The Effect of Heat Treatment on the Digestion and Absorption Properties of Protein in Sea Cucumber Body Wall
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Heat Treatment Program
2.3. The Degree of Protein Oxidation
2.3.1. Free Radical Intensity
2.3.2. Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances Content (TBARS)
2.3.3. Protein Carbonyl Content
2.3.4. Determination of Free Sulfhydryl Groups (SH) and Disulfide Bonds (S–S)
2.3.5. Structural Changes of Water-Soluble Fraction
2.3.6. Protein Surface Hydrophobicity
2.3.7. Protein Aggregation
2.4. In Vitro Simulated Gastrointestinal Tract Digestion
2.4.1. Release of the Primary Free Amino Group
2.4.2. Determination of Trichloroacetic Acid: Soluble Peptide Yield (TCA-Ysp)
2.5. Everted Gut Sac Model
2.5.1. Construction of Everted-Rat-Gut Sacs
2.5.2. Digestion Product Pass across the Rat Gut Wall
2.5.3. Determination of Total Amino Acid Absorption Rate
2.5.4. Determination of Peptide Absorption Rate
2.5.5. Determination of Peptide Content by HPLC-UV Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Oxidative Indicators
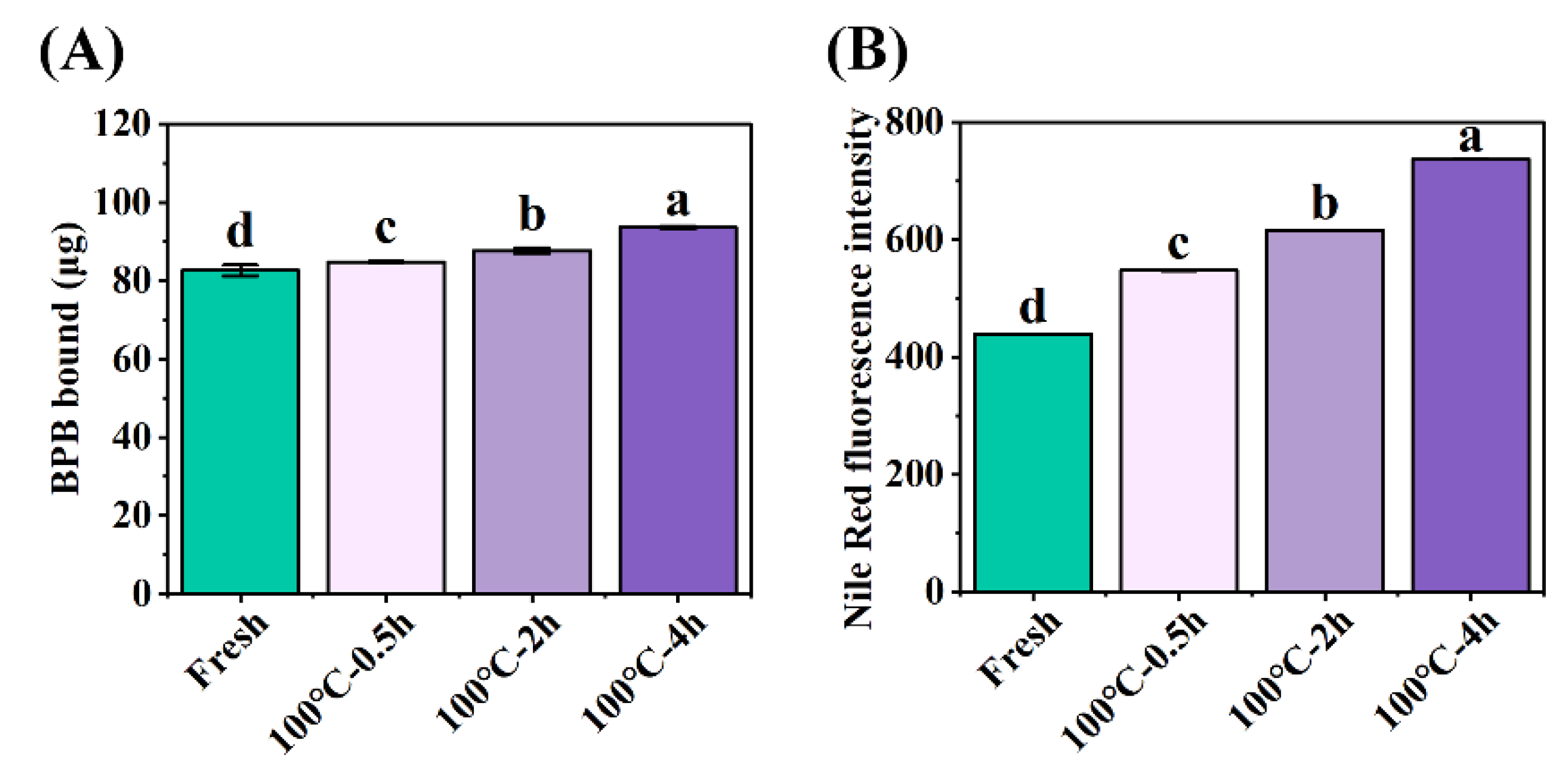
3.2. Structural Modifications of Proteins
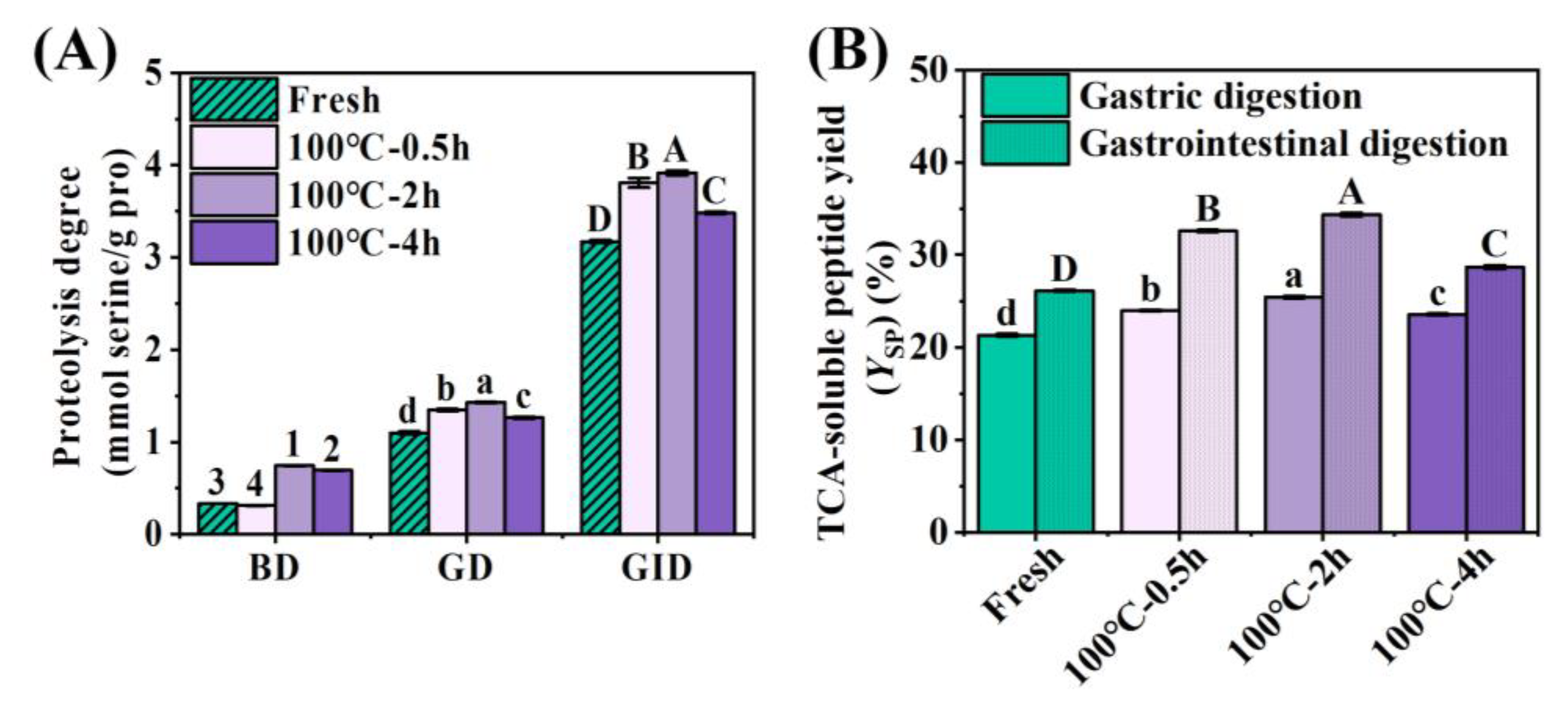
3.3. Protein Digestion Properties of Boiled SCBW
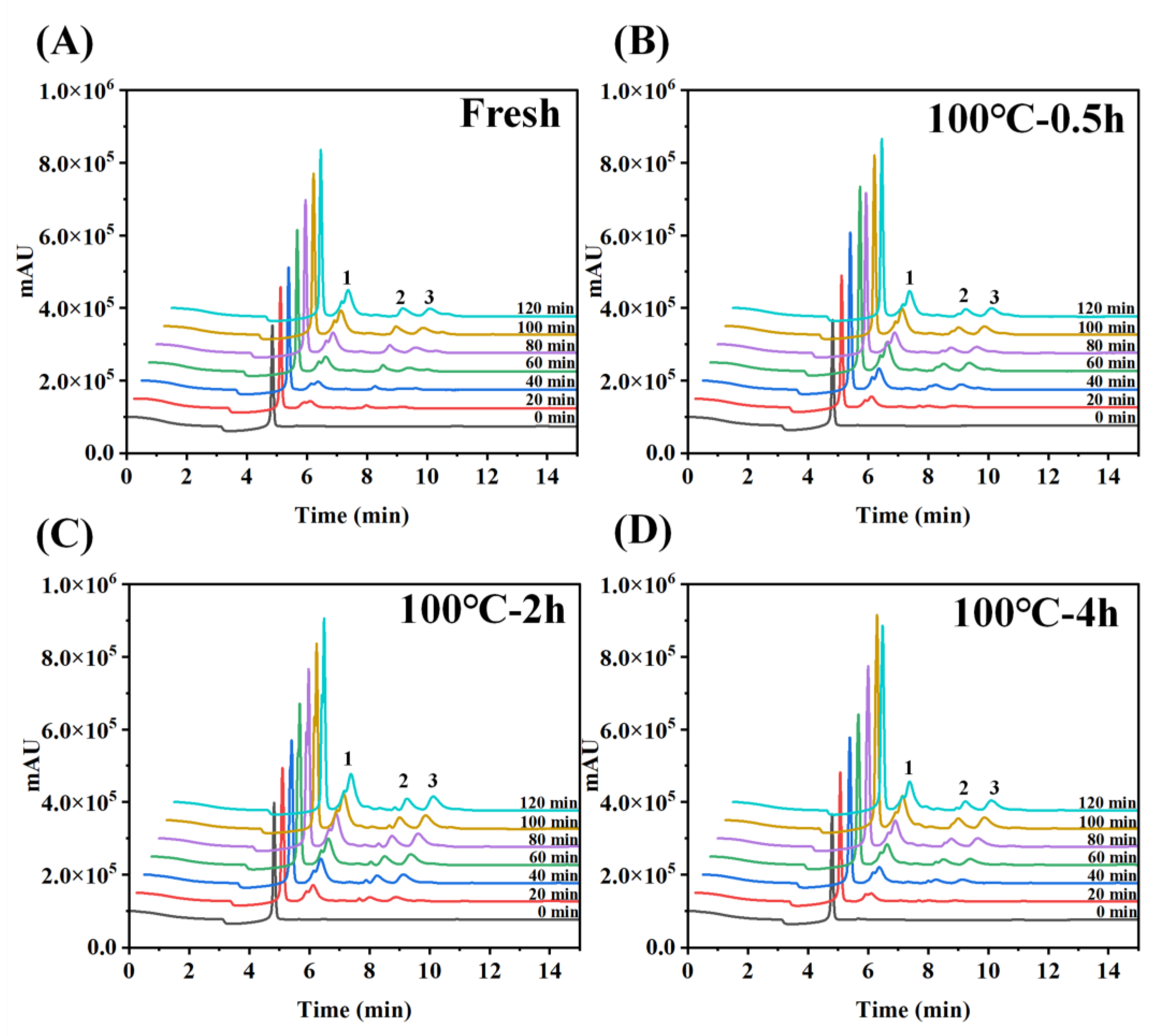
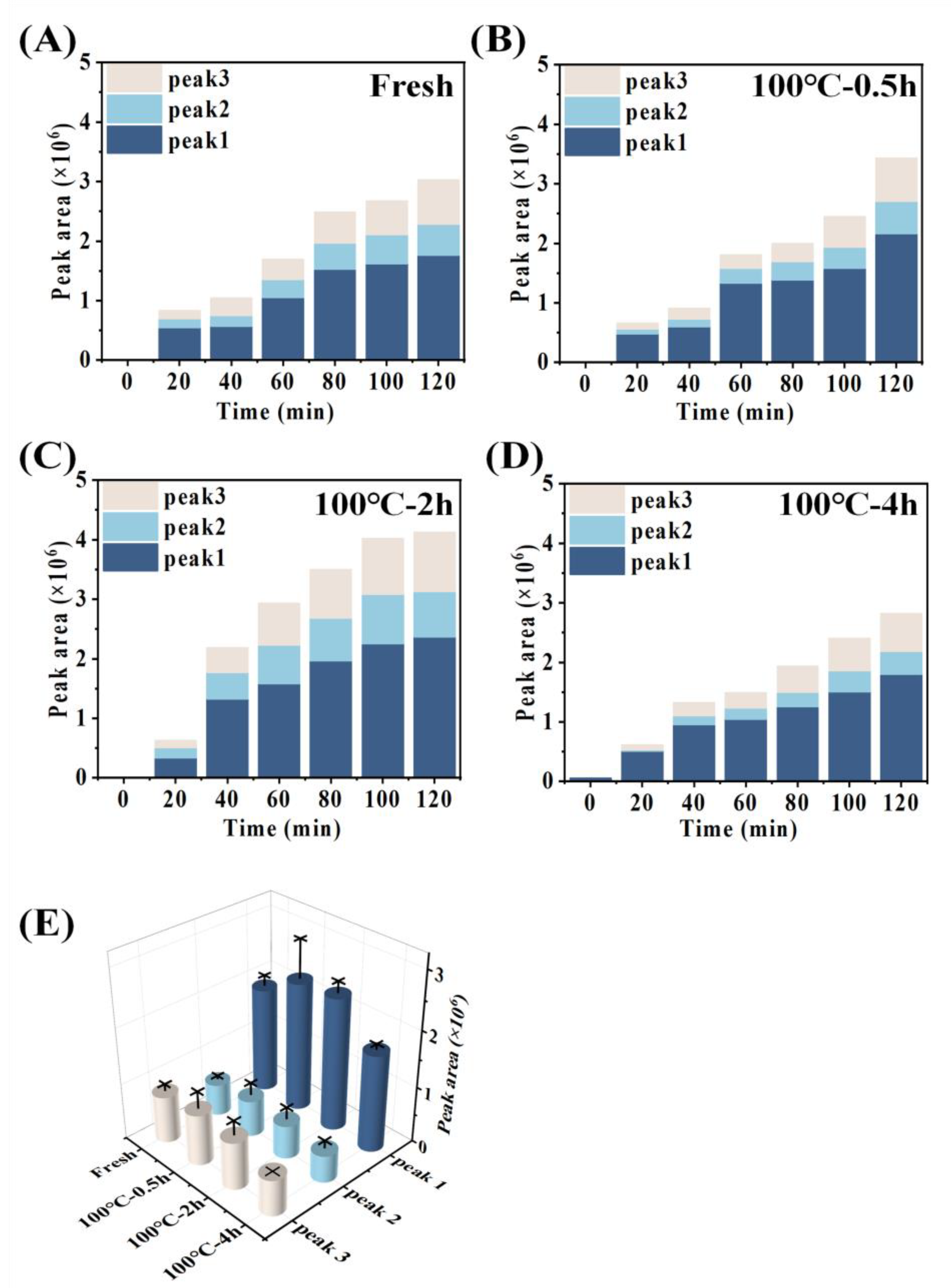
3.4. Absorption Properties Determined by the Everted-Rat-Gut-Sac Model
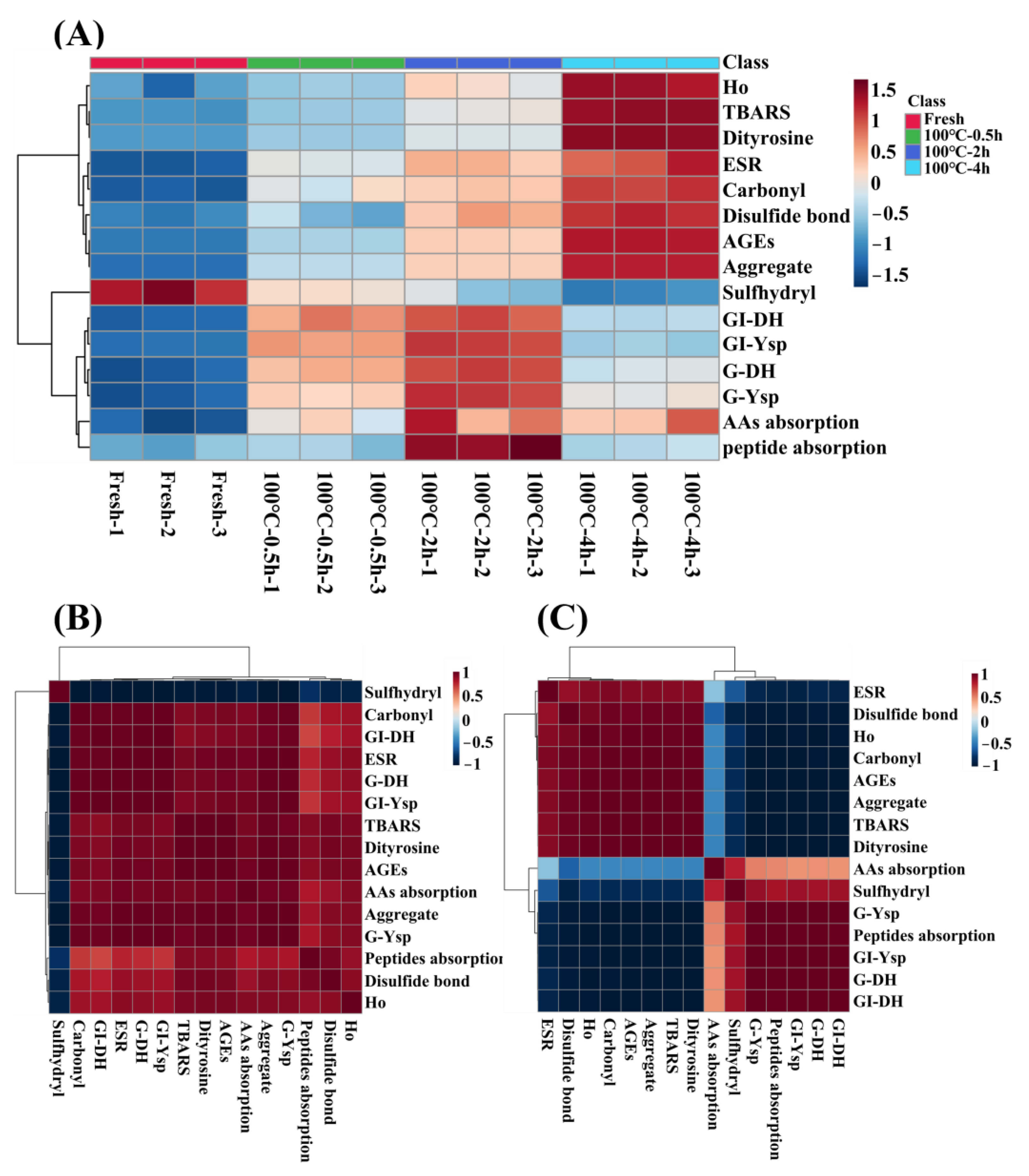
3.5. Heatmap and Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fishery and Fishery Administration Bureau, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sugni, M.; Fassini, D.; Barbaglio, A.; Biressi, A.; Di Benedetto, C.; Tricarico, S.; Bonasoro, F.; Wilkie, I.C.; Candia Carnevali, M.D. Comparing dynamic connective tissue in echinoderms and sponges: Morphological and mechanical aspects and envirometal sensitivity. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 93, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, A.R.; Barbaglio, A.; Benedetto, C.D.; Ribeiro, C.C.; Wilkie, I.C.; Carnevali, M.D.C.; Barbosa, M.A. New Insights into Mutable Collagenous Tissue: Correlations between the Microstructure and Mechanical State of a Sea-Urchin Ligament. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Bekhit, A.E.A.; Kumar, S.; Bhat, H.F. Thermal processing implications on the digestibility of meat, fish and seafood proteins. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4511–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlien, V.; Aalaei, K.; Poojary, M.M.; Nielsen, D.S.; Ahrné, L.; Carrascal, J.R. Effect of processing on in vitro digestibility (IVPD) of food proteins. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 63, 2790–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bax, M.-L.; Aubry, L.; Ferreira, C.; Daudin, J.-D.; Gatellier, P.; Rémond, D.; Santé-Lhoutellier, V. Cooking Temperature Is a Key Determinant of in Vitro Meat Protein Digestion Rate: Investigation of Underlying Mechanisms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2569–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, B.; Rinnan, A.; Ruiz-Carrascal, J. Tracking hydrophobicity state, aggregation behaviour and structural modifications of pork proteins under the influence of assorted heat treatments. Food Res. Int. 2017, 101, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santé-Lhoutellier, V.; Astruc, T.; Marinova, P.; Greve, E.; Gatellier, P. Effect of Meat Cooking on Physicochemical State and in Vitro Digestibility of Myofibrillar Proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promeyrat, A.; Gatellier, P.; Lebret, B.; Kajak-Siemaszko, K.; Aubry, L.; Santé-Lhoutellier, V. Evaluation of protein aggregation in cooked meat. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sante-Lhoutellier, V.; Aubry, L.; Gatellier, P. Effect of Oxidation on In Vitro Digestibility of Skeletal Muscle Myofibrillar Proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5343–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Kumar, S.; Bhat, H.F. Emerging processing technologies for improved digestibility of muscle proteins. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Zhou, G.; Li, L.; Xu, X.; Yu, X.; Bai, Y.; Li, C. Effect of Cooking on in Vitro Digestion of Pork Proteins: A Peptidomic Perspective. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 63, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, S.; Wang, C.; Kim, Y.H.B.; Bian, G.; Han, M.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Application of high-pressure treatment improves the in vitro protein digestibility of gel-based meat product. Food Chem. 2020, 306, 125602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Tian, L.; Jiao, Y.; Tan, Y.; Liu, C.; Luo, Y.; Hong, H. The effect of steam cooking on the proteolysis of pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) proteins: Digestibility, allergenicity, and bioactivity. Food Chem. 2022, 379, 132160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.-X.; Zhao, G.-H.; Song, L.; Wu, Z.-X.; Jiang, P.-F.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Zhu, B.-W. Studying on effects of boiling on texture, microstructure and physiochemical properties of sea cucumber body wall and its mechanism using second harmonic generation (SHG) microscopy. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 134055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-Q.; Li, D.-Y.; Song, L.; Liu, Y.-X.; Yu, M.-M.; Zhang, M.; Rakariyatham, K.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Shahidi, F. Effects of proteolysis and oxidation on mechanical properties of sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus) during thermal processing and storage and their control. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Zhou, D.; Hu, X.; Liu, Z.; Song, L.; Zhu, B.-W. Changes in Lipid Profiles of Dried Clams (Mactra chinensis Philippi and Ruditapes philippinarum) during Accelerated Storage and Prediction of Shelf Life. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7764–7774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; True, A.D.; Chen, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Dual Role (Anti- and Pro-oxidant) of Gallic Acid in Mediating Myofibrillar Protein Gelation and Gel in Vitro Digestion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, P.J.; Williams, S.C. Protein modification by thermal processing. Allergy 1998, 53, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-N.; Shang, W.-H.; Zhao, J.; Han, J.-R.; Jin, W.-G.; Wang, H.-T.; Du, Y.-N.; Wu, H.-T.; Janaswamy, S.; Xiong, Y.L.; et al. Gelation and microstructural properties of protein hydrolysates from trypsin-treated male gonad of scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) modified by κ-Carrageenan/K+. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 91, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiacevich, S.B.; Buera, M.P. A critical evaluation of fluorescence as a potential marker for the Maillard reaction. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelh, I.; Gatellier, P.; Santé-Lhoutellier, V. Technical note: A simplified procedure for myofibril hydrophobicity determination. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carriere, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A standardized static in vitro digestion method suitable for food-an international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, P.M.; Petersen, D.; Dambmann, C. Improved Method for Determining Food Protein Degree of Hydrolysis. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhao, M.; Sun, W. Effect of protein oxidation on the in vitro digestibility of soy protein isolate. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3224–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Hu, X.; Zhou, D.; Ma, X.; Tian, X.; Huo, X.; Rakariyatham, K.; Shahidi, F.; Zhu, B. Hydrolysis and Transport Characteristics of Tyrosol Acyl Esters in Rat Intestine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12521–12526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Standard GB/T5009; 124. Determination of Amino Acids in Foods. China Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Yu, M.-M.; Fan, Y.-C.; Li, D.-Y.; Liu, Y.-X.; Jiang, P.-F.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Zhu, B.-W. Differences in texture and digestive properties of different parts in boiled abalone muscles. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-X.; Fan, Y.-C.; Guo, C.; Liu, Y.-X.; Li, D.-Y.; Jiang, P.-F.; Qin, L.; Bai, Y.-H.; Zhou, D.-Y. Effects of Boiling Processing on Texture of Scallop Adductor Muscle and Its Mechanism. Foods. 2022, 11, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.M.; Jess, T.J.; Price, N.C. How to study proteins by circular dichroism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2005, 1751, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Hang, F.; Wei, T.; Xie, C.; Niu, D. Modification of Ovalbumin by Maillard Reaction: Effect of Heating Temperature and Different Monosaccharides. Front Nutr. 2022, 9, 914416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, J.; Raghavan, V. Impact of microwave processing on the secondary structure, in-vitro protein digestibility and allergenicity of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) proteins. Food Chem. 2020, 337, 127811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Du, X.; Wang, B.; Pan, N.; Xia, X.; Bao, Y. Inhibiting effect of ice structuring protein on the decreased gelling properties of protein from quick-frozen pork patty subjected to frozen storage. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenker, H.E.; van Lieshout, G.A.A.; van Gool, M.P.; Bragt, M.C.E.; Hettinga, K.A. Lysine blockage of milk proteins in infant formula impairs overall protein digestibility and peptide release. Food Funct. 2019, 11, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketnawa, S.; Ogawa, Y. In vitro protein digestibility and biochemical characteristics of soaked, boiled and fermented soybeans. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassompierre, M.; Børresen, T.; Sandfeld, P.; Rønsholdt, B.; Zimmermann, W.; McLean, E. An evaluation of open and closed systems for in vitro protein digestion of fish meal. Aquac. Nutr. 1997, 3, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, D.; Zhu, S.; Nian, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Li, C. Overheating induced structural changes of type I collagen and impaired the protein digestibility. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, L.; Maudens, E.; Haisman, D.R.; Boland, M.J.; Singh, H. Microstructure and protein digestibility of beef: The effect of cooking conditions as used in stews and curries. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Álvarez-Olguín, M.; Beltrán-Barrientos, L.M.; Hernandez-Mendoza, A.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B. Current trends and perspectives on bioaccessibility and bioavailability of food bioactive peptides: In vitro and ex vivo studies. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 6824–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moughan, P.J. Protein: Digestion, Absorption and Metabolism. “Encyclopedia of Food and Health.”; Massey University: Palmerston North, New Zealand, 2016; pp. 524–529. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Feng, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, R.; Zeng, M. Effects of cooking methods on the Maillard reaction products, digestibility, and mineral bioaccessibility of Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 141, 110943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| % | Fresh | 100 °C for 0.5 h | 100 °C for 2 h | 100 °C for 4 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-helix | 37.50 ± 3.25 a | 28.10 ± 5.52 b | 7.33 ± 1.11 c | 0.27 ± 0.25 d |
| β-sheet | 18.87 ± 6.30 c | 39.40 ± 8.79 b | 52.83 ± 1.11 c | 55.17 ± 0.80 a |
| β-turn | 15.53 ± 0.76 a | 4.23 ± 2.37 b | 3.07 ± 2.45 b | 3.13 ± 0.72 c |
| random coil | 28.13 ± 2.44 a | 28.27 ± 2.80 a | 36.80 ± 2.17 b | 41.7 ± 1.37 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Jin, M.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, P.; Zhou, D. The Effect of Heat Treatment on the Digestion and Absorption Properties of Protein in Sea Cucumber Body Wall. Foods 2023, 12, 2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152896
Zhang M, Liu Y, Jin M, Li D, Wang Z, Jiang P, Zhou D. The Effect of Heat Treatment on the Digestion and Absorption Properties of Protein in Sea Cucumber Body Wall. Foods. 2023; 12(15):2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152896
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Min, Yuxin Liu, Mengling Jin, Deyang Li, Ziye Wang, Pengfei Jiang, and Dayong Zhou. 2023. "The Effect of Heat Treatment on the Digestion and Absorption Properties of Protein in Sea Cucumber Body Wall" Foods 12, no. 15: 2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152896
APA StyleZhang, M., Liu, Y., Jin, M., Li, D., Wang, Z., Jiang, P., & Zhou, D. (2023). The Effect of Heat Treatment on the Digestion and Absorption Properties of Protein in Sea Cucumber Body Wall. Foods, 12(15), 2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152896






