Effect of Thermoresponsive Xyloglucan on the Bread-Making Properties and Preservation of Gluten-Free Rice-Flour Bread
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Polysaccharide Thickener Solutions
2.2.2. Bread
2.3. Powder Characteristics of Rice Flour
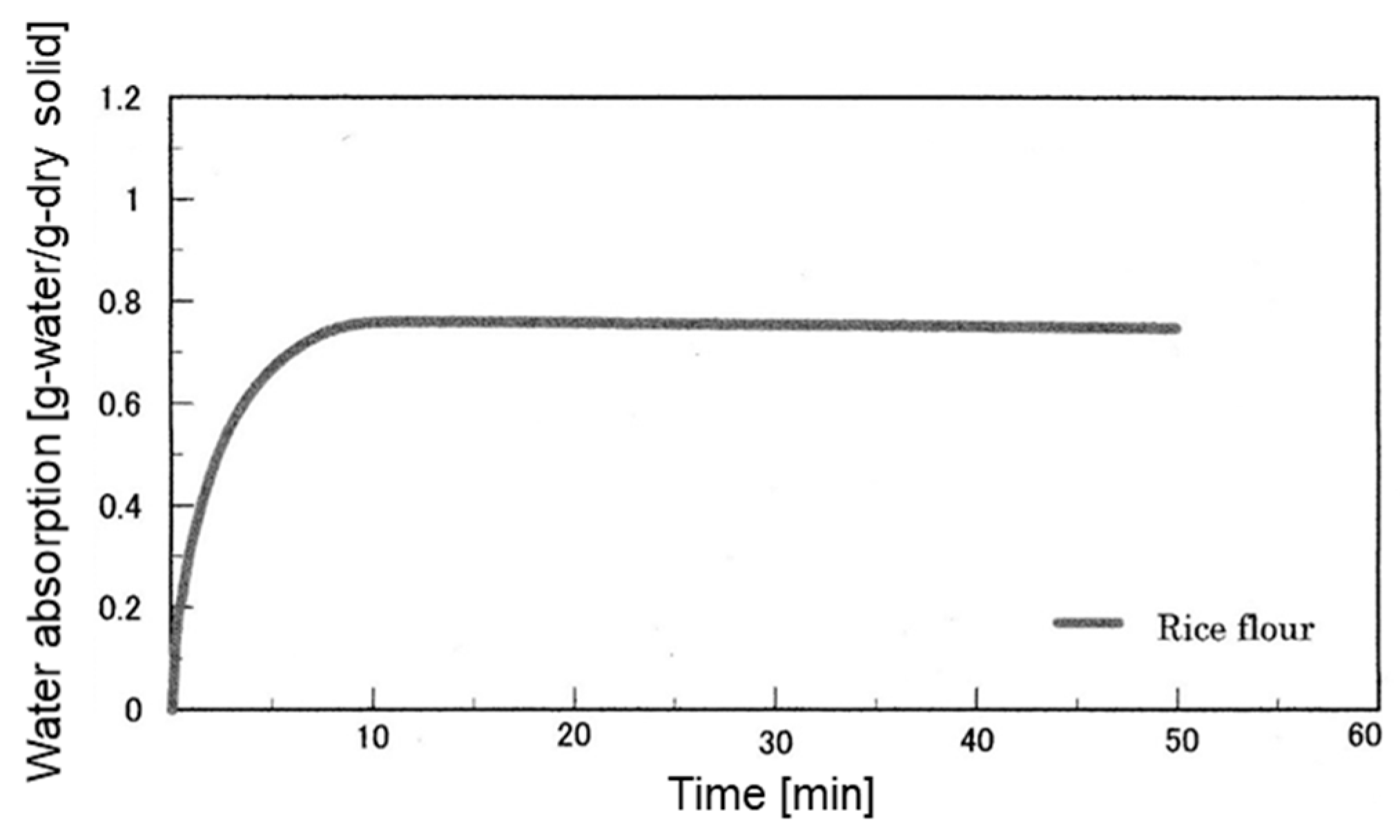
2.3.1. Water Absorption Characteristics
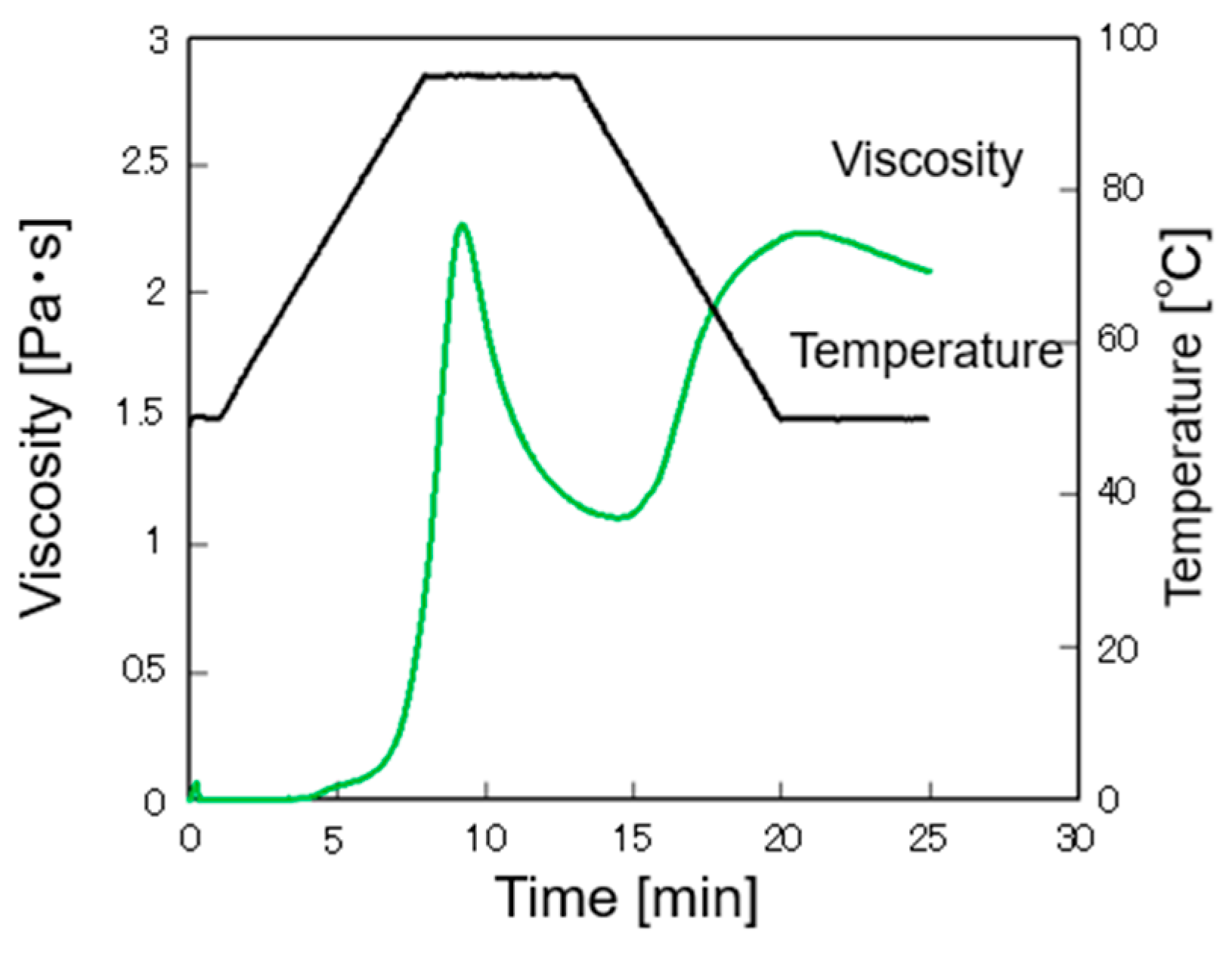
2.3.2. Gelatinization Characteristics
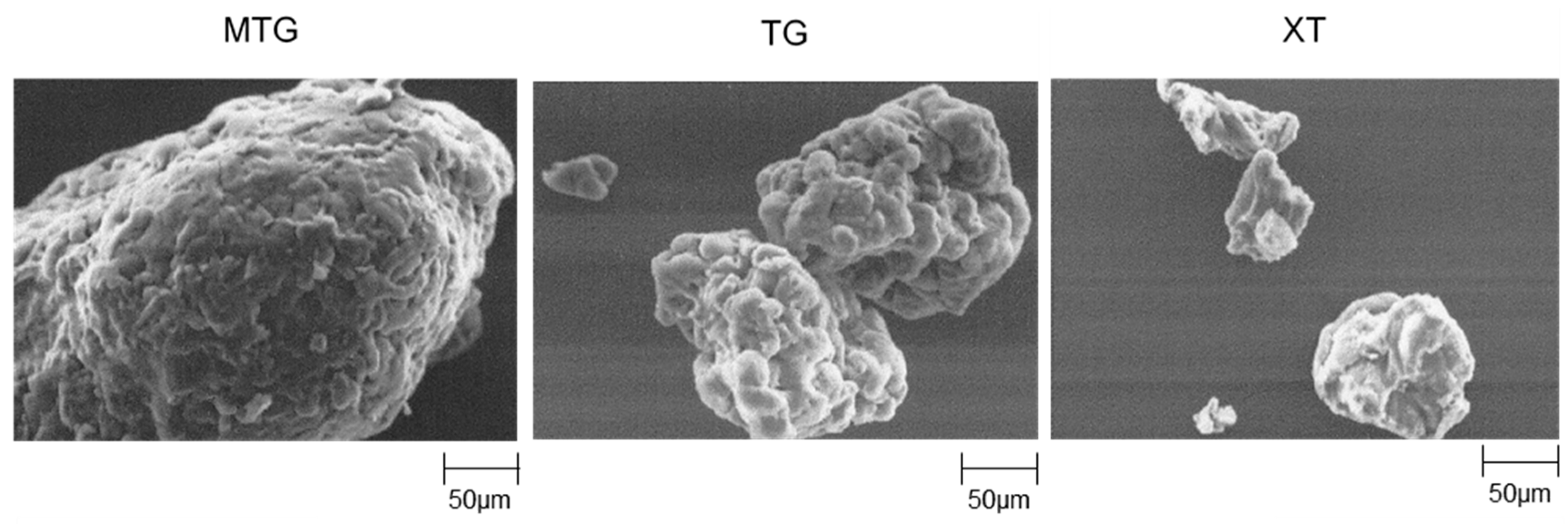
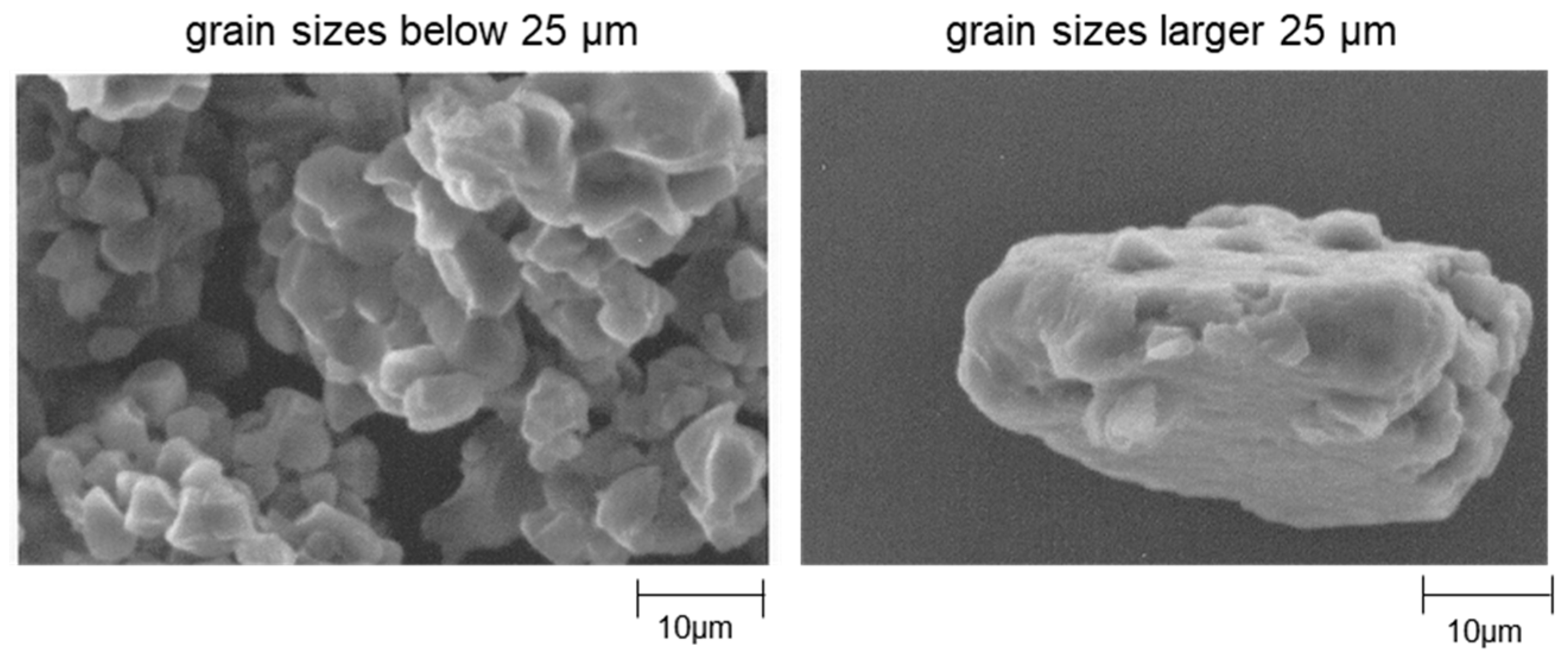
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.4. Batter Characteristics
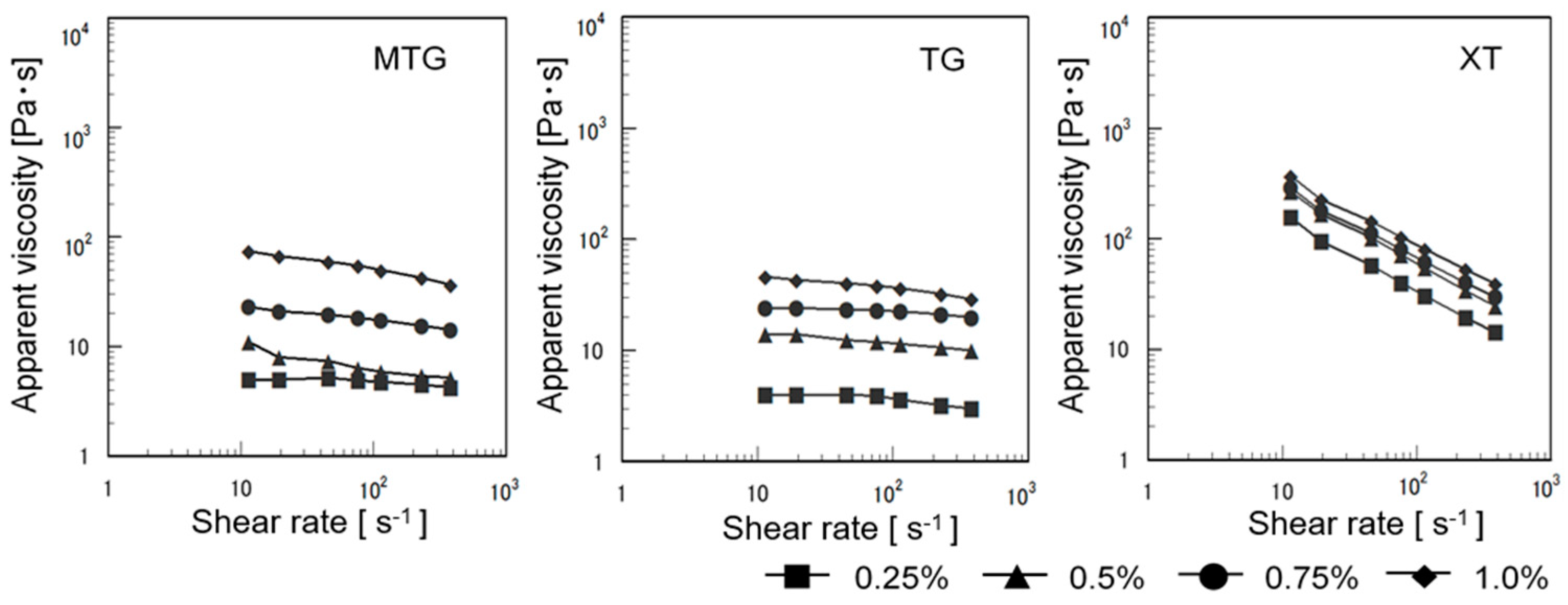
2.4.1. Flow Characteristics (Apparent Viscosity)
2.4.2. Dynamic Viscoelasticity
2.5. Bread Characteristics
2.5.1. Specific Volume
2.5.2. Moisture Content of Bread
2.5.3. Mechanical Properties of Bread
2.5.4. Bread Color
2.5.5. Sensory Evaluation
2.5.6. Retrogradation Characteristics of Bread
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Ethical Considerations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Absorption Characteristics
3.2. Gelatinization Characteristics
3.3. Scanning Electron Micrographs
3.4. Properties of Polysaccharide Thickener Solutions
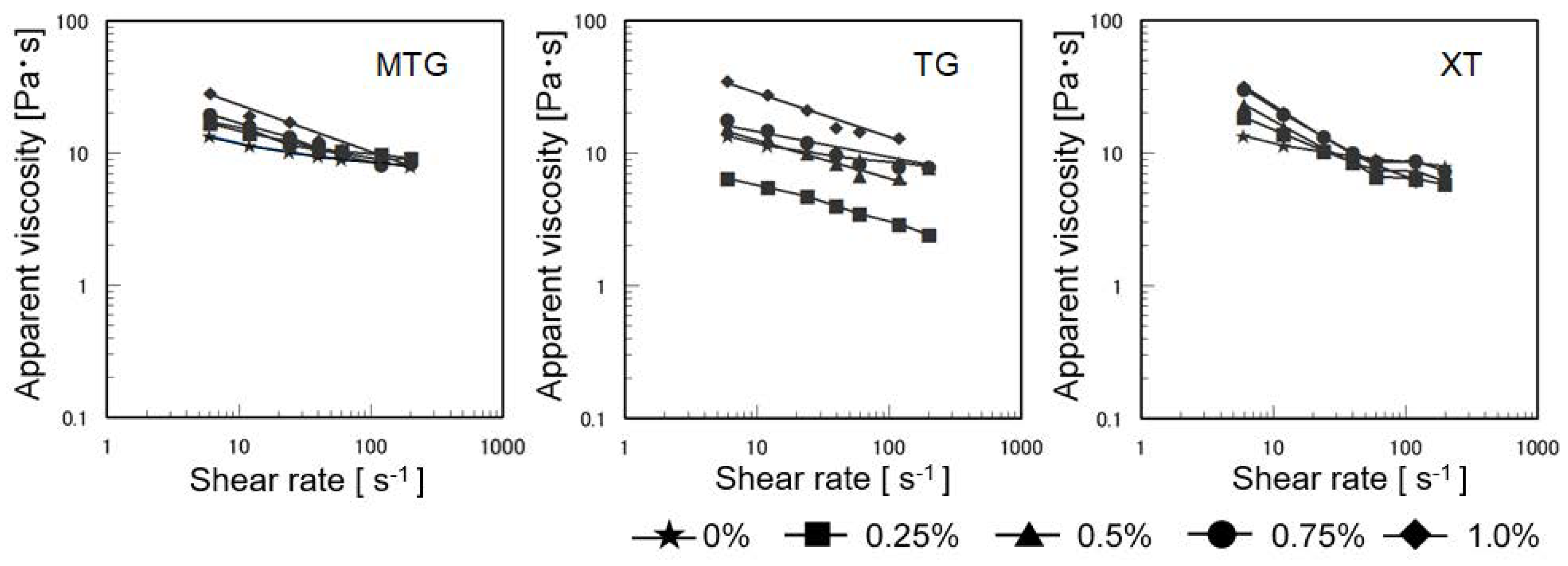
3.4.1. Flow Characteristics
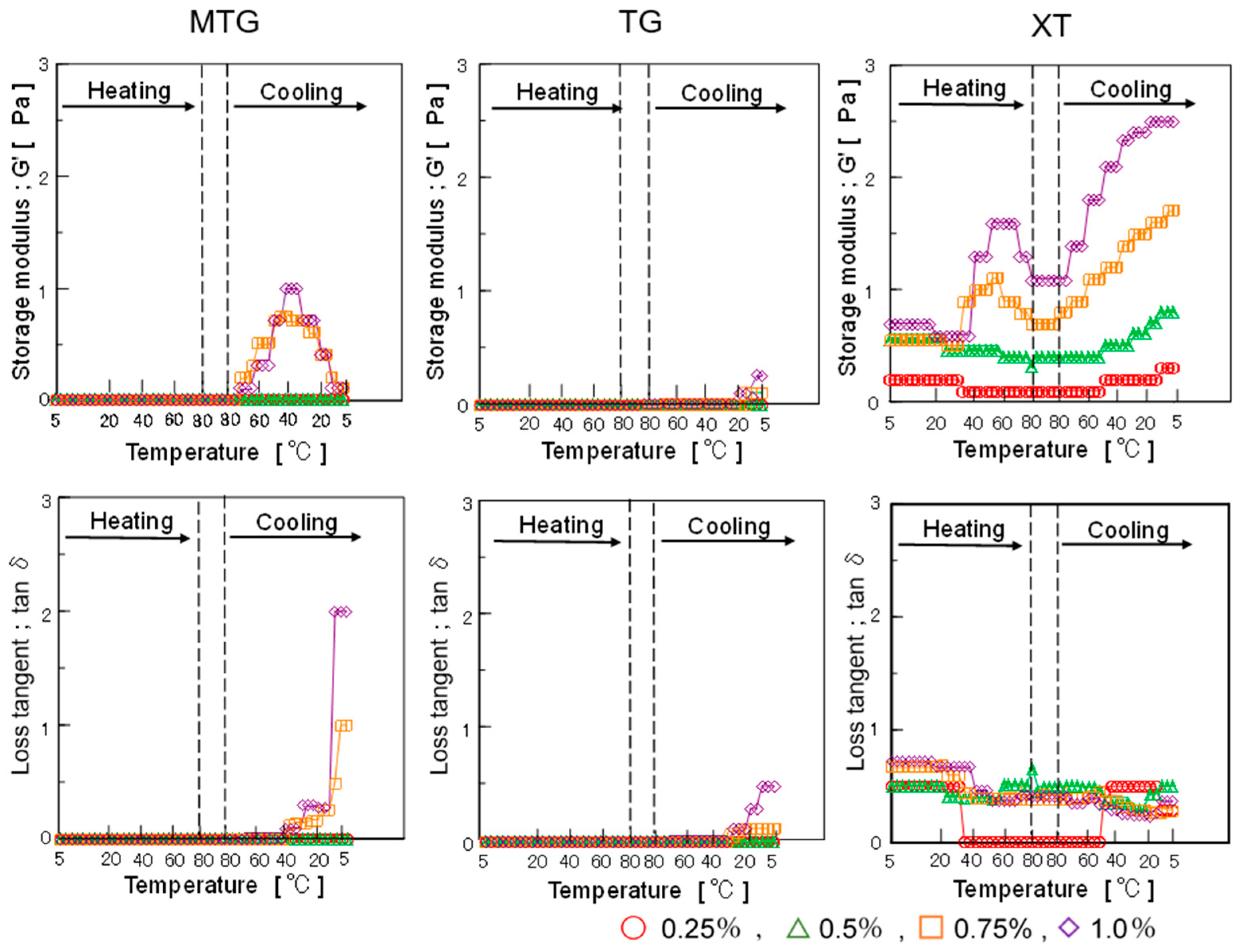
3.4.2. Dynamic Viscoelasticity
3.5. Batter Characteristics
3.5.1. Flow Characteristics
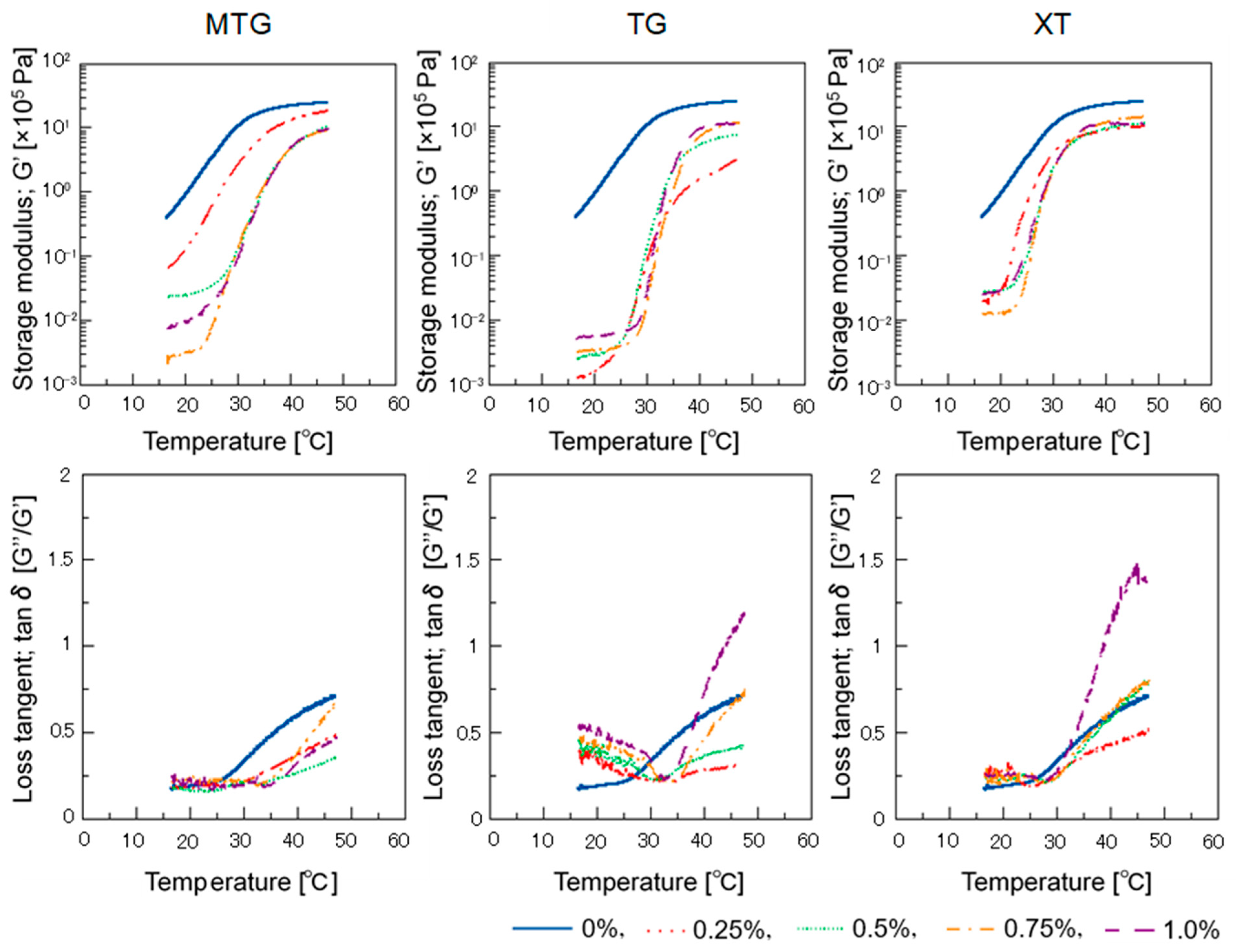
3.5.2. Dynamic Viscoelasticity
3.6. Bread-Making Properties
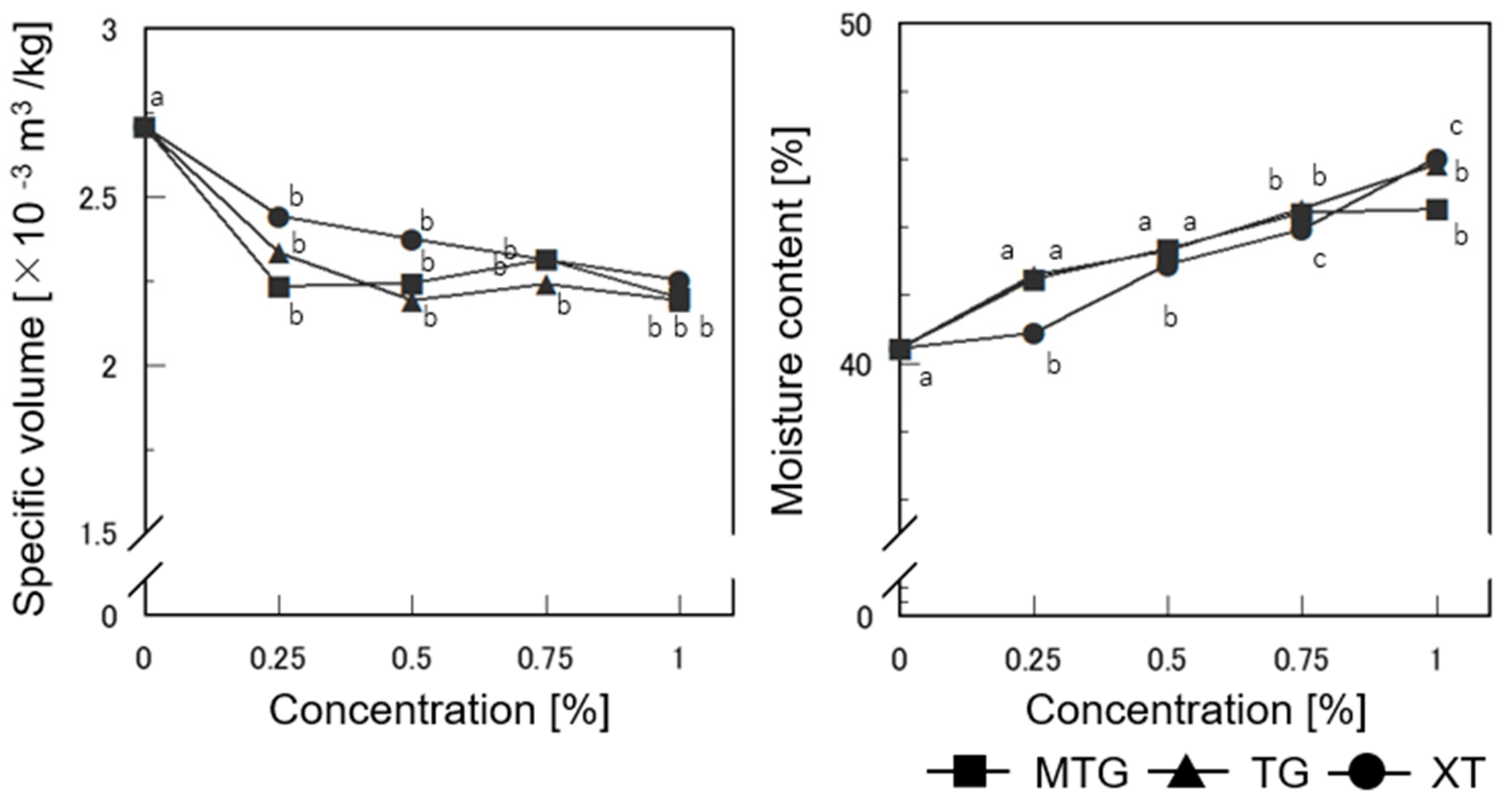
3.6.1. Specific Volume and Moisture Content of Bread
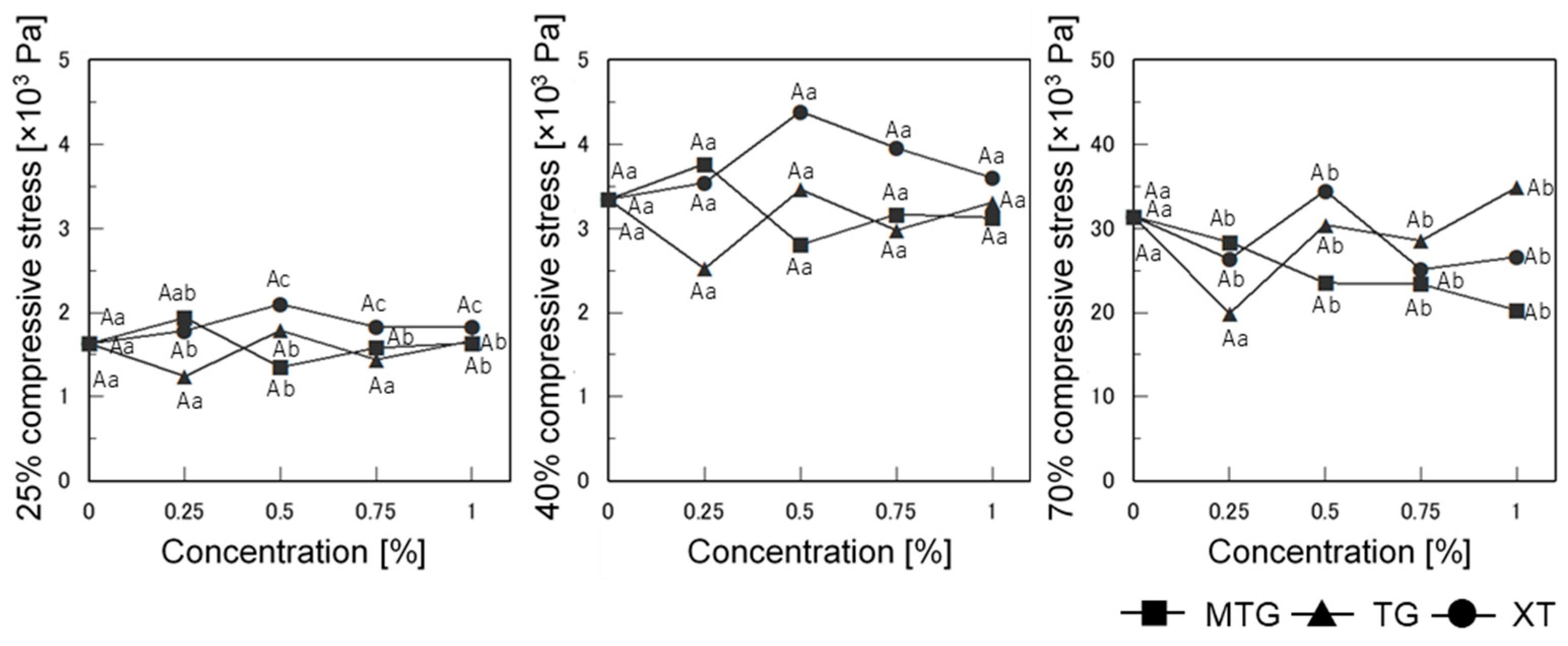
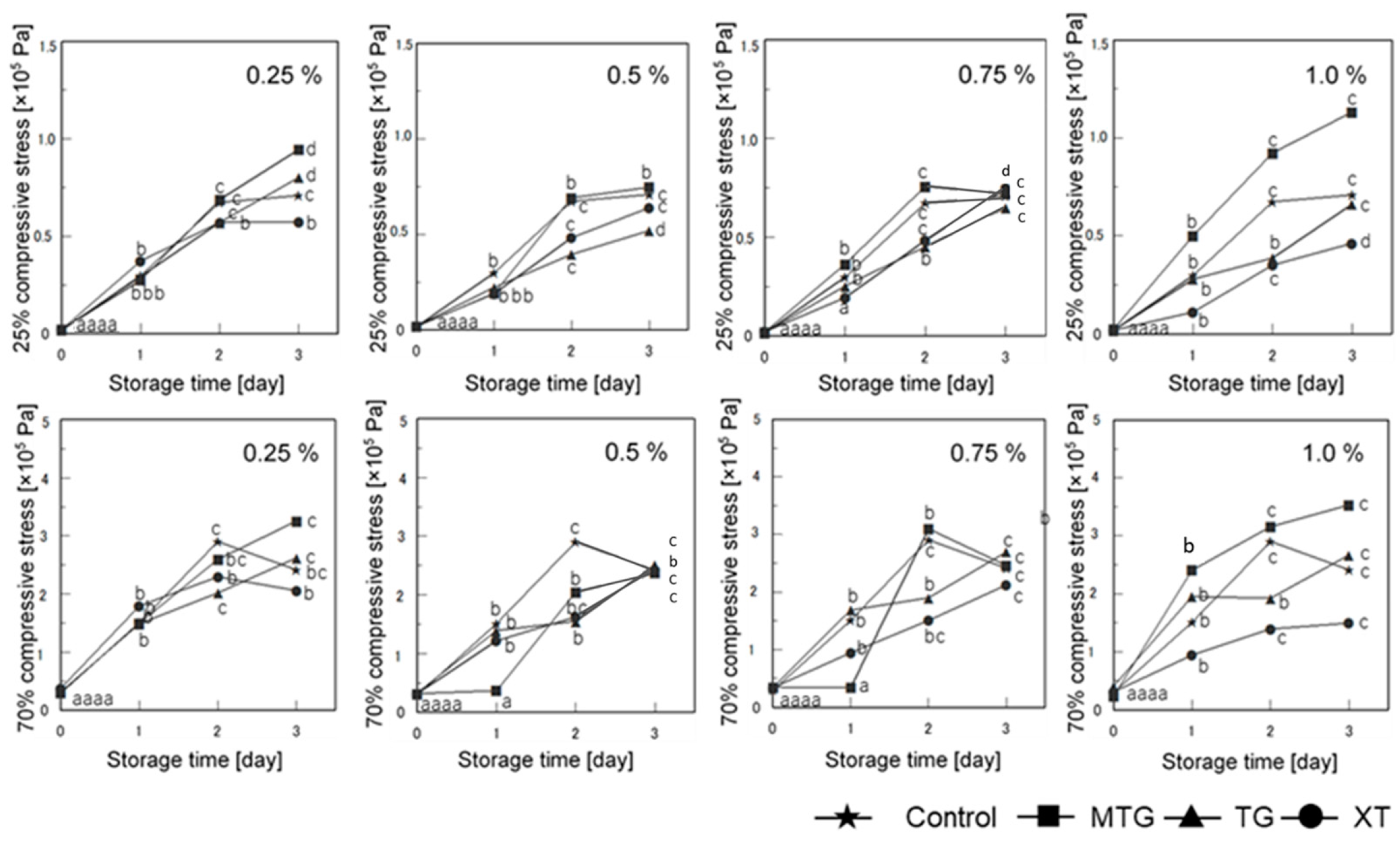
3.6.2. Mechanical Properties of Bread
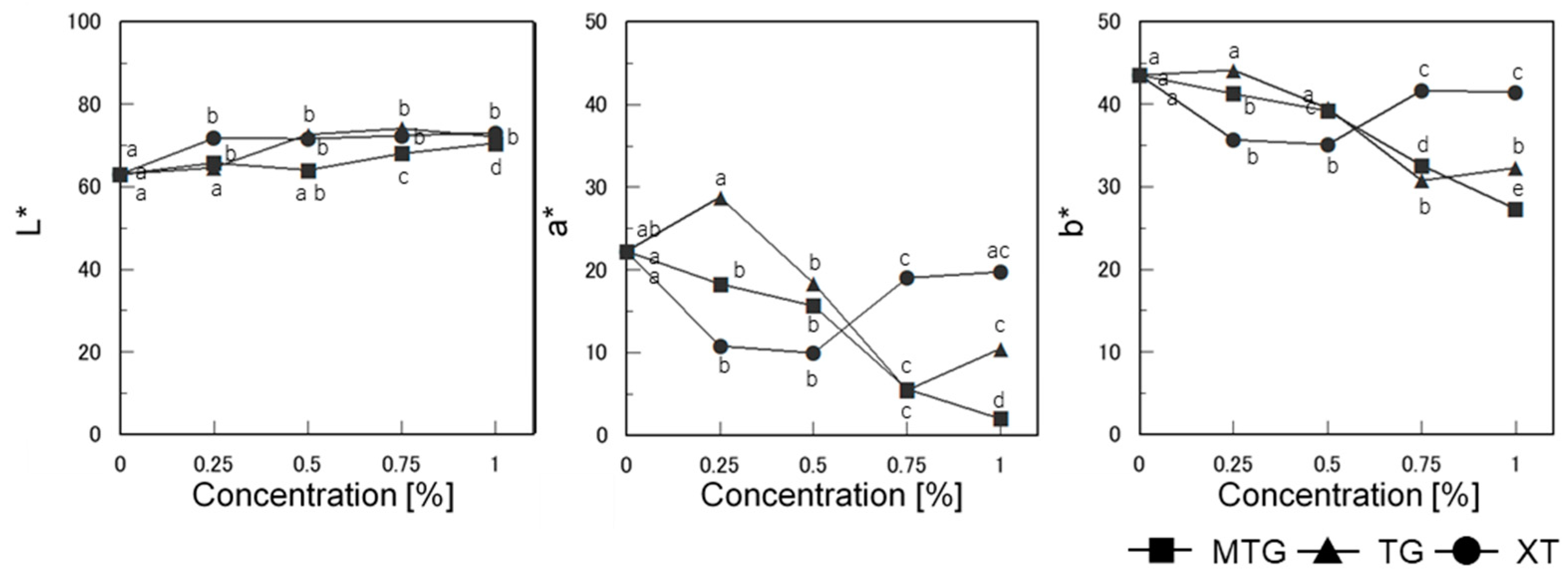
3.6.3. Bread Color
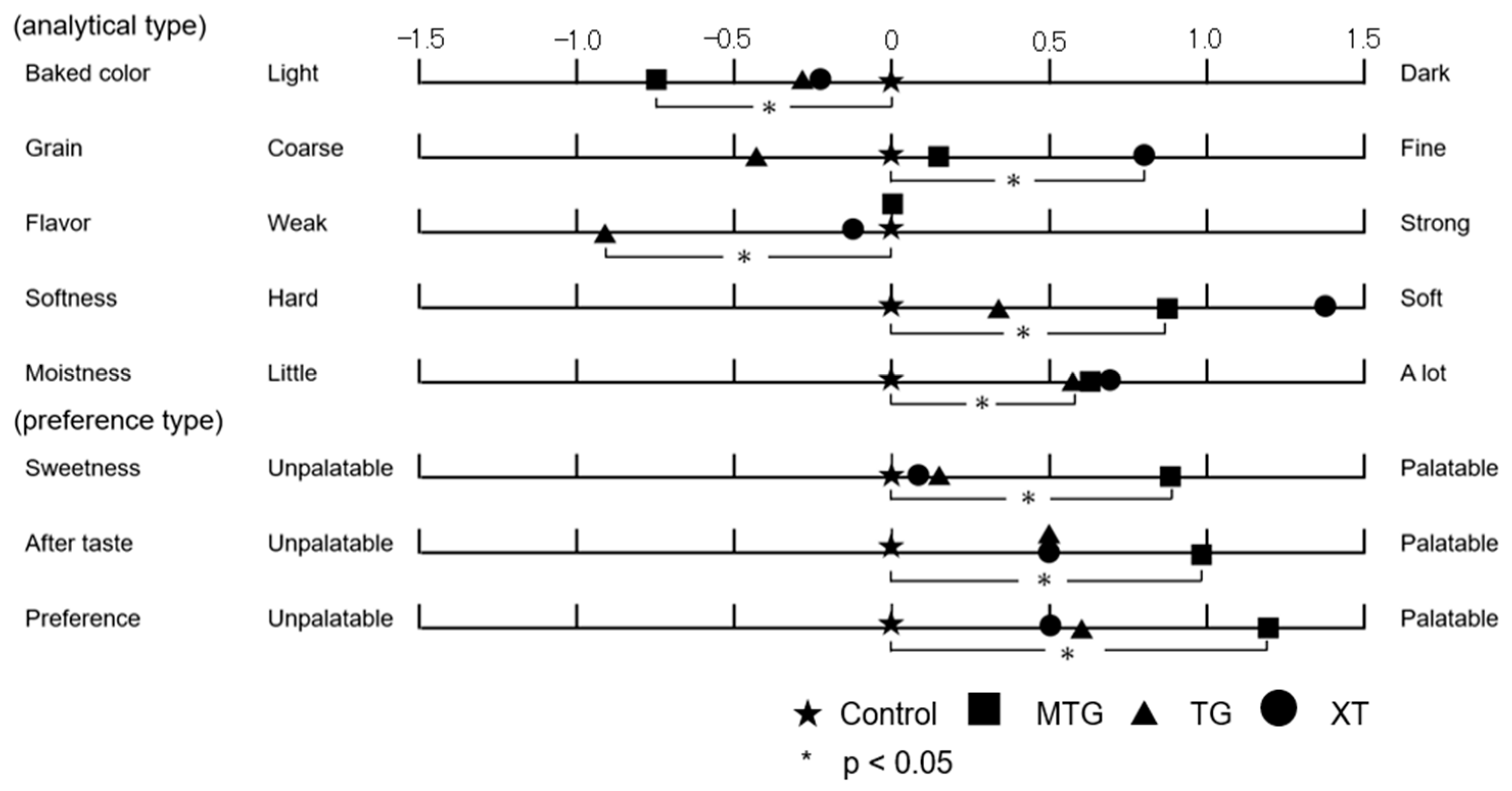
3.6.4. Sensory Evaluation
3.7. Preservation of Gluten-Free Rice-Flour Bread
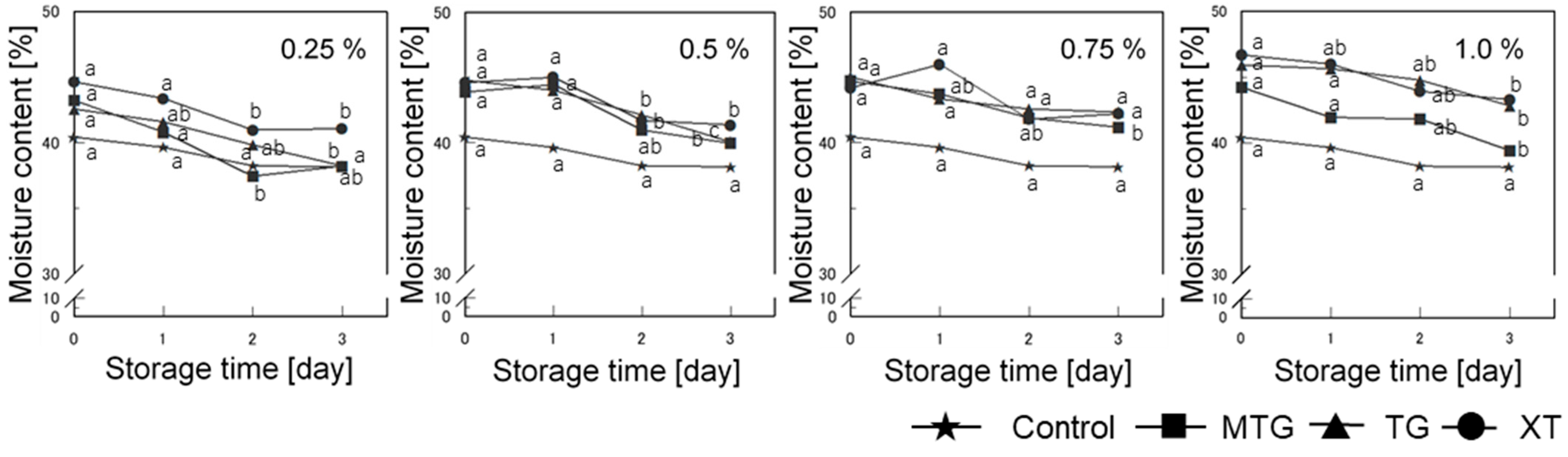
3.7.1. Moisture Content
3.7.2. Mechanical Properties
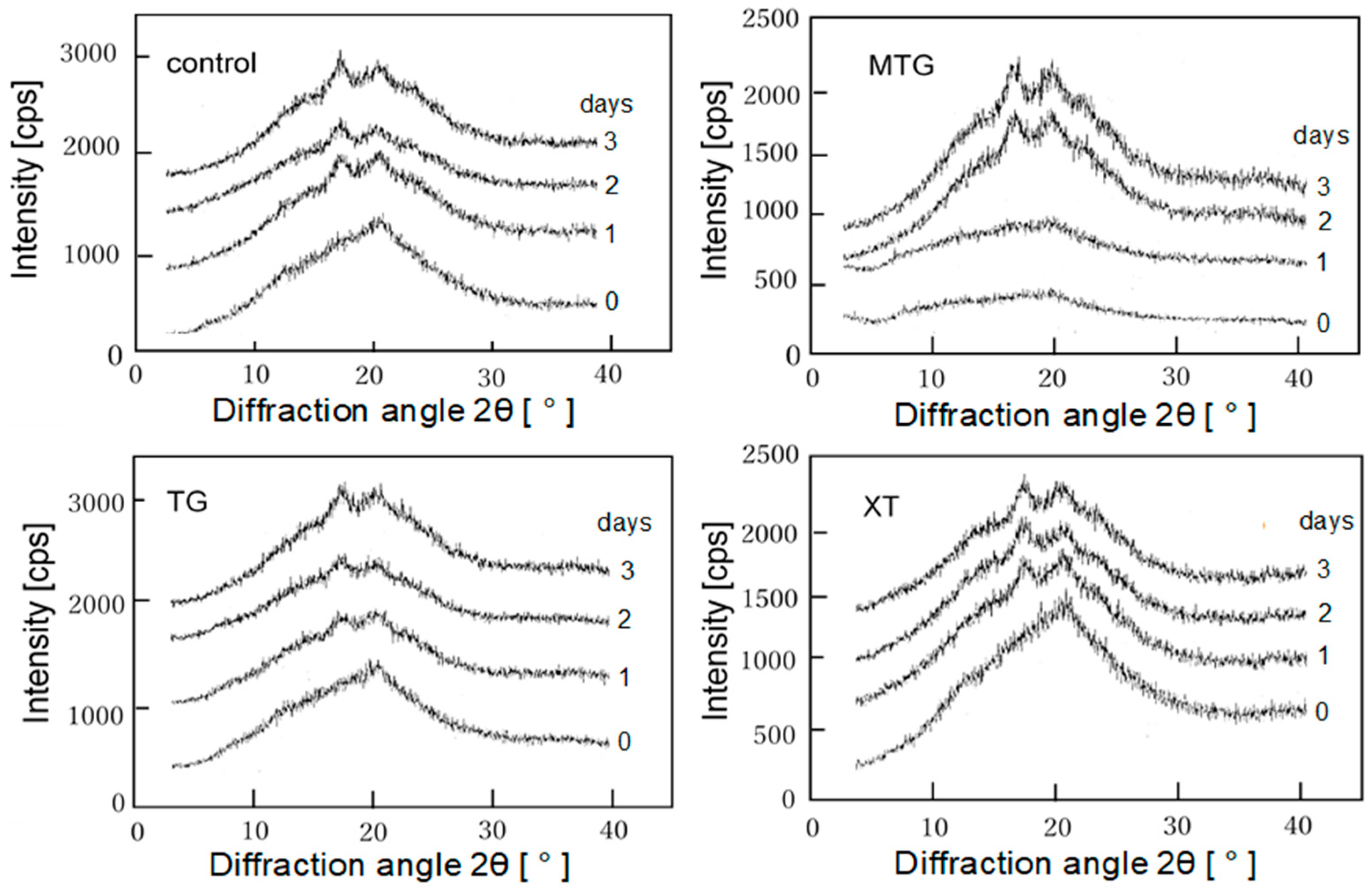
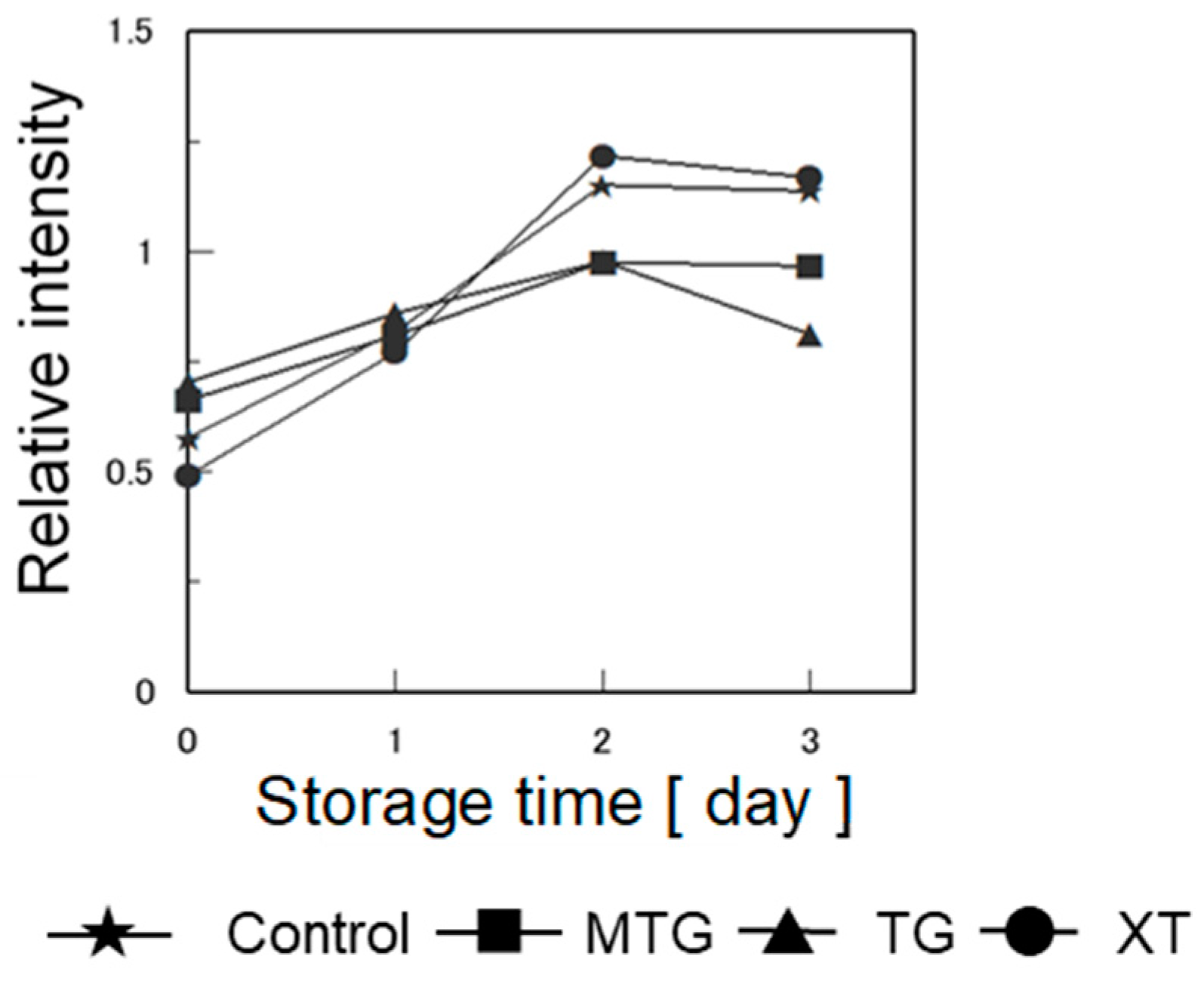
3.7.3. Retrogradation Characteristics of Bread
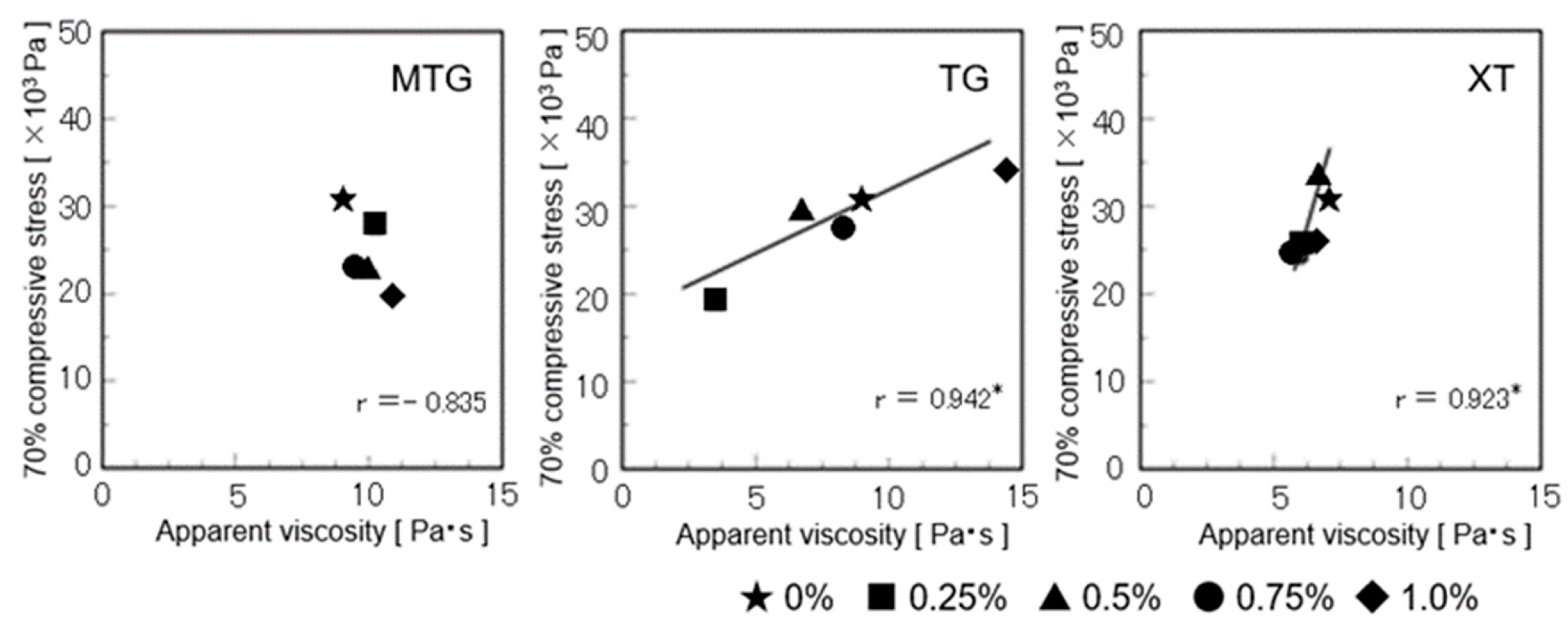
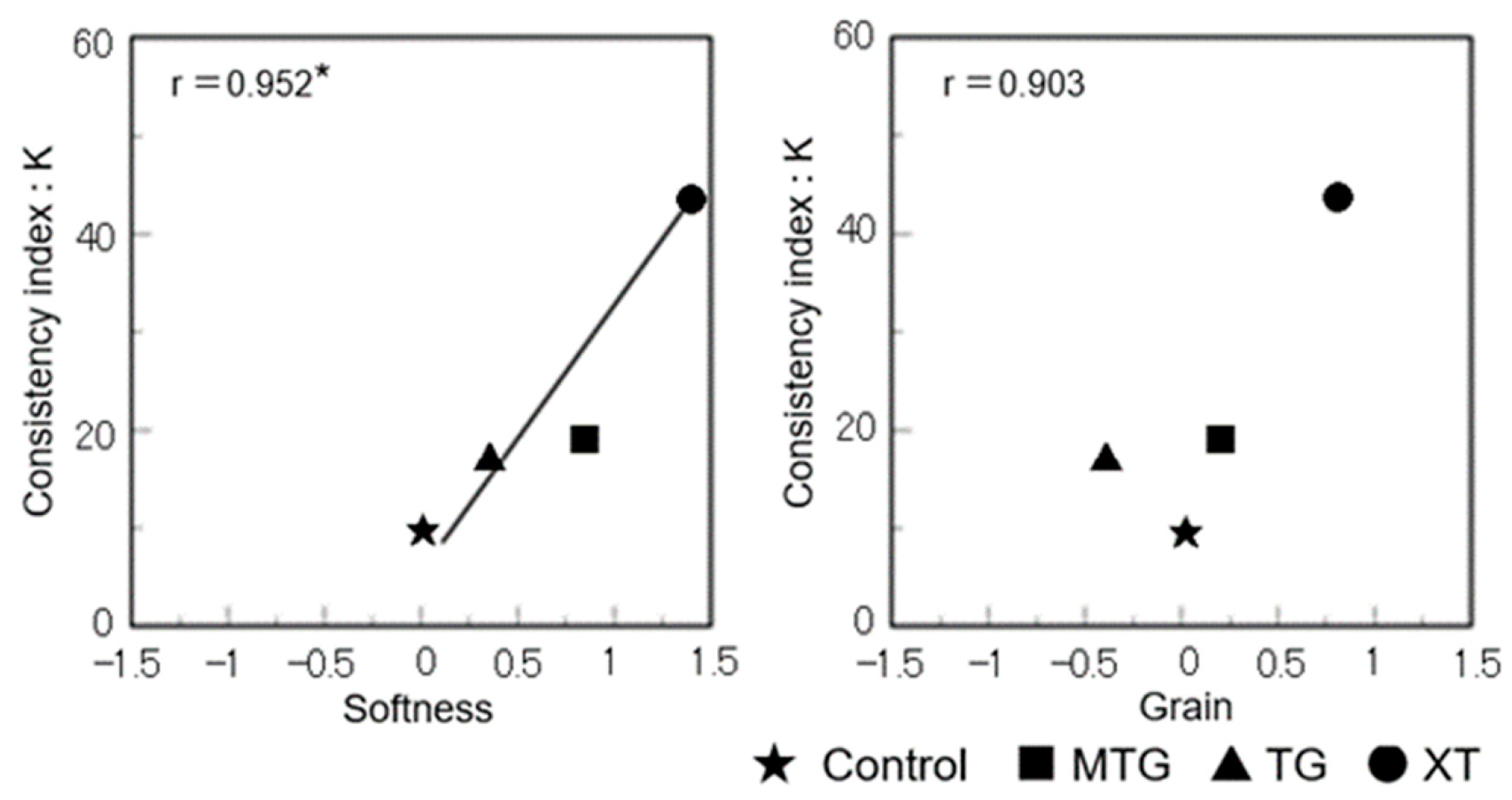
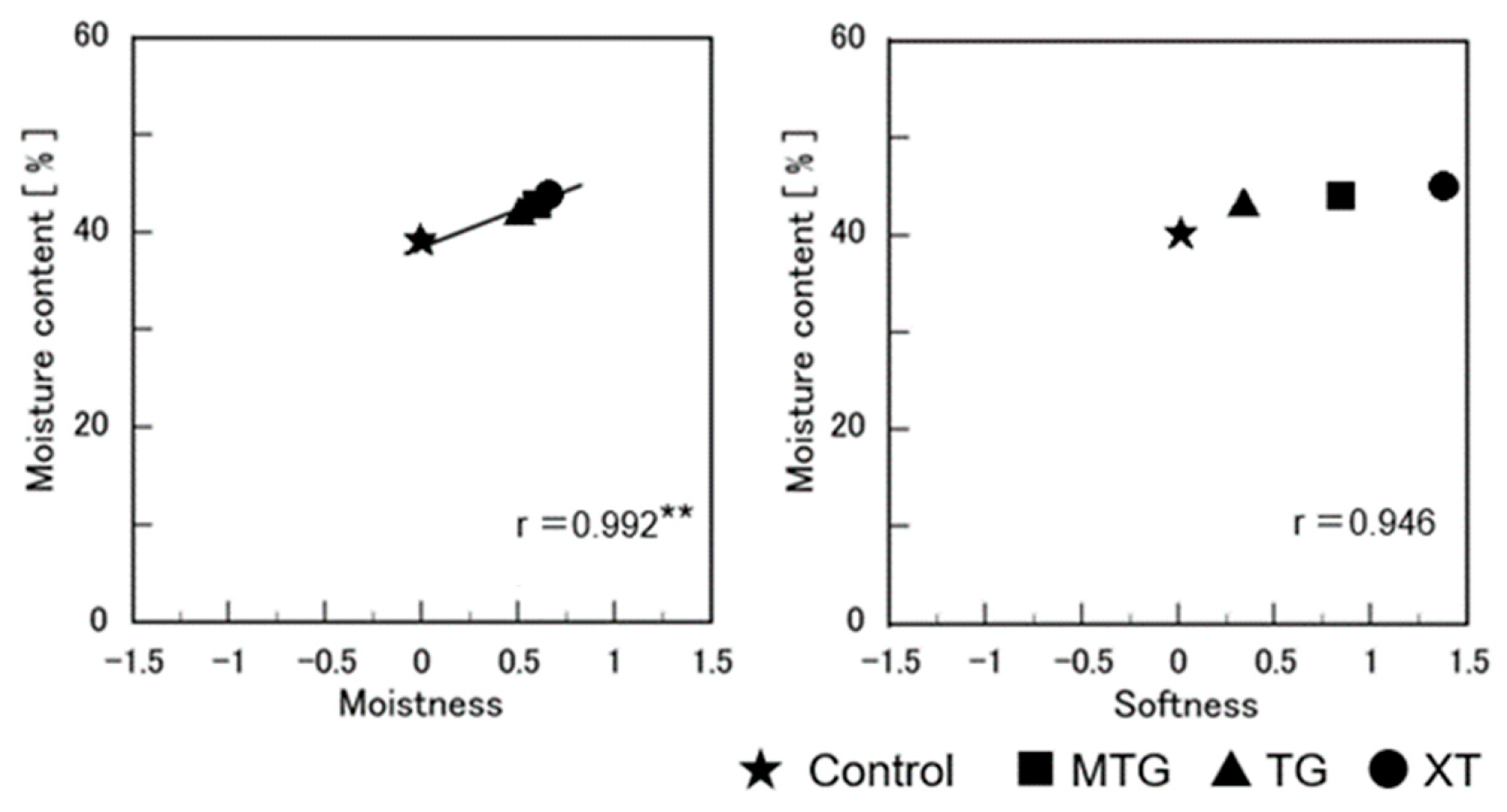
3.8. Relationship between the Objective Characteristic Values and Sensory Evaluation Values of Gluten-Free Rice-Flour Bread
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Japan’s Food Self-Sufficiency Rate in 2020. Available online: https://www.maff.go.jp/j/zyukyu/zikyu_ritu/attach/pdf/012-4.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Food Self-Sufficiency Rates in Other Countries/Regions, Etc. Available online: https://www.maff.go.jp/j/zyukyu/zikyu_ritu/013.html (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Rice Consumption per Capita per Year. Available online: https://www.maff.go.jp/j/heya/kodomo_sodan/0405/05.html (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Meat Consumption per Capita per Year. Available online: https://www.maff.go.jp/j/zyukyu/zikyu_ritu/ohanasi01/01-04.html (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Consumption of 13 Major Oil Types. Available online: https://www.oil.or.jp/kiso/seisan/seisan10_01.html (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Household Purchases of Rice, Bread, and Noodles. Available online: https://www.maff.go.jp/j/council/seisaku/syokuryo/210729/attach/pdf/index-26.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Endo, C.; Goto, T. Rice flour bread without added gluten. Soc. Biosci. Bioeng. Jpn. 2009, 87, 406–407. [Google Scholar]
- Yano, H. Research and development of gluten-free rice flour bread. Agric. Hortic. 2013, 88, 534–539. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, E.; Obikawa, F.; Suzuki, K.; Kainuma, Y. Characteristics of dried powder from rice paste and its use in bread made with dried powder substitute. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 60, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, Y.; Matsumoto, K. Study on the properties of gluten-free rice flour bread improved by protease treatment. In Annual Report of Study for Food under the Supporting Program; The Skylark Food Science Institute: Tokyo, Japan, 2015; Volume 28, pp. 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Yoza, K.; Okabe, M.; Shima, J. Present State and Issues of Rice Powder Utilization: Rice Bread. J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 55, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Allergy Labeling. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/seisaku/2009/01/05.html (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Kaneda, G. Report on the Survey Project on Food Labeling Related to Food Allergy in Fiscal Year; Sagamihara National Hospital: Sagamihara, Japan, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Encina-Zeladaa, C.R.; Cadaveza, V.; Monteirod, F.; Teixei-rab, J.A.; Gonzales-Barrona, U. Combined effect of xanthan gum and water content on physicochemical and textural properties of gluten-free batter and bread. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.; Azizi, M.-H.; Neyestani, T.R.; Hosseini, H.; Mortazavian, A.M. Development of gluten-free bread using guar gum and transglutaminase. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 1398–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, C.; Unbehend, G.; Lindhauer, M.G. Effect of cellulose-derivatives and emulsifiers on creep-recovery and crumb properties of gluten-free bread pre-pared from sorghum and gelatinised cassava starch. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, M.; Pagani, M.A.; Lucisano, M. The role of buckwheat and HPMC on the breadmaking properties of some commercial gluten-free bread mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, I. Development of 100% rice-flour bread based on modern dietary habits. New Food Ind. 2013, 55, 34–48. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K. Ingredient Selection and Product Development. Food Process. Rev. 2005, 478, 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yoza, K.; Matsuki, J. Rice breads made from commercial rice flour. Rep. Natl. Food Res. Inst. 2014, 78, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Matsukura, U. Food Industry NEO, Rice Flour Foods: Technological Development and Its Application in the Food Industry; Korin Corporation: Tokyo, Japan, 2011; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Nikica, S.; Dubravka, N.; Nikolina, C.; Bojana, S.; Duska, C. Conbined effects of inulin, pectin and guar gum on the quality and stability of partially baked frozen bread. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 428–436. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, K.; Takahashi, S.; Kinouchi, R. Preparation and Properties of a Novel Sponge Cake by Combining Rice Flour with Silk Fibroin Protein. Jpn. J. Food Eng. 2000, 47, 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, K.; Onodera, H.; Teraguchi, C.; Ohsuga, A.; Takahashi, A. Optimai preparation for gluten-free rice bread. J. Biorheol. 2021, 35, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Yamashita, H.; Morita, N. Application of xyloglucan to improve the gluten membrane on breadmaking. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.J.; Hong, Y.E.; Moon, Y.; Jeon, S.; Angalet, S.; Kweon, M. Exploring the applicability of tamarind gum for making gluten-free rice bread. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.E.; Kweon, M. Optimization of the foumula and processing factors for gluten-free rice bread with Tamarind gum. Foods 2020, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Suisha, F.; Kawasaki, N.; Shirakawa, M.; Yamatoya, K.; Attwood, D. Thermally Reversible Xyloglucan Gels as Vehicles for Rectal Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 1998, 56, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, M.; Yamatoya, K.; Nishinari, K. Tailoring of xyloglucan properties using an enzyme. Food Hydrocoll. 1998, 12, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispenza, C.; Todaro, S.; Bulone, D.; Sabatino, M.A.; Ghersi, G.; San Biagio, P.L.; Presti, C.L. Physico-chemical and mechanical characterization of in-situ forming xyloglucan gels incorporating a growth factor to promote cartilage reconstruction. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 70, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.K.; Richard, C.; Ducouret, G.; Bessodes, M.; Scherman, D.; Merten, O.W. Xyloglucan-Derivatized Films for the Culture of Adherent Cells and Their Thermocontrolled Detachment: A Promising Alternative to Cells Sensitive to Protease Treatment. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, S. Development of novel cosmetic materials with on skin gelling properties of thermo-responsible intelligent polymers. Cosmetology 2006, 14, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuki, J.; Okunishi, T.; Okadome, H.; Suzuki, K.; Yoza, K.; Tokuyasu, K. Development of a simple method for evaluation of water sbsorption rate and capacity of rice flour samples. Cereal Chem. 2015, 92, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, A.; Takase, N.; Akuzawa, S.; Sawayama, S. Gelatinization Characteristics of Heat-Moisture Treated Potato and Corn Starches. Bull. Appl. Glycosci. 1996, 43, 471–477. [Google Scholar]
- Kumeno, K.; Kurimoto, K.; Nakahama, N.; Watanabe, M. Functional Properties of Freeze-concerntrated Egg White Foam and Its Application for Good Processing Bioscience. Biotechnology 1994, 58, 447–450. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneoya, A.; Takagi, C.; Ogoshi, H.; Fujii, K. Foaming Properties of Soy Milk as Food Material. J. Cook. Sci. Jpn. 2009, 42, 378–385. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, F.; Yoshimatsu, F. Chouri Jikken, 4th ed.; Shibata Publishing Co., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 1997; pp. 136–137. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- American Association of Cereal Chemists. American Association of Cereal Chemist Method, 10th ed.; American Association of Cereal Chemists: Eagan, MN, USA, 2001; pp. 44-15–74-09. [Google Scholar]
- Marco, C.; Rosell, C.M. Bread making performance of protein enriched gluten free breads. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 227, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, E.; Kumeno, K.; Ookubo, M.; Takahashi, M.; Nakahama, N. A Comparative Study on the Retrogradation Process of Starch Gels Using X-ray and Rheological Measurements. J. Jpn. Soc. Starch Sci. 1992, 39, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisaka, M.; Nakamura, K.; Yoshii, Y. Properties of Rice Flour Prepared by Different Milling Methods. J. Jpn. Soc. Starch Sci. 1992, 39, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, K.; Takahashi, S. Physicochemical Properties of Low-Amylose Rice. J. Home Econ. Jpn. 2003, 54, 889–897. [Google Scholar]
- LI, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Kohyama, K.; Hu, Y.; Ohtsubo, K.; Intabon, K.; Satake, T. Quality Evaluation of Rice Noodles Made from Different Rice Varieties. Jpn. J. Food Eng. 2007, 8, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Nagai, K. Effect of Milling Methods on the Quality of Rice Flours and Breads Made from Rice Flours. Bull. Hyogo Prefect. Technol. Cent. Agric. For. Fish. Agric. Sect. 2011, 59, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Nishinari, K.; Takemasa, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Yamatoya, K. Xyloglucan. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids III; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; Elsevier: A’dam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 317–365. [Google Scholar]
- Sworn, G. Xanthan gum. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids III; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; Elsevier: A’dam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 833–854. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, M.; Sandhu, K.S.; Kaur, J. Pasting properties of Tamarind (Tamarindus indica) kernel powder in the presence of Xanthan, Carboxymethylcellulose and Locust bean gum in comparison to Rice and Potato flour. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirakawa, M.; Yamatoya, K. Structure and Physical Properties of Polysaccharides for the Food Industry (2) Xyloglucan: Its Structure and Function. Foods Food Ingred. J. Jpn. 2003, 208, 922–929. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura, M.; Nishinari, K. Dynamic viscoelastic study on the gelation of konjac glucomannan with different molecular weight. Food Hydrocoll. 1999, 13, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Rice Flour | ||
|---|---|---|
| Gelatinization temperature | [°C] | 69.8 |
| Peak viscosity | [Pa·s] | 2.30 |
| Minimum viscosity | [Pa·s] | 1.28 |
| Final viscosity | [Pa·s] | 2.28 |
| Break down | [Pa·s] | 1.03 |
| Set back | [Pa·s] | 1.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujii, K.; Usui, M.; Ohsuga, A.; Tsuji, M. Effect of Thermoresponsive Xyloglucan on the Bread-Making Properties and Preservation of Gluten-Free Rice-Flour Bread. Foods 2023, 12, 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142761
Fujii K, Usui M, Ohsuga A, Tsuji M. Effect of Thermoresponsive Xyloglucan on the Bread-Making Properties and Preservation of Gluten-Free Rice-Flour Bread. Foods. 2023; 12(14):2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142761
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujii, Keiko, Momomi Usui, Akiko Ohsuga, and Michiko Tsuji. 2023. "Effect of Thermoresponsive Xyloglucan on the Bread-Making Properties and Preservation of Gluten-Free Rice-Flour Bread" Foods 12, no. 14: 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142761
APA StyleFujii, K., Usui, M., Ohsuga, A., & Tsuji, M. (2023). Effect of Thermoresponsive Xyloglucan on the Bread-Making Properties and Preservation of Gluten-Free Rice-Flour Bread. Foods, 12(14), 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142761




