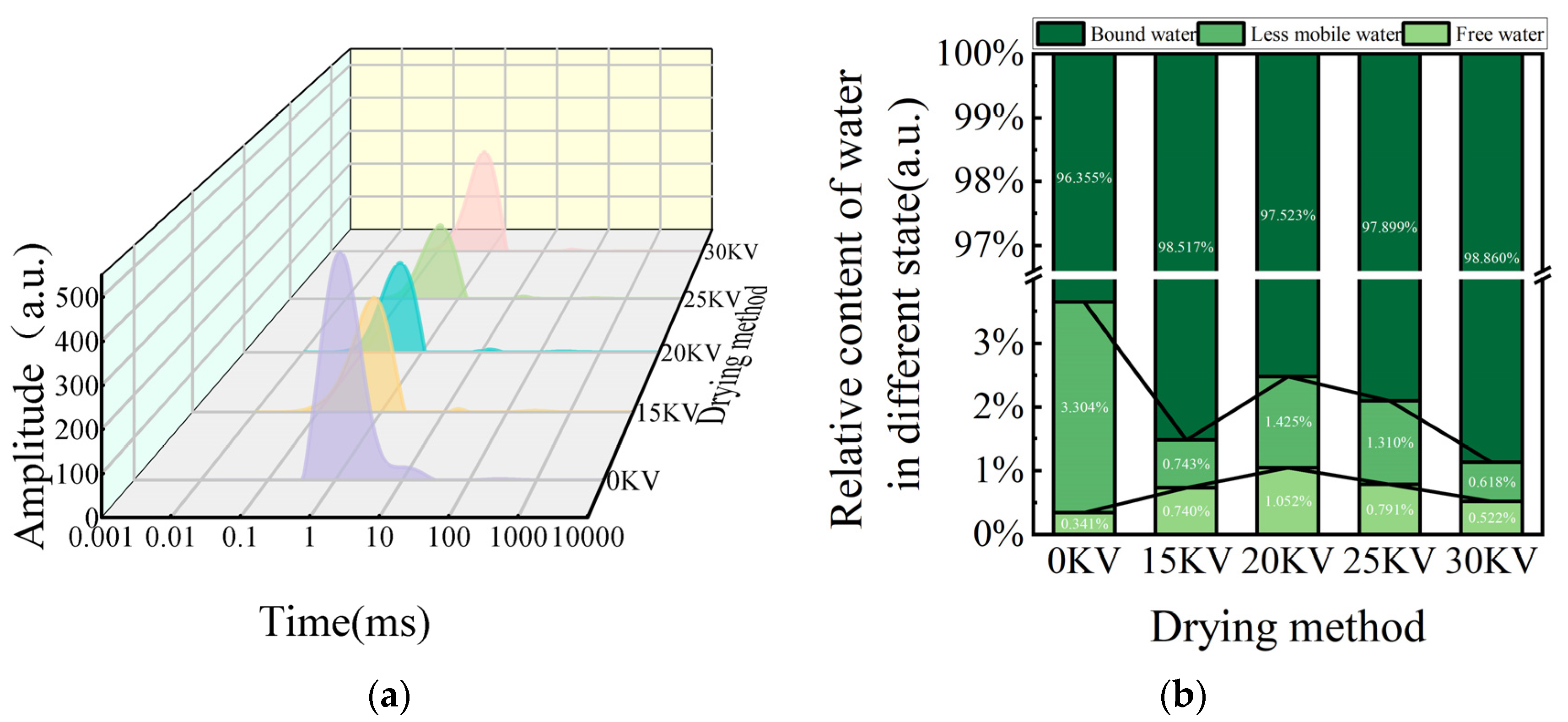
3.7. Low-Field NMR Analysis
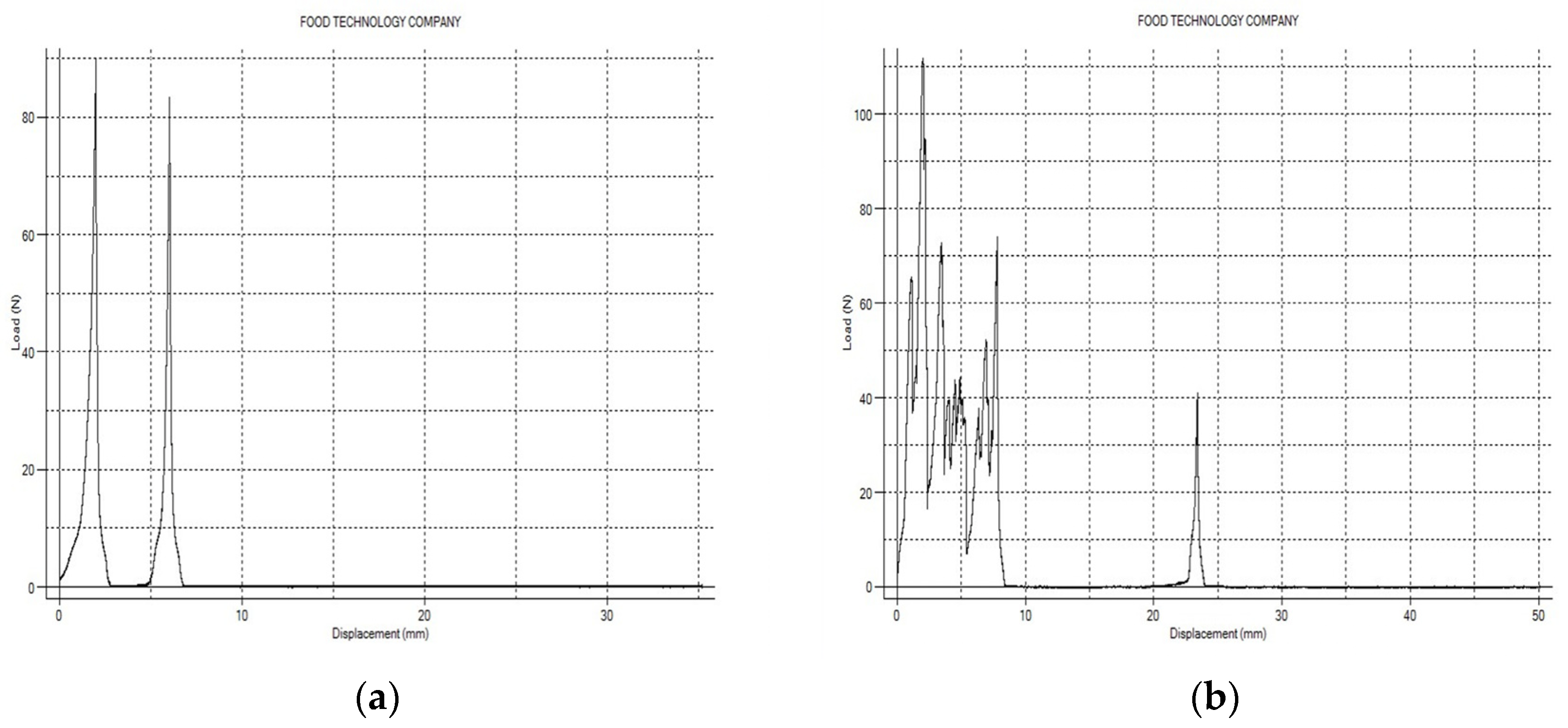
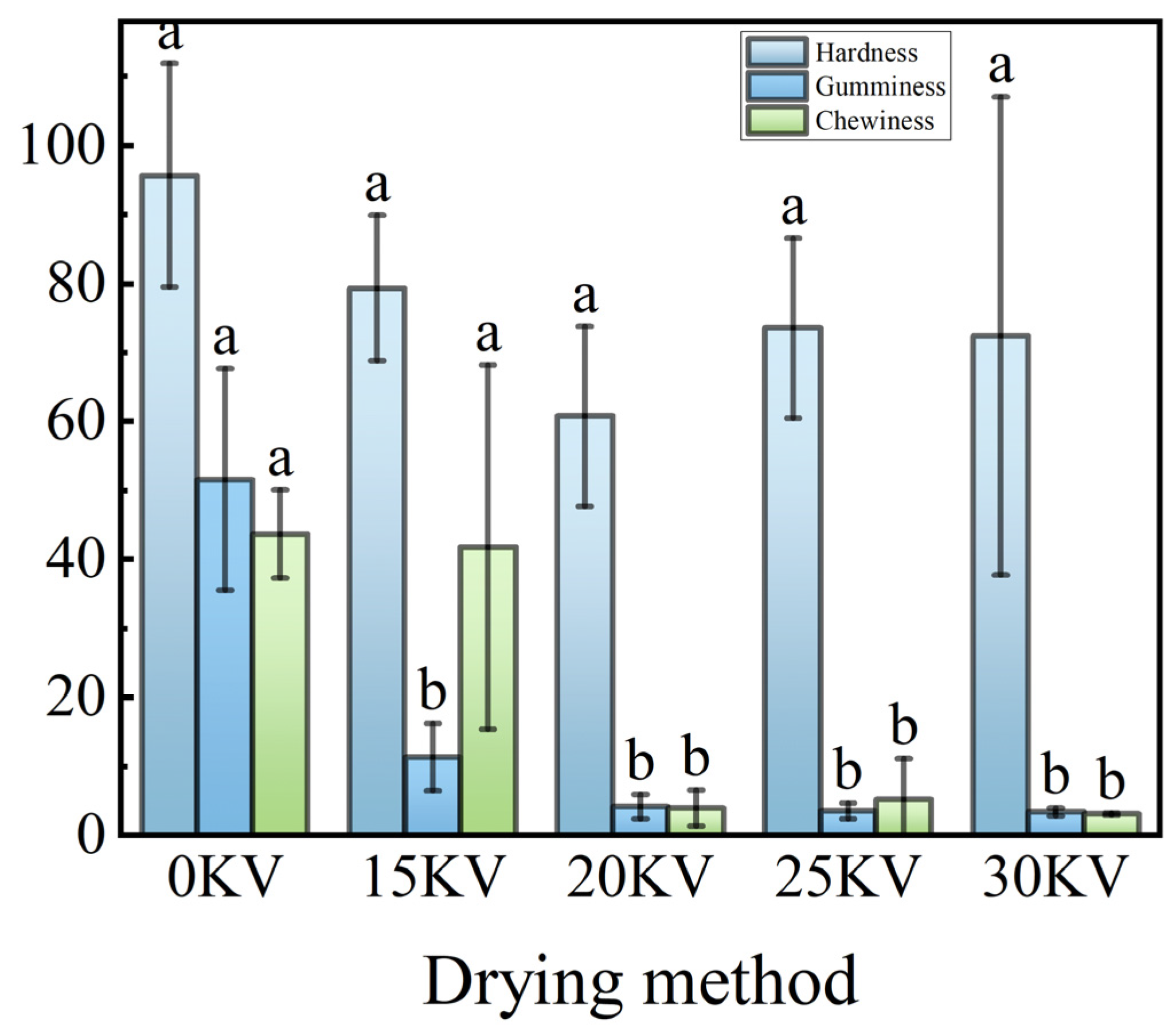
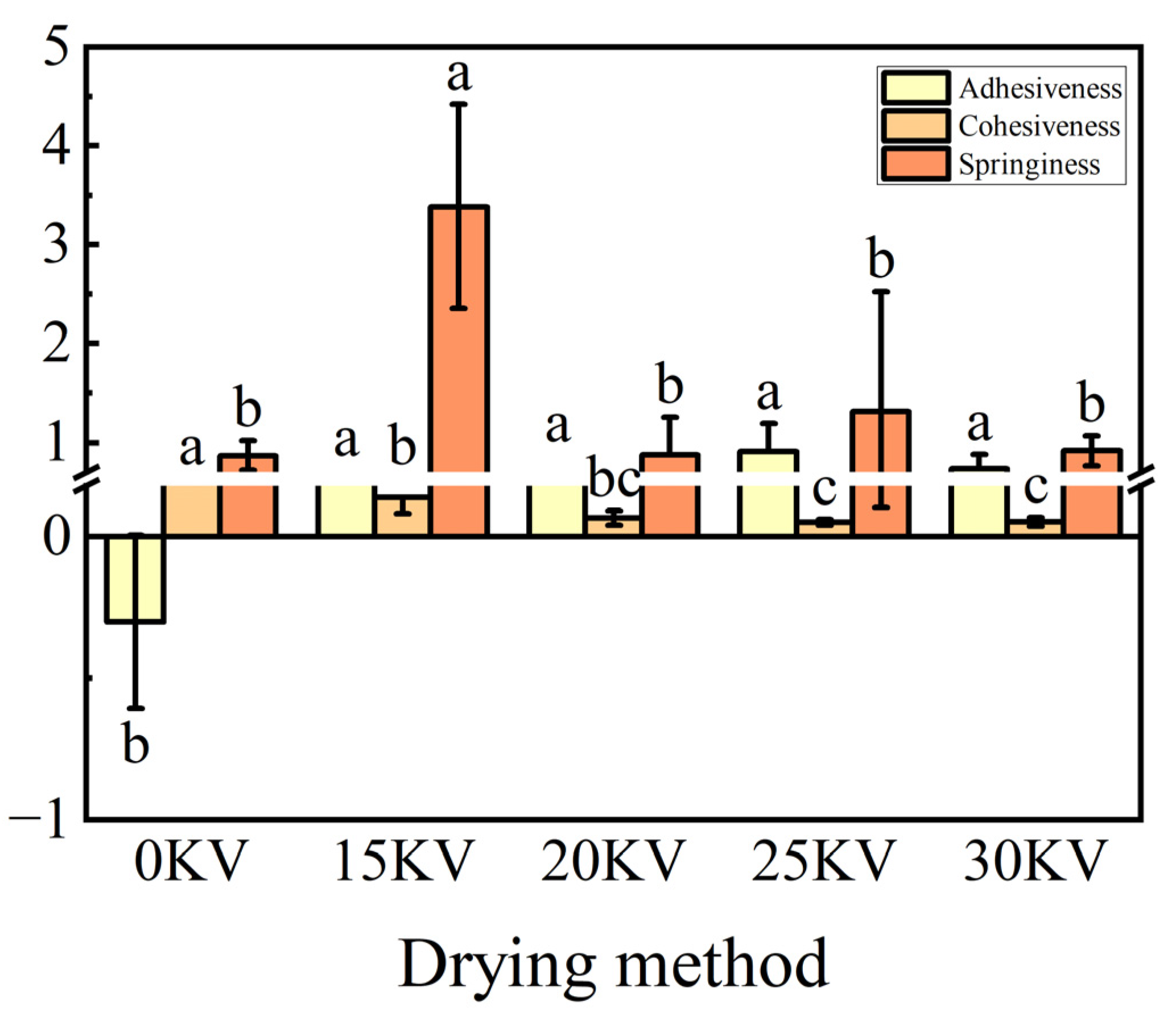
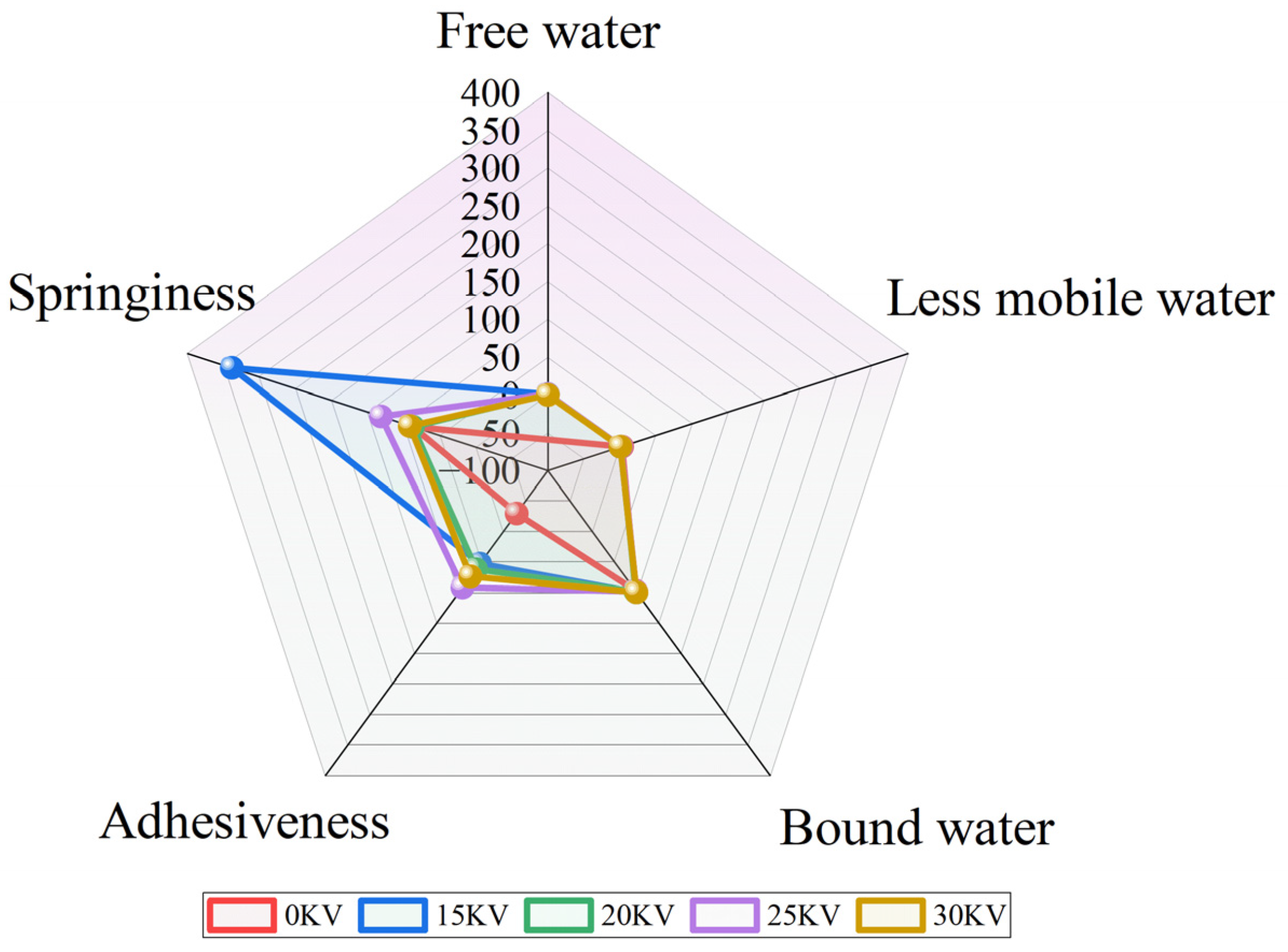
3.8. Texture Properties Analysis
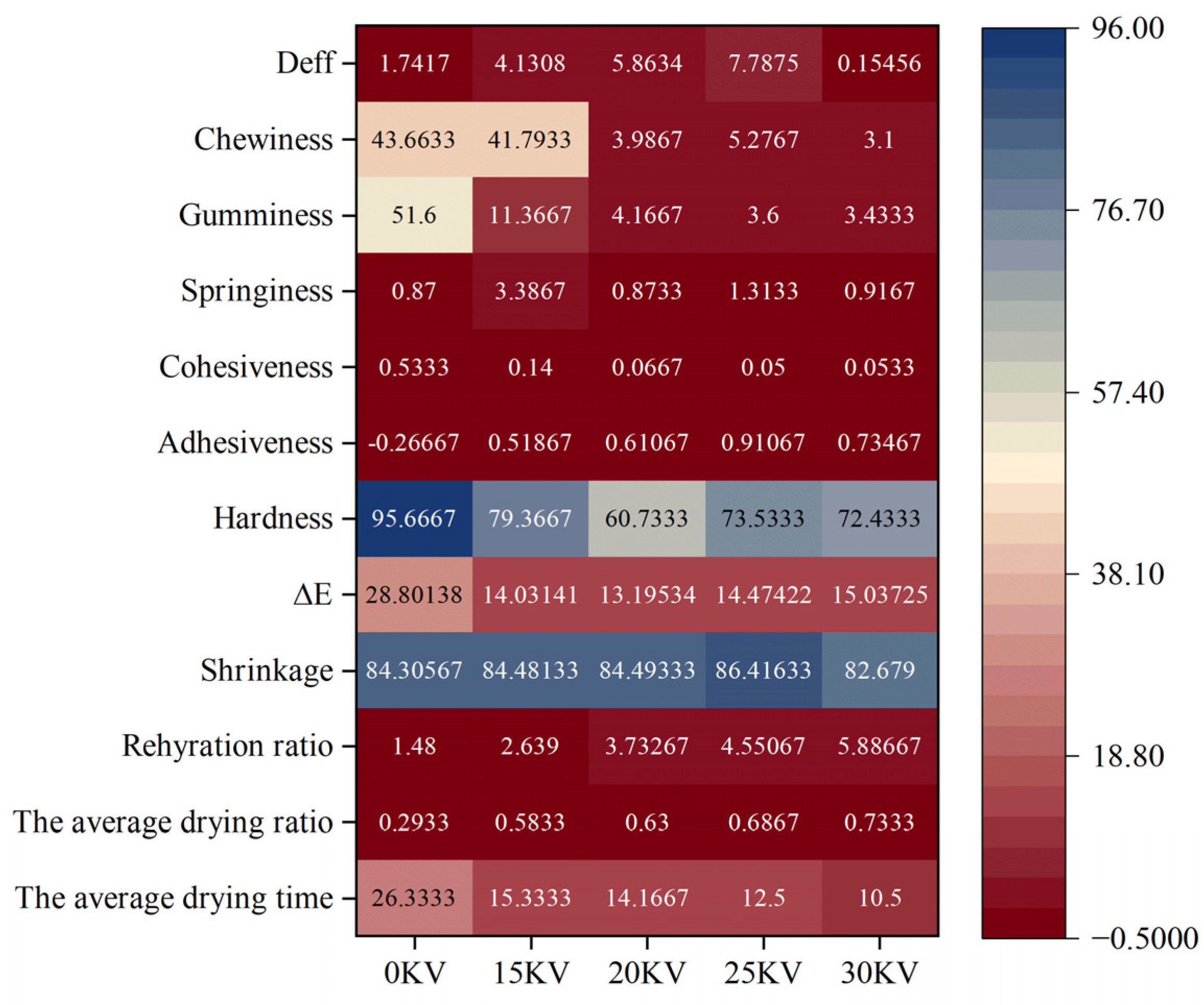
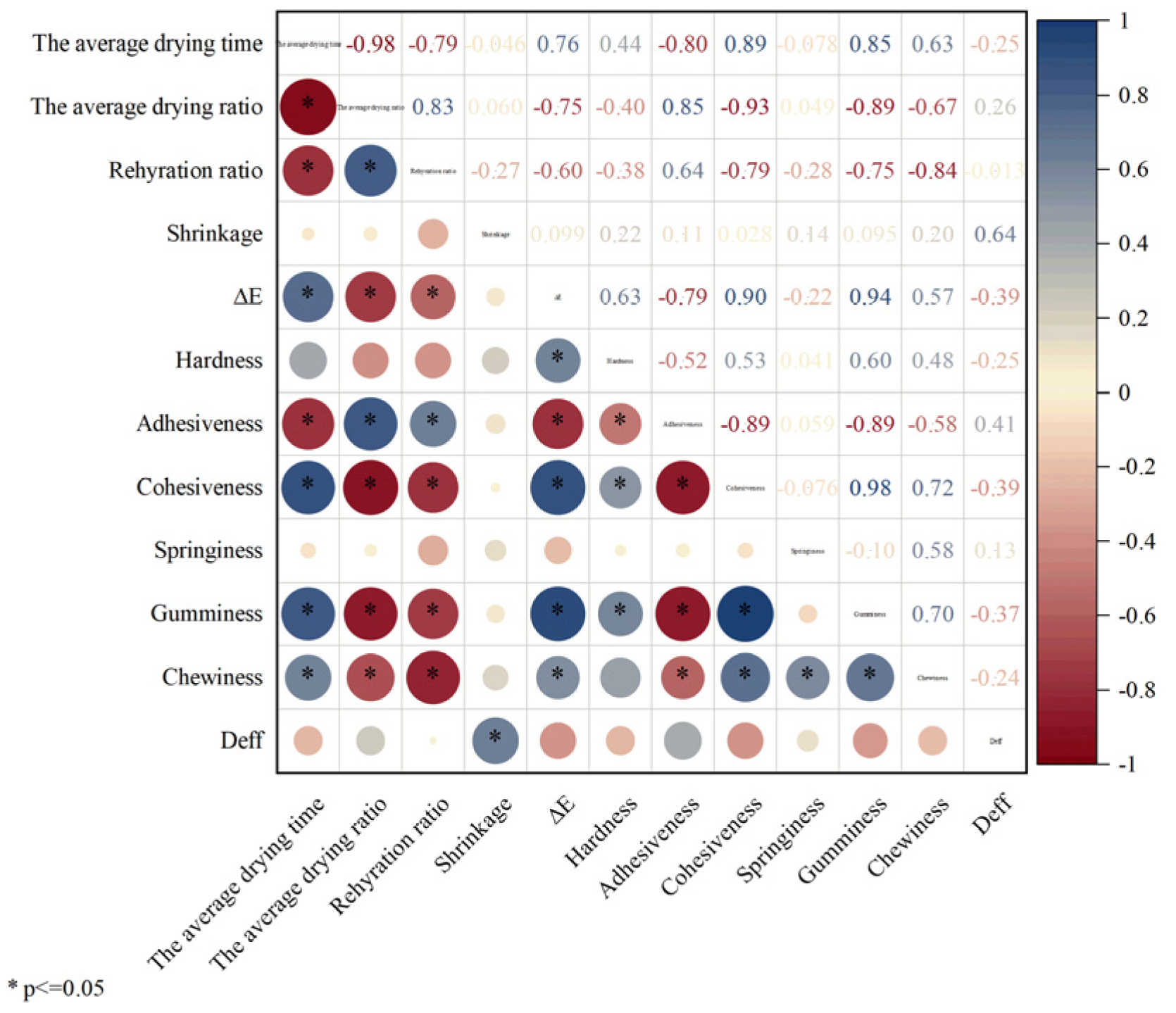
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.J.; Liu, Y.D.; Qin, T.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Fan, Y.F.; Yao, P.F.; Sun, C.; Bi, Z.Z.; Bai, J.P. Estimation of Chlorophyll Content in Potato Leaves Based on Machine Learning. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2024, 44, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, A.; Ma, W.; Cui, M.; Yin, G. My Views on the Strategy of Potato Staple Foodization. China Seed Ind. 2015, 34, 71–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, N.; Si, H.; Tang, X. Investigation and Development Countermeasures of Potato Processing Industry in China. Chin. Potato J. 2024, 38, 176–185. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Jiang, X.; Xie, J. Mathematical Modeling of Hot Air Drying of Thin Layer Litchi Flesh. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2012, 43, 151–158,191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Bai, A.; Yang, X.; Li, R. The Research Progress of Potato Drying Methods. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2017, 31, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikiru, Y.; Paliwal, J.; Erkinbaev, C. Three-Dimensional Characterization of Potatoes Under Different Drying Methods: Quality Optimization for Hybrid Drying Approach. Foods 2024, 13, 3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.B.; Bi, Y.X.; Vidyarthi, S.K.; Xiao, H.W.; Han, L.D.; Wang, J.; Fang, X.M. Non-thermal electrohydrodynamic (EHD) drying improved the volatile organic compounds of lotus bee pollen via HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC-MS. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 176, 114480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.; Wu, X.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, J. A review on recent advances and challenges of ionic wind produced by corona discharges with practical applications. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 2022, 55, 153002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Martynenko, A. The Effect of Material Thickness, Load Density, External Airflow, and Relative Humidity on the Drying Efficiency and Quality of EHD-Dried Apples. Foods 2022, 11, 2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Liang, Y. Experiment study on high electric field drying of carrot. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2004, 20, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Ding, C.; Lu, J.; Wang, H.; Han, B.; Zhang, J.; Duan, S.; Song, Z.; Chen, H. Drying characteristics of potato slices via electrohydrodynamics. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2024, 40, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, H.; Bai, A.; Wen, W.; Wang, Y. Effect of high voltage electric field drying and hot air drying on the secondary structure of potato proteins. Storage Process 2020, 20, 85–89. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynenko, A.; Kudra, T. Alternating versus direct current in electrohydrodynamic drying. Dry. Technol. 2022, 40, 2382–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Song, Z.Q.; Zhang, M.J.; Ma, Q.J.; Hu, W.H.; Ding, C.J.; Chen, H. Study on the damage and variation of Agropyron mongolicum induced by the combined action of discharge plasma and plasma-activated water. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 220, 109486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Shu, Q.; Xu, J.; Luo, X.; Lei, Z.; Jin, L.; Li, F. Identification and selection for anti-browning potato varieties(lines). Acta Agron. Sin. 2020, 46, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wang, W.; Wu, Q.; Xiong, J.; Wu, Y.; Huang, N.; Wang, Q.; Hu, H. Key Challenges and Solutions for Autonomous Preparation of Electronic Grade Ultrapure Water in China. Ind. Water Treat. 2023, 43, 1–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Ding, C.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Z.; Hu, X.; Hao, T. Electrohydrodynamic Drying of Chinese Wolfberry in a Multiple Needle-to-Plate Electrode System. Foods 2019, 8, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.A.; Ni, J.B.; Martynenko, A.; Chen, C.; Fang, X.M.; Ding, C.J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.W.; Xiao, H.W. Electrohydrodynamic drying of citrus (Citrus sinensis L.) peel: Comparative evaluation on the physiochemical quality and volatile profiles. Food Chem. 2023, 429, 136832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansiribhan, S.; Devahastin, S.; Soponronnarit, S. Quantitative Evaluation of Microstructural Changes and their Relations with Some Physical Characteristics of Food during Drying. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, E453–E461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowski, M.; Zielinska, M. Kinetics of water absorption and soluble-solid loss of hot-air-dried carrots during rehydration. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, C. Effect of Electrohydrodynamic Drying on Drying Characteristics and Physicochemical Properties of Carrot. Foods 2023, 12, 4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yi, J.; Bi, J.; Wu, X.; Peng, J.; Hou, C. Sensory, Texture and Nutritional Quality of Dried Shiitake Mushrooms (Lentinus edodes) as Affected by Different Drying Methods. Food Sci. 2019, 40, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wei, Y.; Zuo, X.; Cong, J.; Meng, Y. The atmospheric pressure air plasma jet with a simple dielectric barrier. Thin Solid Film 2012, 521, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Jin, F.; Ma, S.; Liu, X.; Leng, X.; Chen, K. Microanalysis of Active Nitrogen Oxides (RONS) Generation Characteristics during DC Negative Corona Discharge at a Needle-Plate Electrode. Plasma 2023, 6, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciprian Foronda, K.D.; Gafaro Garces, D.C.; Restrepo Rendon, L.; Mendoza Alvites, Y.Y.; Ricardo Sagra, J.P.; Orozco Mendoza, G.L.; Zartha Sossa, J.W. Electrohydrodynamic Drying in Agribusiness: Literature Review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 5, 761297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esehaghbeygi, A.; Basiry, M. Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) drying of tomato slices (Lycopersicon esculentum). J. Food Eng. 2011, 104, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynenko, A.; Kudra, T. Electrically-induced transport phenomena in EHD drying—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 54, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinani, S.T.; Hamdami, N.; Shahedi, M.; Havet, M. Mathematical modeling of hot air/electrohydrodynamic (EHD) drying kinetics of mushroom slices. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 86, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, S.; Liang, Q.; Ma, Z.; Han, F.; Xu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wu, W. Low temperature plasma pretreatment enhances hot-air drying kinetics of corn kernels. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, E13195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Wu, H. Non-enzymatic Browning Mechanism of Orange Juice and Its Control. Food Ferment. Ind. 2011, 37, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Mei, Y.; Kang, D.M. Experiment of drying kelp with high voltage electric fields. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on High Voltage Engineering and Application, Chongqing, China, 9–13 November 2008; pp. 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wang, B.; Lin, J.; Li, C.; Zhao, Q. Experimental study on technological parameters of freeze-drying of mushroom. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2004, 20, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, A.; Ding, C. Effect of Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) on Drying Kinetics and Quality Characteristics of Shiitake Mushroom. Foods 2022, 11, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esehaghbeygi, A.; Pirnazari, K.; Sadeghi, M. Quality assessment of electrohydrodynamic and microwave dehydrated banana slices. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Janabi, A.H.A.; Hayati Roodbari, N.; Homayouni Tabrizi, M. Investigating the anticancer and anti-angiogenic effects of graphene oxide nanoparticles containing 6-gingerol modified with chitosan and folate. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2023, 14, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarazin, J.; Poljansek, I.; Pizzi, A.; Sernek, M. Curing Kinetics of Tannin and Lignin Biobased Adhesives Determined by DSC and ABES. J. Renew. Mater. 2022, 10, 2117–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Gao, X.K.; Wang, R.; Liu, C.; Wu, J.Y.; Huang, Q. Evaluation of Polysaccharide Content in Shiitake Culinary-Medicinal Mushroom, Lentinula edodes (Agaricomycetes), via Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Integrated with Deep Learning. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2023, 25, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Ding, C.; Jia, Y.; Wang, H.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Duan, S.; Song, Z.; Chen, H.; Lu, J. Influence of electrohydrodynamics on the drying characteristics and physicochemical properties of garlic. Food Chem.-X 2023, 19, 100818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladejo, A.O.; Ma, H.; Qu, W.; Zhou, C.; Wu, B.; Yang, X. Influence of ultrasound pretreatments on diffusion coefficients, texture and colour of osmodehydrated sweet potato (Ipomea batatas). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Shi, J.; Walid, E.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Xue, S.J. Reverse micellar extraction of lectin from black turtle bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): Optimisation of extraction conditions by response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Espinosa, M.E.; Guevara-Oquendo, V.H.; He, J.F.; Zhang, W.X.; Yu, P.Q. Research updates and progress on nutritional significance of the amides I and II, alpha-helix and beta-sheet ratios, microbial protein synthesis, and steam pressure toasting condition with globar and synchrotron molecular microspectroscopic techniques with chemometrics. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 65, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Mehmood, W.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, C.; Blecker, C. Effects of low voltage electrostatic field thawing on the changes in physicochemical properties of myofibrillar proteins of bovine Longissimus dorsi muscle. J. Food Eng. 2019, 261, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, J.; Cai, C.; Yan, Q.; Hu, M.; Liu, Q.; Wei, C. Applications of Infrared Spectroscopy in the Analysis of Ordered Structure of Starch Grain. Acta Agron. Sin. 2012, 38, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinsky, L.; Guenther, E.; Mikus, P.; Stehling, M.; Rubinsky, B. Electrolytic Effects During Tissue Ablation by Electroporation. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 15, NP95–NP103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.C. Research on the Influence of New Food Processing Technologies on Food Quality. China Food 2024, 14, 98–100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyssanbek, M.; Kuzina, N.; Kondrashchenko, V.; Azimov, A. Effects of plasma treatment on biodegradation of natural and synthetic fibers. npj Mater. Degrad. 2024, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wei, Y. Effects of Processing Technology on the Water State in Chinese Dried Noodles during Drying Processes. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 19, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, P. Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance of maize seed germination process under salt stress. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cheng, X.; Yang, S.; Luo, Z.; Liu, Z. Model for predicting the moisture content of kiwifruit slices during hot air drying based on low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Li, Y.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, W.; Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Zhang, R. Use of low-field nuclear magnetic resonance for moisture variation analysis of fresh in-shell peanut during different drying methods. J. Food Process Eng. 2023, 46, E14486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowafy, S.; Guo, J.; Lei, D.; Liu, Y. Application of novel blanching and drying technologies improves the potato drying kinetics and maintains its physicochemical attributes and flour functional properties. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 94, 103648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Liang, J.; Liu, H.; Cao, X.; Ge, Y.; Li, J. Sweet cherry softening accompanied with moisture migration and loss during low-temperature storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 3651–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, Y.; Song, P.; Yang, L.; Du, M.; Jiang, F. Analysis of the moisture content and migration changes of blueberries during storage by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhuang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Tian, Y. Influence of microwave vacuum drying on glass transition temperature, gelatinization temperature, physical and chemical qualities of lotus seeds. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, S.; Wang, Z.; Regenstein, J.M.; Luo, Y. Influence of lightly salting and sugaring on the quality and water distribution of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) during super chilled storage. J. Food Eng. 2017, 215, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Peng, C.; Wang, L.; Xie, A.; Liu, Y. Effect of ultrasound power on moisture status change of apple by contact ultrasound reinforced far-infrared radiation drying. Dry. Technol. 2024, 42, 2256–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothibe, K.J.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Wang, Y.C.; Cheng, X. Effects of Ultrasound and Microwave Pretreatments of Apple Before Spouted Bed Drying on Rate of Dehydration and Physical Properties. Dry. Technol. 2014, 32, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaiotto, L.L.; Dello Staffolo, M. Drying kinetics, microstructure, and texture of cheese cracker fillings. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 123, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ali, M.; Parthasarathy, R. Influence of microwave drying and conventional drying methods on the mechanical properties of naproxen sodium drug tablets. Particuology 2020, 53, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Tang, W.; Han, F.; Gao, X. Rheological Properties and Structural Change of Dried Abalone Meat Produced by Two Different Drying Methods during Rehydration. Food Sci. 2015, 36, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Dong, X.; Li, P.; Li, D.; Duan, Y. Changes in Texture Properties of Crisp Peach during Postharvest Storage by Texture Profile Analysis. Food Sci. 2013, 34, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoufi, S.; Lazou, A.E.; Giannakourou, M.C.; Krokida, M.K. Air drying kinetics and quality characteristics of osmodehydrated-candied pumpkins using alternative sweeteners. Dry. Technol. 2021, 39, 2194–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-Y.; Xu, G.-Y. Investigation of Macromolecule/Surfactant Interaction by Interfacial Dilational Rheology Method. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2009, 25, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Bassey, A.P.; Cao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Huang, M.; Yang, H. Food protein aggregation and its application. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


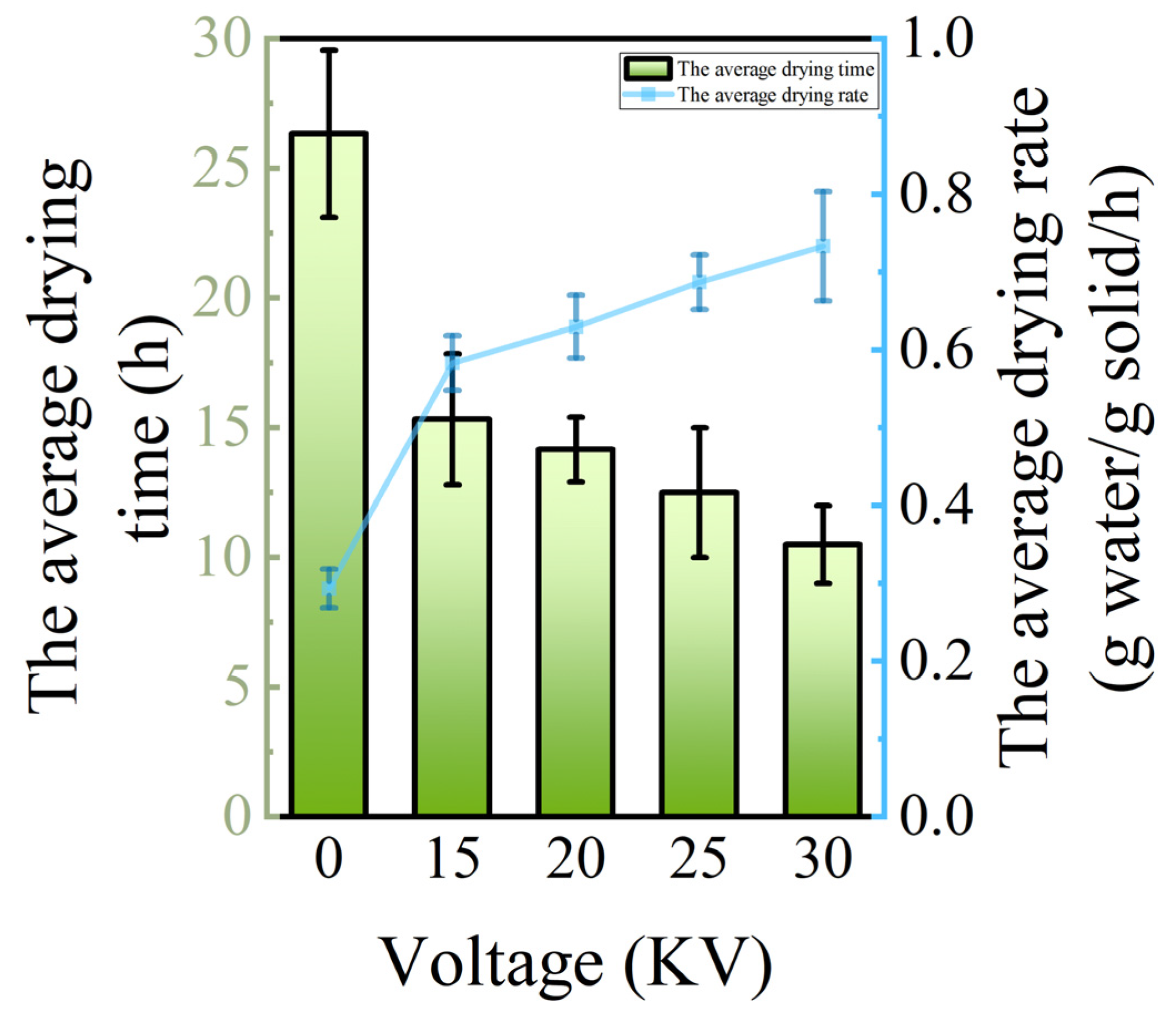
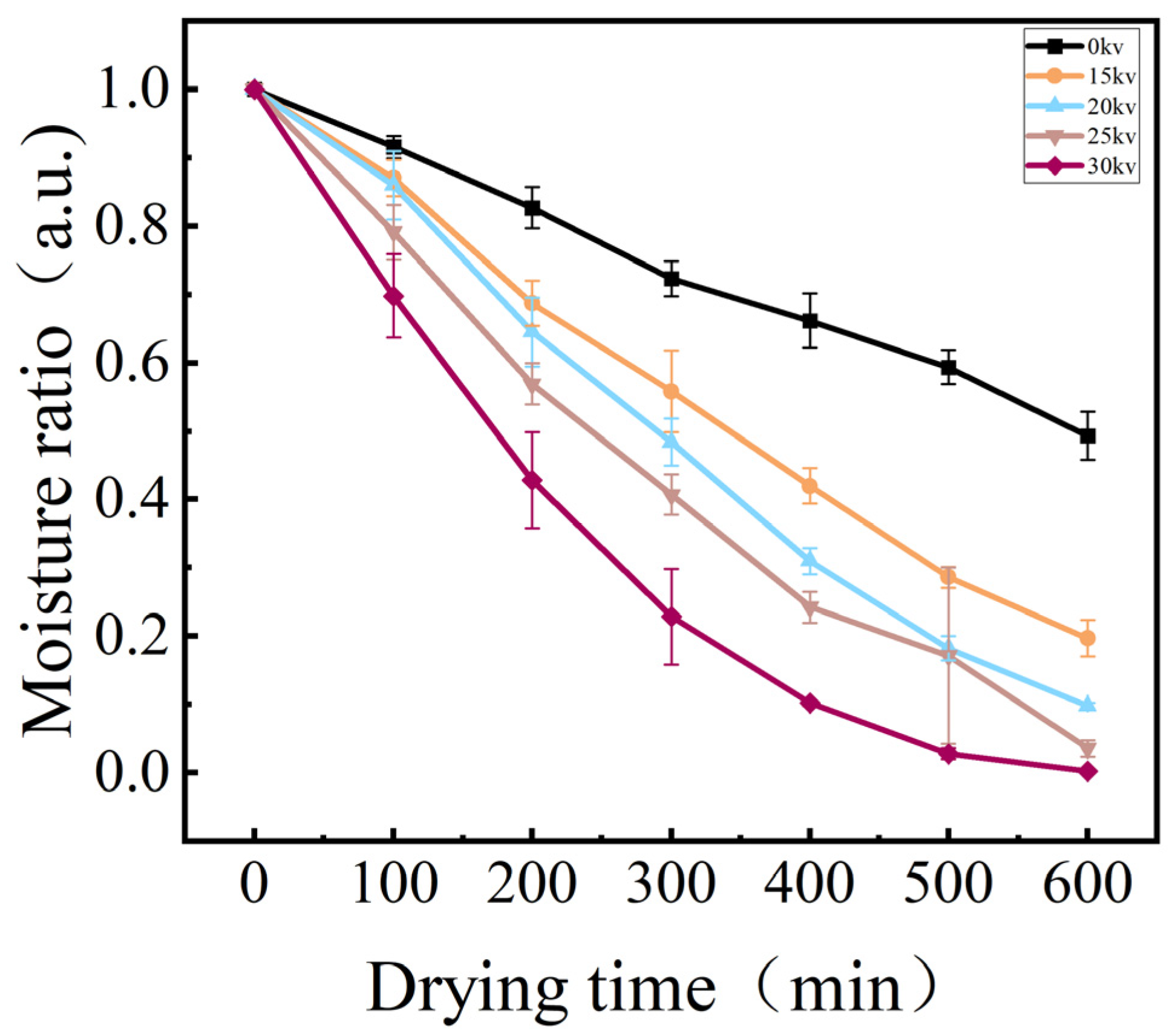
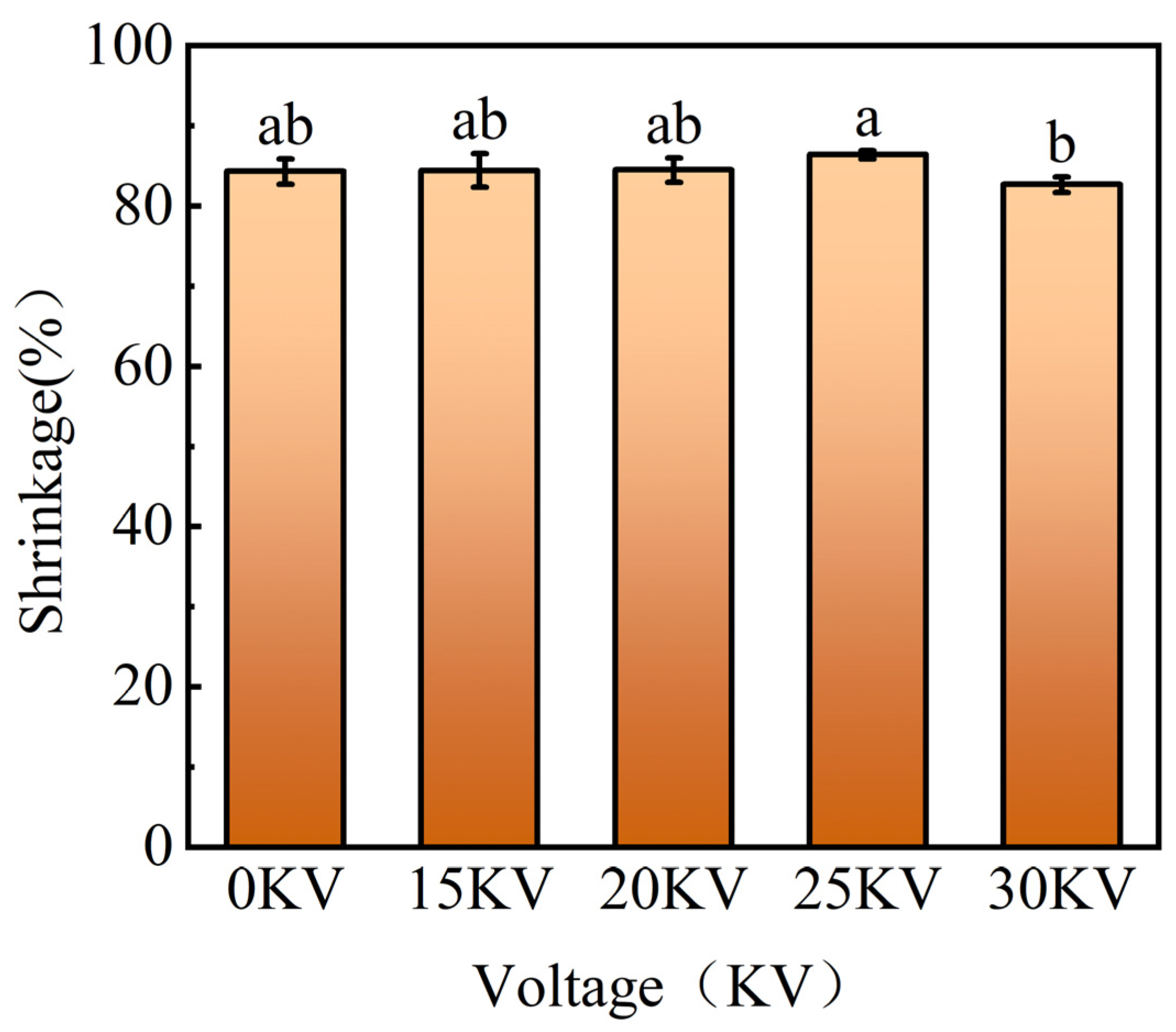
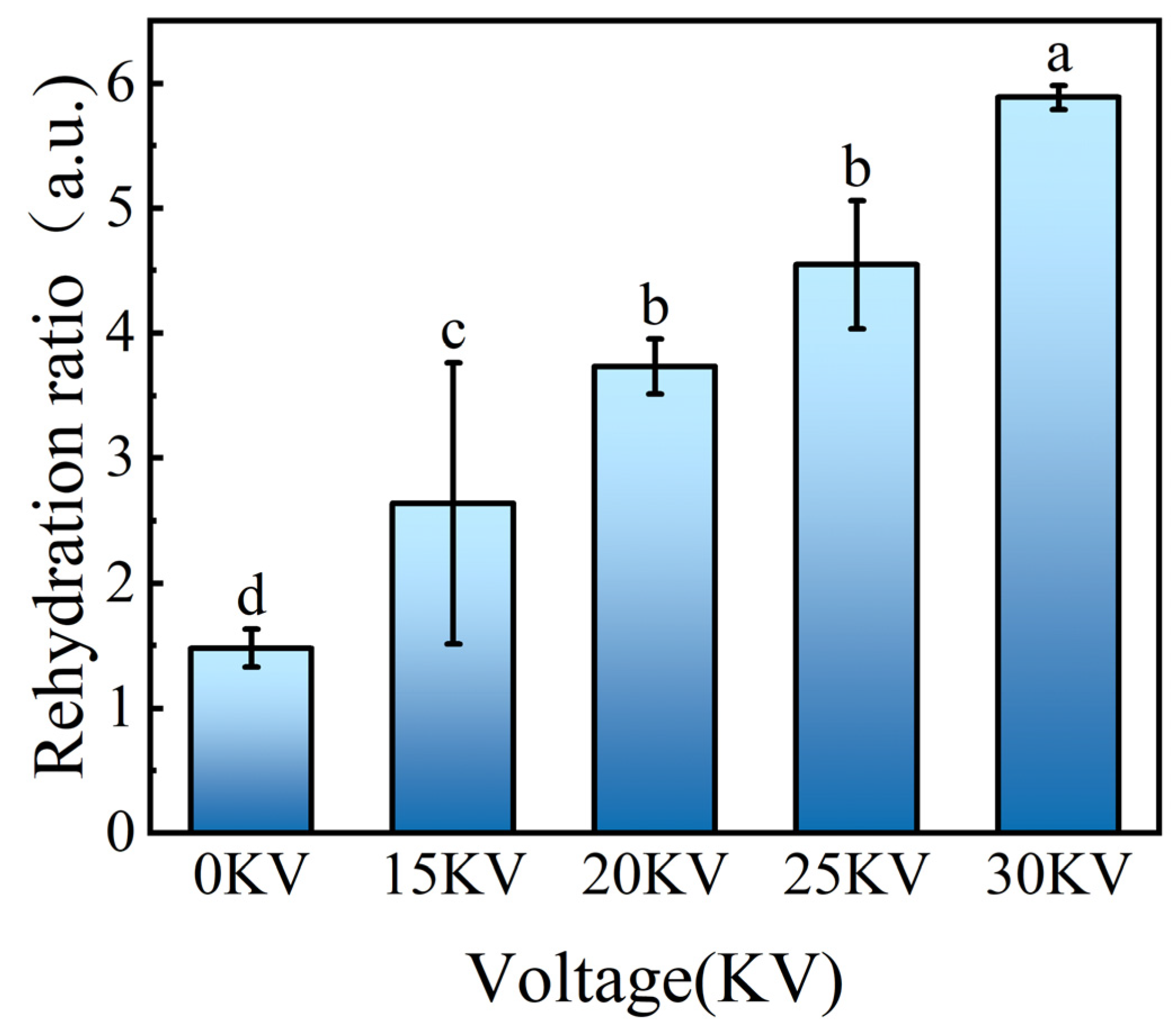

| Voltage | Linear Model | R2 | Deff (m2/s) | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 kV | lnMR = −1.91 × 10−5t + 0.02336 | 0.98958 | 1.7417 × 10−11 | 120.37 | 2.2 × 10−9 |
| 15 kV | lnMR = −4.53 × 10−5t + 0.12226 | 0.97550 | 4.1308 × 10−11 | 128.34 | 1.5 × 10−9 |
| 20 kV | lnMR = −6.43 × 10−5t + 0.22602 | 0.95872 | 5.8634 × 10−11 | 130.20 | 1.2 × 10−9 |
| 25 kV | lnMR = −8.54 × 10−5t + 0.33431 | 0.90363 | 7.7875 × 10−11 | 125.84 | 2.0 × 10−9 |
| 30 kV | lnMR = −1.69 × 10−4t + 0.84121 | 0.84784 | 1.5456 × 10−10 | 130.76 | 1.1 × 10−9 |
| Voltage | L1 | a1 | b1 | ∆E | C | Whiteness | h° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh | 38.20 ± 0.90 a | 5.66 ± 0.33 a | 14.89 ± 0.40 a | — | — | — | — |
| 0 kV | 16.90 ± 6.52 c | 5.80 ± 5.93 a | 6.38 ± 3.18 b | 28.80 ± 7.78 a | 8.96 ± 6.04 b | 16.29 ± 6.87 b | 0.93 ± 0.37 a |
| 15 kV | 26.49 ± 1.65 b | 6.74 ± 1.79 a | 14.08 ± 1.53 a | 14.03 ± 1.79 b | 15.65 ± 1.99 a | 24.82 ± 1.21 a | 1.12 ± 0.07 a |
| 20 kV | 26.52 ± 1.11 b | 4.83 ± 0.87 a | 12.10 ± 0.28 a | 13.19 ± 1.37 b | 13.05 ± 0.57 ab | 25.37 ± 0.99 a | 1.19 ± 0.05 a |
| 25 kV | 25.16 ± 0.58 b | 5.67 ± 0.95 a | 14.56 ± 0.96 a | 14.47 ± 0.42 b | 15.64 ± 0.86 a | 23.54 ± 0.38 a | 1.19 ± 0.06 a |
| 30 kV | 24.65 ± 1.57 b | 4.82 ± 3.86 a | 15.64 ± 2.52 a | 15.03 ± 2.51 b | 16.68 ± 2.28 a | 22.79 ± 1.03 a | 1.27 ± 0.24 a |
| Conditions | Random Coil | α-Helix | β-Turn | β-Antiparallel | β-Sheet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 kV | 15.07% | 12.99% | 27.19% | 2.82% | 41.93% |
| 15 kV | 12.77% | 10.02% | 22.23% | 1.70% | 53.28% |
| 20 kV | 11.99% | 11.50% | 24.14% | 2.21% | 50.16% |
| 25 kV | 12.76% | 10.87% | 22.65% | 3.58% | 50.14% |
| 30 kV | 12.88% | 22.04% | 14.95% | 6.16% | 43.97% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Ding, C.; Xiong, H.; Tian, T.; Zhu, L.; Dou, Y. Influence of Electrohydrodynamics on Drying Characteristics, Physicochemical Properties, and Texture Characteristics of Potato. Foods 2025, 14, 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101752
Zhang L, Ding C, Xiong H, Tian T, Zhu L, Dou Y. Influence of Electrohydrodynamics on Drying Characteristics, Physicochemical Properties, and Texture Characteristics of Potato. Foods. 2025; 14(10):1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101752
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Liye, Changjiang Ding, Huina Xiong, Tian Tian, Lifeng Zhu, and Yufan Dou. 2025. "Influence of Electrohydrodynamics on Drying Characteristics, Physicochemical Properties, and Texture Characteristics of Potato" Foods 14, no. 10: 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101752
APA StyleZhang, L., Ding, C., Xiong, H., Tian, T., Zhu, L., & Dou, Y. (2025). Influence of Electrohydrodynamics on Drying Characteristics, Physicochemical Properties, and Texture Characteristics of Potato. Foods, 14(10), 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101752





