Quantitation of L-cystine in Food Supplements and Additives Using 1H qNMR: Method Development and Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Sample Collection and Pretreatment for qNMR Test
2.3. Quantitation of Cystine by Conventional Titrimetric Analysis
2.4. 1H NMR Analysis
2.4.1. Apparatus
2.4.2. Optimization of qNMR Conditions
2.4.3. NMR Data Processing
2.5. Validation of the qNMR Method
2.6. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
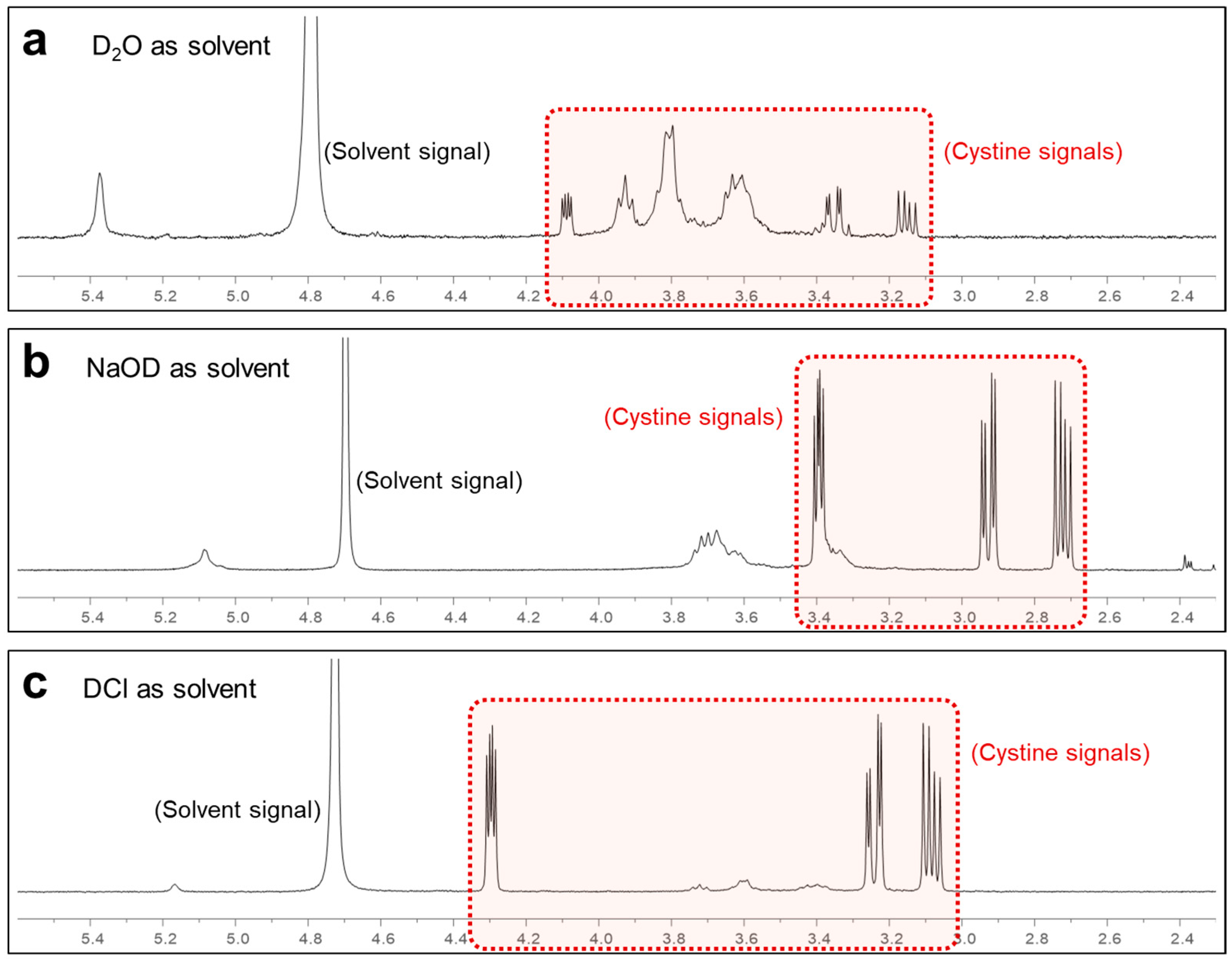
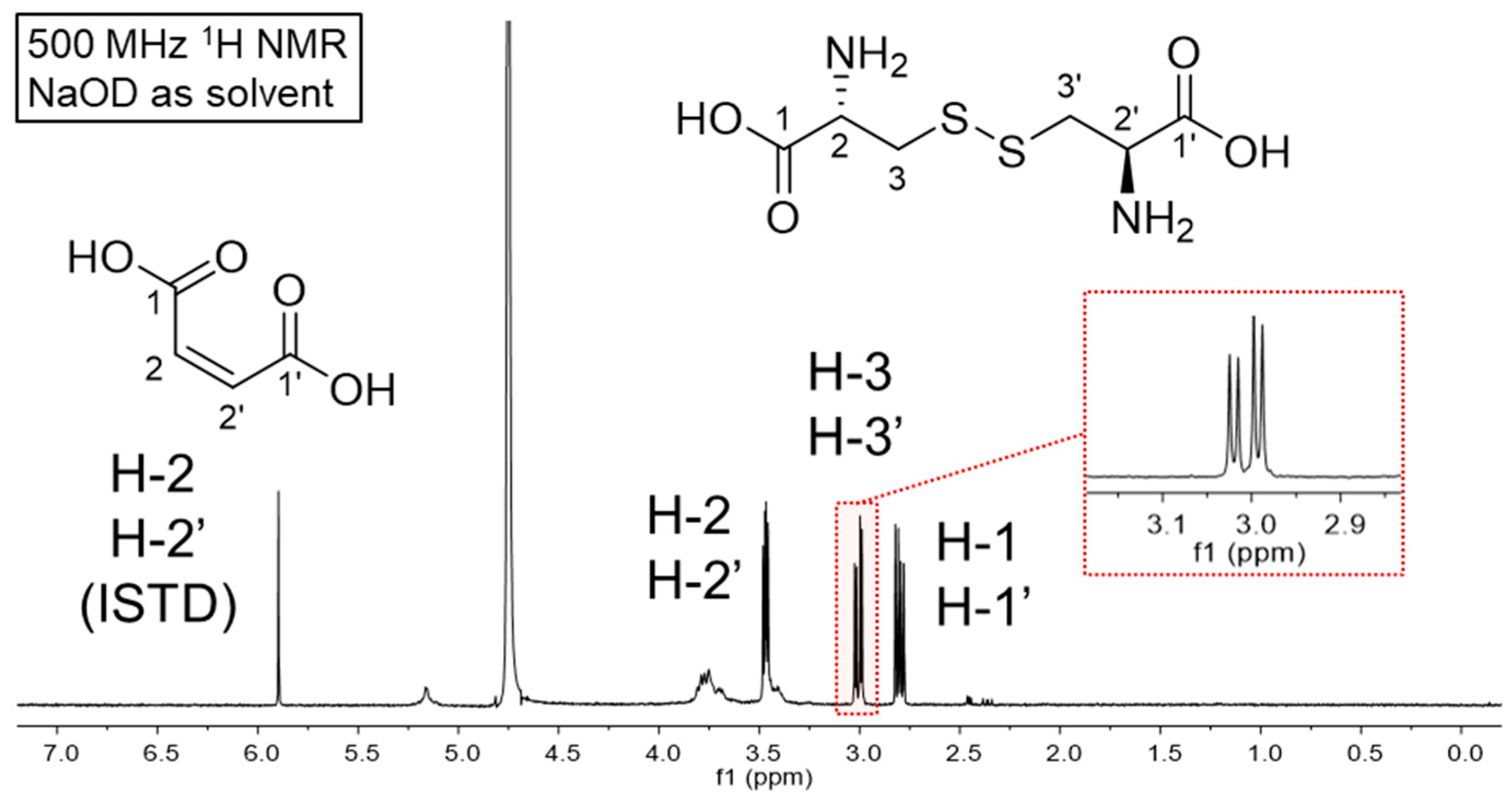
3.1. Detection of Cystine Using 1H NMR and Selection of the Deuterated Solvents
3.2. Optimization of qNMR Parameters
3.2.1. Acquisition Time Length
3.2.2. Relaxation Delay Length
3.3. Validation of the Developed Method
3.4. Quantitation of Cystine in Food Supplements
3.4.1. Variations of Cystine Amount
3.4.2. Correlations among the Properties of Different Food Supplements and Their Relative Actual Amount of Cystine
3.5. Study Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Massey, L.K. Dietary Animal and Plant Protein and Human Bone Health: A Whole Foods Approach. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 862S–865S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, K.; Yokozeki, K.; Tamura, F.; Yasuda, N.; Noda, I.; Mitsugi, K. Microbial Conversion of DL-2-Amino-Delta2-Thiazoline-4-Carboxylic Acid to L-Cysteine and L-Cystine: Screening of Microorganisms and Identification of Products. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1977, 34, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, K.; Mitsugi, K. Enzymatic Production of l-Cysteine from dl-2-Amino-Δ2-Thiazoline-4-Carboxylic Acid by Pseudomonas Thiazolinophilum: Optimal Conditions for the Enzyme Formation and Enzymatic Reaction. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1978, 42, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, M.; Takagi, H. Metabolic Pathways and Biotechnological Production of L-Cysteine. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 73, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, V.; Anton, M.; Santé-Lhoutellier, V. The “Sisters” α-Helices of Collagen, Elastin and Keratin Recovered from Animal by-Products: Functionality, Bioactivity and Trends of Application. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP). Scientific Opinion on the Safety and Efficacy of L-cystine for All Animal Species. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Lupton, J.R.; Turner, N.D.; Fang, Y.-Z.; Yang, S. Glutathione Metabolism and Its Implications for Health. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Ren, W.; Yang, G.; Duan, J.; Huang, X.; Fang, R.; Li, C.; Li, T.; Yin, Y.; Hou, Y.; et al. l-Cysteine Metabolism and Its Nutritional Implications. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, D.M.; Tew, K.D.; Tapiero, H. The Importance of Glutathione in Human Disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2003, 57, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narda, M.; Aladren, S.; Cestone, E.; Nobile, V. Efficacy and Safety of a Food Supplement Containing L-Cystine, Serenoa Repens Extract and Biotin for Hair Loss in Healthy Males and Females. A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blinded, Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Cosmetol. Trichol. 2017, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetto, C.; Arfuso, F.; Giudice, E.; Rizzo, M.; Piccione, G.; Mhalhel, K.; Levanti, M. Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effect of a Nutritional Supplement with Silymarin Phytosome, Choline Chloride, l-Cystine, Artichoke, and Vitamin E in Dogs. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha-Hikim, I.; Sinha-Hikim, A.P.; Parveen, M.; Shen, R.; Goswami, R.; Tran, P.; Crum, A.; Norris, K.C. Long-Term Supplementation With a Cystine-Based Antioxidant Delays Loss of Muscle Mass in Aging. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2013, 68, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilani, G.S.; Ratnayake, W.M.N.; Peace, R.W.; Muller, R. Effects of Supplemental Cystine or Methionine on Growth and Lifespan of Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2006, 95, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Pharmacopoeia Committe. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, 2020th ed.; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Pang, X.; Chen, F. Determination of Cystine in Cystine Tablets by Amino Acid Analyzer. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2018, 38, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, C.E.; Cebi, N.; Develioglu, A.; Olgun, E.O.; Sagdic, O. Detection of Cystine and Cysteine in Wheat Flour Using a Robust LC-MS/MS Method. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 84, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghi, L.; Picone, G.; Capozzi, F. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance for Foodomics beyond Food Analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 59, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, H. Development and Validation of Quantitative 1H NMR Spectroscopy for the Determination of Total Phytosterols in the Marine Seaweed Sargassum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6228–6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minoja, A.P.; Napoli, C. NMR Screening in the Quality Control of Food and Nutraceuticals. Food Res. Int. 2014, 63, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malz, F.; Jancke, H. Validation of Quantitative NMR. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 38, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, P.; Tu, P.; Jiang, Y. A Simple and Specific Quantitative Method for Determination of Dictamnine in Dictamni Cortex by 1H NMR Spectroscopy. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, G.F.; Jaki, B.U.; Lankin, D.C. Quantitative 1 H NMR: Development and Potential of a Method for Natural Products Analysis. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Shen, N.; Wu, X.; Jia, J.; Wu, Y.; Chiba, H.; Hui, S. Extraction and Quantitation of Phytosterols from Edible Brown Seaweeds: Optimization, Validation, and Application. Foods 2023, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, N.K.; Pradhan, S.; Mittal, B.; Kumar, R.; Pandey, C.M.; Gowda, G.A.N. Novel Corrective Equations for Complete Estimation of Human Tissue Lipids after Their Partial Destruction by Perchloric Acid Pre-Treatment: High-Resolution1H-NMR-Based Study. NMR Biomed. 2008, 21, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M. Applications of the Ninhydrin Reaction for Analysis of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins to Agricultural and Biomedical Sciences. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wan, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cui, H.; Xiong, X.; Zhong, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, F.; et al. Direct and Simultaneous Determination of Cystine, Tyrosine and Histidine in Hair of Rat by HPLC. J. Instrum. Anal. 2018, 37, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.-W. Determination of Free L-Cysteine by Automatic Amino Acid Analyzer. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2015, 6, 3129–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žmitek, K.; Krušič, S.; Pravst, I. An Approach to Investigate Content-Related Quality of Nutraceuticals Used by Slovenian Consumers: A Case Study with Folate and Vitamin D Supplements. Foods 2021, 10, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlAli, M.; Alqubaisy, M.; Aljaafari, M.N.; AlAli, A.O.; Baqais, L.; Molouki, A.; Abushelaibi, A.; Lai, K.-S.; Lim, S.-H.E. Nutraceuticals: Transformation of Conventional Foods into Health Promoters/Disease Preventers and Safety Considerations. Molecules 2021, 26, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jairoun, A.A.; Shahwan, M.; Zyoud, S.H. Fish Oil Supplements, Oxidative Status, and Compliance Behaviour: Regulatory Challenges and Opportunities. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, A.; Yamazaki, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Takahashi, S.; Nakayama, T.; Yazaki, K. Developmental and Nutritional Regulation of Isoflavone Secretion from Soybean Roots. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Meza, Y.; Escobar-Ortiz, A.; Buergo-Martínez, F.; Pérez-Ramírez, I.F.; Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Salgado, L.M.; Reynoso-Camacho, R. Three Varieties of Grape Pomace, with Distinctive Extractable:Non-Extractable Polyphenol Ratios, Differentially Reduce Obesity and Its Complications in Rats Fed a High-Fat High-Fructose Diet. Foods 2023, 12, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, S.; Pereira, J.A.; Silva, P.; Perestrelo, R.; Câmara, J.S. Food Fingerprints—A Valuable Tool to Monitor Food Authenticity and Safety. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sample Code | Functions Claimed on Product Label a | Form | Labeled Cystine Amount or Purity b | Other Major Functional Ingredients a | Price c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food supplement | ||||||
| 1 | Preventing hair loss | Tablet | 10.2 | Vitamin B1, Vitamin B6, Vitamin B12, biotin | 1.67 | |
| 2 | Preventing hair loss, anti-aging | Tablet | 12.5 | Vitamin C, anthocyanidin extracted from blueberry | 1.78 | |
| 3 | Preventing hair loss, promoting hair growth | Oral liquid | 25.0 | Vitamin A, Vitamin B6, biotin | 0.39 | |
| 4 | Preventing hair loss, assisting chronic hepatitis treatment | Softgel | 50.0 | Vitamin B6, fish oil | 1.80 | |
| 5 | Relieving hangovers, protecting liver and brain from alcohol | Capsule | 10.0 | Vitamin B1, yeast extracts | 0.24 | |
| 6 | Accelerating skin regeneration | Tablet | 60.0 | Vitamin B2, Vitamin B6, Vitamin C, Vitamin E | 0.12 | |
| 7 | Preventing hair loss, preventing aging | Capsule | 8.0 | Crude polysaccharides extracted from radix astragali | 0.63 | |
| 8 | Improving skin elasticity, preventing skin aging | Softgel | 15.8 | Polyunsaturated fatty acids, collagen | 1.44 | |
| Food additive | ||||||
| 9 | Enhancing dough strength | Powder | 98% | N/A | 18.82 | |
| 10 | Enhancing dough strength | Powder | 98% | N/A | 17.37 | |
| 11 | Enhancing dough strength | Powder | 99% | N/A | 50.00 | |
| Validation Characteristics | qNMR Method | Titrimetric Method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | LOD | 3.8 μg | 42.1 μg |
| LOQ | 12.5 μg | 106.0 μg | |
| Precision | Intra-assay precision (CV%) | 0.93 | 3.59 |
| Intermediate precision (CV%) | 2.20 | 4.87 | |
| Accuracy (recovery) | At 50% spiking level | 103.3% ± 3.1% (CV% = 2.97) | 110.3% ± 9.1% (CV% = 8.28) |
| At 100% spiking level | 102.1% ± 2.4% (CV% = 2.39) | 107.7% ± 3.5% (CV% = 3.27) | |
| At 200% spiking level | 100.7% ± 2.0% (CV% = 1.94) | 102.0% ± 5.4% (CV% = 5.33) | |
| Sample Code | Sample Kind | Cystine Amount (per Serving for Food Supplements, per 20 mg for Food Additives) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labeled Value (mg) | Measured Value (mg) | Relative Actual Amount | ||
| 1 | Food supplement | 10.2 | 9.9 ± 0.3 | 96.6% ± 2.5% |
| 2 | Food supplement | 12.5 | 12.7 ± 0.3 | 101.4% ± 2.1% |
| 3 | Food supplement | 25.0 | 9.3 ± 0.2 | 37.1% ± 0.9% |
| 4 | Food supplement | 50.0 | 33.9 ± 2.7 | 67.9% ± 5.5% |
| 5 | Food supplement | 10.0 | 9.9 ± 0.4 | 99.0% ± 3.6% |
| 6 | Food supplement | 60.0 | 59.2 ± 0.6 | 98.6% ± 1.0% |
| 7 | Food supplement | 8.0 | 8.6 ± 0.3 | 107.2% ± 3.3% |
| 8 | Food supplement | 15.8 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.3% ± 0.4% |
| 9 | Food additive | 20.0 | 19.9 ± 0.4 | 99.4% ± 1.9% |
| 10 | Food additive | 20.0 | 19.4 ± 0.4 | 97.0% ± 1.8% |
| 11 | Food additive | 20.0 | 20.0 ± 0.2 | 99.9% ± 1.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Lian, X.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C. Quantitation of L-cystine in Food Supplements and Additives Using 1H qNMR: Method Development and Application. Foods 2023, 12, 2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122421
Chen Z, Lian X, Zhou M, Zhang X, Wang C. Quantitation of L-cystine in Food Supplements and Additives Using 1H qNMR: Method Development and Application. Foods. 2023; 12(12):2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122421
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhen, Xiaofang Lian, Meichen Zhou, Xiuli Zhang, and Cong Wang. 2023. "Quantitation of L-cystine in Food Supplements and Additives Using 1H qNMR: Method Development and Application" Foods 12, no. 12: 2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122421
APA StyleChen, Z., Lian, X., Zhou, M., Zhang, X., & Wang, C. (2023). Quantitation of L-cystine in Food Supplements and Additives Using 1H qNMR: Method Development and Application. Foods, 12(12), 2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122421