Preparation of Sweet Potato Porous Starch by Marine Dextranase and Its Adsorption Characteristics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
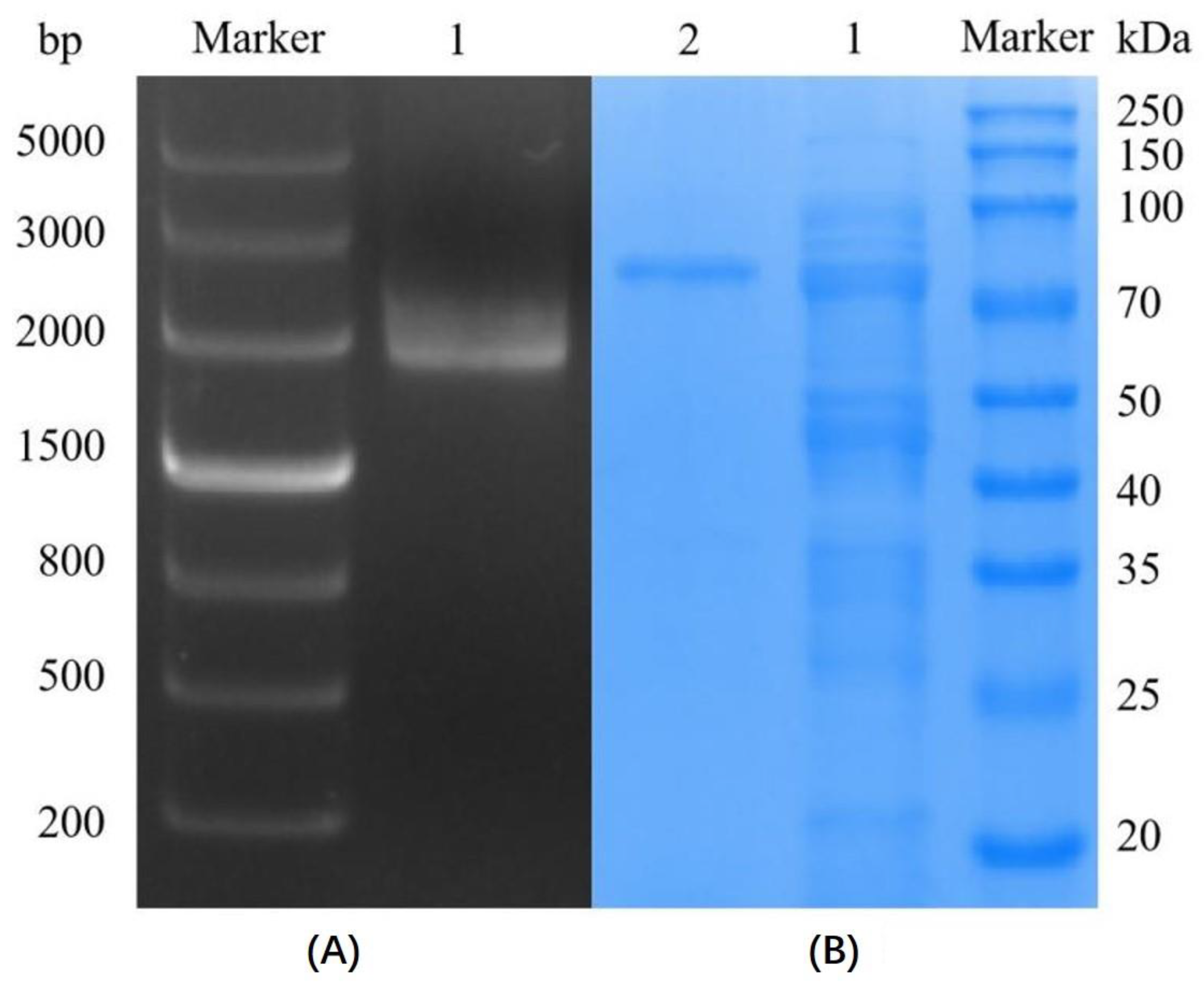
2.2.1. Cloning and Expression of the Marine Dextranase SP5-Badex
SP5-Badex Purification
SP5-Badex Activity Assay
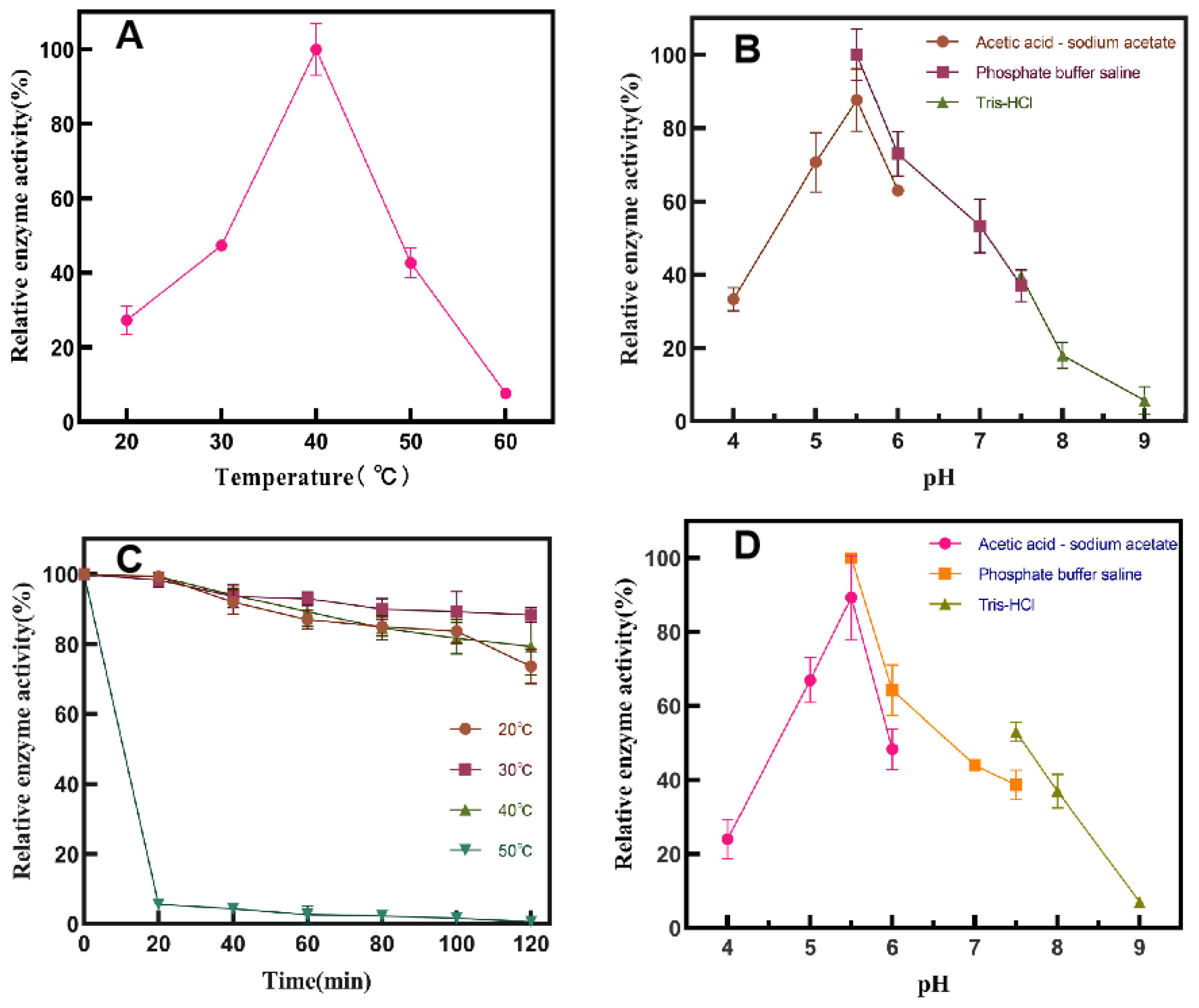
Properties of SP5-Badex
2.2.2. Porous Starch Preparation
2.2.3. Comparison of Different Types of Porous Starch
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
The Water/Oil Adsorption Rate of Porous Starch
2.2.4. Characteristics of the Sweet Potato Porous Starch
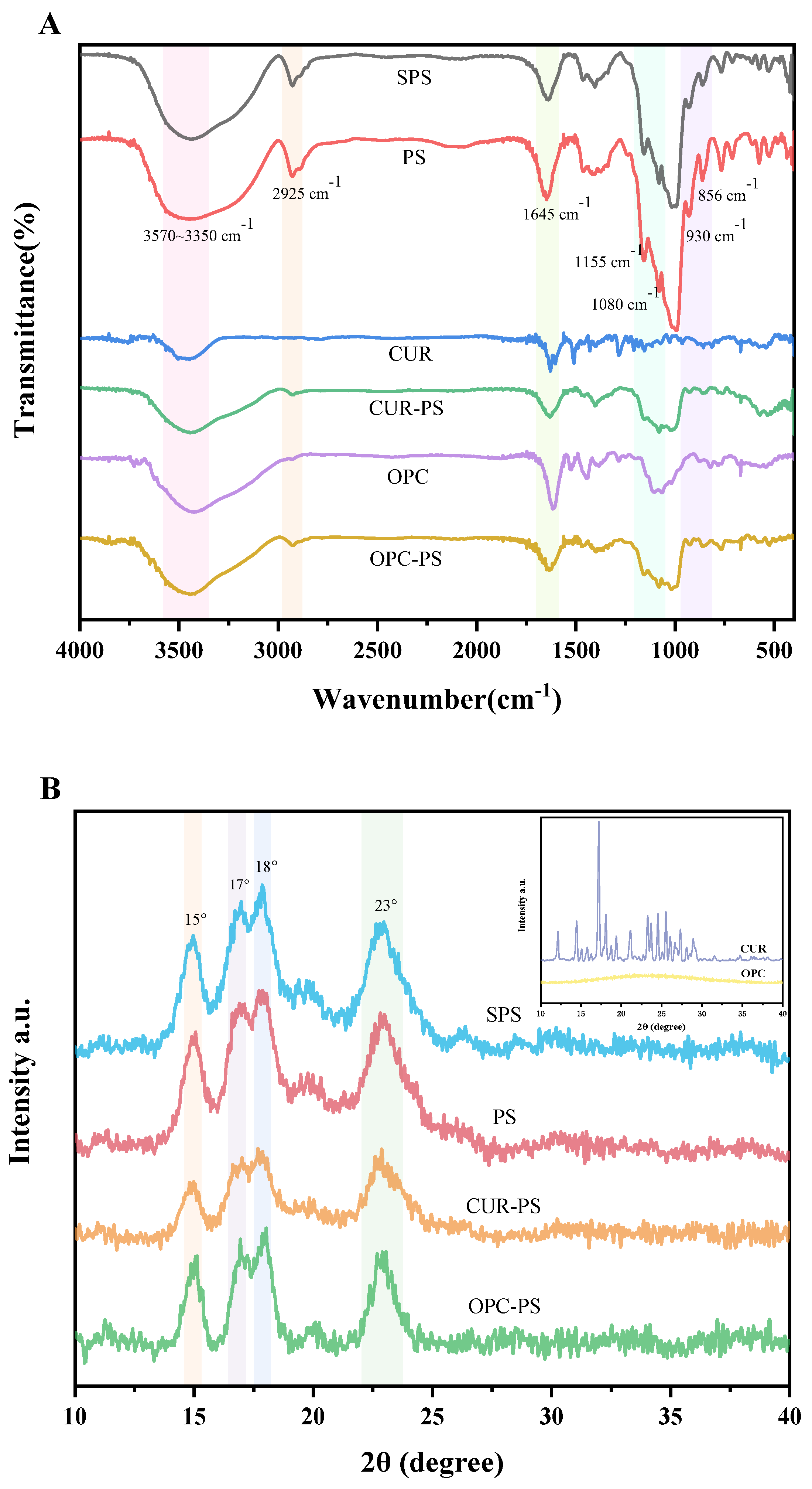
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT–IR)
X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.2.5. Loading Capacity of PS with CUR/OPCs
2.2.6. The Protective Effect of PS on OPCs
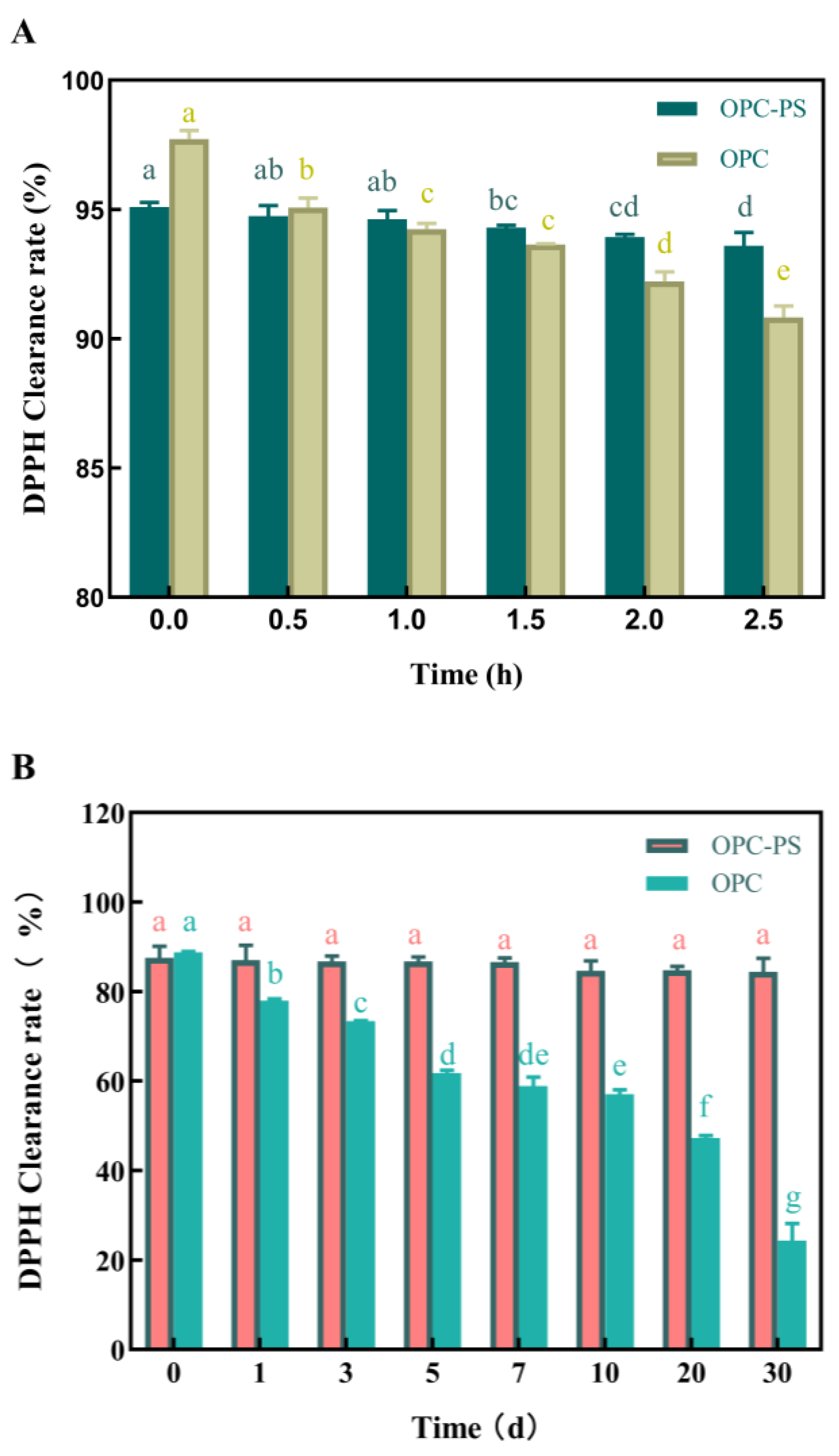
Ultraviolet Irradiation Stability of OPCs
Storage Stability of OPCs
2.2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cloning and Expression of Marine Dextranase SP5-Badex
Study on Enzymatic Properties of SP5-Badex
3.2. Dextranase Hydrolyzed Different Starches
3.2.1. SEM Images of Different PS
3.2.2. The Water/Oil Adsorption Rate of Different PS
3.3. Effect of Treatment Time on Sweet Potato Starch
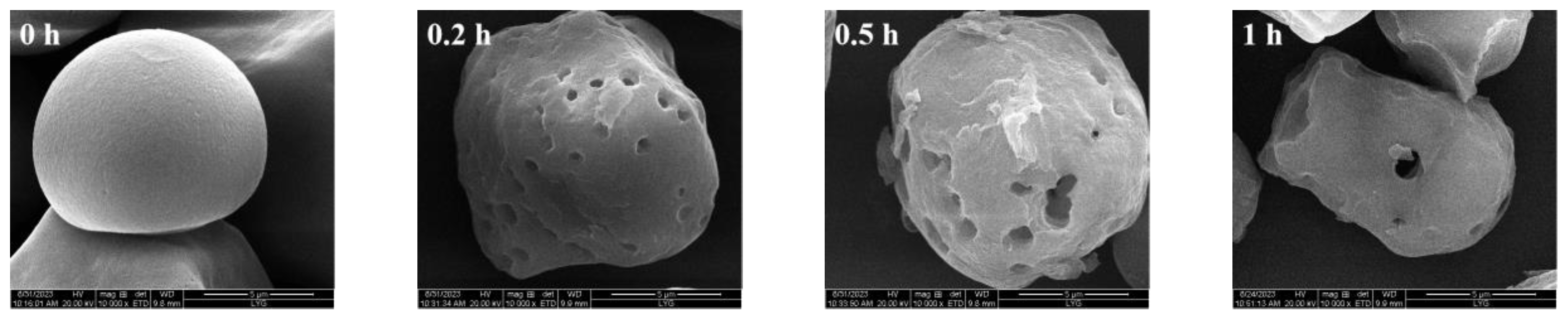
3.3.1. SEM of Sweet Potato Starch with Different Enzyme Digestion Times
3.3.2. The Water/Oil Adsorption Rate of PS
3.4. Loading Amount of PS with CUR or OPCs
3.5. Characterization of Porous Starch
3.6. The Protective Effect of PS on OPCs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanoue Batista, M.C.; Soccol, C.R.; Spier, M.R.; Libardi Junior, N.; Porto de Souza Vandenberghe, L. Potential application of dextranase produced by Penicillium aculeatum in solid-state fermentation from brewer’s spent grain in sugarcane process factories. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 35, 102086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittrof, S.L.; Kaufhold, L.; Fischer, A.; Wefers, D.A.-O. Products Released from Structurally Different Dextrans by Bacterial and Fungal Dextranases. Foods 2021, 10, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Feng, Y.; Xu, L.; Tian, X.; Lai, X.; Lyu, M.; Wang, S. Expression, purification and characterization of a cold-adapted dextranase from marine bacteria and its ability to remove dental plaque. Protein Expr. Purif. 2020, 174, 105678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, W.; Xia, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X. Cloning, expression and enzymatic properties of dextranase from Streptococcus mutans. China Food Addit. 2023, 34, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhong, L.; Xie, F.; Wei, L.; Gan, L.; Wang, X.; Liao, A. Purification, Characterization and Degradation Performance of a Novel Dextranase from Penicillium cyclopium CICC-4022. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkov, P.V.; Gusakov, A.V.; Rubtsova, E.A.; Rozhkova, A.M.; Matys, V.Y.; Nemashkalov, V.A.; Sinitsyn, A.P. Properties of a recombinant GH49 family dextranase heterologously expressed in two recipient strains of Penicillium species. Biochimie 2019, 157, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Z. Preparation and Properties of Rice Porous Starch Assisted by Hydrothermal Treatment. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2022, 37, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Poudel, R.; Dutta, N.; Karak, N. A mechanically robust biodegradable bioplastic of citric acid modified plasticized yam starch with anthocyanin as a fish spoilage auto-detecting smart film. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 125020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J. Preparation of Green Porous Cross-Linked Starch and Adsorption Properties; Qilu University of Technology: Jinan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.; Yao, H. A New Organic Material for Absorption—Researches on Porous Starch(1) Effects of Enzyme and Granular Size on Porous Starch Manufacture. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2001, 17, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Jin, W.; Shen, J. Preparation Technology of Corn Porous Starch by Complex Enzyme-Intermittent Ultrasonic. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2019, 34, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Qing, Z.; Zheng, M.; Lin, N.; Pan, C.; Liu, J. Preparation, Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Proso Millet Porous Starchby Combined-enzyme Method. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 23, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, B. The structure property and adsorption capacity of new enzyme-treated potato and sweet potato starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ma, J.; Lu, H.; Ye, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, C. Oligomeric Proantho Cyanidins provides neuroprotection against early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage possibly via anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects. J. Clin. Neurosci. Off. J. Neurosurg. Soc. Australas. 2017, 46, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, A.; Moore, L.; Leblanc, V.; Dudonné, S.; Desjardins, Y.; Lemieux, S.; Bochard, V.; Guyonnet, D.; Dodin, S. High dose versus low dose standardized cranberry proanthocyanidin extract for the prevention of recurrent urinary tract infection in healthy women: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. BMC Urol. 2021, 21, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yun, P.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Khadka, R.B.; Peng, X. Effects of Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Extract on Obesity. Obes. Facts 2020, 13, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xin, G.; Liu, K.; Liu, X.; Fu, L.; Qi, J.; Kang, K.; Meng, T.; Yi, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Paraventricular Nucleus Infusion of Oligomeric Proantho Cyanidins Improves Renovascular Hypertension. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 642015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coker-Gurkan, A.; Celik, M.; Ugur, M.; Arisan, E.D.; Obakan-Yerlikaya, P.; Durdu, Z.B.; Palavan-Unsal, N. Curcumin inhibits autocrine growth hormone-mediated invasion and metastasis by targeting NF-κB signaling and polyamine metabolism in breast cancer cells. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 1045–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz de Porras, V.; Figols, M.; Font, A.; Pardina, E. Curcumin as a hepatoprotective agent against chemotherapy-induced liver injury. Life Sci. 2023, 332, 122119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewlings, S.J.; Kalman, D.S. Curcumin: A Review of Its Effects on Human Health. Foods 2017, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zia, A.; Farkhondeh, T.; Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Samarghandian, S. The role of curcumin in aging and senescence: Molecular mechanisms. Biomed. Pharmacotherapy. 2021, 134, 111119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Chen, W.; Jiang, F.; Mo, M.; Bi, Y.; Kong, F. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro digestion of folate conjugated chitosan-loaded proanthocyanidins nanoparticles. Food Res. Int. (Ott. Ont.) 2023, 163, 112141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hani, U.; Jaswanth Gowda, B.H.; Siddiqua, A.; Wahab, S.; Begum, M.Y.; Sathishbabu, P.; Usmani, S.; Ahmad, M.P. Herbal approach for treatment of cancer using curcumin as an anticancer agent: A review on novel drug delivery systems. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 390, 123037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Dong, D.; Miao, Q.; Lu, J.; Lyu, M.; Wang, S. Study of key amino acid residues of GH66 dextranase for producing high-degree polymerized isomaltooligosaccharides and improving of thermostability. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 961776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Sharanagat, V.S. Physico-functional and structural characterization of ultrasonic-assisted chemically modified elephant foot yam starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.S.; Lee, B.H.; Yoo, S.H. Physical structure and absorption properties of tailor-made porous starch granules produced by selected amylolytic enzymes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lv, J.; Jiang, S.; Niu, B.; Pang, M.; Jiang, S.J.S.S. Preparation and characterization of porous corn starch and its adsorption toward grape seed proanthocyanidins. Starch-Stärke 2016, 68, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, S.; Wang, Y.; Ni, H.; Liu, S.; Qu, Q.; Kang, X.; Gao, Y. Purification Process by Macroporous Sorbent Resin, Determination of Average Polymerization, and in Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Proanthocyanidins from Pennisetum Purpureum Schumab. Feed Ind. 2023, 44, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Le, Y.; Peng, J.; Wu, H.; Sun, J.; Shao, W. An approach to the production of soluble protein from a fungal gene encoding an aggregation-prone xylanase in Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Lv, M.; Wang, S. Dextranase Preparation and Characterization of Porous Wheat Starch. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2023, 45, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Tian, J.; Ye, X.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.; Zhang, H.J.S.S. Encapsulation and release of curcumin with the mixture of porous rice starch and xanthan gum. Starch-Stärke 2021, 73, 2000042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Guan, M.; Dai, L.; Ji, N.; Qin, Y.; Xu, X.; Xiong, L.; Shi, R.; Sun, Q. Fabrication of starch-based emulsion gel beads by an inverse gelation technique for loading proanthocyanidin and curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridson, J.H.; Al-Hakkak, F.; Steward, D.; Al-Hakkak, J. Preparation and morphological, rheological, and structural characterisation of proanthocyanidin coated starch granules. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 130, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Wang, P.; Wu, F.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X.J.R.a. Effect of freezing rate on rheological, thermal and structural properties of frozen wheat starch. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 97907–97911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Pernell, C.; Ferruzzi, M.G.J.F.H. Complexation with phenolic acids affect rheological properties and digestibility of potato starch and maize amylopectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, L.D.; Leite, D.C.; Soares, R.M.; da Silveira, N.P.J.S.S. Effects of α-Amylase, Amyloglucosidase, and Their Mixture on Hierarchical Porosity of Rice Starch. Starch-Stärke 2018, 70, 1800008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shin, G.H.; Lee, I.W.; Chen, X.; Park, H.J.J.F.H. Soluble starch formulated nanocomposite increases water solubility and stability of curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 56, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Guevara, L.; Nieto-Suaza, L.; Sanchez, L.T.; Pinzon, M.I.; Villa, C.C. Development of native and modified banana starch nanoparticles as vehicles for curcumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Research on the Preparation of Porous Starch by α-Maltotrioyhdrolase in Collaboration with Amyioglucosidase and Its Application in Embedding Proanthocyanidins; Yangzhou University: Yangzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Ma, P.; Shen, M.; Wen, H.; Xie, J. Modified porous starches loading curcumin and improving the free radical scavenging ability and release properties of curcumin. Food Res. Int. (Ott. Ont.) 2023, 168, 112770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhao, J.S.; Li, Z.Y.; Chen, H.H. A pH-sensitive curcumin loaded microemulsion-filled alginate and porous starch composite gels: Characterization, in vitro release kinetics and biological activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 1863–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.K.; Haripriya, S.; Noor Mohamed, A.; Suriya, M. Preparation and characterization of resistant starch III from elephant foot yam (Amorphophallus paeonifolius) starch. Food Chem. 2014, 155, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, B.P.; Carpiné, D.; da Silva Bambirra Alves, F.E.; Barbi, R.C.T.; de Melo, A.M.; Ikeda, M.; Ribani, R.H. Thermal, structural, morphological and bioactive characterization of acid and neutral modified loquat (Eriobotrya japonica lindl.) seed starch and its by-products. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 147, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wu, C.; Junejo, S.A.; Zhang, B.; Fu, X.; Tan, C.P.; Huang, Q. Effect of V-type crystallinity and starch particle structure on the oil loading capacity and anti-oxidation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 297, 120015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ansi, W.; Sajid, B.M.; Mahdi, A.A.; Al-Maqtari, Q.A.; Al-Adeeb, A.; Ahmed, A.; Fan, M.; Li, Y.; Qian, H.; Jinxin, L.; et al. Molecular structure, morphological, and physicochemical properties of highlands barley starch as affected by natural fermentation. Food Chem. 2021, 356, 129665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.; Li, N.; Zhong, Q. Enhancing bioaccessibility of resveratrol by loading in natural porous starch microparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 194, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Xie, C.; Zu, Y.; Li, Y. Effect of UV-B radiation on grain morphology and proanthocyanidins content and distribution of Yuanyang red rice. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 2689–2696. [Google Scholar]
- Mirkov, I.; Stojković, D.; Aleksandrov, A.P.; Ivanov, M.; Kostić, M.; Glamočlija, J.; Soković, M. Plant Extracts and Isolated Compounds Reduce Parameters of Oxidative Stress Induced by Heavy Metals: An up-to-Date Review on Animal Studies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 1799–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.-Q.; Yu, L.; Yang, M.; Wang, C.-J.; Wang, M.-M.; Bai, X. Effects of the combination of freeze-thawing and enzymatic hydrolysis on the microstructure and physicochemical properties of porous corn starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
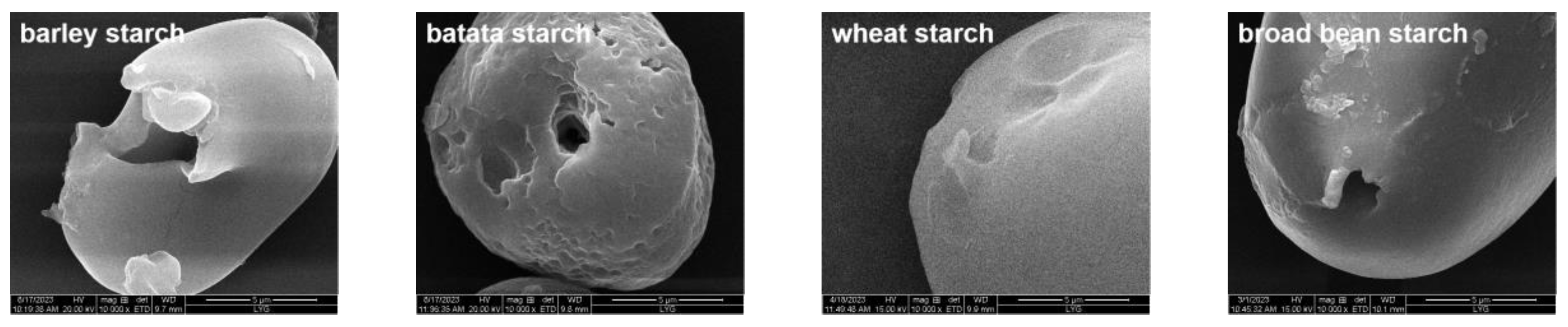

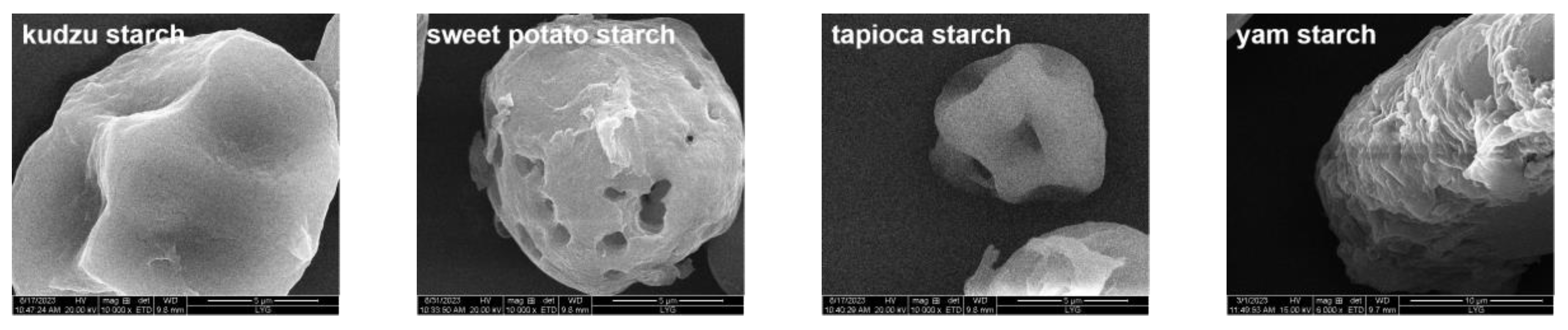

| Starch Type | Water Adsorption (%) | Oil Adsorption (%) |
|---|---|---|
| barley starch | 51.79 ± 3.36 d | 67.86 ± 4.92 b |
| batata starch | 97.27 ± 4.33 ab | 69.85 ± 5.00 b |
| broad bean starch | 47.89 ± 1.05 d | 63.57 ± 5.21 b |
| kudzu starch | 92.84 ± 2.55 b | 70.54 ± 8.01 b |
| sweet potato starch | 102.70 ± 3.75 a | 88.29 ± 4.309 a |
| tapioca starch | 71.25 ± 3.42 c | 68.84 ± 4.29 b |
| wheat starch | 89.21 ± 4.87 b | 87.93 ± 3.72 a |
| yam starch | 69.01 ± 0.41 c | 87.24 ± 3.61 a |
| Time of Enzymatic Digestion of Starch (h) | Water Adsorption (%) | Oil Adsorption (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 72 ± 4.80 d | 59 ± 3.36 b |
| 0.2 | 85 ± 4.64 c | 74 ± 8.30 ab |
| 0.5 | 86 ± 2.78 c | 77 ± 11.83 ab |
| 1 | 86 ± 1.24 c | 78 ± 14.32 ab |
| 3 | 90 ± 5.99 bc | 80 ± 4.24 ab |
| 6 | 92 ± 3.70 bc | 82 ± 14.27 ab |
| 12 | 99 ± 6.12 ab | 84 ± 7.88 ab |
| 24 | 103 ± 3.75 a | 89 ± 4.30 a |
| CUR/OPC:PS (w:w) | Loading Amount with CUR (mg/g) | Loading Amount with OPC (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|
| 2:50 | 3.16 ± 0.35 c | 3.78 ± 0.34 c |
| 1:50 | 6.71 ± 0.40 b | 7.75 ± 0.87 b |
| 1:60 | 9.59 ± 0.57 a | 12.29 ± 2.68 a |
| 1:70 | 9.00 ± 0.32 a | 11.87 ± 0.39 a |
| 1:80 | 9.38 ± 0.28 a | 11.78 ± 0.43 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, Y.; Liu, M.; Ni, H.; Bai, Y.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Kang, X.; Lyu, M.; Wang, S. Preparation of Sweet Potato Porous Starch by Marine Dextranase and Its Adsorption Characteristics. Foods 2024, 13, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13040549
Hao Y, Liu M, Ni H, Bai Y, Hao Q, Zhang L, Kang X, Lyu M, Wang S. Preparation of Sweet Potato Porous Starch by Marine Dextranase and Its Adsorption Characteristics. Foods. 2024; 13(4):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13040549
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Yue, Mingwang Liu, Hao Ni, Yue Bai, Qingfang Hao, Lei Zhang, Xinxin Kang, Mingsheng Lyu, and Shujun Wang. 2024. "Preparation of Sweet Potato Porous Starch by Marine Dextranase and Its Adsorption Characteristics" Foods 13, no. 4: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13040549
APA StyleHao, Y., Liu, M., Ni, H., Bai, Y., Hao, Q., Zhang, L., Kang, X., Lyu, M., & Wang, S. (2024). Preparation of Sweet Potato Porous Starch by Marine Dextranase and Its Adsorption Characteristics. Foods, 13(4), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13040549






