An Ultrasensitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay Based on Metal-Organic Framework-Decorated Polydopamine for Multiple Sulfonylureas Adulteration in Functional Foods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
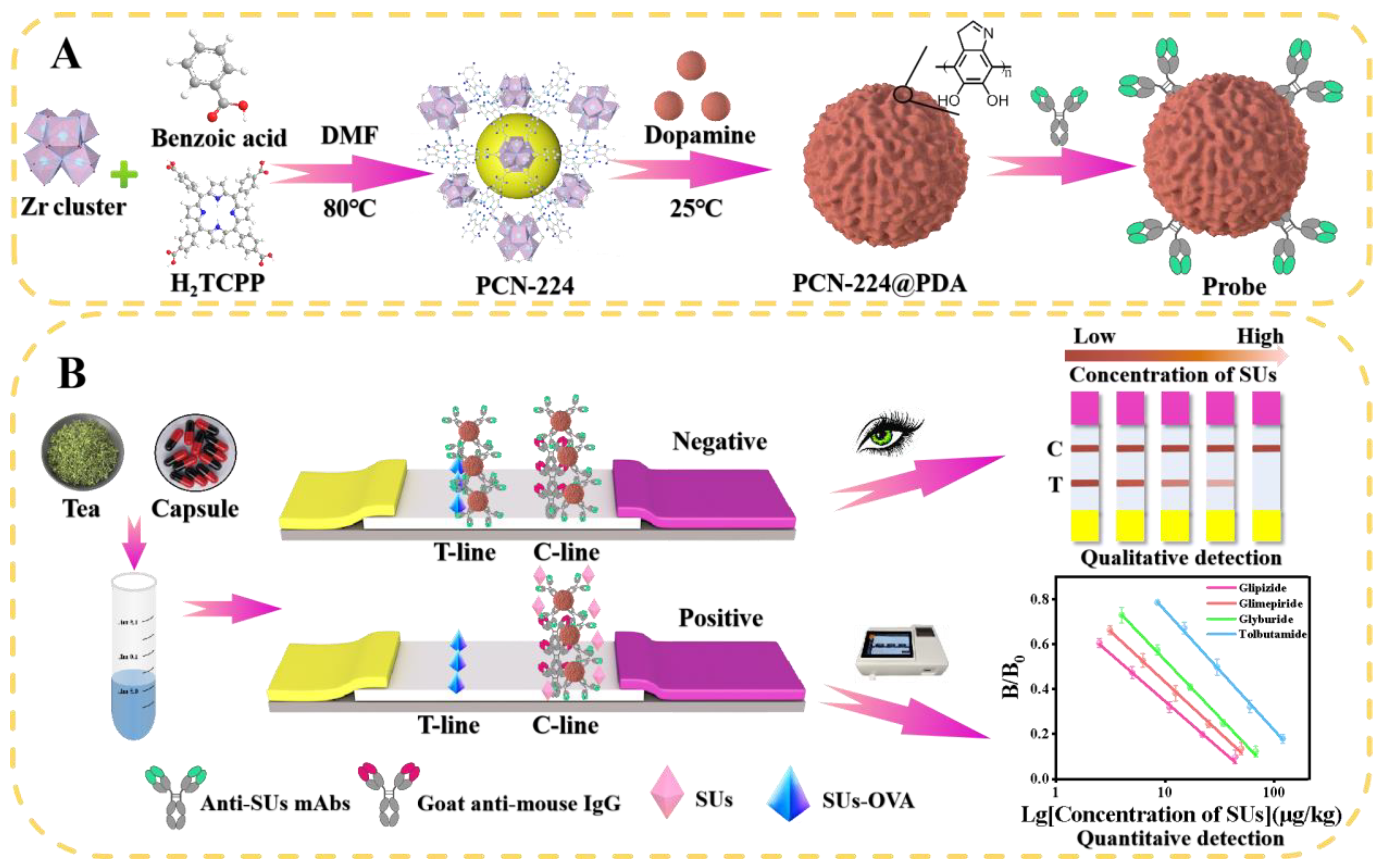
2.2. Preparation of PCN-224@PDA
2.3. Construction of PCN-224@PDA-Abs Probes
2.4. Preparation of the PCN-224@PDA-LFIA
2.5. Sample Preparation and Detection Process
2.6. Performance Evaluation of PCN-224@PDA-LFIA
2.6.1. Sensitivity
2.6.2. Selectivity
2.6.3. Accuracy and Precision
2.6.4. Application of the PCN-224@PDA-LFIA
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of PCN-224 and PCN-224@PDA
3.2. Synthesis Optimization of PCN-224@PDA
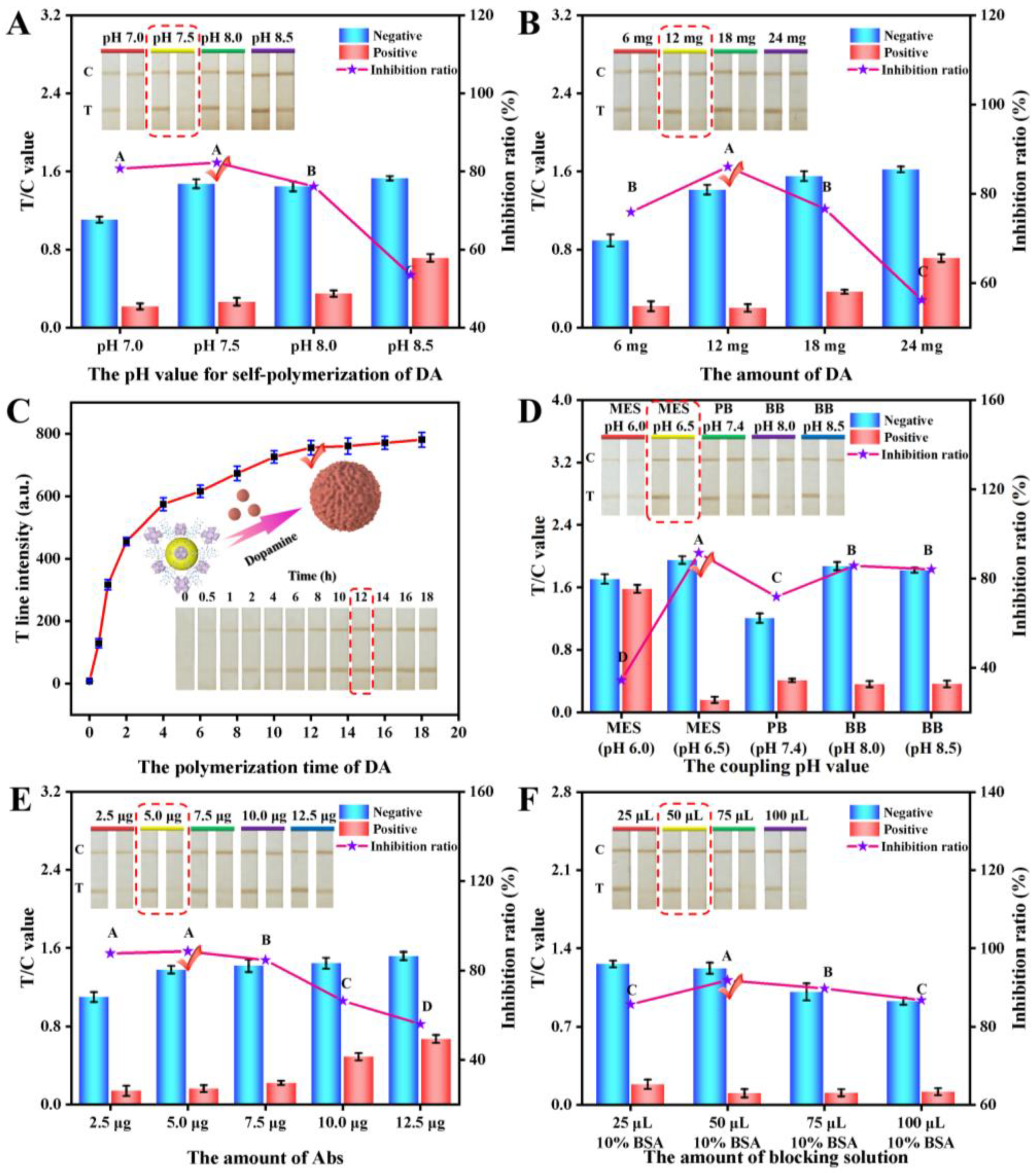
3.2.1. Optimization of the pH Value for the Self-Polymerization of DA
3.2.2. Optimization of the Amount of DA
3.2.3. Optimization of the Polymerization Time of DA
3.3. Optimization of Key Technical Parameters of PCN-224@PDA-LFIA
3.3.1. Optimization of the Coupling pH Value
3.3.2. Optimization of the Amount of Abs
3.3.3. Optimization of the Amount of Blocking Solution
3.3.4. Optimization of the Sample Dilution Ratio
3.4. Performance Evaluation of PCN-224@PDA-LFIA
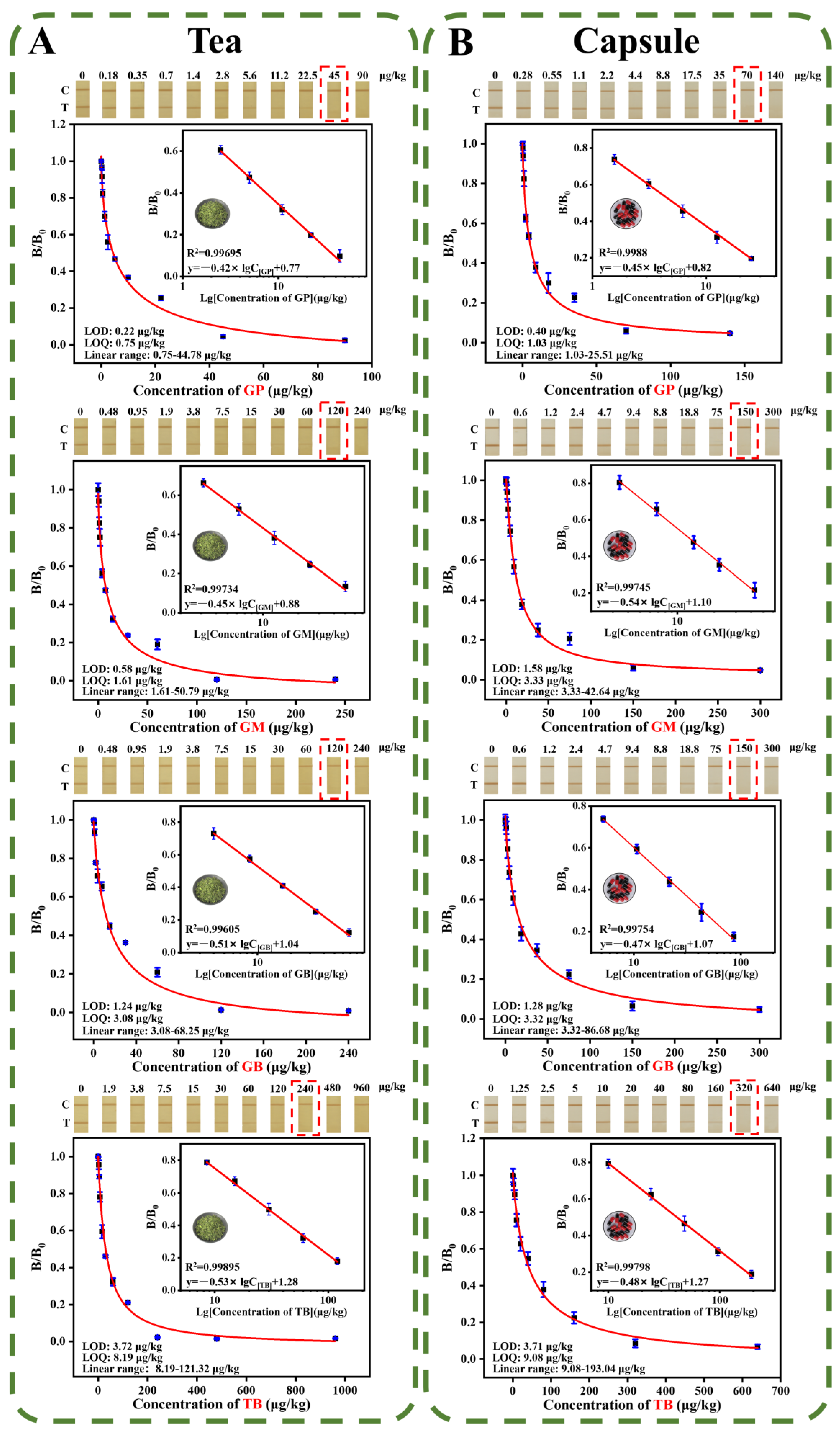
3.4.1. Sensitivity
3.4.2. Selectivity
3.4.3. Accuracy and Precision
3.4.4. Application of the PCN-224@PDA-LFIA
3.5. Comparison of the Methods for the Detection of SUs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ley, S.; Rajpathak, S.; Hu, F. Sulfonylurea use and incident cardiovascular disease among patients with type 2 diabetes: Prospective cohort study among women. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 3106–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcin, L.; Mericq, V.; Fauret-Amsellem, A.; Cave, H.; Polak, M.; Beltrand, J. Neonatal diabetes due to potassium channel mutation: Response to sulfonylurea according to the genotype. Pediatr. Diabetes 2020, 21, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Jiang, Q.; Li, R.; Xu, Q.; Li, H. Nanofibers mat as sampling module of direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry for sensitive and high-throughput screening of illegally adulterated sulfonylureas in antidiabetic health-care teas. Talanta 2019, 204, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Xu, S.; Xu, W.; He, X.; Kuang, Y.; Hu, X. Screening and quantification of fourteen synthetic antidiabetic adulterants in herbal pharmaceuticals and health foods by HPLC and confirmation by LC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. Food Addit. Contam. A 2020, 37, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Yoo, G.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Park, S.; Baek, S.; Kang, H. Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous analysis of 26 anti-diabetic drugs in adulterated dietary supplements and its application to a forensic sample. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 32, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hua, Q.; Wang, J.; Liang, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Shen, X.; Lei, H.; Li, X. A smartphone-based dual detection mode device integrated with two lateral flow immunoassays for multiplex mycotoxins in cereals. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 158, 112178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Lei, Y.; Koidis, A.; Li, X.; Shen, X.; Xu, Z.; Lei, H. Broad-specific immunochromatography for simultaneous detection of various sulfonylureas in adulterated multi-herbal tea. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xie, H.; Fu, T.; Li, Y.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Lei, Y.; Yao, X.; Koidis, A.; Liu, Y.; et al. Complementary strategy enhancing broad-specificity for multiplexed immunoassay of adulterant sulfonylureas in functional food. Biosensors 2022, 12, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shen, X.; Lei, H. Rapid detection of adulteration of dehydroepiandrosterone in slimming products by competitive indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and lateral flow immunochromatography. Food Agric. Immunol. 2019, 30, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardo, F.; Cavalera, P.; Baggiani, C.; Giovannoli, C.; Anfossi, L. Direct vs mediated coupling of antibodies to gold nanoparticles: The case of salivary cortisol detection by lateral flow immunoassay. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 32758–32768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, P.; Liu, Z.; He, Z.; Pang, Y.; Lei, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, X. Rainbow latex microspheres lateral flow immunoassay with smartphone-based device for simultaneous detection of three mycotoxins in cereals. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1221, 340138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Hua, Q.; Wang, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, X.; Lei, H.; Li, X. Prussian blue immunochromatography with portable smartphone-based detection device for zearalenone in cereals. Food Chem. 2020, 369, 131008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, F.; Lo, W.; Hsu, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Shieh, F.; Morabito, J.; Chou, L.; Wu, K.; Tsung, C. Shielding against unfolding by embedding enzymes in metal–organic frameworks via a de novo approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6530–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Long, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; Cheng, Y. A nanozyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) for sensitive detection of aflatoxin B1. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Bu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Bai, F.; Wang, L. Polydopamine coated zirconium metal-organic frameworks-based immunochromatographic assay for highly sensitive detection of deoxynivalenol. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1131, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhand, S.; Razmjou, A.; Azadi, S.; Bazaz, S.; Shrestha, J.; Jahromi, M.; Warkiani, M. Metal–organic framework-enhanced ELISA platform for ultrasensitive detection of PD-L1. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 4148–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Dou, L.; Yao, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Sun, J.; Xu, B.; Zhang, D.; et al. Polydopamine nanospheres as high-affinity signal tag towards lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive furazolidone detection. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; He, Z.; Shen, X.; Lei, H.; Li, X. An enhanced immunochromatography assay based on colloidal gold-decorated polydopamine for rapid and sensitive determination of gentamicin in animal-derived food. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Dong, Y.; Hong, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y. Polydopamine nanoparticle-mediated, click chemistry triggered, microparticle-counting immunosensor for the sensitive detection of ochratoxin A. J. Hazard Mater. 2022, 428, 128206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, Z.; Wu, J.; Lin, H.; Deng, Y.; Shen, X.; Lei, H.; Li, X. Facile immunochromatographic assay based on metal–organic framework-decorated polydopamine for the determination of hydrochlorothiazide adulteration in functional foods. Food Chem. 2023, 406, 135100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Bu, T.; Zhang, M.; Sun, X.; Jia, P.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Bai, F.; Zhao, S.; Wang, L. Metal-polydopamine framework based lateral flow assay for high sensitive detection of tetracycline in food samples. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Deng, S.; Fang, B.; Zhang, G.; Lai, X.; Su, L.; He, W.; Lai, W. Lateral flow immunoassay based on polydopamine-coated metal-organic framework for the visual detection of enrofloxacin in milk. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 7315–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Liu, Z.; Xie, H.; Fang, Y.; Quan, Q.; Shen, X.; Lei, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, X. Ultrasensitive magnetic assisted lateral flow immunoassay based on chiral monoclonal antibody against R-(−)-salbutamol of broad-specificity for 38 β-agonists detection in swine urine and pork. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 70, 4112–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Lei, H. An ultrasensitive microfluidic chip-based immunoassay for multiplex determination of 11 PDE-5 inhibitors in adulterated health foods. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2022, 358, 131450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Cai, G.; Yu, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Tang, D. Metal-polydopamine framework: An innovative signal-generation tag for colorimetric immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11099–11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Fan, H.; Zha, D.; Wang, L.; Jin, Z. Characterizations of the formation of polydopamine-coated halloysite nanotubes in various pH environments. Langmuir 2016, 32, 10377–10386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xiong, Q.; Ma, J.; Ren, J.; Messersmith, P.; Chen, P.; Duan, H. Polydopamine-enabled approach toward tailored plasmonic nanogapped nanoparticles: From nanogap engineering to multifunctionality. ACS Nano. 2016, 10, 11066–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Bu, T.; Li, R.; Zhao, S.; He, K.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Rose petals-like Bi semimetal embedded on the zeolitic imidazolate frameworks based-immunochromatographic strip to sensitively detect acetamiprid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Hua, Q.; Liang, J.; Shen, X.; Xu, Z.; Lei, H.; Sun, Y. Latex microsphere immunochromatography for quantitative detection of dexamethasone in milk and pork. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, S.; Pang, Y.; Shen, X.; Lei, H.; Li, X. Immunochromatographic assays based on three kinds of nanoparticles for the rapid and highly sensitive detection of tylosin and tilmicosin in eggs. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, X.; Lei, H.; Li, X. Magnetic immunochromatographic assay with smartphone-based readout device for the on-site detection of zearalenone in cereals. Food Control 2022, 134, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Luo, P.; Liang, J.; Shen, X.; Lei, H.; Li, X. A highly sensitive and quantitative time resolved fluorescent microspheres lateral flow immunoassay for streptomycin and dihydrostreptomycin in milk, honey, muscle, liver, and kidney. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1192, 339360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pi, J.; Jin, P.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, Z.; Mai, X.; Fan, H.; Zhang, W. Multi-dimensional fingerprint profiling analysis for screening and quantification of illegal adulterated antidiabetics in hypoglycemic health products by aqueous two-phase extraction and multi-wavelength detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1622, 461149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Li, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y. Rapid screening and quantitative detection of 11 illegally added antidiabetics in health care products by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole/electrostatic field orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2015, 33, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Li, N.; Qin, F.; Li, F.; Xiong, Z. Simultaneous determination of 14 illegal adulterants in Chinese proprietary medicines using reversed-phase ion-pair LC. Chromatographia 2010, 72, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, N.; Hur, J.; Kim, B.; Kim, K.; Moon, B.; Oh, H.; Hong, J. Rapid screening of sulfonamides in dietary supplements based on extracted common ion chromatogram and neutral loss scan by LC-Q/TOF-mass spectrometry. J. Food Drug. Anal. 2019, 27, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Analytes | Tea | Capsule | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spiked Level (μg/kg) | Detected Level (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) | CV (%) | Spiked Level (μg/kg) | Detected Level (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) | CV (%) | |
| GP | 1 | 1.14 ± 0.13 | 114.0 | 11.4 | 1 | 1.06 ± 0.14 | 106.0 | 13.2 |
| 2 | 2.02 ± 0.29 | 101.0 | 14.4 | 2 | 2.38 ± 0.19 | 119.0 | 8.0 | |
| 8 | 8.02 ± 1.11 | 100.3 | 13.8 | 10 | 11.63 ± 1.22 | 116.3 | 10.5 | |
| GM | 2 | 1.83 ± 0.23 | 91.5 | 12.6 | 4 | 4.41 ± 0.43 | 110.3 | 9.8 |
| 4 | 3.54 ± 0.42 | 88.5 | 11.9 | 8 | 8.46 ± 0.79 | 105.8 | 9.3 | |
| 20 | 17.06 ± 1.69 | 85.3 | 9.9 | 35 | 41.63 ± 4.91 | 119.0 | 11.8 | |
| GB | 4 | 4.35 ± 0.48 | 108.8 | 11.0 | 4 | 3.52 ± 0.40 | 88.0 | 11.4 |
| 8 | 9.06 ± 0.77 | 113.3 | 8.5 | 8 | 7.53 ± 0.80 | 94.1 | 10.6 | |
| 30 | 34.72 ± 2.64 | 115.7 | 7.6 | 35 | 39.79 ± 3.42 | 113.7 | 8.6 | |
| TB | 8 | 8.88 ± 0.85 | 111.0 | 9.6 | 10 | 9.69 ± 0.78 | 96.9 | 8.0 |
| 16 | 18.05 ± 2.24 | 112.8 | 12.4 | 20 | 16.76 ± 1.28 | 83.8 | 7.6 | |
| 80 | 71.99 ± 6.56 | 90.0 | 9.1 | 100 | 108.21 ± 12.01 | 108.2 | 11.1 | |
| Methods | Sample | Sample Pretreatment | Detection Time | Detection Limit (μg/kg) | Quantification Limit (μg/kg) | Cut-Off Value (μg/kg) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC a | Herbal, Health foods | Ultrasound-assisted extraction, centrifugation, filtration (0.22 μm filter), dilution | 43 min | 216 | 432 | - | [4] |
| HPLC | Milk powder and capsules | Ultrasound-assisted biphasic extraction, Nitrogen blowing concentration, redissolution | 65 min | 2450 | 8170 | - | [33] |
| UPLC b | Tablets, capsules, and particles | Ultrasound-assisted extraction, dilution, filtration (0.45 μm filter) | 25 min | 2.7 | - | - | [34] |
| Ion-Pair LC c | Tablets, pills, granules, and capsules | Ultrasound-assisted extraction, dilution | 47 min | 330 | 1010 | - | [35] |
| LC-MS/MS d | tablets, pills, and capsules | Ultrasound-assisted extraction, dilution, filtration (0.22 μm filter) | 35 min | 0.5 | 15 | - | [5] |
| LC-Q/TOF e | tablets, pills, and capsules | Shake extraction, centrifugation, purification, centrifugation, Nitrogen blowing concentration, redissolution | 47 min | 1.05 | - | - | [36] |
| ELISA f | pills and capsules | Extraction, centrifugation, filtration (0.22 μm filter), dilution | 90 min | 0.3 | 0.7 | - | [8] |
| CG-LFIA g | teas | Extraction, centrifugation, filtration (0.22 μm filter), dilution | 18 min | 32 | - | 96 | [7] |
| PCN-224@ PDA-LFIA | Functional teas and capsules | Extraction, centrifugation, filtration (0.22 μm filter), dilution | 10 min | Tea: 0.22(GP); Capsule: 0.4 (GP) | Tea: 0.75(GP); Capsule: 1.03(GP) | Tea: 45(GP); Capsule: 70 (GP) | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xie, H.; Luo, P.; Li, X. An Ultrasensitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay Based on Metal-Organic Framework-Decorated Polydopamine for Multiple Sulfonylureas Adulteration in Functional Foods. Foods 2023, 12, 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030539
He Z, Liu Z, Xie H, Luo P, Li X. An Ultrasensitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay Based on Metal-Organic Framework-Decorated Polydopamine for Multiple Sulfonylureas Adulteration in Functional Foods. Foods. 2023; 12(3):539. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030539
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zixian, Zhiwei Liu, Haihuan Xie, Pengjie Luo, and Xiangmei Li. 2023. "An Ultrasensitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay Based on Metal-Organic Framework-Decorated Polydopamine for Multiple Sulfonylureas Adulteration in Functional Foods" Foods 12, no. 3: 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030539
APA StyleHe, Z., Liu, Z., Xie, H., Luo, P., & Li, X. (2023). An Ultrasensitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay Based on Metal-Organic Framework-Decorated Polydopamine for Multiple Sulfonylureas Adulteration in Functional Foods. Foods, 12(3), 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030539




