Structural Characterization and Bioactivity Evaluation of Selenium-Modified Dihydromyricetin from Vine Tea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Se-DHM
2.3. Structural Identification of Se-DHM
2.3.1. Color Analysis
2.3.2. Morphological Analysis
2.3.3. Spectroscopic Analysis
2.3.4. HPLC of Se-DHM
2.3.5. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS) of Se-DHM
2.4. In Vitro Hypoglycemic Activity Assay
2.5. Anti-Tumor Activity Experiments
2.5.1. Colony Formation Assay
2.5.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.5.3. Scratch Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chroma Analysis
3.2. SEM Analysis
3.3. UV−Vis Analysis
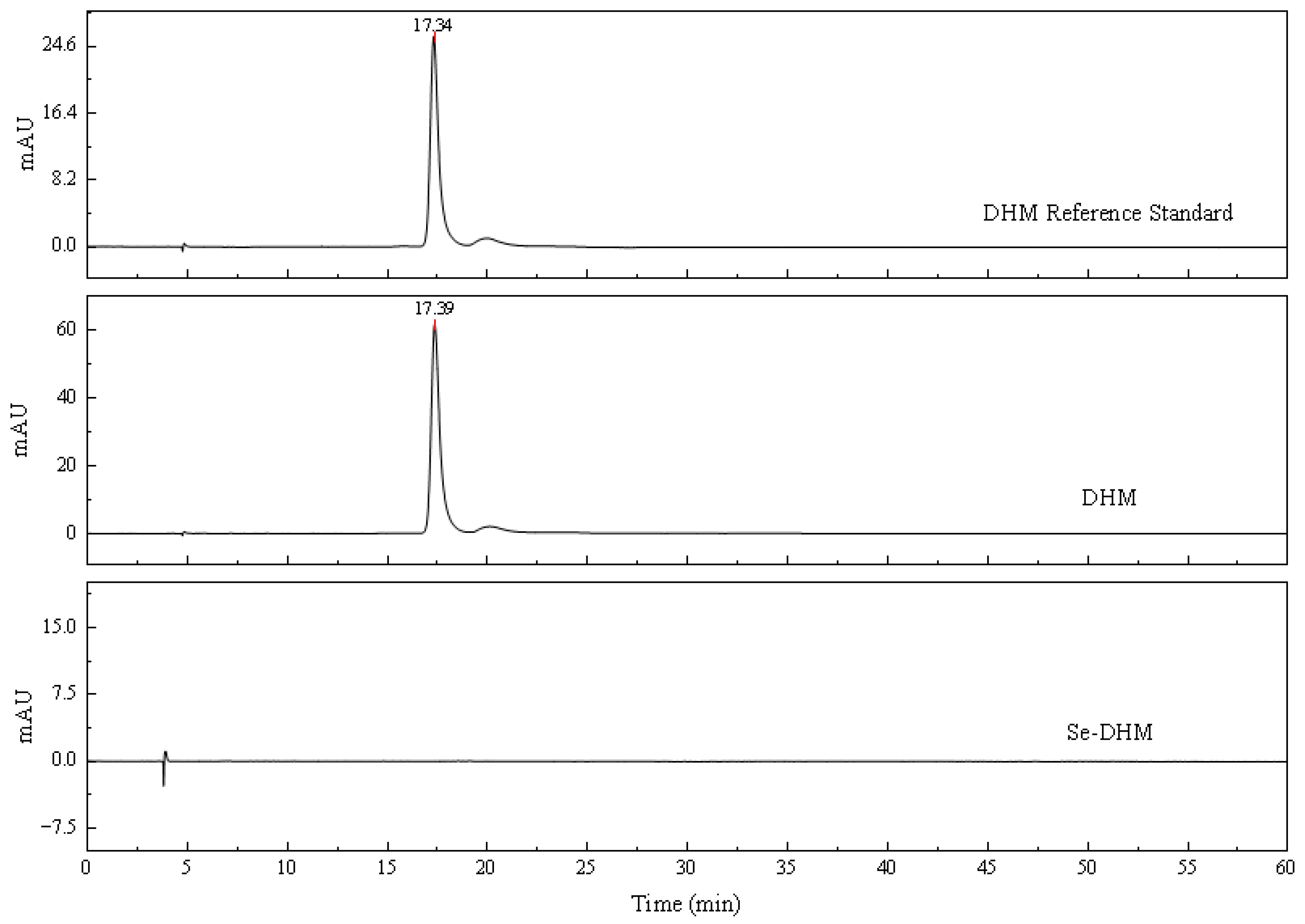
3.4. HPLC Analysis
3.5. FTIR and XRD Analyses
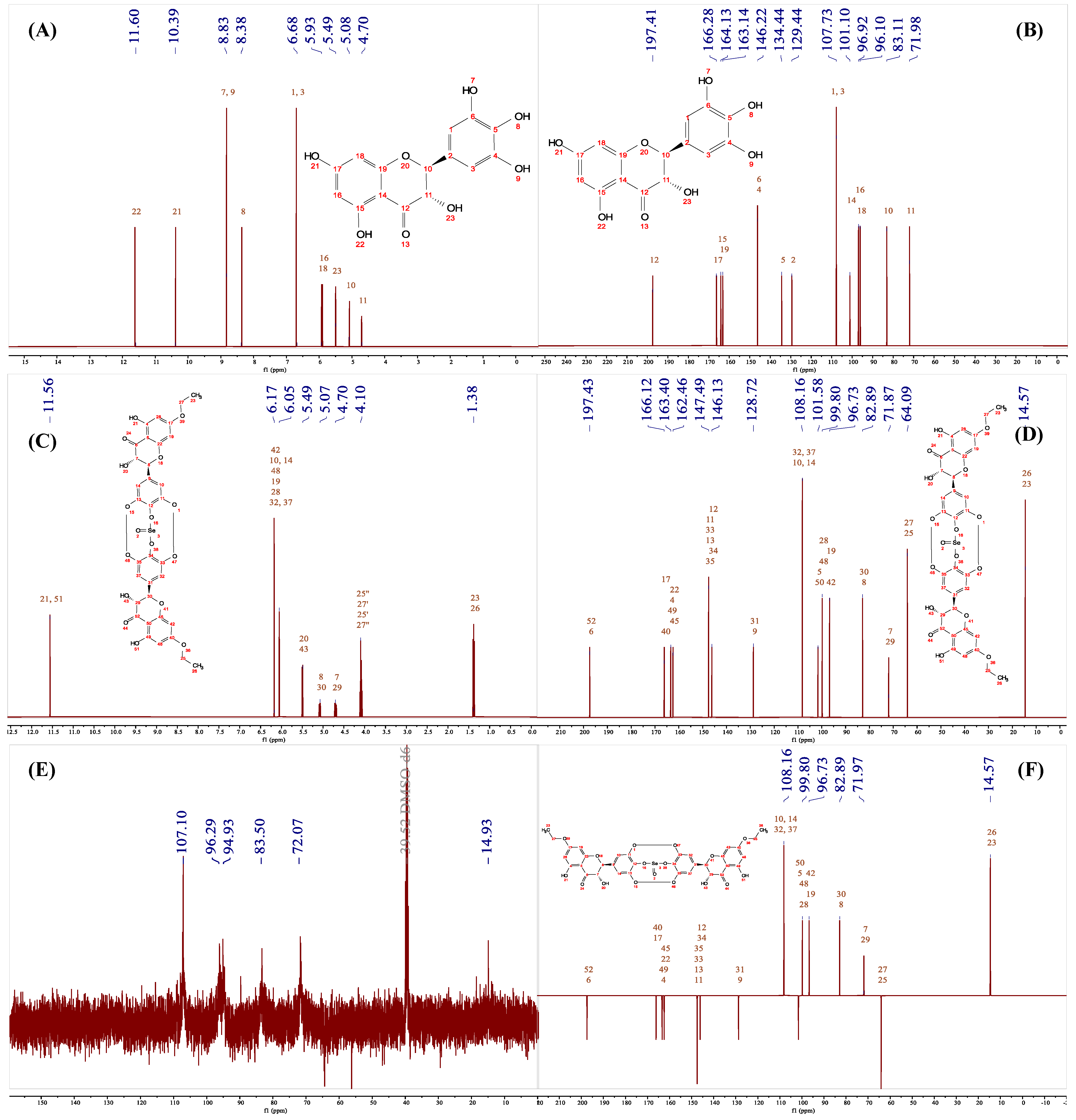
3.6. HRMS and NMR Analysis
3.7. Blood-Glucose-Lowering Ability
3.8. Anti-Tumor Activity
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| α-AMY | α-amylase |
| α-GLU | α-glucosidase |
| CQDs | Carbon quantum dots |
| DHM | Dihydromyricetin |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| HRMS | High-resolution mass spectrometry |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer solution |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| Se | Selenium |
| Se-CPPS | Selenium-modified Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharides |
| Se-DHM | Selenium-modified dihydromyricetin |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| SSNMR | Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance |
| TLC | Thin-layer chromatography |
| UV−Vis | Ultraviolet−visible |
| XRD | X-ray diffractometer |
References
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiang, H.; Ding, P.; Wu, T.; Ji, G. Recent update on application of dihydromyricetin in metabolic related diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 148, 112771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Fei, T.; Lin, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z. Natural α-glucosidase inhibitors from Aquilaria sinensis leaf-tea: Targeted bio-affinity screening, identification, and inhibition mechanism. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Luo, T.; Hou, J.; Fei, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. Natural α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitors from raspberry (Rubus corchorifolius L.) leaf-tea: Screening, identification and molecular docking analysis. LWT 2023, 181, 114763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Teng, H.; Lv, Q.; Gao, H.; Guo, T.; Lin, Y.; Gao, S.; Ma, M.; Chen, L. Anti-hyperglycemic effects of dihydromyricetin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2021, 10, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, Z.; Yue, Z.; Yang, Z. Research progress of dihydromyricetin in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1216907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xiao, Z.; Li, H.; Zhu, N.; Gu, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Qin, L. Present Status, Challenges, and Prospects of Dihydromyricetin in the Battle against Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Guo, Q.; Gu, Y.; Shi, T.-Q. Advances in Flavonoid and Derivative Biosynthesis: Systematic Strategies for the Construction of Yeast Cell Factories. ACS Synth. Biol. 2024, 13, 2667–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Garcia, D.; Uceda, C.; Barahona, L.; Ruiz-Nuñez, M.; Ballesteros, A.O.; Desmet, T.; Sanz-Aparicio, J.; Fernandez-Lobato, M.; Gonzalez-Alfonso, J.L.; Plou, F.J. Enzymatic modification of dihydromyricetin by glucosylation and acylation, and its effect on the solubility and antioxidant activity. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2024, 23, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, M.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. Evaluation of General Synthesis Procedures for Bioflavonoid–Metal Complexes in Air-Saturated Alkaline Solutions. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Yang, L. Brain-Targeting Dihydromyricetin-Decorated Selenium Nanoparticles Attenuate Oxidative Stress for Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 20411–20424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.T.; Liu, K.; Ning, M.; Ullah, K.; Wali, A.; Jatoi, M.A.; Muzaffar, N. Enhanced antioxidant activity of selenium-enriched brown rice protein against oxidative stress in mammalian erythrocytes under various cooking conditions. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroha, M.; Swami, R.; Singh, B.; Kumar, A.; Tomar, D. Selenium dioxide as a selenylating reagent: An overview and its Sanguine future. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202303071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandin, V.; Khalkar, P.; Braude, J.; Fernandes, A.P. Organic selenium compounds as potential chemotherapeutic agents for improved cancer treatment. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 127, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.; Yue, L.; Song, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cui, X. Preparation, characterization and evaluation of microwave-assisted synthesized selenylation Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 133228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Yu, X.; Wu, S.; Nong, G. Synthesis of Luteolin–Selenium Dioxide Complex under Acidic Catalysis. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2022, 92, 1534–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhu, B.; Luo, Y. Changes in chemical interactions and gel properties of heat-induced surimi gels from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) fillets during setting and heating: Effects of different washing solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 75, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Cui, P.; Tan, J.; Zhang, G.; Ge, S.; Cai, X. Separation of principal component dihydromyricetin from Ampelopsis grossedentata by high-speed counter-current chromatography and its interaction with corn starch. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 2350–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Luo, F.; Wang, M.; Fu, Z.; Shu, X. New Method for Extracting and Purifying Dihydromyricetin from Ampelopsis grossedentata. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 13955–13962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indira, A.; Shahar, B.; Joshi, B.; Chongtham, N. Assessment of bioactive compound variations and in-vitro and in-vivo antioxidant activity in edible fresh and processed Bambusa nutans shoot through FTIR, GC/MS and HPLC analyses. Food Chem. 2024, 452, 139552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Ma, F.; He, P.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Z.; Sun, S. Multi-spectroscopic characterization of organic salt components in medicinal plant. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchi, F.; De Rosso, M.; Flamini, R. Coupling between high-resolution mass spectrometry and focalized data-analysis methods provides the identification of new putative glycosidic non-anthocyanic flavonoids in grape. Metabolomics 2022, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qurtam, A.A.; Mechchate, H.; Es-Safi, I.; Al-Zharani, M.; Nasr, F.A.; Noman, O.M.; Aleissa, M.; Imtara, H.; Aleissa, A.M.; Bouhrim, M.; et al. Citrus Flavanone Narirutin, In Vitro and In Silico Mechanistic Antidiabetic Potential. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleixandre, A.; Gil, J.V.; Sineiro, J.; Rosell, C.M. Understanding phenolic acids inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase and influence of reaction conditions. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Ye, W.-C.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Dai, W.; Li, M. Anticancer effects of dihydromyricetin on the proliferation, migration, apoptosis and in vivo tumorigenicity of human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Qin, X.; Xu, Z.; Song, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Y.; Ruan, H.; Chen, J. Comparison of Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Anticancer Drugs between Real-Time Cell Analysis and CCK-8 Method. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 12036–12042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Lai, H.; Cao, Z.; Niu, Y.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, C.; Shang, L. Comparison of an Artificial Neural Network and a Response Surface Model during the Extraction of Selenium-Containing Protein from Selenium-Enriched Brassica napus L. Foods 2022, 11, 3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Sun, Y.; Liu, B.; Ming, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, C.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Shang, L. Selenium Modification of Natural Products and Its Research Progress. Foods 2023, 12, 3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Długosz, O.; Chmielowiec-Korzeniowska, A.; Drabik, A.; Tymczyna, L.; Banach, M. Bioactive Selenium Nanoparticles Synthesized from Propolis Extract and Quercetin Based on Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NDES). J. Clust. Sci. 2023, 34, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Ma, Y.; Lin, W.; Xu, K.; Chen, M. Study on the structure–activity of dihydromyricetin and its new production. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 116, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Su, L.; Xu, H. Selenium as an emerging versatile player in heterocycles and natural products modification. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 2268–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelani, K.M.; Nassar, A.M.W.; Omran, G.A.; Morshedy, S.; Elsonbaty, A.; Talaat, W. Chromatographic reversed HPLC and TLC-densitometry methods for simultaneous determination of serdexmethylphenidate and dexmethylphenidate in presence of their degradation products—With computational assessment. BMC Chem. 2023, 17, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žuvela, P.; Skoczylas, M.; Liu, J.J.; Ba̧czek, T.; Kaliszan, R.; Wong, M.W.; Buszewski, B. Column Characterization and Selection Systems in Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3674–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Haque, A.; Saleem, K. Separation and identification of curcuminoids in turmeric powder by HPLC using phenyl column. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2526–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H.; Xiao, D. Separation of carbon quantum dots on a C18 column by binary gradient elution via HPLC. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 8124–8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, T.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y. Dihydromyricetin solid dispersion: Preparation, characterization, and preservative effects on sturgeon fillets stored at 4 °C. LWT 2023, 174, 114387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Luo, X.; Zhu, R.; Zhong, K.; Ran, W.; Wu, Y.; Gao, H. Development and characterization of active bilayer film incorporated with dihydromyricetin encapsulated in hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin for food packaging application. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, S.; Hu, H.; Hu, T.; Shi, K.; Xu, Y.; Xu, G.; Hu, H.; Pan, S. Synthesis and evaluation of novel hesperidin selenium- enriched derivatives as potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agents. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-B.; Yang, T.; Bao, J.-K.; Fang, D.-M.; Li, G.-Y. Isochaetomium A2, a new bis(naphthodihydropyran-4-one) with antimicrobial and immunological activities from fungus Chaetomium microcephalum. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2014, 37, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krstić, G.; Saidu, M.B.; Barta, A.; Vágvölgyi, M.; Ali, H.; Zupkó, I.; Berkecz, R.; Gallah, U.S.; Rédei, D.; Hohmann, J. Anticancer Meroterpenoids from Centrapalus pauciflorus leaves: Chromone- and 2,4-Chromadione-Monoterpene Derivatives. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 31389–31398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, H.; Liu, X.; Gao, L.; Cheng, N.; Cao, W. Complexation of luteolin with lead (II): Spectroscopy characterization and theoretical researches. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 193, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, M.; Gao, L.; Cheng, N.; Cao, W. Spectroscopy characterization, theoretical study and antioxidant activities of the flavonoids-Pb(II) complexes. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1209, 127919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, I.I. Synthesis and bioactivity of a novel dandelion-like selenium and catechin complex. FARMACIA 2024, 72, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Hao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Cai, X.; Tang, J.; Liao, X.; Tan, J. Research progress on the hypoglycemic activity and mechanisms of natural polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambara Murthy, K.N.; Kim, J.; Vikram, A.; Patil, B.S. Differential inhibition of human colon cancer cells by structurally similar flavonoids of citrus. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Chen, L.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Luo, Y.; Xiong, Y. Antitumor Effects of Baicalein and Its Mechanism via TGFβ Pathway in Cervical Cancer HeLa Cells. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 5527190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, R.M.P.; Gómez, J.T.; Urby, R.B.; Soto, J.G.C.; Parra, H.R. Evaluation of Diabetes Effects of Selenium Nanoparticles Synthesized from a Mixture of Luteolin and Diosmin on Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes in Mice. Molecules 2022, 27, 5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghloul, R.A.; Abdelghany, A.M.; Samra, Y.A. Rutin and selenium nanoparticles protected against STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats through downregulating Jak-2/Stat3 pathway and upregulating Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 933, 175289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, B.; Huang, Q. The inhibitory effects of flavonoids on α-amylase and α-glucosidase. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.-X.; Yang, X.-H.; Zhang, H.-F.; Feng, J.; Zhang, M.-Y. Chemical Structure, Hypoglycemic Activity, and Mechanism of Action of Selenium Polysaccharides. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 4404–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkoana, J.K.; Mphahlele, M.J.; More, G.K.; Choong, Y.S. Exploring the 3,5-Dibromo-4,6-dimethoxychalcones and Their Flavone Derivatives as Dual α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Inhibitors with Antioxidant and Anticancer Potential. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvanathan, R.; Houghton, M.J.; Barber, E.; Williamson, G. Structure-function relationships in (poly)phenol-enzyme binding: Direct inhibition of human salivary and pancreatic α-amylases. Food Res. Int. 2024, 188, 114504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Wang, H.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X. Selenium-layered nanoparticles serving for oral delivery of phytomedicines with hypoglycemic activity to synergistically potentiate the antidiabetic effect. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Sample | L* | a* | b* | ΔE | Selenium Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n(DHM:SeO2) = 1:3 | 54.73 ± 0.10 d | 10.20 ± 0.39 a | 20.42 ± 0.20 c | 50.70 ± 0.10 a | 15.89 ± 0.20 a |
| n(DHM:SeO2) = 1:2 | 62.84 ± 0.00 c | 8.04 ± 0.01 c | 23.05 ± 0.01 b | 44.46 ± 0.00 b | 12.42 ± 0.12 b |
| n(DHM:SeO2) = 1:1 | 62.73 ± 0.60 c | 8.77 ± 0.04 b | 30.09 ± 0.60 a | 48.70 ± 0.09 c | 7.61 ± 0.13 c |
| n(DHM:SeO2) = 2:1 | 74.82 ± 0.17 b | 7.26 ± 0.01 d | 30.16 ± 0.18 a | 39.96 ± 0.03 d | 5.51 ± 0.07 d |
| n(DHM:SeO2) = 3:1 | 78.72 ± 0.13 a | 3.41 ± 0.02 e | 30.36 ± 0.66 a | 37.24 ± 0.46 e | 4.61 ± 0.11 e |
| DHM | 94.45 ± 0.28 | −2.06 ± 0.14 | 10.25 ± 0.40 | 11.84 ± 0.43 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, K.; Hou, G.; Mei, S.; Gao, X.; Zhang, C.; Shang, L.; Chen, S. Structural Characterization and Bioactivity Evaluation of Selenium-Modified Dihydromyricetin from Vine Tea. Foods 2025, 14, 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101735
Cheng K, Hou G, Mei S, Gao X, Zhang C, Shang L, Chen S. Structural Characterization and Bioactivity Evaluation of Selenium-Modified Dihydromyricetin from Vine Tea. Foods. 2025; 14(10):1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101735
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Kaixuan, Guangqian Hou, Shengqi Mei, Xingxing Gao, Chi Zhang, Longchen Shang, and Shuai Chen. 2025. "Structural Characterization and Bioactivity Evaluation of Selenium-Modified Dihydromyricetin from Vine Tea" Foods 14, no. 10: 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101735
APA StyleCheng, K., Hou, G., Mei, S., Gao, X., Zhang, C., Shang, L., & Chen, S. (2025). Structural Characterization and Bioactivity Evaluation of Selenium-Modified Dihydromyricetin from Vine Tea. Foods, 14(10), 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101735







