Characterization and Correlation of Microbiota and Higher Alcohols Based on Metagenomic and Metabolite Profiling during Rice-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
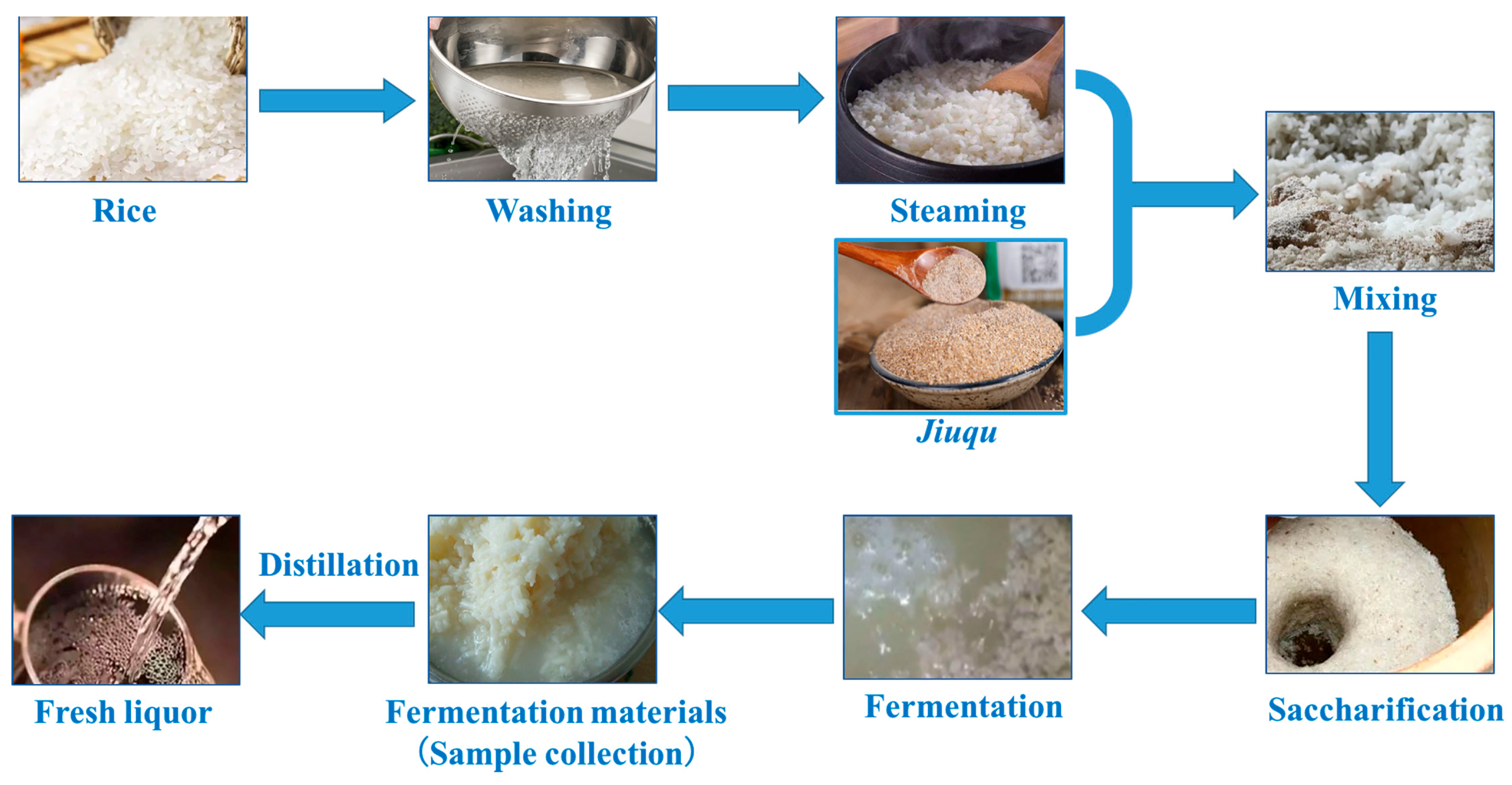
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Analysis of the Content of Higher Alcohols
2.3. Analysis of the Precursors of Higher Alcohols
2.4. Total DNA Extraction
2.5. Illumina Sequencing
2.6. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.7. Function Annotations
2.8. Construction of the Higher Alcohols Metabolic Network
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Higher Alcohols during Rice-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation
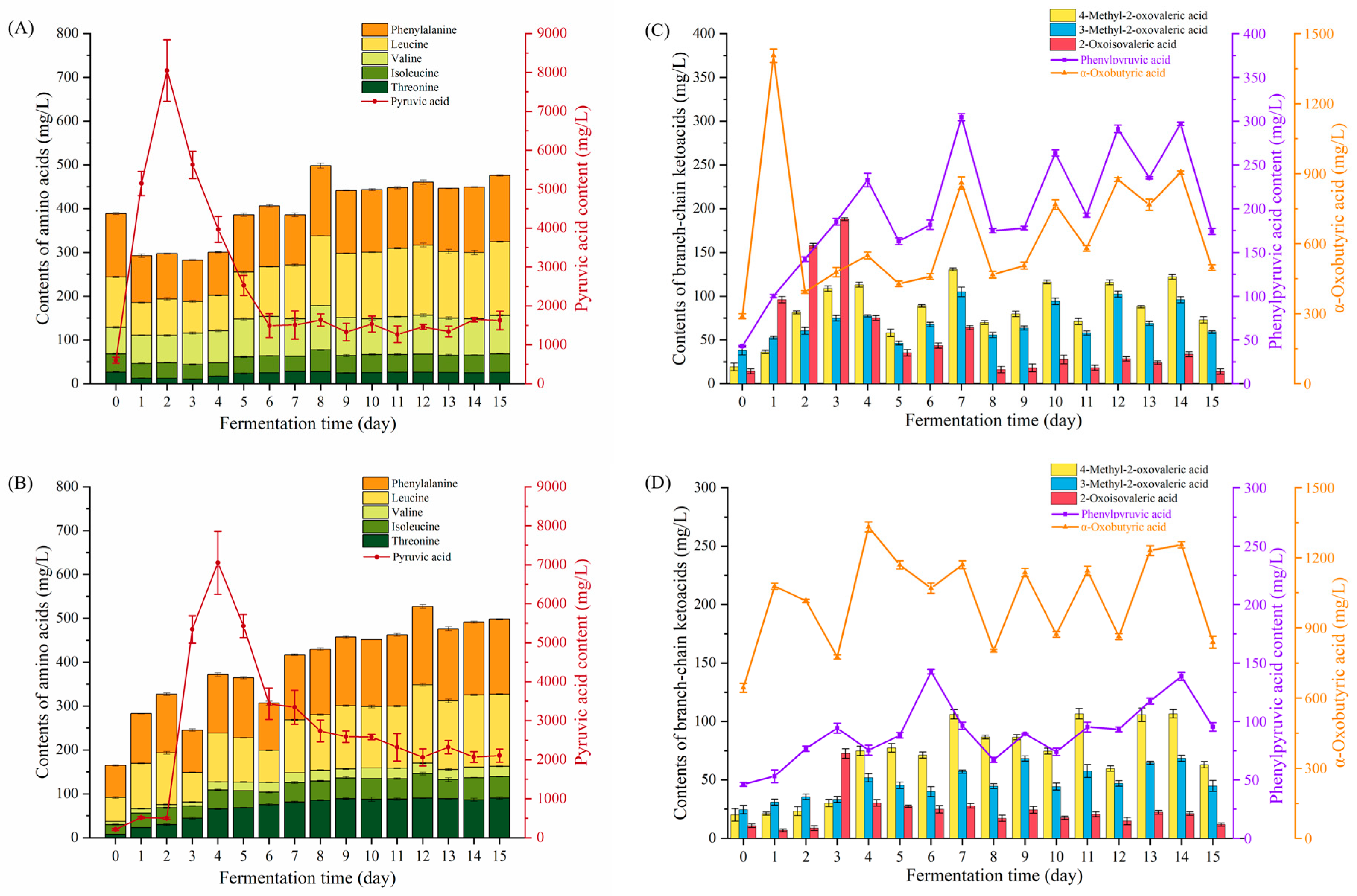
3.2. Changes in Precursors of Higher Alcohols
3.3. Microbiota Dynamics and Species Diversity Analysis during Rice-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation
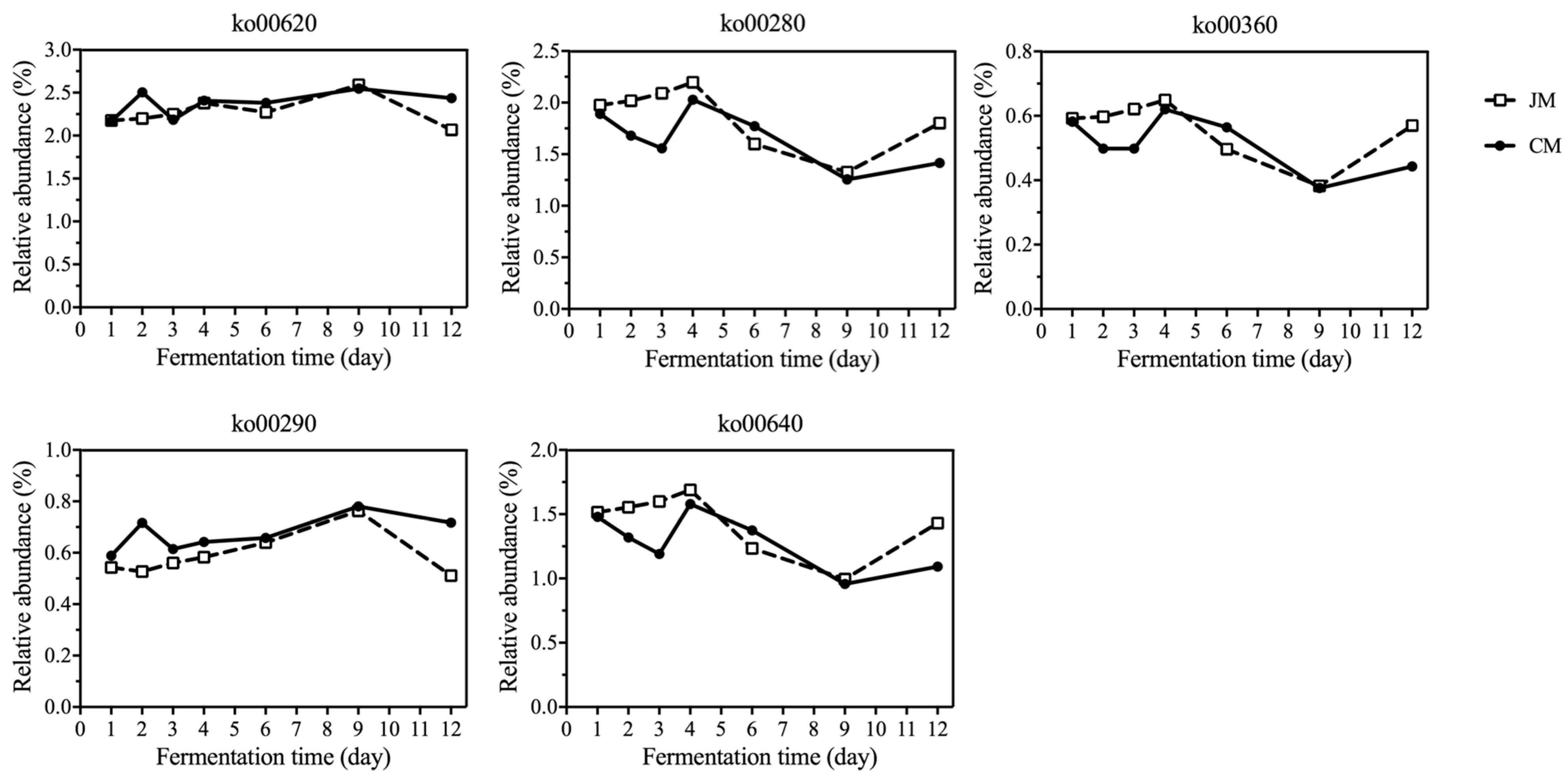
3.4. Distribution of Genes Associated with KEGG Pathways Related to Rice-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation
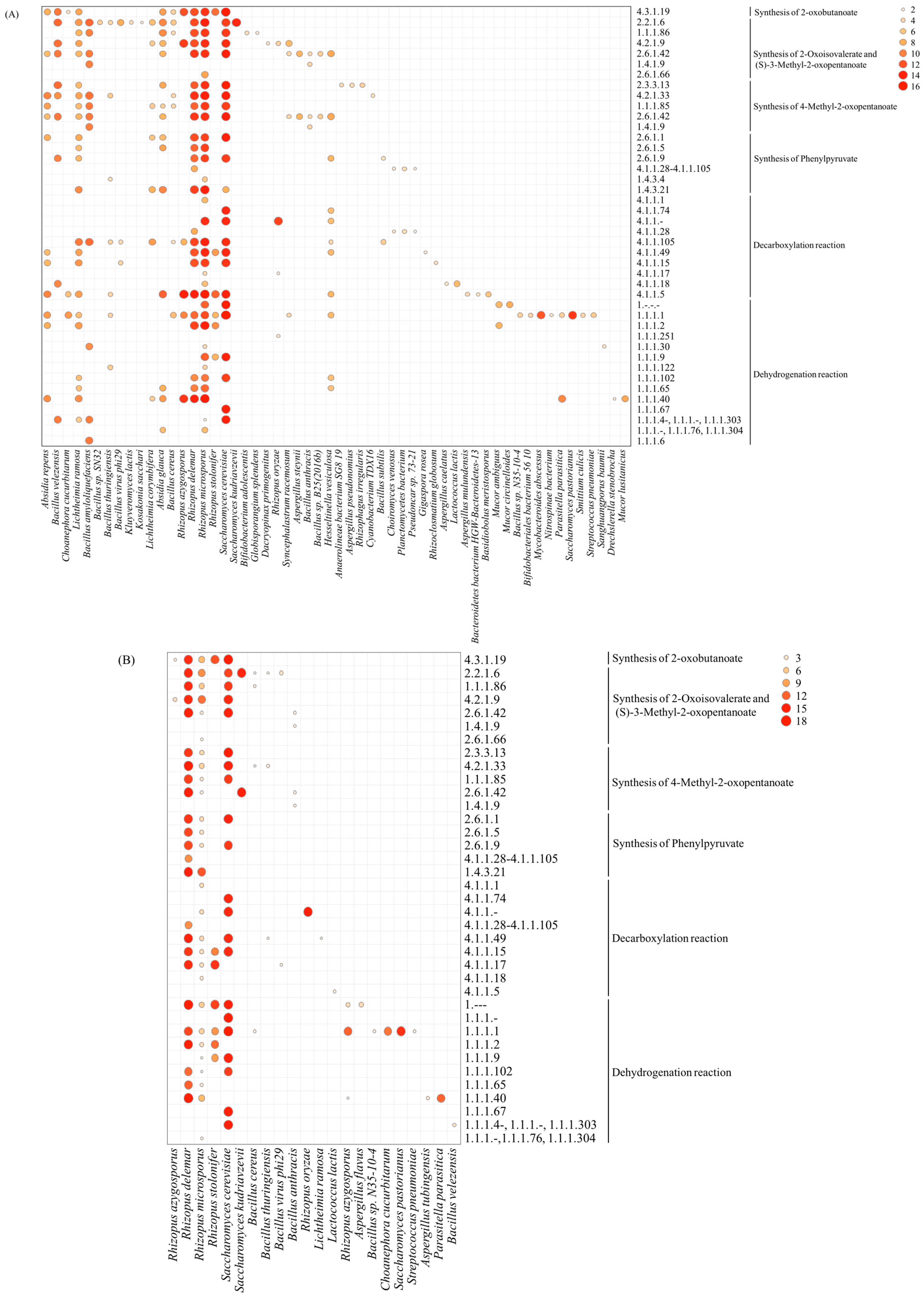
3.5. Metabolic Pathways of Higher Alcohols and Microbial Distribution during Rice-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, H.; Sun, B. Effect of fermentation processing on the flavor of Baijiu. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5425–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lei, X.; Zhang, X.; Guan, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, X.; Tu, J.; Peng, N.; Liang, Y.; et al. Characteristics of the microbial community in the production of Chinese rice-flavor Baijiu and comparisons with the microflora of other flavors of Baijiu. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zou, W.; Shen, C.-H.; Yang, J.-G. Basic flavor types and component characteristics of Chinese traditional liquors: A review. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 4096–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ma, D.; Li, Z.; Sun, H.; Mao, J.; Shi, Y.; Han, X.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, J. Assimilable nitrogen reduces the higher alcohols content of Huangjiu. Food Control. 2021, 121, 107660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.-H.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Ma, H.-X.; Xiao, D.-G. Regulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering on the production of acetate esters and higher alcohols during Chinese Baijiu fermentation. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 2017, 44, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yuan, G.; He, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhou, H.; Qiu, S. The formation of higher alcohols in rice wine fermentation using different rice cultivars. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 978323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sentheshanmuganathan, S. The mechanism of the formation of higher alcohols from amino acids by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem. J. 1960, 74, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazelwood, L.A.; Daran, J.M.; van Maris, A.J.; Pronk, J.T.; Dickinson, J.R. The Ehrlich pathway for fusel alcohol production: A century of research on Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Ren, H.; Wang, A.; Wan, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, X. iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis reveals the molecule mechanism of reducing higher alcohols in Chinese rice wine by nitrogen compensation. Ann. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Qi, Y.N.; Ma, H.X.; Li, W.; Dai, L.H.; Xiao, D.G. Decreased production of higher alcohols by Saccharomyces cerevisiae for Chinese rice wine fermentation by deletion of Bat aminotransferases. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 2015, 42, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, K.; Ishii, J.; Matsuda, F.; Kondo, T.; Kondo, A. Eliminating the isoleucine biosynthetic pathway to reduce competitive carbon outflow during isobutanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb. Cell Fact. 2015, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E. The relative contribution of Ehrlich and biosynthetic pathways to the formation of fusel alcohols. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 1978, 36, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, T.; Tezuka, H.; Ishii, J.; Matsuda, F.; Ogino, C.; Kondo, A. Genetic engineering to enhance the Ehrlich pathway and alter carbon flux for increased isobutanol production from glucose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 159, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Huang, S.; Du, L.; Tang, P.; Xiao, D. Reduced production of higher alcohols by Saccharomyces cerevisiae in red wine fermentation by simultaneously overexpressing BAT1 and deleting BAT2. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6936–6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Chen, D.; Fu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, X.; Peng, N.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, S. Study on microbial communities and higher alcohol formations in the fermentation of Chinese Xiaoqu Baijiu produced by traditional and new mechanical technologies. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Xing, X.; Ren, Q. Changes of microbial community structure and effects on higher alcohols in oat Huangjiu fermentation process. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2020, 38, 43–52, 59. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Dong, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, R. Alteration of microbial community for improving flavor character of Daqu by inoculation with Bacillus velezensis and Bacillus subtilis-ScienceDirect. LWT 2019, 111, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Sun, L.; Xing, X.; Wu, H.; Lu, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Ren, Q. Microbial succession and exploration of higher alcohols-producing core bacteria in northern Huangjiu fermentation. Amb Express 2022, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 10345-2022; National Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2022. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=kxaUMs6x7-5KB1kF296ShrYo9ZoYIWW4VfT4bfQP25xUu13oQhU7-WuP5hooL9QRVogxVUcVJTTht4AljNTw%3d%3d&uniplatform=NZKPT (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Wang, T.; Lin, M.; Feng, X.; Wang, P.; Cao, X.; Zhang, W. Established methods and comparison of 10 organic acids based on reversed phase chromatography and hydrophilic interaction chromatography. CyTA-J. Food 2022, 20, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Ruan, F.; Zhao, W.; Dong, H.; Bai, W.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Li, Y. The dynamics of physicochemical properties, microbial community, and flavor metabolites during the fermentation of semi-dry Hakka rice wine and traditional sweet rice wine. Food Chem. 2023, 416, 135844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, N.; Cao, Y.; Xu, J.; Fan, M. Multivariate analysis reveals effect of glutathione-enriched inactive dry yeast on amino acids and volatile components of kiwi wine. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M. Ab initio gene identification in metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Zou, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, S. A metagenomic analysis of the relationship between microorganisms and flavor development in Shaoxing mechanized huangjiu fermentation mashes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 303, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsumi, S.; Hanai, T.; Liao, J.C.J.N. Non-fermentative pathways for synthesis of branched-chain higher alcohols as biofuels. Nature 2008, 451, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.H.; Lu, Z.M.; Zhang, X.J.; Wang, Z.M.; Yu, Y.J.; Shi, J.S.; Xu, Z.H. Metagenomics reveals flavour metabolic network of cereal vinegar microbiota. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, H.; Fukushige, T.; Yonezawa, T.; Sakai, Y.; Okawa, K.; Iwamatsu, A.; Sone, H.; Tamai, Y. Pyruvate decarboxylase encoded by the PDC1 gene contributes, at least partially, to the decarboxylation of α-ketoisocaproate for isoamyl alcohol formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 92, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Qi, J.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Xu, Q.; Chen, N.; Xie, X. Production of alpha-ketobutyrate using engineered Escherichia coli via temperature shift. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 2054–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, E.J.; Teixeira, J.A.; Branyik, T.; Vicente, A.A. Yeast: The soul of beer’s aroma-a review of flavour-active esters and higher alcohols produced by the brewing yeast. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 98, 1937–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Tang, J.; Qiu, S. Profiling of fungal diversity and fermentative yeasts in traditional Chinese Xiaoqu. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styger, G.; Jacobson, D.; Bauer, F.F. Identifying genes that impact on aroma profiles produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the production of higher alcohols. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 91, 713–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Sun, B.J.A.; Microbiology, E. Synergistic effect of multi-saccharifying enzymes on alcoholic fermentation for Chinese Baijiu production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00013–e00020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Sugimachi, M.; Yoshizaki, Y.; Yin, X.; Han, X.L.; Okutsu, K.; Futagami, T.; Tamaki, H.; Takamine, K. Impact of solid-state saccharification on the flavor of rice-flavor Baijiu. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 4958–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.M.; Larsen, T.O.; Schnurer, J. Production of volatile compounds by Rhizopus oligosporus during soybean and barley tempeh fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 113, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramorski, A.; Christen, P.; Ramirez, M.; Soccol, C.R.; Revah, S. Production of volatile compounds by the edible fungus Rhizopus oryzae during solid state cultivation on tropical agro-industrial substrates. Biotechnol. Lett. 1998, 20, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; He, G.; Huang, J.; Wu, C.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, R. Characterizing relationship of microbial diversity and metabolite in Sichuan Xiaoqu. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Qu, C.; Fei, Y.; Liang, J.; Bai, W.; Zhao, W.; Xiao, G.; Liu, G. Characterization and Correlation of Microbiota and Higher Alcohols Based on Metagenomic and Metabolite Profiling during Rice-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation. Foods 2023, 12, 2720. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142720
Wang H, Zhang M, Qu C, Fei Y, Liang J, Bai W, Zhao W, Xiao G, Liu G. Characterization and Correlation of Microbiota and Higher Alcohols Based on Metagenomic and Metabolite Profiling during Rice-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation. Foods. 2023; 12(14):2720. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142720
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hong, Minqian Zhang, Chunyun Qu, Yongtao Fei, Jinglong Liang, Weidong Bai, Wenhong Zhao, Gengsheng Xiao, and Gongliang Liu. 2023. "Characterization and Correlation of Microbiota and Higher Alcohols Based on Metagenomic and Metabolite Profiling during Rice-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation" Foods 12, no. 14: 2720. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142720
APA StyleWang, H., Zhang, M., Qu, C., Fei, Y., Liang, J., Bai, W., Zhao, W., Xiao, G., & Liu, G. (2023). Characterization and Correlation of Microbiota and Higher Alcohols Based on Metagenomic and Metabolite Profiling during Rice-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation. Foods, 12(14), 2720. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142720





