Evolution in Composition of Kombucha Consortia over Three Consecutive Years in Production Context
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Origin and Composition of Kombucha Samples
2.2. Isolation and Identification of Yeasts and Bacteria Using Culture-Depending Methods
2.2.1. Sampling and Extraction of Microorganisms from the Biofilm
2.2.2. Determination of Biofilm Dry Weight
2.2.3. Isolation of Microorganisms and Population Determination
2.2.4. Macroscopic and Microscopic Examinations
2.2.5. Preparation of Isolates for Identification
2.2.6. DNA Extraction
2.2.7. Amplification
2.2.8. Identification
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Populations of Yeasts and Bacteria
3.2. Identification of Microorganisms
PCR and Electrophoresis
3.3. Macroscopic and Microscopic Examinations
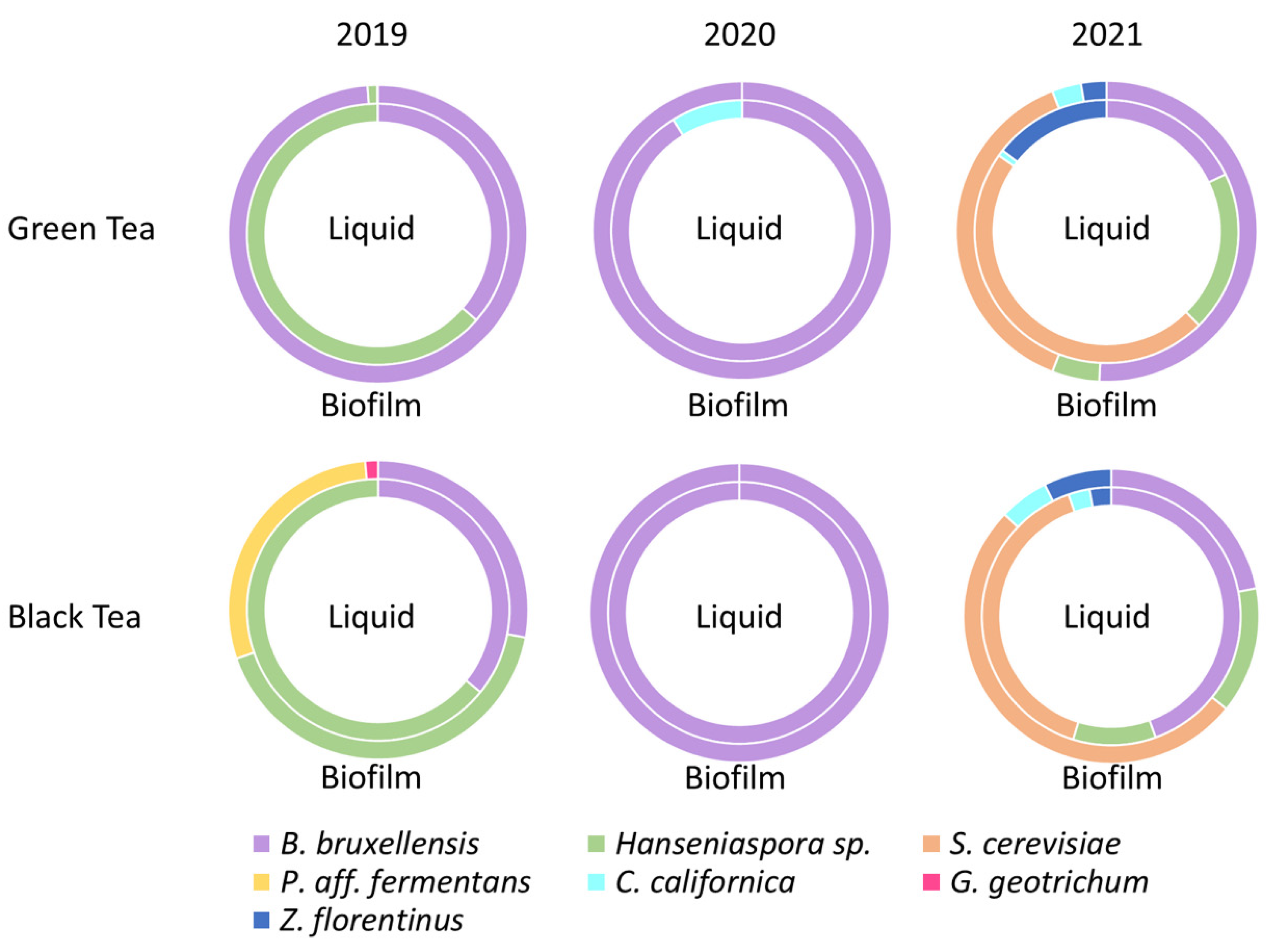
3.4. Proportions in Yeast Species
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Marsh, A.J.; O’Sullivan, O.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Sequence-Based Analysis of the Bacterial and Fungal Compositions of Multiple Kombucha (Tea Fungus) Samples. Food Microbiol. 2014, 38, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal-Soto, S.A.; Beaufort, S.; Bouajila, J.; Souchard, J.-P.; Taillandier, P. Understanding Kombucha Tea Fermentation: A Review. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Harris, H.M.B.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A Taxonomic Note on the Genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 Novel Genera, Emended Description of the Genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and Union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.; Grandvalet, C.; Verdier, F.; Martin, A.; Alexandre, H.; Tourdot-Maréchal, R. Microbiological and Technological Parameters Impacting the Chemical Composition and Sensory Quality of Kombucha. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2050–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayabalan, R.; Malbaša, R.V.; Lončar, E.S.; Vitas, J.S.; Sathishkumar, M. A Review on Kombucha Tea-Microbiology, Composition, Fermentation, Beneficial Effects, Toxicity, and Tea Fungus. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbowy, M.E.; Balentine, D.A.; Davies, A.P.; Cai, Y. Tea Chemistry. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1997, 16, 415–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, A.; Narayanan, S.; Alcock, J.; Varsani, A.; Maley, C.; Aktipis, A. Kombucha: A Novel Model System for Cooperation and Conflict in a Complex Multi-Species Microbial Ecosystem. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Grandvalet, C.; Verdier, F.; Martin, A.; Alexandre, H.; Tourdot-Maréchal, R. Microbial Dynamics between Yeasts and Acetic Acid Bacteria in Kombucha: Impacts on the Chemical Composition of the Beverage. Foods 2020, 9, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Grandvalet, C.; Winckler, P.; Verdier, F.; Martin, A.; Alexandre, H.; Tourdot-Maréchal, R. Shedding Light on the Formation and Structure of Kombucha Biofilm Using Two-Photon Fluorescence Microscopy. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coton, M.; Pawtowski, A.; Taminiau, B.; Burgaud, G.; Deniel, F.; Coulloumme-Labarthe, L.; Fall, A.; Daube, G.; Coton, E. Unraveling Microbial Ecology of Industrial-Scale Kombucha Fermentations by Metabarcoding and Culture-Based Methods. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Adhikari, K. Current Trends in Kombucha: Marketing Perspectives and the Need for Improved Sensory Research. Beverages 2020, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, S.R.; Gray, P.P. A Differential Procedure for Bacteriological Studies Useful in the Fermentation Industry. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1951, 32, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.F. Detection of Wild Yeasts in the Brewery. J. Inst. Brew. 1971, 77, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallmann, C.L.; Brown, J.A.; Olineka, T.L.; Cocolin, L.; Mills, D.A.; Bisson, L.F. Use of WL Medium to Profile Native Flora Fermentations. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2001, 52, 198–203. [Google Scholar]
- Ndoye, B.; Lebecque, S.; Dubois-Dauphin, R.; Tounkara, L.; Guiro, A.-T.; Kere, C.; Diawara, B.; Thonart, P. Thermoresistant Properties of Acetic Acids Bacteria Isolated from Tropical Products of Sub-Saharan Africa and Destined to Industrial Vinegar. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salma, M.; Rousseaux, S.; Sequeira-Le Grand, A.; Alexandre, H. Cytofluorometric Detection of Wine Lactic Acid Bacteria: Application of Malolactic Fermentation to the Monitoring. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, B.E.; Sandine, W.E. Improved Medium for Lactic Streptococci and Their Bacteriophages. Appl. Microbiol. 1975, 29, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoura, N.; Mbaiguinam, M.; Nguyen, H.V.; Gaillardin, C.; Pourquie, J. Identification and Typing of the Yeast Strains Isolated from Bili Bili, a Traditional Sorghum Beer of Chad. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve-Zarzoso, B.; Belloch, C.; Uruburu, F.; Querol, A. Identification of Yeasts by RFLP Analysis of the 5.8S RRNA Gene and the Two Ribosomal Internal Transcribed Spacers. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1999, 49, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huey, B.; Hall, J. Hypervariable DNA Fingerprinting in Escherichia coli: Minisatellite Probe from Bacteriophage M13. J. Bacteriol. 1989, 171, 2528–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reguant, C.; Bordons, A. Typification of Oenococcus oeni Strains by Multiplex RAPD-PCR and Study of Population Dynamics during Malolactic Fermentation. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qian, P.-Y. Conservative Fragments in Bacterial 16S rRNA Genes and Primer Design for 16S Ribosomal DNA Amplicons in Metagenomic Studies. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrison, K.; Curtin, C. Microbial Composition of SCOBY Starter Cultures Used by Commercial Kombucha Brewers in North America. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leech, J.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Walsh, A.M.; Macori, G.; Walsh, C.J.; Barton, W.; Finnegan, L.; Crispie, F.; O’Sullivan, O.; Claesson, M.J.; et al. Fermented-Food Metagenomics Reveals Substrate-Associated Differences in Taxonomy and Health-Associated and Antibiotic Resistance Determinants. mSystems 2020, 5, e00522-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reva, O.N.; Zaets, I.E.; Ovcharenko, L.P.; Kukharenko, O.E.; Shpylova, S.P.; Podolich, O.V.; de Vera, J.-P.; Kozyrovska, N.O. Metabarcoding of the Kombucha Microbial Community Grown in Different Microenvironments. AMB Express 2015, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, B.D.; Divol, B. Brettanomyces Bruxellensis, a Survivalist Prepared for the Wine Apocalypse and Other Beverages. Food Microbiol. 2016, 59, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, A.L.; Heard, G.; Cox, J. Yeast Ecology of Kombucha Fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 95, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Green Tea Kombucha | January 2019 | January 2020 | January 2021 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid (CFU mL−1) | Biofilm (CFU g−1 Dry Mass) | Liquid (CFU mL−1) | Biofilm (CFU g−1 Dry Mass) | Liquid (CFU mL−1) | Biofilm (CFU g−1 Dry Mass) | |
| Yeasts | ||||||
| Wallerstein Lab nutrient (WL) | 1.66 × 106 ±3.39 × 105 | 1.03 × 108 ±2.43 × 105 | 3.40 × 104 ±1.72 × 104 | 1.60 × 106 ±1.55 × 103 | 9.83 × 106 ±4.27 × 106 | 5.70 × 107 ±4.53 × 106 |
| Dekkera/Brettanomyces bruxellensis | 6.03 × 105 ±1.64 × 105 | 1.02 × 108 ±3.16 × 106 | 3.10 × 104 ±2.63 × 104 | 1.60 × 106 ±2.92 × 105 | 7.05. × 06 ±1.30 × 105 | 1.95 × 107 ±6.66 × 105 |
| Hanseniaspora sp. | 1.05 × 106 ±7.42 × 104 | 1.09 × 106 ±4.46 × 105 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | 7.80 × 106 ±2.74 × 104 | 1.95 × 106 ±6.86 × 103 |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | 1.86 × 107 ±2.55 × 104 | 1.47 × 107 ±8.04 × 104 |
| Zygosaccharomyces florentinus | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | 5.70 × 106 ±3.14 × 104 | 1.05 × 106 ±2.94 × 103 |
| Candida sp. | <1 × 103 | 3.68 × 104 ±6.53 × 102 | 3.00 × 103 ±7.84 × 102 | <1 × 103 | 3.00 × 105 ±1.96 × 103 | 1.20 × 106 ±1.18 × 104 |
| Bacteria | ||||||
| Mannitol | 8.47 × 106 ±6.23 × 105 | 9.29 × 107 ±1.16 × 106 | 1.79 × 106 ±4.33 × 105 | 5.51 × 107 ±3.90 × 104 | 9.45 × 106 ±1.95 × 106 | 7.79 × 107 ±4.22 × 106 |
| LAC | 7.13 × 105 ±3.28 × 105 | 2.34 × 106 ±3.60 × 105 | 3.18 × 105 ±3.44 × 104 | 8.98 × 106 ±3.10 × 103 | 8.33 × 106 ±1.27 × 107 | 5.18 × 108 ±1.59 × 107 |
| MRS | 8.67 × 106 ±5.09 × 106 | 1.15 × 106 ±3.64 × 105 | 2.23 ×105 ±1.51 × 104 | 8.98 × 106 ±1.36 × 103 | 1.19 × 106 ±1.57 × 106 | 8.57 × 107 ±2.91 × 106 |
| M17 | nd | nd | 1.73 × 105 ±4.09 × 104 | nd | 1.74 × 106 ±6.23 × 105 | 1.66 × 108 ±5.88 × 106 |
| Black Tea Kombucha | January 2019 | January 2020 | January 2021 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid (CFU mL−1) | Biofilm (CFU g−1 Dry Mass) | Liquid (CFU mL−1) | Biofilm (CFU g−1 Dry Mass) | Liquid (CFU mL−1) | Biofilm (CFU g−1 Dry Mass) | |
| Yeasts | ||||||
| Wallerstein Lab nutrient (WL) | 1.26 × 106 ±1.59 × 105 | >6.29 × 108 | 4.51 × 104 ±1.20 × 104 | 4.70 × 105 ±1.08 × 103 | 9.50 × 106 ±2.45 × 106 | 2.78 × 107 ±1.14 × 106 |
| Dekkera/Brettanomyces bruxellensis | 4.50 × 105 ±2.35 × 105 | >1.76 × 108 | 4.51 × 104 ±1.47 × 103 | 4.70 × 105 ±1.63 × 104 | 1.74 × 107 ±2.20 × 105 | 9.75 × 106 ±2.89 × 105 |
| Hanseniaspora sp. | 8.07 × 105 ±1.63 × 105 | 2.63 × 108 ±1.16 × 106 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | 4.05 × 106 ±4.21 × 104 | 6.15 × 106 ±2.06 × 104 |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 66.7 ±98.0 | 5.52 × 104 ±2.26 × 103 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | 1.56 × 107 ±2.55 × 104 | 2.28 × 107 ±5.68 × 104 |
| Pichia aff. Fermentans | <1 × 103 | 1.82 × 108 ±2.79 × 105 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 |
| Zygosaccharomyces florentinus | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | 1.05 × 106 ±1.27 × 104 | 3.30 × 106 ±2.74 × 104 |
| Galactomyces. Geotrichum | <1 × 103 | 8.81 × 106 ±1.13 × 105 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 |
| Candida sp. | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | <1 × 103 | 1.05 × 106 ±2.94 × 103 | 2.40 × 106 ±3.92 × 103 |
| Bacteria | ||||||
| Mannitol | 5.73 × 106 ±1.31 × 105 | >1.76 × 108 | 1.97 × 105 ±2.94 × 103 | 2.13 × 108 ±2.65 × 102 | 8.47 × 106 ±6.23 × 105 | 4.75 × 107 ±2.72 × 106 |
| LAC | 5.43 × 107 ±2.83 × 107 | 3.47 × 107 ±6.63 × 105 | 1.92 × 106 ±5.37 × 104 | 3.22 × 107 ±4.83 × 103 | 6.31 × 107 ±1.46 × 106 | 1.48 × 108 ±7.37 × 106 |
| MRS | 2.93 × 107 ±4.71 × 106 | 3.00 × 107 ±1.11 × 106 | 8.50 × 105 ±1.35 × 104 | 1.45 × 108 ±1.21 × 103 | 8.67 × 106 ±5.09 × 106 | 8.25 × 106 ±1.77 × 106 |
| M17 | nd | nd | 2.62 × 105 ±4.12 × 104 | 2.22 × 106 ±3.70 × 103 | 4.28 × 106 ±4.02 × 105 | 5.99 × 107 ±5.05 × 106 |
| Species | Green Tea 2019 | Green Tea 2020 | Green Tea 2021 | Black Tea 2019 | Black Tea 2020 | Black Tea 2021 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yeasts | ||||||
| Dekkera/Brettanomyces bruxellensis | L + B | L + B | L + B | L + B | L + B | L + B |
| Hanseniaspora valbyensis | L + B | nd | nd | L + B | nd | L + B |
| Hanseniaspora opuntiae | nd | nd | nd | B | nd | nd |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | nd | nd | L + B | L + B | nd | L + B |
| Pichia aff. fermentans | nd | nd | nd | B | nd | nd |
| Galactomyces geotrichum | nd | nd | nd | B | nd | nd |
| Zygosaccharomyces florentinus | nd | nd | L + B | nd | nd | L + B |
| Candida boidinii | B | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Candida californica | B | L | L + B | nd | nd | L + B |
| Acetic acid bacteria | ||||||
| Acetobacter indonesiensis | nd | nd | nd | L + B | nd | nd |
| Acetobacter tropicalis or senegalis | L + B | B | nd | nd | L | nd |
| Acetobacter pasteurianus or cibinongensis | nd | nd | L | nd | nd | nd |
| Acetobacter okinawensis | nd | nd | B | nd | nd | nd |
| Acetobacter aceti | nd | nd | B | nd | nd | nd |
| Acetobacter peroxydans or papayae | nd | nd | nd | L + B | B | nd |
| Gluconobacter sp | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | L |
| Gluconacetobacter liquefaciens | L + B | nd | nd | nd | L | nd |
| Gluconacetobacter takamatsuzukensis | L + B | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Komagataeibacter rhaeticus | nd | nd | B | nd | nd | nd |
| Komagataeibacter saccharivorans | nd | nd | B | L + B | nd | nd |
| Lactic acid bacteria | ||||||
| Liquorilactobacillus ghanensis | nd | nd | nd | nd | L | L + B |
| Liquorilactobacillus hordei | nd | B | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Liquorilactobacillus satsumensis or oeni | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | L + B |
| Liquorilactobacillus mali | nd | L | L | nd | L | nd |
| Liquorilactobacillus nagelii | L + B | nd | nd | nd | B | B |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mas, P.; Tran, T.; Verdier, F.; Martin, A.; Alexandre, H.; Grandvalet, C.; Tourdot-Maréchal, R. Evolution in Composition of Kombucha Consortia over Three Consecutive Years in Production Context. Foods 2022, 11, 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11040614
Mas P, Tran T, Verdier F, Martin A, Alexandre H, Grandvalet C, Tourdot-Maréchal R. Evolution in Composition of Kombucha Consortia over Three Consecutive Years in Production Context. Foods. 2022; 11(4):614. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11040614
Chicago/Turabian StyleMas, Perrine, Thierry Tran, François Verdier, Antoine Martin, Hervé Alexandre, Cosette Grandvalet, and Raphaëlle Tourdot-Maréchal. 2022. "Evolution in Composition of Kombucha Consortia over Three Consecutive Years in Production Context" Foods 11, no. 4: 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11040614
APA StyleMas, P., Tran, T., Verdier, F., Martin, A., Alexandre, H., Grandvalet, C., & Tourdot-Maréchal, R. (2022). Evolution in Composition of Kombucha Consortia over Three Consecutive Years in Production Context. Foods, 11(4), 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11040614








