The Use of Unconventional Malts in Beer Production and Their Effect on the Wort Viscosity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Analytical Procedures
2.3. Malting Process
2.4. Wort Production
2.5. Wort Samples
2.6. Determination of Carbohydrates by HPLC
2.7. Determination of Dynamic Viscosity
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Malt Characteristics
3.2. Wort Characteristics
3.3. Dynamic Viscosity of Worts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tippmann, J.; Scheuren, H.; Voigt, J.; Sommer, K. Procedural investigations of the lautering process. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2010, 33, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basařová, G.; Šavel, J.; Basař, P.; Lejsek, T. Brewing: Theory and Practice of Beer Production; VŠCHT: Praha, Czrech Republic, 2010; ISBN 978-80-7080-734-7. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Kumbár, V.; Kouřilová, V.; Dufková, R.; Votava, J.; Hřivna, L. Rheological and pipe flow properties of chocolate masses at different temperatures. Foods 2021, 10, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fingas, M.; Yang, C.; Christensen, J.H. Crude oil and refined product fingerprinting: Principles. In Environmental Forensics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1964; pp. 339–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masák, J.; Janata, J.; Basařová, G. Effect of high molecular compounds of extract on beer viscosity. Kvas. Prum. 1987, 33, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, P.; Kordialik-Bogacka, E. Alternatives to malt in brewing. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 65, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
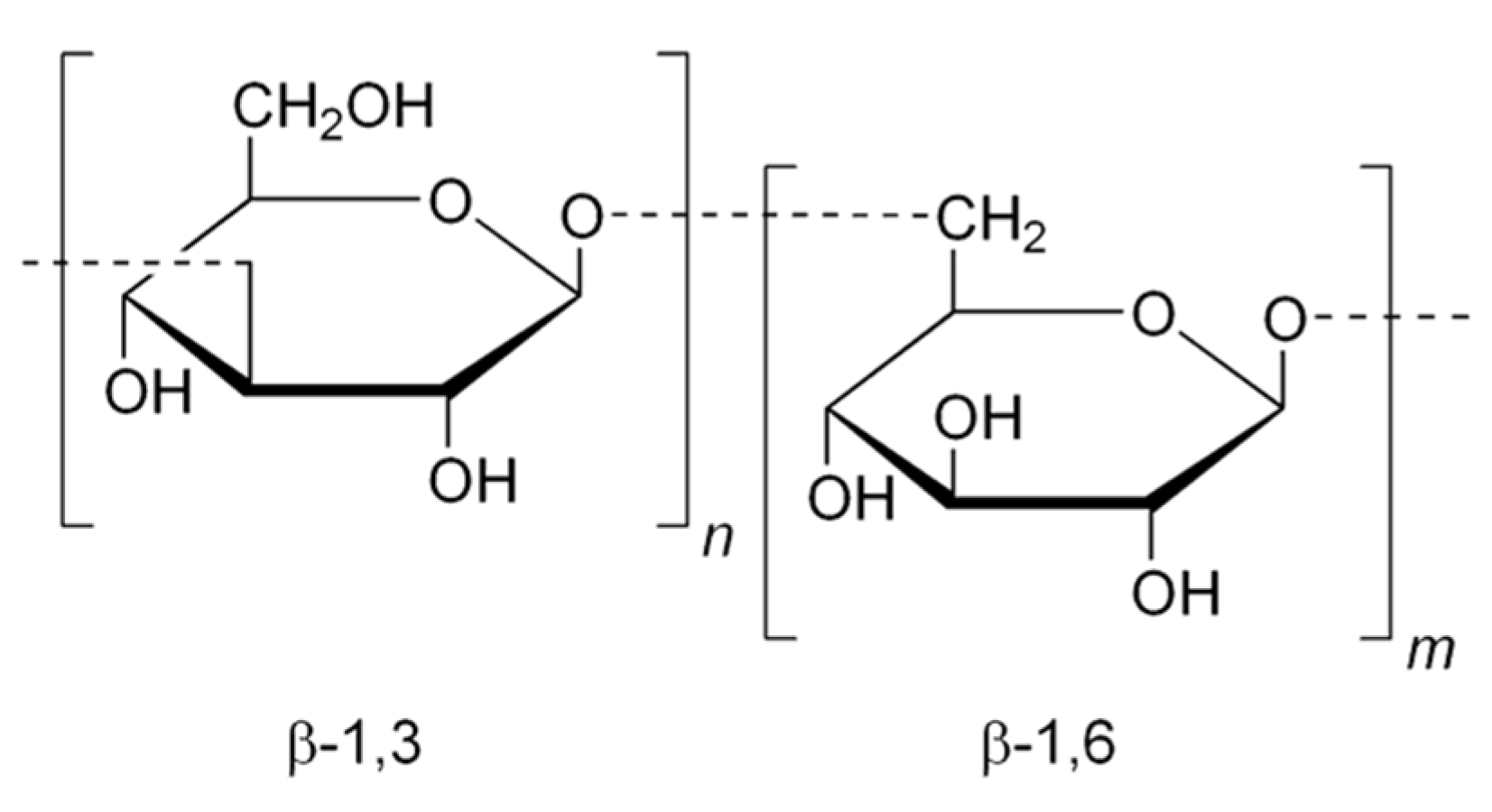
- Jin, Y.; Speers, R.A.; Paulson, A.; Stewart, R. Barley β-glucans and their degradation during malting and brewing. Tech. Q.-Master Brew. Asoc. Am. 2004, 41, 231–240. [Google Scholar]
- Hozová, B.; Kuniak, L.; Moravčíková, P.; Gajdošová, A. Determination of water-insoluble β-D-glucan in the whole-grain cereals and pseudocereals. Czech J. Food Sci. 2008, 25, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.-L.; Speers, A.; Paulson, A.T.; Stewart, R.J. Effects of β-glucans and environmental factors on the viscosities of wort and beer. J. Inst. Brew. 2004, 110, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbar, V.; Nedomova, S.; Trnka, J.; Buchar, J.; Pytel, R. Effect of storage duration on the rheological properties of goose liquid egg products and eggshell membranes. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1693–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howitt, C.A.; Miskelly, D. Identification of grain variety and quality type. In Cereal Grains; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 453–492. ISBN 9780081007198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokeš, J. Evaluation of Older Quality Barley Varieties with New Malt Quality Indicators. Ph.D. Thesis, Mendel University in Brno, Brno, Czech Republic, 2008. (In Czech). [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Dong, J.; Yin, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, R.; Wan, X.; Chen, P.; Hou, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, L. Wort composition and its impact on the flavour-active higher alcohol and ester formation of beer—A review. J. Inst. Brew. 2014, 120, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monošík, R.; Magdolen, P.; Streďanský, M.; Šturdík, E. Monitoring of monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, ethanol and glycerol during wort fermentation by biosensors, HPLC and spectrophotometry. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, S.H.; Henson, C.A. Tracking the progress of wort sugar production during congress mashing with North American barley cultivars and comparisons to wort osmolyte concentrations and malt extract. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2011, 69, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ma, T.; Li, Y.; Li, Q. Permeability analysis of high-adjunct-ratio spent grain layer in the high-gravity wort separation process. Process. Biochem. 2015, 50, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, H.; Ceccaroni, D.; Marconi, O.; Sileoni, V.; Perretti, G.I.F.; Fantozzi, P. Development of an all rice malt beer: A gluten free alternative. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 67, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Shetty, R.; Hansen, M.; Fromberg, A.; Hansen, P.B.; Hobley, T.J. Brewing with 100% unmalted grains: Barley, wheat, oat and rye. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzenbaumer, B.; Arendt, E.K. Effect of unmalted oats (Avena sativa L.) on the quality of high-gravity mashes and worts without or with exogenous enzyme addition. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 238, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coghe, S.; D’Hollander, H.; Verachtert, H.; Delvaux, F.R. Impact of dark specialty malts on extract composition and wort fermentation. J. Inst. Brew. 2005, 111, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennemann, M.; Gastl, M.; Becker, T. Inhomogeneity in the lauter tun: A chromatographic view. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitila, A.; Manninen, J.; Priha, O.; Smart, K.; Tsitko, I.; James, S. Characterisation of barley-associated bacteria and their impact on wort separation performance. J. Inst. Brew. 2018, 124, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kordialik-Bogacka, E.; Bogdan, P.; Diowksz, A. Malted and unmalted oats in brewing. J. Inst. Brew. 2014, 120, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.P.; Munck, L. Evaluation of malting barley quality using exploratory data analysis. I. Extraction of information from micro-malting data of spring and winter barley. J. Cereal Sci. 2003, 38, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Phase | Temperature (°C) | Duration (min) | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mash (1) | 40 | 0 | 0 |
| Mash (2) | 40 | 5 | 5 |
| Proteolysis (3) | 52 | 15 | 20 |
| First saccharification stage (4) | 62 | 30 | 50 |
| Second saccharification stage (5) | 72 | 30 | 80 |
| Mashout (6) | 90 | 10 | 90 |
| Spring Barley | Black Barley | Oat | Wheat | Corn | Rye | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture content (%) | 4.5 | 4.9 | 4.3 | 4.7 | 4.3 | 4.1 |
| Thousand-corn weight (g) | 41.6 | 49.1 | 23.4 | 45.3 | 28.5 | 285.4 |
| Volume weight (g·L−1) | 578.6 | 542.7 | 481.2 | 508.4 | 711.5 | 511.9 |
| Friability (%) | 83 | 74 | 52 | 41 | 35 | 37 |
| Nitrogen compounds (%) | 10.5 | 10.4 | 10.1 | 9.5 | 10.2 | 9.4 |
| Starch (%) | 59.6 | 60.1 | 54.9 | 62.1 | 62.7 | 57.6 |
| Wort extract (%) | 8.4 | 7.9 | 5.9 | 6.8 | 7.4 | 5.8 |
| Malt extract (%) | 82.4 | 77.5 | 57.8 | 66.7 | 72.6 | 56.9 |
| Filtration time (min) | <60 | <60 | >60 | <60 | >60 | >60 |
| Saccharification rest (min) | <10 | <10 | >10 | <10 | >10 | >10 |
| Wort clarity | clear | Light opacity | Strong opacity | Light opacity | Strong opacity | Strong opacity |
| Spring Barley | Black Barley | Oat | Wheat | Corn | Rye | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oligosaccharide (%) | 0.6 | 0.9 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 1.7 |
| Maltotriose (%) | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.4 |
| Maltose (%) | 2.8 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.9 | 1.4 |
| Glucose (%) | 2.5 | 2.1 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 0.9 |
| Fructose (%) | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| β-glucans (mg·L−1) | 64.2 | 134.4 | 205.7 | 125.1 | 141.3 | 168.4 |
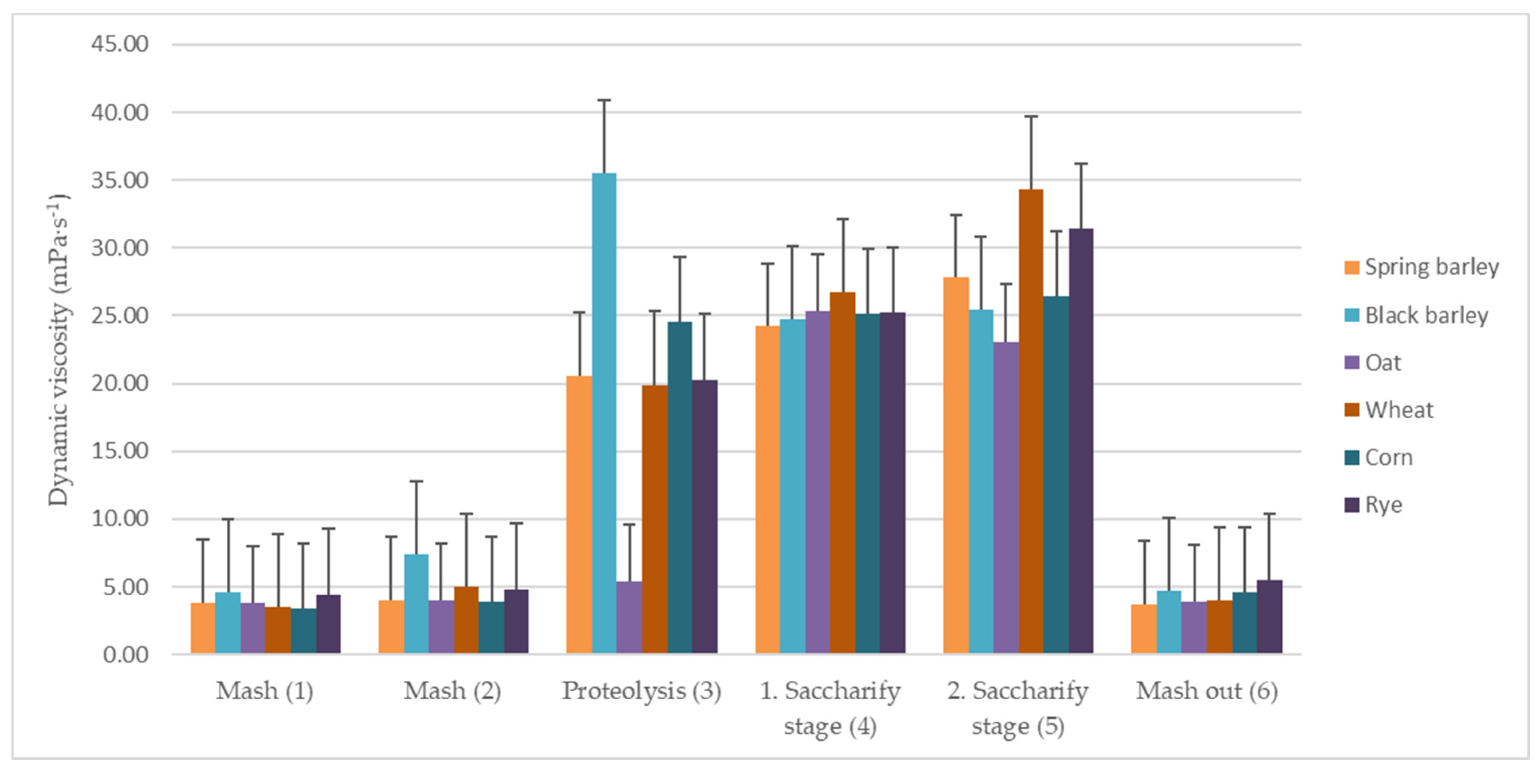
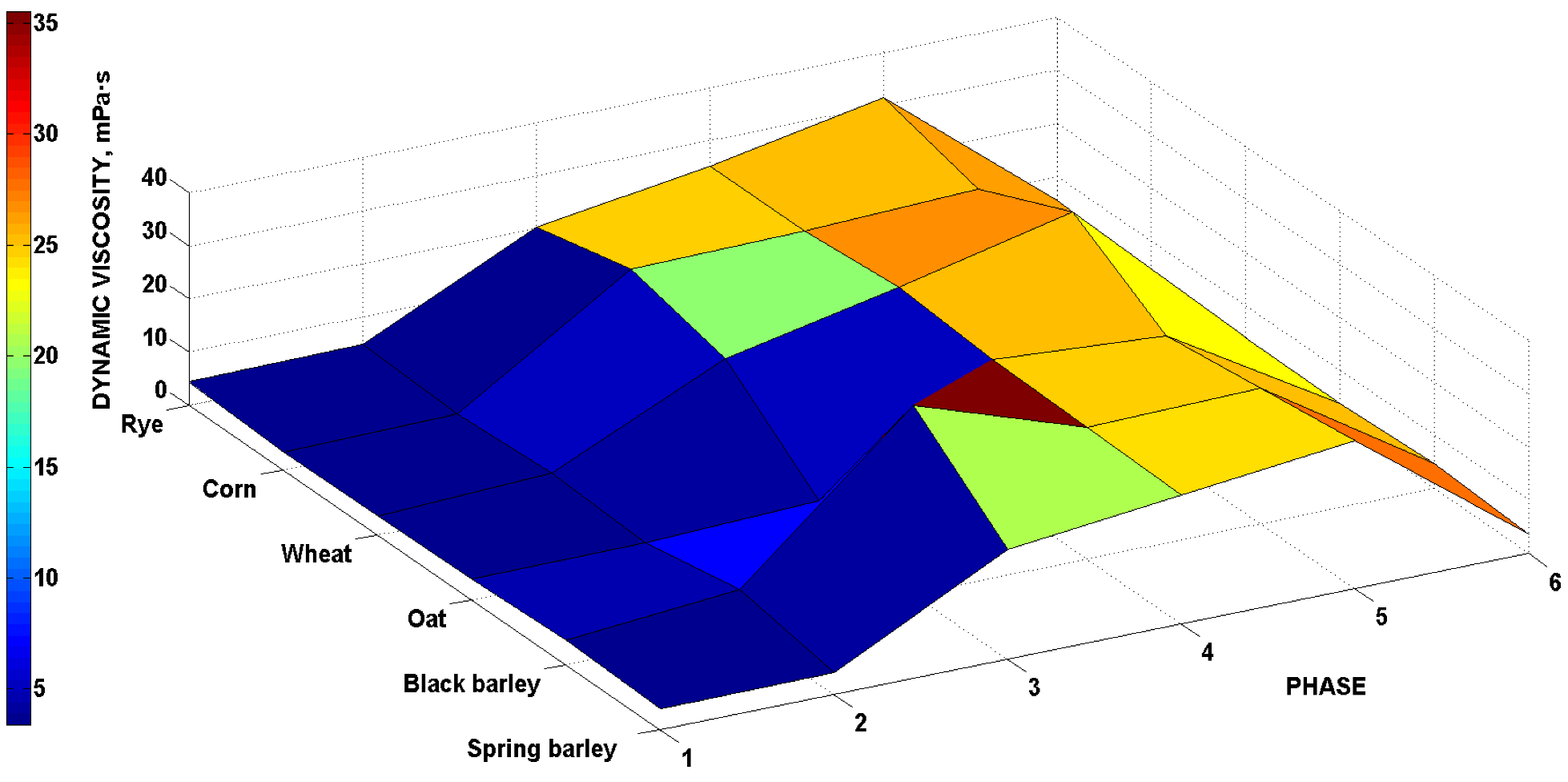
| Phase | Mash (1) | Mash (2) | Proteolysis (3) | First Saccharification Stage (4) | Second Saccharification Stage (5) | Mashout (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malt | Dynamic Viscosity (mPa·s) | |||||
| Spring barley | 3.8 | 4.0 | 20.6 | 24.2 | 27.8 | 3.7 |
| Black barley | 4.6 | 7.4 | 35.5 | 24.7 | 25.4 | 4.7 |
| Oat | 3.8 | 4.0 | 5.4 | 25.3 | 23.1 | 3.9 |
| Wheat | 3.5 | 5.0 | 19.9 | 26.7 | 34.3 | 4.0 |
| Corn | 3.4 | 3.9 | 24.5 | 25.1 | 26.4 | 4.6 |
| Rye | 4.4 | 4.8 | 20.3 | 25.2 | 31.4 | 5.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blšáková, L.; Gregor, T.; Mešťánek, M.; Hřivna, L.; Kumbár, V. The Use of Unconventional Malts in Beer Production and Their Effect on the Wort Viscosity. Foods 2022, 11, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010031
Blšáková L, Gregor T, Mešťánek M, Hřivna L, Kumbár V. The Use of Unconventional Malts in Beer Production and Their Effect on the Wort Viscosity. Foods. 2022; 11(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010031
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlšáková, Lucia, Tomáš Gregor, Matej Mešťánek, Luděk Hřivna, and Vojtěch Kumbár. 2022. "The Use of Unconventional Malts in Beer Production and Their Effect on the Wort Viscosity" Foods 11, no. 1: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010031
APA StyleBlšáková, L., Gregor, T., Mešťánek, M., Hřivna, L., & Kumbár, V. (2022). The Use of Unconventional Malts in Beer Production and Their Effect on the Wort Viscosity. Foods, 11(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010031






