Study on the Structure, Function, and Interface Characteristics of Soybean Protein Isolate by Industrial Phosphorylation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Phosphorylation Treatment of SPI
2.2.1. Treatment of Proteins with Sodium Hexametaphosphate
2.2.2. Treatment of Proteins with Sodium Tripolyphosphate
2.3. Determination of the Level of Phosphorylation
2.4. Particle Size and Turbidity Circulation
2.5. Zeta Potential and Surface Hydrophobicity (H0)
2.6. Free Sulfhydryl (SH) and Disulfide (SS) Bonds
2.7. Solubility
2.8. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
2.9. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.10. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR)
2.11. Intrinsic Fluorescence
2.12. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
2.13. Characteristics of Emulsion
2.13.1. Preparation of Emulsion
2.13.2. Emulsifying Activity Index (EAI) and Emulsifying Steadiness Index (ESI) of Emulsion
2.13.3. Morphology Examination of Emulsion
2.13.4. Interfacial Protein Intensity (Γ) of Emulsion
2.13.5. Interfacial Tension of Emulsion
2.13.6. Rheological Measurement
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Degree of Phosphorylation
3.2. Particle Size Distribution and Turbidity Analysis
3.3. SDS–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared
3.5. Intrinsic Fluorescence Emission Spectra
3.6. Surface Hydrophobicity and ζ-Potential
3.7. Free Sulfhydryl Groups and Disulfide Bonds
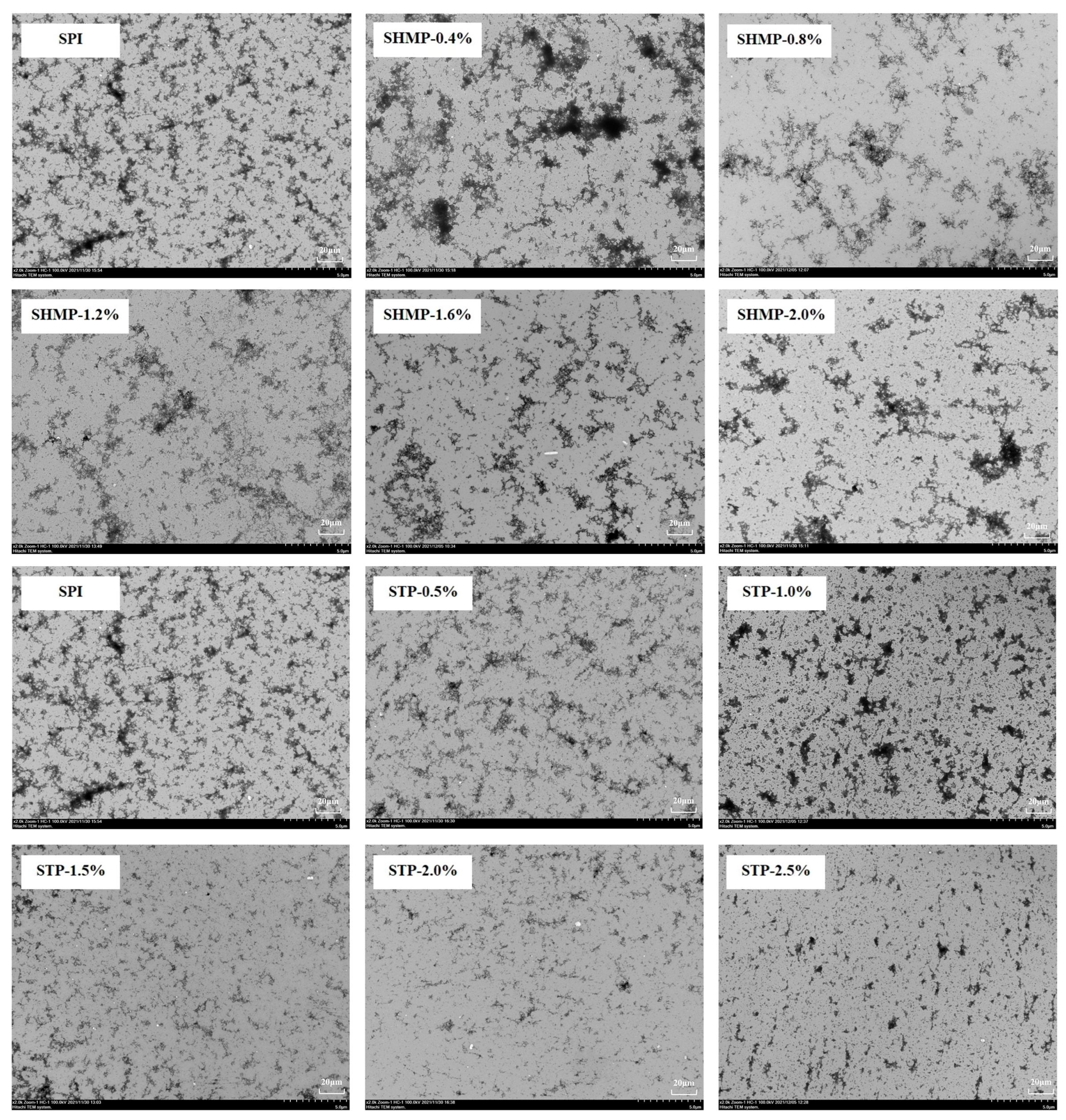
3.8. Transmission Electron Microscope
3.9. Solubility
3.10. Emulsifying Action Index and Emulsion Solidity Index
3.11. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
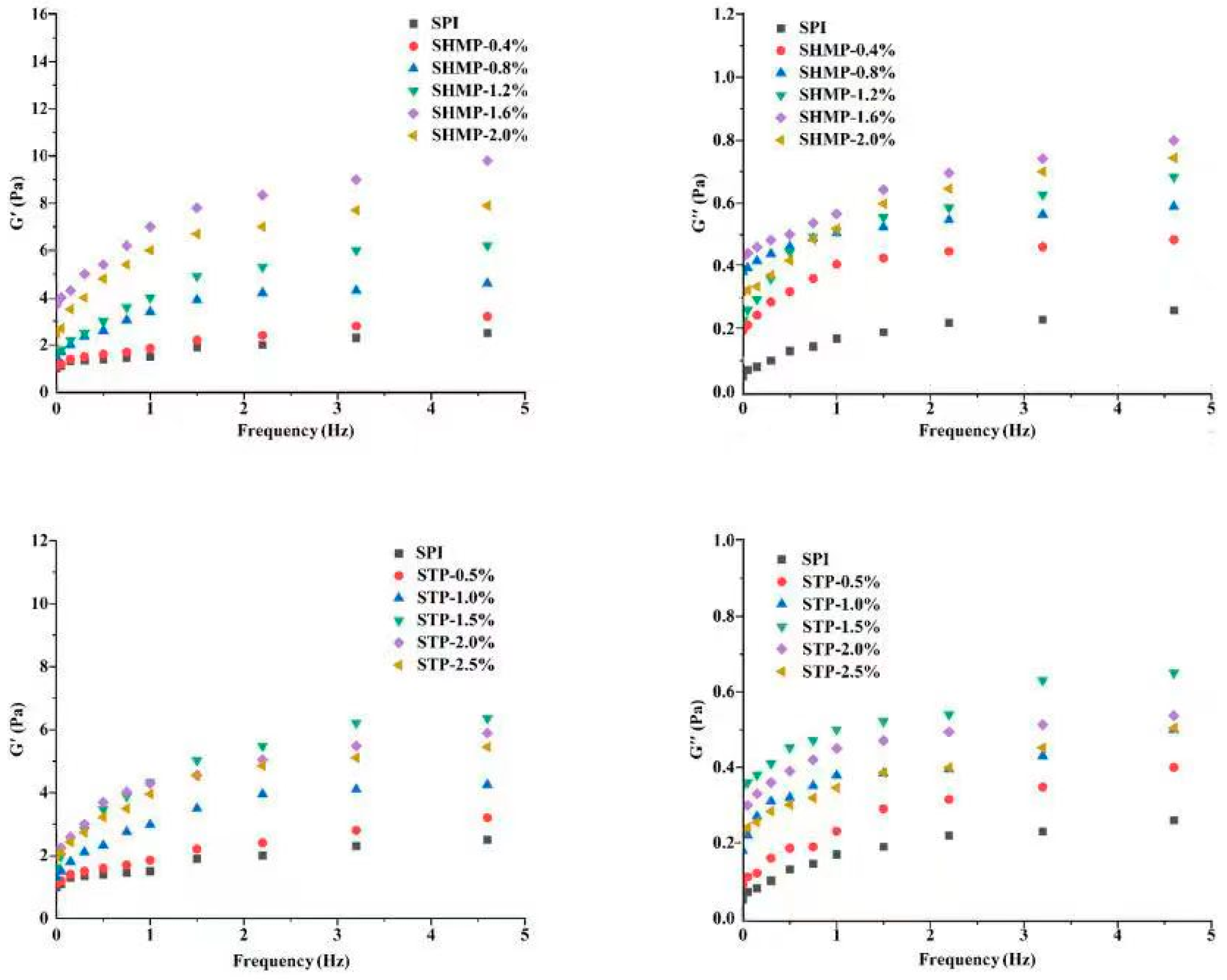
3.12. Emulsion Rheology
3.13. Interfacial Tension
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, M.; Tomar, M.; Punia, S.; Dhakane-Lad, J.; Dhumal, S.; Changan, S.; Senapathy, M.; Berwal, M.K.; Sampathrajan, V.; Sayed, A.A.S.; et al. Plant-based proteins and their multifaceted industrial applications. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Du, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, C.; Pan, D. Recent developments in phosphorylation modification on food proteins: Structure characterization, site identification and function. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tu, Z.; Shangguan, X.; Sha, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Bansal, N. Fish gelatin modifications: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfat, Y.A.; Benjakul, S. Effect of zinc sulphate on gelling properties of phosphorylated protein isolate from yellow stripe trevally. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2848–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.P.; Chen, D.; Peng, J.; Enomoto, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Li, C.; Ou, L.; Aoki, T. Improvement of functional properties of whey soy protein phosphorylated by dry-heating in the presence of pyrophosphate. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giec, A.; Stasińska, B.; Skupin, J. A protein isolate for food by phosphorylation of yeast homogenate. Food Chem. 1989, 31, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, M.L.; Salminen, W.F.; Larson, P.R.; Barter, R.A.; Kranetz, J.L.; Simon, G.S. Toxicological review of inorganic phosphates. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2001, 39, 759–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, F.H.; Gibis, M.; Fritz, M.; Herrmann, K.; Hinrichs, J.; Weiss, J. Optimum hexametaphosphate concentration to inhibit efflorescence formation in dry fermented sausages. Meat Sci. 2018, 139, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheis, G. Phosphorylation of food proteins with phosphorus oxychloride—Improvement of functional and nutritional properties: A review. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Lou, Q.; Wang, C.; Huang, T. Phosphorylation modification on functional and structural properties of fish gelatin: The effects of phosphate contents. Food Chem. 2022, 380, 132209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Cao, J.; He, J.; Dang, Y.; Pan, D.; Zhou, C. Insight into ultrasound-assisted phosphorylation on the structural and emulsifying properties of goose liver protein. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yi, Y.; Solangi, I.; Zan, L.; Zhu, J. Effects of sodium hexametaphosphate, sodium tripolyphosphate and sodium pyrophosphate on the ultrastructure of beef myofibrillar proteins investigated with atomic force microscopy. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Kong, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Hua, Y. Effects of heat treatment on the emulsifying properties of pea proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Ma, M. Enhanced ovalbumin stability at oil-water interface by phosphorylation and identification of phosphorylation site using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 153, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tu, Z.; Shangguan, X.; Wang, H.; Sha, X.; Bansal, N. Rheological behavior, emulsifying properties and structural characterization of phosphorylated fish gelatin. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.; Jiang, A. Phosphorylation modification affects the gelation behavior of alkali-induced duck egg white gels. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 128185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, L.; Wu, C.; Huang, Y.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Effects of combined enzymatic and ultrasonic treatments on the structure and gel properties of soybean protein isolate. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 158, 113123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Zhou, Z. Solubility and emulsifying properties of phosphorylated walnut protein isolate extracted by sodium trimetaphosphate. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 143, 111117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornet, R.; Yang, J.; Venema, P.; van der Linden, E.; Sagis, L.M.C. Optimizing pea protein fractionation to yield protein fractions with a high foaming and emulsifying capacity. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126, 107456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Han, J.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Structure-modification by moderate oxidation in hydroxyl radical-generating systems promote the emulsifying properties of soy protein isolate. Food Struct. 2015, 6, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Wu, C.; Du, M. Enhancing the thermal stability of soy proteins by preheat treatment at lower protein concentration. Food Chem. 2020, 306, 125593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chu, Z.; Miao, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, Y.; Qi, B.; Yan, J. Ultrasound heat treatment effects on structure and acid-induced cold set gel properties of soybean protein isolate. Food Biosci. 2021, 39, 100827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Cui, Y.; Lia, D.; Ding, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, H. The characteristics of soybean protein isolate obtained by synergistic modification of high hydrostatic pressure and phospholipids as a promising replacement of milk in ice cream. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 160, 113223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Arntfield, S.D. Gelation properties of myofibrillar/pea protein mixtures induced by transglutaminase crosslinking. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Ren, Y. Research on the phosphorylation of soy protein isolate with sodium tripoly phosphate. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Hong, X.; Fan, L.; Liu, Y.F.; Li, J.W. Solubility and emulsifying properties of perilla protein isolate: Improvement by phosphorylation in the presence of sodium tripolyphosphate and sodium trimetaphosphate. Food Chem. 2022, 15, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Reséndiz, A.; Rodríguez-Barrientos, S.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J.; Barba-Dávila, B.; Serna-Saldívar, S.O.; Chuck-Hernández, C. Phosphoesterification of soybean and peanut proteins with sodium trimetaphosphate (STMP): Changes in structure to improve functionality for food applications. Food Chem. 2018, 260, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Qiu, L.; Sun, Y.; Xiong, H.; Ogra, Y. Improvement of the solubility and emulsifying properties of rice bran protein by phosphorylation with sodium trimetaphosphate. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Liu, T.Y.; Su, J.C. Improvement of the Functionalities of Soy Protein Isolate through Chemical Phosphorylation. J. Food Sci. 1983, 48, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, M.; Jafarzadeh, S.; Ibarz, A. Modified mung bean protein: Optimization of microwave-assisted phosphorylation and its functional and structural characterizations. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ma, M. Emulsifying properties of ovalbumin: Improvement and mechanism by phosphorylation in the presence of sodium tripolyphosphate. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, L. Impact of phosphates on heat-induced egg white gel properties: Texture, water state, micro-rheology and microstructure. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, C.; Kong, X.Z.; Hua, Y.F. Oxidative modification of soy protein by peroxyl radicals. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.C.; Xu, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Q. Studies on the interaction between chromium(VI) and human serum albumin: Spectroscopic approach. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 86, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yan, X. Optimal controls for impulsive partial stochastic differential equations with weighted pseudo almost periodic coefficients. Int. J. Control. 2021, 94, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, B.; Whent, M.; Yu, L.; Wang, Q. Preparation and characterization of zein/chitosan complex for encapsulation of α-tocopherol, and its in vitro controlled release study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 85, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonaro, M.; Maselli, P.; Nucara, A. Relationship between digestibility and secondary structure of raw and thermally treated legume proteins: A Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopic study. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewruang, P.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T. Characteristics and gelling property of phosphorylated gelatin from the skin of unicorn leatherjacket. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-P.; Hayashi, Y.; Enomoto, H.; Hu, F.; Sawano, Y.; Tanokura, M.; Aoki, T. Phosphorylation of proteins by dry-heating in the presence of pyrophosphate and some characteristics of introduced phosphate groups. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Ogato, S.; Matsudomi, N.; Kunihiko, K. Comparative study of aggregated and disaggregated ovomucin during egg white thinning. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1981, 29, 821–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, F.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, L.; Qi, B.; Li, Y. Effect of pH-shifting treatment on the structural and functional properties of soybean protein isolate and its interactions with (–)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Process Biochem. 2021, 101, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Yang, Q.; Fan, J.L.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H.Q. The effects of phosphorylation modification on the structure, interactions and rheological properties of rice glutelin during heat treatment. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Lv, R.; Balaso Watharkar, R.; Ding, T.; Ye, X.; Liu, D. Effect of pH-shifting treatment on structural and functional properties of whey protein isolate and its interaction with (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Zhao, Q.; Selomulya, C.; Xiong, H. The effect of deamidation on the structural, functional, and rheological properties of glutelin prepared from Akebia trifoliata var. Australis seed. Food Chem. 2015, 178, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Ye, S.; Han, K.; Zhu, G.; Ma, M.; Cai, Z. Consequences of phosphorylation on the structural and foaming properties of ovalbumin under wet-heating conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 91, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhu, H.; Chen, J. Effects of sodium bis(2-ethylhexyl) sulfo succinate (AOT) reverse micelles on physicochemical properties of soy protein. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 94, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhao, W.; Yang, R.; Yan, W.; Sun, Q. Aggregation of egg white proteins with pulsed electric fields and thermal processes: Aggregation of egg white protein under PEF. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3334–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Wu, X.; Hua, Y. Structural modification of soy protein by the lipid peroxidation product acrolein. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, S.; Ye, Y.; Cao, X.; Liu, H.; Wu, Z.; Yue, J.; Sun, H. Enhanced hydrophobicity of soybean protein isolate by low-pH shifting treatment for the sub-micron gel particles preparation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 151, 112475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.D.; Lin, Y.F.; Xu, X.; Meng, L.; Dong, M.S. Effect of non-covalent and covalent complexation of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate with soybean protein isolate on protein structure and in vitro digestion characteristics. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, S. Functional properties and structural characteristics of phosphorylated pea protein isolate. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2002–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.W.; Tan, T.B.; Tan, P.Y.; Abas, F.; Lai, O.M.; Nehdi, I.A.; Tan, C.P. Formation and characterization of thiol-modified fibrillated whey protein isolate solution with enhanced functionalities. J. Food Eng. 2017, 214, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Xu, J.; Gao, H.; Yu, Z.; Liang, J.; Mu, D.; Li, X.; Zhong, X.; Luo, S.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Effects of combined high hydrostatic pressure and pH-shifting pretreatment on the structure and emulsifying properties of soy protein isolates. J. Food Eng. 2021, 306, 110622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Tang, C.-H. Soy glycinin as food-grade Pickering stabilizers: Part. I. Structural characteristics, emulsifying properties and adsorption/arrangement at interface. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Hemar, Y.; Li, N.; Zhou, P. Glycerol induced stability enhancement and conformational changes of β-lactoglobulin. Food Chem. 2020, 308, 125596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Castillo, E.; Aguilar, J.M.; Bengoechea, C.; López-Castejón, M.L.; Guerrero, A. Rheology and Water Absorption Properties of Alginate–Soy Protein Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-R.; Zhang, B.; Fan, J.-L.; Yang, Q.; Chen, H.-Q. Effects of sodium tripolyphosphate modification on the structural, functional, and rheological properties of rice glutelin. Food Chem. 2019, 281, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Chen, G.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Q.; Mei, X.; Kan, J. Heat-induced inulin-gluten gel: Insights into the influences of inulin molecular weight on the rheological and structural properties of gluten gel to molecular and physicochemical characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; You, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, R.; Xiong, S. Effect of CaCl2 on denaturation and aggregation of silver carp myosin during setting. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Ma, M.; Jin, G.; Xu, Q. Effects of site-specific phosphorylation on the mechanical properties of ovalbumin-based hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Yu, J.; Lu, L.; Fu, X.; Cai, Z. Interfacial and enhanced emulsifying behavior of phosphorylated ovalbumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Chi, Y. Improvement of functional properties of ovalbumin phosphorylated by dry-heating in the presence of pyrophosphate. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 235, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Xie, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Qi, B. Homogenization pressure and soybean protein concentration impact the stability of perilla oil nanoemulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
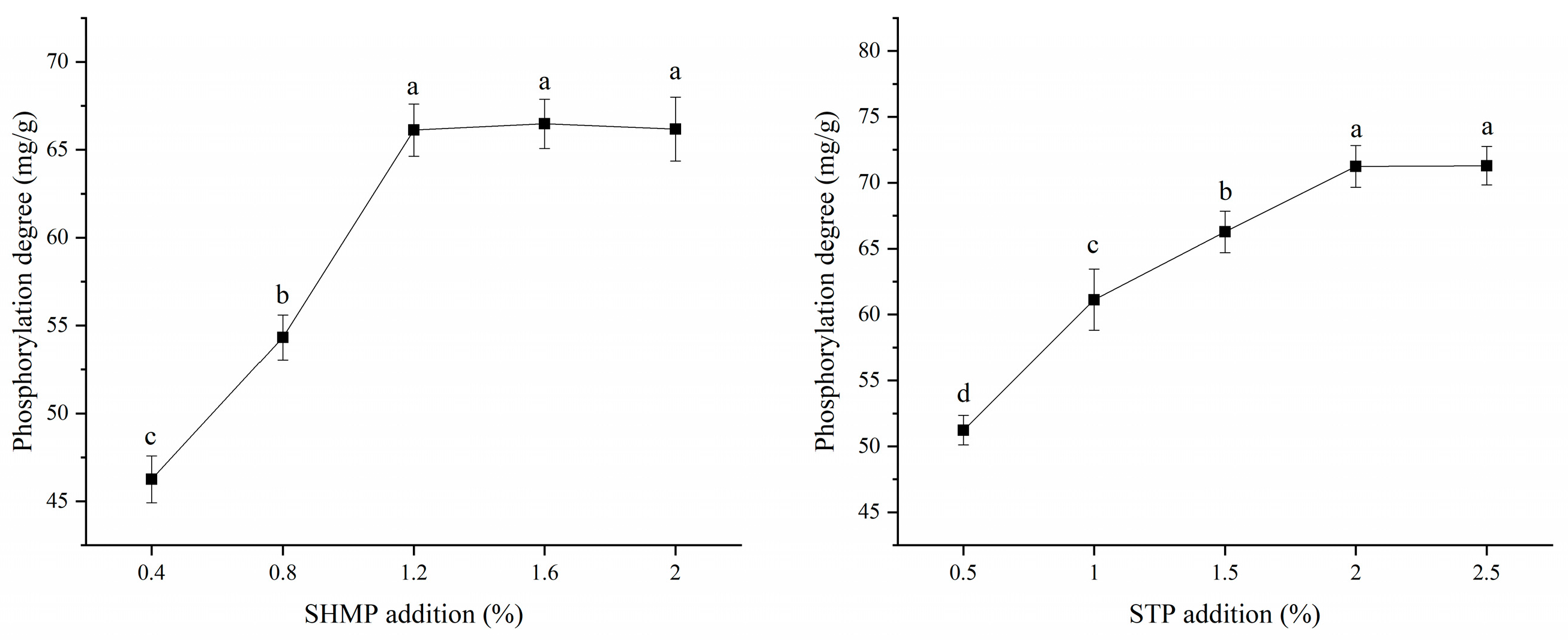
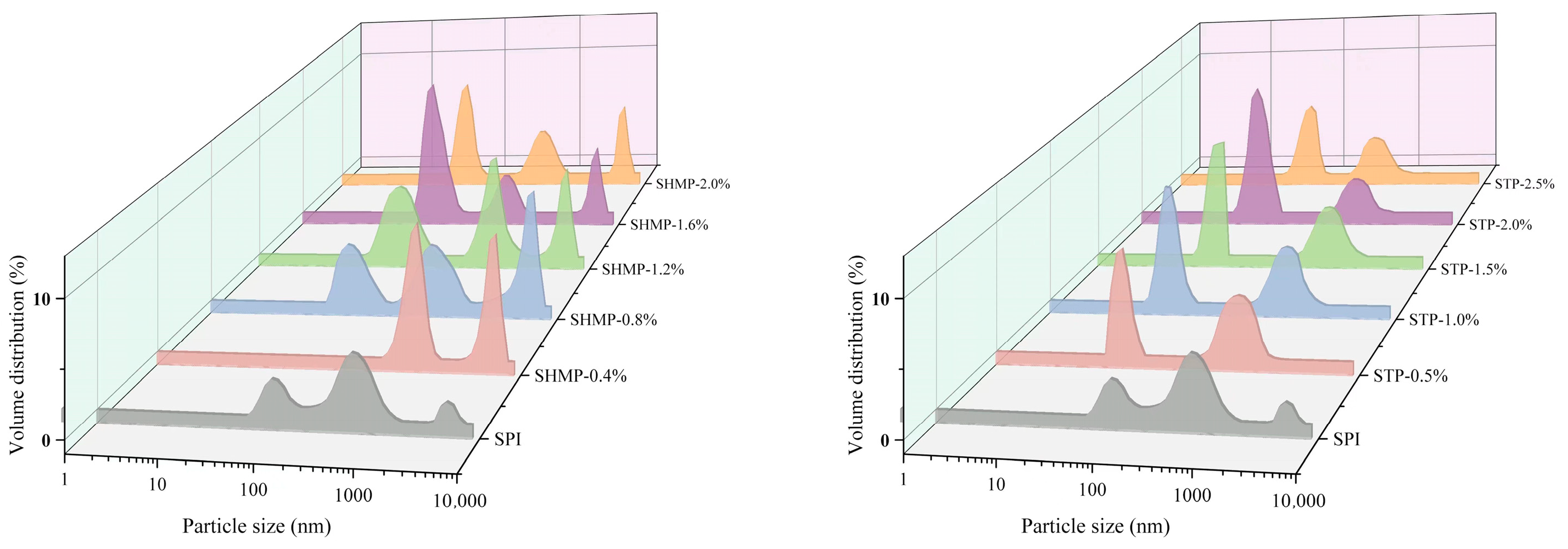
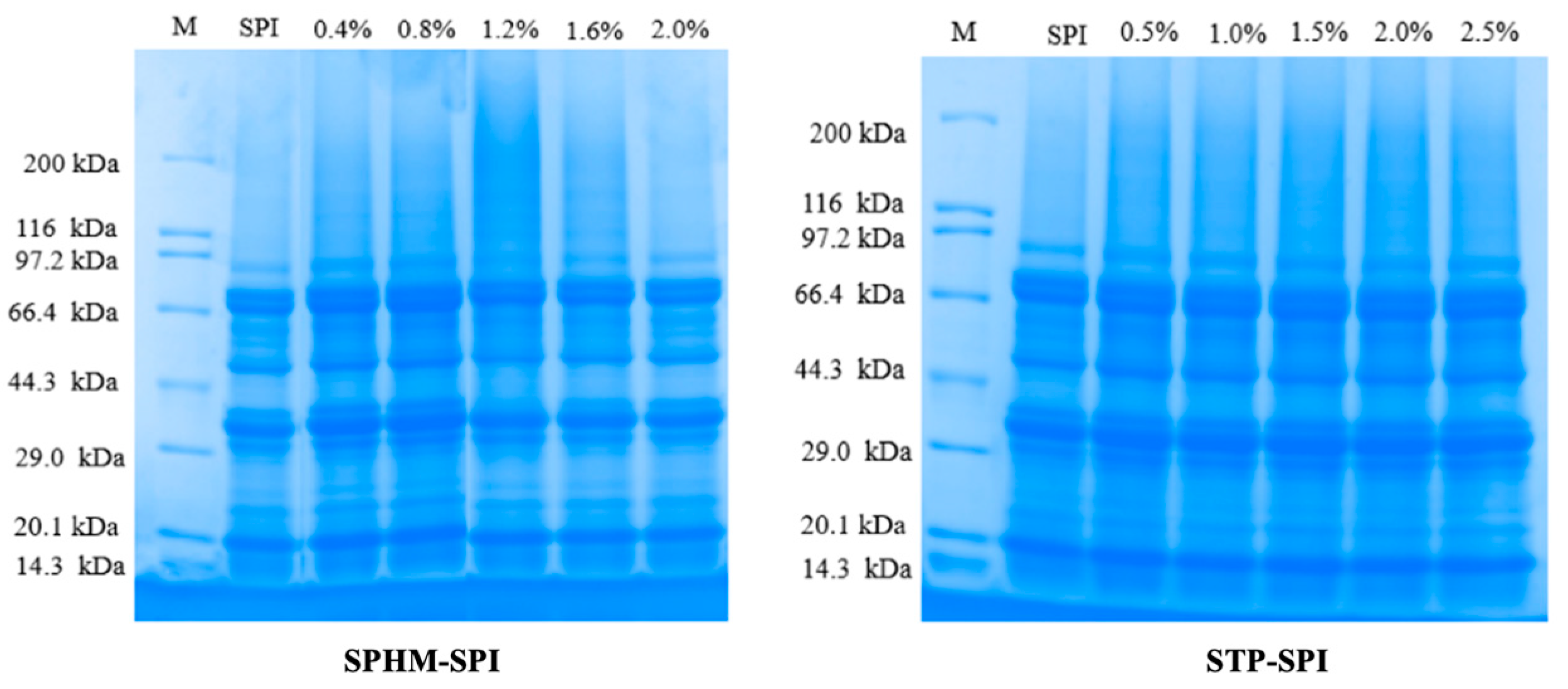

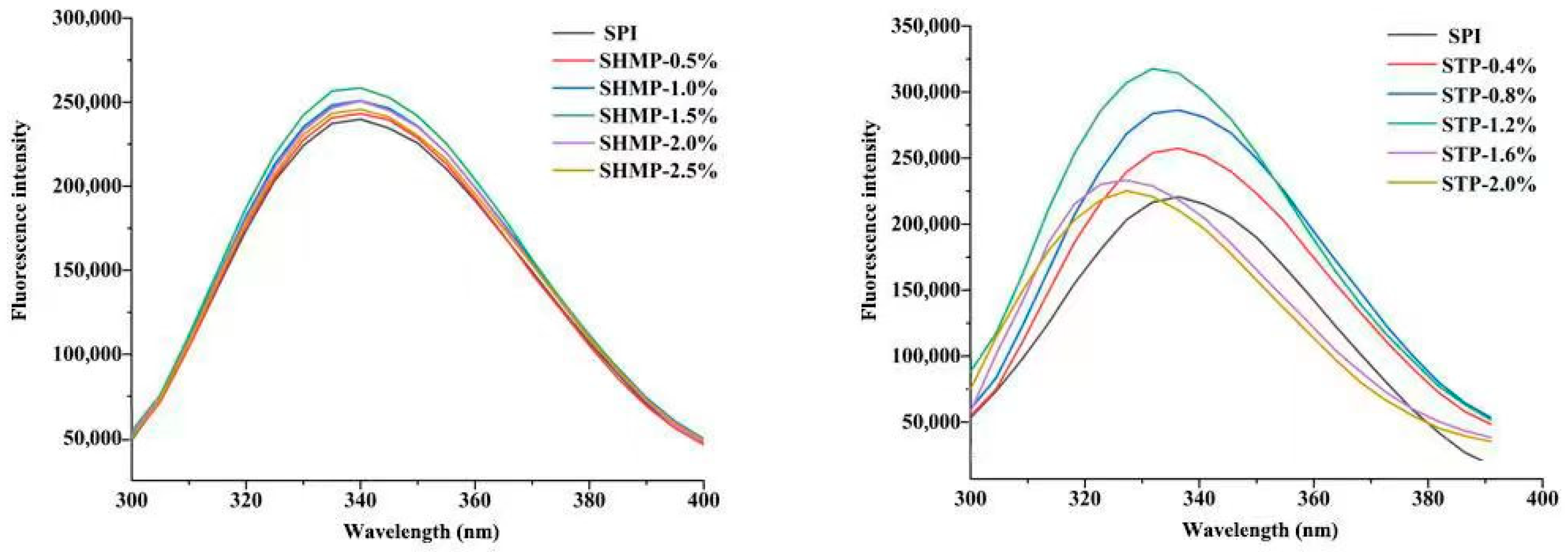

| Sample | Concentration | Average Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Turbidity | Surface Hydrophobicity | ζ-Potential (mV) | Free Sulfhydryl Groups (μmol/g) | Disulfide Bonds (μmol/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI | 0 | 408.82 ± 2.18 fA | 0.45 ± 0.02 aAB | 0.195 ± 0.007 dA | 310.80 ± 6.56 eF | −20.80 ± 0.23 eF | 1.2133 ± 0.0125 eD | 13.5053 ± 0.1990 aA |
| SHMP | 0.4% | 1341.01 ± 7.35 a | 0.38 ± 0.05 b | 0.252 ± 0.002 a | 484.98 ± 7.37 d | −23.34 ± 0.21 d | 2.1268 ± 0.1760 c | 12.0783 ± 0.4114 b |
| 0.8% | 1140.12 ± 5.56 b | 0.31 ± 0.04 c | 0.241 ± 0.004 b | 945.99 ± 8.00 c | −25.86 ± 0.10 c | 2.9100 ± 0.2110 d | 10.3210 ± 0.4780 c | |
| 1.2% | 567.91 ± 3.56 e | 0.18 ± 0.01 e | 0.229 ± 0.005 c | 1183.00 ± 8.82 a | −29.63 ± 0.18 a | 14.7899 ± 0.1210 a | 8.6773 ± 0.2212 e | |
| 1.6% | 664.47 ± 4.19 d | 0.26 ± 0.02 d | 0.236 ± 0.001 b | 984.00 ± 7.46 b | −29.45 ± 0.12 a | 13.2934 ± 0.2930 b | 8.6791 ± 0.2103 e | |
| 2.0% | 759.64 ± 10.21 c | 0.24 ± 0.03 d | 0.237 ± 0.002 b | 950.00 ± 7.90 c | −28.78 ± 0.13 b | 6.0904 ± 0.3010 c | 9.1565 ± 0.3980 d | |
| STP | 0.5% | 299.91 ± 2.12 B | 0.36 ± 0.02 C | 0.089 ± 0.005 B | 1109.10 ± 18.45 E | −25.31 ± 0.23 E | 1.3533 ± 0.0124 C | 12.1268 ± 0.2212 B |
| 1.0% | 297.73 ± 4.21 B | 0.41 ± 0.02 B | 0.082 ± 0.001 C | 1274.30 ± 16.99 C | −29.82 ± 0.10 D | 1.4068 ± 0.0134 B | 10.2836 ± 0.1836 C | |
| 1.5% | 290.37 ± 3.33 C | 0.26 ± 0.02 D | 0.080 ± 0.002 C | 1479.60 ± 18.31 B | −31.45 ± 0.13 C | 1.5059 ± 0.0132 A | 9.9836 ± 0.1735 D | |
| 2.0% | 266.73 ± 5.63 E | 0.11 ± 0.02 E | 0.060 ± 0.003 D | 1864.50 ± 27.17 A | −35.01 ± 0.12 A | 1.4259 ± 0.0101 B | 7.5765 ± 0.1134 F | |
| 2.5% | 281.53 ± 4.87 D | 0.46 ± 0.02 A | 0.068 ± 0.006 D | 1210.50 ± 22.80 D | −33.68 ± 0.25 B | 1.4118 ± 0.0099 B | 8.3846 ± 0.1239 E |
| Secondary Structure Content (%) | β-Sheet/% | α-Helix/% | β-Turn/% | Random Coil/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Concentration | ||||
| SPI | 0 | 26.20 ± 0.35 eC | 36.18 ± 0.05 aA | 15.12 ± 0.03 eA | 22.50 ± 0.23 eF |
| SHMP | 0.4% | 30.39 ± 0.17 d | 25.11 ± 0.01 b | 22.50 ± 0.13 a | 22.00 ± 0.27 e |
| 0.8% | 31.43 ± 0.12 b | 23.74 ± 0.31 d | 21.33 ± 0.21 c | 23.50 ± 0.12 c | |
| 1.2% | 37.34 ± 0.27 a | 20.05 ± 0.14 e | 3.81 ± 0.32 f | 38.80 ± 0.22 a | |
| 1.6% | 31.17 ± 0.98 c | 23.64 ± 0.03 d | 22.19 ± 0.09 b | 23.00 ± 0.23 d | |
| 2.0% | 31.05 ± 0.54 c | 24.55 ± 0.06 c | 20.31 ± 0.16 d | 24.09 ± 0.03 b | |
| STP | 0.5% | 26.52 ± 0.84 C | 27.24 ± 0.12 C | 12.78 ± 0.24 C | 33.46 ± 0.01 D |
| 1.0% | 27.05 ± 0.07 B | 27.14 ± 0.04 CD | 11.66 ± 0.51 E | 33.75 ± 0.07 C | |
| 1.5% | 27.24 ± 0.15 B | 27.04 ± 0.08 D | 12.15 ± 0.20 D | 34.27 ± 0.12 B | |
| 2.0% | 28.39 ± 0.37 A | 25.83 ± 0.08 E | 10.98 ± 0.35 F | 34.80 ± 0.11 A | |
| 2.5% | 25.55 ± 0.28 D | 27.67 ± 0.02 B | 13.22 ± 0.02 B | 33.12 ± 0.04 E | |
| Sample | Concentration | Solubility (%) | (EAI) (m2/g) | (ESI) (min) | Interfacial Tension |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI | 0 | 85.86 ± 0.49 dE | 25.53 ± 0.123 eE | 18.51 ± 0.82 eF | 18.470 ± 0.124 aA |
| SHMP | 0.4% | 88.44 ± 0.28 c | 30.00 ± 0.201 d | 35.91 ± 1.90 d | 16.406 ± 0.163 b |
| 0.8% | 90.26 ± 0.26 b | 33.00 ± 0.167 c | 60.89 ± 1.66 c | 14.726 ± 0.142 cd | |
| 1.2% | 94.64 ± 0.25 a | 35.82 ± 0.158 a | 87.56 ± 1.00 a | 13.340 ± 0.212 e | |
| 1.6% | 90.35 ± 0.27 b | 35.15 ± 0.103 b | 72.80 ± 0.90 b | 14.570 ± 0.225 d | |
| 2.0% | 86.72 ± 0.19 d | 34.65 ± 0.191 b | 68.31 ± 0.99 b | 15.013 ± 0.109 c | |
| STP | 0.5% | 89.19 ± 0.26 D | 27.00 ± 0.15 D | 46.63 ± 1.11 E | 15.175 ± 0.205 B |
| 1.0% | 90.68 ± 0.21 C | 30.00 ± 0.35 C | 70.00 ± 1.38 D | 14.246 ± 0.109 C | |
| 1.5% | 93.55 ± 0.20 B | 35.00 ± 0.29 B | 78.35 ± 1.00 C | 12.365 ± 0.102 D | |
| 2.0% | 97.09 ± 0.21 A | 39.50 ± 0.38 A | 95.00 ± 1.21 A | 11.555 ± 0.163 E | |
| 2.5% | 94.53 ± 0.24 B | 38.47 ± 0.44 A | 90.00 ± 1.09 B | 12.887 ± 0.109 D |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Shen, L.; Gong, Q.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, L. Study on the Structure, Function, and Interface Characteristics of Soybean Protein Isolate by Industrial Phosphorylation. Foods 2023, 12, 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051108
Guo Y, Liu C, Ma Y, Shen L, Gong Q, Hu Z, Wang Z, Liu X, Guo Z, Zhou L. Study on the Structure, Function, and Interface Characteristics of Soybean Protein Isolate by Industrial Phosphorylation. Foods. 2023; 12(5):1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051108
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yanan, Caihua Liu, Yitong Ma, Lulu Shen, Qi Gong, Zhaodong Hu, Zhongjiang Wang, Xin Liu, Zengwang Guo, and Linyi Zhou. 2023. "Study on the Structure, Function, and Interface Characteristics of Soybean Protein Isolate by Industrial Phosphorylation" Foods 12, no. 5: 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051108
APA StyleGuo, Y., Liu, C., Ma, Y., Shen, L., Gong, Q., Hu, Z., Wang, Z., Liu, X., Guo, Z., & Zhou, L. (2023). Study on the Structure, Function, and Interface Characteristics of Soybean Protein Isolate by Industrial Phosphorylation. Foods, 12(5), 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051108





