Electrospun Gelatin/Dextran Nanofibers from W/W Emulsions: Improving Probiotic Stability Under Thermal and Gastrointestinal Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Incubation of Lactobacillus plantarum
2.3. Preparation of Water-in-Water (W/W) Emulsions
2.4. Preparation of Electrospun Fibers
2.5. Characterization
2.6. Microbial Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
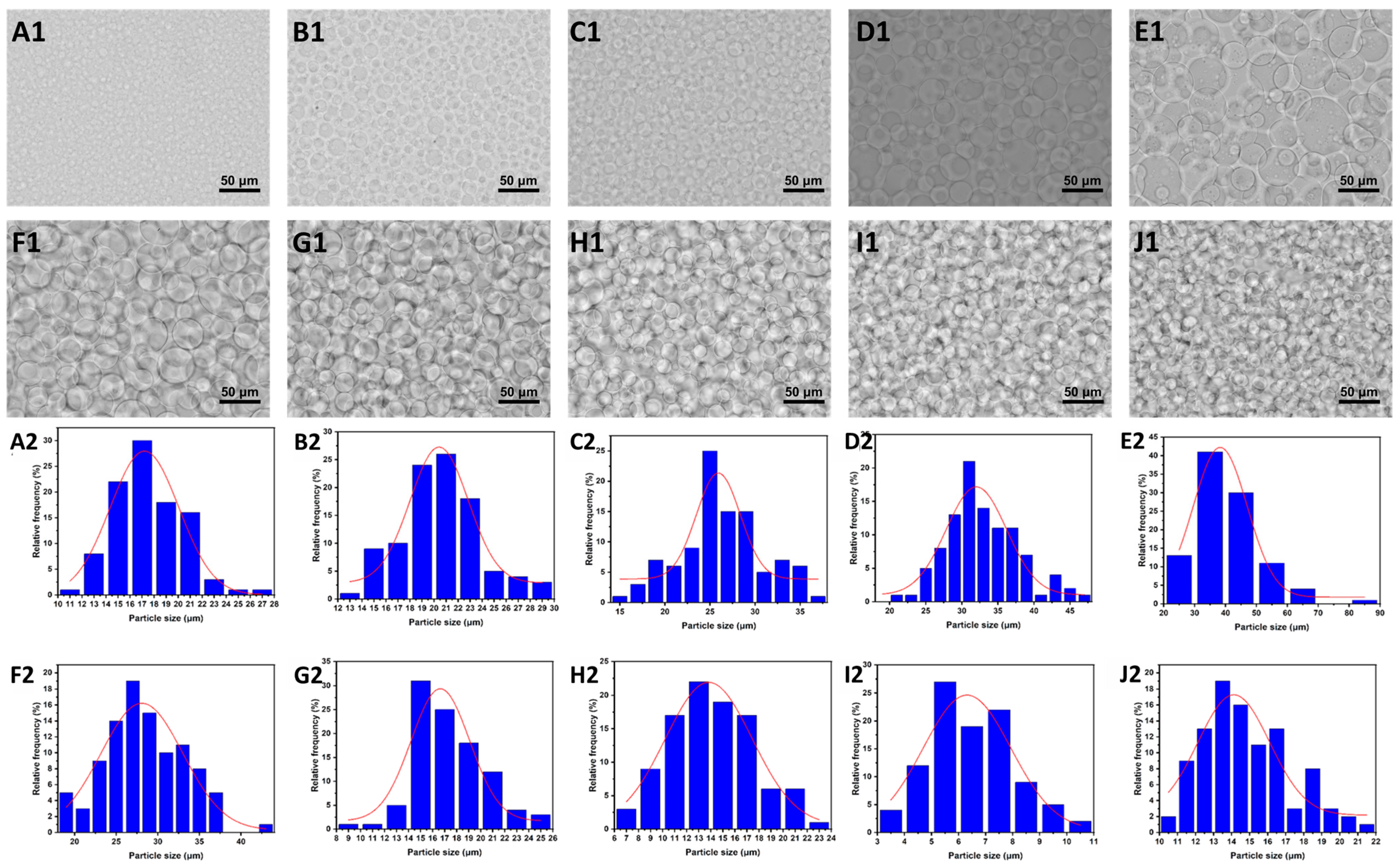
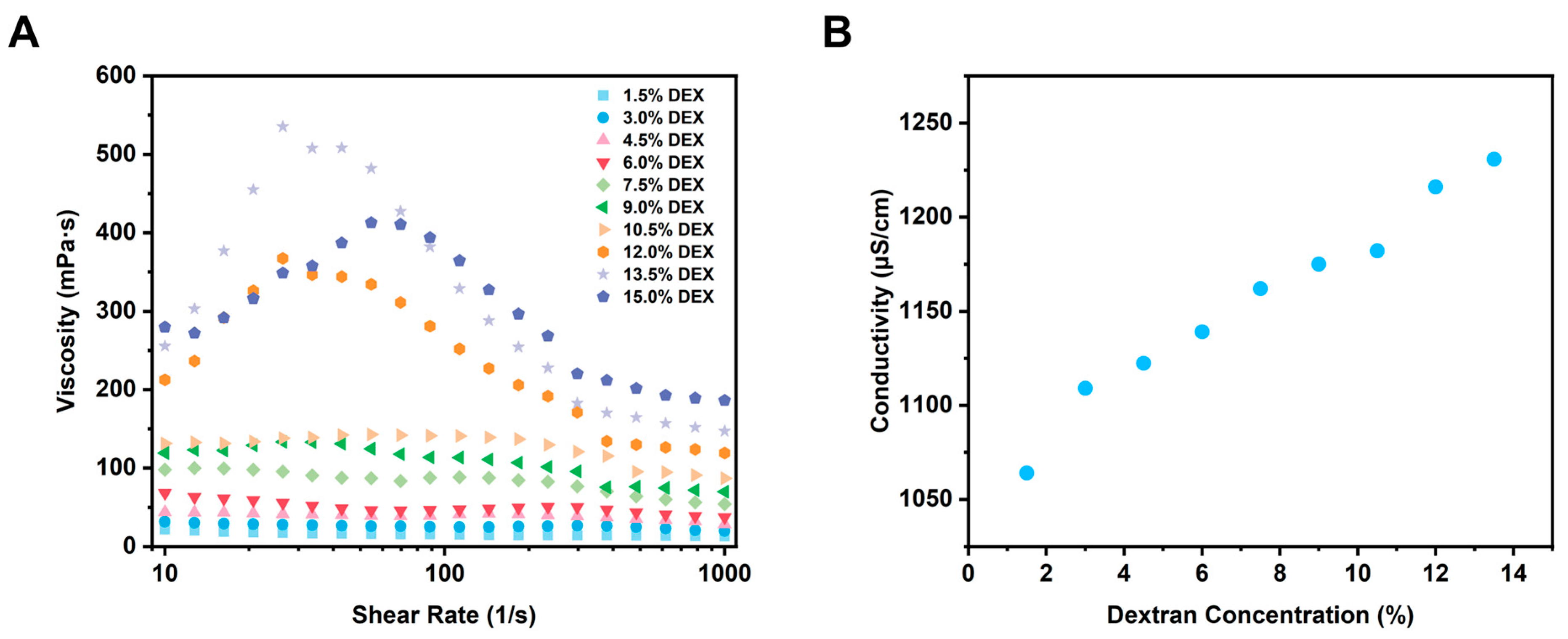
3.1. Characterization of W/W Emulsions
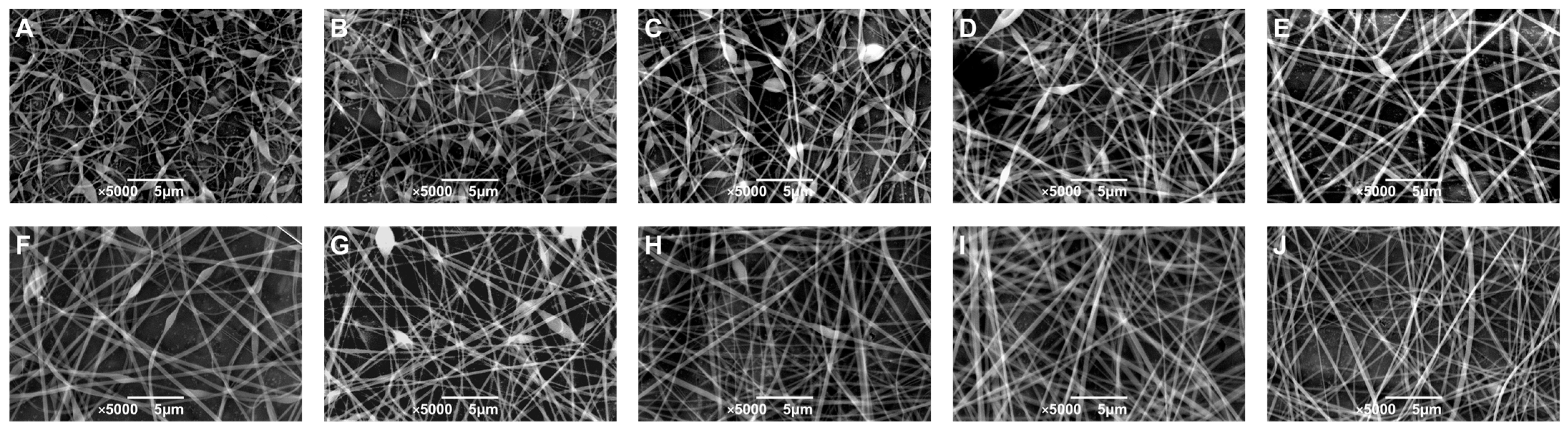
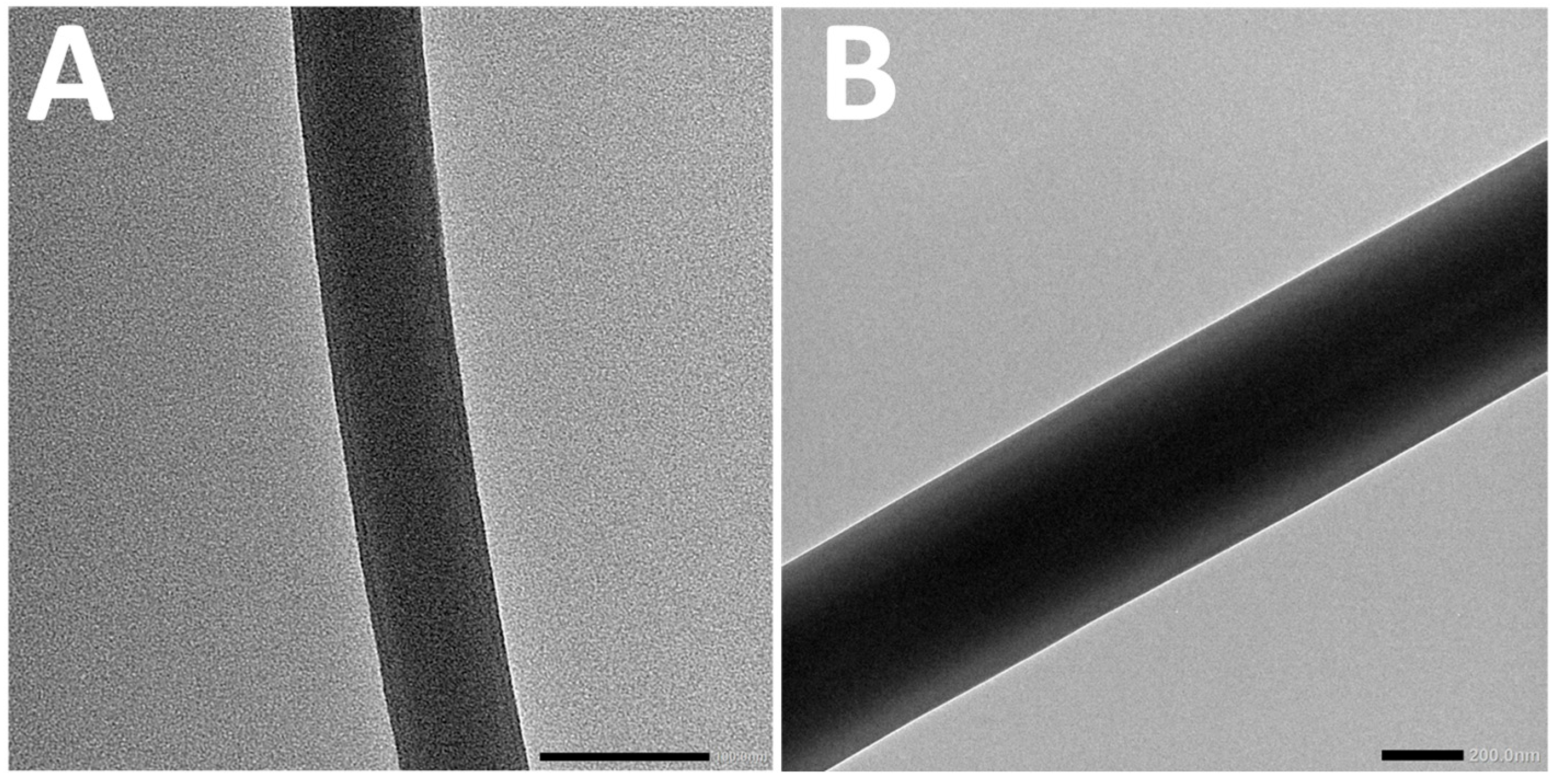
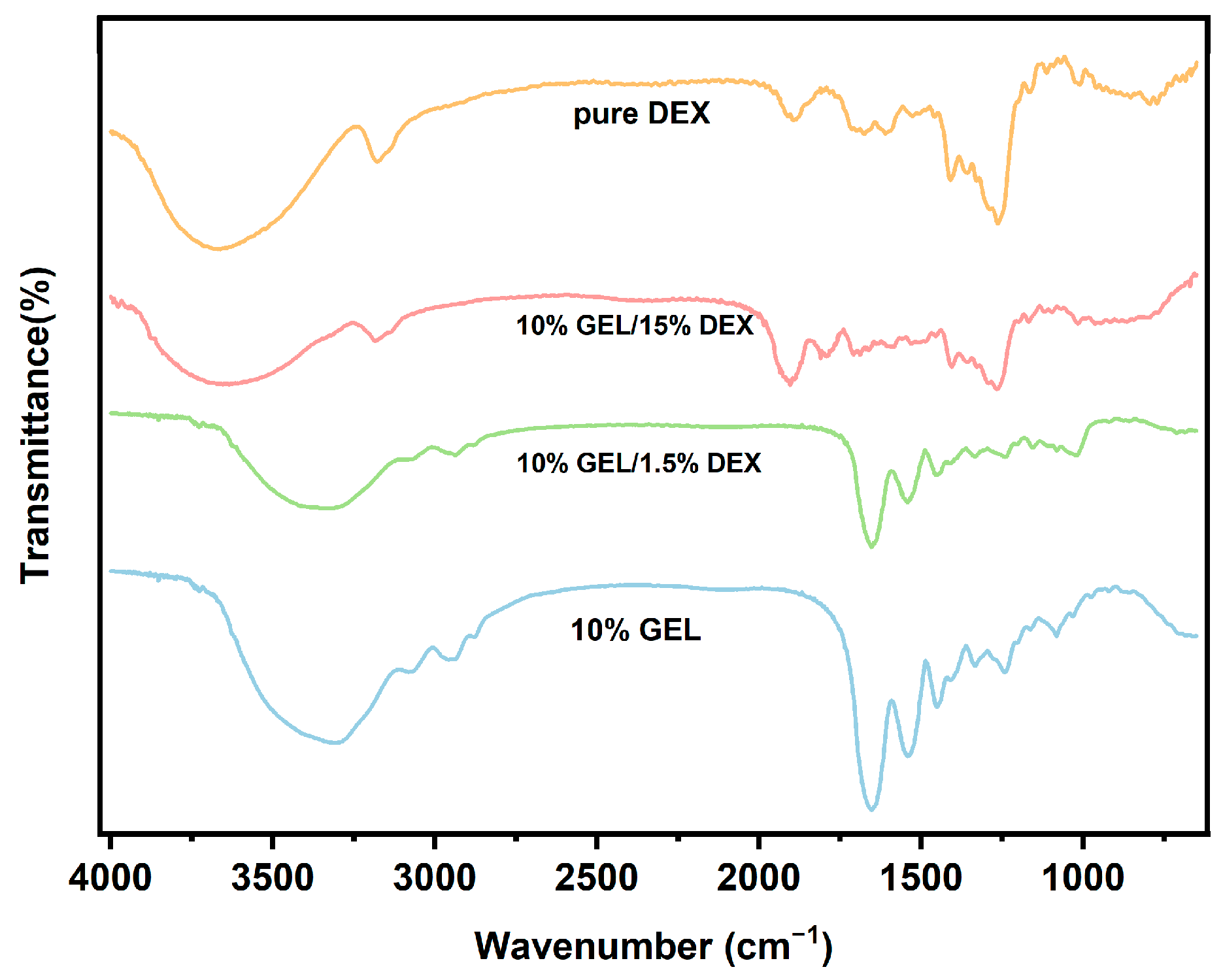
3.2. Characterization of Electrospun Fibers
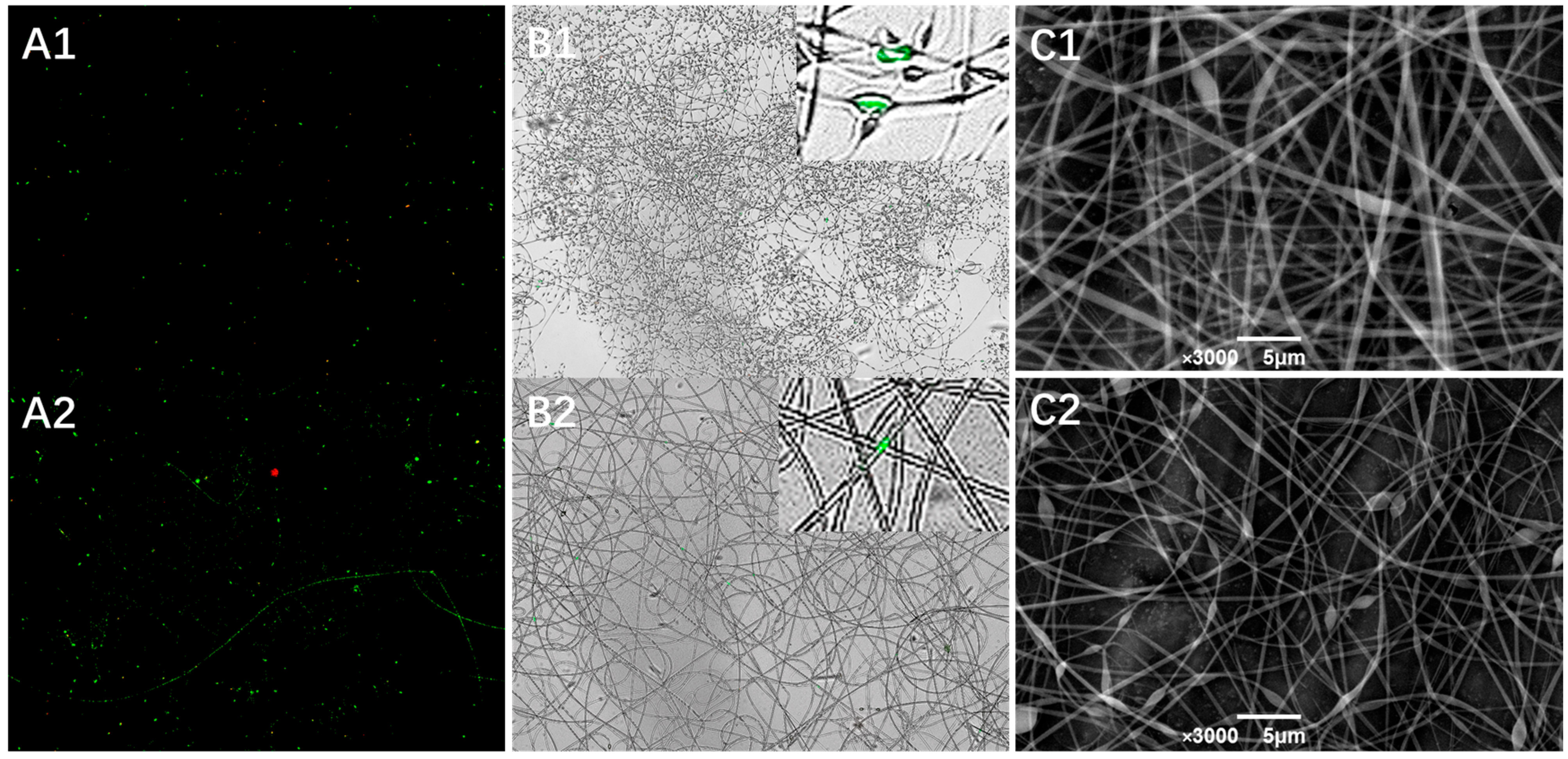
3.3. Structure of Lactobacillus plantarum-Loaded Electrospun Fibers
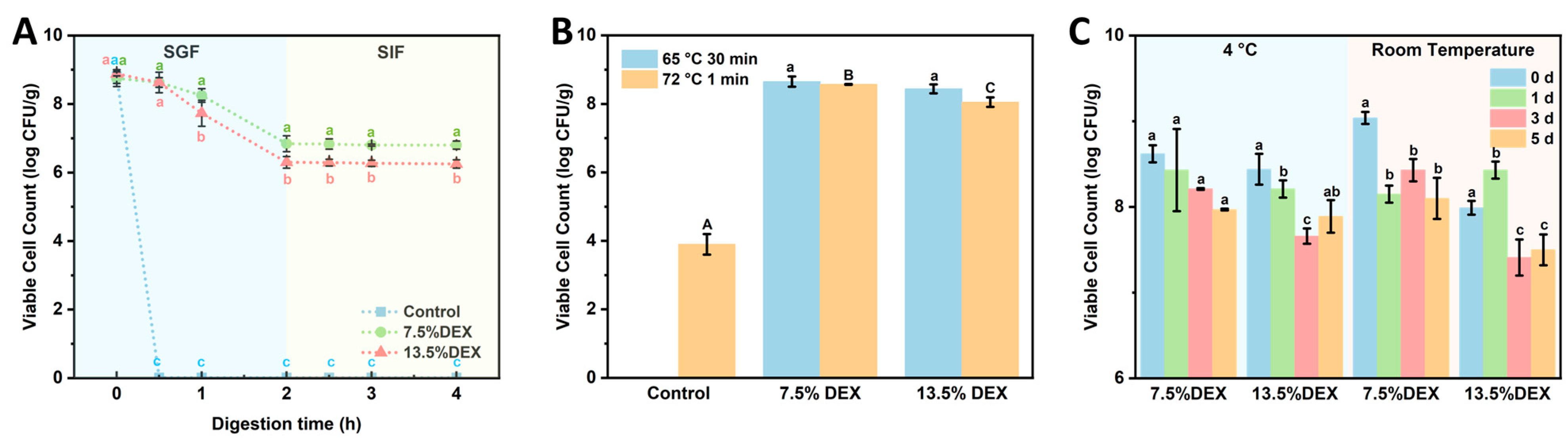
3.4. Survival Ability of Lactobacillus plantarum Loaded Electrospun Fibers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Staniszewski, A.; Kordowska-Wiater, M. Probiotic and Potentially Probiotic Yeasts—Characteristics and Food Application. Foods 2021, 10, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mgomi, F.C.; Zhang, B.-X.; Lu, C.-L.; Yang, Z.-Q.; Yuan, L. Novel Biofilm-Inspired Encapsulation Technology Enhances the Viability of Probiotics during Processing, Storage, and Delivery. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 160, 105032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wei, S.; Wu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Deng, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H. Encapsulation Techniques, Action Mechanisms, and Evaluation Models of Probiotics: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Food Front. 2024, 5, 1212–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassani, L.; Gomez-Zavaglia, A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Technological Strategies Ensuring the Safe Arrival of Beneficial Microorganisms to the Gut: From Food Processing and Storage to Their Passage through the Gastrointestinal Tract. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Zhong, Q. Drying of Probiotics to Enhance the Viability during Preparation, Storage, Food Application, and Digestion: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhong, F. Encapsulation of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG in Double Emulsions: Role of Prebiotics in Improving Probiotics Survival during Spray Drying and Storage. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 151, 109792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dong, M.; Xiao, H.; Young Quek, S.; Ogawa, Y.; Ma, G.; Zhang, C. Advances in Spray-Dried Probiotic Microcapsules for Targeted Delivery: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 64, 11222–11238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.C.; Clark, S.; Qin, H.; Shi, X. Development of a Shelf-Stable, Gel-Based Delivery System for Probiotics by Encapsulation, 3D Printing, and Freeze-Drying. LWT 2022, 157, 113075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premjit, Y.; Mitra, J. Synthesis, Characterization, and In Vitro Digestion of Electrosprayed and Freeze-Dried Probiotics Encapsulated in Soy Protein Isolate-Sunflower Oil Emulsions. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Dong, D.; Hu, J.; Liu, H. Improved Viability of Probiotics Encapsulated in Soybean Protein Isolate Matrix Microcapsules by Coacervation and Cross-Linking Modification. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 138, 108457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, M.; Chan, E.S.; Pushpamalar, J.; Choo, W.S. Advances in Extrusion-Dripping Encapsulation of Probiotics and Omega-3 Rich Oils. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 123, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çanga, E.M.; Dudak, F.C. Improved Digestive Stability of Probiotics Encapsulated within Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Cellulose Acetate Hybrid Fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 264, 117990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Min, T.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, C.; Yin, H.; Yue, J. The Developments and Trends of Electrospinning Active Food Packaging: A Review and Bibliometrics Analysis. Food Control 2024, 160, 110291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, B.S.; Vasile, C. Encapsulation of Natural Bioactive Compounds by Electrospinning—Applications in Food Storage and Safety. Polymers 2021, 13, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Yadav, A.; Gurave, P.M.; Srivastava, R.K. Unique Fiber Morphologies from Emulsion Electrospinning—A Case Study of Poly(ε-Caprolactone) and Its Applications. Colloids Interfaces 2023, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İnan-Çınkır, N.; Ağçam, E.; Altay, F.; Akyıldız, A. Emulsion Electrospinning of Zein Nanofibers with Carotenoid Microemulsion: Optimization, Characterization and Fortification. Food Chem. 2024, 430, 137005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Wang, C.; Xu, E.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, H.; Yuan, C.; Zhao, M.; Yu, B.; Wu, Z.; He, D.; et al. Preparation of Starch-Based Oral Fast-Disintegrating Nanofiber Mats for Astaxanthin Encapsulation and Delivery via Emulsion Electrospinning. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 289, 136466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berraquero-García, C.; Pérez-Gálvez, R.; Espejo-Carpio, F.J.; Guadix, A.; Guadix, E.M.; García-Moreno, P.J. Encapsulation of Bioactive Peptides by Spray-Drying and Electrospraying. Foods 2023, 12, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, R.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Q. Recent Advances in Pickering Double Emulsions and Potential Applications in Functional Foods: A Perspective Paper. Foods 2023, 12, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Schijven, L.M.I.; Velders, A.H.; Bitter, H.J.; Nikiforidis, C.V.; Madadlou, A.; Saggiomo, V. Fabrication of Protein Microgels with Spherical and Urchin-like Shapes within Water-in-Water (W/W) Emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 678, 132479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perro, A.; Coudon, N.; Chapel, J.P.; Martin, N.; Béven, L.; Douliez, J.P. Building Micro-Capsules Using Water-in-Water Emulsion Droplets as Templates. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2022, 613, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, X. Fabrication of Stable Hydrogel Microspheres with Hydrophobic Shell Using Water-in-Water (W/W) Pickering Emulsion Template. Food Res. Int. 2024, 197, 115254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquena, J. Recent Advances on Water-in-Water Emulsions in Segregative Systems of Two Water-Soluble Polymers. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 51, 101010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Current Status and Prospects of Gelatin and Its Derivatives in Oncological Applications: Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 274, 133590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heperkan, Z.D.; Bolluk, M.; Bülbül, S. Structural Analysis and Properties of Dextran Produced by Weissella Confusa and the Effect of Different Cereals on Its Rheological Characteristics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merland, T.; Waldmann, L.; Guignard, O.; Tatry, M.C.; Wirotius, A.L.; Lapeyre, V.; Garrigue, P.; Nicolai, T.; Benyahia, L.; Ravaine, V. Thermo-Induced Inversion of Water-in-Water Emulsion Stability by Bis-Hydrophilic Microgels. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Peng, G.; Ge, L.; Wu, D. Water-in-Water Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by the Starch Nanocrystals with Various Surface Modifications. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, B.P.; Shi, H. Phase Inversion of Silica Particle-Stabilized Water-in-Water Emulsions. Langmuir 2019, 35, 4046–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Particle-Based Stabilization of Water-in-Water Emulsions Containing Mixed Biopolymers. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 83, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Z. Improvement of Stress Resistance of Microencapsulated Lactobacillus Plantarum by Emulsion Electrospinning. Foods 2024, 13, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, L.; Feng, L.; Cui, J.; Dong, S.; Wan, S.; Liu, W.; et al. Water-in-Water Emulsions, Ultralow Interfacial Tension, and Biolubrication. CCS Chem. 2022, 4, 2102–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beldengrün, Y.; Dallaris, V.; Jaén, C.; Protat, R.; Miras, J.; Calvo, M.; García-Celma, M.J.; Esquena, J. Formation and Stabilization of Multiple Water-in-Water-in-Water (W/W/W) Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tea, L.; Nicolai, T.; Benyahia, L.; Renou, F. Viscosity and Morphology of Water-in-Water Emulsions: The Effect of Different Biopolymer Stabilizers. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 3914–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Lin, Y.; Guo, X.; Ramasubramanian, B.; Wang, R.; Radacsi, N.; Jose, R.; Qin, X.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning of Nanofibres. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2024, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Campos, L.; de D. Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.; Tochihuitl-Vázquez, D.; Ramírez-Bon, R.; Yáñez-Limón, J.M.; Pérez-Robles, J.F. Study of the Dextrose Equivalent of Maltodextrins in Electrospinning Using an Ethanol/Water Mixture as the Electrospinning Solvent. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 139, 108498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Du, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, Z. PH Effect on the Structure, Rheology, and Electrospinning of Maize Zein. Foods 2023, 12, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bai, T.C.; Li, Y.L. Density, Viscosity, and Electric Conductance of a Ternary Solution of (Nicotinic Acid + Dextran 40000 + Water). J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajieghrary, F.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Pezeshki, A.; Dadashi, S.; Falcone, P.M. Development of Hybrid Electrospun Nanofibers: Improving Effects of Cellulose Nanofibers (CNFs) on Electrospinnability of Gelatin. Foods 2024, 13, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirouz, A.; Wang, Z.; Reddy, V.S.; Nagy, Z.K.; Vass, P.; Buzgo, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Radacsi, N. The History of Electrospinning: Past, Present, and Future Developments. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong Ta, L.; Bujna, E.; Kun, S.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Electrosprayed Mucoadhesive Alginate-Chitosan Microcapsules for Gastrointestinal Delivery of Probiotics. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, E.; Lin, X.; Tian, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, K.; Skirtach, A.G.; Tan, M.; Su, W. Core-Shell Nanofibers Based on Microalgae Proteins/Alginate Complexes for Enhancing Survivability of Probiotics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 271, 132461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barajas-Álvarez, P.; González-Ávila, M.; Espinosa-Andrews, H. Recent Advances in Probiotic Encapsulation to Improve Viability under Storage and Gastrointestinal Conditions and Their Impact on Functional Food Formulation. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 992–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurić, M.; Goksen, G.; Donsì, F.; Jurić, S. Innovative Applications of Electrospun Nanofibers Loaded with Bacterial Cells Towards Sustainable Agri-Food Systems and Regulatory Compliance. Food Eng. Rev. 2024, 16, 270–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, C.; Yu, H.; Feng, Z.; Yu, W.; Gu, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, J. Electro-Encapsulation of Probiotics in Gum Arabic-Pullulan Blend Nanofibres Using Electrospinning Technology. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Delgado, A.; Quintanilla-Carvajal, M.X. Electrospinning Microencapsulation of Lactobacillus Fermentum K73 Using Gelatin as the Main Component of a Food-Grade Matrix. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Gong, Y.; Gao, Z. Electrospun Gelatin/Dextran Nanofibers from W/W Emulsions: Improving Probiotic Stability Under Thermal and Gastrointestinal Stress. Foods 2025, 14, 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101725
Wu Y, Yan Z, Zhang S, Li S, Gong Y, Gao Z. Electrospun Gelatin/Dextran Nanofibers from W/W Emulsions: Improving Probiotic Stability Under Thermal and Gastrointestinal Stress. Foods. 2025; 14(10):1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101725
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yuehan, Ziyou Yan, Shanshan Zhang, Shiyang Li, Ya Gong, and Zhiming Gao. 2025. "Electrospun Gelatin/Dextran Nanofibers from W/W Emulsions: Improving Probiotic Stability Under Thermal and Gastrointestinal Stress" Foods 14, no. 10: 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101725
APA StyleWu, Y., Yan, Z., Zhang, S., Li, S., Gong, Y., & Gao, Z. (2025). Electrospun Gelatin/Dextran Nanofibers from W/W Emulsions: Improving Probiotic Stability Under Thermal and Gastrointestinal Stress. Foods, 14(10), 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101725




