Novel Gluten-Free Cinnamon Rolls by Substituting Wheat Flour with Resistant Starch, Lupine and Flaxseed Flour
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Flour
2.2. Other Cinnamon Roll Ingredients
2.3. Cinnamon Roll Preparation
2.3.1. Mixing
2.3.2. Filling
2.3.3. Baking
2.4. Chemical Analysis
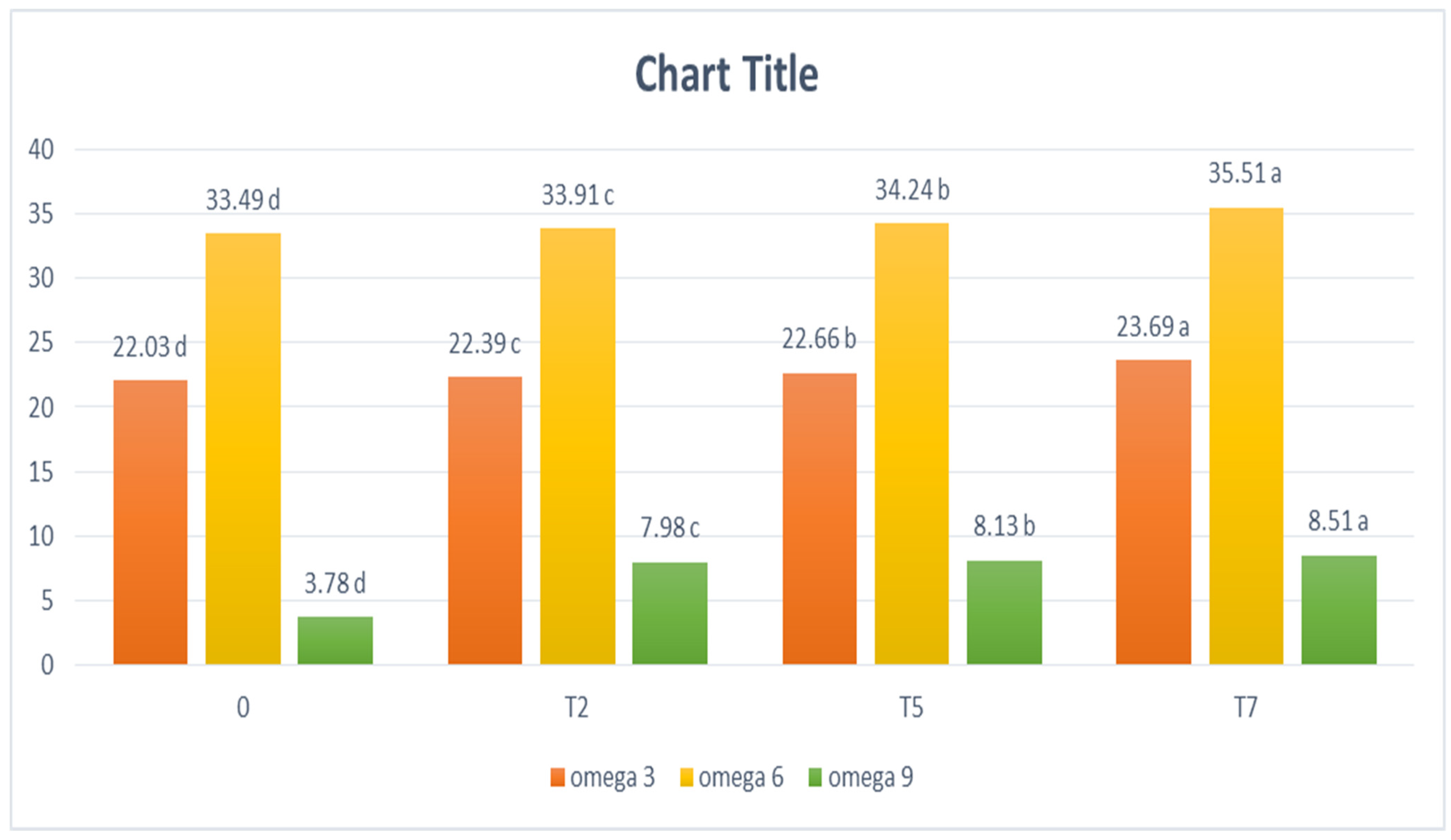
Unsaturated Fatty Acids Determination
2.5. Physical Analysis
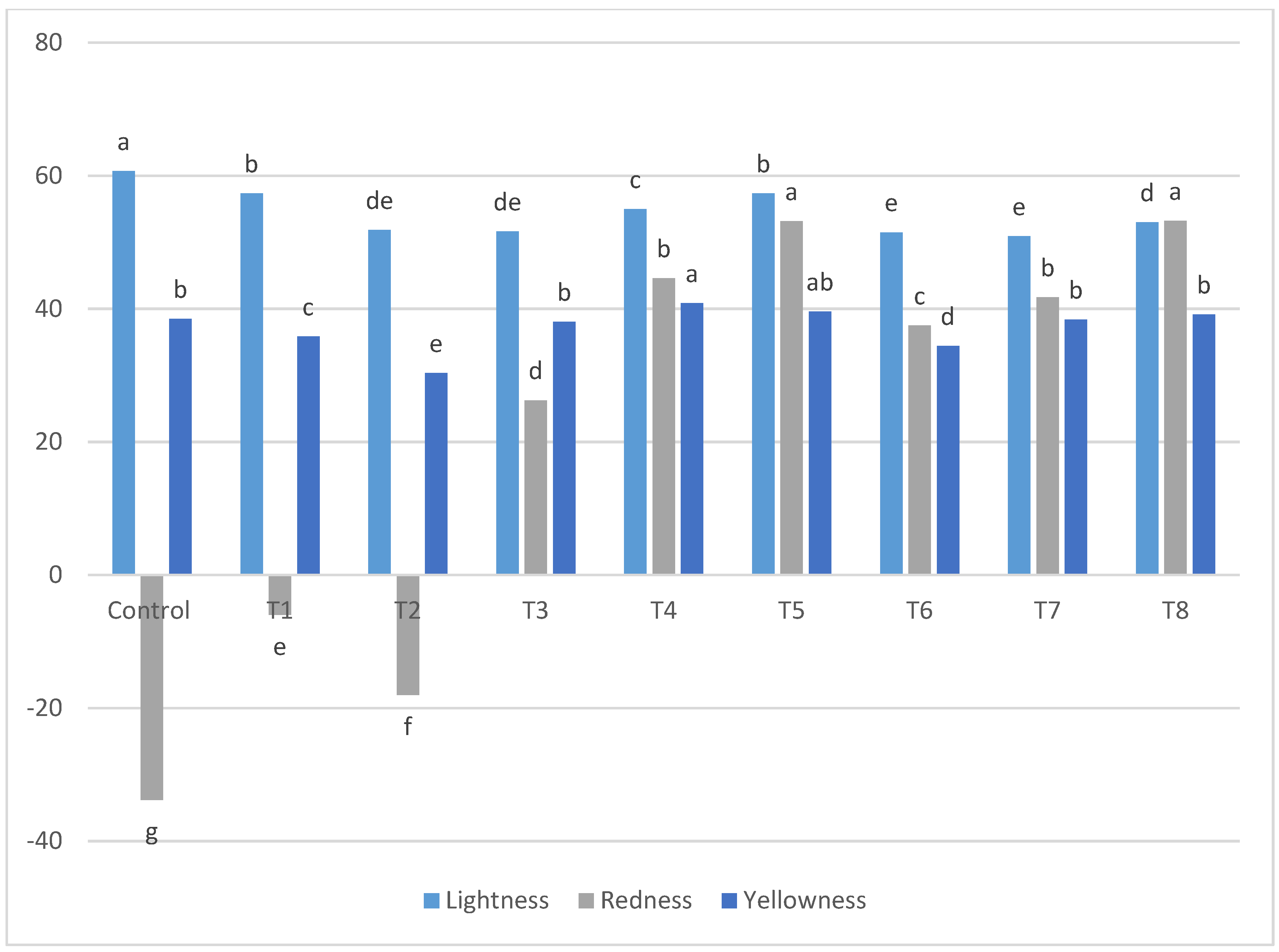
2.6. Color Measurement
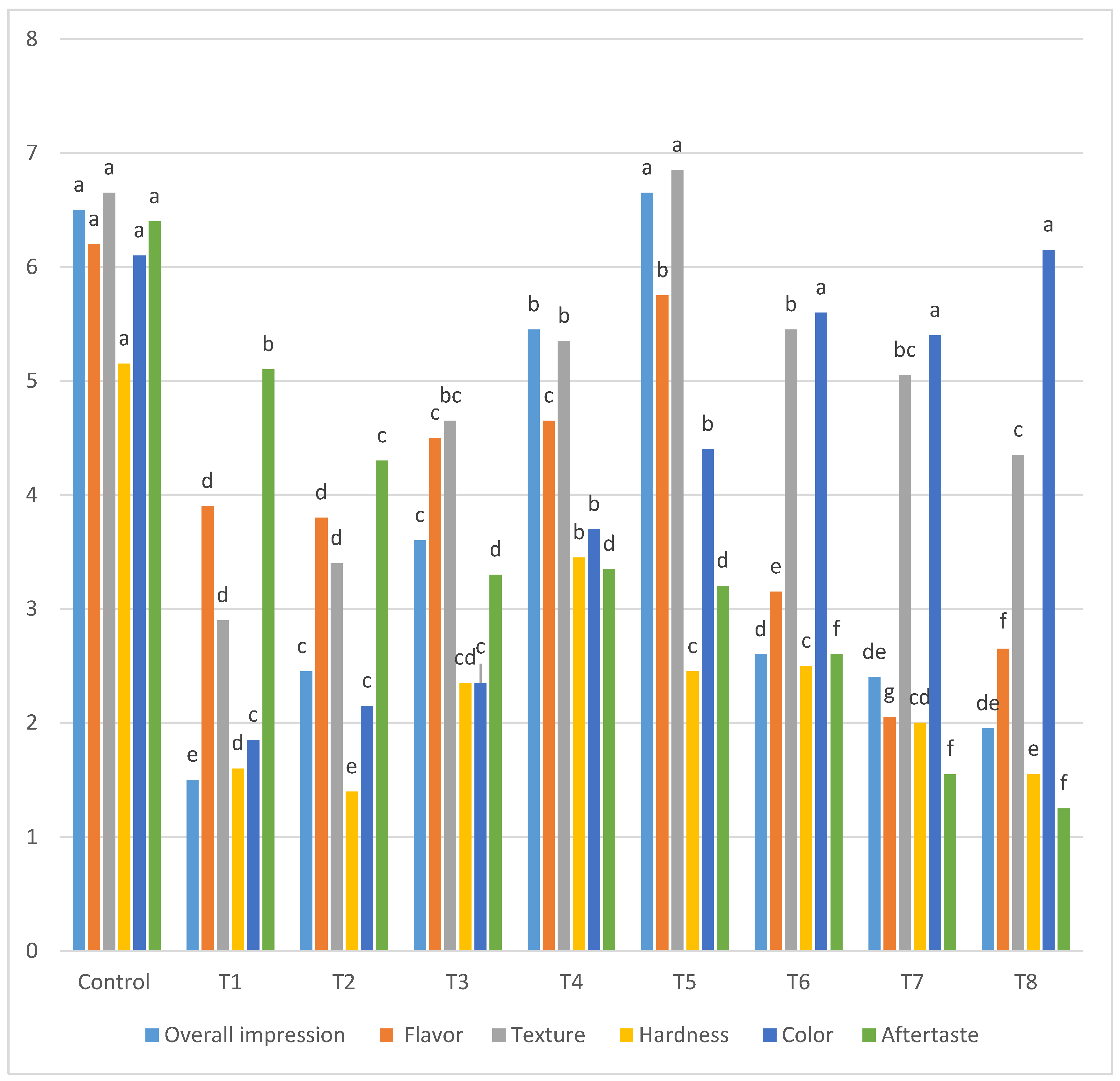
2.7. Trained Organoleptic Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Characteristics
3.2. Color Measurements
3.3. Sensory Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, N.; Bhatia, S.; Chunduri, V.; Kaur, S.; Sharma, S.; Kapoor, P.; Garg, M. Pathogenesis of Celiac Disease and Other Gluten Related Disorders in Wheat and Strategies for Mitigating Them. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abedi, E.; Pourmohammadi, K. Chemical modifications and their effects on gluten protein: An extensive review. Food Chem. 2020, 343, 128398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Qiao, S.-W.; Arentz-Hansen, H.; Molberg, Ø.; Gray, G.M.; Sollid, L.M.; Khosla, C. Identification and Analysis of Multivalent Proteolytically Resistant Peptides from Gluten: Implications for Celiac Sprue. J. Proteome Res. 2005, 4, 1732–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ciacci, C.; Ciclitira, P.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Kaukinen, K.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; McGough, N.; Sanders, D.S.; Woodward, J.; Leonard, J.N.; Swift, G.L. The gluten-free diet and its current application in coeliac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2015, 3, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cranney, A.; Horsley, T.; O’Donnell, S.; Weiler, H.; Puil, L.; Ooi, D.; Atkinson, S.; Ward, L.; Moher, D.; Hanley, D.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health. Évid. Rep. Technol. Assess. 2007, 158, 1–235. [Google Scholar]
- Itzlinger, A.; Branchi, F.; Elli, L.; Schumann, M. Gluten-Free Diet in Celiac Disease—Forever and for All? Nutrients 2018, 10, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schillinga, K.W.; Yohannessena, K.; Araya, M. Perception of following gluten-free diet and adherence to treatment in pediatric patients with celiac disease. Rev. Chil. Pediatr. 2018, 89, 216–223. [Google Scholar]
- Zarkadas, M.; Dubois, S.; MacIsaac, K.; Cantin, I.; Rashid, M.; Roberts, K.C.; La Vieille, S.; Godefroy, S.; Pulido, O.M. Living with coeliac diseaseand a gluten-free diet: A Canadian perspective. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 26, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohajdova, Z.; Karovicova, J.; Schmidt, Š. Lupin Composition and Possible Use in Bakery—A Review. Czech J. Food Sci. 2011, 29, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holscher, H.D. Dietary fiber and prebiotics and the gastrointestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demin, M.A.; Milovanović, M.M.; Stikić, R.I.; Banjac, N.R.; Rabrenović, B.V. Quinoa, Buckwheat and Flaxseed Ingredients in the Wheat Bread Production with Nutritional Quality. In Proceedings of the 8th Croatian Congress of Cereal Technologists, Opatija, Croatia, 12–14 October 2011; pp. 245–251. [Google Scholar]
- Masoodi, L.; Aeri–Khalid Bashir, V. Fortification of Biscuit with Flaxseed: Biscuit Production and Quality Evaluation. J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. Food Technol. 2012, 1, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, M.; Maddaford, T.G.; Austria, A.J.; Aliani, M.; Netticadan, T.; Pierce, G.N. Dietary Flaxseed as a Strategy for Improving Human Health. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; The Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://redcipes.com/recipe/clone-of-a-cinnabon-marsha-fernandez (accessed on 22 February 2022).
- AACC. Approved Methods of the American Association of the Cereal Chemists; Methods 08-01, 30-20, 44-15A, 46-12, 54-10, 54-21, 56-81B; American Association of the Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Trattner, S.; Becker, W.; Wretling, S.; Öhrvik, V.; Mattisson, I. Fatty acid composition of Swedish bakery products, with emphasis on trans-fatty acids. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hallén, E.; İbanoğlu, Ş.; Ainsworth, P. Effect of fermented/germinated cowpea flour addition on the rheological and baking properties of wheat flour. J. Food Eng. 2004, 63, 177–18419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdybel, E.; Zięba, T.; Rymowicz, W.; Tomaszewska-Ciosk, E. Organic Acids of the Microbiological Post-Culture Medium as Substrates to be Used for Starch Modification. Polymers 2019, 11, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prusinski, J. White lupin (Lupinus albus L.)—Nutritional and health values in human nutritionAa review. Czech J. Food Sci. 2017, 35, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wójcik, M.; Różyło, R.; Schönlechner, R.; Berger, M.V. Physico-chemical properties of an innovative gluten-free, low-carbohydrate and high protein-bread enriched with pea protein powder. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bähr, M.; Fechner, A.; Kiehntopf, M.; Jahreis, G. Consuming a mixed diet enriched with lupin protein beneficially affects plasma lipids in hypercholesterolemic subjects: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajla, P.; Sharma, A.; Sood, D.R. Flaxseed—A potential functional food source. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 1857–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikos, V.; Neacsu, M.; Russell, W.; Duthie, G. Comparative study of the functional properties of lupin, green pea, fava bean, hemp, and buckwheat flours as affected by pH. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 2, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasmadi, M.; Noorfarahzilah, M.; Noraidah, H.; Zainol, M.K.; Jahurul, M.H.A. Functional properties of composite flour: A review. Food Res. 2020, 4, 1820–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.R. Influence of Chemical Properties of Wheat-Lupine Flour Blends on Cake Quality. Am. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 2, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubois, V.; Breton, S.; Linder, M.; Fanni, J.; Parmentier, M. Fatty acid profiles of 80 vegetable oils with regard to their nutritional potential. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2007, 109, 710–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levent, H.; Bilgiçli, N. Enrichment of gluten-free cakes with lupin (Lupinus albus L.) or buckwheat (Fagopyrum es-culentum M.) flours. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 62, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortolan, F.; Steel, C.J. Protein Characteristics that Affect the Quality of Vital Wheat Gluten to be Used in Baking: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zucco, G.M.; Bollini, F. Odour recognition memory and odour identification in patients with mild and severe major depressive disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2011, 190, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Singh, N.; Sharma, T.R.; Saxena, S. Physicochemical, rheological and cookie making properties of corn and potato flours. Food Chem. 2003, 83, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Omari, D.Z.; Abdul-Hussain, S.S.; Ajo, R.Y. Germinated lupin (Lupinus albus) flour improves Arabic flat bread properties. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2016, 8, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatsaragkou, K.; Gounaropoulos, G.; Mandala, I. Development of gluten free bread containing carob flour and resistant starch. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 58, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, S.; Colonna, P.; Buleon, A.; Della Valle, G. Physicochemical Behaviors of Sugars, Lipids, and Gluten in ShortDough and Biscuit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasar-Abbas, S.M.; Jayasena, V. Effect of lupin flour incorporation on the physical and sensory properties of muffins. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2012, 4, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, J.; Lima, A.; Ferreira, R.B.; Raymundo, A. Lupin Seed Protein Extract Can Efficiently Enrich the Physical Properties of Cookies Prepared with Alternative Flours. Foods 2020, 9, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McWatters, K.H. Replacement of milk protein with protein from cowpea and field pea flours in baking powder biscuits. Cereal Chem. 1980, 57, 223–226. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, R.S.; Johnson, S.K. Sensory acceptability of foods containing Australian sweet lupin (Lupinus angustifolius) flour. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, SNQ92–SNQ97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasena, V.; Leung, P.P.Y.; Nasar-Abbas, S.M. Effect of Lupin Flour Substitution on the Quality and Sensory Acceptability of Instant Noodles. J. Food Qual. 2010, 33, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredients | % |
|---|---|
| Wheat flour | 44.8 |
| Egg | 9.5 |
| Soy bean oil | 6.8 |
| Dry full fat milk | 13.6 |
| Sugar | 6.8 |
| Yeast | 1.25 |
| Baking soda | 0.27 |
| Vanilla | 0.68 |
| Water | 16.3 |
| Ingredients | % |
|---|---|
| Brown sugar | 42.5 |
| Ground cinnamon | 7.5 |
| Butter | 25 |
| Walnut | 25 |
| Ingredients | % |
|---|---|
| Sweet concentrated milk | 95.2 |
| Ground cinnamon | 4.8 |
| Flours | Moisture % * | Ash % * | Protein % * | Lipid % * | Carbohydrate (Including Soluble Fibers) % * | Fiber % * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat flour | 11.92 ± 0.01 a | 0.44 ± 0.06 c | 9.87 ± 0.24 c | 1.32 ± 0.23 c | 76.06 ± 2.09 b | 0.39 ± 0.17 d |
| Resistant starch | 5.12 ± 0.03 d | 0.18 ± 0.03 d | 0.06 ± 0.01 d | 0.15 ± 0.05 d | 94.08 ± 0.02 a | 0.41± 0.01 c |
| Lupine flour | 8.31 ± 0.08 b | 2.62 ± 0.03 b | 32.07 ± 0.09 a | 6.03 ± 0.04 b | 34.76 ± 0.08 c | 16.21 ± 0.01 b |
| Flaxseed flour | 6.40 ± 0.01 c | 3.86 ± 0.01 a | 17.91 ± 0.01 b | 34.60 ± 0.00 a | 20.70 ± 0.01 d | 16.53 ± 0.03 a |
| Treatment | Moisture % * | Ash % * | Protein % * | Lipid % * | Carbohydrate (Including Soluble Fiber) % * | Fiber % * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 15.87 ± 0.01 h | 1.17 ± 0.01 f | 8.22 ± 0.21 e | 18.04 ± 0.04 g | 54.74 ± 0.04 c | 1.96 ± 0.04 h |
| T1 | 16.40 ± 0.08 g | 1.33 ± 0.08 e | 3.20 ± 0.02 i | 19.35 ± 0.01 f | 56.11 ± 0.06 a | 3.61 ± 0.03 g |
| T2 | 16.59 ± 0.05 g | 1.35 ± 0.02 e | 4.03 ± 0.03 h | 19.37 ± 0.01 f | 54.95 ± 0.03 b | 3.71 ± 0.01 g |
| T3 | 16.72 ± 0.03 f | 1.41 ± 0.01 de | 5.32 ± 0.01 g | 19.51 ± 0.03 e | 53.00 ± 0.04 d | 4.04 ± 0.03 f |
| T4 | 16.83 ± 0.01 e | 1.49 ± 0.01 cd | 7.02 ± 0.05 f | 19.59 ± 0.03 d | 50.90 ± 0.06 e | 4.17 ± 0.02 e |
| T5 | 17.00 ± 0.01 d | 1.54 ± 0.01 c | 9.03 ± 0.03 d | 19.65 ± 0.01 d | 48.08 ± 0.03 f | 4.70 ± 0.02 d |
| T6 | 17.89 ± 0.05 c | 1.60 ± 0.04 b | 10.45 ± 0.06 c | 20.02 ± 0.01 c | 44.63 ± 0.03 g | 5.41 ± 0.02 c |
| T7 | 18.57 ± 0.02 b | 1.64 ± 0.03 b | 11.74 ± 0.04 b | 20.72 ± 0.02 b | 41.31 ± 0.03 h | 6.02 ± 0.03 b |
| T8 | 19.43 ± 0.02 a | 1.74 ± 0.04 a | 12.31 ± 0.02 a | 21.16 ± 0.01 a | 38.52 ± 0.04 i | 6.84 ± 0.06 a |
| Treatment | Weight (g) * | Diameter (cm) * | Thickness (cm) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 26.25 ± 0.49 c | 5.55 ± 0.07 a | 1.65 ± 0.21 ab |
| T1 | 27.80 ± 0.30 bc | 5.65 ± 0.07 a | 1.60 ± 0.00 ab |
| T2 | 28.75 ± 0.35 abc | 5.65 ± 0.07 a | 1.60 ± 0.14 ab |
| T3 | 29.35 ± 1.20 abc | 5.50 ± 0.00 a | 1.60 ± 0.3 ab |
| T4 | 22.05 ± 0.35 d | 5.05 ± 0.07 b | 1.40 ± 0.00 b |
| T5 | 30.75 ± 1.06 a | 5.10 ± 0.14 b | 1.80 ± 0.00 a |
| T6 | 31.50 ± 3.53 a | 5.6 ± 0.14 a | 1.55 ± 0.07 ab |
| T7 | 27.70 ± 0.28 bc | 5.05 ± 0.21 b | 1.50 ± 0.00 ab |
| T8 | 27.83 ± 0.60 bc | 4.95 ± 0.07 b | 1.75 ± 0.07 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maghaydah, S.; Alkahlout, A.; Abughoush, M.; Al Khalaileh, N.I.; Olaimat, A.N.; Al-Holy, M.A.; Ajo, R.; Choudhury, I.; Hayajneh, W. Novel Gluten-Free Cinnamon Rolls by Substituting Wheat Flour with Resistant Starch, Lupine and Flaxseed Flour. Foods 2022, 11, 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11071022
Maghaydah S, Alkahlout A, Abughoush M, Al Khalaileh NI, Olaimat AN, Al-Holy MA, Ajo R, Choudhury I, Hayajneh W. Novel Gluten-Free Cinnamon Rolls by Substituting Wheat Flour with Resistant Starch, Lupine and Flaxseed Flour. Foods. 2022; 11(7):1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11071022
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaghaydah, Sofyan, Asma Alkahlout, Mahmoud Abughoush, Nazieh I. Al Khalaileh, Amin N. Olaimat, Murad A. Al-Holy, Radwan Ajo, Imranul Choudhury, and Waed Hayajneh. 2022. "Novel Gluten-Free Cinnamon Rolls by Substituting Wheat Flour with Resistant Starch, Lupine and Flaxseed Flour" Foods 11, no. 7: 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11071022
APA StyleMaghaydah, S., Alkahlout, A., Abughoush, M., Al Khalaileh, N. I., Olaimat, A. N., Al-Holy, M. A., Ajo, R., Choudhury, I., & Hayajneh, W. (2022). Novel Gluten-Free Cinnamon Rolls by Substituting Wheat Flour with Resistant Starch, Lupine and Flaxseed Flour. Foods, 11(7), 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11071022






