Exploring Technological, Safety and Probiotic Properties of Enterococcus Strains: Impact on Rheological Parameters in Fermented Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Reagents
2.2. Isolation of Strains
2.3. Molecular Identification
2.4. Probiotic Assessment
2.4.1. Safety Profile
2.4.2. Bile Salts and Gastric Juice Tolerance
2.4.3. Resistance to Lysozyme
2.5. Antibacterial Activity
2.6. Antibiofilm Activity
2.7. Physiological and Biochemical Properties
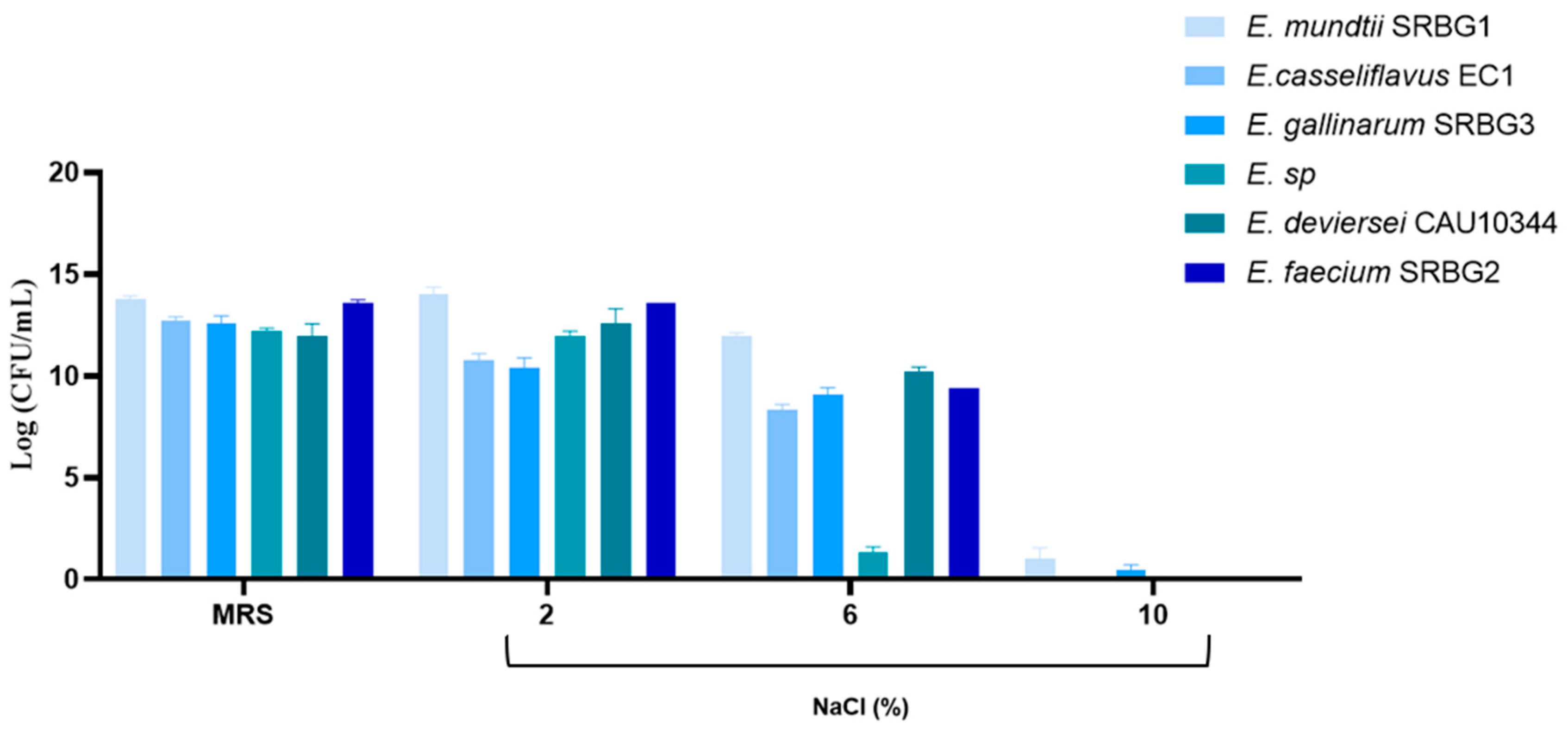
2.7.1. Growth under Different Concentrations of NaCl
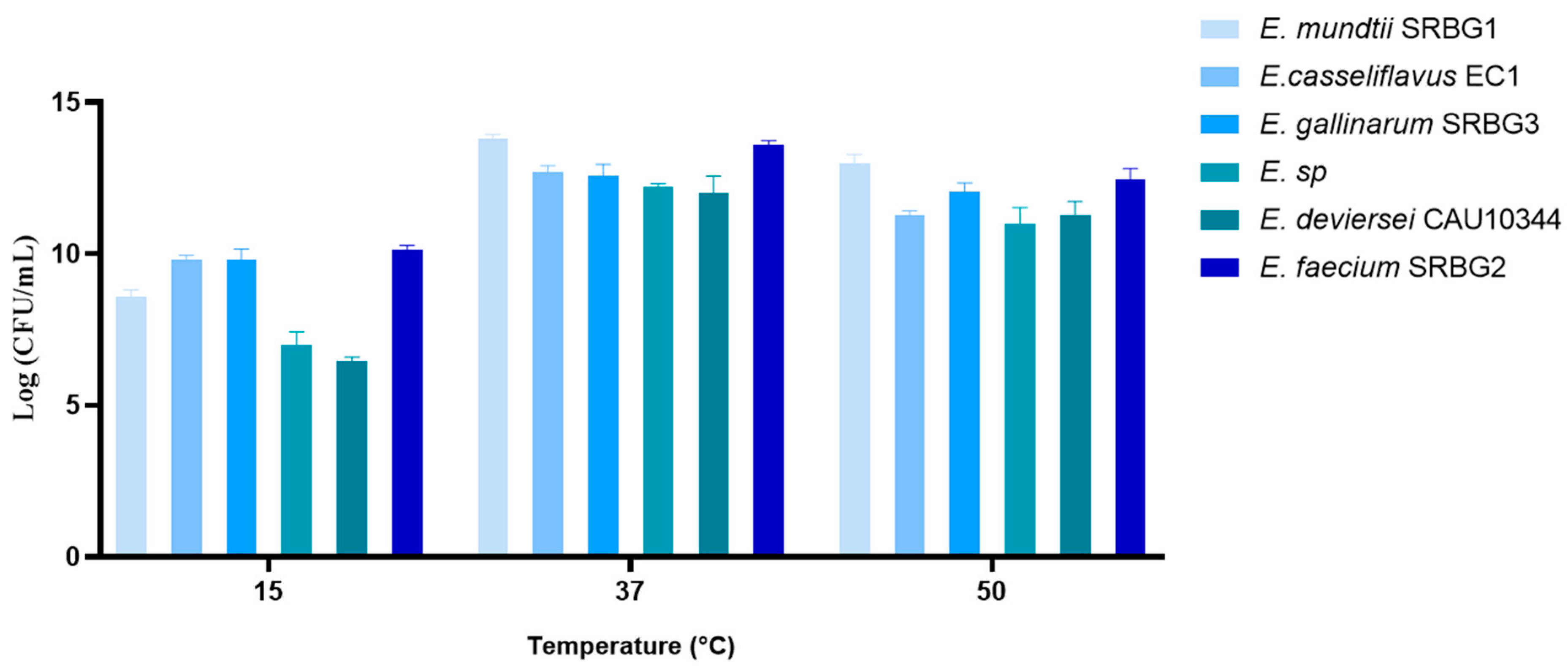
2.7.2. Strains’ Growth under Different Temperatures
2.7.3. Enzymatic Activities
Amylolytic Activity
Proteolytic Activity
Lipolytic Activity
β-Galactosidase
2.7.4. EPS Production
2.8. Fermentation of Milk Process and Rheological Parameters
Bacterial Enumeration and pH Measurement
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
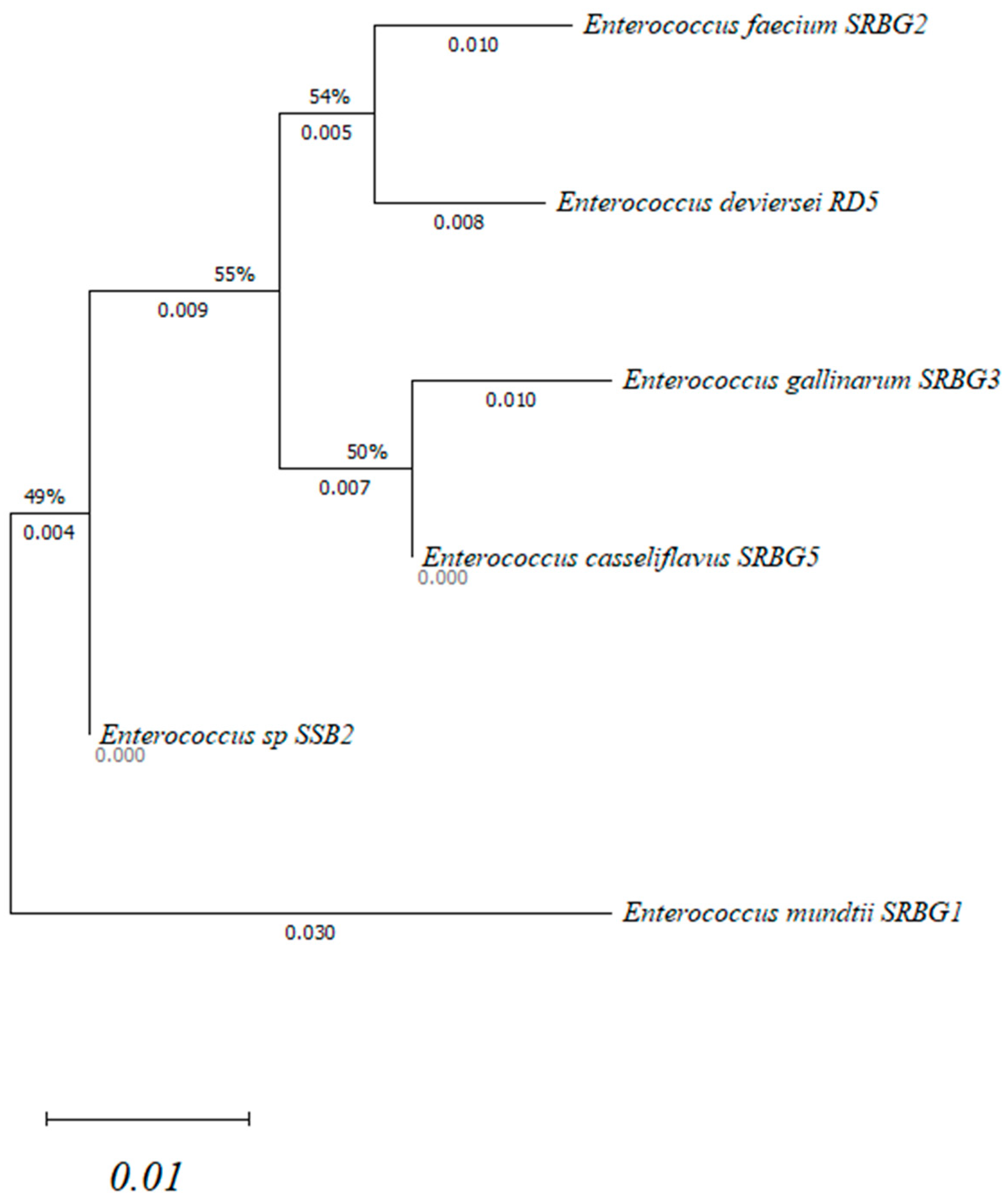
3.1. Phenotypic and Molecular Identification
3.2. Probiotic Assessment
3.2.1. Safety Profile
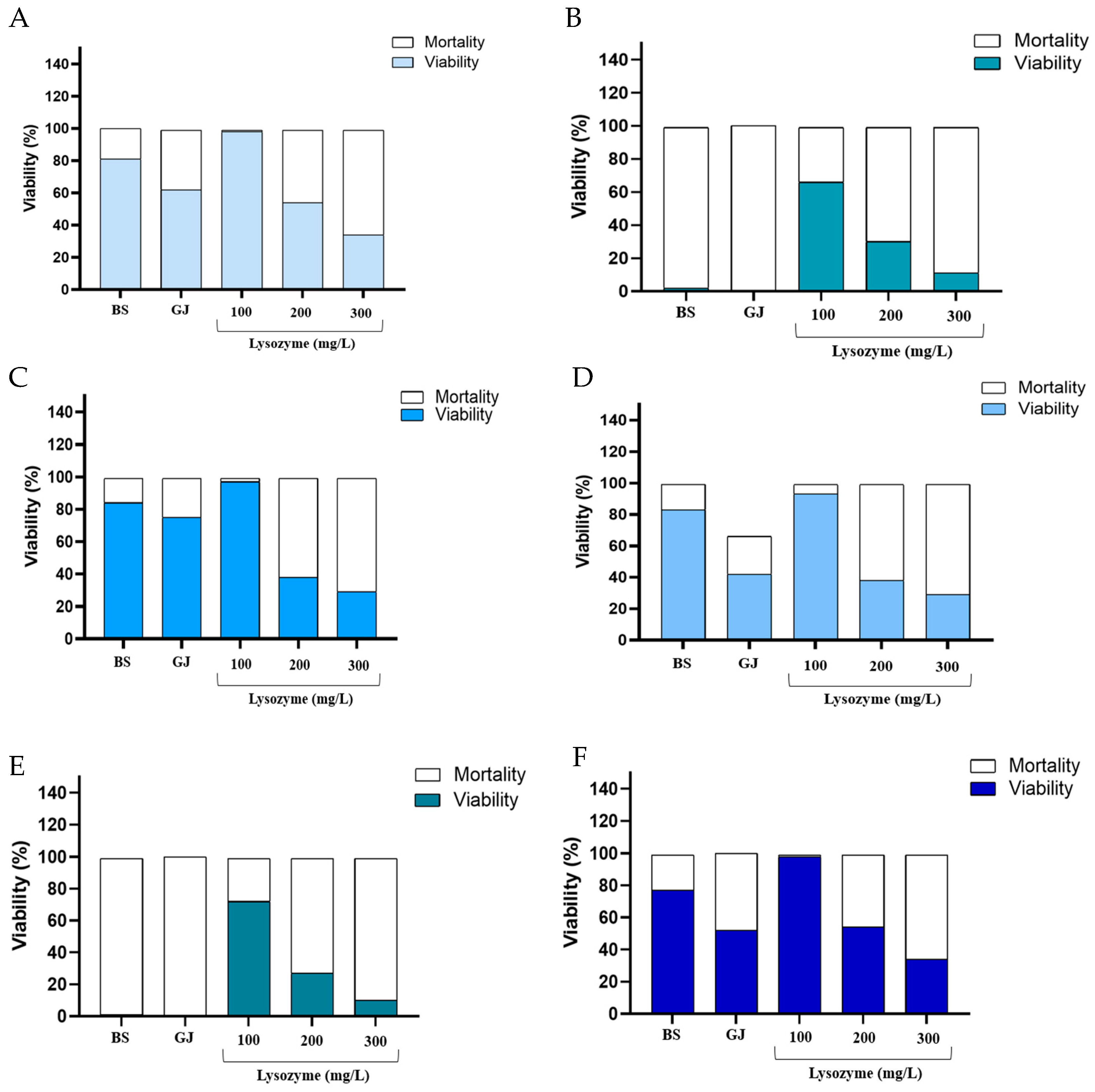
3.2.2. Bile Salts, Gastric Juice and Lysozyme Tolerance
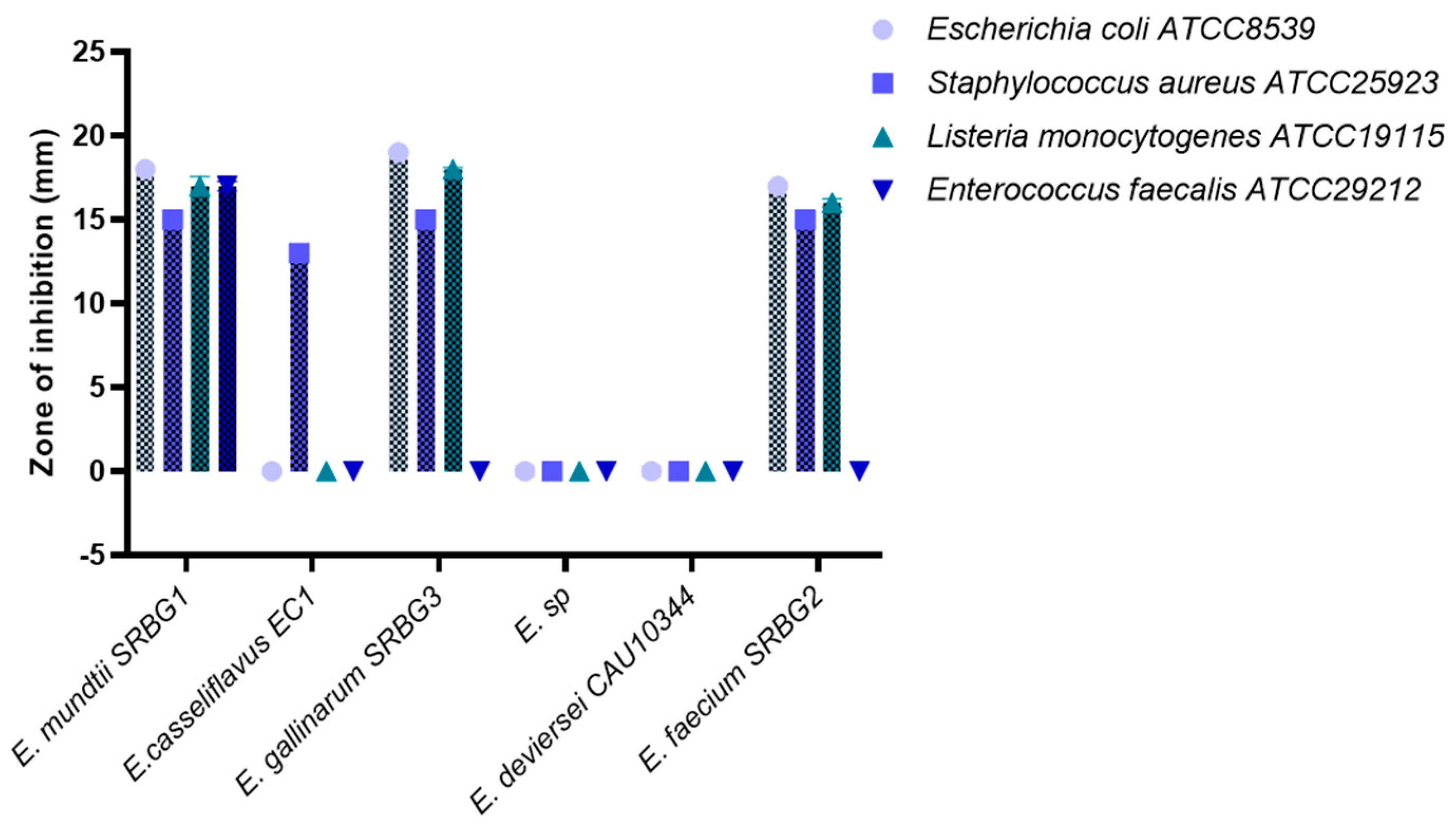
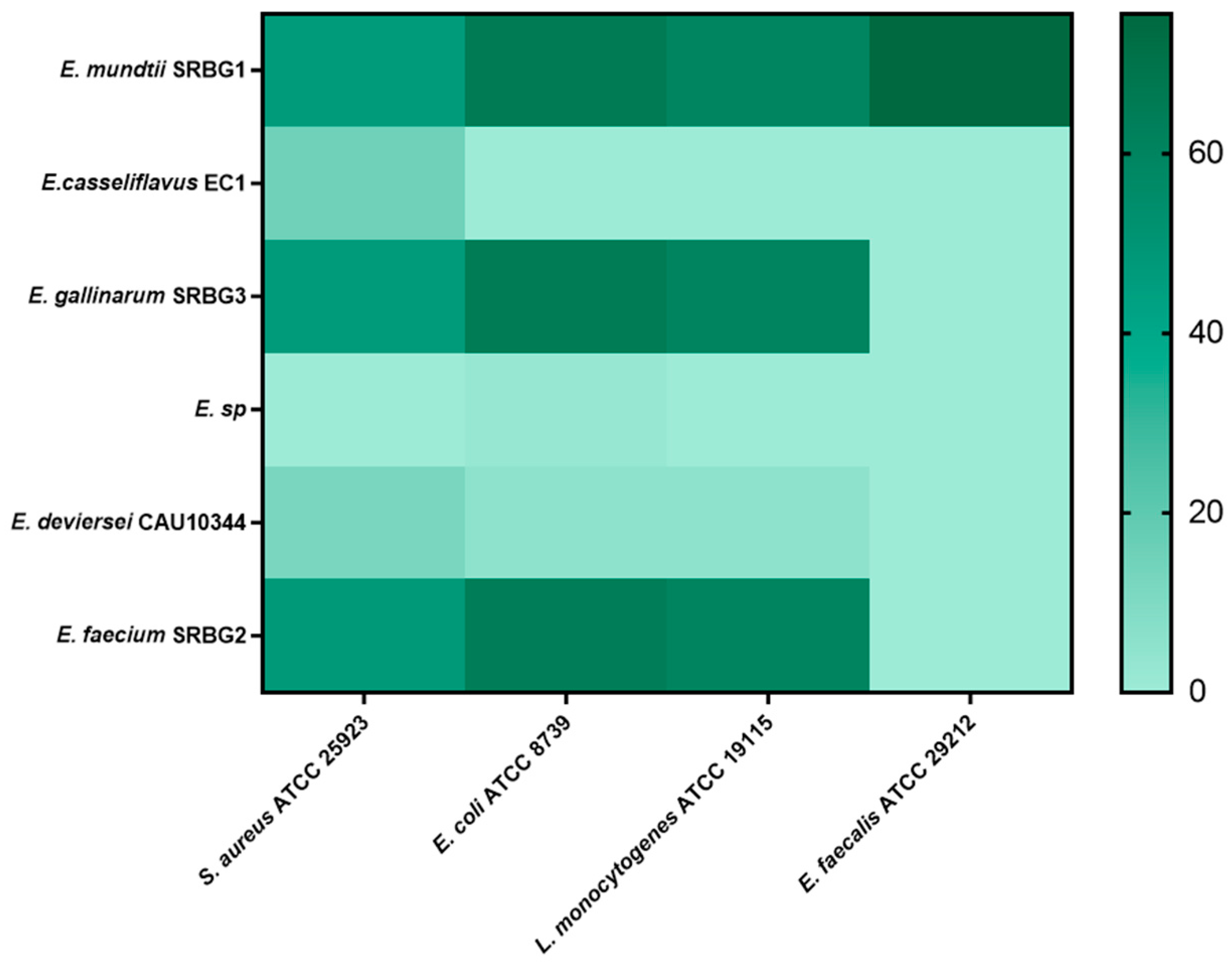
3.2.3. Antibacterial Activity
3.2.4. Antibiofilm Activity
3.3. Physiological and Biochemical Properties
3.3.1. Growth under Different Concentrations of NaCl and Different Temperatures
3.3.2. Enzymatic Activities
3.3.3. EPS Production
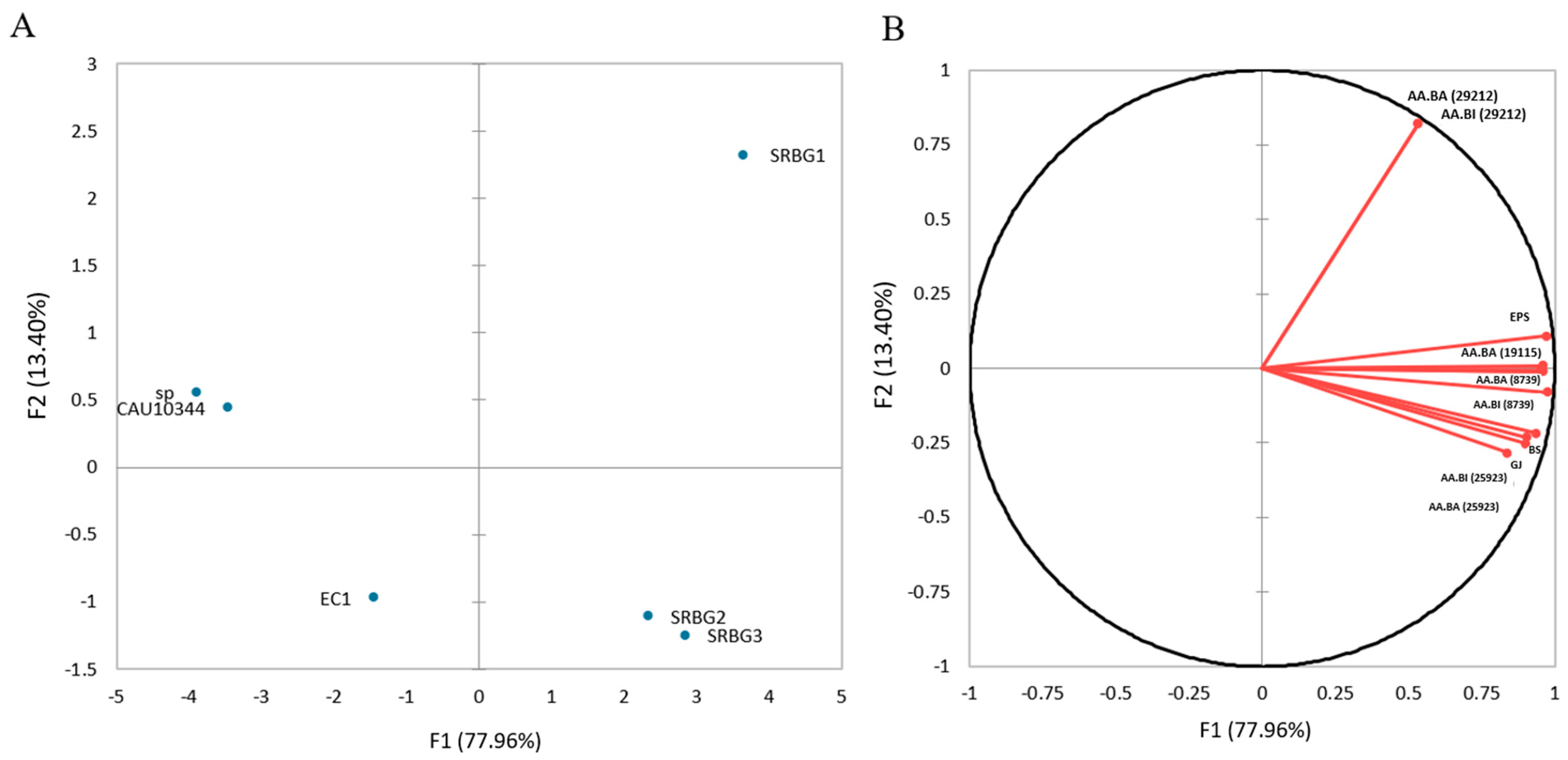
3.4. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
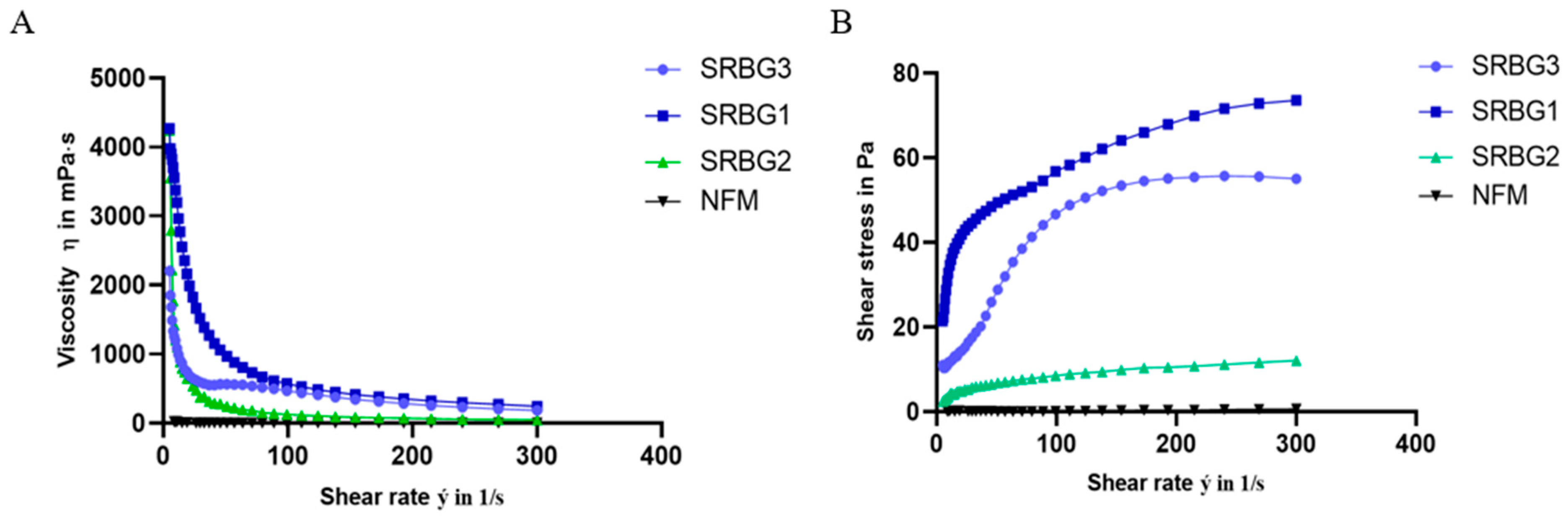
3.5. Apparent Viscosity and Resistance to Shearing
3.6. Bacterial Enumeration and pH Measurement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Belgacem, A.B.; Abriouel, H.; Omar, N.B.; Lucas, R.; Martínez-Canamero, M.; Gálvez, A.; Manai, M. Antimicrobial activity, safety aspects, and some technological properties of bacteriocinogenic Enterococcus faecium from artisanal Tunisian fermented meat. Food Control 2010, 21, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, K.; Stack, H.; Rea, R. Safety, beneficial and technological properties of enterococci for use in functional food applications—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3836–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nami, Y.; Bakhshayesh, R.V.; Jalaly, H.M.; Lotfi, H.; Eslami, S.; Hejazi, M.A. Probiotic properties of enterococcus isolated from artisanal dairy products. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derdak, R.; Sakoui, S.; Pop, O.L.; Muresan, C.I.; Vodnar, D.C.; Addoum, B.; Vulturar, R.; Chis, A.; Suharoschi, R.; Soukri, A.; et al. Insights on Health and Food Applications of Equus asinus (Donkey) Milk Bioactive Proteins and Peptides—An Overview. Foods 2020, 9, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraffa, G. Functionality of enterococci in dairy products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 88, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakoui, S.; Derdak, R.; Addoum, B.; Pop, O.L.; Vodnar, D.C.; Suharoschi, R.; Soukri, A.; El Khalfi, B. The first study of probiotic properties and biological activities of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Bat guano from Er-rachidia, Morocco. LWT 2022, 159, 113224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoui, S.; Derdak, R.; Addoum, B.; Serrano-Delgado, A.; Soukri, A.; El Khalfi, B. The Life Hidden Inside Caves: Ecological and Economic Importance of Bat Guano. Int. J. Ecol. 2020, 2020, 9872532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaouani, I.; Abbassi, M.S.; Ribeiro, S.C.; Khemiri, M.; Mansouri, R.; Messadi, L.; Silva CC, G. Safety and technological properties of bacteriocinogenic enterococci isolates from Tunisia. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarantinopoulos, P.; Andrighetto, C.; Georgalaki, M.D.; Rea, M.C.; Lombardi, A.; Cogan, T.M.; Kalantzopoulos, G.; Tsakalidou, E. Biochemical properties of enterococci relevant to their technological performance. Int. Dairy J. 2001, 11, 621–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, E.J.; Lee HH, Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.K. Evaluation of enterococcal probiotic usage and review of potential health benefits, safety, and risk of antibiotic-resistant strain emergence. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angmo, K.; Kumari, A.; Savitri; Bhalla, T.C. Probiotic characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from fermented foods and beverage of Ladakh. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambadoyiannis, G.; Hatzikamari, M.; Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E.; Tzanetakis, N. Probiotic and technological properties of enterococci isolates from infants and cheese. Food Biotechnol. 2004, 18, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zago, M.; Fornasari, M.E.; Carminati, D.; Burns, P.; Suàrez, V.; Vinderola, G.; Reinheimer, J.; Giraffa, G. Characterization and probiotic potential of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from cheeses. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derdak, R.; Quinteiro, J.; Sakoui, S.; Addoum, B.; Rodríguez Castro, J.; Rey Méndez, M.; Soukri, A.; El Khalfi, B. Isolation and Identification of Dominant Bacteria from Raw Donkey Milk Produced in a Region of Morocco by QIIME 2 and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial Activity. Sci. World J. 2021, 2021, 6664636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Yu, H.H.; Song, Y.J.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, N.K.; Paik, H.D. Anti-biofilm effect of the cell-free supernatant of probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae against Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 2021, 121, 107667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, S.C.; Coelho, M.C.; Todorov, S.D.; Franco BD, G.M.; Dapkevicius, M.L.E.; Silva, C.C.G. Technological properties of bacteriocin-producing lactic acid bacteria isolated from Pico cheese an artisanal cow’s milk cheese. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Tang, H.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Probiotic potential and amylolytic properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Chinese fermented cereal foods. Food Control 2020, 111, 107057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakroo, S.; Tarrah, A.; Takur, R.; Wu, M.; Corich, V.; Giacomini, A. Limosilactobacillus fermentum ING8, a Potential Multifunctional Non-Starter Strain with Relevant Technological Properties and Antimicrobial Activity. Foods 2022, 11, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorizzo, M.; Albanese, G.; Letizia, F.; Testa, B.; Tremonte, P.; Vergalito, F.; Lombardi, S.J.; Succi, M.; Coppola, R.; Sorrentino, E. Probiotic Potentiality from Versatile Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Strains as Resource to Enhance Freshwater Fish Health. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdak, R.; Sakoui, S.; Pop, O.L.; Cristian Vodnar, D.; Addoum, B.; Elmakssoudi, A.; Errachidi, F.; Suharoschi, R.; Soukri, A.; El Khalfi, B. Screening, optimization and characterization of exopolysaccharides produced by novel strains isolated from Moroccan raw donkey milk. Food Chem. X 2022, 14, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devriese, L.A.; Vancanneyt, M.; Descheemaeker, P.; Baele, M.; Van Landuyt, H.W.; Gordts, B.; Butaye, P.; Swings, J.; Haesebrouck, F. Differentiation and identification of Enterococcus durans, E. hirae and E. villorum. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, E.R.; Demirci, T.; Akın, N. In vitro assessment of probiotic and virulence potential of Enterococcus faecium strains derived from artisanal goatskin casing Tulum cheeses produced in central Taurus Mountains of Turkey. LWT 2021, 141, 110908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajikhani, R.; Onal Darilmaz, D.; Yuksekdag, Z.N.; Beyatli, Y. Assessment of some metabolic activities and potential probiotic properties of eight Enterococcus bacteria isolated from white cheese microbiota. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 1259–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y. Effects of Enterococcus faecium (SF68) on immune function in mice. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Gupta, H.; Kapila, S.; Kaur, G.; Vij, S.; Malik, R.K. Safety assessment and evaluation of probiotic potential of bacteriocinogenic Enterococcus faecium KH 24 strain under in vitro and in vivo conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, N.; Maurya, A.K.; Mohanty, S.; Kumar, M.; Virdi, J.S. Evaluation of bile salt hydrolases, cholesterol-lowering capabilities, and probiotic potential of enterococcus faecium isolated from rhizosphere. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, L.; Margolles, A.; Sánchez, B. Bile resistance mechanisms in Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agüero, N.d.L.; Frizzo, L.S.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Aleu, G.; Rosmini, M.R. Technological Characterisation of Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria as Starter Cultures for Dry Fermented Sausages. Foods 2020, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Braïek, O.; Morandi, S.; Cremonesi, P.; Smaoui, S.; Hani, K.; Ghrairi, T. Biotechnological potential, probiotic and safety properties of newly isolated enterocin-producing Enterococcus lactis strains. LWT 2018, 92, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamwal, A.; Sharma, K.; Chauhan, R.; Bansal, S.; Goel, G. Evaluation of commercial probiotic lactic cultures against biofilm formation by Cronobacter sakazakii. Intest. Res. 2019, 17, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Shi, Y.; Gu, S.; Yan, X.; Chen, H.; Ge, J. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional artisanal milk cheese from northeast china against enteropathogenic bacteria. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morandi, S.; Silvetti, T.; Brasca, M. Biotechnological and safety characterization of Enterococcus lactis, a recently described species of dairy origin. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 103, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, H.; Su, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L. Probiotic properties of Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. Paracasei L1 and its growth performance-promotion in chicken by improving the intestinal microflora. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Kennedy, B.T. Raw material selection: Dairy ingredients. In Chilled Foods: A Comprehensive Guide, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Bozoudi, D.; Tsaltas, D. Enterococci Isolated from Cypriot Green Table Olives as a New Source of Technological and Probiotic Properties. Fermentation 2018, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falade, A.T.; Emmambux, M.N.; Buys, E.M.; Taylor JR, N. Improvement of maize bread quality through modification of dough rheological properties by lactic acid bacteria fermentation. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakandar, H.A.; Usman, K.; Imran, M. Isolation and characterization of gluten-degrading Enterococcus mundtii and Wickerhamomyces anomalus, potential probiotic strains from indigenously fermented sourdough (Khamir). LWT 2018, 91, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, P.; Balraj, M.; Ayyanna, R.; Ankaiah, D.; Arul, V. Physicochemical and biosorption properties of novel exopolysaccharide produced by Enterococcus faecalis. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.; Abdalla, A.; Abu-Jdayil, B.; Huppertz, T.; Bhaskaracharya, R.; Al-Mardeai, S.; Mairpady, A.; Ranasinghe, A.; Al-Nabulsi, A. Rheological properties of fermented milk from heated and high pressure-treated camel milk and bovine milk. LWT 2022, 156, 113029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surber, G.; Jaros, D.; Rohm, H. Shear and extensional rheology of acid milk gel suspensions with varying ropiness. J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skriver, A.; Roemer, H.; Gvist, K.B. Rheological characterization of stirred yoghurt: Viscometry. J. Texture Stud. 1993, 24, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, A.; Aziz, T.; Al-Dalali, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Ud Din, J.; Chen, C.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Z. Physicochemical and Microbiological Properties of Synbiotic Yogurt Made with Probiotic Yeast Saccharomyces boulardii in Combination with Inulin. Foods 2019, 8, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO; WHO. Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food; Working Group Report; Food and Health Agricultural Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
| Strain | Accession Number |
|---|---|
| Enterococcus mundtii SRBG1 | ON204234 |
| Enterococcus gallinarum SRBG3 | ON204236 |
| Enterococcus casseliflavus SRBG5 | OQ280989 |
| Enterococcus sp. SSB2 | OQ280990 |
| Enterococcus deviersei RD5 | OQ280993 |
| Enterococcus faecium SRBG2 | ON204235 |
| E. mundtii SRBG1 | E.casseliflavus EC1 | E. gallinarum SRBG3 | E. faecium SRBG2 | E. sp. | E. deviersei CAU10344 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzymes | Amylase | + | − | + | + | − | − |
| Protease | − | − | + | + | − | − | |
| Lipase | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| β-galactosidase | + | − | + | + | − | − | |
| EPS production (g/L) | 3.221 ± 0.3 | − | 2.868 ± 0.6 | 0.134 ± 0.2 | − | − | |
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exopolysaccharide | 0.938 | 0.012 | 0.047 | 0.004 | 0.000 |
| Bile salts | 0.708 | 0.080 | 0.209 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Gastric juice | 0.881 | 0.048 | 0.039 | 0.027 | 0.006 |
| Lysozyme | 0.821 | 0.055 | 0.110 | 0.013 | 0.001 |
| Antibacterial activity (8739) | 0.926 | 0.000 | 0.072 | 0.002 | 0.000 |
| Antibacterial activity (25923) | 0.809 | 0.063 | 0.124 | 0.000 | 0.004 |
| Antibacterial activity (19115) | 0.926 | 0.000 | 0.072 | 0.002 | 0.000 |
| Antibacterial activity (29212) | 0.284 | 0.672 | 0.045 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Antibiofilm activity (8739) | 0.915 | 0.000 | 0.083 | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| Antibiofilm activity (25923) | 0.954 | 0.006 | 0.017 | 0.018 | 0.005 |
| Antibiofilm activity (19115) | 0.910 | 0.000 | 0.088 | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| Antibiofilm activity (29212) | 0.284 | 0.672 | 0.045 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Storage (Day) | SRBG1 | SRBG2 | SRBG3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial count (log10 CFU/mL) | 1 | 6.96 ± 0.10 a | 7.69 ± 0.24 c | 7.00 ± 0.71 e |
| 7 | 7.03 ± 0.60 a | 7.60 ± 0.32 c | 7.34 ± 0.30 e | |
| 14 | 7.00 ± 0.12 a | 7.65 ± 0.11 c | 7.12 ± 0.63 e | |
| 21 | 7.12 ± 0.30 a | 7.67 ± 0.21 c | 7.15 ± 0.42 e | |
| pH measurement | 1 | 4.34 ± 0.10 b | 5.10 ± 0.10 d | 5.24 ± 0.10 f |
| 7 | 4.30 ± 0.00 b | 5.11 ± 0.20 d | 5.20 ± 0.00 f | |
| 14 | 4.26 ± 0.10 b | 5.07 ± 0.00 d | 5.16 ± 0.10 f | |
| 21 | 4.28 ± 0.12 b | 5.10 ± 0.10 d | 5.18 ± 0.2 f |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakoui, S.; Derdak, R.; Pop, O.L.; Vodnar, D.C.; Jouga, F.; Teleky, B.-E.; Addoum, B.; Simon, E.; Suharoschi, R.; Soukri, A.; et al. Exploring Technological, Safety and Probiotic Properties of Enterococcus Strains: Impact on Rheological Parameters in Fermented Milk. Foods 2024, 13, 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13040586
Sakoui S, Derdak R, Pop OL, Vodnar DC, Jouga F, Teleky B-E, Addoum B, Simon E, Suharoschi R, Soukri A, et al. Exploring Technological, Safety and Probiotic Properties of Enterococcus Strains: Impact on Rheological Parameters in Fermented Milk. Foods. 2024; 13(4):586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13040586
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakoui, Souraya, Reda Derdak, Oana Lelia Pop, Dan Cristian Vodnar, Fatimazahra Jouga, Bernadette-Emőke Teleky, Boutaina Addoum, Elemér Simon, Ramona Suharoschi, Abdelaziz Soukri, and et al. 2024. "Exploring Technological, Safety and Probiotic Properties of Enterococcus Strains: Impact on Rheological Parameters in Fermented Milk" Foods 13, no. 4: 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13040586
APA StyleSakoui, S., Derdak, R., Pop, O. L., Vodnar, D. C., Jouga, F., Teleky, B.-E., Addoum, B., Simon, E., Suharoschi, R., Soukri, A., & El Khalfi, B. (2024). Exploring Technological, Safety and Probiotic Properties of Enterococcus Strains: Impact on Rheological Parameters in Fermented Milk. Foods, 13(4), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13040586











