Novel Insights into the Effects of Different Cooking Methods on Salted Egg Yolks: Physicochemical and Sensory Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Physicochemical Properties
2.3.1. Determination of Salt Content and Cooking Loss
2.3.2. Determination of Color Difference
2.3.3. Determination of Oil Exudation
2.4. Structure Properties
2.4.1. Determination of T2 Relaxation Time
2.4.2. Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry (ATR-FTIR)
2.5. Analysis of Fatty Acids
2.6. Analysis of Free Amino Acids
2.7. Multiple Intelligent Sensory Analysis
2.7.1. Determination of Electronic Tongue (E-Tongue)
2.7.2. Determination of Electronic Nose (E-Nose)
2.7.3. Determination of VOCs
2.7.4. Sensory Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of SEY
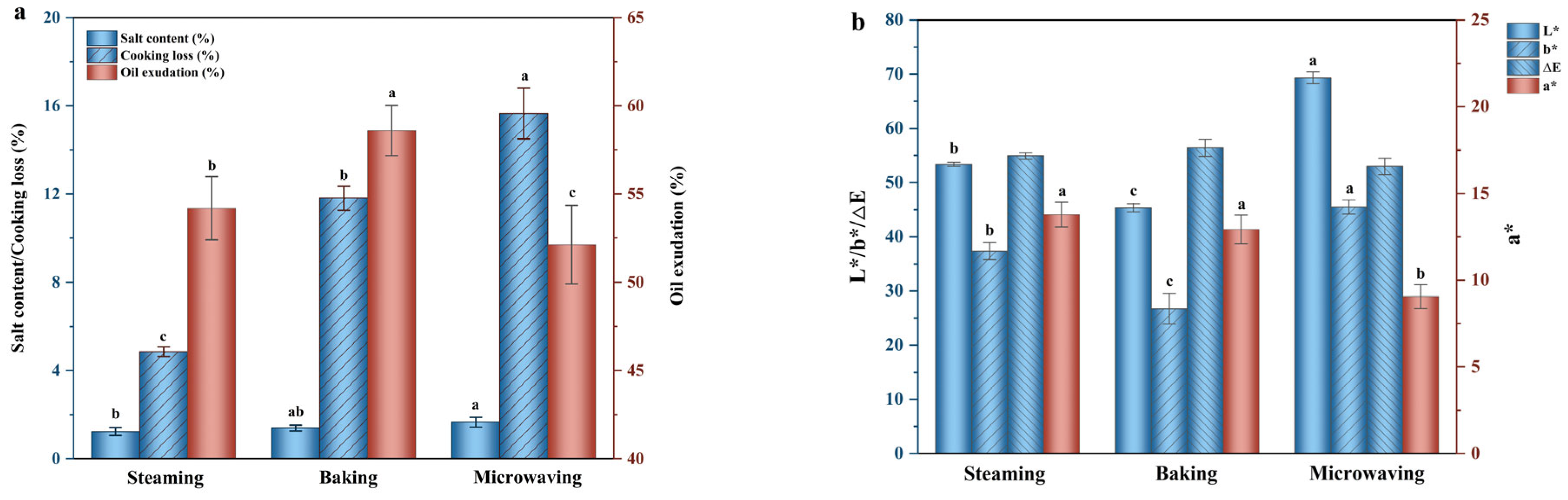
3.1.1. Salt Content and Cooking Loss
3.1.2. Oil Exudation
3.1.3. Instrumental Color
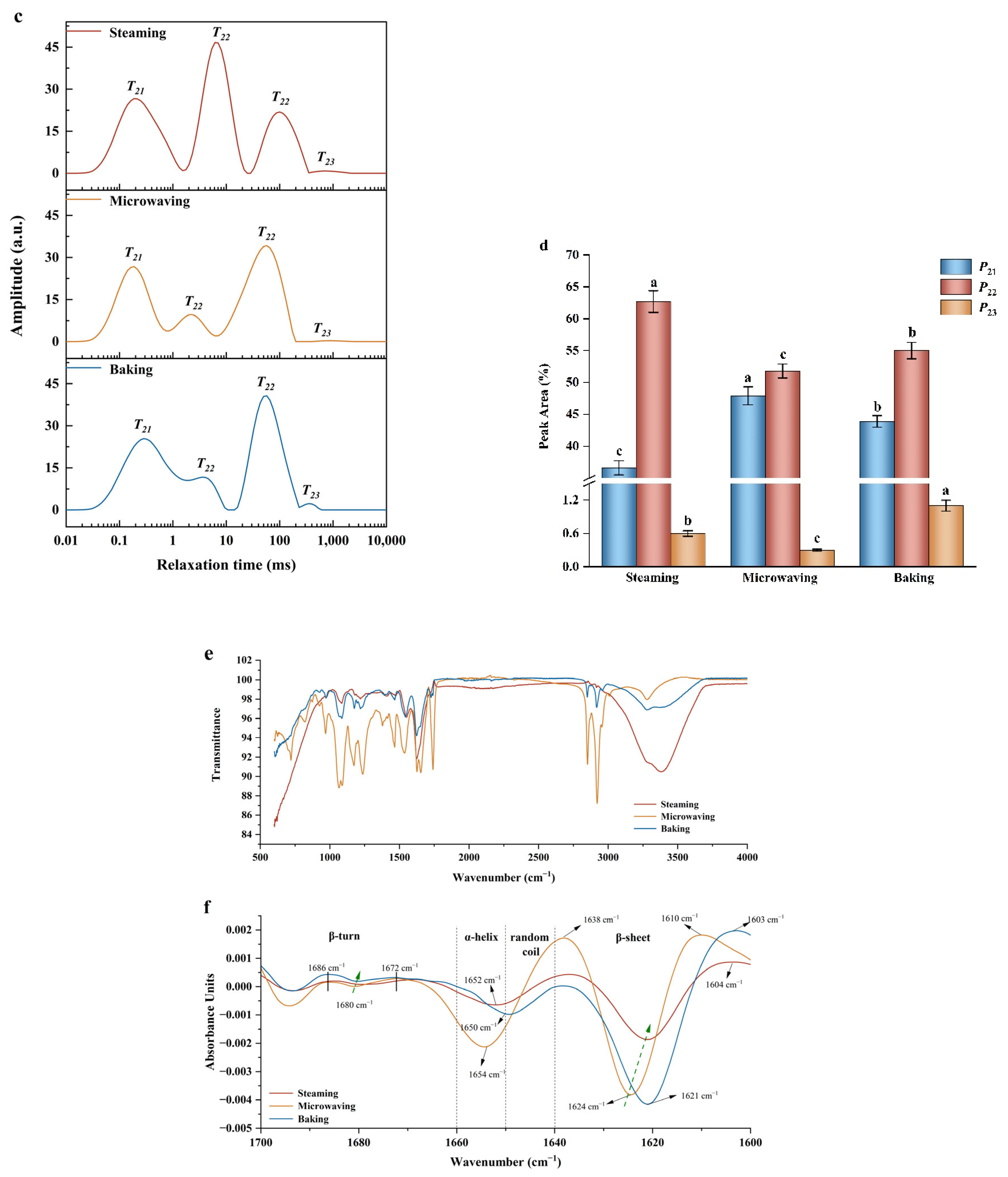
3.1.4. T2 Relaxation Time
3.1.5. FTIR Analysis
3.2. Fatty Acid Analysis
3.3. Free Amino Acids (FAAs)
3.4. Comprehensive Sensory Evaluation
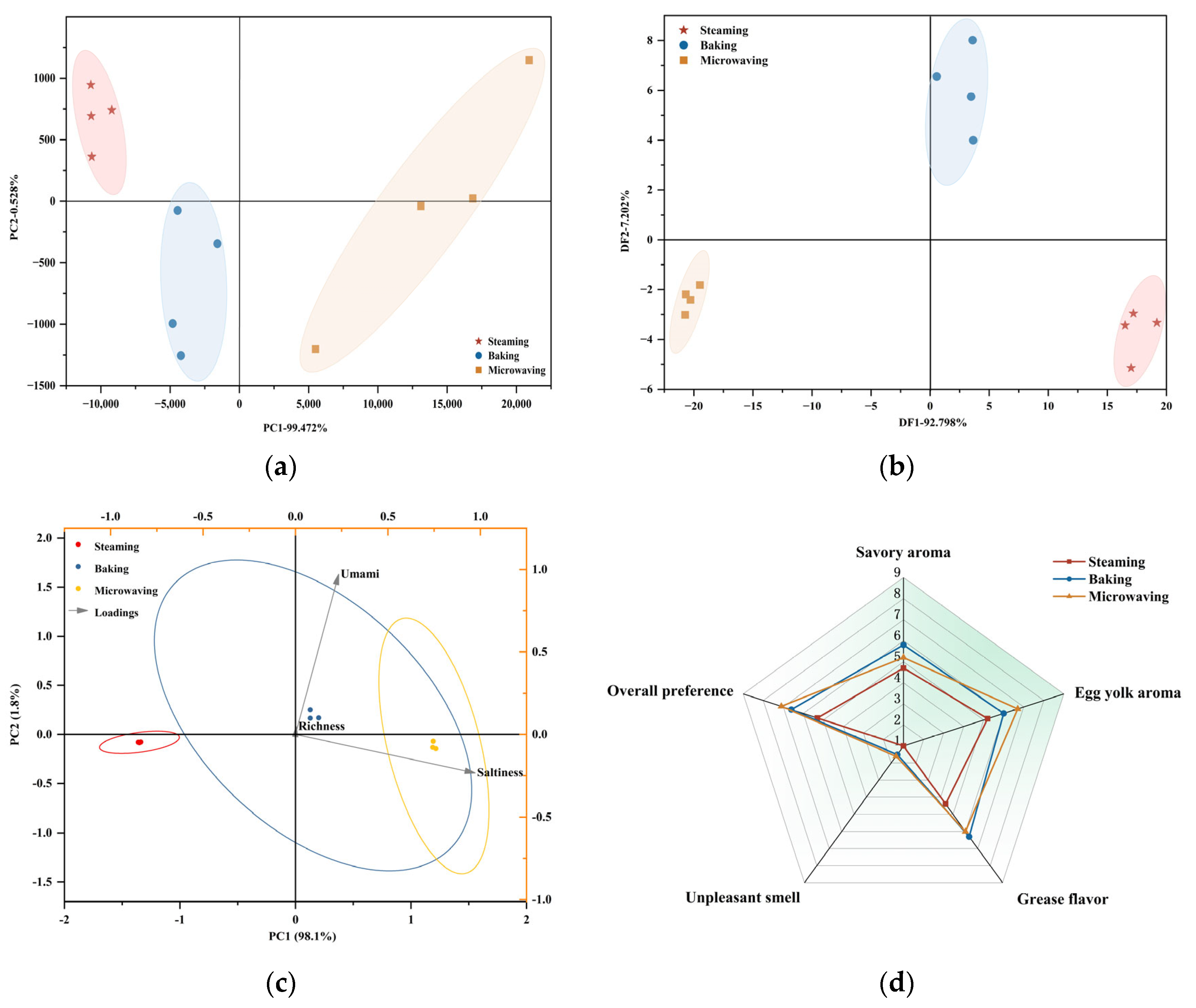
3.4.1. E-Nose Analysis
3.4.2. E-Tongue Analysis
3.4.3. Sensory Profile
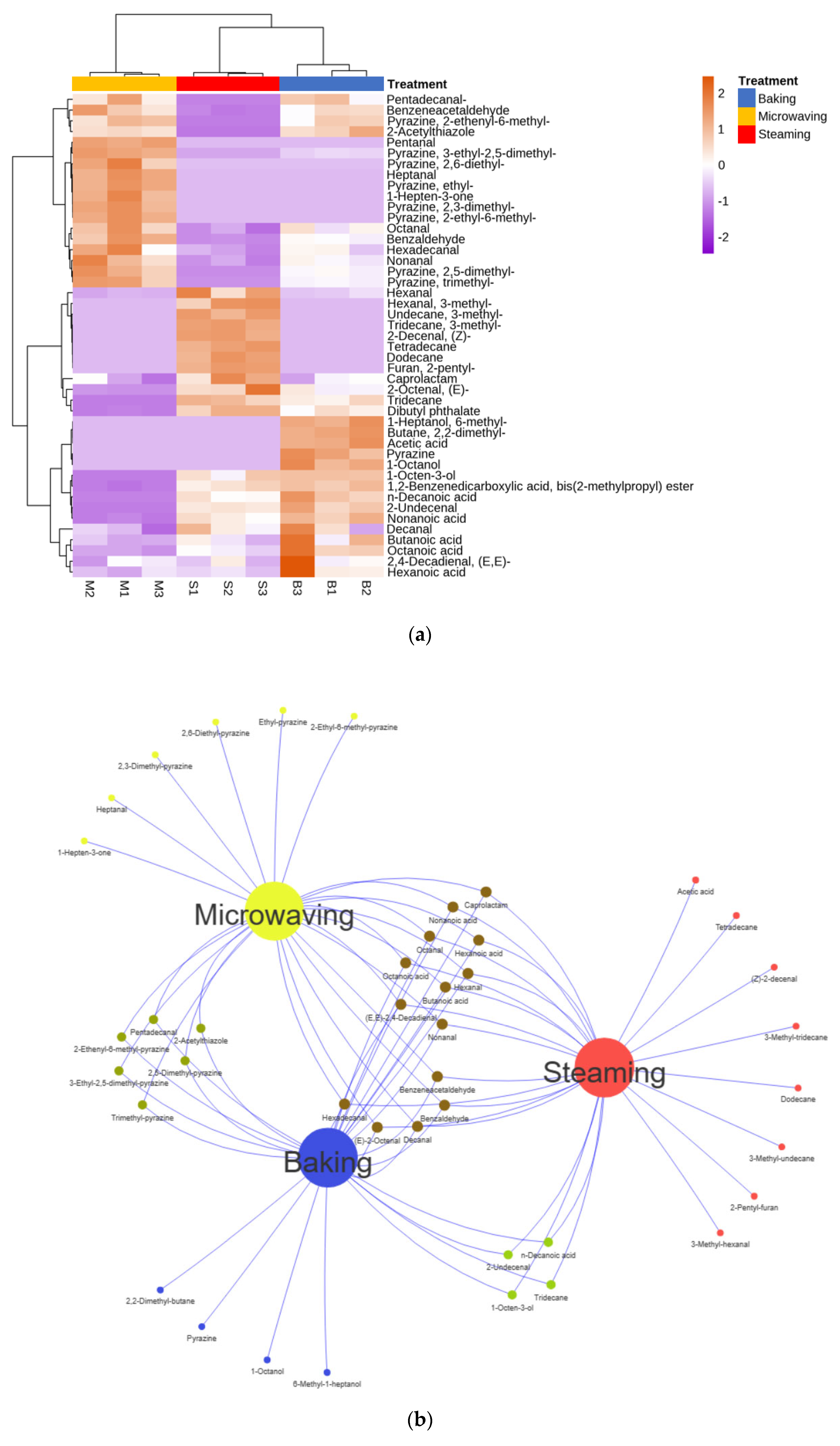
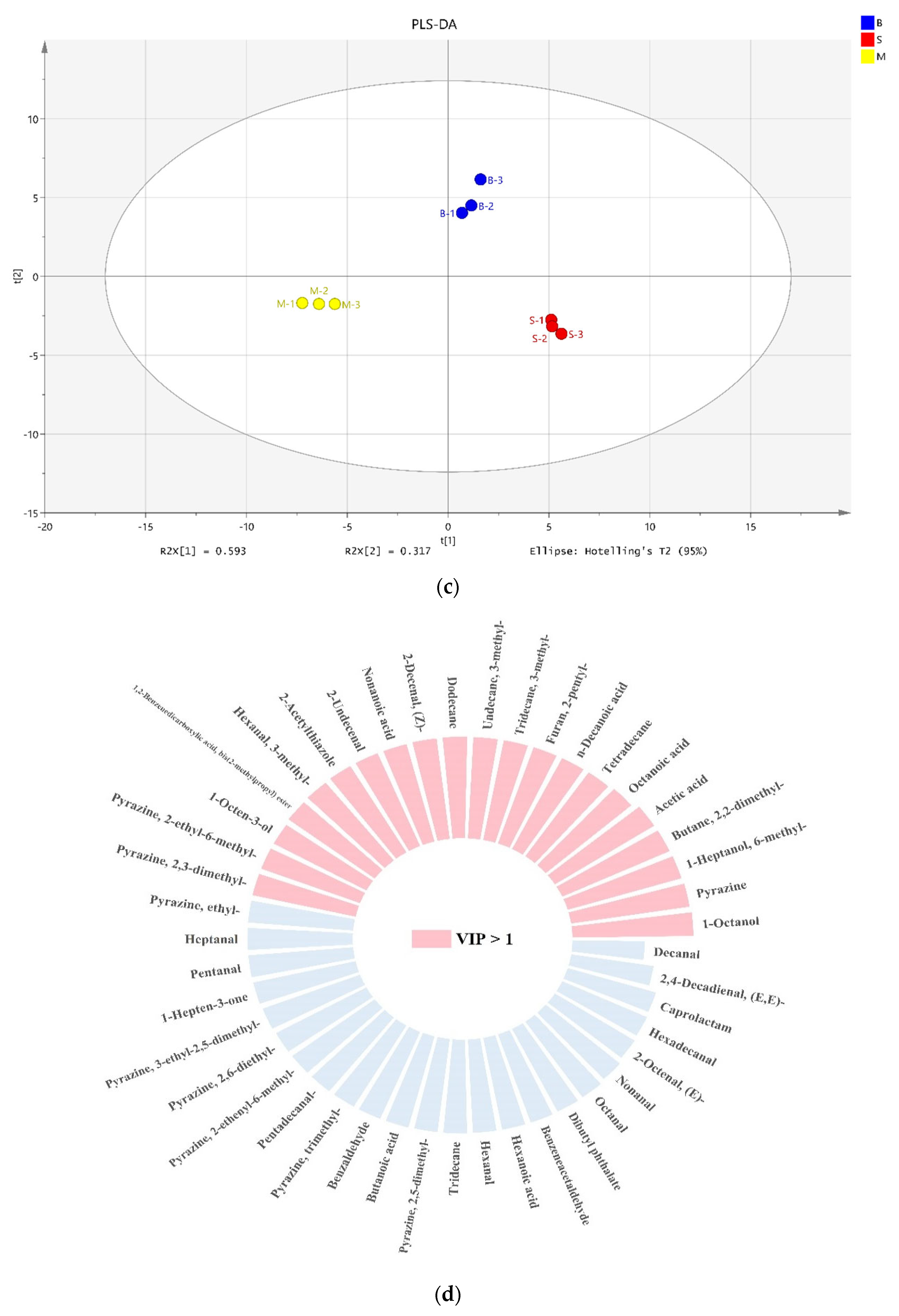
3.5. Profiles of VOCs
3.6. Correlation Analysis of Flavor Profiles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, M.; Yao, Y.; Nie, X.; Du, H.; Tu, Y. Changes in aggregation behavior of raw and cooked salted egg yolks during pickling. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Lv, X.; Li, J.; Cui, H.; Tang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, Y.; Qin, Y.; et al. Comparative characterization of flavor precursors and volatiles of Taihe black-boned silky fowl and Hy-line Brown yolks using multiomics and GC-O-MS-based volatilomics. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Wang, R.; He, X.; Chen, X.; Huo, X.; Lü, X.; Shan, Y. Comparison of the edible quality of liquid egg with different cooking methods and their antioxidant activity after in vitro digestion. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.; Chen, L.; Dong, S.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Li, S.; Ye, L. Multiomics reveals the formation pathway of volatile compounds in preserved egg yolk (PEY) induced by NaCl: Based on the model of PEY and salted egg yolk (SEY) treated with/without NaCl. Food Chem. 2023, 429, 136823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Muhoza, B.; Wang, X.; Feng, T.; Xia, S.; Zhang, X. Comparison between microwave and traditional water bath cooking on saltiness perception, water distribution and microstructure of grass crap meat. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhaimi, F.A.; Uslu, N.; Özcan, M.M. Oil content and fatty acid composition of eggs cooked in drying oven, microwave and pan. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghari, L.; Zeynali, F.; Sahari, M.A. Effects of boiling, deep-frying, and microwave treatment on the proximate composition of rainbow trout fillets: Changes in fatty acids, total protein, and minerals. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2013, 29, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Chang, C.; Gu, L.; Yang, Y. Characterization of salted egg yolk flavoring prepared by enzyme hydrolysis and microwave irradiation. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 127913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Xu, W.; Xiang, X.; Huang, Q.; Li, S. Improvement of quality and flavor of salted egg yolks by ultrasonic assisted cooking. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 75, 105579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.G.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, T.; Lu, W.J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.Y.; Guan, R.F. A Comparative Study of Pickled Salted Eggs by Positive and Negative Pressure-Ultrasonic Method. Foods 2023, 12, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margeta, P.; Kralik, G.; Grcevic, M.; Hanzek, D.; Kralik, Z. Importance of Sensory Evaluation in Assessment of Egg Quality. Poljoprivreda 2019, 25, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.M.; Guo, S.G.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, W.L.; Jiang, A.M. The investigation of the changes in physicochemical, texture and rheological characteristics of salted duck egg yolk during salting. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 88, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.T.; Qing, M.M.; Zang, J.N.; Chi, Y.J.; Chi, Y. Effects of CaCl2 on salting kinetics, water migration, aggregation behavior and protein structure in rapidly salted separated egg yolks. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.J.; Guo, W.B.; Wu, N.; Yao, Y.; Du, H.Y.; Xu, M.S.; Zhao, Y.; Tu, Y.G. Effects of salt and heat treatment on the physicochemical properties, microstructure, secondary structure, and simulated in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of duck egg white. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 6093–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asensio-Grau, A.; Peinado, I.; Heredia, A.; Andrés, A. Effect of cooking methods and intestinal conditions on lipolysis, proteolysis and xanthophylls bioaccessibility of eggs. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 46, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; The Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000; Available online: https://www.scirp.org/reference/ReferencesPapers?ReferenceID=1687699 (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Gao, X.; Li, J.; Chang, C.; Gu, L.; Xiong, W.; Su, Y.; Yang, Y. Characterization of physical properties, volatile compounds and aroma profiles of different salted egg yolk lipids. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, D.L.; Britton, W.M.; Cason, J.A. A Comparison of Various Procedures for Determining Total Yolk Lipid Content. Poult. Sci. 1984, 63, 1759–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, B.A.; Feng, S.; Strom, A.K.; DeVitt, A.A.; Yu, L.; Li, Y. Conjugated Linoleic Acids Alter the Fatty Acid Composition and Physical Properties of Egg Yolk and Albumen. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6870–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekkes, D.; van Dalen, A.; Edelman, M.; Voskuilen, A. Validation of the determination of amino acids in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography using automated pre-column derivatization with o-phthaldialdehyde. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1995, 669, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, J.; Pei, Z.; Wei, P.; Xiang, D.; Cao, X.; Shen, X.; Li, C. Volatile flavour components and the mechanisms underlying their production in golden pompano (Trachinotus blochii) fillets subjected to different drying methods: A comparative study using an electronic nose, an electronic tongue and SDE-GC-MS. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chi, Y.; Chi, Y. Change in rapid salting kinetics and characteristics of hen egg yolks. J. Food Eng. 2022, 329, 111090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chang, C.; Li, J.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, Z.; Xiong, W.; Gu, L.; Yang, Y. Effect of salting and dehydration treatments on the physicochemical and gel properties of hen and duck egg yolks, plasma and granules. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 6070–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewmanee, T.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W. Effects of Salting Processes and Time on the Chemical Composition, Textural Properties, and Microstructure of Cooked Duck Egg. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, S139–S147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betancur, M.I.; Motoki, K.; Spence, C.; Velasco, C. Factors influencing the choice of beer: A review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcone, M.F.; Wang, S.; Albabish, W.; Nie, S.; Somnarain, D.; Hill, A. Diverse food-based applications of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technology. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 729–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, Y. Changes in structure and flavor of egg yolk gel induced by lipid migration under heating. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, X.; Yang, H.; Qin, S.; Hong, L.; Pu, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J. Study of the molecular structure of proteins in fermented Maize-Soybean meal-based rations based on FTIR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, R.S.; Boyaci, I.H. Authentication of liquid egg composition using ATR-FTIR and NIR spectroscopy in combination with PCA. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlina, P.W.; Ma, M.H.; Shahzad, R.; Khalifa, I. Effect of Rosemary Extract on Lipid Oxidation, Fatty Acid Composition, Antioxidant Capacity, and Volatile Compounds of Salted Duck Eggs. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2022, 42, 689–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinn, S.E.; Proctor, A.; Baum, J.I. Egg Yolk as Means for Providing Essential and Beneficial Fatty Acids. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2018, 95, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinsk, M.C.; Murakami, A.E.; Gomes, S.T.M.; Matsushita, M.; de Souza, N.E. Fatty acid profile of egg yolk lipids from hens fed diets rich in n-3 fatty acids. Food Chem. 2003, 83, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Shimamoto, S.; Ohtsuka, A.; Ijiri, D. Analyses of free amino acid and taste sensor traits in egg albumen and yolk revealed potential of value-added eggs in chickens. Anim. Sci. J. 2021, 92, e13510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diepeveen, J.; Moerdijk-Poortvliet, T.C.W.; van der Leij, F.R. Molecular insights into human taste perception and umami tastants: A review. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1449–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kong, B.; Chen, Q. Evaluation of the flavour properties of cooked chicken drumsticks as affected by sugar smoking times using an electronic nose, electronic tongue, and HS-SPME/GC-MS. LWT 2021, 140, 110764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wang, J. Application of Sensory Evaluation, HS-SPME GC-MS, E-Nose, and E-Tongue for Quality Detection in Citrus Fruits. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, S2296–S2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, P.; Kan, J. Discrimination and characterization of the volatile organic compounds in eight kinds of huajiao with geographical indication of China using electronic nose, HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC–MS. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Adhikari, B. Application of electronic tongue for fresh foods quality evaluation: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2018, 34, 746–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.-B.; Obianwuna, U.E.; Zhang, H.-J.; Qiu, K.; Wu, S.-G.; Qi, G.-H.; Wang, J. A Comparison between the Egg Yolk Flavor of Indigenous 2 Breeds and Commercial Laying Hens Based on Sensory Evaluation, Artificial Sensors, and GC-MS. Foods 2022, 11, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Xi, W.; Nie, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, Q.; Yang, B.; Cao, D. Aroma characterization of flaxseed oils using headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-olfactometry. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2013, 115, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lu, L.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, Z. Volatile compounds, affecting factors and evaluation methods for rice aroma: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spada, F.P.; Balagiannis, D.P.; Purgatto, E.; do Alencar, S.M.; Canniatti-Brazaca, S.G.; Parker, J.K. Characterisation of the chocolate aroma in roast jackfruit seeds. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, P.; Liao, L.; Qin, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y. Characteristic fingerprints and volatile flavor compound variations in Liuyang Douchi during fermentation via HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, S.I.F.S.; Jongen, W.M.F.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S. A review of Maillard reaction in food and implications to kinetic modelling. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Luo, D.; Shen, Q.; Wu, J. Effect of cooking on aroma profiles of Chinese foxtail millet (Setaria italica) and correlation with sensory quality. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.G.; Gao, L.B.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, J.; Qiu, K.; Qi, G.H.; Wu, S.G. Discriminating Eggs from Two Local Breeds Based on Fatty Acid Profile and Flavor Characteristics Combined with Classification Algorithms. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2021, 41, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Jin, G.; Jin, Y.; Ma, M.; Wang, N.; Liu, C.; He, L. Discriminating eggs from different poultry species by fatty acids and volatiles profiling: Comparison of SPME-GC/MS, electronic nose, and principal component analysis method. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, F.; Wu, W.; Wang, P.; Ye, N. Comparison of Volatiles in Different Jasmine Tea Grade Samples Using Electronic Nose and Automatic Thermal Desorption-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Followed by Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Molecules 2020, 25, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavarda, C.; Cordero, C.; Strocchi, G.; Bortolini, C.; Bicchi, C.; Liberto, E. Cocoa smoky off-flavour: A MS-based analytical decision maker for routine controls. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Fatty Acids | Steaming | Baking | Microwaving |
|---|---|---|---|
| C14:0 | 0.26 ± 0.01 b | 0.30 ± 0.01 a | 0.25 ± 0.01 b |
| C16:0 | 25.45 ± 0.08 ab | 26.11 ± 0.71 a | 24.77 ± 0.33 b |
| C16:1 | 3.90 ± 0.49 | 4.34 ± 0.75 | 3.37 ± 0.30 |
| C17:0 | 0.17 ± 0.02 a | 0.15 ± 0.01 b | 0.19 ± 0.00 a |
| C17:1 | 0.16 ± 0.00 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.01 |
| C18:0 | 8.01 ± 0.28 b | 7.92 ± 0.11 b | 8.49 ± 0.10 a |
| C18:1 | 42.66 ± 1.19 | 42.94 ± 2.35 | 42.73 ± 0.27 |
| C18:2 | 14.76 ± 0.95 ab | 13.71 ± 0.66 b | 15.82 ± 0.31 a |
| C18:3n6 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.00 | 0.09 ± 0.01 |
| C18:3n3 | 0.34 ± 0.06 | 0.36 ± 0.04 | 0.36 ± 0.01 |
| C20:1 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| C20:2 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 0.17 ± 0.00 |
| C20:3 | 2.57 ± 0.12 | 2.39 ± 0.18 | 2.38 ± 0.01 |
| C22:6 | 1.00 ± 0.18 | 0.94 ± 0.04 | 0.79 ± 0.02 |
| Others | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.01 |
| Σ SFA 1 | 34.03 ± 0.39 | 34.59 ± 0.85 | 33.84 ± 0.44 |
| Σ MUFA 2 | 46.99 ± 1.70 | 47.73 ± 3.13 | 46.53 ± 0.59 |
| Σ PUFA 3 | 18.97 ± 1.33 | 17.68 ± 0.95 | 19.63 ± 0.36 |
| Amino Acids | Steaming | Baking | Microwaving |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asp | 40.73 ± 0.67 c | 56.08 ± 1.67 b | 66.38 ± 1.53 a |
| Glu | 95.33 ± 2.77 c | 124.48 ± 5.11 b | 150.49 ± 2.66 a |
| Ser | 14.05 ± 1.57 c | 17.55 ± 1.78 b | 23.34 ± 1.86 a |
| His | 18.18 ± 1.38 | 19.26 ± 5.78 | 24.16 ± 0.73 |
| Gly | 22.14 ± 0.40 c | 27.56 ± 2.72 b | 33.13 ± 1.55 a |
| Thr | 53.74 ± 4.61 b | 61.38 ± 5.88 b | 80.09 ± 8.50 a |
| Arg | 44.95 ± 0.82 c | 62.99 ± 1.62 b | 76.78 ± 4.53 a |
| Ala | 20.39 ± 0.73 c | 26.65 ± 0.46 b | 32.78 ± 1.08 a |
| Tyr | 55.77 ± 1.74 c | 75.10 ± 1.97 b | 84.76 ± 3.27 a |
| Cys-s | 2.50 ± 0.40 a | 3.12 ± 0.81 a | 1.29 ± 0.28 b |
| Val | 38.49 ± 0.69 c | 48.37 ± 2.41 b | 57.38 ± 3.06 a |
| Met | 14.30 ± 0.31 c | 17.05 ± 0.50 b | 21.05 ± 1.56 a |
| Trp | 9.64 ± 0.64 b | 10.26 ± 0.28 b | 11.52 ± 0.70 a |
| Phe | 28.13 ± 0.52 c | 37.65 ± 2.34 b | 42.46 ± 1.47 a |
| Ile | 24.66 ± 0.45 c | 33.15 ± 1.43 b | 40.29 ± 1.55 a |
| Leu | 47.06 ± 1.21 c | 65.31 ± 0.96 b | 75.92 ± 3.08 a |
| Lys | 49.65 ± 1.04 c | 68.22 ± 1.67 b | 79.54 ± 5.68 a |
| Pro | 21.64 ± 1.25 c | 30.63 ± 1.73 b | 37.25 ± 4.84 a |
| Flavor | 262.50 ± 6.82 c | 347.51 ± 14.28 b | 410.00 ± 11.57 a |
| Essential | 265.66 ± 9.46 c | 341.38 ± 15.46 b | 408.25 ± 25.60 a |
| Total | 601.36 ± 12.49 c | 784.79 ± 13.62 b | 938.58 ± 39.96 a |
| Compound | RI | Steaming | Baking | Microwaving |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acids (6) | ||||
| Acetic acid | 1449 | Nd | 9.11 ± 0.21 | Nd |
| Butanoic acid | 1625 | 6.45 ± 0.65 ab | 8.09 ± 0.49 a | 5.85 ± 0.25 b |
| Hexanoic acid | 1842 | 3.92 ± 0.36 ab | 5.15 ± 0.78 a | 3.31 ± 0.23 b |
| Octanoic acid | 2054 | 2.74 ± 0.09 b | 5.06 ± 0.25 a | 2.59 ± 0.14 b |
| Nonanoic acid | 2155 | 61.62 ± 3.72 b | 85.15 ± 4.34 a | 12.62 ± 1.48 c |
| Decanoic acid | 2271 | 4.15 ± 0.18 | 6.62 ± 0.26 | Nd |
| Alcohols (3) | ||||
| 6-Methyl-1-heptanol | 1226 | Nd | 3.43 ± 0.09 | Nd |
| 1-Octen-3-ol | 1450 | 10.85 ± 0.62 | 14.19 ± 1.36 | Nd |
| 1-Octanol | 1557 | Nd | 2.22 ± 0.17 | Nd |
| Aldehydes (15) | ||||
| Pentanal | 969 | Nd | Nd | 47.92 ± 2.41 |
| Hexanal | 1081 | 60.55 ± 2.85 a | 37.75 ± 1.34 b | 35.86 ± 1.19 b |
| 3-Methyl- hexanal | 1183 | 1.05 ± 0.28 | Nd | Nd |
| Heptanal | 1188 | Nd | Nd | 10.18 ± 0.28 |
| Octanal | 1287 | 6.74 ± 0.19 c | 10.49 ± 0.45 b | 15.65 ± 0.63 a |
| Nonanal | 1392 | 27.36 ± 1.84 c | 45.11 ± 2.80 b | 66.48 ± 2.40 a |
| (E)-2-Octenal | 1413 | 9.24 ± 0.41 a | 8.86 ± 0.23 a | 4.25 ± 0.12 b |
| Decanal | 1495 | 3.72 ± 0.07 | 3.82 ± 0.16 | 3.57 ± 0.06 |
| Benzaldehyde | 1518 | 12.24 ± 0.24 c | 35.86 ± 2.61 b | 61.87 ± 3.71 a |
| Benzeneacetaldehyde | 1631 | 4.87 ± 0.08 b | 14.13 ± 0.63 a | 15.86 ± 0.57 a |
| (Z)-2-Decenal | 1640 | 2.54 ± 0.14 | Nd | Nd |
| 2-Undecenal | 1712 | 2.45 ± 0.12 | 2.59 ± 0.11 | Nd |
| (E,E)-2,4-Decadienal | 2143 | 2.55 ± 0.10 | 2.76 ± 0.26 | 2.54 ± 0.19 |
| Hexadecanal | 2149 | 6.57 ± 0.17 b | 10.16 ± 0.30 a | 10.93 ± 0.62 a |
| Pentadecanal | 2242 | Nd | 2.41 ± 0.12 | 2.43 ± 0.14 |
| Alkanes (6) | ||||
| 3-Methyl-undecane | 1154 | 10.29 ± 0.26 | Nd | Nd |
| 2,2-Dimethyl-butane | 1205 | Nd | 7.50 ± 0.14 | Nd |
| Dodecane | 1201 | 10.41 ± 0.31 | Nd | Nd |
| Tridecane | 1302 | 8.83 ± 0.21 | 7.38 ± 0.19 | Nd |
| 3-Methyl-tridecane | 1369 | 4.91 ± 0.05 | Nd | Nd |
| Tetradecane | 1403 | 6.48 ± 0.14 | Nd | Nd |
| Esters (2) | ||||
| 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis(2-methyl propyl) ester | 2590 | 50.34 ± 1.17 b | 60.59 ± 2.75 a | 7.76 ± 0.33 c |
| Dibutyl phthalate | 2684 | 75.32 ± 2.14 a | 50.42 ± 1.81 b | 4.73 ± 0.15 c |
| Furans (1) | ||||
| 2-pentyl-furan | 1236 | 25.55 ± 0.57 | Nd | Nd |
| Ketones (1) | ||||
| 1-Hepten-3-one | 1307 | Nd | Nd | 5.09 ± 0.22 |
| Pyrazines (9) | ||||
| Pyrazine | 1211 | Nd | 2.49 ± 0.10 | Nd |
| 2,5-Dimethyl-pyrazine | 1315 | Nd | 45.27 ± 2.02 | 99.73 ± 3.99 |
| Ethyl-pyrazine | 1334 | Nd | Nd | 2.48 ± 0.05 |
| 2,3-Dimethyl-pyrazine | 1340 | Nd | Nd | 2.53 ± 0.08 |
| 2-Ethyl-6-methyl-pyrazine | 1379 | Nd | Nd | 2.54 ± 0.07 |
| Trimethyl-pyrazine | 1398 | Nd | 10.28 ± 0.11 | 10.38 ± 1.05 |
| 3-Ethyl-2,5-dimethyl- pyrazine | 1437 | Nd | 3.70 ± 0.08 | 15.20 ± 0.23 |
| 2,6-Diethyl-pyrazine | 1433 | Nd | Nd | 3.60 ± 0.18 |
| 2-Ethenyl-6-methyl- pyrazine | 1504 | Nd | 2.53 ± 0.13 | 3.64 ± 0.11 |
| Thiazoles (1) | ||||
| Caprolactam | 2196 | 4.89 ± 0.17 a | 4.52 ± 0.23 a | 2.42 ± 0.18 b |
| Sulfides (1) | ||||
| 2-Acetylthiazole | 1642 | Nd | 4.83 ± 0.16 | 3.70 ± 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Gu, L.; Chang, C.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Su, Y. Novel Insights into the Effects of Different Cooking Methods on Salted Egg Yolks: Physicochemical and Sensory Analysis. Foods 2024, 13, 1963. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13131963
Gao X, Zhang M, Li J, Gu L, Chang C, Huang Z, Yang Y, Su Y. Novel Insights into the Effects of Different Cooking Methods on Salted Egg Yolks: Physicochemical and Sensory Analysis. Foods. 2024; 13(13):1963. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13131963
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xuejing, Mengya Zhang, Junhua Li, Luping Gu, Cuihua Chang, Zijian Huang, Yanjun Yang, and Yujie Su. 2024. "Novel Insights into the Effects of Different Cooking Methods on Salted Egg Yolks: Physicochemical and Sensory Analysis" Foods 13, no. 13: 1963. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13131963
APA StyleGao, X., Zhang, M., Li, J., Gu, L., Chang, C., Huang, Z., Yang, Y., & Su, Y. (2024). Novel Insights into the Effects of Different Cooking Methods on Salted Egg Yolks: Physicochemical and Sensory Analysis. Foods, 13(13), 1963. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13131963







