Progress in Multisensory Synergistic Salt Reduction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Salty Taste Perception Mechanism and Sodium Salt Reduction Strategies
2.1. Current Status of Salt Content in Food and Hazards of Excessive Salt Intake
2.2. Salty Taste Perception Mechanism
2.3. Salty Taste Evaluation System
2.4. Sodium Salt Reduction Strategies
2.4.1. Salt Substitutes
2.4.2. Modification of the Shape and Structure of Salt
2.4.3. Innovation of Food Processing Technology
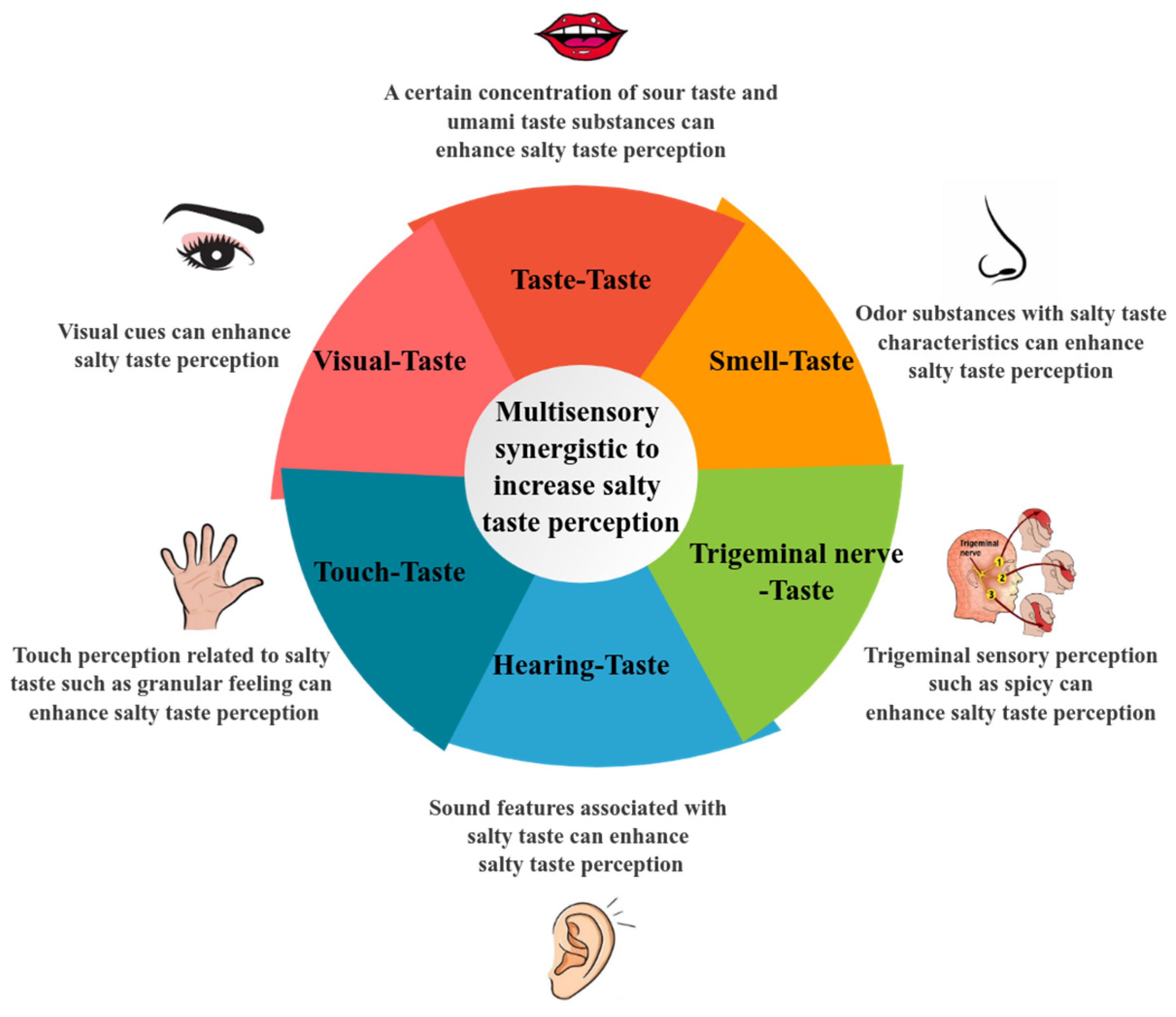
3. Detailed Multisensory Synergistic Effect
3.1. Enhancement of Salty Taste Perception through Taste Interaction
3.2. Enhancement of Salty Taste Perception through Olfactory Interaction
3.3. Enhancement of Salty Taste Perception through Auditory Interaction
3.4. Enhancement of Salty Taste Perception through Visual Interaction
3.5. Enhancement of Salty Taste Perception through Tactile Interaction
3.6. Enhancement of Salty Taste Perception through Trigeminal Interaction
3.7. Enhancement of Salty Taste Perception through Multisensory Synergistic Interaction
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Huang, X.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, S.; Dong, X.; Qin, L. Effect of sodium salt on meat products and reduction sodium strategies—A review. Meat Sci. 2023, 205, 109296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liem, D.G.; Miremadi, F.; Keast, R. Reducing Sodium in Foods: The Effect on Flavor. Nutrients 2011, 3, 694–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.W.; Dhaun, N.; Bailey, M.A. The impact of excessive salt intake on human health. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.L.; Tan, T.C.; Easa, A.M. The use of salt substitutes to replace sodium chloride in food products: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 6997–7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas-Danguin, T.; Guichard, E.; Salles, C. Cross-modal interactions as a strategy to enhance salty taste and to maintain liking of low-salt food: A review. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5269–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogas, M.; Statescu, C.; Padurariu, M.; Ciobica, A.; Bilha, S.C.; Haisan, A.; Timofte, D.; Hogas, S. Salt, Not Always a Cardiovascular Enemy? A Mini-Review and Modern Perspective. Medicina 2022, 58, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umakanthan, T.; Mathi, M. Increasing saltiness of salts (NaCl) using mid-infrared radiation to reduce the health hazards. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 3535–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endaltseva, A.; Coeurquetin, P.; Thomas-Danguin, T.; Poulain, J.-P.; Tibere, L.; Dupuy, A. Eater-oriented knowledge framework for reducing salt and dietary sodium intake (scoping review). Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 10446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zeng, L.; Jha, V.; Cobb, L.K.; Shibuya, K.; Appel, L.J.; Neal, B.; Schutte, A.E. Potassium-Enriched Salt Substitutes: A Review of Recommendations in Clinical Management Guidelines. Hypertension 2024, 81, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, T.; Huang, S.; Yang, Y.; Hu, A.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, W. A review of the world’s salt reduction policies and strategies-preparing for the upcoming year 2025. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 2836–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briar, L.M.; Feisul Idzwan, M.; Bat-Erdene, B.; Enkhtungalag, B.; Arunah, C.; Viola, M.; Jacqui, W.; Kathy, T. Strengthening national salt reduction strategies using multiple methods process evaluations: Case studies from Malaysia and Mongolia. Public Health Nutr. 2024, 27, e89. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, K.; He, T.; Ji, Y.; Zhu, T.; Jiang, E. The perspective of hypertension and salt intake in Chinese population. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 25608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Liang, L.; Pu, D.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of Sodium Content in 4082 Kinds of Commercial Foods in China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rýdlová, L.; Hrubá, M.; Škorpilová, T.; Pivoňka, J.; Tobolka, A.; Suchopárová, M.; Rajchl, A. Sodium content of foods sold in the Czech market. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2022, 28, 100526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia-Blonval, K.; Blanco-Metzler, A.; Montero-Campos, M.; Dunford, E.K. The salt content of products from popular fast-food chains in Costa Rica. Appetite 2014, 83, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israr, T.; Rakha, A.; Sohail, M.; Rashid, S.; Shehzad, A. Salt reduction in baked products: Strategies and constraints. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jachimowicz-Rogowska, K.; Winiarska-Mieczan, A. Initiatives to Reduce the Content of Sodium in Food Products and Meals and Improve the Population’s Health. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, C.; Liu, J.; Bech, A.C.; Pagliarini, E.; Bredie, W.L.P. Cross-cultural differences in lingual tactile acuity, taste sensitivity phenotypical markers, and preferred oral processing behaviors. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 80, 103803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigiani, A. Does ENaC Work as Sodium Taste Receptor in Humans? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liu, X.-D.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, J.; Wang, P.; Yang, W.; Luo, J. Modeling and simulation of ion channels and action potentials in taste receptor cells. Sci. China Ser. C 2009, 52, 1036–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, K.E.; Hewson, L.; Fisk, I.D. Sensory perception and consumer acceptance of commercial and salt-reduced potato crisps formulated using salt reduction design rules. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugamprema, D.; Muthuswamy, K.; Krishnan, V.; Subramaniam, S. Insights on modulators in perception of taste modalities: A review. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2019, 32, 231–246. [Google Scholar]
- Pallante, L.; Malavolta, M.; Grasso, G.; Korfiati, A.; Mavroudi, S.; Mavkov, B.; Kalogeras, A.; Alexakos, C.; Martos, V.; Amoroso, D.; et al. On the human taste perception: Molecular-level understanding empowered by computational methods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, L.; Liu, R.; Chen, Q. Epigenetic regulation of ion channels in the sense of taste. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 172, 105760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, M.; Hinton, A.; Kirabo, A. Dendritic cell epithelial sodium channel induced inflammation and salt-sensitive hypertension. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2024, 33, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Badar, I.H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, H.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Insights into the flavor perception and enhancement of sodium-reduced fermented foods: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2022, 64, 2248–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumatsu, K.; Atsumi, N.; Takashina, Y.; Ito, C.; Yasui, N.; Margolskee, R.F.; Yamashita, A. Chloride ions evoke taste sensations by binding to the extracellular ligand-binding domain of sweet/umami taste receptors. Elife 2023, 12, e84291. [Google Scholar]
- Pilic, L.; Lubasinski, N.; Berk, J.M.; Ward, D.; Graham, C.A.-M.; Da Silva Anastacio, V.; King, A.; Mavrommatis, Y. The associations between genetics, salt taste perception and salt intake in young adults. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 84, 103954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, B.; Wu, L.; Mao, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y. Characteristics of saltiness-enhancing peptides derived from yeast proteins and elucidation of their mechanism of action by molecular docking. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, S.; Lee, Y. Salt Sensation and Regulation. Metabolites 2021, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, M.; Kinchla, A.J.; Nolden, A.A. Role of Sensory Evaluation in Consumer Acceptance of Plant-Based Meat Analogs and Meat Extenders: A Scoping Review. Foods 2020, 9, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, B.; Li, L. Effect of ginger on chemical composition, physical and sensory characteristics of chicken soup. Foods 2021, 10, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munekata, P.E.S.; Finardi, S.; de Souza, C.K.; Meinert, C.; Pateiro, M.; Hoffmann, T.G.; Domínguez, R.; Bertoli, S.L.; Kumar, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Applications of Electronic Nose, Electronic Eye and Electronic Tongue in Quality, Safety and Shelf Life of Meat and Meat Products: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Moazzem, M.S. Recent Applications of Potentiometric Electronic Tongue and Electronic Nose in Sensory Evaluation. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 27, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueiro, J.; Negreira, N.; Simal-Gandara, J. Challenges in relating concentrations of aromas and tastes with flavor features of foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2017, 57, 2112–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Rosa, A.R.; Leone, F.; Cheli, F.; Chiofalo, V. Fusion of electronic nose, electronic tongue and computer vision for animal source food authentication and quality assessment-A review. J. Food Eng. 2017, 210, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, D.; Hu, N.; Wang, H.; Hsia, K.J.; Wang, P. Bioelectronic tongue of taste buds on microelectrode array for salt sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Wilkin, J.D.; Szymkowiak, A.; Grigor, J. Sensory and affective response to chocolate differing in cocoa content: A TDS and facial electromyography approach. Physiol. Behav. 2023, 270, 114308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrico, D.D.; Mehta, A.; Borssato, A.B. New methods to assess sensory responses: A brief review of innovative techniques in sensory evaluation. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 49, 100978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Pu, D.; Yan, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zuo, M.; Zhang, Y. Recent advances and application of machine learning in food flavor prediction and regulation. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2023, 138, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, C. Behavioural Nudges, Physico-Chemical Solutions, and Sensory Strategies to Reduce People’s Salt Consumption. Foods 2022, 11, 3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiselman, H.L. The future in sensory/consumer research: ……….....evolving to a better science. Food Qual. Prefer. 2013, 27, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, C.A. Dietary salt intake in chronic kidney disease. Recent studies and their practical implications. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2024. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- van Rompay, T.; van Ooijen, I.; Groothedde, S.; Saakes, D. (Not to be taken) with a grain of salt: Enhancing perceived saltiness by 3D-printed surface textures. Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 93, 104279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkin, B.M.; Bandy, L.K.; Hollowell, S.; Jebb, S.A.; Scarborough, P. Changes in the salt content of packaged foods sold in supermarkets between 2015–2020 in the United Kingdom: A repeated cross-sectional study. Plos. Med. 2022, 19, e1004114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Feng, Y.; Thomas-Danguin, T.; Zhao, M. Enhancement of saltiness perception by odorants selected from Chinese soy sauce: A gas chromatography/olfactometry-associated taste study. Food Chem. 2021, 335, 127664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissaisorakarn, V.; Ormseth, G.; Earle, W.; Morales-Alvarez, M.C.; Hiremath, S.; Juraschek, S.P.P. Less sodium, more potassium, or both: Population-wide strategies to prevent hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. 2023, 325, F99–F104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidona, F.; Zago, M.; Carminati, D.; Giraffa, G. The Reduction of Salt in Different Cheese Categories: Recent Advances and Future Challenges. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 859694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppu, U.; Hopia, A.; Pohjanheimo, T.; Rotola-Pukkila, M.; Mäkinen, S.; Pihlanto, A.; Sandell, M. Effect of Salt Reduction on Consumer Acceptance and Sensory Quality of Food. Foods 2017, 6, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroukhi, I.; Dominguez, J.; Bord, C.; Guerinon, D.; Chassard, C.; Mardon, J. How can the NaCl content of ripened Fourme d’Ambert cheese be reduced using innovative dry surface salting processes? Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2024, 77, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudette, N.J.; Pietrasik, Z.; Johnston, S.P. Application of taste contrast to enhance the saltiness of reduced sodium beef patties. LWT 2019, 116, 108585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Huang, J.; Vincent, G.; Wang, S. Advances in flavor peptides with sodium-reducing ability: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunteman, A.N.; McKenzie, E.N.; Yang, Y.; Lee, Y.; Lee, S.Y. Compendium of sodium reduction strategies in foods: A scoping review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1300–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Rosa, J.L.; Rios-Mera, J.D.; Castillo, C.J.C.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Pinton, M.B.; dos Santos, B.A.; Correa, L.P.; Henn, A.S.; Cichoski, A.J.; Flores, E.M.M.; et al. High-power ultrasound, micronized salt, and low KCl level: An effective strategy to reduce the NaCl content of Bologna-type sausages by 50%. Meat Sci. 2023, 195, 109012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forde, C.G.; de Graaf, K. Influence of Sensory Properties in Moderating Eating Behaviors and Food Intake. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 841444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keast, R.S.J.; Breslin, P.A.S. An overview of binary taste-taste interactions. Food Qual. Prefer. 2003, 14, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Niu, Y.; Sun, B.; Liu, Z.; Mao, X.; Zhang, Y. Virtual screening and characteristics of novel umami peptides from porcine type I collagen. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Inui-Yamamoto, C. The flavor-enhancing action of glutamate and its mechanism involving the notion of kokumi. Npj Sci. Food. 2023, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe-White, K.M.; Baumler, M.; Gradwell, E.; Juturu, V.; White, D.A.; Handu, D. Application of Umami Tastants for Sodium Reduction in Food: An Evidence Analysis Center Scoping Review. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2023, 123, 1606–1620.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breslin, P.A.S. Interactions among salty, sour and bitter compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1996, 7, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Venkitasamy, C.; Pan, Z.; Ke, H.; Guo, S.; Wu, D.; Wu, W.; Zhao, L. Potential effects of umami ingredients on human health: Pros and cons. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2019, 60, 2294–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delwiche, J. The impact of perceptual interactions on perceived flavor. Food Qual. Prefer. 2004, 15, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Tian, T.; Yu, H.; Yuan, H.; Lou, X.; Tian, H. Cross-modal aromaetaste interactions between lactone aroma and sourness and saltiness in solutions at concentrations relevant to Cheddar cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 144, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridi Esfanjani, A.; Mohebbi, M. Enhancing saltiness perception by chemosensory interaction: An fMRI study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; Han, P. Neurocognitive mechanisms of odor-induced taste enhancement: A systematic review. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2022, 28, 100535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivone Carraro, C.; Machado, R.; Espindola, V.; Bastianello Campagnol, P.C.; Rodrigues Pollonio, M.A. The effect of sodium reduction and the use of herbs and spices on the quality and safety of bologna sausage. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 32, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syarifuddin, A.; Septier, C.; Salles, C.; Thomas-Danguin, T. Reducing Sodium Content in Cheeses While Increasing Salty Taste and Fat Perception Using Aroma. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 873427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.P.; Wang, M.; Fang, X.; Liya, A.; Zhang, H.; Blank, I.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y. Odorants Identified in Chinese Dry-Cured Ham Contribute to Salty Taste Enhancement. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 72, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tournier, C.; Sulmont-Rosse, C.; Semon, E.; Vignon, A.; Issanchou, S.; Guichard, E. A study on texture-taste-aroma interactions: Physico-chemical and cognitive mechanisms. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, P.; Xing, L.; Hu, J.; Feng, R.; Zhong, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, Y.; et al. Insights into brain perceptions of the different taste qualities and hedonic valence of food via scalp electroencephalogram. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Varshney, S.; Hossain, M.M.; Saleem, S.M.; Gupta, P.; Singh, A. “Taste modification” strategy for prevention and control of hypertension in India: Need for robust clinical trials. Lancet Reg. Health Southeast Asia 2023, 14, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, D.; Vaz Garrido, M.; Lamy, E.; Pereira Cavalheiro, B.; Prada, M. Crossmodal interactions between audition and taste: A systematic review and narrative synthesis. Food Qual. Prefer. 2023, 107, 104856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swahn, J.; Nilsen, A. ‘Sounds salty!’ How a soundtrack affects the liking and perception of the salty balance in bread. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2023, 32, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.N.; Ranasinghe, N.; Tang, A.; Oehlberg, L. Flavor-Videos: Enhancing the Flavor Perception of Food while Eating with Videos. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Interactive Media Experiences, Aveiro, Portugal, 22–24 June 2022; pp. 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Woods, A.T.; Poliakoff, E.; Lloyd, D.M.; Kuenzel, J.; Hodson, R.; Gonda, H.; Batchelor, J.; Dijksterhuis, G.B.; Thomas, A. Effect of background noise on food perception. Food Qual. Prefer. 2011, 22, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rompay, T.J.L.; Groothedde, S. The taste of touch: Enhancing saltiness impressions through surface texture design. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 73, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.P.; Spence, C. Synergistic Combination of Visual Features in Vision–Taste Crossmodal Correspondences. Multisens. Res. 2023, 36, 573–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delwiche, J.F. You eat with your eyes first. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 107, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chonpracha, P.Z. Sensory Analysis for Determining the Influence of Visual Stimuli upon Eating Experiences. Ph.D. Thesis, Louisiana State University and Agricultural & Mechanical College, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Motoki, K.; Spence, C.; Velasco, C. When visual cues influence taste/flavour perception: A systematic review. Food Qual. Prefer. 2023, 111, 104996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, C. Background colour & its impact on food perception & behaviour. Food Qual. Prefer. 2018, 68, 156–166. [Google Scholar]
- Motoki, K.; Velasco, C. Taste-shape correspondences in context. Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 88, 104082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, S.; Hasford, J.; Boman, L. Less light, better bite: How ambient lighting influences taste perceptions. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2022, 65, 102732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa Escobar, F.; Wang, Q.J. Tasty vibes: Uncovering crossmodal correspondences between tactile vibrations and basic tastes. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, B.L.; Berkowitz, K.; Mueller, H.; Simons, C.T. Assessing tactile acuity in oral tissues: Challenges of stimulus development. Food Qual. Prefer. 2022, 101, 104630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.G.; Nachtigal, D. Somatosensory factors in taste perception: Effects of active tasting and solution temperature. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 107, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, R.; Fisher, C.; Gorman, M.; Knowles, S.; LeBlanc, J.; Ritchie, C.; Schindell, K.; Ettinger, L.; McSweeney, M.B. Effect of Piperine on Saltiness Perception. Foods 2023, 12, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braud, A.; Boucher, Y. Intra-oral trigeminal-mediated sensations influencing taste perception: A systematic review. J. Oral Rehabil. 2019, 47, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayeux, I.; Saint-Léger, C.; Starkenmann, C. Trigeminal Sensations to enhance and enrich flavor perception-Sensory Approaches. Clin. Nutr. Open Sci. 2023, 47, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amyoony, J.; Gorman, M.; Dabas, T.; Moss, R.; McSweeney, M.B. The effect of allyl isothiocyanate addition on consumers′ saltiness perception. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 59, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhong, K.; Shi, B.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, L.; Gao, H. Cross-modal effect of capsaicin and pepper oleoresin on the enhancement of saltiness perception in a NaCl model solution. Food Qual. Prefer. 2022, 98, 104542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-B.; Zhao, L.; Gao, H.-Y.; Zhang, L.-L.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zhong, K.; Shi, B.-L.; Liu, L.-Y.; Xie, R. The enhancement of the perception of saltiness by Sichuan pepper oleoresin in a NaCl model solution. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Yang, Q.; Chen, J.; Fisk, I. Impact of capsaicin on aroma release and perception from flavoured solutions. LWT 2021, 138, 110613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Liang, L.; Zhang, Y. Pungency Perception and the Interaction with Basic Taste Sensations: An Overview. Foods 2023, 12, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Q.-B.; Shi, B.-L.; Zhong, K.; Wang, H.-Y.; Xie, R.; Liu, L.-Y. The effect of the pungent sensation elicited by Sichuan pepper oleoresin on the sensory perception of saltiness throughout younger and older age groups. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 86, 103987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Niu, Y.; Sun, B.; Liu, Z.; Mao, X.; Zhang, Y. Screening and Characterization of novel umami peptides in Cheddar cheese using peptidomics and bioinformatics approaches. LWT 2024, 194, 115780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, C.E.F.; Hollowood, T.A.; Wulfert, F.; Hort, J. Colour-coolant-aroma interactions and the impact of congruency and exposure on flavour perception. Food Qual. Prefer. 2007, 18, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Bustos, V.; Madera-Santana, T.J.; Martínez-Núñez, Y.Y.; Robles-Ozuna, L.E.; Montoya-Ballesteros, L.D.C. Techniques of incorporation of salty compounds, food matrix, and sodium behaviour and its effect over saltiness perception: An overview. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 61, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Salt Reduction Strategy Category | Introduction to Salt Reduction Strategy | Advantage | Disadvantage | Improved Method | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salt substitutes | Replacing partial NaCl with metal salts | Suitable for most food, put into food production already | Excessive addition can introduce a bad flavor | Various metal salts are prepared in a certain proportion | [1,15,42,43] |
| Changing the shape and structure of salt | Change the particle size, specific surface area of the salt, etc. | No adverse effects on food quality | High preparation cost and difficult application | Optimize the preparation technique | [19,46,47] |
| Food processing technology innovation | High pressure, ultrasonic technology, etc. | Improves the decline of sensory texture of food caused by salt reduction | The cost of technology development is high | For the study of new salt-reducing foods | [37] |
| Multisensory synergistic effect | Using the interaction of multiple senses | Excellent effect in taste, color, aroma, acceptability | The interaction mechanism needs further investigation | The interaction mechanism is expounded from multiple levels | [36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, R.; Sun, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Progress in Multisensory Synergistic Salt Reduction. Foods 2024, 13, 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111659
Liu S, Gu Y, Zheng R, Sun B, Zhang L, Zhang Y. Progress in Multisensory Synergistic Salt Reduction. Foods. 2024; 13(11):1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111659
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shujing, Yuxiang Gu, Ruiyi Zheng, Baoguo Sun, Lili Zhang, and Yuyu Zhang. 2024. "Progress in Multisensory Synergistic Salt Reduction" Foods 13, no. 11: 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111659
APA StyleLiu, S., Gu, Y., Zheng, R., Sun, B., Zhang, L., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Progress in Multisensory Synergistic Salt Reduction. Foods, 13(11), 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111659





