Effect of Homogenization Modified Rice Protein on the Pasting Properties of Rice Starch
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Homogenization of Rice Protein and Sample Preparation
2.3. Characterization of Protein Properties
2.3.1. Particle Size Analysis
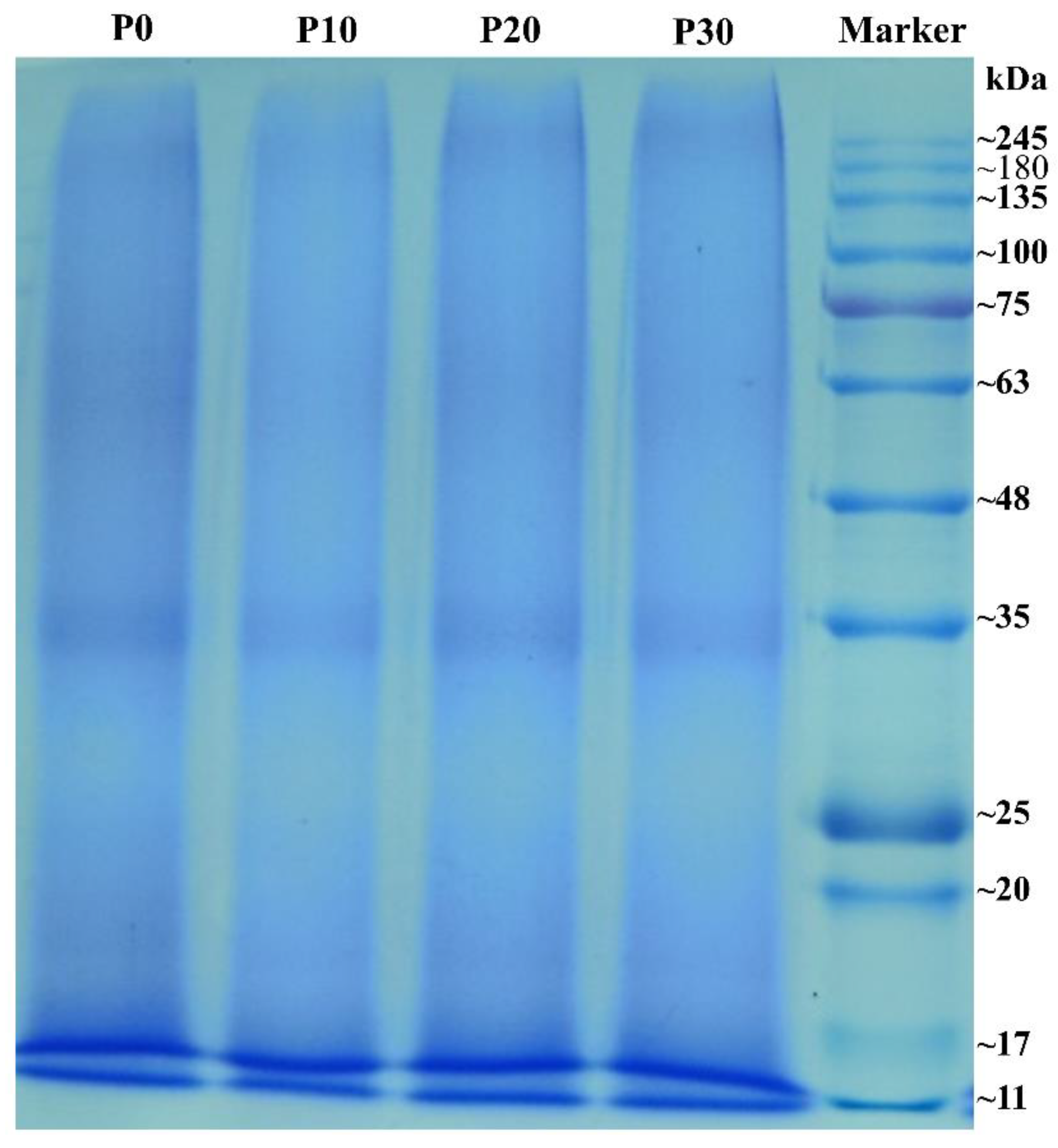
2.3.2. Gel Electrophoresis Analysis
2.3.3. Water Holding Capacity Analysis
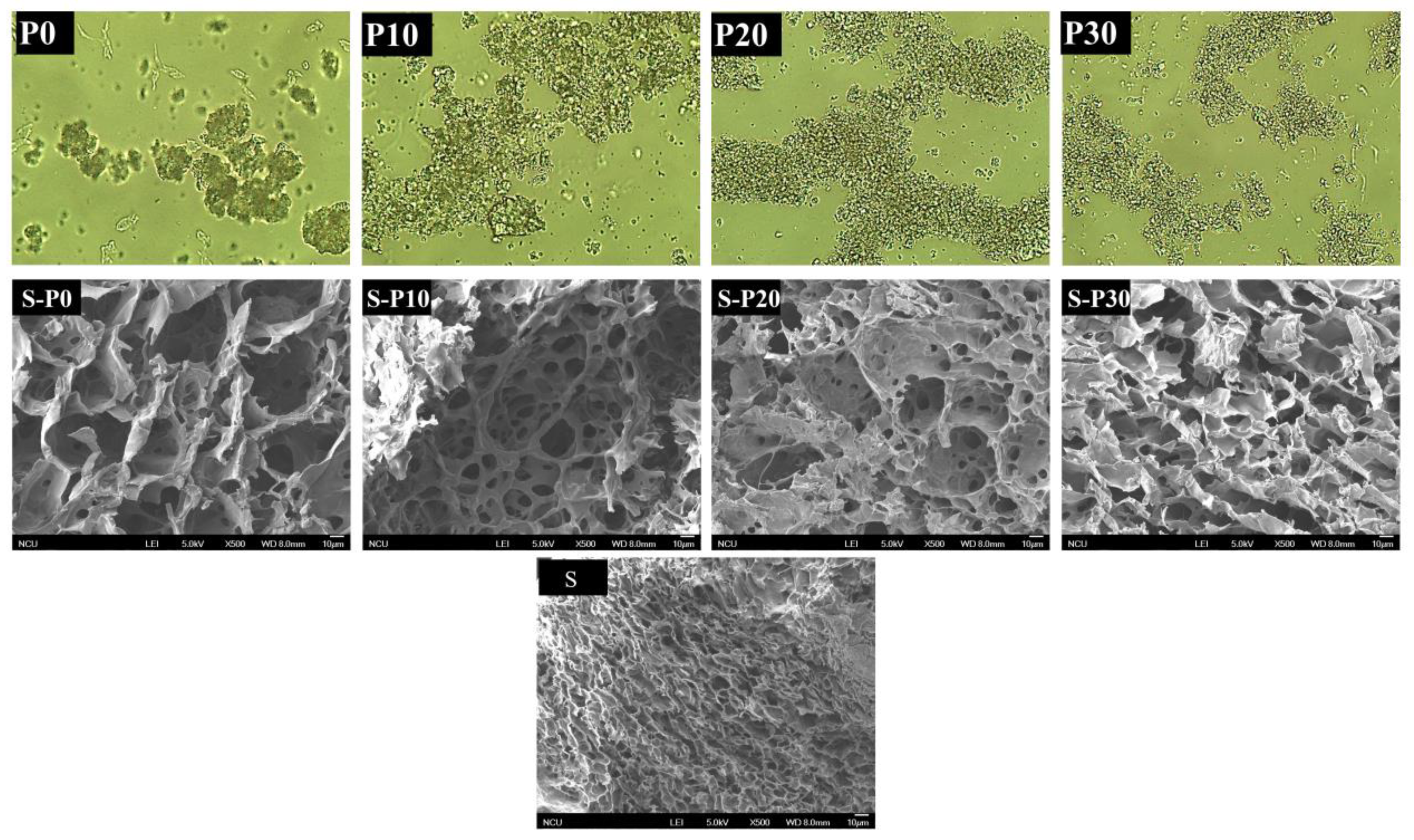
2.3.4. Microstructure Analysis
2.4. Characterization of Pasting Properties of Protein-Starches
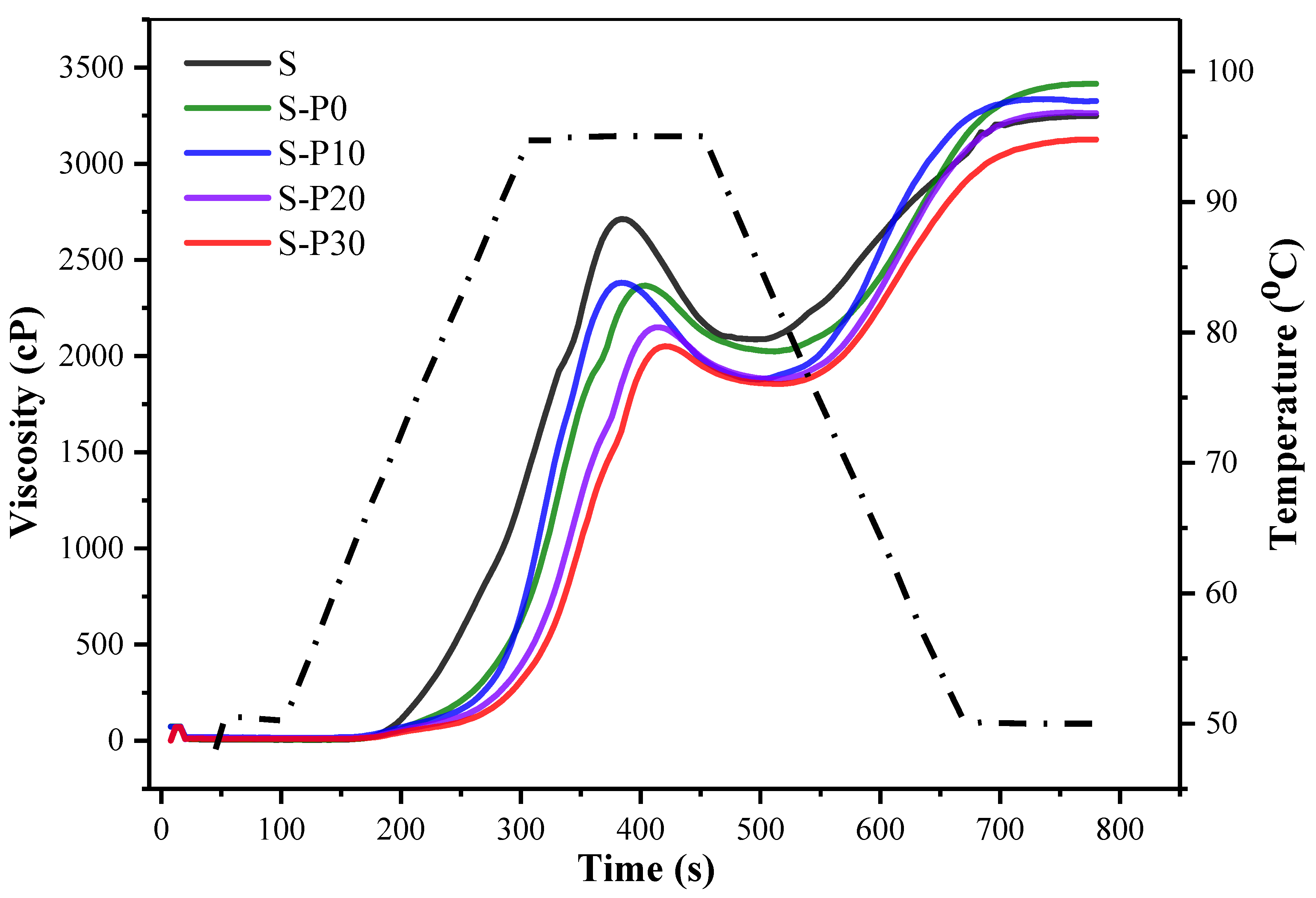
2.4.1. Rapid Visco-Analyzer Analysis of Protein-Starch Paste
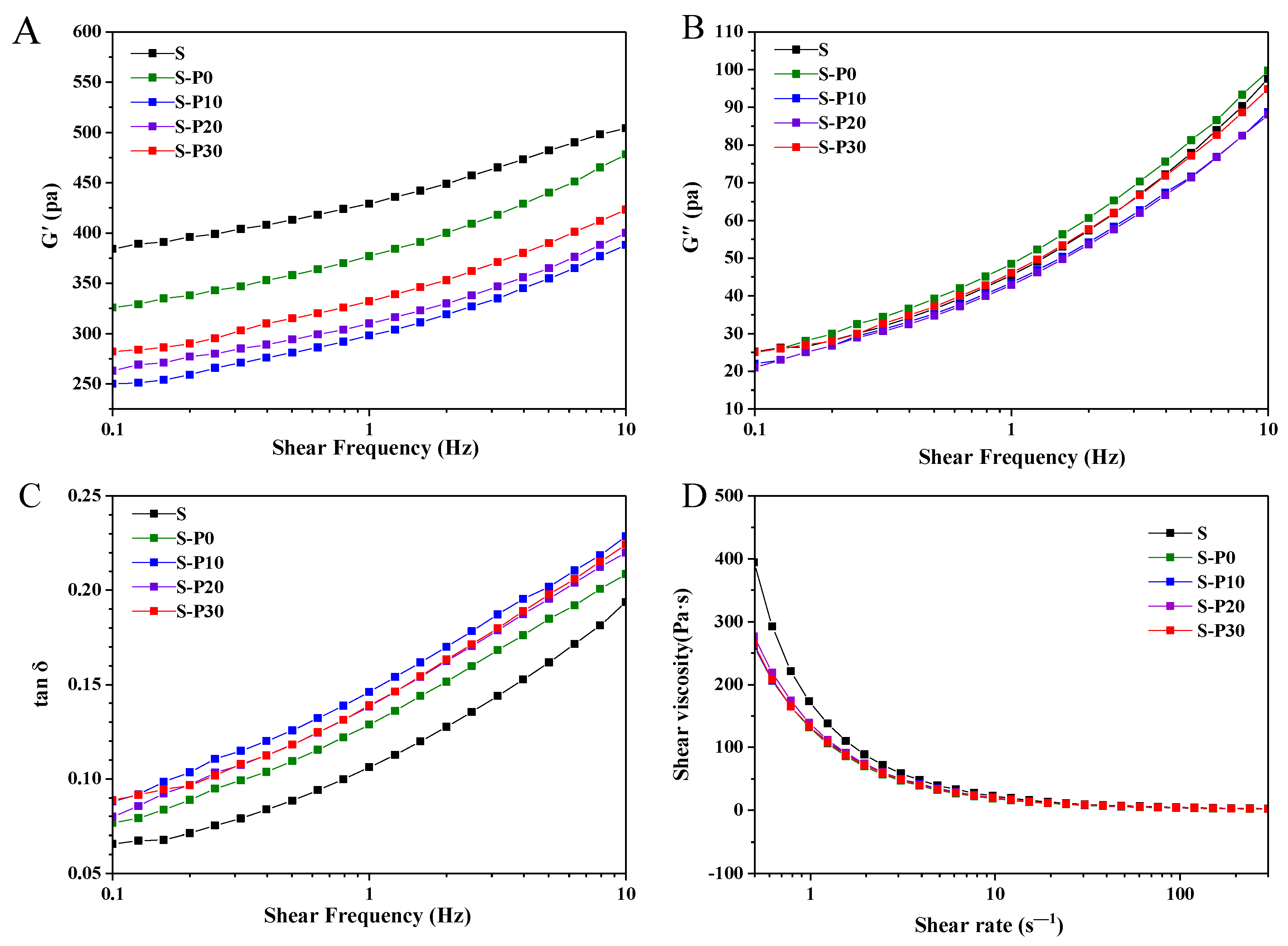
2.4.2. Rheology of Protein-Starch Paste
2.4.3. Microstructure of Protein-Starch Paste
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Homogenization on Physicochemical Properties of Protein
3.1.1. Effect of Homogenization on Average Particle Size of Rice Protein
3.1.2. Effect of Homogenization on Protein Profiles of Rice Protein
3.1.3. Effect of Homogenization on WHC of Rice Protein
3.1.4. Effect of Microstructure of Rice Protein
3.2. Effect of Homogenized Rice Protein Addition on Pasting Properties of Rice Starch
3.2.1. RVA Pasting Profile
3.2.2. Rheological Properties
3.2.3. Microstructure of Starch Pastes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Q.; Xiong, H.; Selomulya, C.; Chen, X.D.; Huang, S.; Ruan, X.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, W. Effects of spray drying and freeze drying on the properties of protein isolate from rice dreg protein. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 6, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagliani, L.; O’Regan, J.; Kelly, A.L.; O’Mahony, J.A. The composition, extraction, functionality and applications of rice proteins: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 64, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagampang, G.; Cruz, L.; Espiritu, S.; Santiago, R.; Juliano, B. Studies on the extraction and composition of rice proteins. Cereal Chem. 1996, 43, 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Borght, A.; Vandeputte, G.E.; Derycke, V.; Brijs, K.; Daenen, G.; Delcour, J.A. Extractability and chromatographic separation of rice endosperm proteins. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 44, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; He, H.-Y.; Chao, D.; Ju, X.; Aluko, R. Effects of high pressure and heat treatments on physicochemical and gelation properties of rapeseed protein isolate. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 7, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor Afizah, M.; Rizvi, S.S.H. Functional properties of whey protein concentrate texturized at acidic pH: Effect of extrusion temperature. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Roginski, H.; Williams, R.P.W.; Versteeg, C.; Wan, J. Effect of pulsed electric field and thermal treatment on the physicochemical and functional properties of whey protein isolate. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, K.; Zhou, H.; Peng, W. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on some functional and nutritional properties of soy protein isolate for infant formula. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12028–12036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhao, M.; Sun, W.; Zhao, G.; Ren, J. Effects of microfluidization treatment and transglutaminase cross-linking on physicochemical, functional, and conformational properties of peanut protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8886–8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ma, H.; Ding, Q.; Lin, L.; Yu, X.; Luo, L.; Dai, C.; Yagoub, A.E.-G.A. Ultrasonic pretreatment of corn gluten meal proteins and neutrase: Effect on protein conformation and preparation of ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme) inhibitory peptides. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, B.-S.; Jafri, H.; Cao, T.; Robertson, G.H.; Gregorski, K.S.; Imam, S.H.; Glenn, G.M.; Orts, W.J. Modification of wheat gluten with citric acid to produce superabsorbent materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 3192–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasran, M.; Cui, S.W.; Goff, H.D. Emulsifying properties of soy whey protein isolate–fenugreek gum conjugates in oil-in-water emulsion model system. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Alvarenga, M.S.; Martinez-Rodriguez, E.Y.; Garcia-Amezquita, L.E.; Olivas, G.I.; Zamudio-Flores, P.B.; Acosta-Muniz, C.H.; Sepulveda, D.R. Effect of Maillard reaction conditions on the degree of glycation and functional properties of whey protein isolate – Maltodextrin conjugates. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabanon, G.; Chevalot, I.; Framboisier, X.; Chenu, S.; Marc, I. Hydrolysis of rapeseed protein isolates: Kinetics, characterization and functional properties of hydrolysates. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.Y.J.; SRVA; Chiang, J.H.; Henry, C.J. Plant proteins for future foods: A roadmap. Foods 2021, 10, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narciso, J.O.; Brennan, C. Whey and pea protein fortification of rice starches: Effects on protein and starch digestibility and starch pasting properties. Starch-Starke 2018, 70, 1700315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Niu, L.; Wu, L.; Li, D.; He, H. Preparation of an in vitro low-digestible rice starch by addition of grass carp protein hydrolysates and its possible mechanisms. Starch-Starke 2019, 71, 1800159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, J.; Zhong, Q. Suppression of retrogradation of gelatinized rice starch by anti-listerial grass carp protein hydrolysate. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 72, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Tang, C.-H. Microfluidization as a potential technique to modify surface properties of soy protein isolate. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, G.; Zeng, H.; Chen, L. Effects of high pressure homogenization on faba bean protein aggregation in relation to solubility and interfacial properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saricaoglu, F.T. Application of high-pressure homogenization (HPH) to modify functional, structural and rheological properties of lentil (Lens culinaris) proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-M.; Zhong, J.-Z.; Liu, W.; Tu, Z.-C.; Wan, J.; Cai, X.-F.; Song, X.-Y. Relationship between functional properties and aggregation changes of whey protein induced by high pressure microfluidization. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, E341–E347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; McClements, D.J.; Luo, S.; Chen, T.; Ye, J.; Liu, C. Fabrication of rutin-protein complexes to form and stabilize bilayer emulsions: Impact of concentration and pretreatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Liu, C.; Luo, S.; Wu, J.; Hu, X.; McClements, D.J. A simulated gastrointestinal tract study of texturized rice grains: Impact of texturization on starch digestibility. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 89, 102800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuchat, L.R. Functional and electrophoretic characteristics of succinylated peanut flour protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1977, 25, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.-J.; Chen, R.-Y.; Huang, L.; Liang, R.-H.; Liu, C.-M.; Chen, J. Investigation on the influence of pectin structures on the pasting properties of rice starch by multiple regression. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagliani, L.; O’Regan, J.; Kelly, A.L.; O’Mahony, J.A. Physical and flow properties of rice protein powders. J. Food Eng. 2016, 190, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagliani, L.; O’Regan, J.; Kelly, A.L.; O’Mahony, J.A. Composition and protein profile analysis of rice protein ingredients. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 59, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saricaoglu, F.T.; Gul, O.; Besir, A.; Atalar, I. Effect of high pressure homogenization (HPH) on functional and rheological properties of hazelnut meal proteins obtained from hazelnut oil industry by-products. J. Food Eng. 2018, 233, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhao, M.; Yang, B.; Yang, X.; Shi, J.; Jiang, Y. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on the functional property of peanut protein. J. Food Process Eng. 2011, 34, 2191–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhou, C.; Fu, F.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Q. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on particle size and film properties of soy protein isolate. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Ai, L.; Xiong, W. Insight into protein-starch ratio on the gelatinization and retrogradation characteristics of reconstituted rice flour. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Xiang, X.; Chen, T.; Zou, P.; Liu, Y.; Ye, J.; Luo, S.; Wu, J.; Liu, C. Accelerated aging of rice by controlled microwave treatment. Food Chem. 2020, 304, 126853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Considine, T.; Noisuwan, A.; Hemar, Y.; Wilkinson, B.; Bronlund, J.; Kasapis, S. Rheological investigations of the interactions between starch and milk proteins in model dairy systems: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 2008–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, R.F.; Morrison, W.R. Swelling and gelatinization of cereal starches. 2. Waxy rice starch. Cereal Chem. 1990, 67, 558–563. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, M.; De lamo, B.; Harasym, J.; Ronda, F. Microwave radiation and protein addition modulate hydration, pasting and gel rheological characteristics of rice and potato starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 201, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, M.; Yadav, B.S.; Yadav, R.B.; Dangi, N. Assessing the influence of lentil protein concentrate on pasting and rheological properties of barley starch. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y. Effect of rice protein on the water mobility, water migration and microstructure of rice starch during retrogradation. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 91, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohizua, E.R.; Adeola, A.A.; Idowu, M.A.; Sobukola, O.P.; Afolabi, T.A.; Ishola, R.O.; Ayansina, S.O.; Oyekale, T.O.; Falomo, A. Nutrient composition, functional, and pasting properties of unripe cooking banana, pigeon pea, and sweetpotato flour blends. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 5, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.-M.; Liang, R.-H.; Dai, T.-T.; Ye, J.-P.; Zeng, Z.-C.; Luo, S.-J.; Chen, J. Effect of dynamic high pressure microfluidization modified insoluble dietary fiber on gelatinization and rheology of rice starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 57, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Yang, R.; Liu, C.; Luo, S.; Chen, J.; Hu, X.; Wu, J. Improvement in freeze-thaw stability of rice starch gel by inulin and its mechanism. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, M.; Aldred, P.; Panozzo, J.F.; Kasapis, S.; Adhikari, B. Rheological and microstructural characteristics of lentil starch–lentil protein composite pastes and gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | WHC (g/g) | Particle Size (μm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D10 | D50 | D90 | ||
| P0 | 1.65 ± 0.02 d | 4.48 ± 0.01 a | 24.2 ± 0.3 a | 54.1 ± 0.1 a |
| P10 | 1.90 ± 0.03 c | 2.27 ± 0.02 b | 13.8 ± 0.2 b | 34.4 ± 0.4 b |
| P20 | 2.06 ± 0.04 b | 2.01 ± 0.01 c | 10.8 ± 0.1 c | 27.4 ± 0.5 c |
| P30 | 2.23 ± 0.08 a | 1.80 ± 0.01 d | 8.74 ± 0.4 d | 23.0 ± 0.2 d |
| Samples | Pasting Properties | Flow Behavior | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak Viscosity (cP) | Trough Viscosity (cP) | Breakdown Viscosity (cP) | Final Viscosity (cP) | Setback Viscosity (cP) | Pasting Temperature (°C) | K (Pa⋅sn) | n | R2 | |
| S | 2718 ± 12 a | 2085 ± 10 a | 633 ± 22 a,b | 3245 ± 4 b,c | 1159 ± 13 c | 76.4 ± 0.4 d | 133.3 ± 1.0 a | 0.27 ± 0.02 a | 0.92 |
| S-P0 | 2047 ± 16 d | 1426 ± 34 d | 712 ± 19 a | 3081 ± 47 d | 1823 ± 24 a | 88.0 ± 0.1 c | 117.2 ± 5.7 b | 0.23 ± 0.01 b | 0.93 |
| S-P10 | 2156 ± 25 c | 1575 ± 66 c | 580 ± 45 b | 3240 ± 23 c | 1717 ± 22 a | 90.7 ± 1.3 c | 117.4 ± 5.3 b | 0.26 ± 0.01 a | 0.96 |
| S-P20 | 2208 ± 12 b | 1791 ± 35 b | 498 ± 4 c | 3313 ± 12 a,b | 1491 ± 35 b | 91.6 ± 0.5 b | 116.5 ± 6.3 b | 0.26 ± 0.01 a | 0.94 |
| S-P30 | 2341 ± 23 b | 1920 ± 33 b | 418 ± 31 c | 3327 ± 26 a | 1472 ± 3 b | 93.1 ± 0.9 a | 114.2 ± 6.1 b | 0.27 ± 0.01 a | 0.95 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Xu, S.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Li, Q.; Ye, J.; Liu, C. Effect of Homogenization Modified Rice Protein on the Pasting Properties of Rice Starch. Foods 2022, 11, 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11111601
Wu J, Xu S, Yan X, Zhang X, Xu X, Li Q, Ye J, Liu C. Effect of Homogenization Modified Rice Protein on the Pasting Properties of Rice Starch. Foods. 2022; 11(11):1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11111601
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jianyong, Shunqian Xu, Xiaoyan Yan, Xuan Zhang, Xingfeng Xu, Qian Li, Jiangping Ye, and Chengmei Liu. 2022. "Effect of Homogenization Modified Rice Protein on the Pasting Properties of Rice Starch" Foods 11, no. 11: 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11111601
APA StyleWu, J., Xu, S., Yan, X., Zhang, X., Xu, X., Li, Q., Ye, J., & Liu, C. (2022). Effect of Homogenization Modified Rice Protein on the Pasting Properties of Rice Starch. Foods, 11(11), 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11111601






