Physicochemical, Pasting Properties and In Vitro Starch Digestion of Chinese Yam Flours as Affected by Microwave Freeze-Drying
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Drying Experiments
2.3. Determination of Physicochemical Properties
2.3.1. Color
2.3.2. Water- and Oil-Absorption Capacity
2.3.3. Solubility
2.3.4. Bulk Density
2.3.5. Iodine Blue Value (IBV)
2.4. Pasting Properties
2.5. Thermal Properties
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
2.7. In Vitro Starch Digestibility Properties
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
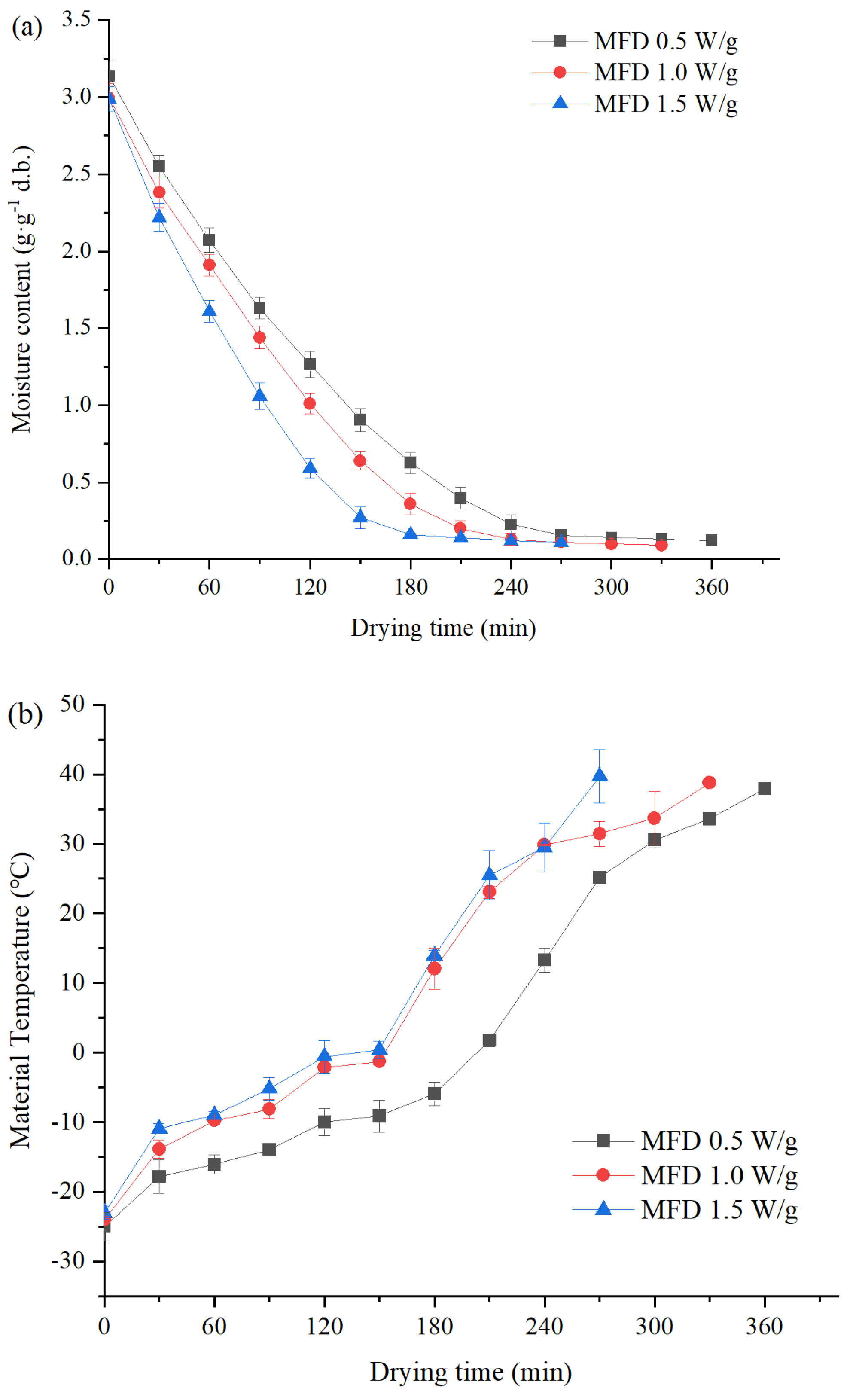
3.1. Drying Characteristics
3.2. Physicochemical and Functional Properties
3.2.1. Color and Bulk Density
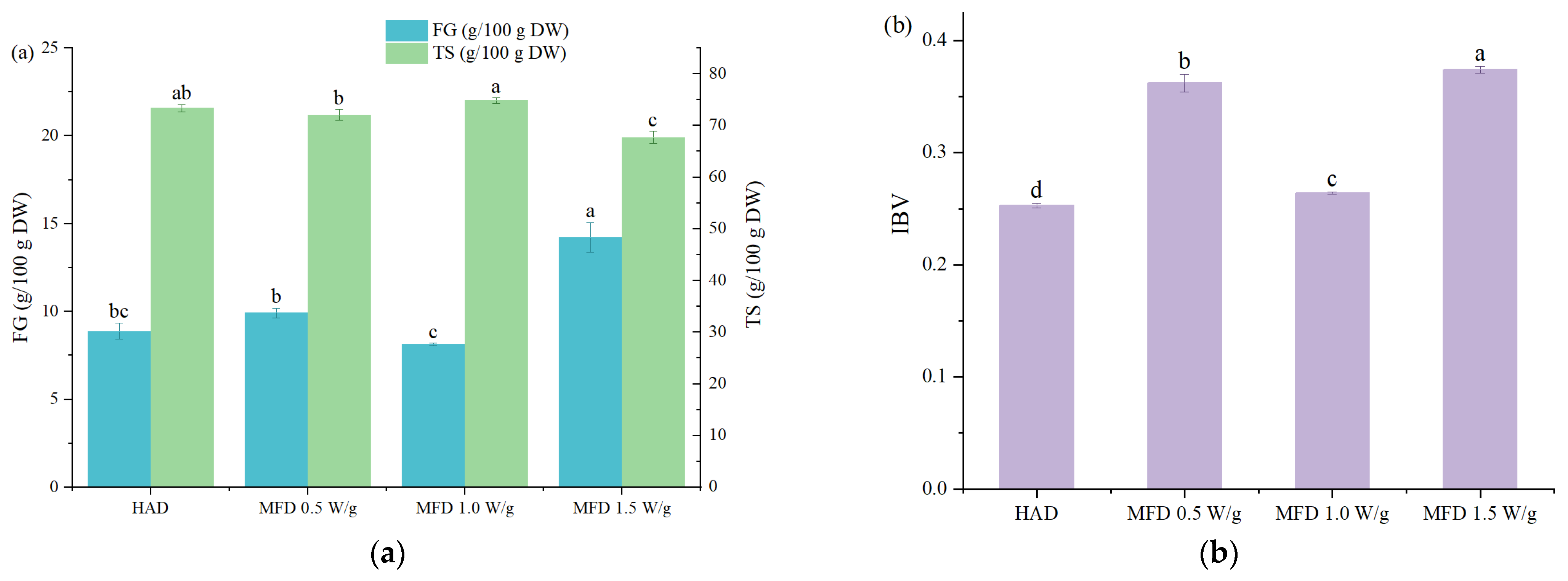
3.2.2. Total Starch Content, Free Glucose Content, and IBV
3.2.3. Functional Properties
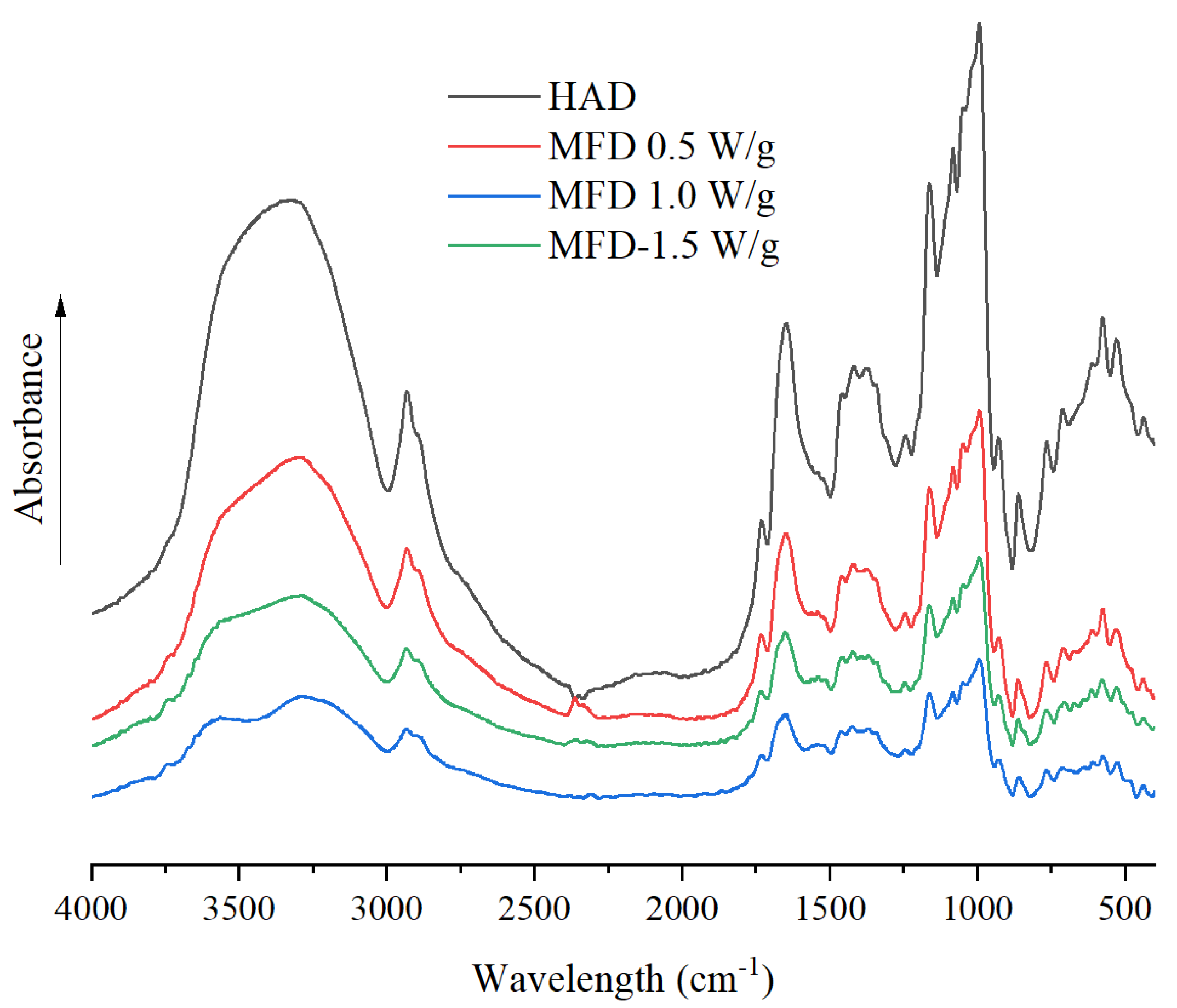
3.3. FTIR Spectral Analysis
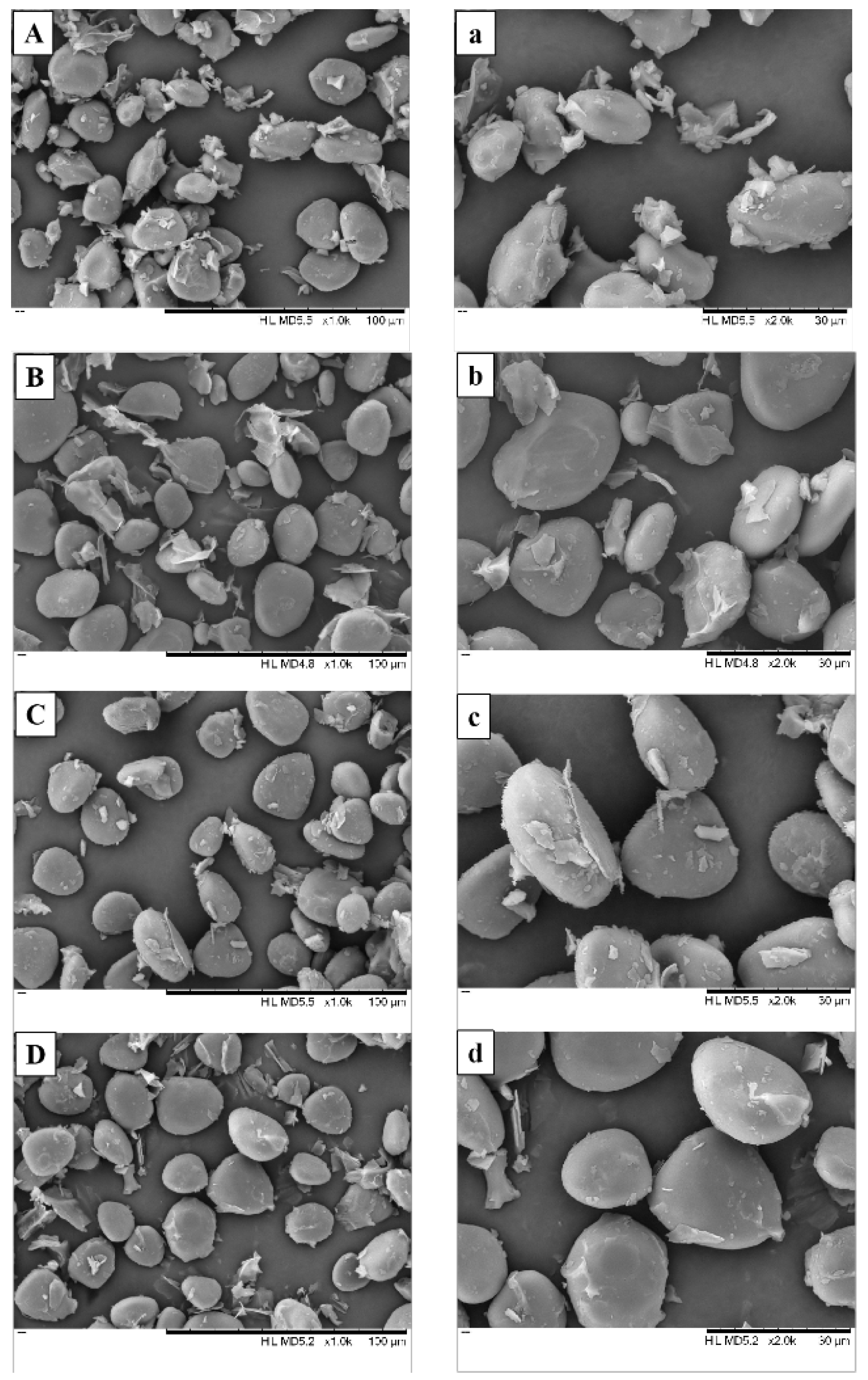
3.4. Micromorphology Observed by SEM
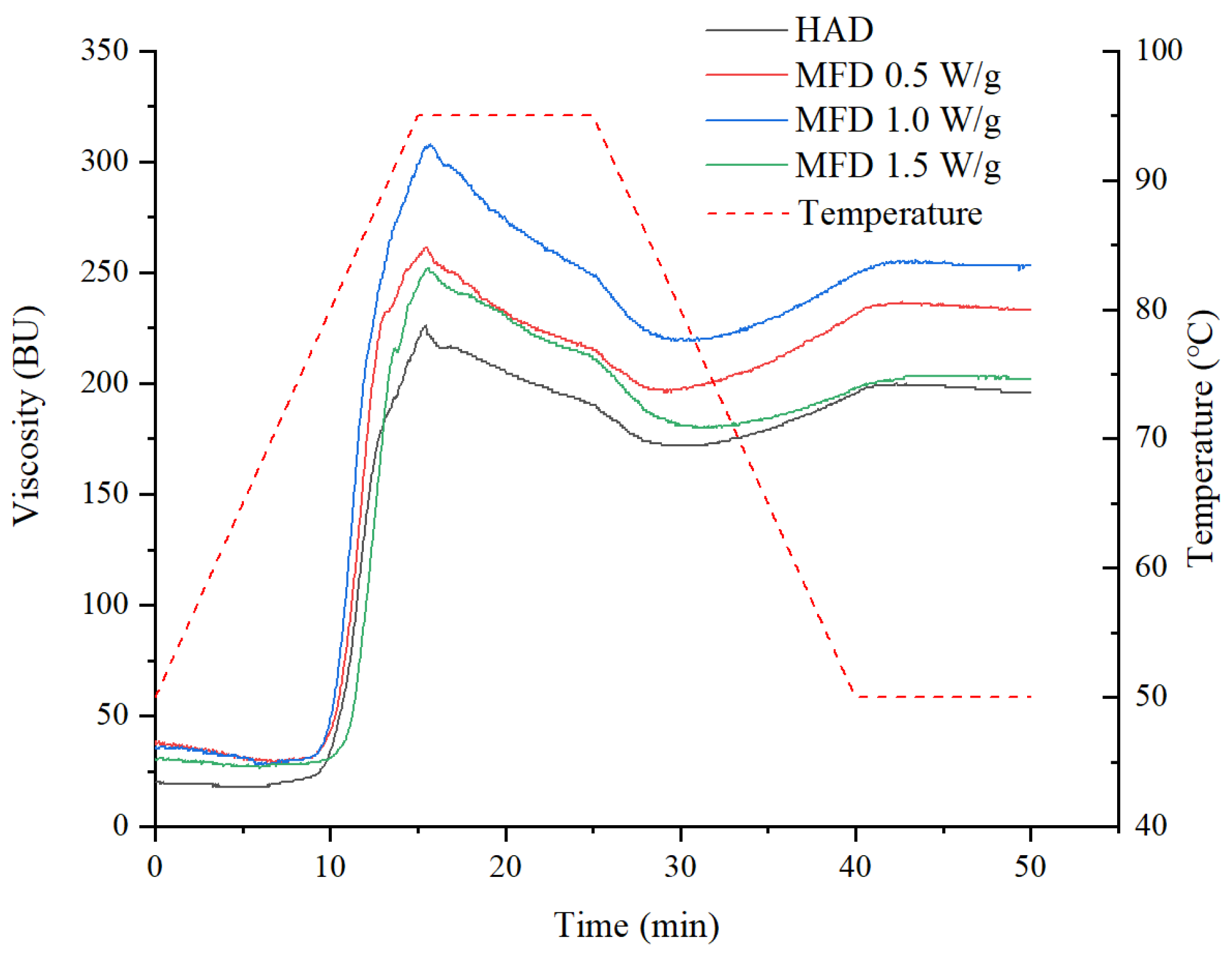
3.5. Pasting Properties
3.6. Thermal Properties
3.7. In Vitro Starch Digestibility
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.-N.; Gao, Q.; Liu, C.-J.; Li, D.-J.; Liu, C.-Q.; Xue, Y.-L. Comparison of volatile components in 11 Chinese yam (Dioscorea spp.) varieties. Food Biosci. 2020, 34, 100531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoticha, J.; Wojdyło, A.; Lech, K. The influence of different the drying methods on chemical composition and antioxidant activity in chokeberries. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S. Recent developments in high efficient freeze-drying of fruits and vegetables assisted by microwave: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 59, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, L. A promising pulse-spouted microwave freeze drying method used for Chinese yam cubes dehydration: Quality, energy consumption, and uniformity. Dry. Technol. 2019, 39, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Duan, X.; Ren, G.Y.; Liu, L.L.; Liu, Y.H. Optimization of microwave freeze drying strategy of mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus) based on porosity change behavior. Dry. Technol. 2017, 35, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W. Ultrasound-assisted osmotic dehydration pretreatment before pulsed fluidized bed microwave freeze-drying (PFBMFD) of Chinese yam. Food Biosci. 2020, 35, 100548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Al-Attar, H. Effect of drying method on rheological, thermal, and structural properties of chestnut flour doughs. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B. Influence of drying methods on some physicochemical, functional and pasting properties of Chinese yam flour. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 111, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mao, X.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Gao, W. Study on the physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of starch from yam with different drying methods. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1787–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ouyang, J. The role of drying methods in determining the in vitro digestibility of starch in whole chestnut flour. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 153, 112583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Li, H.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Qiu, B.; Liu, W.; Jia, M.; Xu, T.; Zong, A. Changes in physicochemical properties and digestive characteristics of yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) powder under different processing conditions using principal component analysis. Dry. Technol. 2019, 37, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Xiang, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Xu, J.; Luo, S.; Wu, J.; Liu, C. Microwave pretreatment promotes the annealing modification of rice starch. Food Chem. 2020, 304, 125432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Z.; Lu, X. Different variations in structures of A- and B-type starches subjected to microwave treatment and their relationships with digestibility. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 99, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, A.; Wang, X.; Zheng, J. Physicochemical and in vitro digestion of millet starch: Effect of moisture content in microwave. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Guo, Z.; Miao, S.; Zeng, S.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, B. Preparation and characterization of lotus seed starch-fatty acid complexes formed by microfluidization. J. Food Eng. 2018, 237, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englyst, H.N.; Kingman, S.M.; Cummings, J.H. Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 46, S33–S35. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Zhang, W. Enhancement of water removing and the quality of fried purple-fleshed sweet potato in the vacuum frying by combined power ultrasound and microwave technology. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 44, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, S.; Kong, F.; Trabelsi, S.; Singh, R.K. Dielectric properties of dried vegetable powders and their temperature profile during radio frequency heating. J. Food Eng. 2016, 169, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, X.; Mao, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, T.; Qu, Z.; Miao, J.; Gao, W. Effects of drying processes on starch-related physicochemical properties, bioactive components and antioxidant properties of yam flours. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Mendoza, M.E.; Martínez-Bustos, F.; Castaño-Tostado, E.; Amaya-Llano, S.L. Effect of microwave irradiation on acid hydrolysis of Faba bean starch: Physicochemical changes of the starch granules. Molecules 2022, 27, 3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaratne, A.; Hoover, R. Effect of heat–moisture treatment on the structure and physicochemical properties of tuber and root starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 49, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Zhu, S.; Chen, F.; Gao, Q.; Yu, S. Effect of different drying methods on the structure and digestibility of short chain amylose crystals. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Z.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Xu, B. Effect of different dielectric drying methods on the physic-chemical properties of a starch–water model system. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Nema, P.K.; Bashir, K. Effect of different drying techniques on physicochemical, thermal, and functional properties of seera. Dry. Technol. 2018, 36, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, X.; Mao, X.; Huang, H.; Miao, J.; Gao, W. Study on the effects of different drying methods on physicochemical properties, structure, and in vitro digestibility of Fritillaria thunbergii Miq. (Zhebeimu) flours. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 98, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheesh, C.; Sunooj, K.V.; George, J. Kithul palm (Caryota urens) as a new source of starch: Effect of single, dual chemical modifications and annealing on the physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Yao, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, F.; Ying, Y.; Shao, Z.; Bao, J. Pasting, gelatinization, and retrogradation characteristics related to structural properties of tea seed starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Qi, L.; Luo, Z.; Kong, X.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, P.; Peng, X. Effect of microwave irradiation on internal molecular structure and physical properties of waxy maize starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 69, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Singh, L.; Sharanagat, V.S.; Patel, A.; Kumar, K. Effect of microwave treatment (low power and varying time) on potato starch: Microstructure, thermo-functional, pasting and rheological properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Jiao, A.; Liu, Q.; Ren, X.; Zhu, K.; Jin, Z. The effects of removing endogenous proteins, β-glucan and lipids on the surface microstructure, water migration and glucose diffusion in vitro of starch in highland barley flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 127, 107457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Li, Y.; Luo, D.-H.; Zhao, Q.; Cheng, J.-H.; Wang, J.-H. Structural variations of rice starch affected by constant power microwave treatment. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dying Conditions | L* | a* | b* | WI | Bulk Density (g/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAD | 91.34 ± 0.22 b | −0.28 ± 0.23 a | 8.04 ± 0.69 a | 88.16 ± 0.30 b | 0.67 ± 0.01 a |
| MFD, 0.5 W/g | 96.49 ± 0.05 a | −1.50 ± 0.08 b | 5.14 ± 0.19 b | 93.59 ± 0.16 a | 0.62 ± 0.04 b |
| MFD, 1.0 W/g | 96.85 ± 0.76 a | −1.67 ± 0.01 b | 5.27 ± 0.74 b | 93.63 ± 1.00 a | 0.58 ± 0.02 b |
| MFD, 1.5 W/g | 96.66 ± 0.08 a | −1.55 ± 0.03 b | 4.95 ± 0.05 b | 93.83 ± 0.06 a | 0.59 ± 0.01 b |
| Dying Conditions | WAC (g/g) | OAC (g/g) | Solubility (%) | R1047/1022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAD | 2.86 ± 0.10 b | 0.24 ± 0.07 b | 15.81 ± 0.45 d | 0.984 ± 0.002 a |
| MFD, 0.5 W/g | 3.31 ± 0.05 a | 0.77 ± 0.11 a | 19.79 ± 0.83 b | 0.956 ± 0.002 c |
| MFD, 1.0 W/g | 3.46 ± 0.03 a | 0.80 ± 0.07 a | 25.46 ± 0.39 a | 0.963 ± 0.005 b |
| MFD, 1.5 W/g | 3.50 ± 0.12 a | 0.59 ± 0.06 a | 17.44 ± 0.49 c | 0.969 ± 0.003 b |
| Drying Conditions | Tp (°C) | tp (min) | PV (BU) | TV (BU) | FV (BU) | BD (BU) | SB (BU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAD | 79.0 ± 0.2 a | 9 ± 0 b | 226 ± 5 c | 172 ± 3 d | 196 ± 1 d | 54 ± 4 d | 24 ± 2 b |
| MFD, 0.5 W/g | 79.0 ± 0.4 a | 9 ± 0.5 b | 261 ± 3 b | 199 ± 5 b | 233 ± 3 b | 62 ± 4 b | 34 ± 3 a |
| MFD, 1.0 W/g | 78.7 ± 0.5 a | 9 ± 0 b | 308 ± 7 a | 219 ± 2 a | 253 ± 4 a | 89 ± 5 a | 34 ± 3 a |
| MFD, 1.5 W/g | 79.8 ± 0.7 a | 10 ± 0.5 a | 252 ± 4 b | 181 ± 6 c | 202 ± 3 c | 71 ± 3 c | 21 ± 1 b |
| Dying Conditions | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Te (°C) | ΔH (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAD | 74.52 ± 0.13 b | 84.78 ± 0.22 a | 93.14 ± 1.23 a | 3.18 ± 0.12 a |
| MFD, 0.5 W/g | 74.29 ± 0.21 b | 83.74 ± 0.21 ab | 90.08 ± 0.38 b | 2.27 ± 0.21 c |
| MFD, 1.0 W/g | 75.95 ± 0.01 a | 83.48 ± 0.63 b | 90.40 ± 0.39 b | 2.59 ± 0.06 bc |
| MFD, 1.5 W/g | 74.26 ± 0.50 b | 84.57 ± 0.24 a | 92.51 ± 0.64 a | 2.96 ± 0.16 ab |
| Drying Conditions | RDS (%) | SDS (%) | RS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HAD | 10.16 ± 0.01 c | 42.88 ± 0.5 c | 46.96 ± 0.49 a |
| MFD, 0.5 W/g | 15.99 ± 1.06 ab | 57.37 ± 1.18 a | 26.64 ± 2.25 bc |
| MFD, 1.0 W/g | 20.94 ± 2.37 a | 54.43 ± 2.09 ab | 24.63 ± 4.45 c |
| MFD, 1.5 W/g | 14.85 ± 2.45 bc | 47.67 ± 4.86 bc | 37.48 ± 7.32 ab |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Chen, J.; Bai, D.; Xu, M.; Cao, W.; Ren, G.; Ren, A.; Duan, X. Physicochemical, Pasting Properties and In Vitro Starch Digestion of Chinese Yam Flours as Affected by Microwave Freeze-Drying. Foods 2022, 11, 2324. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152324
Li L, Chen J, Bai D, Xu M, Cao W, Ren G, Ren A, Duan X. Physicochemical, Pasting Properties and In Vitro Starch Digestion of Chinese Yam Flours as Affected by Microwave Freeze-Drying. Foods. 2022; 11(15):2324. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152324
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Linlin, Junliang Chen, Danqi Bai, Mengshuo Xu, Weiwei Cao, Guangyue Ren, Aiqing Ren, and Xu Duan. 2022. "Physicochemical, Pasting Properties and In Vitro Starch Digestion of Chinese Yam Flours as Affected by Microwave Freeze-Drying" Foods 11, no. 15: 2324. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152324
APA StyleLi, L., Chen, J., Bai, D., Xu, M., Cao, W., Ren, G., Ren, A., & Duan, X. (2022). Physicochemical, Pasting Properties and In Vitro Starch Digestion of Chinese Yam Flours as Affected by Microwave Freeze-Drying. Foods, 11(15), 2324. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152324






