What Is Authentic Maple Water? A Twelve-Month Shelf-Life Study of the Chemical Composition of Maple Water and Its Biological Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Maple Water
2.3. Physiochemical Properties of Maple Water
2.4. Sugar Contents of Maple Water by HPLC-Refractive Index (RI)
2.5. Measurement of the Amino Acid Content of Maple Water by HPLC-Fluorescence (FL)
2.6. Organic Acid Content of Sap Samples by HPLC-DAD
2.7. Mineral Content of Maple Water by ICP-MS
2.8. Preparation of Maple Extracts
2.9. Total Polyphenol Content by Folin-Ciocalteau Method
2.10. LC-MS/MS Analysis and Molecular Networking
2.11. Antioxidant Activity by Free Radicals (DPPH) Scavenging Assay
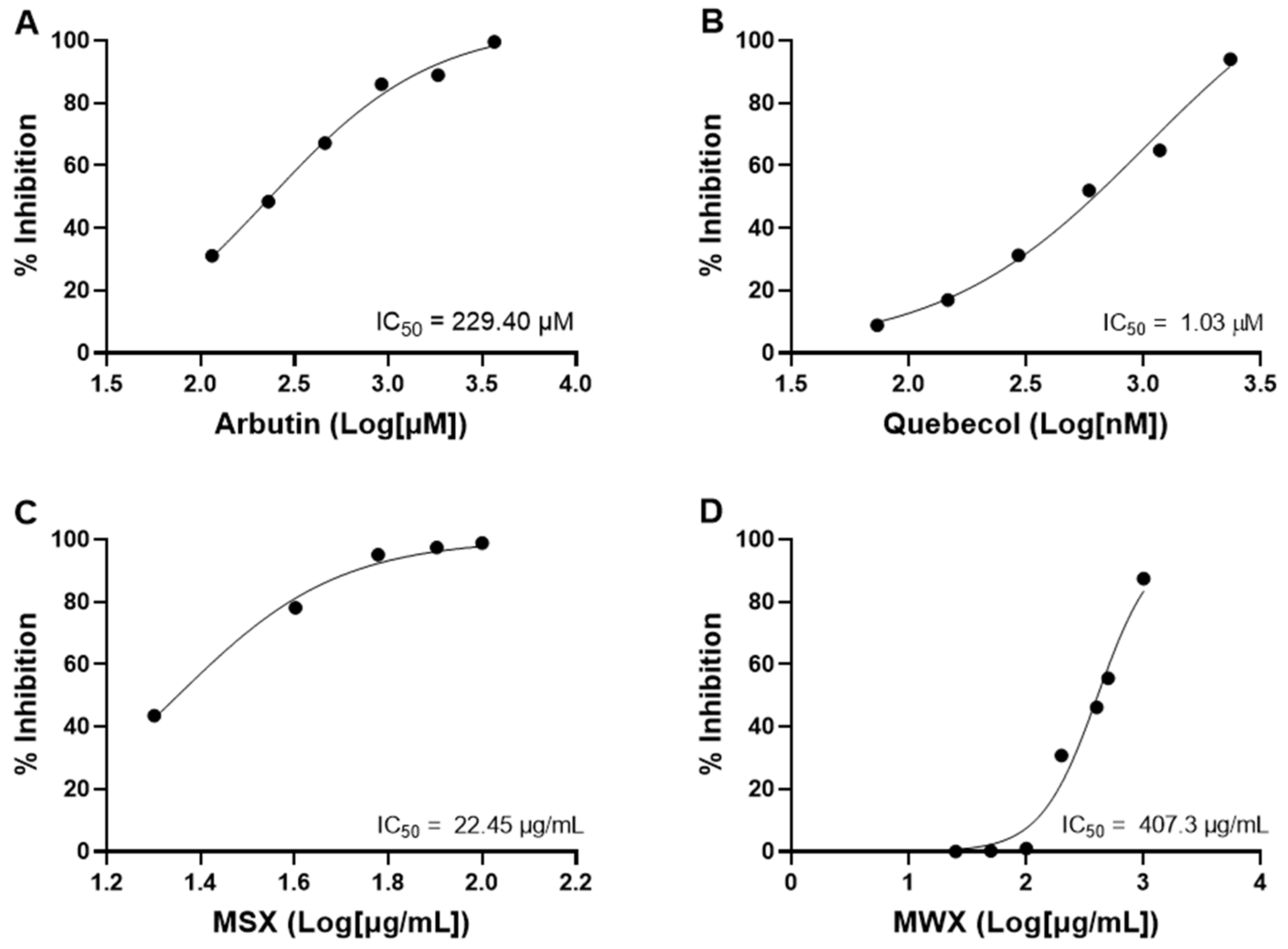
2.12. Tyrosinase Inhibition
2.13. Anti-Inflammatory Assays (Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase and Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibition Assays)
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
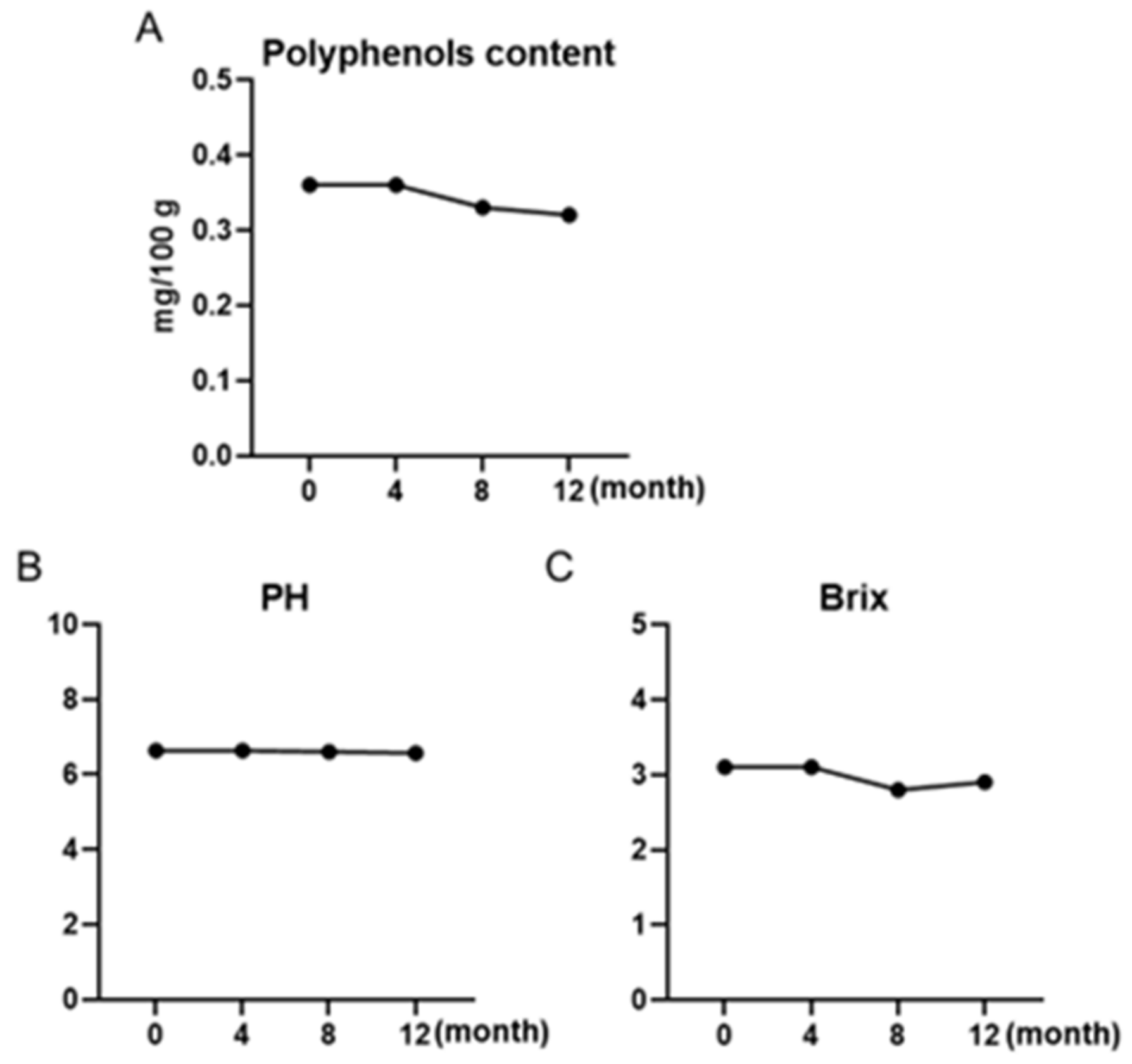
3.1. Maple Water’s Total Phenolic Content, °Bx, and pH Maintained for 12 Months
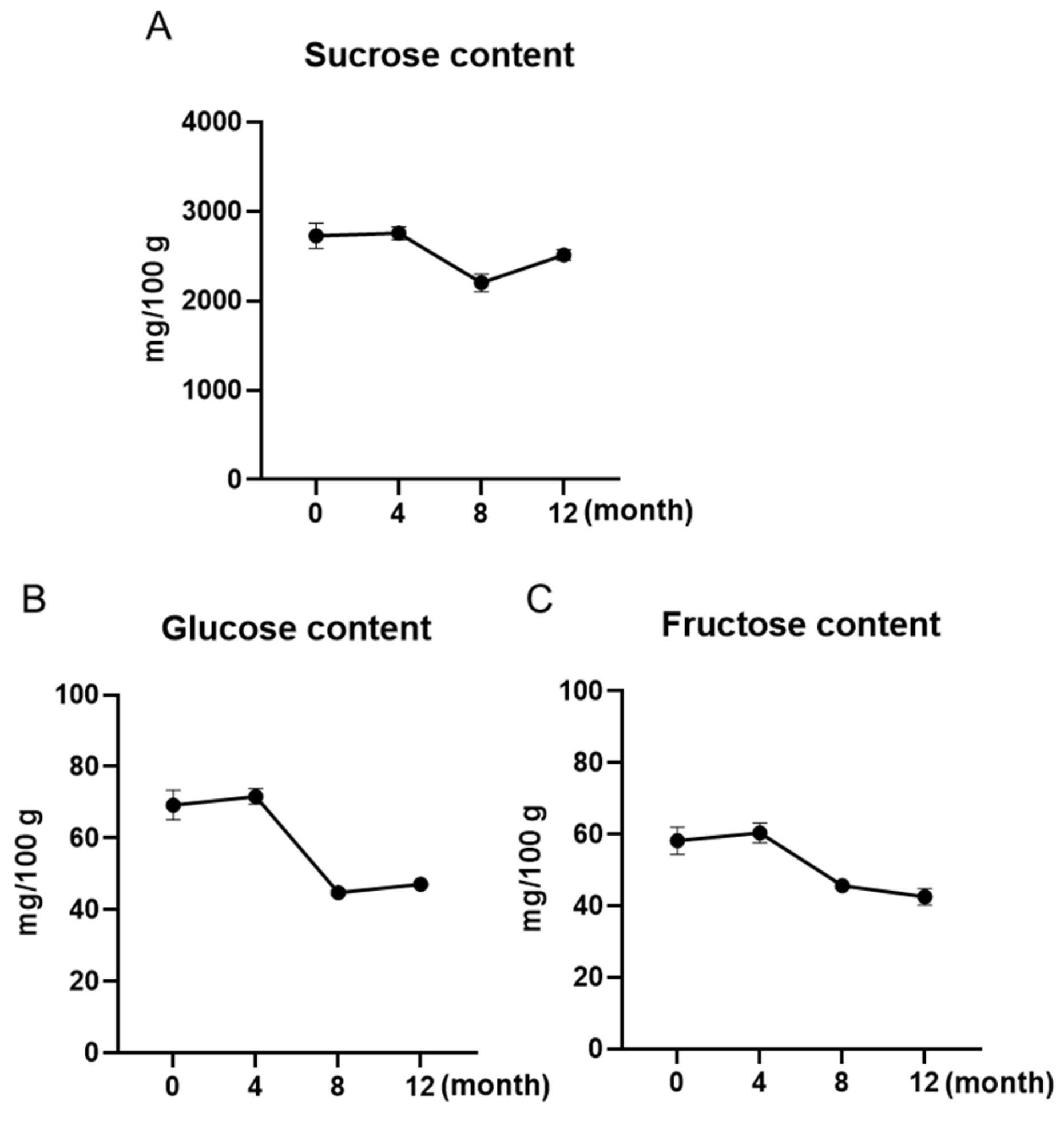
3.2. Sugar Contents of Maple Water Slightly Decreased over a 12-Month Shelf-Life
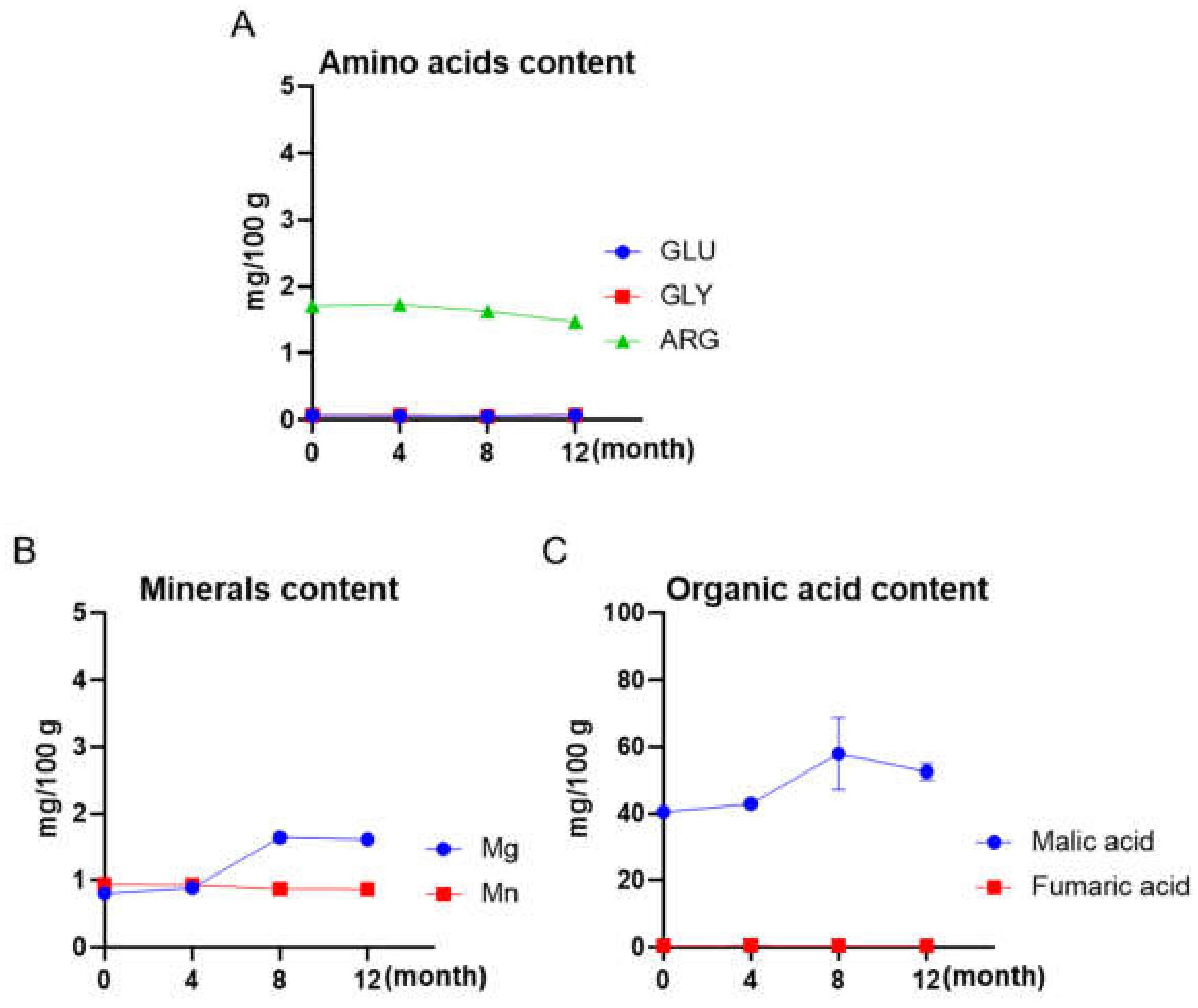
3.3. Other Chemical Contents of Maple Water Maintained over a 12-Month Shelf-Life
3.4. Maple Food Extracts (MSX and MWX) Had Comparable Phenolic Content
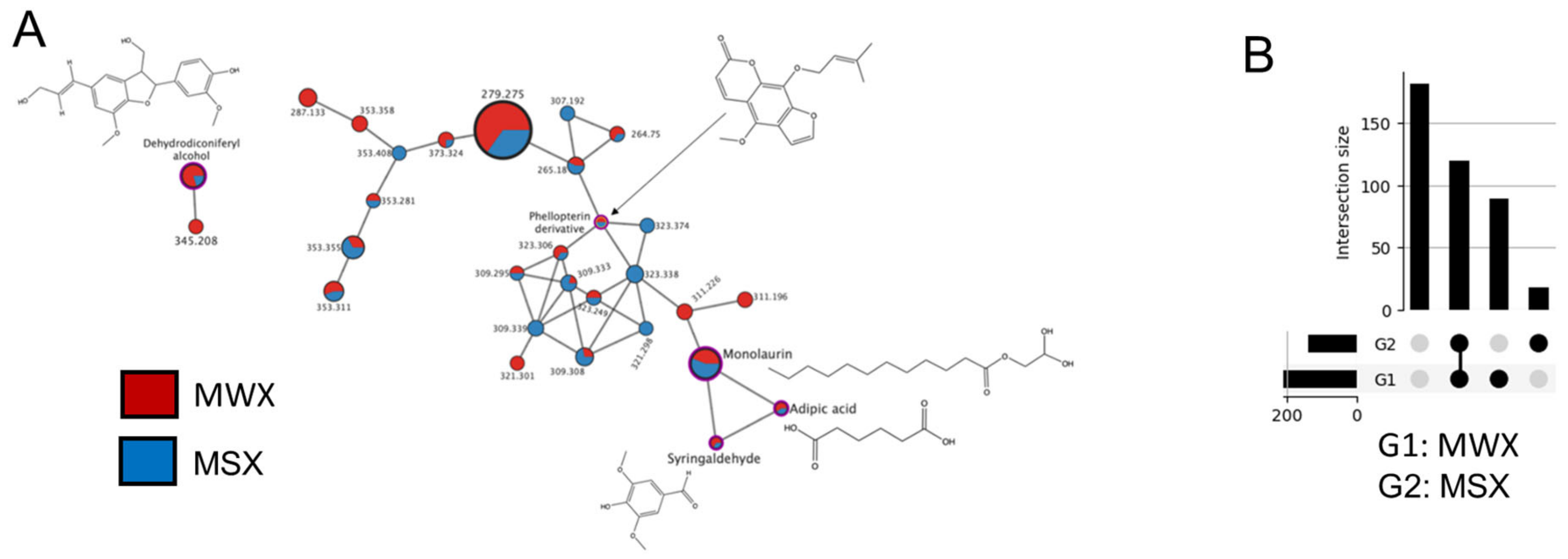
3.5. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Maple Food Extracts
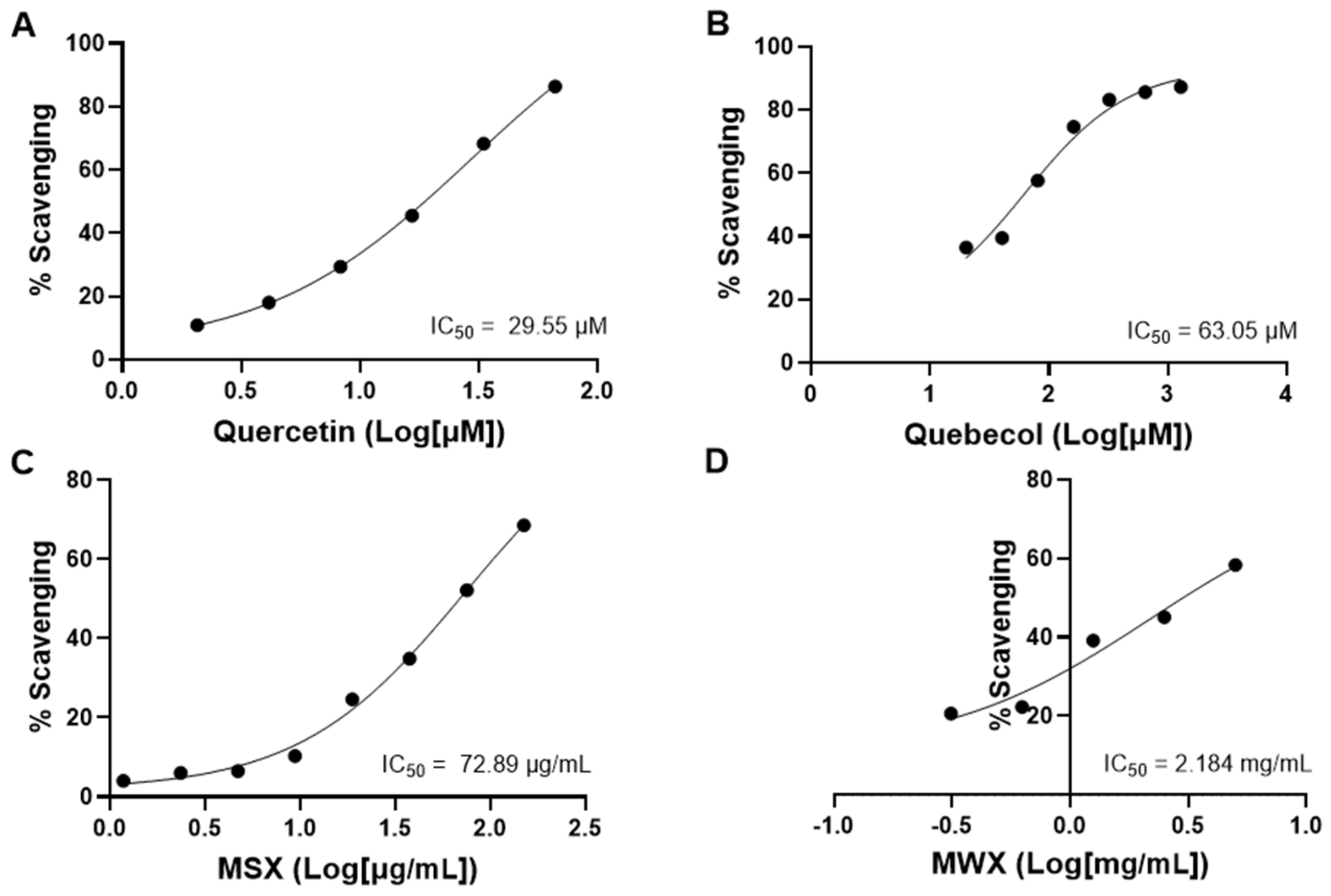
3.6. Maple Food Extracts Showed Promising Antioxidant Activity
3.7. Maple Food Extracts Exerted Moderate Anti-Inflammatory Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Perkins, T.D.; van den Berg, A.K. Chapter 4 Maple Syrup—Production, Composition, Chemistry, and Sensory Characteristics. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2009, 56, 101–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldret, R.L.; McDermott, M.; Aldret, S.; Davis, G.; Bellar, D. The Acute Effects of a Maple Water Drink on Exercise Responses, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Overweight College Males. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2022, 10, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuy, O.; Tremblay, J. Impact of Carbohydrate Ingestion on Cognitive Flexibility and Cerebral Oxygenation during High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise: A Comparison between Maple Products and Usual Carbohydrate Solutions. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias, A.; Dudar, M.; Kauzlaric, J.; Frederick, K.A.; Fitzpatrick, S.; Ives, S.J. Rehydrating efficacy of maple water after exercise-induced dehydration. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2019, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, L.; Tremblay, J. Ingestion of maple-based and other carbohydrate sports drinks: Effect on sensory perceptions during prolonged exercise. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Seeram, N.P. Quebecol, a novel phenolic compound isolated from Canadian maple syrup. J. Funct. Foods 2011, 3, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Seeram, N.P. Maple Syrup Phytochemicals Include Lignans, Coumarins, a Stilbene, and Other Previously Unreported Antioxidant Phenolic Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11673–11679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Seeram, N.P. Further Investigation into Maple Syrup Yields 3 New Lignans, a New Phenylpropanoid, and 26 Other Phytochemicals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7708–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, T.; Li, L.; Nahar, P.; Slitt, A.; Seeram, N.P. Chemical Compositional, Biological, and Safety Studies of a Novel Maple Syrup Derived Extract for Nutraceutical Applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6687–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Seeram, N.P. Pasteurized and sterilized maple sap as functional beverages: Chemical composition and antioxidant activities. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Rose, K.N.; DaSilva, N.A.; Johnson, S.L.; Seeram, N.P. Isolation, Identification, and Biological Evaluation of Phenolic Compounds from a Traditional North American Confectionery, Maple Sugar. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4289–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, H.; Seeram, N.P. Development and UFLC-MS/MS Characterization of a Product-Specific Standard for Phenolic Quantification of Maple-Derived Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3311–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, D.W. The Chemical Composition of Maple Syrup. J. Chem. Educ. 2007, 84, 1647–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, F.; Sibley, P.; Guillaume, D.; Abdulwali, N. Chemical composition and mineralogical residence of maple syrup: A comprehensive review. Food Chem. 2021, 374, 131817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Zaid, M.M.; Nozzolillo, C.; Tonon, A.; Coppens, M.; Lombardo, D.A. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Characterization and Identification of Antioxidant Polyphenols in Maple Syrup. Pharm. Biol. 2008, 46, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbo, M.R.; Bevilacqua, A.; Petruzzi, L.; Casanova, F.P.; Sinigaglia, M. Functional Beverages: The Emerging Side of Functional Foods: Commercial Trends, Research, and Health Implications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 1192–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.F.; Gad, H.A.; Farag, M.A. Chemistry, processing, and functionality of maple food products: An updated comprehensive review. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maple Syrup: Markets & Growth Opportunities. Available online: https://agriculture.vermont.gov/form/maple-syrup-markets-growth-opportunities (accessed on 3 May 2020).
- Larochelle, F.; Forget, É.; Rainville, A.; Bousquet, J. Sources of temporal variation in sap sugar content in a mature sugar maple (Acer saccharum) plantation. For. Ecol. Manag. 1998, 106, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.J.; McDowell, T.; Ketola, C.; Jennings, M.; Miller, J.D.; Renaud, J.B. Metabolomics reveals chemical changes in Acer saccharum sap over a maple syrup production season. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagacé, L.; Leclerc, S.; Charron, C.; Sadiki, M. Biochemical composition of maple sap and relationships among constituents. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 41, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, L.H. Variation in mineral content of red maple sap across an atmospheric deposition gradient. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1997, 28, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellado-Mojica, E.; López, M.G. Identification, classification, and discrimination of agave syrups from natural sweeteners by infrared spectroscopy and HPAEC-PAD. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleixandre, M.; Santos, J.P.; Sayago, I.; Cabellos, J.M.; Arroyo, T.; Horrillo, M.C. A Wireless and Portable Electronic Nose to Differentiate Musts of Different Ripeness Degree and Grape Varieties. Sensors 2015, 15, 8429–8443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, R.D.; He, H.; Wahome, P.G.; Wu, S.; Carter, G.T.; Bertin, M.J. New Micropeptins with Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity Isolated from a Cyanobacterial Bloom. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 15472–15478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, W.; Frost, L.; Kirschenbaum, L.; Dain, J.A.; Seeram, N.P. Glucitol-core containing gallotannins inhibit the formation of advanced glycation end-products mediated by their antioxidant potential. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; DaSilva, N.A.; Liu, W.; Xu, J.; Dombi, G.W.; Dain, J.A.; Li, D.; Chamcheu, J.C.; Seeram, N.P.; Ma, H. Thymocid®, a Standardized Black Cumin (Nigella sativa) Seed Extract, Modulates Collagen Cross-Linking, Collagenase and Elastase Activities, and Melanogenesis in Murine B16F10 Melanoma Cells. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Xu, J.; DaSilva, N.A.; Wang, L.; Wei, Z.; Guo, L.; Johnson, S.L.; Lu, W.; Xu, J.; Gu, Q.; et al. Cosmetic applications of glucitol-core containing gallotannins from a proprietary phenolic-enriched red maple (Acer rubrum) leaves extract: Inhibition of melanogenesis via down-regulation of tyrosinase and melanogenic gene expression in B16F10 melanoma cells. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 309, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.A.; Maclean, K.S.; Macconnell, H.M. Heavy Metal, pH, and Total Solid Content of Maple Sap and Syrup Produced in Eastern Canada. J. AOAC Int. 1989, 72, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannangara, A.C.; Chandrajith, V.; Ranaweera, K. Comparative Analysis of Coconut Water in Four Different Maturity Stages. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 1814–1817. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Chen, B.; Liu, A.; Zhu, W.; Yao, S. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometric Multiple Reaction Monitoring-based Strategies for Expanding Targeted Profiling towards Quantitative Metabolomics. Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 13, 1226–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beretov, J.; Wasinger, V.C.; Graham, P.H.; Millar, E.K.; Kearsley, J.H.; Li, Y. Proteomics for Breast Cancer Urine Biomarkers. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2013, 63, 123–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; DaSilva, N.; Liu, W.; Nahar, P.P.; Wei, Z.; Liu, Y.; Pham, P.T.; Crews, R.; Vattem, D.A.; Slitt, A.L.; et al. Effects of a Standardized Phenolic-Enriched Maple Syrup Extract on β-Amyloid Aggregation, Neuroinflammation in Microglial and Neuronal Cells, and β-Amyloid Induced Neurotoxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 2836–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, K.N.; Barlock, B.J.; DaSilva, N.A.; Johnson, S.L.; Liu, C.; Ma, H.; Nelson, R.; Akhlaghi, F.; Seeram, N.P. Anti-neuroinflammatory effects of a food-grade phenolic-enriched maple syrup extract in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 24, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Liu, C.; Petrovas, S.; Wan, Y.; Chen, H.; Seeram, N.P.; Ma, H. Phenolic-enriched maple syrup extract protects human keratinocytes against hydrogen peroxide and methylglyoxal induced cytotoxicity. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahar, P.P.; Driscoll, M.V.; Li, L.; Slitt, A.L.; Seeram, N.P. Phenolic mediated anti-inflammatory properties of a maple syrup extract in RAW 264.7 murine macrophages. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 6, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wei, Z.; Ma, H.; Cai, A.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; DaSilva, N.A.; Johnson, S.L.; Kirschenbaum, L.J.; Cho, B.P.; et al. Anti-glycation and anti-oxidative effects of a phenolic-enriched maple syrup extract and its protective effects on normal human colon cells. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolidis, E.; Li, L.; Lee, C.; Seeram, N.P. In vitro evaluation of phenolic-enriched maple syrup extracts for inhibition of carbohydrate hydrolyzing enzymes relevant to type 2 diabetes management. J. Funct. Foods 2011, 3, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, T.; Kamei, A.; Ishijima, T.; Abe, K.; Okada, S. A maple syrup extract alters lipid metabolism in obese type 2 diabetic model mice. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Shinozaki, F.; Yasuoka, A.; Shimada, K.; Kondo, K.; Ishijima, T.; Toyoda, T.; Arai, S.; Kondo, T.; et al. Quantitative deviating effects of maple syrup extract supplementation on the hepatic gene expression of mice fed a high-fat diet. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 61, 1600477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Shinozaki, F.; Yasuoka, A.; Kondo, T.; Ishijima, T.; Toyoda, T.; Arai, S.; Abe, K. Administration of a maple syrup extract to mitigate their hepatic inflammation induced by a high-fat diet: A transcriptome analysis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 1893–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample | Total Phenolic Content (%) | Average (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSX | 40.31 | 40.30 | 40.43 | 40.35 |
| MWX | 32.38 | 31.89 | 31.76 | 32.01 |
| Compound | Presence | Exact Mass | Spectrum m/z | Error (ppm) | Adduct | Cosine Score | Shared Peaks | Molecule Class | Identification Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,2-amino-1,9-dimethyl-6,9-dihydro-1H-purin-6-one | MSX, MWX | 179.08 | 202.08 | <1 | [M+Na]+ | 0.91 | 5 | Imidazopyrimidines | GNPS |
| Monolaurin * | MSX, MWX | 274.21 | 240.21 | 1.004 | [M+H]+-H2O | 0.86 | 8 | Glycerolipids | GNPS |
| Adipic acid * | MSX, MWX | 146.06 | 165.02 | <1 | [M+Na]+ | 0.83 | 5 | Fatty acyls | GNPS |
| Decanedioic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester | MSX, MWX | 426.67 | 427.43 | <1 | [M+H]+ | 0.65 | 4 | Fatty acyls | GNPS |
| Syringaldehyde * | MSX, MWX | 182.17 | 182.94 | <1 | [M+H]+ | - | - | Hydroxybenzaldehyde | [9,10] |
| Phellopterin derivative * | MSX, MWX | 300.10 | 337.34 | 14 | [M+Na]+ | 0.64 | 6 | Coumarins and derivatives | GNPS |
| Dehydrodiconiferyl alcohol * | MSX, MWX | 358.40 | 359.18 | <1 | [M+H]+ | - | - | Lignans | [9,10] |
| (-) Catechin | MSX | 290.08 | 313.01 | <1 | [M+Na]+ | 0.62 | 4 | Flavonoids | GNPS; [14,15] |
| Sample | % Inhibition (100 µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| sEH | COX-2 | |
| MSX | 91.53 ± 7.4% | 10.97 ± 2.5% |
| MWX | 6.27 ± 7.1% | 21.87 ± 9.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torrey, K.J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, H.; Via, C.W.; Bertin, M.J.; Seeram, N.P. What Is Authentic Maple Water? A Twelve-Month Shelf-Life Study of the Chemical Composition of Maple Water and Its Biological Activities. Foods 2023, 12, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020239
Torrey KJ, Liu Y, Li H, Ma H, Via CW, Bertin MJ, Seeram NP. What Is Authentic Maple Water? A Twelve-Month Shelf-Life Study of the Chemical Composition of Maple Water and Its Biological Activities. Foods. 2023; 12(2):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020239
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorrey, Kara J., Yongqiang Liu, Huifang Li, Hang Ma, Christopher W. Via, Matthew J. Bertin, and Navindra P. Seeram. 2023. "What Is Authentic Maple Water? A Twelve-Month Shelf-Life Study of the Chemical Composition of Maple Water and Its Biological Activities" Foods 12, no. 2: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020239
APA StyleTorrey, K. J., Liu, Y., Li, H., Ma, H., Via, C. W., Bertin, M. J., & Seeram, N. P. (2023). What Is Authentic Maple Water? A Twelve-Month Shelf-Life Study of the Chemical Composition of Maple Water and Its Biological Activities. Foods, 12(2), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020239









