Modifications of Thermal-Induced Northern Pike (Esox lucius) Liver Ferritin on Structural and Self-Assembly Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Purification of Ferritin
2.3. Thermal Treatment of Ferritin
2.4. Determination of the Solubility and Iron Content of NPLF
2.5. Protein Gel Electrophoresis
2.6. Dynamic Light Scattering Experiments
2.7. Circular Dichroism Measurements
2.8. UV-Visible Absorption Spectrum
2.9. Intrinsic Fluorescence Measurements
2.10. Transmission Electron Microscope Experiments
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
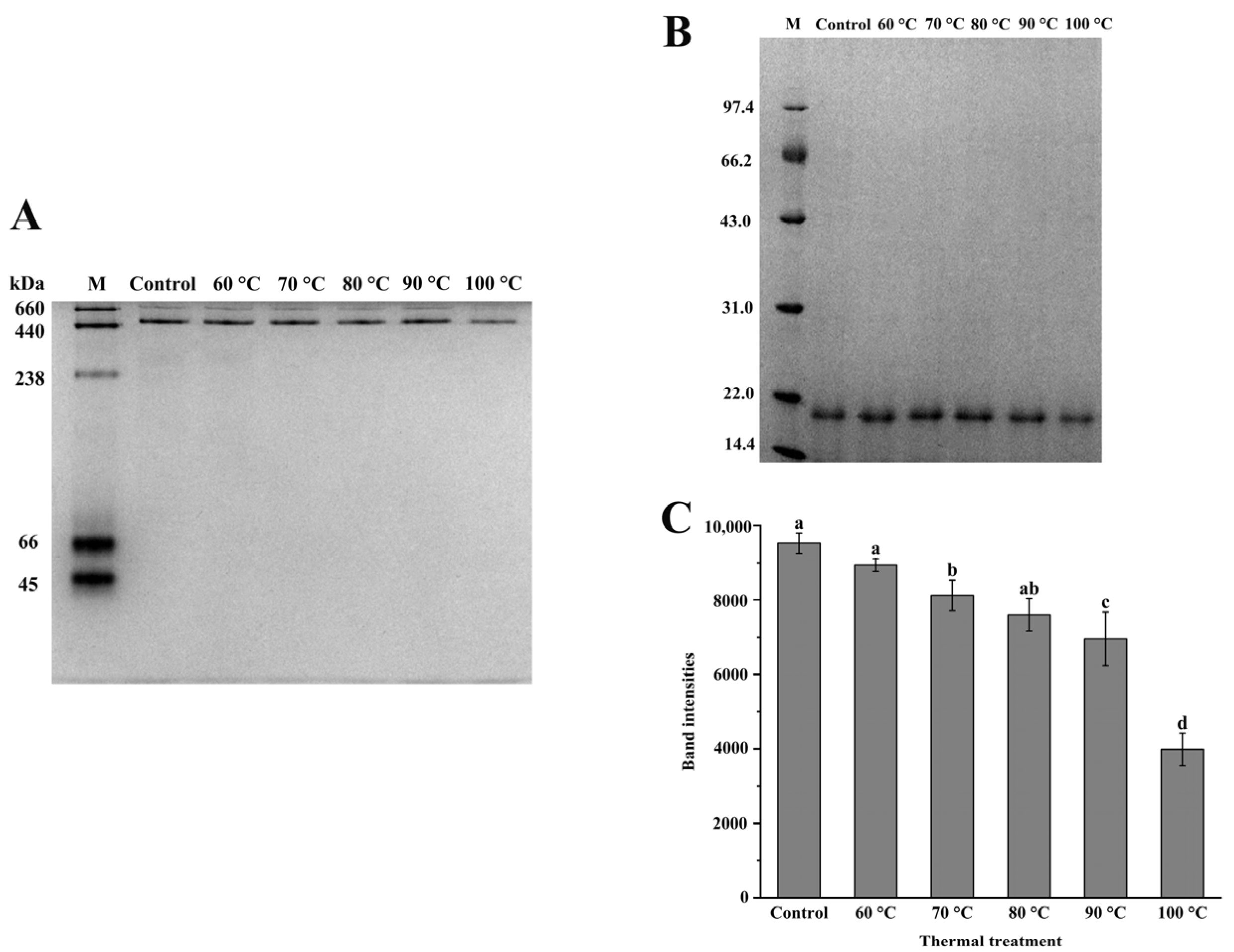
3.1. Characterization and Thermal Stability of NPLF
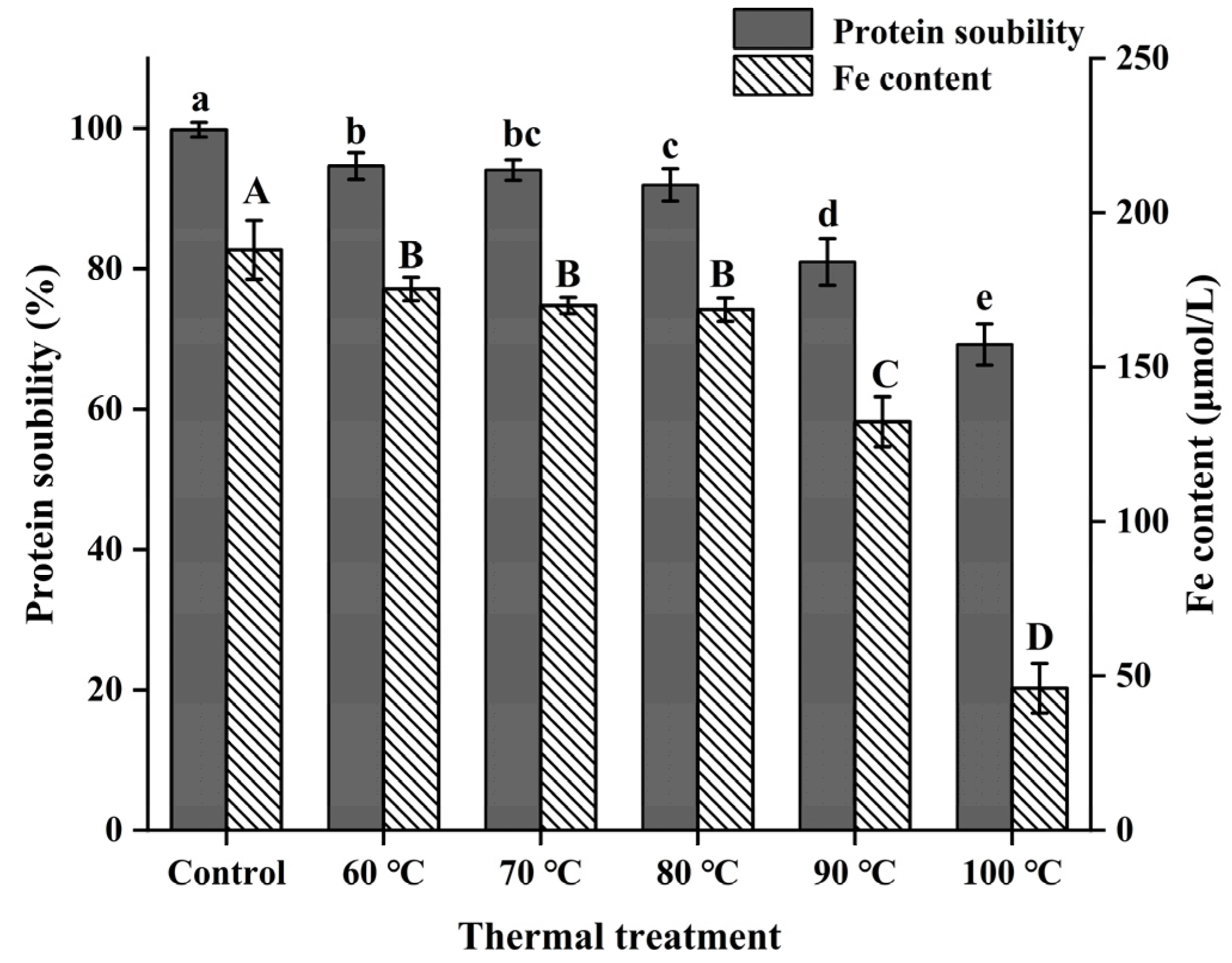
3.2. Solubility and Iron Content of NPLF
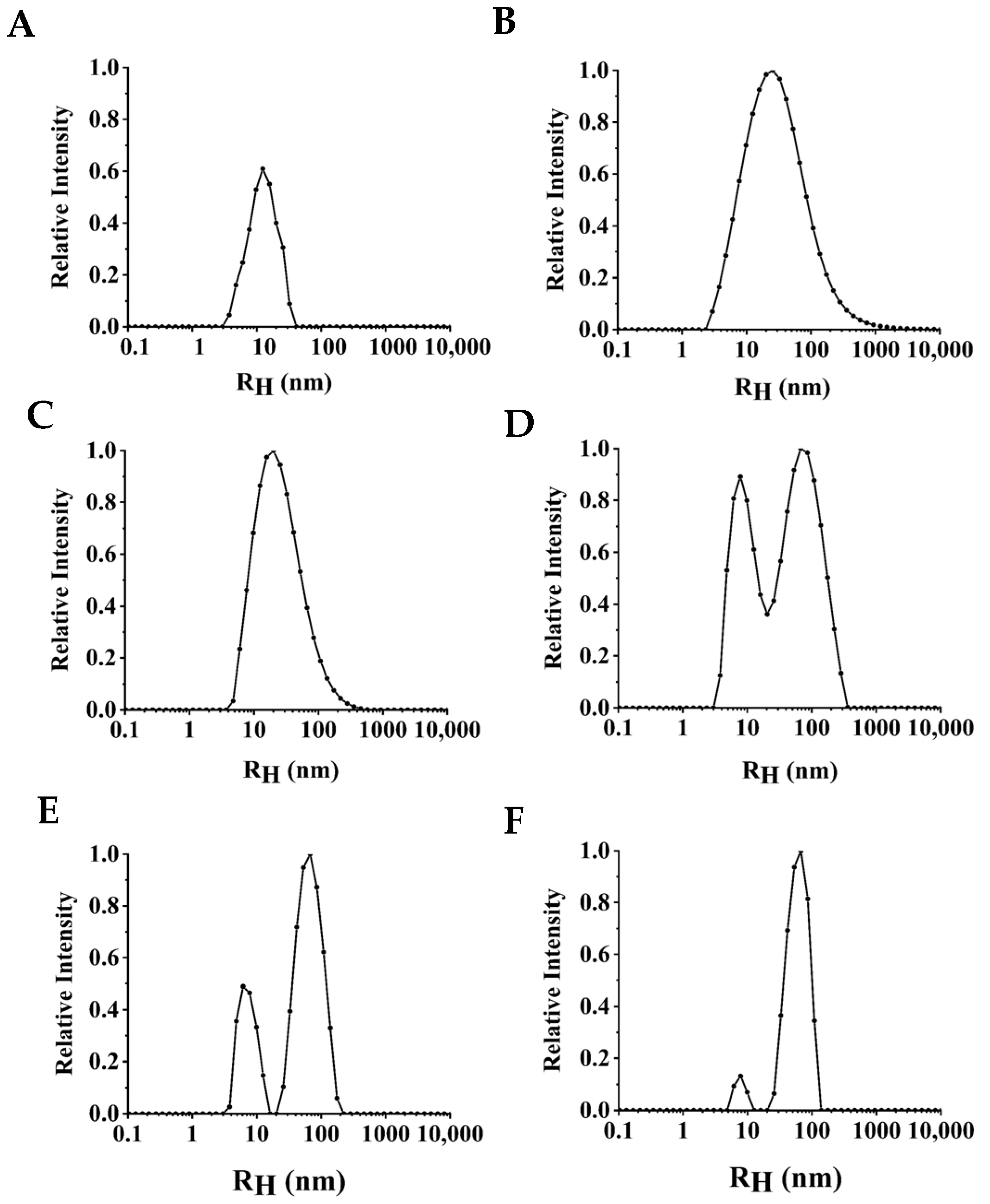
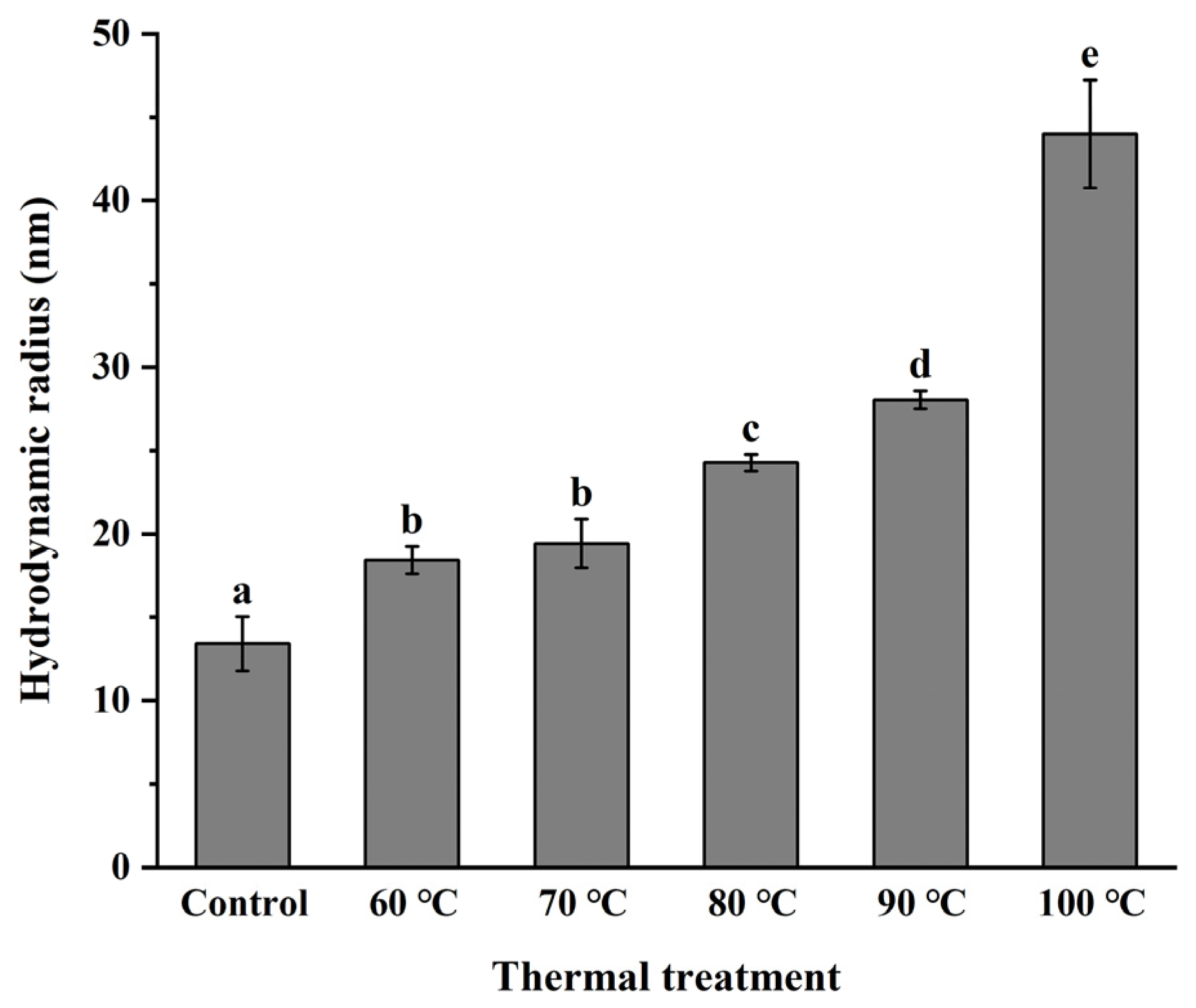
3.3. Monodispersity of NPLF under Thermal Treatment
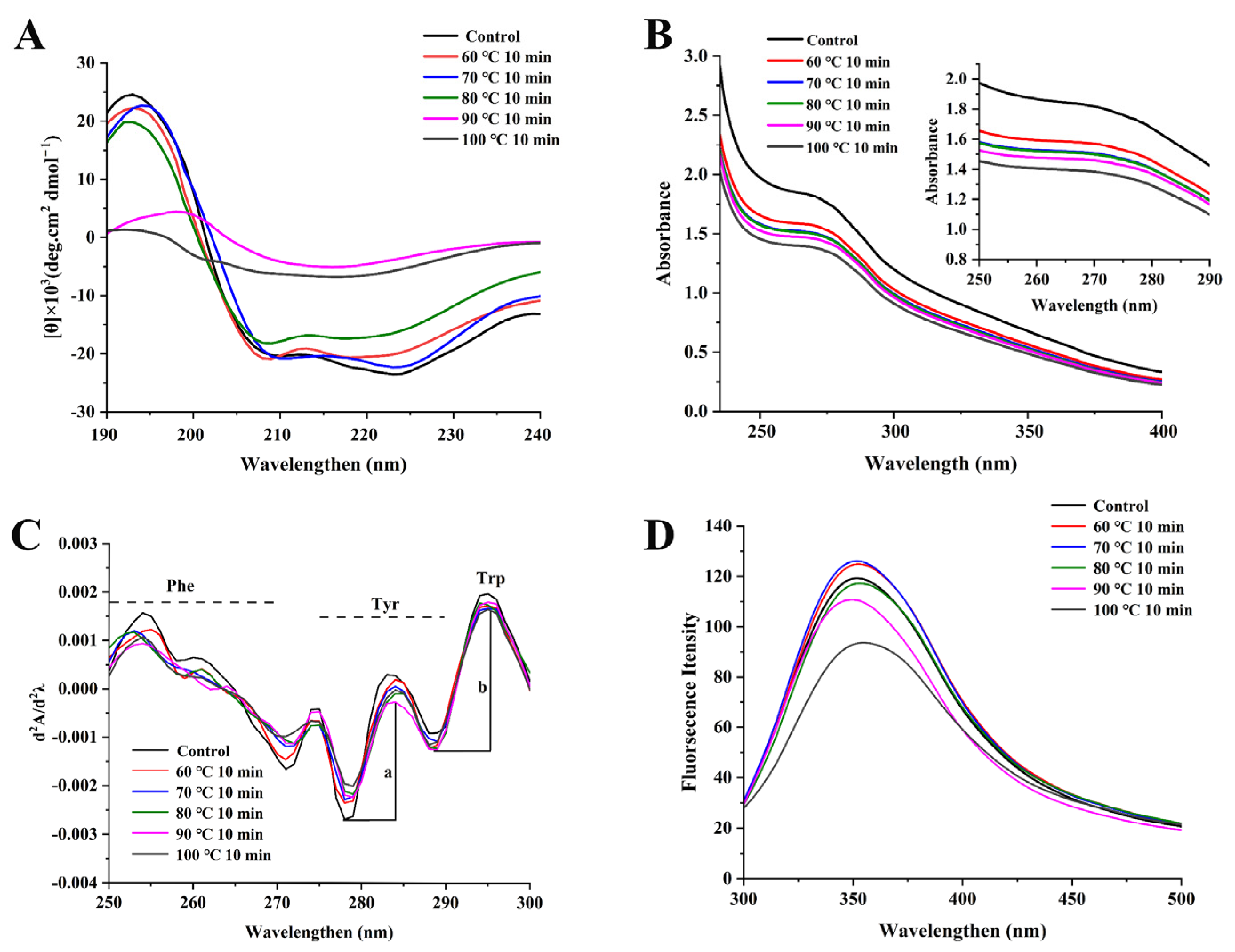
3.4. Secondary Structure Changes of NPLF under Thermal Treatment
3.5. Tertiary Structure Changes in NPLF under Thermal Treatment
3.5.1. UV–Visible Absorption Spectrum Analysis
3.5.2. Intrinsic Fluorescence Analysis
3.6. Microstructure Changes in NPLF under Thermal Treatment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yokoi, K.; Konomi, A. Iron deficiency without anaemia is a potential cause of fatigue: Meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials and cross-sectional studies. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 1422–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hashim, H.; Foda, O.; Ghayaty, E. Lactoferrin or ferrous salts for iron deficiency anemia in pregnancy: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2017, 219, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkien, Z.; Stecher, L.; Mander, A.P.; Pereira, D.I.A.; Powell, J.J. Ferrous sulfate supplementation causes significant gastrointestinal side-effects in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, E.; Churio, O.; Arias, J.L.; Neira-Carrillo, A.; Valenzuela, C. Preparation and characterization of novel edible matrices based on alginate and whey for oral delivery of iron. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 1052771–1052779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Yang, R.; Liu, J.G.; Meng, D.M.; Zhou, Z.K.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Blanchard, C. Fabrication, structure, and function evaluation of the ferritin based nanocarrier for food bioactive compounds. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.H. Phytoferritin and its implications for human health and nutrition. BBA-Gen. Subj. 2010, 1800, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.Y.; Yun, S.J.; Zhao, G.H. Structure, function, and nutrition of phytoferritin: A newly functional factor for iron supplement. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H.; Shi, D.S.; Ha, Y.; Allewell, N.M.; Theil, E.C. Localized unfolding at the junction of three ferritin subunits-A mechanism for iron release? J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 18685–18688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirivech, S.; Frieden, E.; Osaki, S. The release of iron from horse spleen ferritin by reduced flavins. Biochem. J. 1974, 143, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienfait, H.F.; Van der Briel, M.L. Rapid mobilization of ferritin iron by ascorbate in the presence of oxygen. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1980, 631, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.C.; Chai, Z.; Huang, W.Y.; Cui, L.; Li, C.Y.; Ma, K.Y.; Hu, X.D.; Feng, J. Entrapment of an ACE inhibitory peptide into ferritin nanoparticles coated with sodium deoxycholate: Improved chemical stability and intestinal absorption. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 147, 111547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, J.L.; Burton, J.W.; Theil, E.C. Purified ferritin and soybean meal can be sources of iron for treating iron deficiency in rats. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonnerdal, B.; Bryant, A.; Liu, X.F.; Theil, E.C. Iron absorption from soybean ferritin in nonanemic women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beliciu, C.M.; Moraru, C.I. Physico-chemical changes in heat treated micellar casein-soy protein mixtures. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 54, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Xie, Y.Y.; Wang, H.; Xia, X.F. Effects of heat treatment temperature and time on thermal aggregation behavior of myofibrillar proteins from Mirror Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Food Sci. 2021, 42, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveday, S.M. β-Lactoglobulin heat denaturation: A critical assessment of kinetic modelling. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 52, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, M.; Guyomarc’H, F.; Pezennec, S.; Famelart, M.H. On how κ-casein affects the interactions between the heat-induced whey protein/κ-casein complexes and the casein micelles during the acid gelation of skim milk. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhao, G.H. Thermal treatment greatly improves storage stability and monodispersity of pea seed ferritin. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tan, X.Y.; Xia, X.Y.; Zang, J.C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Du, M. Thermal treatment modified the physicochemical properties of re- combinant oyster (Crassostrea gigas) ferritin. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 126210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, T.; Chen, B.; Leng, X.; Zhao, G. Binding of proanthocyanidins to soybean (Glycine max) seed ferritin inhibiting protein degradation by protease in vitro. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zang, J.; Tan, X.; Xia, X.; Du, M. Purification and characterizations of a nanocage ferritin GF1 from oyster (Crassostrea gigas). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 127, 109416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.R.; Qi, X.; Li, M.L.; Zhao, G.H.; Hu, X.S. Phosphate facilitates Fe (II) oxidative deposition in pea seed (Pisum sativum) ferritin. Biochimie 2009, 91, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.N.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Sun, F.D.; Liu, H.T.; Kong, B.H. Synergistic modification of pea protein structure using high-intensity ultrasound and pH-shifting technology to improve solubility and emulsification. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 88, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Luo, Y.E. Determination of Fe2+, Fe3+ and total iron ion with improved ferrozine UV-spectrophotometry. Sci. Tech. Engrg. 2016, 16, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Huang, H.Q.; Lin, Q.M.; Kim, W.S.; Cai, Z.W.; Cao, T.M.; Miao, H.; Luo, D.M. Purification, electrophoretic behavior, and kinetics of iron release of liver ferritin of Dasyatis akajei. J. Protein Chem. 2003, 22, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, T.; Yang, S.; Leng, X.; Zhao, G. Self-assembly of ferritin nanocages into linear chains induced by poly (alpha, L-lysine). Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, A.J.; Ramalli, S.G.; Wallace, B.A. DichroWeb, a website for calculating protein secondary structure from circular dichroism spectroscopic data. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.M.; Chen, S.N.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.E.; Wang, D.S.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhou, Z.K.; Yang, R. Double-interface binding of two bioactive compounds with cage-Like ferritin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 7779–7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.X.; Sun, X.W.; Wang, S.H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, D.F. Formation of nanocomplexes comprising whey proteins and fucoxanthin: Characterization, spectroscopic analysis, and molecular docking. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Bi, T.T.; Zhang, J.F.; Song, S.Q.; Chen, Y.L. The non-covalent interaction between ferritin and chlorogenic acid. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 37, 8–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Huang, H.Q.; Lin, Q.M.; Chen, X.; Huang, H.Y. Polymer characteristics of shark liver ferritin and its subunits by electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2007, 35, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgentini, D.A.; Wagner, J.R.; Anon, M.C. Effects of thermal treatment of soy protein isolate on the characteristics and structure-function relationship of soluble and insoluble fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 15607–15613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Goto, F.; Yoshihara, T.; Mikami, B. Crystal structure of plant ferritin reveals a novel metal binding site that functions as a transit site for metal transfer in ferritin. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4049–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Tian, J.; Liu, Y.Q.; Yang, Z.Y.; Wu, D.D.; Zhou, Z.K. Thermally induced encapsulation of food nutrients into phy 5toferritin through the flexible channels without additives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9950–9955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Qu, X.; Deng, C.; Dai, L.; Liu, C. Heat sensitive protein-heat stable protein interaction: Synergistic enhancement in the thermal co-aggregation and gelation of lactoferrin and α-lactalbumin. Food Res. Int. 2021, 142, 110179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, B.; Li, Z.P.; Niwase, K.; Ganser, C.; Furuta, T.; Uchihashi, T.; Lu, D.N.; Ueno, T. Single-molecule level dynamic observation of disassembly of the apo-ferritin cage in solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 18562–18572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.L.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.Y. Effects of high pressure modification on conformation and gelation properties of myofibrillar protein. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.R.; Ma, Y.G.; Lei, Y.D.; Zhu, X.R.; Zhang, L.F.; Hu, L.; Lu, S.L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J. Ultrasonic structural modification of myofibrillar proteins from Coregonus peled improves emulsification properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 76, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momen, S.; Salami, M.; Alavi, F.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A. The techno-functional properties of camel whey protein compared to bovine whey protein for fabrication a model high protein emulsion. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 101, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.Q.; Luo, S.Z.; Zhong, X.Y.; Cai, J.; Jiang, S.T.; Zheng, Z. Changes in chemical interactions and protein conformation during heat-induced wheat gluten gel formation. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.M.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L.Q.; Ma, T.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Chen, L.Y.; Shan, Y.M.; Wang, Y.W.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhou, Z.K.; et al. Succinylated ferritin as a novel nanocage-like vehicle of polyphenol: Structure, stability, and absorption analysis. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.H.; Chen, L.; Ma, C.Y. Thermal aggregation, amino acid composition and in vitro digestibility of vicilin-rich protein isolates from three Phaseolus legumes: A comparative study. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Kong, B.H.; Li, F.F.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.W.; Xia, X.F. Changes in the thermal stability and structure of protein from porcine longissimus dorsi induced by different thawing methods. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Mithra, K.; Jena, S.S.; Behera, R.K. Kinetics of ferritin self-assembly by laser light scattering: Impact of subunit concentration, pH, and ionic strength. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Bao, Z.J.; Sun, N.; Lin, S.Y. Internal cavity amplification of shell-like ferritin regulated with the change of the secondary and tertiary structure induced by PEF technology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.F.; Pang, Y.C.; Liu, Y.L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.K.; Hu, Q.L. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with high antimicrobial activity and low cytotoxicity using catechol-conjugated chitosan. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 64357–64363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfi, L.; Bellini, M.; Vanna, R.; Morasso, C.; Zago, A.; Carcano, S.; Avvakumova, S.; Bertolini, J.A.; Rizzuto, M.A.; Colombo, M.; et al. H-ferritin enriches the curcumin uptake and improves the therapeutic efficacy in triple negative breast cancer cells. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3318–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment Temperature | α-Helix (%) | β-Sheet (%) | β-Turn (%) | Random Coils (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| control | 62.83 ± 0.65 a | 22.17 ± 0.50 c | 7.67 ± 0.72 f | 7.33 ± 1.25 f |
| 60 °C | 59.70 ± 0.50 b | 17.37 ± 0.95 d | 11.33 ± 0.60 e | 11.60 ± 1.08 e |
| 70 °C | 50.60 ± 1.06 c | 22.57 ± 0.85 c | 12.93 ± 0.68 d | 13.90 ± 0.60 d |
| 80 °C | 48.57 ± 0.86 d | 15.25 ± 0.46 e | 15.34 ± 0.93 c | 20.83 ± 0.76 c |
| 90 °C | 8.10 ± 0.79 e | 36.13 ± 0.84 a | 23.43 ± 1.35 b | 32.33 ± 0.12 b |
| 100 °C | 1.90 ± 0.56 f | 27.40 ± 0.20 b | 35.66 ± 0.68 a | 35.03 ± 0.42 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Deng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J. Modifications of Thermal-Induced Northern Pike (Esox lucius) Liver Ferritin on Structural and Self-Assembly Properties. Foods 2022, 11, 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11192987
Zhang S, Guo X, Deng X, Zhao Y, Zhu X, Zhang J. Modifications of Thermal-Induced Northern Pike (Esox lucius) Liver Ferritin on Structural and Self-Assembly Properties. Foods. 2022; 11(19):2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11192987
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Siying, Xin Guo, Xiaorong Deng, Yunfeng Zhao, Xinrong Zhu, and Jian Zhang. 2022. "Modifications of Thermal-Induced Northern Pike (Esox lucius) Liver Ferritin on Structural and Self-Assembly Properties" Foods 11, no. 19: 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11192987
APA StyleZhang, S., Guo, X., Deng, X., Zhao, Y., Zhu, X., & Zhang, J. (2022). Modifications of Thermal-Induced Northern Pike (Esox lucius) Liver Ferritin on Structural and Self-Assembly Properties. Foods, 11(19), 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11192987






