The Stability, Rheological Properties and Interfacial Properties of Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions Prepared from Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Cold Plasma-Treated Chickpea Protein Isolate and Myofibrillar Protein Complexes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Emulsions with a Mixed Protein System
2.2.1. Preparation of Chickpea Protein Isolate
2.2.2. Preparation of Chicken MP
2.2.3. Emulsion Preparation
2.3. Emulsifying Activity Index (EAI) and Emulsifying Stability Index (ESI)
2.4. Turbiscan Stability Index (TSI)
2.5. Optical Microscopy
2.6. Particle Distribution and Size Measurement
2.7. Creaming Index (CI)
2.8. Rheological Property Analysis
2.8.1. Apparent Viscosity
2.8.2. Frequency Sweep Testing
2.8.3. Temperature Sweep Measurements
2.9. Interfacial Properties
2.9.1. Interfacial Tension
2.9.2. Surface Protein Adsorption
2.9.3. Composition of Interfacial Proteins
2.10. Microstructure
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. EAI and ESI
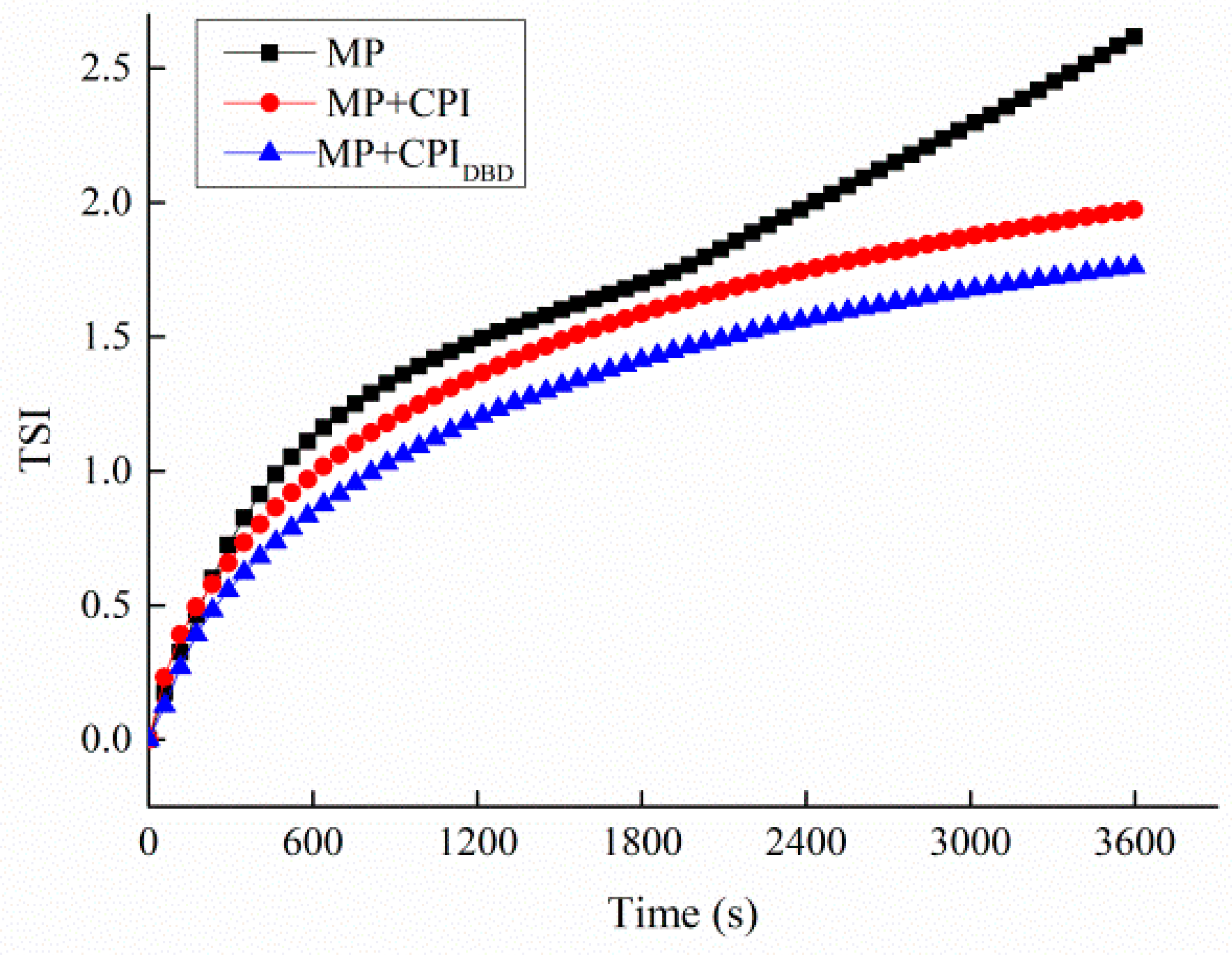
3.2. TSI
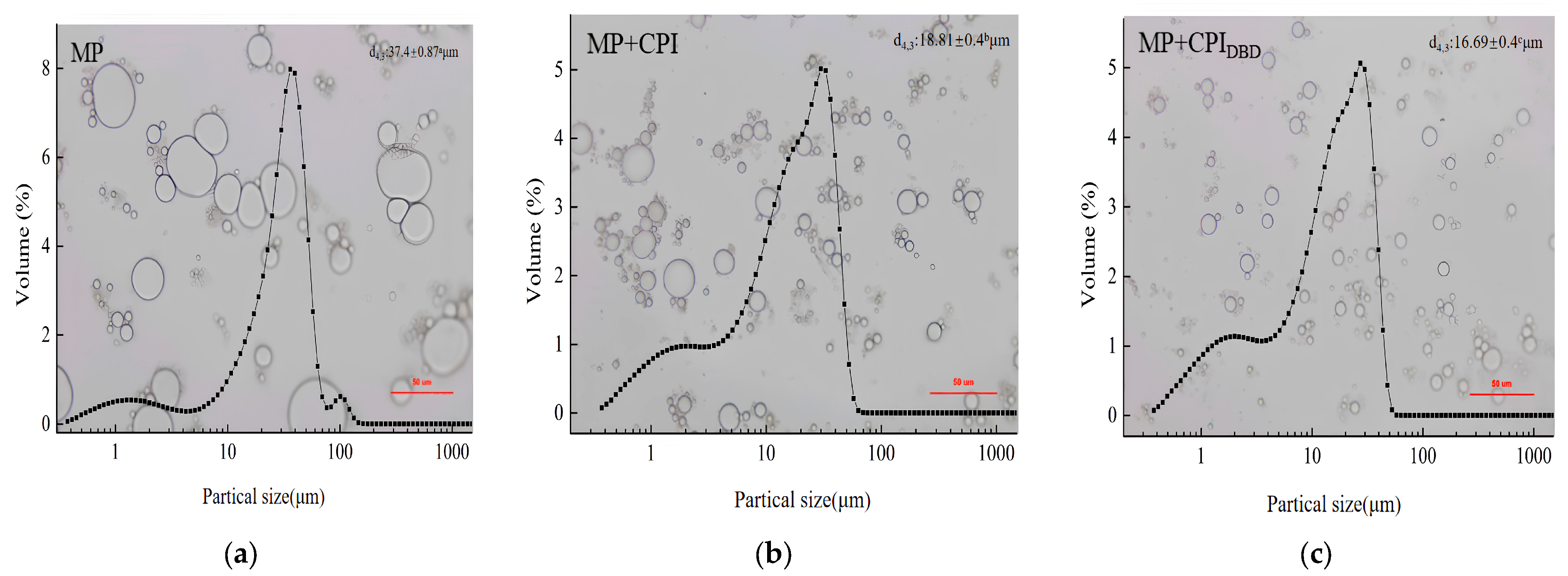
3.3. Optical Microscopy and Particle Size
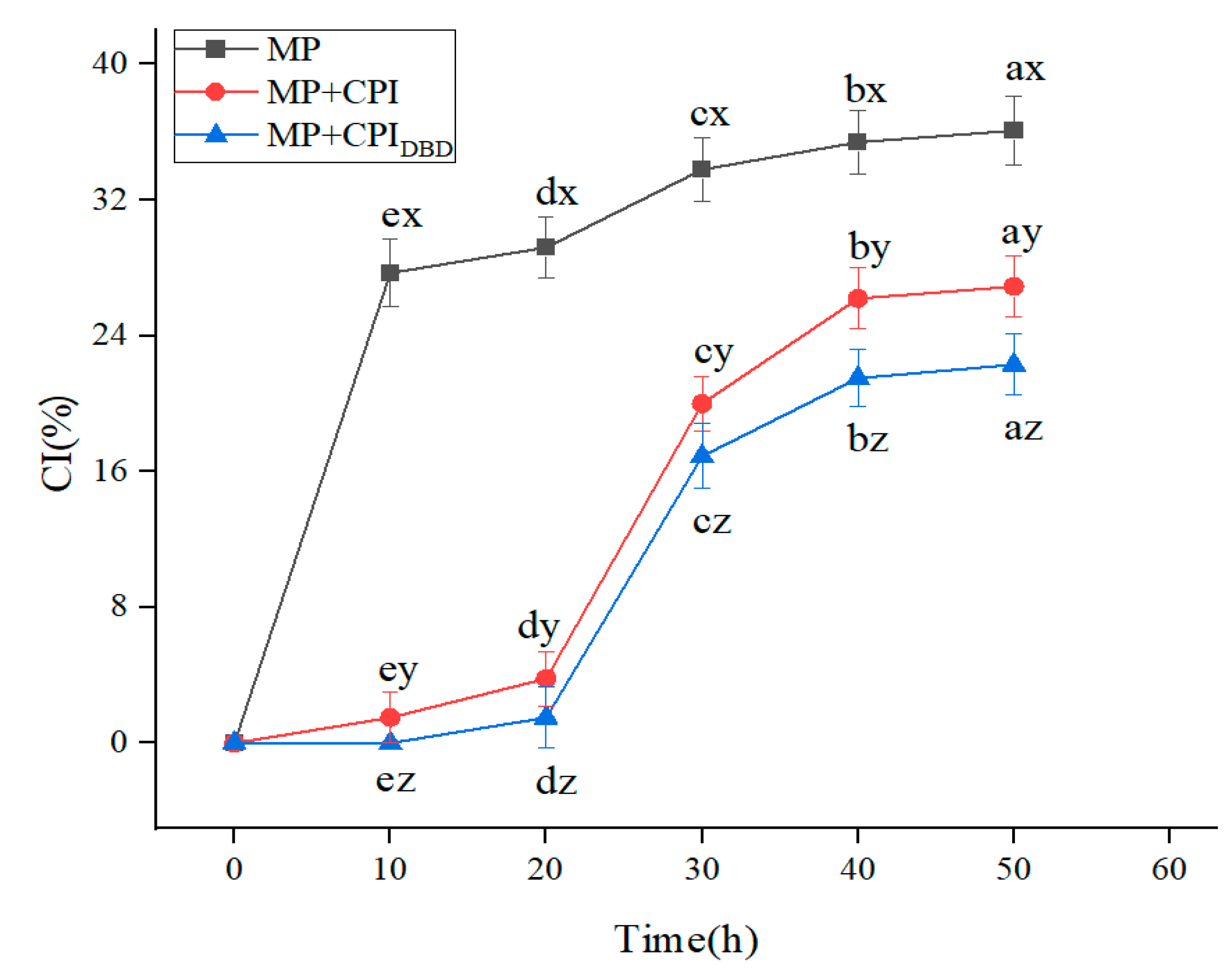
3.4. CI
3.5. Rheological Property Analysis
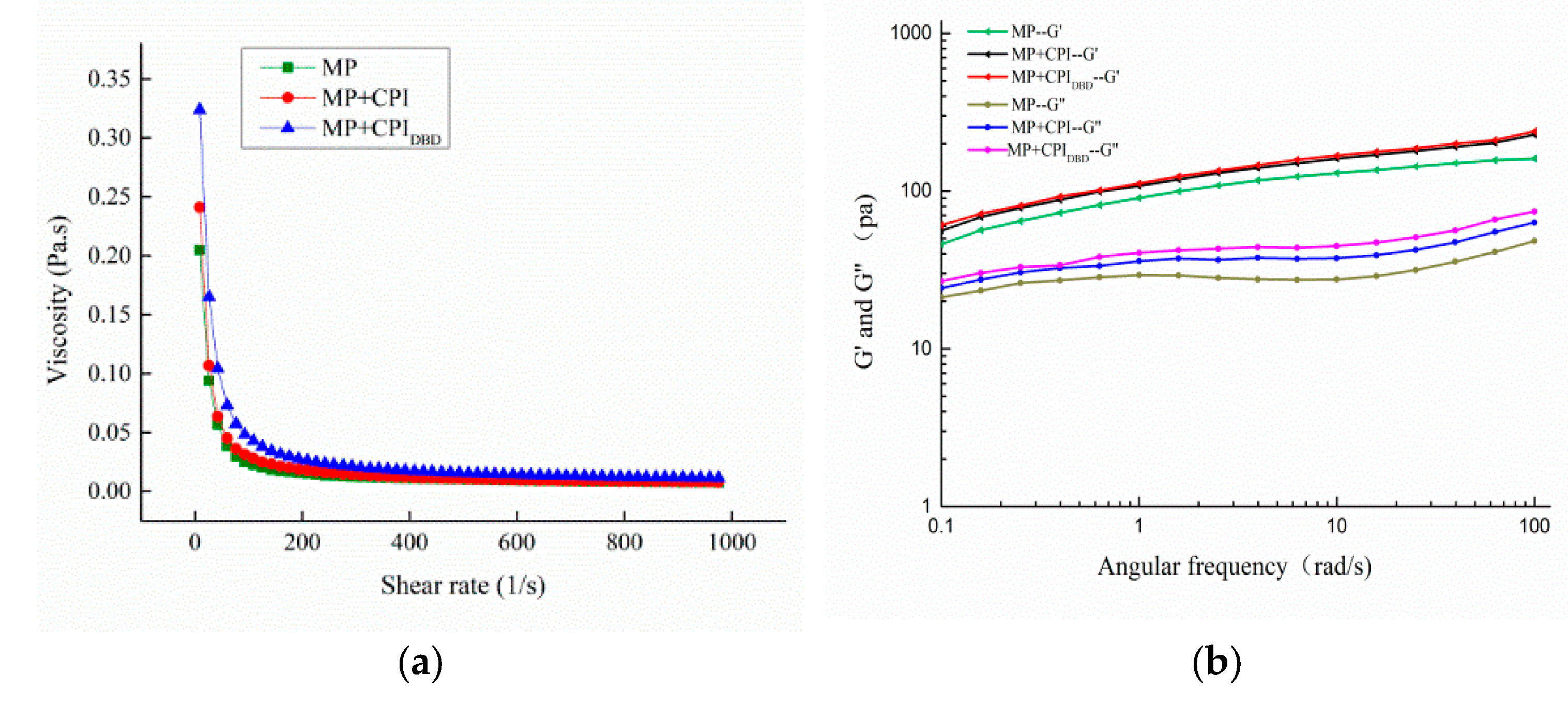
3.5.1. Apparent Viscosity
3.5.2. Frequency Sweep Testing
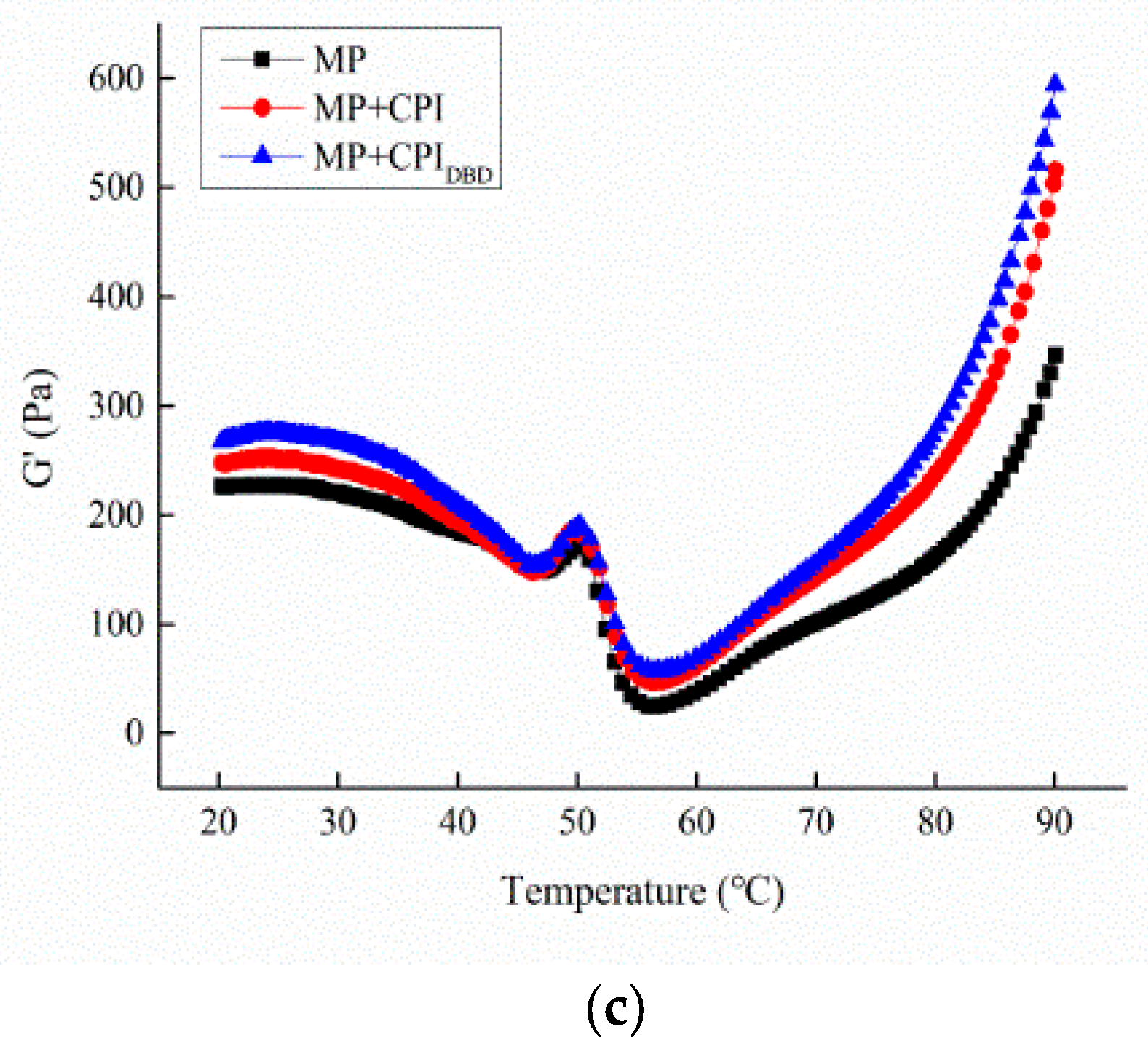
3.5.3. Temperature Sweep Measurement
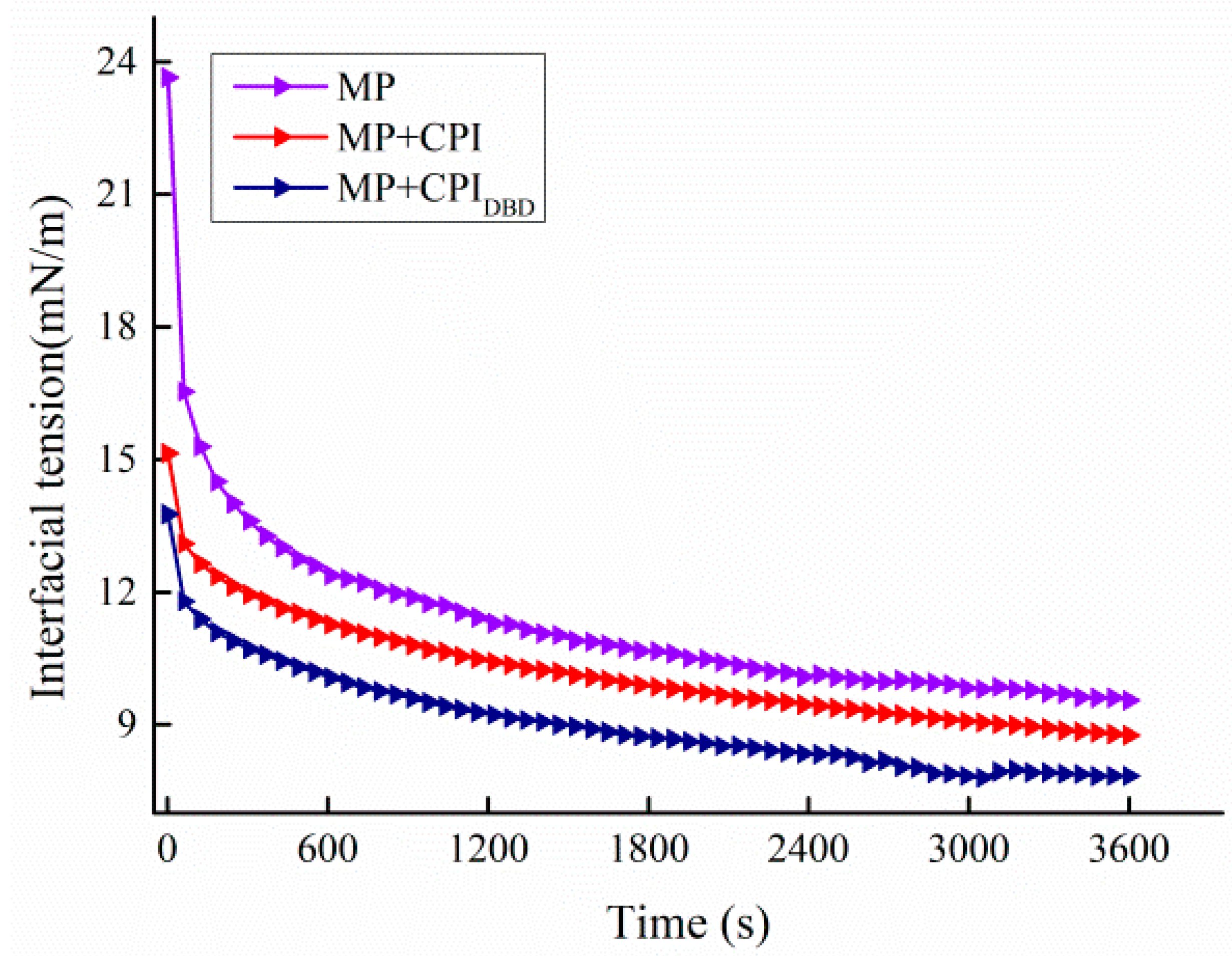
3.6. Interfacial Tension
3.7. Interfacial Protein Content
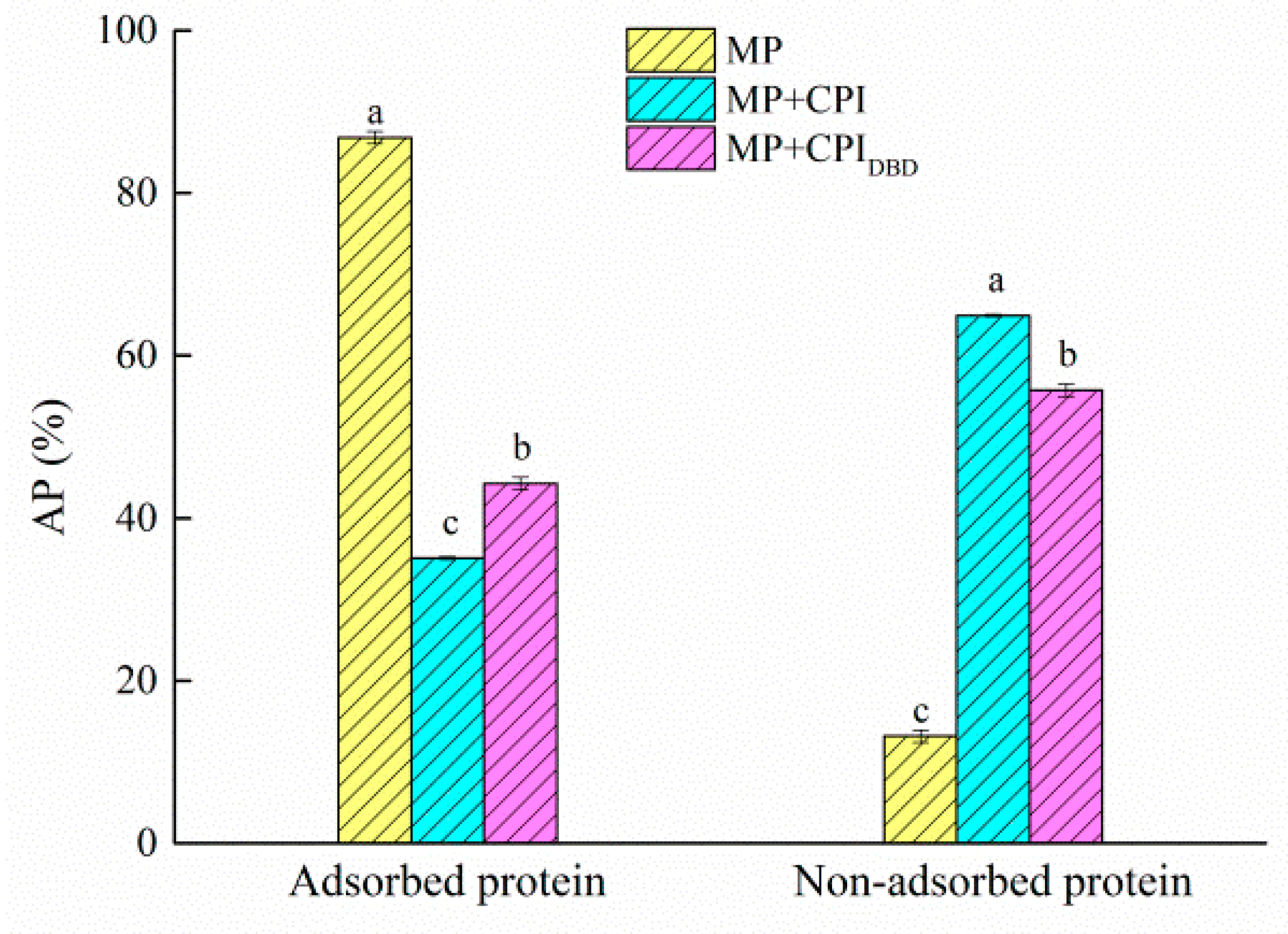
3.8. Interfacial Protein Composition
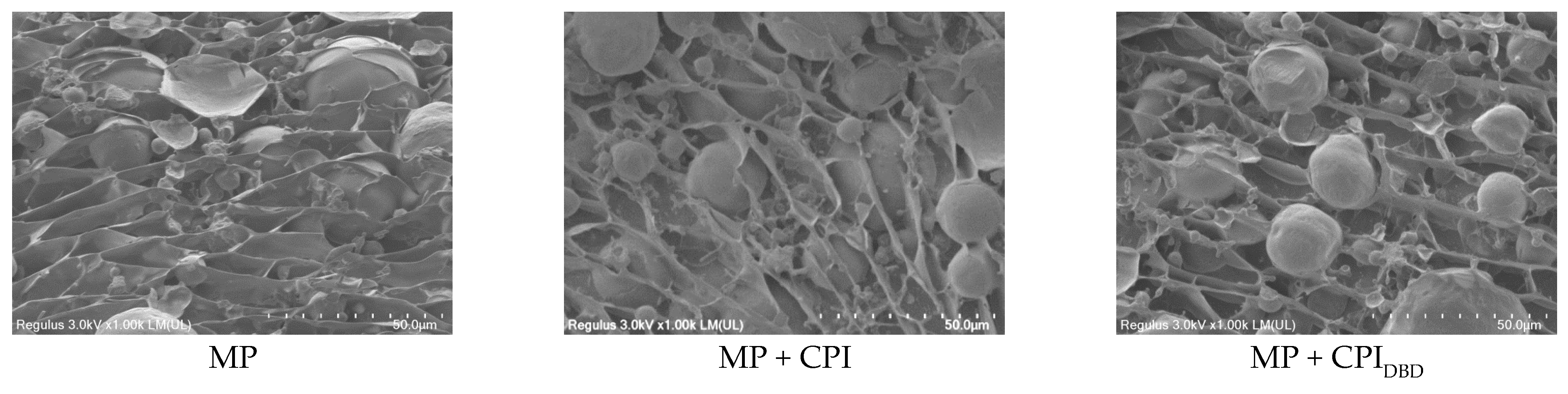
3.9. Microstructure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Tume, R.K.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Solubilization of myofibrillar proteins in water or low ionic strength media: Classical techniques, basic principles, and novel functionalities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3260–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.D.; Holley, R.A. Factors influencing gel formation by myofibrillar proteins in muscle foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.J.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H.; Li, C.B.; Huang, M. Effects of characteristics changes of collagen on meat physicochemical properties of beef semitendinosus muscle during ultrasonic processing. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xu, J.; Yu, D.; Kong, B.; Liu, Q. Recent advances in the application of emulsion gels as fat replacers in meat products. Shipin Kexue/Food Sci. 2019, 40, 236–242, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Barbut, S. Importance of fat emulsification and protein matrix characteristics in meat batter stability. J. Muscle Foods 1995, 6, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, X.; Li, T.; Yu, G. Mechanism and application of emulsifiers for stabilizing emulsions: A review. Shipin Kexue/Food Sci. 2020, 41, 303–310, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, D.; Xiong, Y.L.; Castillo, M.; Payne, F.A.; Garrido, M.D. Textural and viscoelastic properties of pork frankfurters containing canola-olive oils, rice bran, and walnut. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, E.; Mekhloufi, G.; Rosilio, V.; Grossiord, J.; Agnely, F. Proteins, polysaccharides, and their complexes used as stabilizers for emulsions: Alternatives to synthetic surfactants in the pharmaceutical field. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.X.; Aihemaiti, Z.; Cao, Y.P.; Teng, C.; Li, X.T. Physicochemical stability, microrheological properties and microstructure of lutein emulsions stabilized by multilayer membranes consisting of whey protein isolate, flaxseed gum and chitosan. Food Chem. 2016, 202, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhu, B.; Liu, Y.F.; Xiong, Y.L. Interfacial structural role of pH-shifting processed pea protein in the oxidative stability of oil/water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhang, J.P.; Chen, J.S.; Wang, Y.L.; Dong, N.; Hu, C.L.; Chen, H.P.; Li, G.; Pan, X.; Wu, C.B. Preparation and stabilization of emulsions stabilized by mixed sodium caseinate and soy protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukanti, A.K.; Gaur, P.M.; Gowda, C.L.L.; Chibbar, R.N. Nutritional quality and health benefits of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): A review. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108 (Suppl. S1), S11–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chelikani, V.; Serventi, L. Evaluation of chickpea as alternative to soy in plant-based beverages, fresh and fermented. LWT 2018, 97, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Zeng, X.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y. Preparation, functional properties, and nutritional evaluation of chickpea protein concentrate. Cereal Chem. 2023, 100, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.; Tavares, G.M. Thermal treatments and emerging technologies: Impacts on the structure and techno-functional properties of milk proteins. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 90, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bußler, S.; Steins, V.; Ehlbeck, J.; Schlueter, O. Impact of thermal treatment versus cold atmospheric plasma processing on the techno-functional protein properties from Pisum sativum ‘Salamanca’. J. Food Eng. 2015, 167, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Dong, S.; Han, F.; Li, Y.T.; Chen, G.Y.; Li, L.; Chen, Y. Effects of dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) cold plasma treatment on physicochemical and functional properties of peanut protein. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Tian, J.F.; Zheng, S.Y.; He, Y.Y.; Xiang, Q.S.; Bai, Y.H. Effects of plasma on solubility and emulsifying properties of chickpea protein isolates. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 31–39, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mession, J.L.; Roustel, S.; Saurel, R. Interactions in casein micelle-Pea protein system (part I): Heat-induced denaturation and aggregation. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 67, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, K.; Bai, Y.H.; Li, B.; Xu, W. Effect of high intensity ultrasound on physicochemical, interfacial and gel properties of chickpea protein isolate. LWT 2020, 129, 109563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Fu, L.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Xue, S.W.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.L.; Bai, Y.H. Use of high-intensity ultrasound to improve emulsifying properties of chicken myofibrillar protein and enhance the rheological properties and stability of the emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xiong, Y.L. Competitive adsorption and dilatational rheology of pork myofibrillar and sarcoplasmic proteins at the O/W emulsion interface. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106816. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.L.; Fu, L.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Bai, Y.H. Improving interfacial properties, structure and oxidative stability by ultrasound application to sodium caseinate prepared pre-emulsified soybean oil. LWT 2020, 131, 109755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, M.; Niakousari, M.; Golmakani, M.T.; Ajalloueian, F.; Khalesi, M. Effect of dielectric barrier discharge atmospheric cold plasma treatment on structural, thermal and techno-functional characteristics of sodium caseinate. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 66, 102542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.C.; Jiang, W.; Chen, G.P.; Wang, Q.K.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, X.B.; Liu, F.G.; Ngai, T. Sonochemical effects on formation and emulsifying properties of zein-gum arabic complexes. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 114, 106557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.; Murray, B.; Flynn, C.; Norton, I. The effect of ultrasound treatment on the structural, physical and emulsifying properties of animal and vegetable proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathé, C.; Devineau, S.; Aude, J.C.; Lagniel, G.; Chedin, S.; Legros, V.; Mathon, M.H.; Renault, J.P.; Pin, S.; Boulard, Y.; et al. Structuraldeterminants for protein adsorption/non-adsorption to silica surface. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.Z.; Zhao, Z.H.; Zhou, Z.P.; Deng, Y.Y.; Wei, Z.C.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.J.; Liu, G.; Li, P.; Zhang, M.W. Effects of red removal and ultrasonic treatment on peanut oil extraction and emulsification characteristics. China Oils Fats 2023, 10, 1–10, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Wang, T.; Ren, C.; Ma, W.; Wu, D.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Du, M. Advancement of food-derived mixed protein systems: Interactions, aggregations, and functional properties. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 627–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Interaction and functionality of mixed myofibrillar and enzyme-hydrolyzed soy proteins. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, S.; Xie, F.Y.; Han, L.; Li, L.; Jiang, L.Z.; Qi, B.K.; Li, Y. Soy/whey protein isolates: Interfacial properties and effects on the stability of oil-in-water emulsions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 101, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.L.; Jin, Y.; Xiong, Y.L. Heating-aided pH shifting modifies hemp seed protein structure, cross-linking, and emulsifying properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10827–10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Jia, S.X.; Tian, J.F.; Wu, L.L. Emulsifying characteristics of chickpea powder. Food Res. Dev. 2023, 44, 13–19, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Li, M.; Ersan, S.; Hu, R.; Geng, N.; Ni, Y.Y. Formation and stability of zeaxanthin dipalmitate emulsions. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 354–361. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.N.; Yang, J.J.; Shao, G.Q.; Qu, D.N.; Zhao, H.K.; Yang, L.N.; Zhu, L.J.; He, Y.T.; Liu, H.; Zhu, D.S. Soy protein isolated-soy hull polysaccharides stabilized O/W emulsion: Effect of polysaccharides concentration on the storage stability and interfacial rheological properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladjal-Ettoumi, Y.; Boudries, H.; Chibane, M.; Romero, A. Pea, chickpea and lentil protein isolates: Physicochemical characterization and emulsifying properties. Food Biophys. 2016, 11, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.; Hu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Bakry, A.M.; Khalifa, I.; Pan, S.; Hu, H. Effect of different oils and ultrasound emulsification conditions on the physicochemical properties of emulsions stabilized by soy protein isolate. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2018, 49, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.Q.; Guan, H.N.; Zhao, X.X.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B.H. Properties and oxidative stability of emulsions prepared with myofibrillar protein and lard diacylglycerols. Meat Sci. 2016, 115, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengoechea, C.; Romero, A.; Aguilar, J.M.; Cordobes, F.; Guerrero, A. Temperature and pH as factors influencing droplet size distribution and linear viscoelasticity of O/W emulsions stabilised by soy and gluten proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Mao, D.B. Preparation of citral emulsion stabilized by chickpea whey protein. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 44, 274–278. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, T.T.; Wang, X.W.; Wang, X.J.; Xia, S.Q.; Huang, Q.R. Plant protein-based antioxidant pickering emulsions and high internal phase pickering emulsions against broad pH range and high ionic strength: Effects of interfacial rheology and microstructure. LWT 2021, 150, 111953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, T.; Xing, T.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Rheological and physical properties of O/W protein emulsions stabilized by isoelectric solubilization/precipitation isolated protein: The underlying effects of varying protein concentrations. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.X.; Zhao, X.; Li, R.; Bassey, A.; Bai, Y.; Ye, K.; Deng, S.L.; Zhou, G.H. Synergistic effects of polysaccharide addition-ultrasound treatment on the emulsified properties of low-salt myofibrillar protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, H.; Lyu, F.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, Y. Physicochemical properties and microstructure of fish myofibrillar protein-lipid composite gels: Effects of fat type and concentration. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 90, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, S.Y.; He, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Du, M.T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Bai, Y.H. Application of ultrasound-assisted alkaline extraction for improving the solubility and emulsifying properties of pale, soft, and exudative (PSE)-like chicken breast meat protein isolate. LWT 2022, 172, 114234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Feng, J.R.; Sun, P.L.; Ritzoulis, C. Improved emulsion stability and resveratrol encapsulation by whey protein/gum arabic interaction at oil-water interface. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, R.S.; Nickerson, M.T. Food proteins: A review on their emulsifying properties using a structure–function approach. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.H.; Gunasekaran, S. Rheology and oxidative stability of whey protein isolate-stabilized menhaden oil-in-water emulsions as a function of heat treatment. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafe, A.; Glikman, D.; Rey, N.G.; Haller, N.; Kulozik, U.; Braunschweig, B. Structure-property relations of β-lactoglobulin/κ-carrageenan mixtures in aqueous foam. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 640, 128267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkatch, S.R.; Levachov, S.M.; Kuhkushkina, A.N.; Novosyolova, N.V.; Kharlov, A.E.; Matveenko, V.N. Rheological properties of concentrated emulsions stabilized by globular protein in the presence of nonionic surfactant. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 298, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Bi, S.; Qi, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y. Impact of ultrasonic treatment on an emulsion system stabilized with soybean protein isolate and lecithin: Its emulsifying property and emulsion stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Nikolov, A.D.; Wasan, D.T.; Diaz-Arauzo, H.; Shelly, C.S. Demulsification of water in crude oil emulsions: Effects of film tension, elasticity, diffusivity and interfacial activity of demulsifier individual components and their blends. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 1996, 17, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.S.; Dickinson, E. Interfacial rheology and the dynamic properties of adsorbed films of food proteins and surfactants. Food Sci. Technol. Int. Tokyo 1996, 2, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, M.; Colosimo, A.; Conti, F.; Giuliani, A.; Grottesi, A.; Manetti, C.; Zbilut, J.P. Early events in protein aggregation: Molecular flexibility and hydrophobicity/charge interaction in amyloid peptides as studied by molecular dynamics simulations. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2005, 58, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.R.; Ma, Y.G.; Lei, Y.D.; Zhu, X.R.; Zhang, L.F.; Hu, L.; Lu, S.L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J. Ultrasonic structural modification of myofibrillar proteins from Coregonus peled improves emulsification properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 76, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acton, J.C.; Saffle, R.L. Emulsifying capacity of muscle protein: Phase volumes at emulsion collapse. J. Food Sci. 1972, 37, 904–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourtzinos, I.; Kiosseoglou, V. Protein interactions in comminuted meat gels containing emulsified corn oil. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Qiu, S.; Xu, W.; Bai, Y. Synergistic effect of corn fiber gum and chitosan in stabilization of oil in water emulsion. LWT 2022, 154, 112592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani-HasanSaraei, A.; Rafe, A.; Shahidi, S.A.; Atashzar, A. Microstructure and chemorheological behavior of whipped cream as affected by rice bran protein addition. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Emulsifying Activity Index (m2/g) | Emulsion Stability Index (%) |
|---|---|---|
| MP | 55.17 ± 0.18 c | 66.31 ± 1.09 c |
| MP + CPI | 70.96 ± 1.12 b | 94.74 ± 0.49 b |
| MP + CPIDBD | 74.99 ± 1.45 a | 99.87 ± 0.37 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, L.; Tian, J.; Xiang, Q.; Li, K. The Stability, Rheological Properties and Interfacial Properties of Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions Prepared from Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Cold Plasma-Treated Chickpea Protein Isolate and Myofibrillar Protein Complexes. Foods 2023, 12, 3629. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193629
Zhao D, Zhou Y, Sun L, Tian J, Xiang Q, Li K. The Stability, Rheological Properties and Interfacial Properties of Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions Prepared from Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Cold Plasma-Treated Chickpea Protein Isolate and Myofibrillar Protein Complexes. Foods. 2023; 12(19):3629. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193629
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Dianbo, Yanfang Zhou, Lixue Sun, Jinfeng Tian, Qisen Xiang, and Ke Li. 2023. "The Stability, Rheological Properties and Interfacial Properties of Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions Prepared from Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Cold Plasma-Treated Chickpea Protein Isolate and Myofibrillar Protein Complexes" Foods 12, no. 19: 3629. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193629
APA StyleZhao, D., Zhou, Y., Sun, L., Tian, J., Xiang, Q., & Li, K. (2023). The Stability, Rheological Properties and Interfacial Properties of Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions Prepared from Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Cold Plasma-Treated Chickpea Protein Isolate and Myofibrillar Protein Complexes. Foods, 12(19), 3629. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193629






